Summary
Orofaciodigital syndrome (OFD) is a genetically heterogeneous ciliopathy characterized by anomalies of the oral cavity, face, and digits. We describe individuals with OFD from three unrelated families having bi-allelic loss-of-function variants in SCNM1 as the cause of their condition. SCNM1 encodes a protein recently shown to be a component of the human minor spliceosome. However, so far the effect of loss of SCNM1 function on human cells had not been assessed. Using a comparative transcriptome analysis between fibroblasts derived from an OFD-affected individual harboring SCNM1 mutations and control fibroblasts, we identified a set of genes with defective minor intron (U12) processing in the fibroblasts of the affected subject. These results were reproduced in SCNM1 knockout hTERT RPE-1 (RPE-1) cells engineered by CRISPR-Cas9-mediated editing and in SCNM1 siRNA-treated RPE-1 cultures. Notably, expression of TMEM107 and FAM92A encoding primary cilia and basal body proteins, respectively, and that of DERL2, ZC3H8, and C17orf75, were severely reduced in SCNM1-deficient cells. Primary fibroblasts containing SCNM1 mutations, as well as SCNM1 knockout and SCNM1 knockdown RPE-1 cells, were also found with abnormally elongated cilia. Conversely, cilia length and expression of SCNM1-regulated genes were restored in SCNM1-deficient fibroblasts following reintroduction of SCNM1 via retroviral delivery. Additionally, functional analysis in SCNM1-retrotransduced fibroblasts showed that SCNM1 is a positive mediator of Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. Our findings demonstrate that defective U12 intron splicing can lead to a typical ciliopathy such as OFD and reveal that primary cilia length and Hh signaling are regulated by the minor spliceosome through SCNM1 activity.
Keywords: orofaciodigital syndrome, SCNM1, minor spliceosome, U12 introns, primary cilia, ciliopathy, hedgehog signaling
This work uncovers bi-allelic loss-of-function mutations in SCNM1 as a cause of orofaciodigital syndrome. Absence of SCNM1 impairs the minor intron splicing process leading to changes in the expression of genes, some of which are directly related to primary cilia. As a result, cilia length and hedgehog signaling are altered.
Introduction
Splicing of eukaryotic introns from precursor messenger RNAs is accomplished by the major and minor spliceosomes, two macromolecular machineries composed of five uridine-rich small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles (U snRNPs) and a collection of auxiliary proteins. U1, U2, U4, and U6 snRNPs are exclusive of the major spliceosome; U11, U12, U4atac, and U6atac are restricted to the minor spliceosome; and U5 is shared by the two complexes.1,2 Major and minor spliceosomes excise different class of intronic sequences. Introns removed by the minor spliceosome, also known as minor introns or U12 introns, are primarily distinguished from those spliced by the major spliceosome (U2 introns) by having specific donor splice site and branchpoint consensus sequences.1, 2, 3, 4 Both types of introns and corresponding spliceosomal complexes are present in most eukaryotes and are thought to have co-existed in the last eukaryotic common ancestor.1,5 However, the percentage of U12 introns in eukaryotic genomes is low, and they have been lost in certain organisms.4,6 In humans, about 714 genes are featured with U12 introns, the majority of which have one single minor intron.7 Furthermore, minor spliceosome particles are present in cells in a small proportion, and the excision rate of U12 introns is considered less efficient than that of U2 introns.8,9 In spite of this, minor intron splicing has a fundamental role in development.5 Inactivation of minor spliceosome genes was shown to be lethal at early developmental stages in model organisms, and pathogenic variants in genes encoding minor spliceosome components have been identified in a handful of human disorders.1,2,5 Microcephalic osteodysplastic primordial dwarfism type I (MIM: 210710), Roifman syndrome (MIM: 616651), and Lowry-Wood syndrome (MIM: 226960) are all caused by variants in RNU4ATAC (MIM: 601428) encoding U4atac small nuclear RNA (snRNA). Early onset cerebellar ataxia and CDAGS syndrome (MIM: 603116) are associated with mutations in the gene coding for U12 snRNA (RNU12 [MIM: not available]), and causative variants in the minor spliceosome protein RNPC3 (MIM: 618016) were described in isolated growth hormone deficiency (MIM: 618160). Additionally, somatic mutations in ZRSR2 (MIM: 300028), a protein involved in both major and minor splicing, were identified in myelodysplastic syndrome.1,2,10
Previous computational studies have revealed that a significant number of genes containing minor introns are related to the biology of the primary cilium.7,11 Vertebrate primary cilia are nearly ubiquitous organelles composed of a 9 + 0 axoneme extending from a basal body and a specialized region between the basal body and the axoneme named transition zone (TZ). This region includes a group of bifurcated fibers (Y-links) connecting the axonemal microtubules to the cilium membrane, which help maintain the unique protein composition of the cilium.12,13 Trafficking of proteins within cilia depends on a specific intraflagellar transport system (IFT) comprising two multimeric protein complexes, each of which is in charge of anterograde (IFT-B) or retrograde (IFT-A) ciliary transport.14 Primary cilia have a major role in signal transduction and are indispensable for vertebrate Hedgehog (Hh) signaling, a developmental pathway that directs the morphogenesis of most vertebrate organs.13,15 Critical components of the Hh pathway, including the 7-pass transmembrane protein Smoothened (SMO), which is a principal mediator of Hh signaling, enter or exit the cilium in response to Hh ligands.16 Earlier work demonstrated that primary cilia play a dual function in the Hh pathway because they are required for generating both GLI-repressors and fully competent GLI transcriptional activators, which are the final effectors of Hh signaling.17,18
Mutations in genes disrupting the structure or function of primary cilia underlie a wide range of multi-organ congenital disorders termed ciliopathies, among which is orofaciodigital syndrome (OFD).19 Individuals with OFD have distinctive features involving the face, the mouth, and the patterning of the autopod. Affected individuals may also present additional malformations including cerebral and/or cerebellar structural anomalies, cystic renal disease, and skeletal and ocular anomalies. OFD was divided in different subtypes (OFD I–XIV) according to these extra findings and inheritance patterns.20,21 Although most individuals with OFD have mutations in the X-linked gene OFD1 (MIM: 300170), there is also a proportion of them that have been identified with pathogenic variants in autosomal recessive genes. So far, 18 genes encoding proteins that localize to the basal body, TZ, or transition fibers, or are involved in IFT or ciliary biogenesis, have been associated with OFD.22, 23, 24
In this manuscript, we reveal that recessive deleterious mutations in the gene called sodium channel modifier 1 (SCNM1 [MIM: 608095]) cause OFD and demonstrate that loss of function of this gene results in cilia anomalies associated with this condition. SCNM1 (GenBank: NM_024041.4 and NP_076946.1) has seven exons and encodes a 230 amino acid protein encompassing a C2H2 zinc finger (ZF) domain at the N-terminal and a C-terminal acidic domain. The SCNM1 protein was recently identified as a new specific component of the minor spliceosome following purification and structural characterization of the human minor Bact complex by cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM).25 Herein, we show that the protein encoded by SCNM1 is essential for the splicing of a set of U12 intron-containing genes, some of them linked to primary cilia, that have relevant functions in human development.
Material and methods
Genetic studies
SNP-array hybridization was performed as described previously.26 In brief, a total amount of 200 ng of genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood was hybridized to Illumina CytoSNP-850K BeadChip SNP-based arrays following the protocol indicated by the manufacturer (Illumina). We identified homozygous regions with GenomeStudio software (Illumina) by assessing B allele frequencies for all SNPs. Whole-exome sequencing (WES) of DNA from peripheral blood was provided by Sistemas Genomicos S. L. (Valencia, Spain) and NIMGenetics (Madrid, Spain). Exome capture was carried out with SureSelect Human All Exon Target Enrichment kit for 51 Mb or SureSelectXT Human All Exon V6 (Agilent Technologies). WES reads were aligned to the human genome reference sequence GRCh38/hg38/GRCh37/hg19 and variant calling was conducted as described earlier27 or with DRAGEN v3.6.3 software (Illumina). Variants were filtered by minor allele frequency (MAF; absent or <0.01 in 1000 Genomes Project [1000G]28 or gnomAD29) and by their predicted functional effect on transcripts (missense, nonsense, indel, or splice site variants). In addition, variants embedded in homozygosity regions > 1.5 Mb were prioritized. For Sanger sequencing validation of genomic variants, PCR products amplified from genomic DNA were enzymatically purified with ExS-Pure (Nimagen) and directly sequenced. All studies were performed according to the Declaration of Helsinki for medical research involving human subjects. The research was approved by institutional ethics committees of National Research Centre, Medical Research Institute-Alexandria University, and Hospital La Paz-CSIC. Parental consent was provided for clinical and molecular studies and for publication of photographs.
Cell culture and Hh signaling assay
Human dermal primary fibroblasts of an affected individual (P2) and a control subject (C2) were generated from skin biopsies with methods described earlier.27 Human neonatal dermal fibroblasts purchased from Lonza (CC-2509 neonatal [C1]) or Sigma-Aldrich (106-05N, neonatal) were included as controls in some experiments. Culturing of primary fibroblasts was carried out in a humidified atmosphere at 37°C/5% CO2 in fibroblast growth medium [DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and antibiotic-antimycotic (A-A) solution (Gibco, 100 units/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 0.25 μg/mL amphotericin B)]. For the analysis of the Hh pathway, primary fibroblasts were seeded in fibroblast growth medium at a density of 1 × 106 cells/100 mm plate (immunoblot), 3 × 105 cells/60 mm plate (reverse-transcription quantitative PCR [RT-qPCR]) or 5 × 104 cells/well in 24-well plate (immunofluorescence). After 24 h, cells were changed to low serum medium (DMEM with 0.5% FBS + A-A) supplemented with 100 nM SAG (Calbiochem) or its vehicle (DMSO) and cultured for an additional 24 h before being analyzed. In all studies, primary fibroblasts from less than ten passages were used. hTERT-immortalized retinal pigment epithelial cells (hTERT RPE-1 (ATCC); hereafter RPE-1) were cultured in RPE-1 complete medium (DMEM/F-12 (1:1) supplemented with 10% FBS and A-A solution). RPE-1 cells were authenticated by short tandem repeat DNA profiling, and they tested negative for mycoplasma.
RT-PCR
Fibroblasts or RPE-1 cells were plated in 60 mm dish plates (3 × 105 fibroblasts/plate; 5.5 × 105 RPE-1/plate) and kept in their corresponding growth medium for 48 h. Subsequently, cells were washed with PBS and total RNA was extracted with the Speedtools total RNA extraction kit (Biotools B&M Labs) according to the instructions of the manufacturer. 1 μg of RNA was retrotranscribed with random hexamers and the SuperScript IV First-Strand Synthesis System kit (Invitrogen). Reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) reactions were performed with 15 ng of cDNA as template assuming 1:1 RNA-cDNA conversion. RT-PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, and both canonical and abnormal length PCR fragments were excised from the agarose, purified with QIAquick Gel Extraction kit (Qiagen), and sequenced by Sanger sequencing. Exon-exon and exon-intron (U12) RT-PCR primers used in this study are listed in Table S1.
RT-qPCR
For RT-qPCR, fibroblasts and RPE-1 seeding conditions and RNA extraction were as described for the RT-PCR assays. Synthesis of cDNA was carried out with the high-capacity reverse-transcription kit (Applied Biosystem) with 250 ng of total RNA and random primers. Quantification of transcripts with TaqMan real-time PCR gene expression assays (Applied Biosystems) was performed with a QS7 Flex Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystem) in a final reaction volume of 10 μL containing 2.5 ng of cDNA. The following TaqMan expression assays were used: SCNM1 (Hs00276716_m1), TMEM107 (Hs00766060_m1), FAM92A (Hs01584032_g1), DERL2 (Hs00959155_m1), ZC3H8 (Hs01056139_m1), GLI1 (Hs01110766_m1), GUSB (Hs99999908_m1), and GAPDH (Hs99999905_m1). In the case of C17orf75, mRNA quantification was conducted with Power Syber Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems) in a final reaction volume of 10 μL containing 15 ng of cDNA and the following primers for C17orf75 and GUSB: C17orf75-Fw (5ʹ-GGACTTGAGCTTTTCAGGCTTG-3ʹ), C17orf75-Rv (5ʹ-CCCTTTGGATTGGGCATACAAC-3ʹ), GUSB-Fw (5ʹ-CACCAGGGACCATCCAATACC-3ʹ), and GUSB-Rv (5ʹ-GCAGTCCAGCGTAGTTGAAAAA-3ʹ). C17orf75 amplification reactions were performed in a StepOne Plus system (Applied Biosystem). Expression assays for TMEM107, DERL2, ZC3H8, and C17orf75 cover the junction of the two exons bordering the minor intron of interest. The FAM92A expression assay spans the second and third exons downstream the minor intron. Relative mRNA levels of each sample were calculated on the basis of Ct values and normalized against the geometric mean of the expression of the housekeeping genes GAPDH and GUSB, or against GUSB expression in the case of C17orf75. For each gene, we used the ΔCt mean value from a control sample as calibrator to calculate ΔΔCt. Relative quantification was obtained by the 2−ΔΔCt method. At least three biological replicates were analyzed for each experiment and every sample was run in triplicate.
