Abstract
An easy, rapid, and reproducible test to distinguish residual cytomegalovirus (CMV) immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies from antibodies produced in primary infection could be useful, especially for pregnant women. The CMV avidity of IgG antibodies with the VIDAS automated enzyme-linked fluorescent assay and 6 M urea was evaluated in a multicenter study to differentiate between primary CMV infections and past infections or reactivations. A total of 416 serum specimens were tested: 159 specimens were from follow-up of primary infections, and 257 were from past infections. All of the specimens from primary infections collected within 4 months (17 weeks) after the onset of the infection had an avidity index lower than 0.8. An avidity index higher than 0.8 excludes a recent primary infection of less than 4 months. However, an avidity index higher than 0.8 cannot confirm all past infections, since 48 specimens (18%) from past infections had an avidity index lower than 0.8 (between 0.5 and 0.8). The exclusion capacity could be improved (96.9%) by using a cutoff of 0.7, but this index would decrease the specificity of the technique, since the avidity index was found to be between 0.7 and 0.8 in two patients with recent primary infection. All specimens from primary infections obtained more than 4 months after the onset of infection had an avidity index more than 0.2. In this study, an avidity index less than 0.2 confirms the presence of a recent primary infection of less than 4 months. The VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test is a rapid, reproducible test with very good performance.
Human cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections are common in immunocompromised patients as well as in immunocompetent patients. In immunocompromised patients, diagnosis of CMV infection is usually performed directly by detecting the virus itself, its viral antigens, or its genome. In immunocompetent patients, and especially in pregnant women (considered immunocompetent patients), diagnosis of CMV infection is, most of the time, performed indirectly by detecting CMV antibodies. In this population, it is very important to differentiate primary from secondary infection, since primary infection is much more deleterious for the fetus than secondary infection (2). Detection of primary infection is based on the observation of a seroconversion or the detection of both immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM. Seroconversion is rarely observed, and the presence of IgM antibody is sometimes very difficult to interpret, since, although IgM is always found in primary infection, it can also be detected for a long time after primary infection (in secondary infection), because of cross-reactions and polyclonal stimulation of the immune system. Therefore, when IgM is detected, it is advisable to use complementary tests to establish the date of CMV infection. Among them, the most useful complementary test is the measurement of the IgG avidity index. The principle behind this test is based on the fact that, after primary infection, the antibody response matures from low- to high-avidity antibody production over a period of several weeks to several months, and afterwards, IgG avidity remains high. Studies by researchers interested in determining the IgG avidity index for the diagnosis of recent primary infection have been published (1, 3, 5, 6), but so far, no rapid and completely automated method of measuring CMV IgG avidity has been described. The present study shows the results obtained with such a user-friendly method (VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test; bioMerieux, Marcy-l'Etoile, France).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Serum specimens.
A total of 416 specimens from three different hospital laboratories were tested in this study: 159 specimens were from follow-up of primary infection, and 257 were from past infections. All specimens were from patients with no known immunodeficiencies. Of the 159 primary infection specimens, 61 were from asymptomatic pregnant women, 15 were from patients with clinical symptoms during or just after delivery, 38 were from liver pathologies, 3 were from pulmonary pathologies, and 42 were from miscellaneous pathologies. Of the 257 specimens from past infections, 119 were from pregnant women, and 138 were from miscellaneous pathologies.
Diagnosis of CMV infection.
