Abstract
Background and objectives
The identification of predictors of response to antiCGRP mAbs could favor tailored therapies and personalized treatment plans. This study is aimed at investigating predictors of ≥ 50%, ≥ 75% and 100% response at 24 weeks in patients with high-frequency episodic (HFEM: 8–14 days/month) or chronic migraine (CM).
Methods
This is a large, multicenter, cohort, real-life study. We considered all consecutive adult patients affected by HFEM or CM who were prescribed antiCGRP mAbs for ≥ 24 weeks in 20 headache centers. Patients were interviewed face-to-face using a shared semi-structured questionnaire carefully exploring socio-demographic and clinical characteristics. Patients received subcutaneous erenumab (70 mg or140 mg, monthly), galcanezumab (120 mg monthly, following a 240 mg loading dose), or fremanezumab (225 mg, monthly or 675 mg, quarterly) according to drug market availability, physician’s choice, or patient’s preference. The primary endpoint of the study was the assessment of ≥ 50% response predictors at 24 weeks. Secondary endpoints included ≥ 75% and 100% response predictors at 24 weeks.
Results
Eight hundred sixty-four migraine patients had been treated with antiCGRP mAbs for ≥ 24 weeks (erenumab: 639 pts; galcanezumab: 173 pts; fremanezumab: 55 pts). The ≥50% response (primary endpoint) in HFEM was positively associated with unilateral pain (UP) + unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms (UAs) (OR:4.23, 95%CI:1.57–11.4; p = 0.004), while in CM was positively associated with UAs (OR:1.49, 95%CI:1.05–2.11; p = 0.026), UP + UAs (OR:1.90, 95%CI:1.15–3.16; p = 0.012), UP + allodynia (OR:1.71, 95%CI:1.04–2.83; p = 0.034), and negatively associated with obesity (OR:0.21, 95%CI:0.07–0.64; p = 0.006). The 75% response (secondary endpoint) was positively associated with UP + UAs in HFEM (OR:3.44, 95%CI:1.42–8.31; p = 0.006) and with UP + UAs (OR:1.78, 95%CI:1.14–2.80; p = 0.012) and UP + allodynia (OR:1.92, 95%CI:1.22–3.06; p = 0.005) in CM. No predictor of 100% response emerged in patients with HFEM or CM.
Conclusions
A critical evaluation of headache characteristics indicating peripheral or central sensitization may help in predicting responsiveness to antiCGRP mAbs in HFEM and CM. A more precise pain profiling may represent a steppingstone for a mechanism-based approach and personalized treatment of migraine with compounds targeting specific molecular mechanisms.
Keywords: Migraine, Predictors, AntiCGRP mAbs, Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, Allodynia, Registry
Introduction
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting the Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (CGRP) or its receptor have been launched since 2018 for the prevention of episodic and chronic migraine and represent the first specific and selective migraine prophylactic treatment [1]. Despite some differences in terms of type (fully human, humanized), target (CGRP, CGRP receptor), way of administration (subcutaneous, intravenous) and dosing (monthly, quarterly), antiCGRP mAbs share a remarkably similar clinical profile, being effective and well tolerated in patients with episodic or chronic migraine, even in presence of medication overuse or prior therapeutic failures (i.e. treated unsuccessfully - in terms of either efficacy or tolerability, or both - with 2 to 4 preventive treatments) [2]. Their distinguishing feature is the considerable proportions of responders (≥ 50% reduction in monthly migraine days) and super-responders (≥ 75% reduction in monthly migraine days), and the excellent efficacy and tolerability ratio which represents a substantial step forward compared to the usual standard of care [3, 4]. Thus, mAbs to CGRP emerge as a tremendous opportunity for alleviating migraine and lifting patients’ burden, ultimately improving their quality of life [5].
Yet it should be recognized that some clinical and economic concerns exist, because antiCGRP mAbs are ineffective in one third of the patients and their elevated cost has led some European Countries to apply restrictive reimbursement norms. In this view, the identification of response predictors could have a clinical and economic impact, being of help in implementing tailored therapies and personalized treatment plans, optimizing resource allocation [6].
Some studies have suggested that responsiveness to antiCGRP mAbs could be related to several demographic and clinical features - including age, sex, body mass index, basal migraine frequency and disability, pain side and severity, allodynia, dopaminergic symptoms, response to triptans and psychiatric comorbidities and personality trait. The heterogeneity of these findings could depend on differences on populations studied, sample sizes, study designs and clinical endpoints investigated [7–18].
Seeking reliable information that might shed light on socio-demographic or clinical profiling of responders to antiCGRP mAbs, we designed this study aimed at investigating potential predictors of response (≥ 50% response rate) or super-response (≥ 75%, 100% response rates) at 24 weeks in patients affected by high-frequency episodic (HFEM: 8–14 days/month) or chronic migraine (CM) in a large, prospective, multicenter, real-life population.
Methods
Trial design and participants
This is a multicenter, cohort, real-life study ongoing at 20 headache centers distributed throughout 7 Italian regions from December 20th, 2018, with the latest patient recruited on March 7th, 2021. This study is part of the I-NEED (Italian NEw migrainE Drugs database) project, included in the Italian Migraine Registry (I-GRAINE). All consecutive ≥ 18 years old patients affected by HFEM or CM [19] who were prescribed antiCGRP mAbs for ≥ 24 weeks according to the criteria required by the Italian Medicine Agency (AIFA) (adult patients with ≥ 8 monthly migraine days over the last 3 months, MIDAS score > 11, and documented failure, contraindications, or low tolerability to > 3 pharmacological classes of migraine preventive medications among beta-blocker, anticonvulsants and tryciclics, or onabotulinum toxinA for CM) were evaluated [20].
The study was approved by the IRCCS San Raffaele Roma Institutional Review Board as coordinating center (11/2018) and mutually recognized by the other local Institutional Review Boards. Each participant provided informed consent. After signing the informed consent, all patients underwent a thorough physical and neurological evaluation and were interviewed by specifically trained, board-certified neurologists with face-to-face interviews using a shared semi-structured questionnaire carefully exploring the following socio-demographic and clinical characteristics [21]: sex, age, body mass index (BMI) and BMI classes (underweight: < 18.5; normal weight: 18.5 to < 25; overweight: 25 to < 30; obesity: ≥ 30), disease duration, migraine type, migraine frequency at baseline, pain side (unilateral pain = hemicranial location, same side or alternating side), quality and intensity [using the Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) score], disability [using the Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6) score], presence of unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms (defined as ≥ 1 of the following unilateral symptoms during the migraine attack: lacrimation, eye redness, nasal congestion, ptosis, eyelid swelling, miosis or forehead/facial sweating) [21], allodynia, presence of dopaminergic symptoms (defined as ≥ 1 of the following symptoms during prodromes, headache stage or postdromes: yawning, somnolence, nausea, vomiting, mood changes, fatigue or diuresis) [22], response to triptans, response to onabotulinum toxinA; concomitant prophylaxis; prior treatment failures; comorbidities and concomitant medications [21]. The current study, as part of the Italian Migraine Registry initiative included a large proportion of patients admitted to the 20 participating centers in the study period. Given the large number of subjects recruited, the sample size of the study, i.e., 864 patients (208 HFEM and 565 CM), was determined by a non-probability convenience sampling. The size of the convenient sample is considerably larger than that needed to test a single hypothesis, nevertheless the observational nature of the study does not imply ethical concern, and a substantially larger sample size is recommended when the study involves the testing of many hypotheses [23]. According to the findings of our previous study [21], symptoms related to peripheral sensitization (unilateral pain: UP; unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms: UAs) or central sensitization (allodynia) were explored also in combination in each subject as follows: UP associated with UAs (UP + UAs), UP associated with allodynia (UP + allodynia); UP associated with UAs and allodynia (UP + UAs + allodynia).