RNA-seq and intron retention bioinformatics analysis
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was conducted on four RNA samples isolated from four independent primary fibroblast cultures, two corresponding to an affected individual (P2) and the other two to control fibroblasts (Sigma-Aldrich, 106-05N). Seeding of cells and RNA purification were performed as described above. RNA-seq was provided by Sistemas Genomicos S. L. Briefly, RNA was treated with Ambion DNAse I and concentrated with the RNeasy MinElute Cleanup Kit (Qiagen) following the instructions recommended by the manufacturer. An amount of 1 μg of RNA with an RIN (RNA integrity number) higher than 8.0 was used for sequencing. RNA strand-specific libraries were prepared with the NEBNext UltraTM Directional RNA Library Prep Kit (New England Biolabs), and high-throughput sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq 2500 ultra-sequencing platform (Illumina). Reads were mapped to the human genome version hg19 with STAR aligner v.2-7-9a30 and the knownGene table (UCSC) annotations for hg19 with default parameters. BAM files were subsequently used for differential intron retention analysis with the R package IntEREst by using the DESeq2-based function of this package as described in Oghabian A. et al.,31 except that an adjusted p value threshold of 0.05 was used instead of 0.01. For visualization of reads across genes showing significant U12 intron retention, sashimi plots were generated with the ggsashimi command-line tool32 as follows: ./ggsashimi.py -b /path/to/input_bams.tsv -c DesiredGenomicCoordinates -g /path/to/hg19.knownGene.gtf -o /path/to/output -S positive/negative -M 10 -C 3 -O 3 --alpha 1 --base-size=20 --ann-height=4 --height=3 --width=18 -P /path/to/palette.txt --fix-y-scale -A mean -F tiff -R 600.
Minigene assay
To generate the SCNM1 wild-type minigene, we used primers 5ʹ-GAATTCTTCATTGCTCTGGCAACAAC-3ʹ (forward) and 5ʹ- CTCGAGCCCAGCCAAAATTCTCCTTT-3ʹ (reverse) to amplify a 1,286 bp genomic DNA fragment spanning from intron 1 to intron 5 of SCNM1 by using as template genomic DNA from a control individual. PCR was conducted with proofreading hot-start Platinum SuperFi II DNA Polymerase (Invitrogen). The resulting PCR product was cloned into the exon trapping vector pSPL3 (Invitrogen) with EcoRI/XhoI restriction sites, and the DNA sequence of the selected construct was verified by Sanger sequencing against the SCNM1 reference sequence obtained from Ensembl. pSPL3 contains a SV40 promoter, two artificial exons A and B harboring functional donor and acceptor splice sites, respectively, and a 2.4 kb intron, which includes a multicloning site. We subsequently used the wild-type minigene as template to generate a mutant construct carrying the c.152C>A (p.Pro51Gln [GenBank: NM_024041.4]) variant through PCR-mediated site-directed mutagenesis also by using Platinum SuperFi II DNA Polymerase. Sanger sequencing was performed to ensure the presence of the c.152C>A change in the mutant minigene and that there were no other nucleotide changes with respect to the wild-type construct. RPE-1 cells were transfected with either the wild-type or c.152C>A minigenes or the empty pSPL3 vector with Lipofectamine 2000 Reagent (Invitrogen) by reverse transfection. Briefly, 5 × 105 cells were resuspended in 2 mL Opti-MEM (Gibco) containing the DNA (2.5 μg)-Lipofectamine mixture and seeded in a 6-well plate following the manufacturer’s instructions. 4 h later, the medium was replaced with complete RPE-1 medium. RNA was extracted 24 h after transfection, and cDNA was synthetized as described before. RT-PCR was performed with 50 ng of cDNA and primers SD6 and SA2 annealing to exons A and B of pSPL3, respectively. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis, purified from the gel and sequenced by Sanger sequencing.
Generation of CRISPR-Cas9 SCNM1 knockout cell lines
Disruption of SCNM1 in RPE-1 cells was accomplished with the SCNM1 Human Gene Knockout Kit (KN400987) from OriGene Technologies. A gRNA-Cas9 vector targeting exon 2 of SCNM1 and a linear donor DNA bearing a fusion of the red fluorescent protein (RFP) to blasticidin deaminase (BSD) under the control of a constitutive promoter to enable selection of mutant clones were used. Two different transfection experiments were performed with either Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen) or DharmaFECT Kb (Horizon) following the indications of the manufacturers. Briefly, 1 day before transfection, 2 × 105 cells/6-well plate were seeded and subsequently transfected with 1 μg of gRNA-Cas9 vector and 1 μg of donor DNA. Cells were cultured for 10 days in RPE-1 complete medium prior to addition of blasticidin (7 μg/mL). After 2 weeks in selective medium, clones were isolated by trypsinization with cloning cylinders (Merck CLS31668) and expanded. Genomic DNA from blasticidin resistant clones was extracted by standard methods and disruption of SCNM1 exon 2 by the insertion of the donor DNA cassette was tested by PCR with one primer located in the RFP-blasticidin cassette and the other in the region flanking the integration site. Bi-allelic knockout of SCNM1 in selected clones was confirmed by PCR-amplification of SCNM1 exon 2 with intronic primers followed by direct sequencing. In addition to the insertion of the blasticidin cassette, selected clones were found with indel mutations in the second allele.
siRNA transfection
RPE-1 cells were plated in 35 mm dish plate (1 × 105 cells/P35) and the next day transfected with 50 nM of ON-TARGETplus siRNA against SCNM1 (SMARTpool, L014273-00-0005, Dharmacon) or control siRNA (non-targeting pool, D-001810-10-05, Dharmacon) in antibiotic-free RPE-1 complete medium with DharmaFECT 1 reagent (Dharmacon). Transfection medium was replaced 24 h later with RPE-1 complete medium, and cells were maintained in this medium for another 48 h before being processed for RT-PCR and RT-qPCR assays. In the case of immunoblot analysis, cells were kept for 24 h in complete medium and then changed to low serum medium (DMEM:F-12 with 0.2% FBS + A-A) for an additional 48 h. For cilia studies, RPE-1 cells were seeded on coverslips in a 24-multiwell plate (5 × 104 cells/well) and transfected with siRNAs as indicated above. 24 h after transfection, the media was changed and cells were left to recover for another 24 h in RPE-1 complete medium. After this, we transferred cells to RPE-1 low serum medium for 48 h to promote ciliation and subsequently fixed and analyzed them by immunofluorescence.
Retroviral infections
Wild-type SCNM1 cDNA (GenBank: NM_024041.4) was amplified from RPE-1 cells with Platinum SuperFi II DNA Polymerase (Invitrogen) and cloned into the pBABE-Puro retroviral vector. We performed DNA sequencing to verify the absence of nucleotide variations with respect to the reference sequence. For retroviral infections, 4 × 106 HEK293T cells were seeded in 100 mm dish plates and, after 24 h, co-transfected with 10 μg of pBABE or pBABE-SCNM1 and 10 μg of the packaging vector pCL-Ampho with the calcium phosphate method. Supernatants containing retroviruses were collected 36, 48, and 60 h after transfection, passed through a 0.45 μm nitrocellulose filter, and mixed 1:1 with fibroblast growth medium containing polybrene (final polybrene concentrations after dilution: 8 μg/mL, 4 μg/mL, and 8 μg/mL, respectively). Diluted supernatants were applied in a total of three consecutive infections to primary fibroblasts plated at a density of 6.5 × 105 cells/P100. Fibroblasts were left to recover 24 h after the last infection and subsequently were selected with 2 μg/mL of puromycin during 3 days. Puromycin-resistant fibroblasts were then used in experimental procedures. For experimental replicates, independent retroviral infections were conducted.
Immunofluorescence
Fibroblasts or RPE-1 (5 × 104 cells/well) were seeded on coverslips in 24-multiwell plates and maintained 24 h or 48 h, respectively, in their corresponding low serum media to induce ciliation. Cells were subsequently fixed with 4% PFA/PBS for 5 min on ice (for acetylated tubulin and ARL13B staining) or 10 min at room temperature (for SMO visualization). An additional step consisting of a 5 min incubation in chilled methanol (−20°C) was conducted for γ-tubulin detection. Cells were permeabilized in 0.1% Triton X-100/PBS for 15 min and maintained 1 h in blocking solution (4% goat serum/PBS/0.05% Tween 20). Coverslips were kept overnight at 4°C in a wet chamber with primary antibodies diluted in blocking buffer. The next day, cells were washed with PBS and PBS/0.05% Tween 20, and fluorescence-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:800; Molecular Probes) were added for 1 h at room temperature. Primary antibodies: acetylated tubulin (1:2,000; Sigma, T7451), γ-tubulin (1:2,000; Sigma, T5326), ARL13B (1:1,000; Proteintech, 17711-1-AP), and SMO (1:1,000, Abcam, ab38686). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (1:2,000; Molecular Probes, D1306). Coverslips were mounted with Prolong Diamond (Molecular Probes) for image acquisition in a Nikon 90i microscope.
Primary cilia analysis
Cilia length was measured with NIS-Elements Software (Nikon). The percentage of ciliated cells was calculated as the ratio of the number of cilia labeled with acetylated tubulin with respect to the number of nuclei stained with DAPI. For each assay, the percentage of ciliated cells of at least three independent experimental replicates was determined and the mean value was plotted. The proportion of ciliary translocation of SMO in cells incubated with DMSO or SAG was quantified by counting the number of SMO-positive cilia per total number of cilia identified by acetylated tubulin staining. For quantification of ARL13B immunofluorescence, three confocal microscopy images (Z-project; Zeiss LSM710) containing several cilia were acquired per fibroblast cell line in each experimental replicate. Fluorescence quantification was performed with the help of ImageJ Fiji software as follows: to exclude non-stained areas, we used a threshold for the ARL13B fluorescent channel and maintained it constantly within the analysis of control and affected individual fibroblasts. For each cilium, ARL13B staining was delimited in an individual region of interest (ROI) and the integrated density calculated.
Immunoblot
Cells were washed with PBS and lysed in RIPA buffer (150 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl, 2 mM EDTA, 0.5% sodium deoxicolate, 0.1% SDS, 1% NP-40) supplemented with a protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma-Aldrich; P8340) and phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma-Aldrich, P0044 and P5726, 2.5 mM Na3OV4 and 10 mM NaF). The protein concentration in cell extracts was determined by the BCA colorimetric assay (Pierce, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Samples were boiled 5 min in Laemmli buffer at 95°C before loading onto SDS-PAGE gels, except the ones for DERL2 detection that were heated for 30 min at 37°C. Immunoblots were performed as previously described.33 Primary antibodies: SCNM1 (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-376328), DERL2 (1:500; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-398573), FAM92A (1:1,000; Proteintech, 24803-1-AP), ZC3H8 (1:1,000; Proteintech, 26152-1-AP), C17orf75 (1:250, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-81862), GLI1 (1:1,000; Cell Signaling, (C68H3) 3538), GLI3 (0.4 μg/mL; R&D, AF3690), α-Tubulin (1:80,000; Sigma, T9026), and vinculin (1:2,000, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-73614). HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:10,000) were acquired from Jackson ImmunoResearch. Immunoblot membranes were developed with enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent (GE Healthcare), and signal detection was achieved by exposure to Agfa X-ray films. Densitometry analysis of immunoblots was carried out with ImageJ Fiji software.
Homology search and common taxonomy tree generation
We used the human SCNM1 sequence (GenBank: NP_076946.1) as query to search for SCNM1 orthologous proteins across different species with the help of the blastp tool from NCBI. The search was conducted against the NCBI non-redundant protein sequences (nr) database. Entries with a query cover ≥ 75% and an E-value ≤1 × 10−10 were considered positive hits. Multiple sequence alignment was generated with the MUSCLE algorithm34 included in Unipro UGENE v40.1 bioinformatics toolkit.35 We used the NCBI Taxonomy Common tree tool to create a taxonomy-based tree of selected species, which was then displayed with iTOL v.5 online tool.36 Full names of the species included in Figure 2D: Acanthamoeba castellanii (A. castellanii) and Dictyostelium discoideum (D. discoideum) (protists); Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae), Rhizopus oryzae (R. oryzae), and Basidiobolus meristosporus (B. meristosporus) (fungi); Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (C. reinhardtii), Zea mays (Z. mays), Solanum lycopersicum (S. lycopersicum), Arabidopsis thaliana (A. thaliana), and Prosopis alba (P. alba) (algae and plants); Trichoplax adhaerens (T. adhaerens), Aplysia californica (A. californica), Capitella teleta (C. teleta), Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster), Melanaphis sacchari (M. sacchari), Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (S. purpuratus), and Branchiostoma floridae (B. floridae) (invertebrates); Takifugu rubripes (T. rubripes), Xenopus laevis (X. laevis), Gallus gallus (G. gallus), Mus musculus (M. musculus), and Homo sapiens (H. sapiens) (vertebrates).
Figure 2.
