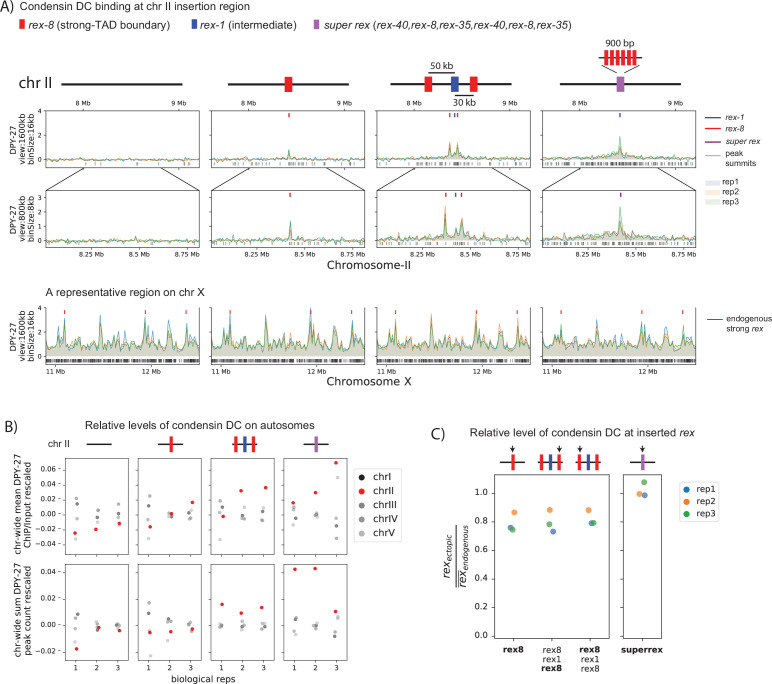
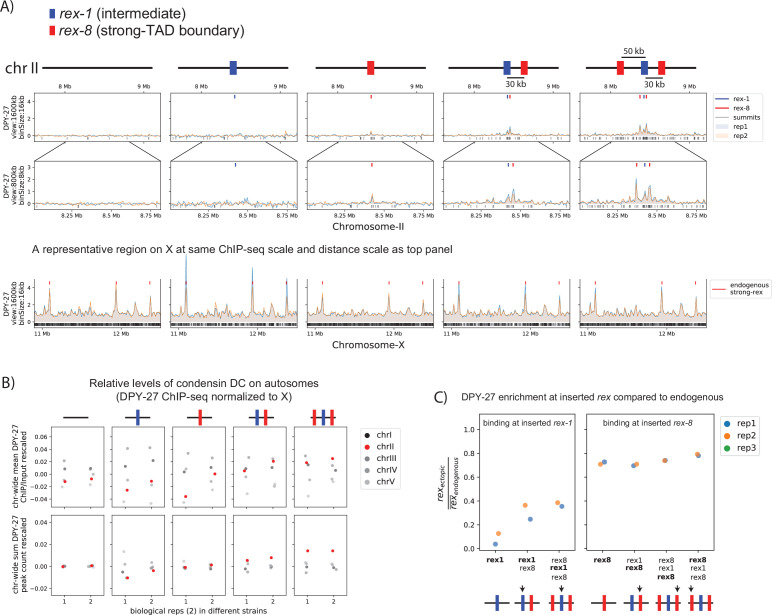
Figure 5. Condensin dosage compensation (DC) is recruited to and spreads in either direction from the ectopically inserted recruitment elements on the X-chromosome (rex) sites on chromosome-II in L3.
(A) Snapshot of a region on chromosome-II where rex sites are inserted. Shown are four different conditions in L3 stage: wild-type, ERC61 (single rex-8 insertion) (Albritton et al., 2017), ERC63 (rex-8, rex-1, rex-8) [33], and ERC90 super rex, an array of six truncated, midsection (150 bp) of three strong rex’s: rex-40, rex-8, rex-35, repeated. Binding surrounding the insertion sites in both directions increases with increased number and strength of inserted rexes. The levels of condensin DC ectopically recruited to chromosome-II remain weaker than the endogenous binding at X-chromosome (lower panel). (B) The enrichment of condensin DC on each autosome plotted as chromosome-wide mean enrichment and total number of binding peaks calculated from DPY-27 ChIP-seq data. The ChIP-seq values or the total number of peaks are rescaled for each data, such that the mean of autosomes excluding chromosome-II is fixed to 0 and that of X-chromosome is at 1. The plot highlights weak but reproducible recruitment of more condensin DC to chromosome-II by rex insertion. (C) The level of condensin DC binding at the inserted strong rex-8 (indicated by arrow in each strain) is comparable to the endogenous, as indicated by the ChIP-seq signal at inserted rex site (400 bp) normalized to the mean of all endogenous strong rex sites on the X.