All the patients were antiCGRP mAbs naïve. Starting 28-days prior to the first antiCGRP mAb dose, and throughout the whole study duration, patients filled-out a paper-pencil diary recording monthly migraine days (for HFEM), monthly headache days (for CM), monthly acute medication intake, pain intensity of the monthly most painful attack, and pain disability. Patients received subcutaneous erenumab (70 mg or 140 mg) every 28 days, galcanezumab (120 mg following a loading dose of 240 mg) every 30 days, or subcutaneous fremanezumab 225 mg monthly (every 30 days) or 675 mg quarterly (every 90 days) according to drug market availability, physician’s choice, or patient’s preference. In agreement with the Italian distribution rules, the pharmacy provides 3 mAbs doses to each patient at week 0, 3 doses at week 12 and 6 doses at week 24.
Concomitant migraine prophylaxis was allowed. Patients were re-evaluated at 12 weeks and 24 weeks, as required by AIFA regulation.
The primary endpoint of the study was the assessment of ≥ 50% response predictors at 24 weeks. Secondary endpoints included ≥ 75% and 100% response predictors at 24 weeks.
Statistical analysis
Categorical data, were analysed with the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test when appropriate. Shapiro–Wilk test was used for normality determination of the data. Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA were used to compare normal distributed data, and the Mann-Whitney U-test was used for non-normal distributed data. The proportion of missing data was low, in most cases below 5%. The highest proportion of missing data was found for BMI, i.e., 133 patients (15.4%). A sensitivity analysis compared selected features of subjects included in the study versus missing subjects to rule out the hypothesis of a selection bias. Whenever the proportion of missing was higher than 5%, monthly migraine days, the M/F ratio, and the mean age of the two groups were compared. In no cases significant differences were found. Binary logistic regression was used for the multivariate analysis. All models investigated the associations between > 50%, > 75%, and 100% response and potential clinical and epidemiological predictors. Variables significantly associated with response in the univariate analysis (including their combinations), variables associated with migraine characteristics in the literature or in our previous studies [21], and gender and age as fixed parameters were included as covariates in logistic regression models. A backward removal procedure of all the independent variables that did not substantially contribute to the regression equation (p < 0.10) was applied. The large number of hypotheses tested reveals the substantially explorative nature of the analysis. P-values generated by univariate and multivariate testing have a two-fold meaning, to generate hypotheses which will address further research on this topic, and to rank the credibility of study findings [24]. As an additional data, the Holm-Bonferroni method was applied to the analysis of potential response predictors to deal with the effect of multiple hypothesis testing. The presence of multiple co-primary outcomes of clinical interest, suggested to combine these into a composite outcome, as already done in our previous research [21]. The three variables reflecting different features of central/peripheral sensitization were evaluated jointly or two-by-two in the univariate analysis and fitting different regression models [25]. To check the assumption that different components of the combined outcome share similar influence on the probability of response, the ORs of individual components were estimated and reported together with estimates for combined measures [26]. The results of multivariate analysis are extensively reported only for 50% and 75% response because of the small number of patients with a 100% response. All models were compared with the Akaike information criterion (AIC), while model calibration and discrimination were evaluated with the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test. The analysis was performed using SPSS software package (v27.0), and R Statistical Software (v3.6.2).
Results
At the time of the analysis, 864 migraine patients had been treated with antiCGRP mAbs for ≥ 24 weeks (erenumab: 639 pts; galcanezumab: 173 pts; fremanezumab: 55 pts). Their demographic and clinical characteristics are reported in Table 1. Patients were mostly females (78.1%), affected by CM (75.9%), with concomitant medication overuse headache (87%) and were characterized by very high disability (HIT-6 score: 66.0 ± 9.2) and multiple prior therapeutic failures (4.9 ± 2.3). Patients affected by CM differed from those with HFEM for higher prevalence of obesity (5.7% vs 0.6%; p = 0.032), NRS score (7.8 ± 1.3 vs 7.5 ± 1.4; p = 0.005), pain side (unilateral 46.8% vs 58.2%; p = 0.005), UAs (51.4% vs 39.8%; p = 0.004), allodynia (59.9% vs 44.2%; p < 0.001), prior therapeutic failures (5.2 ± 2.3 vs 4.1 ± 2.2; p < 0.001), response to triptans (61.7% vs 70.2%; p = 0.036), response to onabotulinum toxin (7.5% vs 23.1%: p < 0.001) and psychiatric comorbidities (22.6% vs 13.9%; p = 0.007).
Table 1.