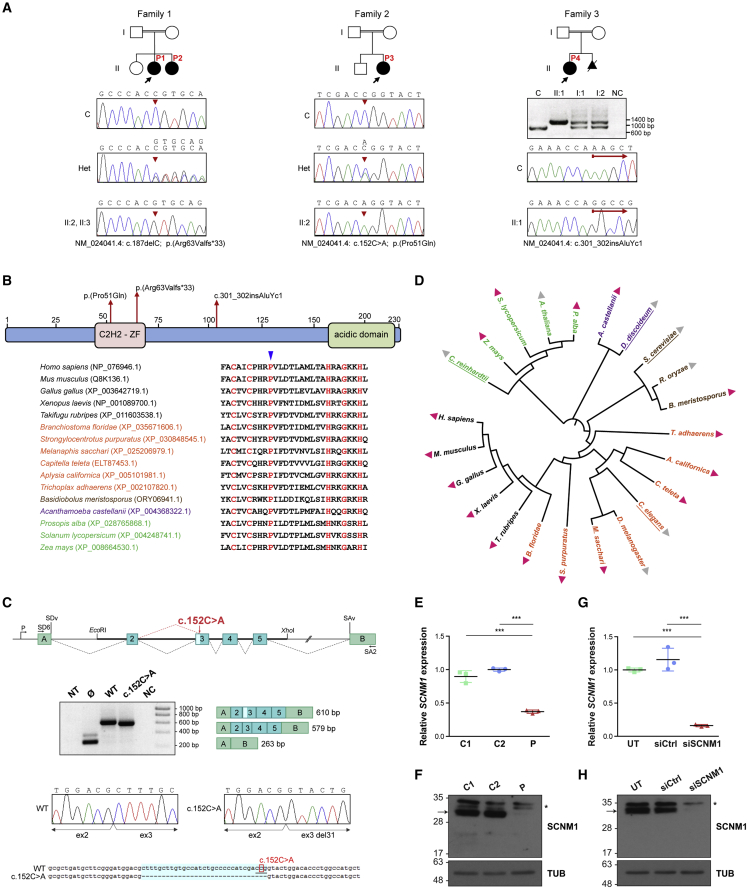
Identification of loss-of-function mutations in SCNM1 in individuals with OFD
(A) Family pedigrees of affected individuals P1–P4 described in this report. Probands are designated with black arrows. Genomic DNA sequence chromatograms of SCNM1 illustrating the homozygous mutation (red arrowheads) identified in each family are displayed underneath. The sequence of affected individuals, heterozygous carriers (Het), and a control sample (C) are shown. Nucleotide sequences corresponding to mutant (top) and normal (underneath) alleles are written on Het electropherograms. The agarose gel image below the pedigree of family 3 shows the PCR products resulting from the amplification of a genomic DNA fragment containing SCNM1 exon 4 in P4 (II:1), both of her parents (I:1, I:2), and in a control individual (C). NC, no DNA control. The red arrows in family 3 chromatograms designate the site of the AluYc1 insertion after which control and P4 DNA sequences diverge.
(B) Schematic representation of the SCNM1 protein indicating the position of the C2H2 zinc finger (C2H2-ZF) domain and the acidic domain of this protein, and the location of the three mutations indicated in (A). A sequence alignment of the C2H2-ZF domain from different SCNM1 orthologs showing high degree of conservation of Pro51 (blue arrowhead), is also indicated.
(C) SCNM1 minigene assay. Top: schematic representation of pSPL3/SCNM1 hybrid minigene. Boxes are exons and dotted lines connecting exons indicate normal (black) or altered (red) splicing events. The two artificial exons (A and B), promoter (P), donor (SDv), and acceptor (SAv) splice sites of pSPL3 are depicted. EcoRI and XhoI restriction sites used to clone the wild-type (WT) and c.152C>A SCNM1 genomic fragments as well as primers SD6 and SA2 used for RT-PCR are shown. Middle: representative gel electrophoresis image (n = 3) showing RT-PCR products obtained in cells transfected with the WT or the c.152C>A minigene or the empty vector (Ø). NT, non-transfected; NC, no cDNA control. Exon composition and sizes (WT [610 bp] and c.152C>A [579 bp]) of the amplified products are on the right. The light blue box in exon 3 of the WT PCR product represents the 31 bp that are missing in the c.152C>A PCR fragment. Sanger sequencing chromatograms of WT and c.152C>A RT-PCR products show the loss of the first 31 bp of SCNM1 exon 3 in the product from the mutant minigene. Bottom: DNA sequence alignment of WT and c.152C>A RT-PCR products highlighting (light blue) the 31 nucleotides missing in the c.152C>A sequence. Note the new CAG acceptor splice site (underlined nucleotides) created by the c.152C>A mutation (boxed nucleotide).
(D) Common taxonomy tree of representative eukaryotic species from distantly related phylogenetic taxa. Presence and absence of SCNM1 is indicated with pink and gray triangles, respectively. Species previously reported with no minor introns are underlined. Protists, fungi, algae and plants, and invertebrate and vertebrate animals are indicated in different colors. Full names and taxa of species are listed in material and methods.
(E) Relative quantification of SCNM1 expression by RT-qPCR in fibroblasts from controls (C1, C2) and affected individual P2 (P). Gene expression was normalized against the geometric mean of GAPDH and GUSB mRNA levels, and the ΔCt mean value of C2 was used as calibrator sample. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(F) Representative anti-SCNM1 immunoblot (n = 3) showing absence of SCNM1 in fibroblasts from P2 (P). Control fibroblasts: C1, C2. SCNM1 is indicated with an arrow, and the asterisk designates nonspecific bands. Tubulin (TUB) was used as a loading control.
(G) Relative quantification of SCNM1 expression (n = 3) by RT-qPCR in RPE-1 cells untransfected (UT) or transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or with siRNA against SCNM1 (siSCNM1). Gene expression analysis was performed as in (E) using the ΔCt mean value of UT cells as the calibrator sample. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(H) Representative anti-SCNM1 immunoblotting (n = 4) showing reduced levels of the SCNM1 protein in SCNM1-KD RPE-1 cells (siSCNM1) compared to UT and siCtrl cells. SCNM1 is indicated with an arrow, and the asterisk designates a nonspecific band. Loading control: tubulin (TUB).
Statistical analysis
We used GraphPad 5.0 software to perform statistical analysis. Normal distribution of data was checked with Shapiro-Wilk, D’Agostino-Pearson, and Kolmogorov-Smirnov normality tests or skewness and kurtosis normality scores. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey’s or Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons tests were carried out when data followed a normal distribution. If normality of data was not verified, non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple comparison test as post-hoc was applied. For the quantification of GLI3 protein isoforms, as a result of variations in absolute values between experiments, replicate blots were individually analyzed by densitometry and are included in supplemental information.
Results
Clinical description
We studied four individuals from three unrelated families with clinical manifestations of OFD, all born to healthy consanguineous parents (Figure 1 and Table 1). The proband of family 1 (P1) had a sister with the same condition (P2), the proband of family 2 (P3) had no affected siblings, and in family 3, in addition to the proband (P4), there was an affected fetus (Figure 2A). All OFD subjects presented with typical orofacial features in the form of tongue nodules, dental anomalies including congenital absence or abnormal shape of incisors, narrow, high arched or cleft palate, and retrognathia. Three of them also had midline notching of the upper or lower lip and accessory oral frenulae (Figures 1A–1D). Digital anomalies were present in all affected individuals and included postaxial polydactyly of both hands and feet, in combination with preaxial polydactyly mostly of the feet, which manifested as bifid or duplicated big toes. Syndactyly and brachydactyly were observed in the four affected subjects. All affected individuals had limb shortening and two had hypoplastic nails (Figures 1E–1N). Brain MRI was unremarkable in all of them, except for ectatic supratentorial ventricular system that was found in P1. Delayed speech was observed in two individuals, but intellectual and motor development were reported normal in all affected subjects. None of the affected individuals had history of epilepsy. Abdominal/renal ultrasounds were normal in all the affected subjects and echocardiography only identified patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and small atrial septal defect in P2. Clinical findings are summarized in Table 1.
Figure 1.
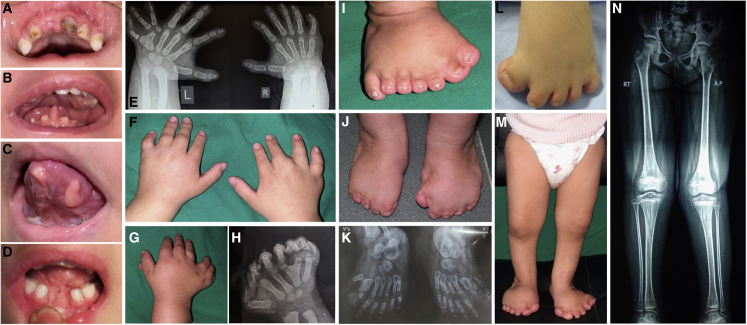
Clinical features of the OFD-affected individuals described in this study
(A) Orodental characteristics of P1 with accessory frenula of the upper lip, hypodontia, median notching of the lower lip, and excessive dental caries.
(B and C) Images showing lobulated tongue with nodules in P2 (B) and P3 (C).
(D) Hypodontia in the form of congenital absence of lower central incisors and median notching of the upper lip in P4.
(E) X-ray of the hands of P1 showing bilateral postaxial polydactyly (left, seven fingers; right, six fingers), left Y-shaped fifth metacarpal and severe mesophalangeal shortening.
(F) Brachydactyly, broad hands, and interdigital webbing in P1. Extra digits were surgically removed.
(G) Right hand of P2 demonstrating pre- and postaxial polydactyly (eight fingers) with syndactylous lateral three fingers.
(H) Left hand radiograph of P2 showing polydactyly and Y-shaped fourth metacarpal.
(I) Right foot of P2 showing broad duplicated hallux, syndactyly between toes, and triplicated fifth toe.
(J) Brachydactyly, partial skin syndactyly, dystrophic nails, and broad halluces in P3 feet post-surgery.
(K) X-ray (AP view) of the feet of P3 showing pre- and postaxial polydactyly, hypoplastic middle and distal phalanges, medially deviated extra preaxial metatarsals, and Y-shaped fifth metatarsal on the right foot.
(L) Brachydactyly, partial cutaneous syndactyly of the toes, broad and medially deviated halluces, and small nails of P4.
(M) Severe shortening of the legs of P2.
(N) X-ray lower limbs of P3 showing bilateral coxa valga with mild shortening of tibiae.
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of affected individuals included in this report
| Feature | Family 1 |
Family 2 |
Family 3 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | |
| Parental consanguinity | 1st cousins once removed | 1st cousins once removed | 2nd cousins | 1st cousins |
| Additional affected family members | + | + | – | +a |
| Age at last assessment | 5 years, 1 month | 1 year, 10 months | 7 years, 5 months | 3 years, 6 months |
| Gender | female | female | female | female |
| Anthropometric measurements | ||||
| Weight (SDS) | 17 kg (−0.45 SD) | 11 kg (−0.49 SD) | 34.5 kg (+1.66 SD) | 16.2 kg (+0.65 SD) |
| Height (SDS) | 103 cm (−1.12 SD) | 78 cm (−1.23 SD) | 126.5 cm (+0.41 SD) | 92.4 cm (−1.38 SD) |
| Head circumference (SDS) | 50 cm (−0.62 SD) | 46 cm (−0.53 SD) | 51 cm (−0.41 SD) | 47 cm (−1.61 SD) |
| Oral cavity | ||||
| Tongue | lobulated with nodules | lobulated with nodules | lobulated with nodules | tongue nodules |
| Dental anomalies | hypodontia (missing lower central incisors), excessive caries | hypodontia (missing lower lateral incisors) | microdontia of upper central incisors | hypodontia (congenital absence of lower central and lateral incisors) |
| Palate | narrow and high-arched | narrow and high-arched | narrow and high arched | soft palate cleft (operated) |
| Oral frenula | accessory frenula | accessory frenula | – | accessory frenula |
| Other oral features | – | – | serrated and thick alveolar ridge, spoon shaped tongue | – |
| Facial | ||||
| Cranium and forehead | dolichocephaly, frontal bossing | broad prominent forehead | high forehead | high forehead |
| Eyes and periorbital region | upslanted palpebral fissures | hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, strabismus | hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, downslanted palpebral fissures, strabismus (corrected by age) | mild epicanthal folds |
| Nose | broad nasal bridge, thick alae nasi | broad nasal bridge, broad nasal tip | broad nasal bridge, underdeveloped alae nasi, short columella, bifid nasal tip | broad nasal bridge, mildly short nose with anteverted nares |
| Ears | protruding, cupped, low-set ears | protruding, low-set ears, underfolded helices | bifid right ear lobe, low-set ears | small ear lobes, additional crus of the left antihelix |
| Mouth | narrow mouth | downturned corners of the mouth | narrow mouth, downturned corners of the mouth | downturned corners of the mouth |
| Lips | median notching of lower lip | median notching of upper lip | thin vermilion of the upper and lower lip | median notching of upper lip |
| Mandible and chin | retrognathia, horizontal chin crease | retrognathia, horizontal chin crease | mild retrognathia, horizontal chin crease | mild retrognathia, horizontal chin crease |
| Other | – | – | low posterior hairline | – |
| Hands and feet | ||||
| Polydactyly of the hands | bilateral postaxial polydactyly with six fingers on the right and seven fingers on the left (operated) | bilateral pre- and postaxial polydactyly with eight fingers | bilateral postaxial polydactyly with seven fingers on the right (with a shorter, more rudimentary fifth finger in between the well-developed fourth and sixth fingers), and six fingers on the left (a broad sixth finger low-inserted at a right angle to the ulnar side (operated) | bilateral postaxial type A polydactyly with six fingers (operated) |
| Preaxial polydactyly or broad halluces of the feet with postaxial polydactyly | broad, medially deviated halluces, bilateral postaxial polydactyly with six toes | bilateral pre- and postaxial polydactyly with complete duplication of halluces, with seven toes on the right and eight toes on the left | broad, medially deviated halluces with fused distal phalanges and bifid nails on the right, bilateral postaxial polydactyly (operated) | broad, medially deviated halluces with broad first metatarsals and bifid and fused distal phalanges, left postaxial hexadactyly (operated) |
| Syndactyly | bilateral partial skin syndactyly of the toes | bilateral partial skin syndactyly of the toes, complete skin syndactyly of digits six to eight on the left | bilateral partial skin syndactyly of the toes | bilateral partial skin syndactyly of the toes |
| Brachydactyly | type A brachydactyly of the hands and feet | type A brachydactyly of the hands and feet | type A brachydactyly of the hands and feet | type A brachydactyly of the hands and brachydactyly of the feet |
| Other hand/feet anomalies | broad hands, interdigital webbing, single flexion crease in several fingers, broad feet | broad hands, abnormal palmar creases, bilateral Y-shaped metacarpals, very broad feet | clinodactyly of right fifth finger with single palmar crease and camptodactyly of left fifth finger, broad and flat feet, bilateral talipes partially corrected by casting | reduced palmar creases, bilateral fifth finger clinodactyly with single flexion crease |
| Nails | normal | normal | hypoplastic nails more prominent on the feet | broad nails of halluces, small nails of the hands and the remaining digits of the feet |
| CNS | ||||
| Brain MRI | ectatic supratentorial ventricular system | not performed | normal | normal |
| History of epilepsy | – | – | – | – |
| Development and/or intelligence | timely acquisition of motor and social skills, delayed speech, normal intellectual performance | timely acquisition of motor and social skills, speech N/A | timely acquisition of motor skills, normal intellectual performance | timely acquisition of motor and social skills, delayed speech |
| Other features | ||||
| Short upper and lower limbs | mild shortening of forearms, mildly short of tibiae | mild shortening of forearms, markedly short tibiae | short arm span and mild shortening of tibia | short arm span of 87 cm (−2.67 SD) with arm span to height ratio of 0.94, lower limbs not evaluated |
| Congenital heart defects | normal ECHO | PDA and small ASD | normal ECHO | normal ECHO |
| Ophthalmological evaluation | normal eye examination and fundoscopy | normal eye examination and fundoscopy | normal vision | normal vision, no ophthalmological examination |
| Gastrointestinal and urogenital anomalies | normal abdominal and pelvic ultrasound | normal abdominal and pelvic ultrasound | normal abdominal and pelvic ultrasound | normal abdominal ultrasound, hypoplastic labia minora |
| Other | – | – | generalized thin skin with xerosis exacerbating in winter, more prominent over the feet (improved with age) | – |
| Genetic variant | c.187delC (GenBank: NM_024041.4), bi-allelic | c.187delC (GenBank: NM_024041.4), bi-allelic | c.152C>A (GenBank: NM_024041.4), bi-allelic | c.301_302 insAluYc1 (GenBank: NM_024041.4), bi-allelic |
ECHO, echocardiogram; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; ASD, atrial septal defect; N/A, not applicable as the affected individual was still an infant.
