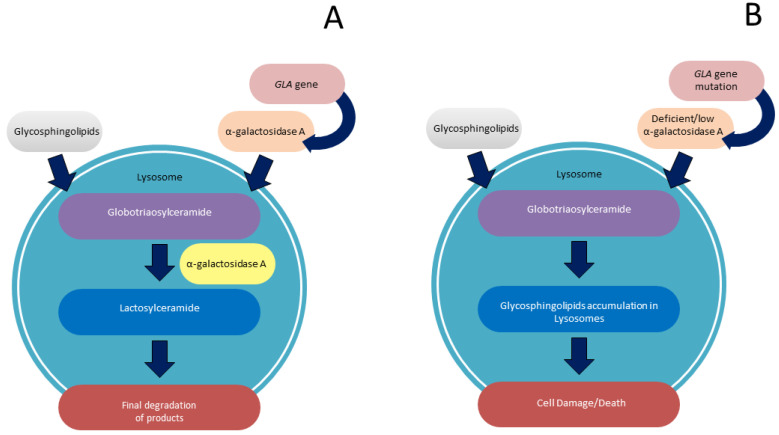
Figure 1.
(A): In physiological condition, inside the lysosome, α-galactosidase A catalyses the hydrolysis of glycosphingolipids, with terminal α-galactose residues in the course of sphingolipid degradation; (B) in Fabry Disease, deficiency of GLA activity results in defects in degradation of glycosphingolipids, causing abnormal accumulation of enzyme substrate in the lysosome.