Demographic and clinical features of migraine patients by high-frequency episodic (HFEM) or chronic migraine (CM)
| Number (%) or mean ± SD | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | HFEM | CM | ||
| Patients | 864 | 208 (24.1) | 656 (75.9) | |
| Age, yrs | 47.8 ± 11.5 | 48.2 ± 11.0 | 47.7 ± 11.6 | 0.629 |
| Females | 675 (78.1) | 158 (76.0) | 517 (78.8) | 0.388 |
| BMI | 23.2 ± 3.7 | 22.7 ± 2.7 | 23.3 ± 3.9 | 0.069 |
| BMI class | 0.032 | |||
| Underweight | 42 (5.8) | 8 (4.6) | 34 (6.1) | |
| Normal | 504 (68.9) | 126 (73.3) | 378 (67.6) | |
| Overweigh | 152 (20.8) | 37 (21.5) | 115 (20.6) | |
| Obesity | 33 (4.5) | 1 (0.6) | 32 (5.7) | |
| Disease duration, yrs | 30.3 ± 12.6 | 29.5 ± 12.3 | 30.6 ± 12.7 | 0.305 |
| MMDs/MHDs at baseline | 20.6 ± 7.5 | 10.9 ± 2.0 | 23.7 ± 5.8 | – |
| MOH | – | 571 (87.0) | – | |
| MOH duration | – | 9.1 ± 8.9 | – | |
| Monthly analgesic intake at baseline | 23.8 ± 21.2 | 12.6 ± 5.5 | 27.4 ± 23.0 | < 0.001 |
| NRS score | 7.7 ± 1.3 | 7.5 ± 1.4 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | 0.005 |
| UP | 418 (49.5) | 117 (58.2) | 301 (46.8) | 0.005 |
| Pain quality | 0.286 | |||
| Pulsating | 556 (67.2) | 127 (64.8) | 429 (68.0) | |
| Pressing/tightening | 243 (29.4) | 59 (30.1) | 184 (29.2) | |
| Other | 28 (3.4) | 10 (5.1) | 18 (2.8) | |
| UAs | 406 (48.6) | 80 (39.8) | 326 (51.4) | 0.004 |
| Allodynia | 472 (56.2) | 89 (44.2) | 383 (59.9) | < 0.001 |
| Dopaminergic symptoms | 563 (67.5) | 146 (72.6) | 417 (65.9) | 0.075 |
| UP + allodynia | 261 (58.0) | 55 (53.9) | 206 (59.1) | 0.343 |
| UP + UAs | 248 (55.4) | 54 (53.5) | 194 (55.9) | 0.664 |
| UP + UAs + allodynia | 221 (64.6) | 47 (59.5) | 174 (66.2) | 0.277 |
| Triptan responders | 512 (63.8) | 139 (70.2) | 373 (61.7) | 0.036 |
| Concomitant prophylaxis | 464 (56.0) | 105 (50.5) | 359 (54.7) | 0.322 |
| Prior treatment failures | 4.9 ± 2.3 | 4.1 ± 2.2 | 5.2 ± 2.3 | < 0.001 |
| BoNT/A respondersa | 38 (10.3) | 15 (23.1) | 23 (7.5) | < 0.001 |
| ≥ 1 comorbidity | 401 (46.4) | 102 (49.0) | 299 (45.5) | 0.428 |
| Psychiatric comorbidities | 174 (20.5) | 28 (13.9) | 146 (22.6) | 0.007 |
| HIT-6 score | 66.0 ± 9.2 | 65.1 ± 6.6 | 66.2 ± 9.9 | 0.133 |
| Erenumab | 639 (74.0) | 169 (81.2) | 470 (71.6) | |
| Galcanezumab | 173 (20.0) | 28 (13.5) | 145 (22.1) | |
| Fremanezumab | 52 (6.0) | 11 (5.3) | 41 (6.3) | |
| Monthly regimen | 43 (5.0) | 7 (3.4) | 36 (5.5) | |
| Quaterly regimen | 9 (1.0) | 4 (1.9) | 5 (0.8) | |
HFEM High frequency episodic migraine, CM Chronic migraine, BMI Body mass index, Underweight < 18.5, Normal weight 18.5 to < 25, Overweight 25 to < 30, Obesity ≥ 30, MMDs Monthly migraine days, MHDs Monthly headache days, MOH Medication overuse headache, NRS Numerical Rating Scale, UP Unilateral pian, UAs Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, BoNT/A Onabotulinum toxin A, HIT-6 Headache Impact Test-6. aProportion calculated on the 18 subjects who were treated with BoNT/A
The > 50%, > 75% and 100% response rates at week 24 were 64.9% (135/208), 30.8% (64/208) and 1% (2/208) in patients with HFEM, and 61.4% (403/656), 30.2% (198/656) and 2.4% (16/656) in patients affected by CM.
Univariate analyses
In HFEM, we found a significant association between UP + UAs and both ≥50% response (61.8% vs 28%; p = 0.007) and ≥ 75% response (72.2% vs 43.1%; p = 0.005), and a trend for a positive association between UP + allodynia and ≥ 75% response rate (66.7% vs 47%; p = 0.056) (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 2.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of < 50% responders and ≥ 50% responders in patients with high-frequency episodic (HFEM) or chronic migraine (CM)
| Number (%) or mean ± SD | Number (%) or mean ± SD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFEM | CM | |||||
| < 50% responders |
≥50% responders |
p-value | < 50% responders |
≥50% responders |
p-value | |
| Patients | 73 (35.1%) | 135 (64.9%) | 253 (38.6%) | 403 (61.4%) | ||
| Age, yrs | 47.3 ± 10.2 | 48.6 ± 11.4 | 0.418 | 46.9 ± 11.9 | 48.3 ± 11.4 | 0.129 |
| Females | 58 (79.4) | 100 (74.1) | 0.386 | 204 (80.6) | 313 (77.7) | 0.366 |
| BMI | 226 ± 2.4 | 22.8 ± 2.9 | 0.549 | 23.8 ± 4.5 | 23.0 ± 3.5 | 0.020 |
| BMI class | 0.370 | 0.192 | ||||
| Underweight | 4 (6.9) | 4 (3.5) | 12 (5.5) | 22 (6.5) | ||
| Normal | 45 (77.6) | 81 (71.1) | 147 (67.4) | 231 (67.7) | ||
| Overweight | 9 (15.5) | 28 (24.5) | 41 (18.8) | 74 (21.7) | ||
| Obesity | 0 | 1 (0.9) | 18 (8.3) | 14 (4.1) | ||
| Disease duration, yrs | 29.6 ± 11.0 | 29.5 ± 13.0 | 0.971 | 29.5 ± 12.7 | 31.1 ± 12.7 | 0.094 |
| MMDs/MHDs at baseline | 10.7 ± 2.1 | 11.0 ± 2.0 | 0.439 | 24.3 ± 5.7 | 23.4 ± 5.8 | 0.039 |
| MOH | – | – | – | 220 (87.0) | 351 (87.1) | 0.958 |
| MOH duration, yrs | – | – | – | 9.3 ± 10.4 | 8.9 ± 7.9 | 0.593 |
| Monthly analgesic intake at baseline | 12.2 ± 5.2 | 13.0 ± 6.7 | 0.479 | 28.5 ± 23.0 | 26.7 ± 22.9 | 0.324 |
| NRS score | 7.7 ± 1.3 | 7.4 ± 1.5 | 0.206 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | 7.8 ± 1.2 | 0.997 |
| UP | 41 (56.9) | 76 (58.9) | 0.786 | 104 (42.4) | 197 (49.5) | 0.082 |
| Pain quality | 0.562 | 0.948 | ||||
| Pulsating | 46 (65.7) | 81 (64.3) | 162 (67.2) | 267 (68.5) | ||
| Pressing/tightening | 22 (31.4) | 37 (29.4) | 72 (29.2) | 112 (28.7) | ||
| Other | 2 (2.9) | 8 (6.3) | 7 (2.9) | 11 (2.8) | ||
| UAs | 27 (38.0) | 53 (40.8) | 0.704 | 115 (47.5) | 211 (53.8) | 0.123 |
| Allodynia | 28 (39.4) | 61 (46.9) | 0.307 | 143 (58.6) | 240 (60.8) | 0.589 |
| Dopaminergic symptoms | 46 (64.8) | 100 (76.9) | 0.065 | 167 (69.0) | 250 (63.9) | 0.191 |