The mother had a miscarriage with polydactyly of the feet. Two first cousins once removed who had polydactyly died in the neonatal period due to congenital heart defects.
Identification of bi-allelic loss-of-function mutations in SCNM1 in individuals with OFD
To determine the etiology of the condition of affected subjects P1–P4, we conducted whole-exome sequencing (WES) in the proband of each family. Evaluation of WES variants excluded pathogenic changes in previously described OFD genes in any of the probands, which prompted us to search for a new gene responsible for this condition. Taken into account that all affected individuals had consanguineous parents (Table 1), we assumed an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance and that the mutations were homozygous by descent. On this basis, we performed a genome-wide SNP-array hybridization analysis in the four affected individuals of this study to identify chromosomal regions of homozygosity (ROH) candidate to contain the mutated gene. Notably, all four affected subjects shared a single homozygous block of 40 Mb that was located on chromosome 1 (chr1 [GRCh37]: g.111531126–151547397), pointing to a common causative gene (Table S2). In accordance with this hypothesis, the unaffected brother of family 2 was not homozygous for this chromosomal segment by SNP-array hybridization. Despite this result, given the genetic heterogeneity of OFD, we analyzed the probands of the three families independently by using a combination of homozygosity mapping and WES. For each proband, we selected coding and splicing variants predicted as pathogenic that were comprised within ROHs > 1.5 Mb and were absent or with low allele frequency in control databases (MAF < 0.01, gnomAD/1000G). In the case of the proband of family 1, only variants within ROHs common to her affected sister were considered. This analysis identified a homozygous single nucleotide deletion in exon 3 of SCNM1 in the proband of family 1, which was prioritized as the cause of the disease in this family (c.187delC [p.Arg63Valfs∗33] [GenBank: NM_024041.4]) (Figure 2A). As expected, SCNM1 was comprised within the 40 Mb ROH of chromosome 1 shared by all affected subjects (Table S2). The c.187delC variant causes a frameshift that runs into a premature stop codon 33 triplets later, thus most likely triggering the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway (NMD).37 Segregation analysis of this mutation in family 1 by Sanger sequencing confirmed that the two affected sisters were homozygous for the c.187delC variant, while their non-affected sibling and both parents had the SCNM1 change in the heterozygous state. Since SCNM1 encodes a protein that was identified as a new specific component of the minor spliceosome,25 we considered the function of SCNM1 to be in line with this gene’s being responsible for OFD because five previously described OFD genes, as well as other ciliary genes, contain U12 introns. Furthermore, according to databases, SCNM1 seems widely expressed across tissues (The GTEx Portal [bulk tissue gene expression]; HPA RNAseq project [NCBI, Gene database]).
Examination of the WES variants that remained after filtering in the proband of family 2 (P3) also revealed a homozygous missense change in SCNM1 exon 3 (c.152C>A [p.Pro51Gln] [GenBank: NM_024041.4]) classed as pathogenic by bioinformatics predictor programs (Figure 2A). Pro51 is a highly evolutionary conserved residue located within the C2H2-ZF domain of SCNM1 (Figure 2B). Sanger sequencing showed the c.152C>A variant to be in homozygosis in P3 and in the heterozygous state in both parents. The unaffected brother of P3 had wild-type sequence. Neither the c.152C>A variant nor the c.187delC nucleotide deletion from family 1 were detected in gnomAD. Additionally, in silico evaluation of the c.152C>A variant with the splice site predictor NNSPLICE 0.9v38 indicated that this change could alter the splicing of the SCNM1 transcript either by increasing the strength of a potential donor splice site located two nucleotides downstream or by directly introducing a new acceptor splice site. To investigate this, we conducted a minigene assay by using pSPL3 as backbone vector. We generated wild-type and mutant minigenes by inserting a genomic DNA fragment extending from −200 exon 2 to exon 5 + 142 of SCNM1 carrying either normal or c.152C>A sequence into pSPL3 (Figure 2C). RPE-1 cells were transfected with control or c.152C>A minigenes and the resulting splicing products were analyzed by RT-PCR with primers from the vector. While a product of the expected size was amplified in the cells transfected with the wild-type minigene, a slightly smaller PCR fragment was obtained in the transfections with the c.152C>A construct. Sequencing of these products demonstrated that in the cDNA fragment amplified from the cells expressing the mutant minigene, the first 31 bp of SCNM1 exon 3 were absent because of the use of the acceptor splice site created by the mutation (Figure 2C). Deletion of these 31 nucleotides in the SCNM1 transcript results in a frameshift and an early termination codon (c.123_153del [p.Phe42Tyrfs∗8] [GenBank: NM_024041.4]) predicted to lead to NMD.
Variant filtering in the affected individual of family 3 (P4) did not reveal a homozygous change in SCNM1 or an alternative candidate variant in a different gene. However, during WES analysis, we noted two consecutive nucleotide changes in the fourth exon of SCNM1 that were annotated as heterozygous (chr1[GRCh37]: g.151139668T>A, g.151139669T>A; c.283T>A, c.284T>A [GenBank: NM_024041.4]). Since this was inconsistent with SCNM1’s being embedded in an ROH in this subject, we amplified SCNM1 exon 4 in P4, her parents, and a control individual. This experiment yielded a single PCR product in P4, which was about 300 bp longer than the predicted size. This product was present in the heterozygous state in both parents and absent in the control sample (Figure 2A). Sequencing of the PCR fragment amplified in P4 followed by homology search against repetitive DNA with the Repbase database (GIRI) and Censor39 identified the insertion of a complete AluYc1 sequence interrupting exon 4 of SCNM1 (c.301_302insAluYc1 [GenBank: NM_024041.4]), thus explaining the increment in size of this fragment (Figure S1). This mutation is bound to lead to an aberrant SCNM1 transcript and subsequent absence or severe alteration of the protein. Typical target-site duplications of 17 bp were observed flanking the Alu40 (Figure S1). Technical difficulties in detecting Alu insertions by standard WES41,42 justify that the P4 mutation went initially unnoticed. The two SCNM1 variants annotated as heterozygous on WES corresponded to the two nucleotide positions preceding the 17 bp direct repeats flanking the Alu.
Phylogenetic analysis of SCNM1
Given the particular phylogenetic distribution of the minor intron splicing pathway,6 we investigated the presence of SCNM1 orthologs across eukaryotes by using blastp against the NCBI non-redundant protein sequences (nr) database. Proteins were retrieved from species of all eukaryotic kingdoms including the protist Acanthamoeba castellanii, the fungus Basidiobolus meristosporus, plants, and animals, but not from species known to have lost the minor intron splicing system such as Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Dictyostelium discoideum, Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Caenorhabditis elegans.1,6,43,44 SCNM1 orthologs were not identified in some other organisms containing minor introns including Rhizopus oryzae, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Drosophila melanogaster1,6,43 (Figure 2D). These cases could have a different minor spliceosome structure or another protein that replaces SCNM1 function. Both, the C2H2-ZF domain and the acidic domain of SCNM1 were conserved in all SCNM1 orthologs (Figure S2).
SCNM1 deficiency impairs splicing of a number of genes containing minor introns
To understand the molecular and cellular processes disrupted by SCNM1 mutations, we developed primary dermal fibroblasts from a skin biopsy of P2. Consistent with the prediction that the SCNM1 variant of this individual (c.187delC) activates NMD, P2 fibroblasts were identified with diminished levels of SCNM1 mRNA with respect to control cells by RT-qPCR. Immunoblot analysis also showed absence of SCNM1 protein in P2 cells (Figures 2E and 2F). Due to unavailability of biological material from other affected subjects, we knocked out SCNM1 in RPE-1 cells through CRISPR-Cas9-mediated editing to have an additional model where findings in P2 fibroblasts could be tested. SCNM1-knockout (KO) RPE-1 clones were selected through locus-specific genomic PCR and the loss of normal SCNM1 protein in these clones was subsequently validated by immunoblot analysis (Figure S3). Complementary to the CRISPR-Cas9 approach, we made use of a second cellular model by suppressing SCNM1 expression in RPE-1 by using small interfering RNA silencing (siRNA). Knockdown of SCNM1 (SCNM1-KD) in these cells was confirmed at the mRNA and protein level through RT-qPCR and immunoblot, respectively (Figures 2G and 2H).
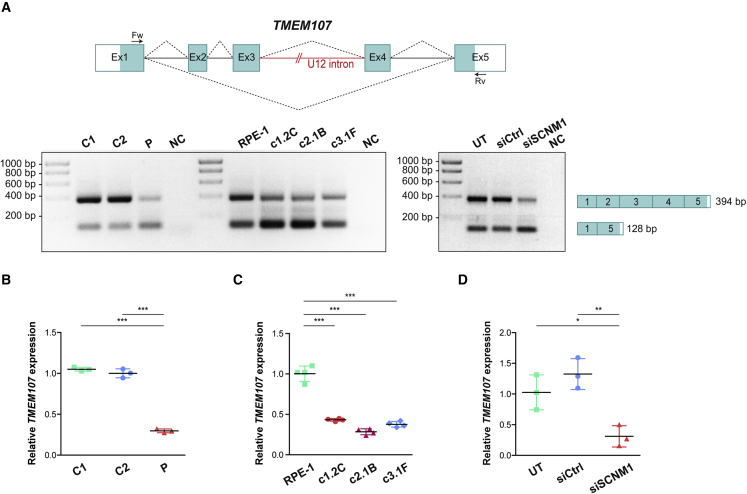
Considering the clinical phenotype of the affected individuals of this report, we checked the effect of loss of SCNM1 function on the splicing of previously described OFD genes listed in the Minor Intron DataBase (MIDB)7 as U12 intron-containing genes: C2CD3 (MIM: 615944), TBC1D32 (MIM: 615867), TCTN3 (MIM: 613847), TMEM107 (MIM: 616183), and TMEM231 (MIM: 614949). SCN8A (MIM: 600702), another U12 intron-containing gene, was added to this analysis because mutations in Scnm1 reduce the amount of normally spliced Scn8a transcript in mice carrying the Scn8amedj hypomorphic allele.45 We evaluated the splicing of the U12 introns of these genes in fibroblasts originated from P2 and control fibroblasts by RT-PCR with primers from exons on either side of the U12 introns (Table S1). This experiment showed differences in the expression of TMEM107, a gene comprising five coding exons, with exons 3 and 4 separated by a U12 intron (Figure 3A). TMEM107 RT-PCR primers were located in exons 1 and 5 and yielded two PCR products of 394 and 128 bp confirmed by sequencing to correspond to the full-length mRNA of TMEM107 encompassing all five coding exons (GenBank: NM_183065.4) and the non-coding alternative transcript containing only exons 1 and 5 (GenBank: NR_147092.2), respectively. RT-PCR analysis of TMEM107 showed a marked reduction in the amount of the large PCR product of this gene in P2 fibroblasts. This result was reproduced in three independent SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones (Figure 3A). Quantification of the mRNA levels of the coding isoform of TMEM107 by RT-qPCR with a Taqman gene expression assay spanning exons 3 and 4 revealed that the amount of this transcript relative to control samples was diminished by 70% in P2 fibroblasts and by 57%–72% in SCNM1-KO clones (Figures 3B and 3C). TMEM107 expression was also analyzed in SCNM1 siRNA-treated RPE-1 cells. Both RT-PCR and RT-qPCR assays showed lower levels of the full-length transcript of TMEM107 in SCNM1-KD cells than in cells incubated with a non-targeting control RNAi, or than in untreated cultures, thus providing further evidence for the critical role of SCNM1 in maintaining the normal expression levels of the TMEM107 coding isoform (Figures 3A and 3D).
Figure 3.
SCNM1 depletion reduces the expression of the coding transcript of TMEM107
(A) Schematic representation of TMEM107. Exons are depicted with blue boxes, and dotted lines indicate splicing events. White areas in exons 1 and 5 correspond to untranslated regions. TMEM107 U12 intron is represented as a red line, and RT-PCR primers used are denoted by arrows. Representative images of agarose gels corresponding to RT-PCR analysis of TMEM107 are underneath. Left: TMEM107 RT-PCR products from primary fibroblasts (controls: C1, C2; affected individual P2: P) and SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones (SCNM1-KO clones: c1.2C, c2.1B, c3.1F; parental control cells: RPE-1) (n = 3). Right: TMEM107 RT-PCR products from RPE-1 cells untransfected (UT) or transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or with siRNA against SCNM1 (siSCNM1) (n = 3). NC, no cDNA control. RT-PCR product sizes and exon composition of the amplified bands are on the right.