Primary infections were defined either by seroconversion or by the concomitant presence of IgG (determined with either of the enzyme immunoassay [EIA] tests CMV IgG Enzygnost Behring or VIDAS CMV IgG) and IgM (determined with either of the EIAs Wellcozyme anti-CMV IgM Murex or VIDAS CMV IgM). The presence of a low IgG avidity was determined in two centers by a commercialized test modified to measure IgG avidity (4) and was determined in the third center with the commercialized Behring CMV IgG avidity test. According to the modified Behring test, an index lower than 0.3 confirms primary infection of less than 3 months, and an index higher than 0.7 excludes recent primary infection. According to the commercialized Behring test, if CMV infection occurred during the past 4 months, the avidity index is probably less than 0.4, while an index higher than 0.4 excludes any occurrence of primary infection within the past 4 months. In some cases, a complementary CMV Western blot IgM test from Genelabs Diagnostic was used. This test uses structural recombinant proteins p38 (43 kDa), p150 (22 kDa), and p52 (38 kDa). The onset of a CMV infection is always difficult to determine. In the case of this study, the date of onset was estimated from the serological results and the analysis of the clinical data. The diagnosis of a past infection was based on serological results, such as IgG-positive and IgM-negative sera and the existence of a previous IgG-positive specimen.
Methods.
The VIDAS CMV IgG assay is an automated enzyme-linked fluorescent immunoassay that enables the quantitative measurement of CMV-specific IgG.
A pipette tip-like disposable device, coated with inactivated virus, constitutes the solid phase and serves as the pipettor. All of the other reagents (mouse monoclonal anti-human IgG antibodies labeled with alkaline phosphatase, washing buffers, and substrate) are available in a 10-well foil-sealed strip. The test is performed by addition of the specimen to the first well. The results are expressed as a relative fluorescence value (RFV) and, in the absence of international units, as VIDAS arbitrary units (AU per milliliter). For the determination of avidity, two VIDAS CMV IgG tests are used. One test serves as the reference test. In the second test, the wash buffer in well 4 of the strip is replaced by a buffer containing 6 M urea. The avidity index is determined by calculating the ratio of the RFV result obtained with the reference test to the RFV result obtained with the strip containing urea. According to the manufacturer, an index greater than or equal to 0.80 enables exclusion of a primary infection of less than 3 months.
VIDAS CMV IgG avidity reproducibility was determined by testing a panel of nine specimens, with eight different lots of VIDAS CMV IgG for each specimen. Reproducibility testing was completed before clinical testing was begun.
RESULTS
Reproducibility.
The results of reproducibility studies (Table 1) for the VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test have coefficients of variation of less than 4.9 and 12%, respectively, for specimens with an index greater than 0.8 and for those with an index less than 0.8. For the latter specimens, with a mean value of 0.07, the results fall between 0.06 and 0.08.
TABLE 1.
Reproducibility of the VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test with several lots of VIDAS CMV IgG
| Serum specimen | Avidity index value (mean) | CV (%)a |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.99 | 3 |
| 2 | 0.91 | 4.9 |
| 3 | 0.93 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 0.82 | 3.8 |
| 5 | 0.83 | 3.7 |
| 6 | 0.77 | 3.1 |
| 7 | 0.54 | 6.6 |
| 8 | 0.39 | 1.9 |
| 9 | 0.07 | 12 |
CV, coefficient of variation.
Kinetics of IgG avidity during primary infections.
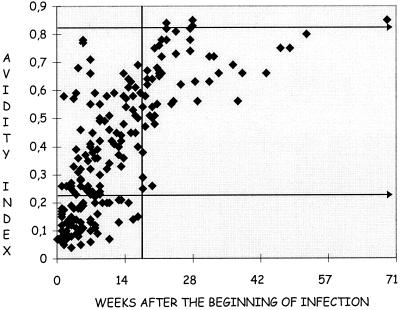
Figure 1 shows the evolution of the avidity index during primary infections. There was a strong increase in avidity during the first weeks of infection, corresponding to the maturation of antibodies. Then, between approximately the 20th and 25th weeks, the avidity began to stabilize. The specimens obtained during CMV infections were distributed in relation to both the avidity index and the time of infection (Table 2).
FIG. 1.
Scatter plot of results in the VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test plotted against the number of weeks after the beginning of infection. A total of 416 specimens were tested. The avidity index increases during primary infection.
TABLE 2.