| UP + allodynia | 11 (42.3) | 44 (57.9) | 0.169 | 59 (50.4) | 147 (63.6) | 0.024 |
| UP + UAs | 7 (28.0) | 47 (61.8) | 0.007 | 55 (47.0) | 139 (60.4) | 0.017 |
| UP + UAs + allodynia | 9 (52.9) | 38 (61.3) | 0.534 | 45 (57.0) | 129 (70.1) | 0.039 |
| Triptan responders | 50 (70.4) | 89 (70.0) | 0.925 | 133 (57.6) | 240 (64.2) | 0.105 |
| Concomitant prophylaxis | 34 (51.5) | 71 (55.9) | 0.668 | 148 (61.4) | 211 (53.6) | 0.058 |
| Prior treatment failures | 4.0 ± 2.0 | 4.2 ± 2.3 | 0.537 | 5.0 ± 2.2 | 5.3 ± 2.5 | 0.132 |
| BoNT/A respondersa | 6 (40.0) | 9 (60.0) | 0.792 | 10 (43.5) | 13 (56.5) | 0.851 |
| ≥ 1 comorbidity | 31 (42.5) | 71 (52.6) | 0.211 | 115 (45.4) | 194 (48.1) | 0.762 |
| Psychiatric comorbidities | 13 (18.1) | 15 (11.5) | 0.199 | 60 (24.4) | 86 (21.6) | 0.403 |
| HIT-6 score | 66.0 ± 7.3 | 64.6 ± 6.3 | 0.197 | 66.5 ± 8.5 | 66.1 ± 10.7 | 0.587 |
HFEM High frequency episodic migraine, CM Chronic migraine, BMI Body mass index, Underweight < 18.5, Normal weight 18.5 to < 25, Overweight 25 to < 30, Obesity ≥ 30, MMDs Monthly migraine days, MHDs Monthly headache days, MOH Medication overuse headache, NRS Numerical Rating Scale, UP Unilateral pain, UAs Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, BoNT/A Onabotulinum toxin A, HIT-6 Headache Impact Test-6. aProportion calculated on the 18 subjects who were treated with BoNT/A
Table 3.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of < 75% responders and ≥ 75% responders in patients with high-frequency episodic (HFEM) or chronic migraine (CM)
| Number (%) or mean ± SD | Number (%) or mean ± SD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFEM | CM | |||||
| < 75% responders |
≥75% responders |
p-value | < 75% responders |
≥75% responders |
p-value | |
| Patients | 144 (69.2%) | 64 (30.8%) | 458 (69.8%) | 198 (30.2%) | ||
| Age, yrs | 47.5 ± 11.2 | 49.8 ± 10.5 | 0.167 | 47.6 ± 11.7 | 47.9 ± 11.5 | 0.815 |
| Females | 133 (78.4) | 45 (70.3) | 0.204 | 367 (80.1) | 150 (75.8) | 0.208 |
| BMI | 22.8 ± 2.5 | 22.6 ± 3.1 | 0.789 | 23.5 ± 4.1 | 23.0 ± 3.7 | 0.173 |
| BMI class | 0.457 | 0.848 | ||||
| Underweight | 5 (4.3) | 3 (5.5) | 24 (6.1) | 10 (6.0) | ||
| Normal | 88 (75.2) | 38 (69.1) | 261 (66.6) | 117 (70.1) | ||
| Overweight | 24 (20.5) | 13 (23.6) | 83 (21.2) | 32 (19.2) | ||
| Obesity | 0 | 1 (1.8) | 24 (6.1) | 8 (4.8) | ||
| Disease duration, yrs | 29.5 ± 11.9 | 29.6 ± 13.1 | 0.932 | 30.2 ± 12.8 | 31.3 ± 12.6 | 0.321 |
| MMDs/MHDs at baseline | 10.8 ± 2.1 | 11.0 ± 1.8 | 0.713 | 24.0 ± 5.8 | 23.3 ± 5.7 | 0.180 |
| MOH | – | – | – | 400 (70.0) | 171 (30.0) | 0.733 |
| MOH duration, yrs | – | – | – | 9.5 ± 9.8 | 8.0 ± 6.3 | 0.073 |
| Monthly analgesic intake at baseline | 12.6 ± 6.0 | 12.7 ± 4.1 | 0.926 | 28.0 ± 24.6 | 26.1 ± 18.6 | 0.333 |
| NRS score | 7.5 ± 1.5 | 7.6 ± 1.4 | 0.751 | 7.8 ± 1.3 | 7.7 ± 1.2 | 0.314 |
| UP | 77 (55.8) | 40 (63.5) | 0.305 | 201 (44.9) | 100 (51.3) | 0.134 |
| Pain quality | 0.770 | 0.951 | ||||
| Pulsating | 87 (64.5) | 40 (65.6) | 301 (68.1) | 128 (67.7) | ||
| Pressing/tightening | 42 (31.1) | 17 (27.8) | 129 (29.2) | 55 (29.1) | ||
| Other | 6 (4.4) | 4 (6.6) | 12 (2.7) | 6 (3.2) | ||
| UAs | 55 (39.9) | 25 (39.7) | 0.982 | 219 (49.3) | 107 (56.3) | 0.107 |
| Allodynia | 57 (41.3) | 32 (50.8) | 0.209 | 262 (58.6) | 121 (63.0) | 0.297 |
| Dopaminergic symptoms | 95 (68.8) | 51 (81.0) | 0.074 | 297 (669) | 120 (63.5) | 0.409 |
| UP + allodynia | 31 (47.0) | 24 (66.7) | 0.056 | 118 (53.6) | 88 (68.8) | 0.006 |
| UP + UAs | 28 (43.1) | 26 (72.2) | 0.005 | 111 (50.7) | 83 (64.8) | 0.010 |
| UP + UAs + allodynia | 26 (55.3) | 21 (65.6) | 0.360 | 96 (60.4) | 78 (75.0) | 0.014 |
| Triptan responders | 93 (68.9) | 46 (7.0) | 0.554 | 252 (59.4) | 121 (66.8) | 0.085 |
| Concomitant prophylaxis | 72 (54.5) | 33 (54.1) | 0.835 | 259 (58.6) | 100 (51.8) | 0.112 |
| Prior treatment failures | 5.6 ± 3.2 | 5.2 ± 3.0 | 0.471 | 6.9 ± 3.4 | 7.0 ± 3.4 | 0.777 |
| BoNT/A respondersa | 9 (18.3) | 6 (37.5) | 0.216 | 19 (8.7) | 4 (4.7) | 0.350 |
| ≥ 1 comorbidity | 74 (51.4) | 28 (43.7) | 0.386 | 213 (46.5) | 86 (43.4) | 0.522 |
| Psychiatric comorbidities | 19 (13.7) | 9 (14.3) | 1.000 | 106 (23.6) | 40 (20.4) | 0.372 |
| HIT-6 score | 64.9 ± 7.1 | 65.4 ± 5.4 | 0.657 | 66.3 ± 9.4 | 66.0 ± 11.0 | 0.754 |
HFEM High frequency episodic migraine, CM Chronic migraine, BMI Body mass index, Underweight < 18.5, Normal weight 18.5 to < 25, Overweight 25 to < 30, Obesity ≥ 30, MMDs Monthly migraine days, MHDs Monthly headache days, MOH Medication overuse headache, NRS Numerical Rating Scale, UP Unilateral pain, UAs Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, BoNT/A Onabotulinum toxin A, HIT-6 Headache Impact Test-6. aProportion calculated on the 18 subjects who were treated with BoNT/A
In CM, ≥50% response rate was associated with lower BMI (23.0 ± 3.5 vs 23.8 ± 4.5; p = 0.020), lower MHD at baseline (23.4 ± 5.8 vs 24.3 ± 5.7; p = 0.039), UP + UAs (60.4% vs 47%; p = 0.017), UP + allodynia (63.6% vs 50.4%; p = 0.024), UP + UAs + allodynia (70.1% vs 57%; p = 0.039). The ≥75% response was associated with UP + UAs (64.8% vs 50.7%; p = 0.010), UP + allodynia (68.8% vs 53.6%; p = 0.006) and UP + UAs + allodynia (75% vs 60.4%; p = 0.014) (Tables 2 and 3). None of these results remained significant after correction for multiple comparison. No predictor of 100% response emerged in patients with HFEM or CM. 100% responders were on average older, had longer disease duration and lower analgesic intake at baseline (data not shown).