(B–D) Relative expression of TMEM107 determined by RT-qPCR in primary fibroblasts (B); SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones (C); and siRNA-treated RPE-1 cells (D). Samples in (B)–(D) are labeled as in (A). Gene expression was normalized against the geometric mean of GAPDH and GUSB mRNA levels. The ΔCt mean value of C2, RPE-1, or UT was used as calibrator sample in (B), (C), and (D), respectively. Scatter plots show mean ± SD (n = 3 for B and D; and n = 4 for C). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
We next investigated SCNM1 function in U12 intron processing at the whole-transcriptome level. To this end, we conducted RNA-seq on P2-derived and control fibroblasts and assessed differences in U12 intron retention levels in transcripts between these samples with the R package IntEREst.31 Using an adjusted p value < 0.05, we identified 25 U12 introns significantly more retained in P2 fibroblasts in comparison to control samples, while no U12 introns were observed with increased retention in the control cells (Figure S4A, Data S1, and Table S3). We selected 18 of the 25 U12 introns identified via IntEREst for further evaluation. These introns included all those with adjusted p value < 0.01 and three additional U12 introns contained in genes involved in IFT (KIFAP3) or intracellular transport (DCTN3, C17orf75). To empirically evaluate the retention levels of the selected U12 introns in their respective transcripts, we performed exon-intron (U12) semi-quantitative RT-PCR in SCNM1-deficient cells, including primary fibroblasts from P2 and RPE-1 cellular models (SCNM1-KO and SCNM1-KD cells), as well as in the corresponding control cultures. To exclude amplification of any possible residual genomic DNA, exon primers were designed to span at least one U2 intron (Table S1). Consistent with bioinformatics results, for all the 18 transcripts analyzed, we found a higher amount of exon-intron (U12) PCR product in the different SCNM1-deficient cells than in their control cultures, thus indicating increased quantity of pre-mRNA containing unspliced U12 intron of these genes in the absence of SCNM1 (Figure S4B). Splicing efficiency of U12 introns was also compared between SCNM1-deficient and control cells by exon-exon semi-quantitative RT-PCR. For this purpose, primers were designed to span the U12 intron and at least one additional U2 intron (Table S1). Notably, in 12 of the 18 transcripts evaluated, we detected the presence of abnormally spliced variants that were either exclusively amplified or enriched in all SCNM1-depleted cells. Sequence analysis of abnormal-length PCR products demonstrated that they resulted from diverse U12 intron splicing alterations, including complete U12 intron retention, skipping of exons adjacent to U12 introns, and activation of cryptic splice sites located within U12 introns or in the flanking exons (Figures 4A, 4B, 4D, 4E, 4G, 4H, 4J, 4K, S4C–S4F, Table S3A, and Data S2). All the activated cryptic 5′ splice sites matched the U2-type consensus sequence,4 and no transcripts were observed to be originated from combined usage of U12 and cryptic splice sites. Remarkably, exon-exon RT-PCR studies also showed a dramatic decrease in the amplification of the correctly spliced transcripts of four genes, FAM92A (also named as CIBAR1 [MIM: 617273]), DERL2 (MIM: 610304), ZC3H8 (MIM: not available), and C17orf75 (MIM: not available), both in the cells originated from P2 and in SCNM1-depleted RPE-1 cultures (Figures 4B, 4E, 4H, and 4K). The strong effect of the absence of SCNM1 in the expression of these genes was additionally demonstrated through RT-qPCR (Figure S5) and by immunoblot analysis (Figures 4C, 4F, 4I, and 4L). FAM92A and DERL2 protein levels were found to be more severely reduced than those of ZC3H8 and C17orf75 in SCNM1-deficient cells. Because the extent of the decrease in mRNA levels of the four genes was within a similar range (Figure S5), other factors related to the rates of protein translation and degradation must account for this difference.46
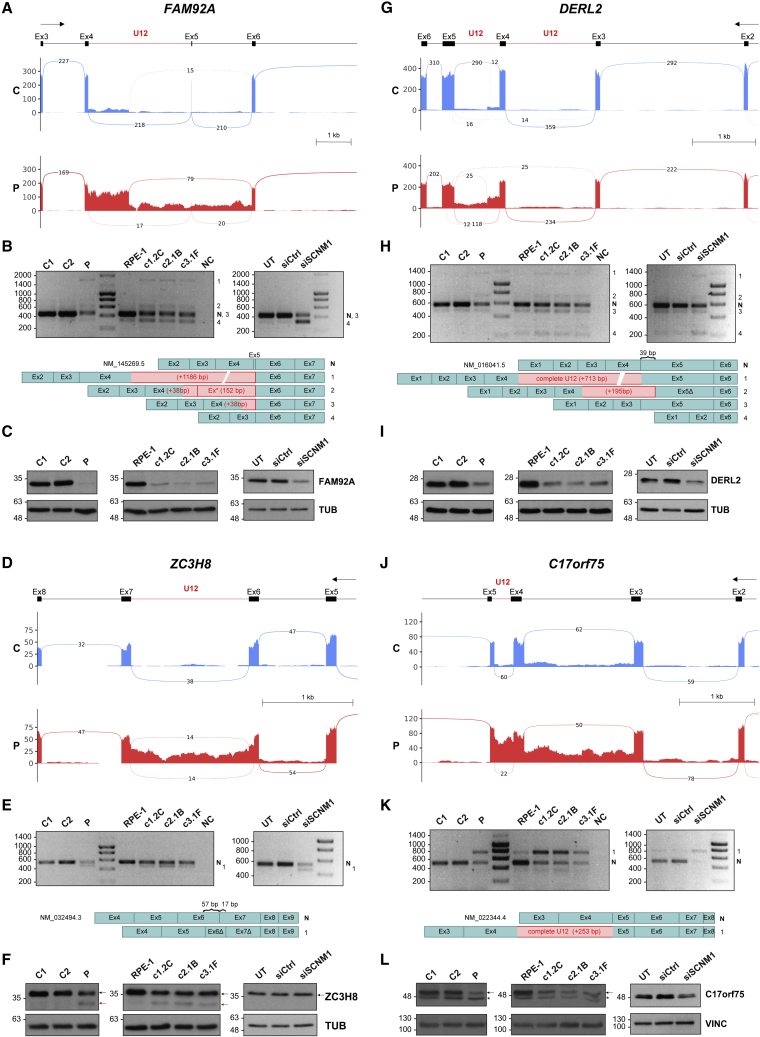
Figure 4.
SCNM1 deficiency causes defects in the splicing of a set of U12 intron-containing genes
(A–L) Sashimi plot visualization of aligned RNA-seq reads, RT-PCR, and protein expression analysis of FAM92A (A–C), ZC3H8 (D–F), DERL2 (G–I), and C17orf75 (J–L). For (A), (D), (G), and (J), the diagram on top shows a schematic representation of the genomic region containing the U12 intron of each gene. Boxes indicate exons and lines introns. U12 introns are represented with a red line. The top arrow indicates transcription direction. Sashimi plots corresponding to the genomic region of interest from control (C; in blue) and affected individual P2 (P; in red) fibroblasts are underneath. In each sashimi plot, the mean of the counts from two independent RNA-seq experiments is represented. Splicing events supported by a minimum of ten reads are denoted with lines and the number of reads supporting each event is indicated. Note that in the case of DERL2, which contains two U12 introns, only the one between exons 4 and 5 was detected as significantly retained in fibroblasts from P2 by bioinformatics analysis. (B), (E), (H), and (K) Representative agarose gel images showing exon-exon RT-PCR products of the indicated genes in primary fibroblasts (controls [C1, C2] and affected individual P2 [P]), SCNM1-KO RPE-1 cells (SCNM1-KO clones: c1.2C, c2.1B, c3.1F; parental control cells: RPE-1), and siRNA-treated RPE-1 cells (untransfected [UT], transfected with non-targeting siRNA [siCtrl], or with siRNA against SCNM1 [siSCNM1]) (n = 2). NC, no cDNA control. Normal transcript isoforms are designated with an N and the numbers on the right of each gel denote abnormally spliced products detected in this assay. Schematic representation of the exon composition of RT-PCR products is underneath showing, in each case, partial or complete inclusion of the U12 intron (red) and/or complete or partial exclusion of different canonical exons (blue). Ex∗ in (B) designates inclusion of a cryptic exon contained within the U12 intron of FAM92A. Exons with nucleotide deletions due to activation of internal cryptic splice sites (E and H) are identified with a Δ symbol and the number of deleted nucleotides is indicated with curly brackets in the normal transcript. (C), (F), (I), and (L) Representative immunoblots of FAM92A, ZC3H8, DERL2, and C17orf75 in protein extracts from primary fibroblasts, SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones, and siRNA-treated RPE-1 cells (n = 3). Samples are labeled as in (B), (E), (H), and (K). In (F), the WT isoform of the ZC3H8 protein and the truncated variant resulting from defective U12 intron splicing are indicated with a black or a red arrow, respectively. In (L), the black arrow designates the band corresponding to the C17orf75 protein and the asterisk an unspecific band. Tubulin (TUB) or vinculin (VINC) were used as loading controls.
Although the majority of abnormally spliced transcripts identified in SCNM1-deficient cells contain premature truncation codons that make them prone to degradation by NMD, some may escape this pathway. Exon-exon RT-PCR of ZC3H8 in SCNM1-deficient cells revealed the presence of an mRNA variant containing an internal deletion of 74 nucleotides (nt) with respect to the canonical ZC3H8 transcript (Figure 4E and Data S2). This variant results from activation of two cryptic splice sites, donor and acceptor, each located in one of the two exons flanking the U12 intron. The deletion of these 74 nt produces a frameshift in the ZC3H8 transcript that leads to an early stop codon 25 nt upstream of the last exon-exon junction, and thus is expected to avoid NMD (c.677_750del [p.Cys226Phefs∗24] [GenBank: NM_032494.3]). In agreement with this, an extra ZC3H8 protein variant of lower molecular weight than the wild-type was detected in anti-ZC3H8 immunoblots of SCNM1-deficient primary fibroblasts and SCNM1-KO RPE-1 cells (Figure 4F). The new protein variant predictably lacks the last 66 amino acids of the normal protein comprising two of the three C3H1-type zinc fingers of ZC3H8 and incorporates 23 new residues. Hence, loss of SCNM1 not only reduces the expression levels of normal proteins but can also give rise to new protein variants that may hinder the function of wild-type proteins or acquire new functions.
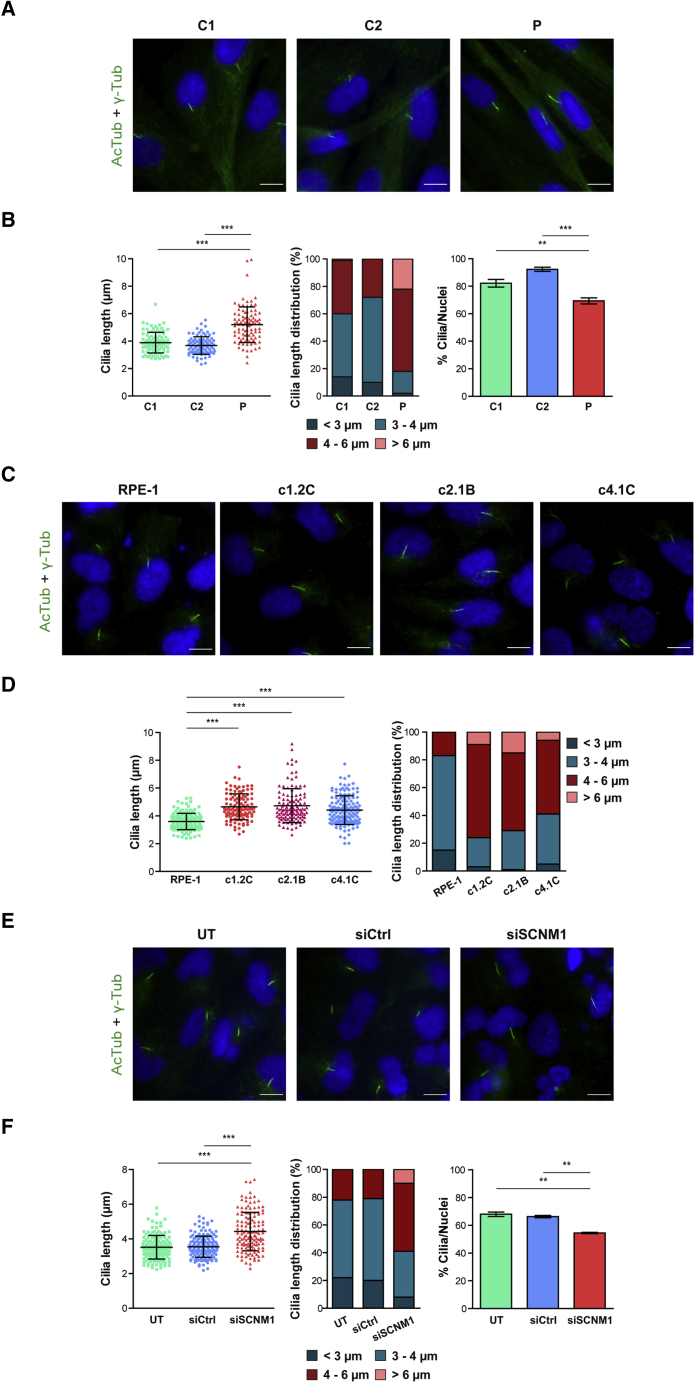
SCNM1 regulates cilia length and promotes Hh signaling
We studied primary cilia length and frequency in serum-starved P2 and control fibroblasts by immunofluorescence with acetylated tubulin as cilium marker. This showed that, compared to control cells, the fibroblasts originated from P2 had longer cilia on average. While in control cultures the majority of cilia were 3–4 μm long, most cilia from P2 cells were between 4–6 μm in length. Furthermore, 20% of the cilia from P2 fibroblasts were larger than 6 μm, whereas only one cilia of this category was detected in control cultures (Figures 5A and 5B). Elongation of cilia was consistently replicated in SCNM1-deficient RPE-1 cultures. The average length of cilia measured in five independent SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones was significantly increased as compared to the parental cells (Figures 5C, 5D, and S6). Similarly, RPE-1 cells treated with SCNM1 siRNA also developed cilia that were longer on average than the cilia of cells treated with a non-targeted RNAi control or the cilia of untreated cells (Figures 5E and 5F).