Distribution of avidity indices during primary and nonprimary infections
| Avidity index | No. (%) of specimens from primary infection at moa:
|
No. (%) of specimens from nonprimary infection | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ≥6 | ||
| 0.01–0.09 | 9 (25.0) | 2 (5.0) | |||||
| 0.10–0.19 | 19 (52.8) | 13 (32.5) | 4 (22.2) | 1 (4.8) | |||
| 0.20–0.29 | 5 (13.9) | 8 (20.0) | 2 (11.1) | 2 (9.5) | 3 (15.0) | ||
| 0.30–0.4 | 1 (2.8) | 8 (20.0) | 7 (38.9) | 6 (28.6) | 1 (5.0) | ||
| 0.40–0.49 | 4 (10.0) | 5 (27.8) | 7 (33.3) | 2 (10.0) | |||
| 0.50–0.59 | 2 (5.6) | 0 (0.0) | 5 (23.8) | 8 (40.0) | 3 (12.5) | 4 (1.6) | |
| 0.60–0.69 | 2 (5.0) | 4 (20.0) | 8 (33.3) | 4 (1.6) | |||
| 0.70–0.79 | 3 (7.5) | 1 (5.0) | 7 (29.1) | 40 (15.6) | |||
| 0.80–0.89 | 1 (5.0) | 6 (25) | 130 (50.5) | ||||
| >0.89 | 79 (30.7) | ||||||
| Total | 36 (100) | 40 (100) | 18 (100) | 21 (100) | 20 (100) | 24 (100) | 257 (100) |
Time after onset of a CMV infection.
Value of IgG avidity in primary infections.
Out of the 115 specimens obtained during the first 4 months of infection, 3 (2.6%) had an index between 0.7 and 0.8. These specimens were obtained from two different subjects. The complete results from these two patients are shown in Table 3. It is interesting that they have identical patterns, with a high avidity index at the beginning of infection. The indexes decreased during the third month and eventually increased again at about 5 to 6 months. Out of the 115 specimens obtained during the first 4 months of infection, no specimen had an index higher than 0.8 and 48 specimens (41%) had an index lower than 0.2. Of the 44 specimens obtained after the first 4 months of infection, none had an index lower than 0.2 and 7 specimens (16%) had an index higher than 0.8.
TABLE 3.
Complete results for the two patients with high avidity indices
| Patienta | No. of wk after infectionb | Avidity index valuee
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| VIDAS | Behring | ||
| PPLc | 5.5 | 0.78 | 0.02 |
| 7 | 0.71 | 0.14 | |
| 11 | 0.51 | 0.2 | |
| 21.5 | 0.76 | 0.05 | |
| 23 | 0.78 | 0.15 | |
| 5099824d | 5.5 | 0.77 | 0.16 |
| 6.5 | 0.66 | 0.26 | |
| 14 | 0.57 | ||
Patient names have been coded to remain anonymous.
Number of weeks after the estimated date of CMV infection.
Cutoff with the commercialized Behring test is 0.4 (primary infection within the past 4 months).
The low cutoff with the modified Behring test is 0.3, and the high cutoff is 0.7 (primary infection within the past 3 months).
Boldface values indicate discrepant results.
Value of IgG avidity in past infections.
Of the 257 specimens tested (Table 2), 209 (81.2%) had an index higher than 0.8 (96.8% had an index higher than 0.7). No specimens had an index lower than 0.5.
DISCUSSION
The results obtained by our automated method show that no specimens from primary infections collected within 4 months (17 weeks) after the estimated onset of infection had an avidity index above 0.8. Therefore, an avidity index higher than 0.8 enables exclusion of a recent primary infection of less than 4 months. However, an avidity index higher than 0.8 cannot confirm all past infections, since 48 specimens (18%) from past infections had an avidity index lower than 0.8 (between 0.5 and 0.8). The exclusion capacity (percentage of recent infections excluded) with a cutoff of 0.8 is only 81%. This exclusion capacity could be improved (96.9%) with a cutoff of 0.7, but the use of this cutoff would decrease the exclusion specificity of the technique (from 100% to 97.39%), since in three specimens from two patients with recent primary infection, the avidity index was found to be between 0.7 and 0.8 by the VIDAS test. (The avidity index was confirmed as being less than 0.3 by the Behring tests.) The reason for the discrepancy between the VIDAS CMV IgG avidity method and the Behring avidity method remains largely unexplained (Table 3). A technical problem could be the cause of the discrepancy, but all of the results were reproducible. Because the antigens used in the VIDAS system are complexed viral lysates, it could be supposed that contamination of CMV with cellular proteins could induce false-positive reactions due to the presence of autoantibodies. Antinuclear antibodies as well non-organ-specific antitissue antibodies were investigated and were found to be negative (data not shown). These results do not exclude autoantibodies as the cause of the discrepancies, since other autoantibodies, not presently investigated, could be present in the specimens.