Multivariate analysis
The logistic regression analysis showed that in HFEM both ≥50% and ≥ 75% responses were independently and positively associated with presence of UP + UAs (≥50% response OR: 4.23, 95%CI: 1.57–11.4; p = 0.004) (≥75% response OR: 3.44, 95%CI: 1.42–8.31; p = 0.006) (Table 4).
Table 4.
Variables predicting ≥ 50% response and ≥ 75% response in patients with high frequency episodic migraine (HFEM): A logistic regression model
| ≥ 50% response rate | ≥ 75% response rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value |
| Sex | ||||
| M | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| F | 0.70 (0.34–1.44) | 0.334 | 0.64 (0.32–1.27) | 0.205 |
| Age (yrs) | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.454 | 1.02 (0.99–1.05) | 0.310 |
| UP | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.11 (0.61–2.00) | 0.738 | 1.43 (0.77–2.67) | 0.262 |
| UAs | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.17 (0.64–2.13) | 0.614 | 0.99 (0.54–1.86) | 0.995 |
| UP + UAs | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 4.23 (1.57–11.4) | 0.004 | 3.44 (1.42–8.31) | 0.006 |
UP Unilateral pain, UAs Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, Hosmer–Lemeshow test for different models ranged from χ2 = 1.800 to χ2 = 8.960, with corresponding p-values ranging from 0.987 to 0.346
In CM, we found that ≥50% response was independently positively associated with UP (OR: 1.46, 95%CI: 1.02–2.08; p = 0.039), UAs (OR: 1.49, 95%CI: 1.05–2.11; p = 0.026), UP + UAs (OR: 1.90, 95%CI: 1.15–3.16; p = 0.012), UP + allodynia (OR: 1.71, 95%CI: 1.04–2.83; p = 0.034), and negatively associated with obesity (OR: 0.21, 95%CI: 0.07–0.64; p = 0.006). Conversely, ≥75% response was independently positively associated with and UP + UAs (OR: 1.78, 95%CI: 1.14–2.80; p = 0.012) (Table 5) and UP + allodynia (OR: 1.92, 95%CI: 1.22–3.06; p = 0.005). The models with UP + UAs combined were significantly better than those with UP and UAs separated, both for HFEM (AIC50% = 108.7 vs 264.1 and AIC75% = 130.6 vs 252.9) and for CM (AIC50% = 370.9 vs 739.2 and AIC75% = 457.8 vs 773.8). The combination of UP and UAs for HFEM patients significantly increased ≥ 50% response rate even after correction for multiple comparison, while the same combination is only borderline significant for ≥ 75% response rate. In the group of CM patients, the ORs for obesity and for the combination of UP and allodynia resulted borderline significant.
Table 5.
Variables predicting ≥ 50% response and ≥ 75% response in patients with chronic migraine (CM): A logistic regression model
| Variable | ≥ 50% response rate | ≥ 75% response rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value | Odds ratio (95% CI) |
p-value | |
| Sex | ||||
| M | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| F | 0.93 (0.60–1.35) | 0.623 | 0.86 (0.57–1.30) | 0.469 |
| Age (yrs) | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.271 | 1.00 (0.99–1.02) | 0.805 |
| BMI | ||||
| Normal | 1.00 | |||
| Underweight | 1.19 (0.41–3.40) | 0.750 | ||
| Overweight | 1.06 (0.56–2.03) | 0.849 | ||
| Obesity | 0.21 (0.07–0.64) | 0.006 | ||
| UP | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.35 (0.95–1.91) | 0.093 | 1.29 (0.92–1.81) | 0.133 |
| UAs | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.49 (1.05–2.11) | 0.026 | 1.34 (0.95–1.88) | 0.099 |
| Allodynia | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.14 (0.79–1.64) | 0.483 | 1.23 (0.86–1.74) | 0.253 |
| UP + allodynia | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.71 (1.04–2.83) | 0.034 | 1.92 (1.22–3.06) | 0.005 |
| UP + UAs | ||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Yes | 1.90 (1.15–3.16) | 0.012 | 1.78 (1.14–2.80) | 0.012 |
UP Unilateral pain, UAs Unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms, BMI Body mass index, Underweight < 18.5, Normal weight 18.5 to < 25, Overweight 25 to < 30, Obesity ≥ 30, Hosmer–Lemeshow test for different models ranged from χ2 = 1.233 to χ2 = 8.420, with corresponding p-values ranging from 0.996 to 0.394
Discussion
New costly targeted treatments prompt to reconsider migraine management in terms of customized healthcare and tailored therapy in the modern precision medicine era [27]. Clinical predictors could favor personalized therapy in migraine, because despite the advances in the understanding of its pathophysiology no reliable disease biomarker exists to date [28, 29].
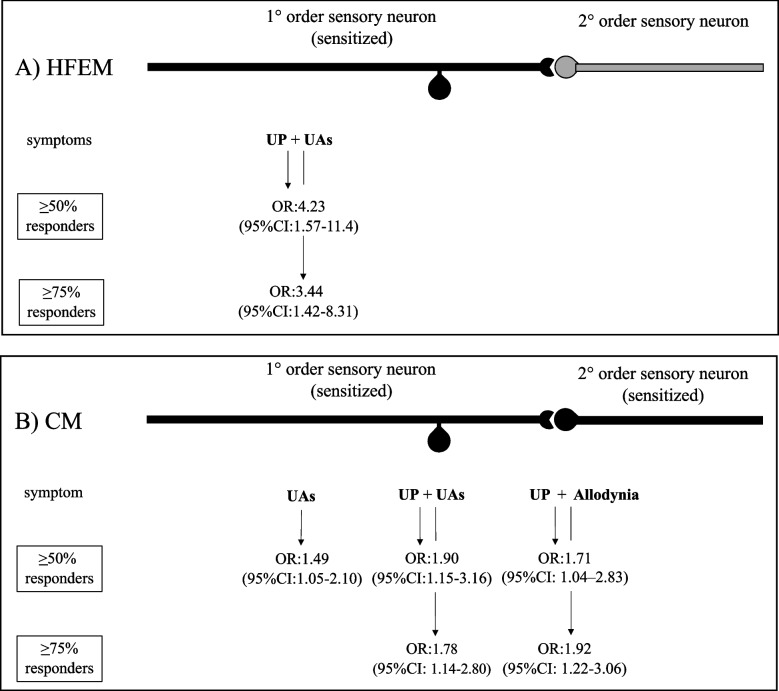
The main finding of the present study is that easily obtainable clinical features could be of help in predicting response to antiCGRP mAbs. In fact, we document that the most reliable predictor of ≥50% and ≥ 75% responses to antiCGRP mAbs in HFEM is a combination of symptoms related to trigeminal sensitization (UP + UAs), while in CM is a combination of symptoms referred to both peripheral sensitization and central sensitization (allodynia) (Fig. 1). These observations echo the hypothesis raised by Hargreaves and Olesen who astutely questioned whether CGRP hyperresponders could have “exaggerated sensory (allodynia) or autonomic signs such as flushing or vasodilation in tissues innervated by the trigeminal system during their attacks suggestive of sensory activation” [30]. This pooling of different study outcomes, as planned in advance, increases statistical precision due to the higher event rates, and allows to avoid competing risks in outcome assessment when there is no obvious choice of a primary trial outcome. In addition, this approach helps investigators to avoid an arbitrary choice between several important outcomes that refer to the same disease process, and to have a deeper insight into pathogenetic mechanisms.