Figure 5.
Loss of SCNM1 causes defects in primary cilia
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing cilia with increased length in fibroblasts from affected individual P2 (P) compared to control fibroblasts (C1, C2). Green [acetylated tubulin (AcTub) + gamma tubulin (γ-Tub)]: cilia; blue (DAPI): nuclei. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(B) From left to right, graphs correspond to cilia length, distribution of cilia length, and frequency of ciliated cells in fibroblasts from affected individual P2 (P) versus controls (C1, C2). For cilia length, a minimum of 90 cilia were measured per cell line (n = 3 independent experiments) and for cilia number calculation, at least 160 cells were analyzed (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(C) Representative immunofluorescence images showing elongated primary cilia in three independent SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones (c1.2C, c2.1B, c4.1C) compared to RPE-1 control cells. Green (AcTub + γ-Tub): cilia; blue (DAPI): nuclei. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(D) Cilia length and cilia length distribution in SCNM1-KO RPE-1 clones (c1.2C, c2.1B, c4.1C) and RPE-1 control cells. At least 110 cilia from three different experiments were measured per cell line. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Data from two additional SCNM1-KO clones are in Figure S6.
(E) Representative immunofluorescence images showing extended primary cilia in RPE-1 cells transfected with SCNM1 siRNA (siSCNM1) compared to un-transfected (UT) or transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) cells. Green (AcTub + γ-Tub): cilia; blue (DAPI): nuclei. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(F) Data corresponding to cilia length, distribution of cilia length and frequency of ciliated cells in RPE-1 cells untransfected (UT) or transfected with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or with siRNA against SCNM1 (siSCNM1). For cilia length, a minimum of 130 cilia were measured, and for the calculation of ciliated cells, at least 280 cells were analyzed per condition from two independent experiments. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test and one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test were performed for cilia length and ciliation frequency, respectively.
Evaluation of the number of ciliated cells in P2-derived and control fibroblast cultures showed a small reduction in the percentage of ciliated cells in the cultures from P2 with respect to control cell lines (mean value decrease of 14% and 24% relative to controls C1 and C2, respectively) (Figure 5B). SCNM1 siRNA-treated RPE-1 cells were also found with a slight reduction (14%) in the ciliation percentage compared to the corresponding RPE-1 controls (Figure 5F). We additionally assessed the subcellular localization of ARL13B in the fibroblasts from P2 because the presence of this protein in the cilium membrane has been described to be altered in cells from affected individuals and mouse embryonic fibroblasts with mutations in some OFD genes.47, 48, 49 However, we observed no differences in the localization or abundance of ARL13B between control and P2 fibroblasts by immunofluorescence analysis (Figure S7).
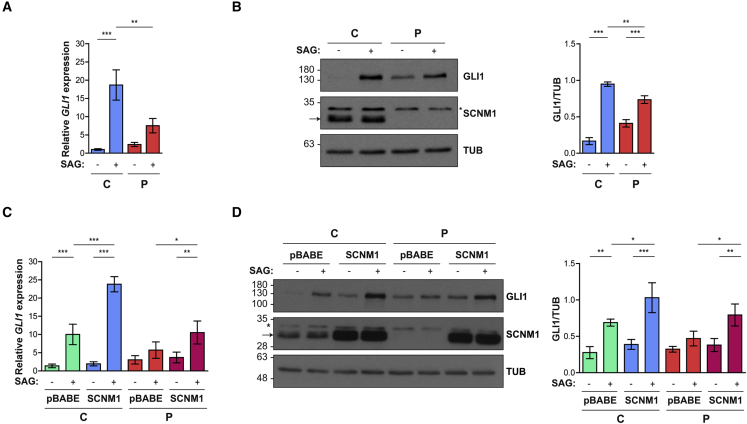
All affected individuals of this study presented with postaxial polydactyly or with a combination of post and preaxial polydactyly (Table 1). Given that polydactyly is a common ciliopathy feature typically caused by Hh signaling defects secondary to cilia alterations,50 we analyzed the response of fibroblasts from P2 to the stimulation of the Hh pathway. To this end, P2 and control cells were incubated with the SMO agonist SAG, or its vehicle (DMSO), and the output of the Hh pathway was subsequently analyzed by RT-qPCR and immunoblotting. Control fibroblasts (C2) were derived from an age- and gender-matched donor and had a number of passages equivalent to that of cells derived from P2. This experiment showed that although the P2 fibroblast cultures were able to respond to SAG stimulation, the extent of this response was diminished compared to control cells. The mRNA and protein levels of the Hh-target GLI1 were found to be lower in SAG-treated P2 fibroblasts than in control cells cultivated in the same condition, indicating impaired Hh signaling in the absence of SCNM1 (Figures 6A and 6B). To further investigate SCNM1 function, we cloned the cDNA of SCNM1 into pBABE and re-introduced this gene into P2-derived fibroblasts through retroviral delivery. This also provided a model to study the Hh pathway within the same cell line. Quantification of the mRNA levels of GLI1, as well as anti-GLI1 immunobloting, showed the cells originated from P2 with a more robust response to SAG when they were rescued with SCNM1 than when they were transduced with the empty vector pBABE, thus providing support for a positive role of SCNM1 in Hh signaling (Figures 6C and 6D). Normal control fibroblasts were similarly retrotransduced with SCNM1 or the empty vector and subjected to the same assay. Control fibroblasts overexpressing SCNM1 also exhibited an increased response to SAG compared to normal control cells transduced with pBABE, indicating a positive correlation between the levels of SCNM1 and the output of the Hh pathway (Figures 6C and 6D).
Figure 6.
SCNM1 positively regulates Hh signaling
(A) Relative quantification of GLI1 mRNA levels by RT-qPCR in control C2 (C) and affected individual P2 (P) primary fibroblasts treated with SAG (+) or its vehicle DMSO (−). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). Gene expression was normalized against the geometric mean of GAPDH and GUSB mRNA levels. The ΔCt mean value of C in DMSO was used as calibrator sample. ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(B) Representative immunoblot showing GLI1 protein levels in response to SAG (+) or DMSO (−) in control (C) and affected individual (P) fibroblasts. Anti-SCNM1 immunoblotting is also included. Loading control: tubulin (TUB). The graph on the right shows densitometric values of GLI1 levels normalized to tubulin. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(C) Relative quantification of GLI1 mRNA levels by RT-qPCR in control (C) and affected individual (P) primary fibroblasts transduced with SCNM1 or the empty retroviral vector pBABE-puro in response to SAG (+) or its vehicle DMSO (−). Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 [C], n = 4 [P]). Gene expression was normalized against the geometric mean of GAPDH and GUSB mRNA levels. The ΔCt mean value of DMSO-treated control cells transduced with pBABE was used as calibrator sample. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(D) Representative immunoblot of GLI1 protein levels in response to SAG (+) or DMSO (−) in control (C) and affected individual (P) primary fibroblasts transduced with SCNM1 or the empty vector (pBABE). Anti-SCNM1 immunoblotting is also included. The arrow and the asterisk on anti-SCNM1 blots (B and D) designate SCNM1 and a nonspecific band, respectively. Tubulin (TUB) was used as loading control. The graph on the right shows densitometric values of GLI1 levels normalized to tubulin. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3 [C], n = 4 [P]). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
Ciliary translocation of SMO and the proteolytic processing of the full-length GLI3 (GLI3FL) transcriptional activator into its truncated repressor form (GLI3R), which are critical steps of the Hh pathway, were assessed in retrotransduced cultures. Immunofluorescence analysis showed no statistically significant differences in the percentage of SMO positive cilia between pBABE and SCNM1 retrotransduced P2 cells after SAG-stimulation (Figure S8A). Regarding GLI3, we repeatedly observed, in three independent biological replicates, an increase in the levels of GLI3R and the GLI3R/GLI3FL ratio in DMSO-treated cells from P2 rescued with SCNM1 compared to P2 cells transduced with pBABE in the same condition (Figures S8B–S8D). This result suggests that SCNM1 might also have a positive role in promoting GLI3 processing, which would be in agreement with the levels of GLI3R’s being lower in the cells derived from P2 than in the normal control fibroblasts (Figures S8B–S8D). Altogether, the data on the readout of the Hh pathway in retrotransduced cells indicates that in the absence of SCNM1, both the activator functions of GLI factors and the generation of GLI3R appear to be disturbed, which could resemble what has been described for IFT mutants.17,18
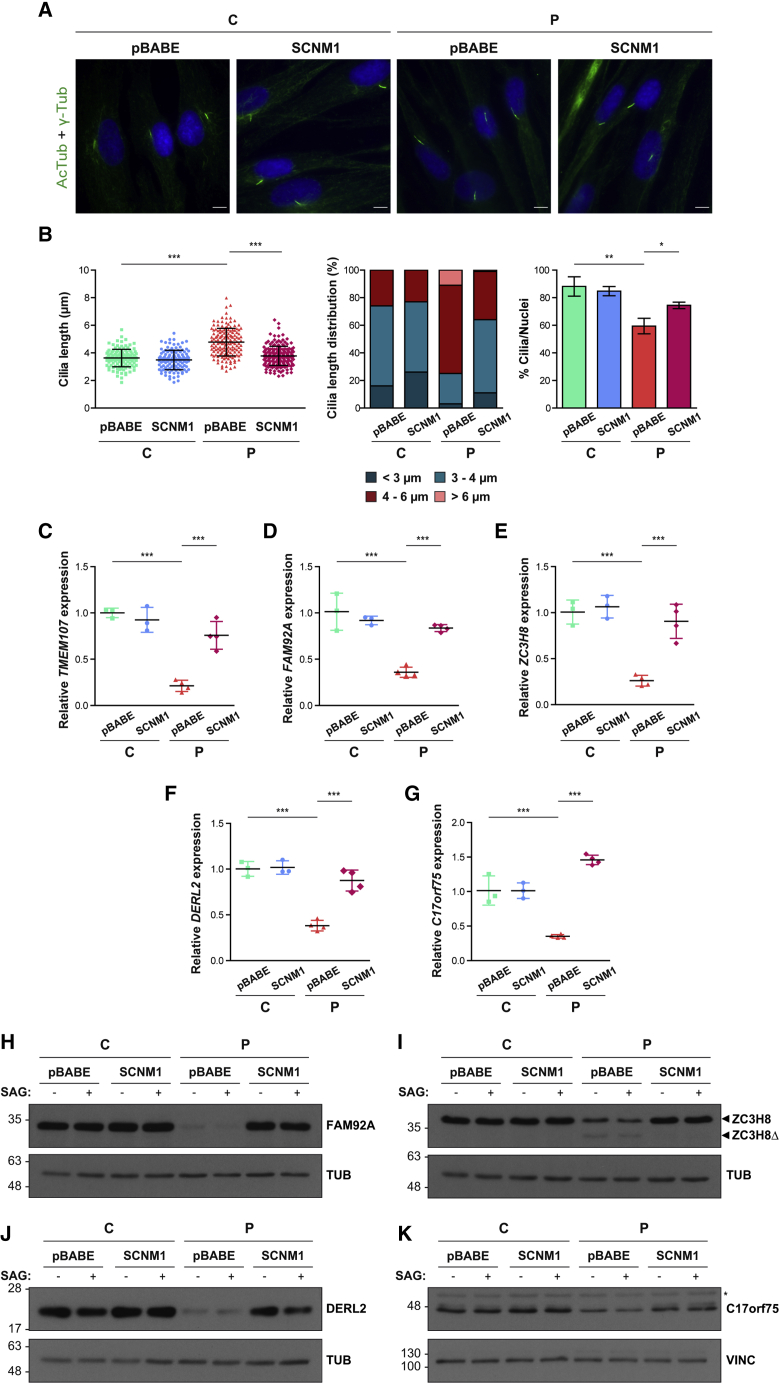
Reintroduction of SCNM1 in SCNM1-deficient primary fibroblasts restores cilia length and U12 intron processing
Primary fibroblasts retrotransduced with SCNM1 or the empty vector were additionally checked for the presence of the cilium anomalies and U12 intron splicing alterations previously identified in cells deficient for SCNM1. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that re-introduction of SCNM1 in fibroblasts derived from P2 restored the length of cilia to the normal range and improved the proportion of ciliated cells in these cultures (Figures 7A and 7B). Furthermore, RT-qPCR quantification of the mRNA levels of TMEM107, FAM92A, ZC3H8, DERL2, and C17orf75 showed the quantity of these transcripts to be recovered in P2 cells following reestablishment of SCNM1 expression (Figures 7C–7G). In the same manner, except for TMEM107 for which no suitable antibody was available, immunoblot analysis demonstrated that the expression of the proteins encoded by these genes returned to normal levels in P2 cells after they were rescued with SCNM1 (Figures 7H–7K).
Figure 7.