It was also observed that no specimens from primary infections obtained more than 4 months after the estimated onset of the infection had an avidity index lower than 0.2. Under these conditions, an avidity index lower than 0.2 enables confirmation of the presence of a recent primary infection of less than 4 months. However, with such a threshold, it is important to note that only 48 specimens (42%) from patients with primary infection of less than 4 months were correctly identified. It is well known that, depending on the patient, the avidity index can mature differently. In very rare cases, maturation of the avidity index is very slow. Maturation of the avidity index depends not only on the patient, but also on the technique used. For this reason, results must also be interpreted according the technique used.
Up to now, avidity methods have often been time-consuming and difficult to perform. The VIDAS CMV IgG avidity test provides rapid results (40 min), and its automation improves the reproducibility required for an avidity test.
In conclusion, the VIDAS CMV IgG avidity method is an automated technique that can perform single-dose testing of the CMV IgG avidity index with the right level of reproducibility. Our results show that it is possible to exclude a recent primary infection of less than 4 months when the avidity index is higher than 0.8. However, bioMerieux has chosen to reduce the period of time from 4 months to 3 months in order to exclude a recent primary infection with a greater level of security. On the other hand, when the avidity index is lower than 0.2, a recent primary infection of less than 4 months is confirmed. If bioMerieux claims that a cutoff of 0.2 confirms recent primary infection of less than 4 months, then they should determine the reproducibility around this cutoff value. However, when the avidity index is lower than 0.2, a recent primary infection of less than 4 months is highly probable. As a final comment, it should be noted that for such a conclusion to be firmly determined, extended use of this avidity test is required.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by bioMerieux.
We thank Gerard Baudino and Frederic Lacroix for support during the preparation of this article.
REFERENCES
- 1.Blackburn N K, Besselaar T G, Schoub B D, O'Connell K F. Differentiation of primary cytomegalovirus infection from reactivation using the urea denaturation test for measuring antibody avidity. J Med Virol. 1991;33:6–9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890330103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fowler K B, Stagno S, Pass R F, Britt W J, Boll T J, Alfor C A. The outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in relation to maternal antibody status. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:663–667. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Grangeot-Keros L, Mayaux M J, Lebon P, Freymuth F, Eugene G, Sricker R, Dussaix E. Value of cytomegalovirus (CMV) IgG avidity for the diagnosis of primary CMV infection in pregnant women. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:944–946. doi: 10.1086/513996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Grangeot-Keros L, Simon B, Audibert F, Vial M. Should we routinely screen for cytomegalovirus antibody during pregnancy? Intervirology. 1998;41:158–162. doi: 10.1159/000024930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lazzarotto T, Spezzacatena P, Varani S, Gabrielli L, Pradelli P, Guerra B, Landini M P. Anticytomegalovirus (anti-CMV) immunoglobulin G avidity in identification of pregnant women at risk of transmitting congenital CMV infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 1999;6:127–129. doi: 10.1128/cdli.6.1.127-129.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ruellan-Eugene G, Barjot P, Campet M, Vabret A, Herlicoviez M, Muller G, Levy G, Guillois B, Freymuth F. Evaluation of virological procedures to detect fetal human cytomegalovirus infection: avidity of IgG antibodies, virus detection in amniotic fluid and maternal serum. J Med Virol. 1996;50:9–15. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9071(199609)50:1<9::AID-JMV3>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]