Fig. 1.
A In patients with HFEM, unilateral pain (UP) associated with unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms (UAs) – clinical manifestation of CGRP-mediated peripheral sensitization - predict both ≥ 50 and ≥ 75% response to antiCGRP mAbs. B In patients with CM, UAs and UP + UAs predict ≥ 50 response to antiCGRP mAbs, while UP + UAs and UP associated with allodynia - a CGRP-mediated symptom of central sensitization - predict ≥ 75% response
Our results fit well with current knowledge on the role of CGRP in the genesis of migraine and of its chronification [31]. During the migraine attack, CGRP is antidromically released from peripheral nociceptive endings, and triggers a cascade of events ultimately leading to peripheral trigeminal sensitization [32]. Indeed, we found that HFEM responders to antiCGRP mAbs have symptoms of intense CGRP-related trigeminal activation, being characterized by a unilateral headache (UP) tracing the overactive primary afferent sensory neurons accompanied by homolateral cranial parasympathetic symptoms (UAs) due to the activation of the trigemino-autonomic reflex, a physiological defensive response to intense trigeminal stimuli [33]. CGRP also contributes to sensitize second-order nociceptive neurons within the central nervous system, favoring the development of central sensitization, the pathophysiological condition underpinning CM. Not surprisingly, the endophenotype of CM responder to antiCGRP mAbs is characterized by symptoms of peripheral sensitization (UP, UAs) coupled to allodynia, the clinical manifestation of central sensitization [33].
Obesity emerged as a negative predictor of antiCGRP mAbs responsiveness in patients with CM. A possible explanation is that although increased neuropeptides’ release in patients with trigeminal overactivation seems associated with a favorable response to trigeminal-targeted treatments, current antiCGRP mAbs treatments might be unable to properly counteract the excessive CGRP activity characterizing obese individual [29, 34, 35]. Weight reduction strategies could thus be advantageous in increasing antiCGRP mAbs responsivity in these patients.
The present study points out that pain characteristics are more relevant than other clinical or sociodemographic factors in determining antiCGRP mAbs response. Further, their accurate assessment may represent one way to envisage different pain-generating mechanisms [28]. The concept that precise pain profiling may be helpful in unravelling its distinct pathophysiological machinery and in improving treatment is well established in pain research [36]. The sodium channel blocker oxcarbazepine provided equivocal findings in peripheral neuropathic pain but showed indeed clear-cut different therapeutic effects when tested in a phenotype-stratified clinical trial differentiating patients with the irritable vs the non-irritable nociceptor sensory profile [37]. Thus, efforts are needed also in migraine to identify different mechanism-based endophenotypes which could aid its diagnosis and treatment [38]. In previous works, we documented that patients showing symptoms of trigeminal peripheral sensitization (UP + UAs) are likely to be more sensitive to triptans and, broadly speaking, to trigeminal-targeted treatments [39–41]. The present study extends this hypothesis also to antiCGRP mAbs. The relevance of pain characteristic in predicting therapeutic response in migraine has been pointed out also by other research groups. Sarchielli et al. documented that rizatriptan responders have clinical and biochemical evidence of increased trigeminal activation [42]. Directionality and site of pain have been considered neurological markers to single out botulinum toxin responders in migraine by Jakubowski et al., who reported considerable differences in the responders’ rates between patients with imploding, ocular o exploding headache (94%, 100% and 19%, respectively) in a migraine population including a large proportion (57.1%) of patients affected by the episodic form, usually considered unresponsive to onabotulinum toxin A [43]. Likewise, migraine patients with imploding or ocular headache are more likely to be super-responders (> 75% reduction in monthly headache days) to rimabotulinumtoxin B compared to those with exploding pain. For the above reasons, it has been suggested to include subjective pain perception in migraine diagnosis [44].
This study has several limitations. Firstly, the proportion of patients treated with the diverse antiCGRP mAbs is heterogeneous and not comparable (erenumab 74%; galcanezumab: 20%; fremanezumab 6%). This discrepancy reflects the different pre-reimbursement access to the various antiCGRP mAbs in our Country, erenumab having been available since December 2018, galcanezumab since September 2019 and fremanezumab since July 2020. Secondly, our study does not include eptinezumab, not yet approved in Italy. Thirdly, among patients affected by episodic migraine, we considered only those having at least 8 monthly migraine day (according to Italian reimbursement rules) and therefore our findings cannot be simply transferred to patients affected by lower frequency episodic migraine. Lastly, we acknowledge that the factors investigated as potential predictors could sound somehow arbitrary and, in any case, do not exclude the existence other predictive characteristics. The main strength of this study is surely the large number of patients recruited by several headache centers nationwide and interviewed - after method standardization - with a shared semi-structured questionnaire to obtain comprehensive information on sociodemographic and clinical features.
In conclusion, our study suggests that a critical evaluation of easily obtainable patient-reported clinical findings - such as migraine pain characteristics indicating peripheral or central sensitization - may be of help in predicting responsiveness to antiCGRP mAbs in HFEM and CM. In addition, a more precise pain profiling may represent a steppingstone for a mechanism-based approach and personalized treatment of migraine with compounds targeting specific molecular mechanisms. Future drug trials should hopefully provide a better definition of migraine phenotype to minimize migraine pathophysiological heterogeneity and to favor tailored therapy to the individual patient [28].
Acknowledgements
We thank Liliana Baiamonte for technical assistance.
Glossary
CM: chronic migraine; HFEM: high-frequency episodic migraine; CGRP: Calcitonin gene-related peptide; mAbs: monoclonal antibodies; UP: unilateral pain; UAs: unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms; BMI: body mass index; MMDs: monthly migraine days; MHDs: monthly headache days; MOH: medication overuse headache; NRS: Numerical Rating Scale, BoNT/A: onabotulinum toxinA; HIT-6: Headache Impact Test; MIDAS: Migraine Disability Assessment Scale; SD: standard deviation.