Cilia length and U12 intron splicing are restored in cells derived from an affected individual upon reintroduction of SCNM1
(A) Representative immunofluorescence images showing normal cilia length in fibroblasts derived from P2 (P) retrotansduced with SCNM1 but not in P2 fibroblasts transduced with the empty viral vector (pBABE). No significant differences were observed in similarly retrotransduced normal control C2 (C) cells included in the same assay. Green [acetylated tubulin (AcTub) + gamma tubulin (γ-Tub)]: cilia; blue (DAPI): nuclei. Scale bars: 10 μm.
(B) Graphs illustrating cilia length, distribution of cilia length, and frequency of ciliated cells in control (C) and affected individual (P) primary fibroblasts retrotransduced with SCNM1 or the empty vector (pBABE). For each cell line, the length of a minimum of 120 cilia was measured (n = 3 [C], n = 4 [P]), and at least 125 cells were analyzed to calculate the ratio of ciliated cells (n = 3 [C], n = 3 [P]). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparison test and one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test for comparison of selected pairs were used for cilia length and ciliation frequency, respectively.
(C–G) Relative quantification of TMEM107 (C), FAM92A (D), ZC3H8 (E), DERL2 (F), and C17orf75 (G) mRNA levels by RT-qPCR in control (C) and affected individual (P) cultured primary fibroblasts retrotransduced with SCNM1 or the empty retroviral vector (pBABE). RNA samples used were isolated from DMSO-treated cultures. Scatterplots show mean ± SD (n = 3 [C], n = 4 [P]). Gene expression for TMEM107, FAM92A, ZC3H8, and DERL2 was normalized against the geometric mean of GAPDH and GUSB mRNA levels. For C17orf75, GUSB expression was used for normalization. The ΔCt mean value of control cells (C) retrotransduced with pBABE was used as calibrator sample. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(H–K) Representative immunoblots of FAM92A (H), ZC3H8 (I), DERL2 (J), and C17orf75 (K) showing reestablishment of the normal levels of these proteins in affected individual (P) primary fibroblasts after SCNM1 retroviral delivery. Control fibroblasts are labelled as C. Blots were conducted in cell extracts from DMSO (−)- and SAG (+)-treated cells. (H and I): n = 3 (C), n = 4 (P); (J and K): n = 2 (C and P). In (I), arrowheads mark WT (ZC3H8) and truncated (ZC3H8Δ) ZC3H8 isoforms. In (K), the asterisk designates a non-specific band. Tubulin (TUB) and vinculin (VINC) served as a loading control.
Discussion
In this work, we report that bi-allelic loss-of-function mutations in SCNM1 cause OFD. Three distinct homozygous deleterious mutations in SCNM1 were identified in OFD-affected individuals from three unrelated families whose exomes showed no mutations in genes previously associated with this condition. All affected subjects of this study presented with cardinal orofacial and digital OFD features in addition to variable expressivity of other clinical phenotypes. Recent reviews on this condition indicate that extensive splitting into clinical OFD subtypes is difficult because, except OFD I, IV, and VI, the remaining subgroups have been reported in isolated families.22 Nonetheless, the phenotype we describe here is mainly compatible with OFD II (MIM: 252100)21 due to cross-polydactyly, lack of developmental delay and/or intellectual deficit or renal problems, and the presence of median Y-shaped metacarpal as observed in P2. Notably, no gene has yet been assigned to OFD II. The identification and clinical characterization of additional individuals with SCNM1 mutations will define whether the SCNM1-associated phenotype fits into this category or represents a new OFD subtype.
SCNM1 was first described as a putative auxiliary splice factor that modulates the neurological phenotype of Scn8amedj mice. The medj mutation consists of the deletion of nucleotides +5 to +8 of a U2-type 5′ splice site in Scn8a. This results in skipping of the two preceding exons in a high proportion of transcripts but allows the synthesis of a small amount of normally spliced Scn8a mRNA. Of note, the two skipped exons are separated by a U12 intron both in mouse and human. Scn8amedj mice bred onto the C57BL/6J genetic background, which is characterized by a Scnm1 C-terminal truncation mutation (Scnm1R187X) or Scn8amedj;Scnm1Δ3-5 double mutants carrying a deletion of Scnm1 exons 3–5 that was originally generated in a C57BL/6J background both express less amount of normal Scn8a transcript and have a more severe neuropathic phenotype than Scn8amedj mice wild-type for Scnm1.45,51,52 We studied the splicing of the U12 intron of SCN8A by RT-PCR and observed no differences between control and SCNM1-deficient cells, and similarly the U12 intron of SCN8A was not identified by an algorithm that looked for U12 intron retention in RNA-seq data from human dermal fibroblasts. Thus, at least in the cells tested in this study, SCN8A appears not to be affected by the loss of the SCNM1 protein. In addition, no neurological features including epileptic encephalopathy, seizures, or cognitive impairment, which are human phenotypes associated with mutations in SCN8A53 were observed in the individuals identified in this study with SCNM1 mutations.
Recently, Bai et al. demonstrated that SCNM1 is part of the human minor spliceosome following purification of the minor Bact complex and subsequent determination of its atomic model by cryo-EM.25 Our data provide additional insight into the function of SCNM1 by uncovering a set of genes containing U12 introns with a substantially altered splicing due to the loss of this protein. As observed in other studies involving mutations in different subunits of the minor spliceosome,54,55 SCNM1 deficiency increased U12 intron retention and induced the production of aberrant alternative splicing isoforms around U12 introns, while not completely abolishing the synthesis of normally spliced transcripts. Nonetheless, the levels of the correctly spliced mRNA isoforms of TMEM107, FAM92A, C17orf75, ZC3H8, and DERL2 were severely reduced in the absence of SCNM1. The possible involvement of these genes in the OFD clinical phenotype is discussed next. TMEM107 has been associated with OFD and OFD-overlapping ciliopathies such as Joubert syndrome (JBTS) and Meckel-Gruber syndrome (MIMs for TMEM107-associated conditions: 617563, 617562).48,56,57 This gene encodes a TZ protein that regulates ciliary protein composition and function,56 and human dermal fibroblasts with TMEM107 mutations were described with elongated cilia48,56,57 and impaired Hh signaling.57 Mutant mice with a Tmem107 missense mutation (schlei) were also characterized with Hh-signaling defects in the neural tube and limb buds.58 It is then likely that the defects in primary cilia and Hh signaling observed in primary fibroblasts lacking SCNM1 could be due, at least in part, to the very low mRNA levels of the coding isoform of TMEM107 present in these cells. However, we cannot accurately determine the extent of the contribution of this gene to the SCNM1-associated phenotype because we could not evaluate TMEM107 protein levels. FAM92A is also likely to contribute significantly to the clinical features of SCNM1-affected individuals. FAM92A codes for a basal body protein,59 and loss-of-function mutations in this gene have been associated with nonsyndromic postaxial polydactyly in human and with metatarsal osteomas and polysyndactyly along with some other skeletal features in mice.60 Regarding C17orf75, this gene encodes a protein that interacts with WDR11 and FAM91A1 to form a stable protein complex that localizes to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) and is suggested to be involved in endosome-to-TGN trafficking.61 Although not much is known about the function of the C17orf75 protein, WDR11 is a modulator of Hh signaling, which is required for ciliogenesis and GLI3 processing.62 The ZC3H8 protein is also poorly characterized. This protein was described to localize to Cajal bodies and promyelocytic leukaemia (PML) bodies and to be a component of the little elongation complex, which participates in the transcription of snRNAs, including spliceosomal snRNAs.63,64 According to data from the International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC),65 Zc3h8−/− mice are not viable and Zc3h8+/− heterozygous mice exhibit multi-organ defects including abnormal digit, heart, kidney, liver, spleen, and skeleton morphology, indicating that this gene has a relevant role in development. Finally, DERL2, which encodes a protein of the Derlin family (Derlins 1, 2, 3) that functions in the endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) process,66 may also be involved in the SCNM1-phenotype. Of interest, DERL2 was reported to be required for ERAD of the C-terminal fragment of SHH ligand.67 Derlin2−/− mice are mostly perinatal lethal, and the mice surviving this period (4%) are smaller, have chondrocytic abnormalities, and developed skeletal defects involving the rib cage in adulthood.68 Hence, DERL2 might be implicated in the skeletal features observed in affected individuals with SCNM1 mutations.
We cannot rule out the possibility that other genes identified in this study with abnormal U12 intron splicing, but for which the levels of normally spliced transcript were found to be less affected, could be contributing to the clinical features associated with SCNM1 mutations. Among these genes, it is worth noting KIFAP3, encoding a subunit of the IFT-B motor, trimeric kinesin-II,69 and RABL2B that codes for a small GTPase that interacts with IFT-B and seems to initiate the entry of this complex into the cilium.70,71 Mutations in two IFT genes have been described to be associated with OFD.22,24 It could be hypothesized that the effect of the loss of SCNM1 could become more damaging for the splicing of U12 introns of these genes in cell types/tissues different from those used in this study, or during specific developmental time points, due to distinct splicing dynamics and proportions of splicing factors across tissues. It was reported that the levels of minor intron retention vary in a tissue-specific manner, and differential expression of splicing-related genes between tissues or along differentiation processes has also been identified.7,72
Importantly, at the cellular level, our data demonstrate that SCNM1 deficiency results in the elongation of the primary cilium. Cilia length is a highly regulated process that is altered in a number of ciliopathies.73 A proportion of these conditions, including several phenotypes caused by mutations in genes that have been associated with OFD such as TMEM107 or FAM149B1, are characterized by elongated cilia.23,48,56,57,73 Another feature that can be observed in some OFD and OFD-related ciliopathy syndromes is the alteration of the localization of cilium membrane proteins such as ARL13B,47, 48, 49 a protein that is mutated in JBTS (MIM: 612291).74 We found the localization of ARL13B in SCNM1-deficient fibroblasts to be normal, which is in agreement with the clinical data presented here showing that the typical severe neurological manifestations of JBTS, like psychomotor delay or molar tooth sign, are not present in the affected individuals of this study.
In summary, we report that mutations in SCNM1, a component of the minor spliceosome, cause OFD, and reveal an array of genes containing U12 introns that depend on SCNM1 function for their correct splicing. Among those genes there are some with relevant roles in cilia biology, vesicle trafficking, snRNA transcription regulation, protein homeostasis, and other essential cellular processes. This work also provides evidence for the involvement of the minor spliceosome in the control of primary cilia length and Hh signaling through the activity of SCNM1, which has important implications in human development.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to patients, their siblings, and their parents for their participation in this study. This work was supported by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (PID2019-105620RB-I00/AEI/10.13039/501100011033). We would like to thank the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) Project. The GTEx project was supported by the Common Fund of the Office of the Director of the National Institutes of Health and by NCI, NHGRI, NHLBI, NIDA, NIMH, and NINDS. The data used for the analyses described in this manuscript were obtained from the GTEx Portal on 03/2022.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Published: September 8, 2022
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2022.08.009.
