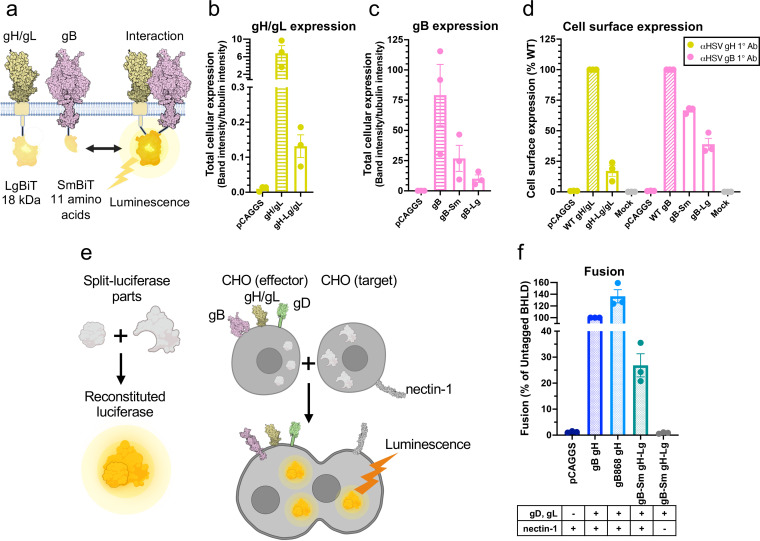
FIG 2.
Tagging HSV-1 gH/gL and gB with split luciferases to probe their interaction. (a) NanoBiT protein-protein interaction assay approach (49). The interaction between gH/gL and gB was tested by tagging gH and gB with complementary parts of a split luciferase and transfecting into cells. Reconstitution of luciferase reports on fusion. (b to d) Total cellular expression and cell-surface expression of Lg- and Sm- tagged gH and gB by Western blotting and flow cytometry, respectively. R137 and R68 antibodies for gH/gL and gB for Western blotting, respectively. LP11 and R68 antibodies for gH/gL and gB for flow cytometry, respectively. pCAGGS was an empty vector negative control. The mock control was an untransfected negative control, incubated with a nontargeting primary antibody. Columns show the mean. Error bars are the standard error of the mean (SEM). e) Split-luciferase cell-cell fusion assay (51) experimental setup to test whether tagged proteins retain their function. Cells transfected with viral proteins fuse to cells transfected with nectin-1 receptor. Reconstitution of Rluc8 luciferase reports on fusion. (b) Total fusion of gB-Sm and gH-Lg/gL, 8 h after mixing effector and target cells. gB868 was a hyperfusogenic positive-control gB construct. pCAGGS and the condition without nectin-1 receptor are negative controls. Columns show the mean. Error bars are the SEM. Data are three biological replicates from independent experiments. Diagrams and cartoons were created using BioRender.com.