Competing interests
Piero Barbanti reports personal compensation for consulting, serving on a scientific advisory board, speaking, research support, collaborated for clinical trials, or other activities with Abbvie, Amgen, Alder, Allergan, Angelini, Assosalute, Bayer, Biohaven, ElectroCore, Eli-Lilly, GSK, Lundbeck, Lusofarmaco, 1MED, MSD, New Penta, Noema Pharma, Novartis, Stx-Med, Teva, Visufarma, Zambon and serves as President with Italian Neurological Association for Headache Research and with Italian Association of Headache Sufferers.
Gabriella Egeo received travel grants and honoraria from Eli-Lilly, Novartis, Lusofarmaco, New Penta and Ecupharma.
Cinzia Aurilia received travel grants from FB-Health, Lusofarmaco, Almirall, Eli-Lilly Novartis and Teva;
Claudia Altamura received travel grants or honoraria for speaker panels from Eli-Lilly, Novartis, Teva, Lusofarmaco, Almirall, Laborest.
Florindo d’Onofrio received travel grant, honoraria as a speaker or for partecipating in advisory boards from Novartis, Teva, NeopharmedGentili, Qbgroupsrl, K link srl and Eli-Lilly.
Cinzia Finocchi received grants and honoraria from Novartis, Eli Lilly, TEVA, AIM group.
Maria Albanese received travel grants and honoraria from Novartis, Teva, Eli-Lilly and Lundbeck.
Marco Aguggia received grants from Novartis and Lilly.
Renata Rao received honoraria for speaker panels from Teva, Lilly, Novartis, Allergan, Lundbeck;
Maurizio Zucco received travel grants and honoraria from Novartis.
Fabio Frediani has received fees for participation on advisory boards, speaker honoraria or consulting activities from Angelini, Cristalfarma, Ecupharma, IBSA, Lundbeck, Novartis, PIAM, Teva.
Massimo Filippi is Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of Neurology and Associate Editor of Radiology, Human Brain Mapping and Neurological Sciences; received compensation for consulting services and/or speaking activities from Almiral, Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Janssen, Merck-Serono, Neopharmed Gentili, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries; and receives research support from Biogen Idec, Merck-Serono, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, Almiral, Eli Lilly, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Italian Ministry of Health, Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla, and ARiSLA (Fondazione Italiana di Ricerca per la SLA).
Roberta Messina received honoraria for advisory boards or speaker activity from Eli Lilly, Bromatech and Lundbeck.
Sabina Cevoli received travel grants, honoraria for advisory boards, speaker panels or clinical investigation studies from Novartis, Teva, Lilly, Allergan, Abvie, Ibsa, Amgen, Angelini and Lundbeck.
Antonio Carnevale has no disclosures to declare.
Giulia Fiorentini has no disclosures to declare.
Stefano Messina has no disclosures to declare.
Francesco Bono received honoraria as a speaker or for participating in advisory boards from Teva, Novartis, Ipsen.
Paola Torelli received travel grants and honoraria from Allergan, Teva, Eli-Lilly and Novartis.
Stefania Proietti has no disclosures to declare.
Stefano Bonassi has no disclosures to declare.
Fabrizio Vernieri received travel grants, honoraria for advisory boards, speaker panels or clinical investigation studies from Allergan, Eli-Lilly, Novartis, Teva, Amgen, Angelini and Lundbeck.
Appendix
Table 6.
Coinvestigators
| Name | Location | Role | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laura Di Clemente | San Camillo Hospital, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Paola Di Fiore | ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo, Milan | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Nicoletta Brunelli | Campus Bio-Medico, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Maria C. costa | Campus Bio-Medico, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Bruno Colombo | San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Ilaria Cetta | San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milan | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Luigi d'Onofrio | Campus Bio-Medico, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Gerardo Casucci | Casa di Cura S. Fracesco, Benevento | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Domenica Le Pera | IRCCS San Raffaele Roma, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Carlo Tomino | IRCCS San Raffaele Roma, Rome | S.I. | Led and coordinated communication among sites |
| Giovanna Viticchi | Politechnic Universuty, Ancona | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Antonio Salerno | S. Giovanni Addolorata Hospital, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Bruno Mercuri | S. Giovanni Addolorata Hospital, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Licia Grazzi | IRCCS Carlo Besta, Milan | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Domenico D’Amico | IRCCS Carlo Besta, Milan | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Cecilia Camarda | University of Palermo | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Massimo Autunno | University of Messina | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Alessandro Valenza | Belcolle Hospital, Viterbo | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Steno Rinalduzzi | S. Camillo de Lellis Hospital, Rieti | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Miriam Tasillo | S. Camillo de Lellis Hospital, Rieti | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Giuliano Sette | Sant’Andrea University Hospital, Rome | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
| Giorgio Spano | AOU Mater Domini Hospital, Catanzaro | S.I. | Collection and evaluation data |
S.I. Site investigator
Authors’ contributions
The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Health (Institutional Funding Ricerca Corrente) IRCCS San Raffaele Roma.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Piero Barbanti and Gabriella Egeo contributed equally to this work.