Web resources
1000 Genomes Project, http://www.internationalgenome.org/
Blast, https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi
CENSOR, https://www.girinst.org/censor/
Ensembl, https://www.ensembl.org/index.html
GIRI Repbase database, https://www.girinst.org/repbase/
gnomAD, https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/
GTEX, https://www.gtexportal.org/home/
IMPC, https://www.mousephenotype.org/
Minor Intron DataBase (MIDB), https://midb.pnb.uconn.edu/
NCBI (GENE), https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene
NNSPLICE 0.9v, https://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/splice.html
OMIM, http://www.omim.org/
UCSC genome browser, https://genome.ucsc.edu/
Supplemental information
Data and code availability
Because of ethical restrictions and patient confidentiality, Exome and RNA sequencing datasets generated during this work have not been deposited in public repositories. Datasets supporting this work not subjected to ethical restrictions are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
- 1.El Marabti E., Malek J., Younis I. Minor intron splicing from basic science to disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:6062. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Verma B., Akinyi M.V., Norppa A.J., Frilander M.J. Minor spliceosome and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018;79:103–112. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.09.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sharp P.A., Burge C.B. Classification of Introns: U2-Type or U12-Type. Cell. 1997;91:875–879. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80479-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Turunen J.J., Niemela E.H., Verma B., Frilander M.J. Vol. 4. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA; 2013. The Significant Other: Splicing by the Minor Spliceosome; pp. 61–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baumgartner M., Drake K., Kanadia R.N. An integrated model of minor intron emergence and conservation. Front. Genet. 2019;10:1113. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bartschat S., Samuelsson T. U12 type introns were lost at multiple occasions during evolution. BMC Genom. 2010;11:106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Olthof A.M., Hyatt K.C., Kanadia R.N. Minor intron splicing revisited: identification of new minor intron-containing genes and tissue-dependent retention and alternative splicing of minor introns. BMC Genom. 2019;20:686. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6046-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Montzka K.A., Steitz J.A. Additional low-abundance human small nuclear ribonucleoproteins: U11, U12, etc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1988;85:8885–8889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Patel A.A., McCarthy M., Steitz J.A. The splicing of U12-type introns can be a rate-limiting step in gene expression. EMBO J. 2002;21:3804–3815. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xing C., Kanchwala M., Rios J.J., Hyatt T., Wang R.C., Tran A., Dougherty I., Tovar-Garza A., Purnadi C., Kumar M.G., et al. Biallelic variants in RNU12 cause CDAGS syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2021;42:1042–1052. doi: 10.1002/humu.24239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Olthof A.M., Rasmussen J.S., Campeau P.M., Kanadia R.N. Disrupted minor intron splicing is prevalent in Mendelian disorders. Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. 2020;8:e1374. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garcia-Gonzalo F.R., Reiter J.F. Open sesame: how transition fibers and the transition zone control ciliary composition. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017;9:a028134. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nachury M.V., Mick D.U. Establishing and regulating the composition of cilia for signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019;20:389–405. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0116-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lechtreck K.F. IFT–cargo interactions and protein transport in cilia. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015;40:765–778. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.09.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bangs F., Anderson K.V. Primary cilia and mammalian hedgehog signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017;9:a028175. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kong J.H., Siebold C., Rohatgi R. Biochemical mechanisms of vertebrate hedgehog signaling. Development. 2019;146 doi: 10.1242/dev.166892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Liu A., Wang B., Niswander L.A. Mouse intraflagellar transport proteins regulate both the activator and repressor functions of Gli transcription factors. Development. 2005;132:3103–3111. doi: 10.1242/dev.01894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Huangfu D., Anderson K.V. Cilia and Hedgehog responsiveness in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:11325–11330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505328102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sreekumar V., Norris D.P. Cilia and development. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2019;56:15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2019.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Franco B., Thauvin-Robinet C. Update on oral-facial-digital syndromes (OFDS) Cilia. 2016;5:12. doi: 10.1186/s13630-016-0034-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gurrieri F., Franco B., Toriello H., Neri G. Oral-facial-digital syndromes: review and diagnostic guidelines. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2007;143A:3314–3323. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bruel A.L., Franco B., Duffourd Y., Thevenon J., Jego L., Lopez E., Deleuze J.F., Doummar D., Giles R.H., Johnson C.A., et al. Fifteen years of research on oral-facial-digital syndromes: from 1 to 16 causal genes. J. Med. Genet. 2017;54:371–380. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-104436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shaheen R., Jiang N., Alzahrani F., Ewida N., Al-Sheddi T., Alobeid E., Musaev D., Stanley V., Hashem M., Ibrahim N., et al. Bi-allelic mutations in FAM149B1 cause abnormal primary cilium and a range of ciliopathy phenotypes in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019;104:731–737. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yamada M., Uehara T., Suzuki H., Takenouchi T., Fukushima H., Morisada N., Tominaga K., Onoda M., Kosaki K. IFT172 as the 19th gene causative of oral-facial-digital syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2019;179:2510–2513. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bai R., Wan R., Wang L., Xu K., Zhang Q., Lei J., Shi Y. Structure of the activated human minor spliceosome. Science. 2021;371:eabg0879. doi: 10.1126/science.abg0879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Palencia-Campos A., Ullah A., Nevado J., Yildirim R., Unal E., Ciorraga M., Barruz P., Chico L., Piceci-Sparascio F., Guida V., et al. GLI1 inactivation is associated with developmental phenotypes overlapping with Ellis-van Creveld syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017;26:4556–4571. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Estañ M.C., Fernández-Núñez E., Zaki M.S., Esteban M.I., Donkervoort S., Hawkins C., Caparros-Martin J.A., Saade D., Hu Y., Bolduc V., et al. Recessive mutations in muscle-specific isoforms of FXR1 cause congenital multi-minicore myopathy. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:797. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08548-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.1000 Genomes Project Consortium. Auton A., Brooks L.D., Durbin R.M., Garrison E.P., Kang H.M., Korbel J.O., Marchini J.L., McCarthy S., McVean G.A., et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526:68–74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Karczewski K.J., Francioli L.C., Tiao G., Cummings B.B., Alföldi J., Wang Q., Collins R.L., Laricchia K.M., Ganna A., Birnbaum D.P., et al. The mutational constraint spectrum quantified from variation in 141, 456 humans. Nature. 2020;581:434–443. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2308-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dobin A., Davis C.A., Schlesinger F., Drenkow J., Zaleski C., Jha S., Batut P., Chaisson M., Gingeras T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29:15–21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oghabian A., Greco D., Frilander M.J. IntEREst: intron-exon retention estimator. BMC Bioinf. 2018;19:130. doi: 10.1186/s12859-018-2122-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garrido-Martín D., Palumbo E., Guigó R., Breschi A. ggsashimi: Sashimi plot revised for browser- and annotation-independent splicing visualization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018;14:e1006360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Caparrós-Martín J.A., Valencia M., Reytor E., Pacheco M., Fernandez M., Perez-Aytes A., Gean E., Lapunzina P., Peters H., Goodship J.A., Ruiz-Perez V.L. The ciliary Evc/Evc2 complex interacts with Smo and controls Hedgehog pathway activity in chondrocytes by regulating Sufu/Gli3 dissociation and Gli3 trafficking in primary cilia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013;22:124–139. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Edgar R.C. MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinf. 2004;5:113. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Okonechnikov K., Golosova O., Fursov M., UGENE team Unipro UGENE: a unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1166–1167. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Letunic I., Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:W293–W296. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nagy E., Maquat L.E. A rule for termination-codon position within intron-containing genes: when nonsense affects RNA abundance. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998;23:198–199. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reese M.G., Eeckman F.H., Kulp D., Haussler D. Improved splice site detection in Genie. J. Comput. Biol. 1997;4:311–323. doi: 10.1089/cmb.1997.4.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Kohany O., Gentles A.J., Hankus L., Jurka J. Annotation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Censor. BMC Bioinf. 2006;7:474. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Deininger P. Alu elements: know the SINEs. Genome Biol. 2011;12:236. doi: 10.1186/gb-2011-12-12-236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bujakowska K.M., White J., Place E., Consugar M., Comander J. Efficient in silico identification of a common insertion in the MAK gene which causes retinitis pigmentosa. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0142614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Torene R.I., Galens K., Liu S., Arvai K., Borroto C., Scuffins J., Zhang Z., Friedman B., Sroka H., Heeley J., et al. Mobile element insertion detection in 89, 874 clinical exomes. Genet. Med. 2020;22:974–978. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-0749-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Burge C.B., Padgett R.A., Sharp P.A. Evolutionary fates and origins of U12-type introns. Mol. Cell. 1998;2:773–785. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80292-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Dávila López M., Rosenblad M.A., Samuelsson T. Computational screen for spliceosomal RNA genes aids in defining the phylogenetic distribution of major and minor spliceosomal components. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:3001–3010. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Howell V.M., de Haan G., Bergren S., Jones J.M., Culiat C.T., Michaud E.J., Frankel W.N., Meisler M.H. A targeted deleterious allele of the splicing factor SCNM1 in the mouse. Genetics. 2008;180:1419–1427. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.094227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vogel C., Abreu R.d.S., Ko D., Le S.Y., Shapiro B.A., Burns S.C., Sandhu D., Boutz D.R., Marcotte E.M., Penalva L.O. Sequence signatures and mRNA concentration can explain two-thirds of protein abundance variation in a human cell line. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2010;6:400. doi: 10.1038/msb.2010.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Roberson E.C., Dowdle W.E., Ozanturk A., Garcia-Gonzalo F.R., Li C., Halbritter J., Elkhartoufi N., Porath J.D., Cope H., Ashley-Koch A., et al. TMEM231, mutated in orofaciodigital and Meckel syndromes, organizes the ciliary transition zone. J. Cell Biol. 2015;209:129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201411087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shylo N.A., Christopher K.J., Iglesias A., Daluiski A., Weatherbee S.D. TMEM107 is a critical regulator of ciliary protein composition and is mutated in orofaciodigital syndrome. Hum. Mutat. 2016;37:155–159. doi: 10.1002/humu.22925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang C., Li J., Meng Q., Wang B. Three Tctn proteins are functionally conserved in the regulation of neural tube patterning and Gli3 processing but not ciliogenesis and Hedgehog signaling in the mouse. Dev. Biol. 2017;430:156–165. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Verma P.K., El-Harouni A.A. Review of literature: genes related to postaxial polydactyly. Front. Pediatr. 2015;3:8. doi: 10.3389/fped.2015.00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Buchner D.A., Trudeau M., Meisler M.H. SCNM1, a putative RNA splicing factor that modifies disease severity in mice. Science. 2003;301:967–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1086187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sprunger L.K., Escayg A., Tallaksen-Greene S., Albin R.L., Meisler M.H. Dystonia associated with mutation of the neuronal sodium channel Scn8a and identification of the modifier locus Scnm1 on mouse chromosome 3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1999;8:471–479. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Meisler M.H. SCN8A encephalopathy: mechanisms and models. Epilepsia. 2019;60(Suppl 3):S86–S91. doi: 10.1111/epi.14703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Argente J., Flores R., Gutiérrez-Arumí A., Verma B., Martos-Moreno G.Á., Cuscó I., Oghabian A., Chowen J.A., Frilander M.J., Pérez-Jurado L.A. Defective minor spliceosome mRNA processing results in isolated familial growth hormone deficiency. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014;6:299–306. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201303573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Olthof A.M., White A.K., Mieruszynski S., Doggett K., Lee M.F., Chakroun A., Abdel Aleem A.K., Rousseau J., Magnani C., Roifman C.M., et al. Disruption of exon-bridging interactions between the minor and major spliceosomes results in alternative splicing around minor introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49:3524–3545. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lambacher N.J., Bruel A.L., van Dam T.J.P., Szymańska K., Slaats G.G., Kuhns S., McManus G.J., Kennedy J.E., Gaff K., Wu K.M., et al. TMEM107 recruits ciliopathy proteins to subdomains of the ciliary transition zone and causes Joubert syndrome. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016;18:122–131. doi: 10.1038/ncb3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Shaheen R., Almoisheer A., Faqeih E., Babay Z., Monies D., Tassan N., Abouelhoda M., Kurdi W., Al Mardawi E., Khalil M.M.I., et al. Identification of a novel MKS locus defined by TMEM107 mutation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015;24:5211–5218. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Christopher K.J., Wang B., Kong Y., Weatherbee S.D. Forward genetics uncovers Transmembrane protein 107 as a novel factor required for ciliogenesis and Sonic hedgehog signaling. Dev. Biol. 2012;368:382–392. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Li F.Q., Chen X., Fisher C., Siller S.S., Zelikman K., Kuriyama R., Takemaru K.I. BAR domain-containing FAM92 proteins interact with chibby1 to facilitate ciliogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016;36:2668–2680. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00160-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Schrauwen I., Giese A.P., Aziz A., Lafont D.T., Chakchouk I., Santos-Cortez R.L.P., Lee K., Acharya A., Khan F.S., Ullah A., et al. FAM92A underlies nonsyndromic postaxial polydactyly in humans and an abnormal limb and digit skeletal phenotype in mice. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2019;34:375–386. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Navarro Negredo P., Edgar J.R., Manna P.T., Antrobus R., Robinson M.S. The WDR11 complex facilitates the tethering of AP-1-derived vesicles. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:596. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02919-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kim Y.J., Osborn D.P., Lee J.Y., Araki M., Araki K., Mohun T., Känsäkoski J., Brandstack N., Kim H.T., Miralles F., et al. WDR11-mediated Hedgehog signalling defects underlie a new ciliopathy related to Kallmann syndrome. EMBO Rep. 2018;19:269–289. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Egloff S., Vitali P., Tellier M., Raffel R., Murphy S., Kiss T. The 7SK snRNP associates with the little elongation complex to promote snRNA gene expression. EMBO J. 2017;36:934–948. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schmidt J.A., Danielson K.G., Duffner E.R., Radecki S.G., Walker G.T., Shelton A., Wang T., Knepper J.E. Regulation of the oncogenic phenotype by the nuclear body protein ZC3H8. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:759. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4674-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Dickinson M.E., Flenniken A.M., Ji X., Teboul L., Wong M.D., White J.K., Meehan T.F., Weninger W.J., Westerberg H., Adissu H., et al. High-throughput discovery of novel developmental phenotypes. Nature. 2016;537:508–514. doi: 10.1038/nature19356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Oda Y., Okada T., Yoshida H., Kaufman R.J., Nagata K., Mori K. Derlin-2 and Derlin-3 are regulated by the mammalian unfolded protein response and are required for ER-associated degradation. J. Cell Biol. 2006;172:383–393. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200507057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Huang C.H., Hsiao H.T., Chu Y.R., Ye Y., Chen X. Derlin2 protein facilitates HRD1-mediated retro-translocation of sonic hedgehog at the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:25330–25339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Dougan S.K., Hu C.C.A., Paquet M.E., Greenblatt M.B., Kim J., Lilley B.N., Watson N., Ploegh H.L. Derlin-2-deficient mice reveal an essential role for protein dislocation in chondrocytes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011;31:1145–1159. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00967-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Funabashi T., Katoh Y., Okazaki M., Sugawa M., Nakayama K. Interaction of heterotrimeric kinesin-II with IFT-B-connecting tetramer is crucial for ciliogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2018;217:2867–2876. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201801039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Nishijima Y., Hagiya Y., Kubo T., Takei R., Katoh Y., Nakayama K. RABL2 interacts with the intraflagellar transport-B complex and CEP19 and participates in ciliary assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2017;28:1652–1666. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-01-0017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Kanie T., Abbott K.L., Mooney N.A., Plowey E.D., Demeter J., Jackson P.K. The CEP19-RABL2 GTPase complex binds IFT-B to initiate intraflagellar transport at the ciliary base. Dev. Cell. 2017;42:22–36.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Grosso A.R., Gomes A.Q., Barbosa-Morais N.L., Caldeira S., Thorne N.P., Grech G., von Lindern M., Carmo-Fonseca M. Tissue-specific splicing factor gene expression signatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:4823–4832. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Avasthi P., Marshall W.F. Stages of ciliogenesis and regulation of ciliary length. Differentiation. 2012;83:S30–S42. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2011.11.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cantagrel V., Silhavy J.L., Bielas S.L., Swistun D., Marsh S.E., Bertrand J.Y., Audollent S., Attié-Bitach T., Holden K.R., Dobyns W.B., et al. Mutations in the cilia gene ARL13B lead to the classical form of Joubert syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;83:170–179. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.06.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Because of ethical restrictions and patient confidentiality, Exome and RNA sequencing datasets generated during this work have not been deposited in public repositories. Datasets supporting this work not subjected to ethical restrictions are available from the corresponding author on request.