Abstract
Background
The immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have improved the prognosis of many cancers in the last years but concerning cardiovascular toxicity (CVtox) have been reported. Nowadays, specific surveillance protocols are lacking, and early diagnosis of toxicity may be challenging.
Purpose
To characterize the cardiovascular (CV) effects of immunotherapy and to seek for the mechanisms of CVtox of ICI in a protocolize surveillance program of cardio-oncology.
Methods
A multicentre national registry was developed by a research consortium of scientific societies of Cardiology and Oncology (SEC and SEOM) and the cardiovascular research centre (CNIC) in Spain (Figure 1). A total of 18 hospitals participate in recruiting since Q4 2021. A follow-up protocol was stablished with clinical, electrocardiographic (EKG), echocardiography, cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) and laboratory assessment, including cardiac biomarkers, inflammatory panel and the expression of miR-721, a specific myocarditis biomarker. Toxicity management is performed at each institution following international guidelines.
Results
53 patients were currently included. Median age was 68 [59, 75] years-old, 79% were male. 83% had at least 1 CV-risk factor (75% smoking history, 20% diabetes mellitus, 50% hyperlipemia, 57% hypertension, 19% chronic kidney injury) and up to34% had previous CV disease. 93% had at least one dose of COVID19 vaccine. Dyspnoea was referred by 23% of patients, 28% have abnormal EKG findings and one-third (33%) abnormal cardiac biomarkers (median Troponin I-hs 5.30 [2.60, 11.00]; NT-proBNP 199 [68, 736]). Mean LVEF (60% [56.15, 66.78]) and GLS (−18 [−19.75, −16]) were within the normal range but 26% showed LGE at baseline. Cancer characteristics are summarized in Table 1.
Conclusion
Real-world SIR-CVT patients show a high CV risk profile and frequent pre-existing CV diseases before ICI treatment. The prospective follow-up of this cohort will help to develop personalized surveillance protocols according to baseline CVtox risk and to define different grades of cardiotoxicity.
Funding Acknowledgement
Type of funding sources: None.
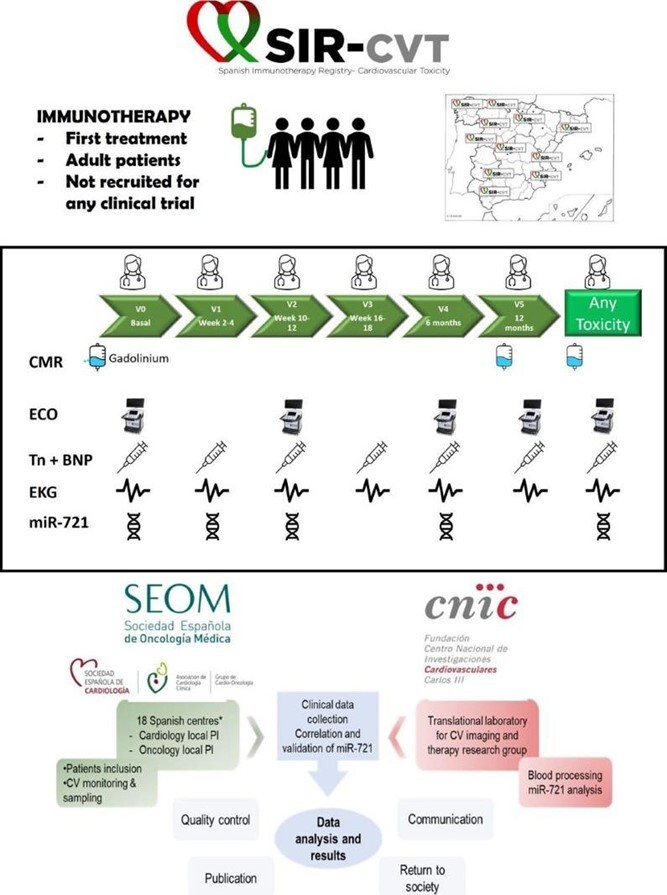
Figure 1

Table 1