References
- 1.Garland SG, Smith SM, Gums JG. Erenumab: A First-in-Class Monoclonal Antibody for Migraine Prevention. Ann Pharmacother. 2019;53(9):933–939. doi: 10.1177/1060028019835166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wang X, Chen Y, Song J, You C. Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody against calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor for migraine: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:649143. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.649143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drellia K, Kokoti L, Deligianni CI, Papadopoulos D, Mitsikostas DD Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies for migraine prevention: a systematic review and likelihood to help or harm analysis. Cephalalgia 41(7):851–864 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Vandervorst F, Van Deun L, Van Dycke A, et al. CGRP monoclonal antibodies in migraine: an efficacy and tolerability comparison with standard prophylactic drugs. J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01335-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Torres-Ferrus M, Alpuente A, Pozo-Rosich P. How much do calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibodies improve the quality of life in migraine? A patient's perspective Curr Opin Neurol. 2019;32(3):395–404. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ginsburg GS, Phillips KA. Precision medicine: from science to value. Health Aff (Millwood) 2018;37(5):694–701. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2017.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Altamura C, Costa C, Fofi L et al (2020) Migraineurs' psychological traits do not influence response to erenumab. Neurol Sci. 10.1007/s10072-020-04661-6 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Vernieri F, Altamura C, Aurilia C et al (2020) Effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of galcanezumab in a real-life setting in patients with migraine in Italy (the GARLIT study). Neurol Sci. 10.1007/s10072-020-04669-y [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Egeo G, et al. Erenumab in the prevention of high-frequency episodic and chronic migraine: EARLY (ErenumAb in real life in ItalY), the first Italian multicenter, prospective real-life study. Headache. 2021;61(2):363–372. doi: 10.1111/head.14032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Cevoli S et al (2021) Long term (48 weeks) effectiveness, safety and tolerability of erenumab in the prevention of high-frequency episodic and chronic migraine in real-world: results of the EARLY 2 study. Headache. 10.1111/head.14194 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Vernieri F, Altamura C, Brunelli N, et al. GalcanezumAb for the prevention of high frequency episodic and chronic migraine in real life in ITaly: a multicenter prospective cohort study (the GARLIT study) J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01247-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vernieri F, Altamura C, Brunelli N et al (2021) Rapid response to galcanezumab and predictive factors in chronic migraine patients: a 3-month observational, longitudinal, cohort, multicenter, Italian real-life study. Eur J Neurol. 10.1111/ene.15197 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Bottiroli S, De Icco R, Vaghi G, et al. Psychological predictors of negative treatment outcome with Erenumab in chronic migraine: data from an open label long-term prospective study. J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01333-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Caronna E, Gallardo VJ, Alpuente A, Torres-Ferrus M, Pozo-Rosich P. Anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies in chronic migraine with medication overuse: real-life effectiveness and predictors of response at 6 months. J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s10194-021-01328-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Iannone LF, Fattori D, Benemei S, Chiarugi A, Geppetti P, De Cesaris F. Long-term effectiveness of three anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies in resistant chronic migraine patients based on the MIDAS score. CNS Drugs. 2022;36(2):191–202. doi: 10.1007/s40263-021-00893-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Iannone LF, Fattori D, Benemei S, Chiarugi A, Geppetti P, De Cesaris F (2022) Predictors of sustained response and effects of the discontinuation of anti-calcitonin gene related peptide antibodies and reinitiation in resistant chronic migraine. Eur J Neurol. 10.1111/ene.15260 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Ornello R, Baraldi C, Guerzoni S, et al. Gender differences in 3-month outcomes of Erenumab treatment—study on efficacy and safety of treatment with Erenumab in men. Front Neurol. 2021;12:774341. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.774341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Frattale I, Caponnetto V, Casalena A, et al. Association between response to triptans and response to erenumab: real-life data. J Headache Pain. 2021;22(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s10194-020-01213-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Headache classification Committee of the International Headache Society The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition (beta version) Cephalalgia. 2013;33:629–808. doi: 10.1177/0333102413485658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gazzetta Ufficiale n.182, 21-7-2020
- 21.Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Dall'Armi V, Egeo G, Fofi L, Bonassi S. The phenotype of migraine with unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms documents increased peripheral and central trigeminal sensitization. A case series of 757 patients. Cephalalgia. 2016;36(14):1334–1340. doi: 10.1177/0333102416630579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Barbanti P, Aurilia C, Egeo G, Fofi L, Guadagni F, Ferroni P. Dopaminergic symptoms in migraine: a cross-sectional study on 1148 consecutive headache center-based patients. Cephalalgia. 2020;2:333102420929023. doi: 10.1177/0333102420929023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Silverstein AB. Statistical power lost and statistical power regained: the Bonferroni procedure in exploratory research. Educational Phsycol Measur. 1986;46(2):303–307. doi: 10.1177/001316448604600202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gaus W, Mayer B, Muche R. Interpretation of statistical significance - exploratory versus confirmative testing in clinical trials, epidemiological studies, Meta-analyses and toxicological screening (using Ginkgo biloba as an example) Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2015;5(4):1000182. doi: 10.4172/2161-1459.1000182. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.(1999) ICH harmonised tripartite guideline statistical principles for clinical trials. International conference on harmonisation E9 expert working group. Stat Med 18(15):1905–1942 [PubMed]
- 26.McCoy CE. Understanding the use of composite endpoints in clinical trials. West J Emerg Med. 2018;19(4):631–634. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2018.4.38383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bardakjian T, Gonzalez-Alegre P. Towards precision medicine. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;147:93–102. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63233-3.00008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Barbanti P, Egeo G. Pharmacological trials in migraine: It’s time to reappraise where the headache is and what the pain is like. Headache. 2015;55:439–441. doi: 10.1111/head.12498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ashina M, Terwindt GM, Al-Karagholi MA, de Boer I, Lee MJ, Hay DL, Schulte LH, Hadjikhani N, Sinclair AJ, Ashina H, Schwedt TJ, Goadsby PJ. Migraine: disease characterisation, biomarkers, and precision medicine. Lancet. 2021;397(10283):1496–1504. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hargreaves R, Olesen J. Calcitonin gene-related peptide modulators - the history and renaissance of a new migraine drug class. Headache. 2019;59(6):951–970. doi: 10.1111/head.13510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Iyengar S, Ossipov MH, Johnson KW. The role of calcitonin gene-related peptide in peripheral and central pain mechanisms including migraine. Pain. 2017;158(4):543–559. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Iyengar S, Johnson KW, Ossipov MH, Aurora SK. CGRP and the trigeminal system in migraine. Headache. 2019;59(5):659–681. doi: 10.1111/head.13529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Barbanti P, Egeo G, Mitsikostas DD. Trigeminal-targeted treatments in migraine: is 60% the magic number? Headache. 2019;59(9):1659–1661. doi: 10.1111/head.13635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bigal ME, Lipton RB, Holland PR, Goadsby PJ. Obesity, migraine, and chronic migraine: possible mechanisms of interaction. Neurology. 2007;68(21):1851–1861. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000262045.11646.b1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Recober A, Goadsby PJ. Calcitonin gene-related peptide: a molecular link between obesity and migraine? Drug News Perspect. 2010;23(2):112–117. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2010.23.2.1475909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Truini A, Garcia-Larrea L, Cruccu G. Reappraising neuropathic pain in humans--how symptoms help disclose mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurol. 2013;9(10):572–582. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Demant DT, Lund K, Vollert J, et al. The effect of oxcarbazepine in peripheral neuropathic pain depends on pain phenotype: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phenotype-stratified study. Pain. 2014;155(11):2263–2273. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2014.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Olesen J. Migraine: are migraine endophenotypes needed? Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(6):320–321. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Barbanti P, Fabbrini G, Vanacore N, Pesare M, Buzzi MG. Sumatriptan in migraine with unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms: an open study. Headache. 2003;43(4):400–403. doi: 10.1046/j.1526-4610.2003.03077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Barbanti P, Fofi L, Dall'Armi V, et al. Rizatriptan in migraineurs with unilateral cranial autonomic symptoms: a double-blind trial. J Headache Pain. 2012;13(5):407–414. doi: 10.1007/s10194-012-0440-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Barbanti P, Egeo G. Predictors of response to onabotulinumtoxin a in chronic migraine. Eur J Neurol. 2018;25(3):e40. doi: 10.1111/ene.13550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sarchielli P, Pini LA, Zanchin G, et al. Clinical-biochemical correlates of migraine attacks in rizatriptan responders and non-responders. Cephalalgia. 2006;26(3):257–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2005.01016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jakubowski M, McAllister PJ, Bajwa ZH, Ward TN, Smith P, Burstein R. Exploding vs. imploding headache in migraine prophylaxis with Botulinum toxin a. Pain. 2006;125(3):286–295. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2006.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Grogan PM, Alvarez MV, Jones L. Headache direction and aura predict migraine responsiveness to rimabotulinumtoxin B. Headache. 2013;53(1):126–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]