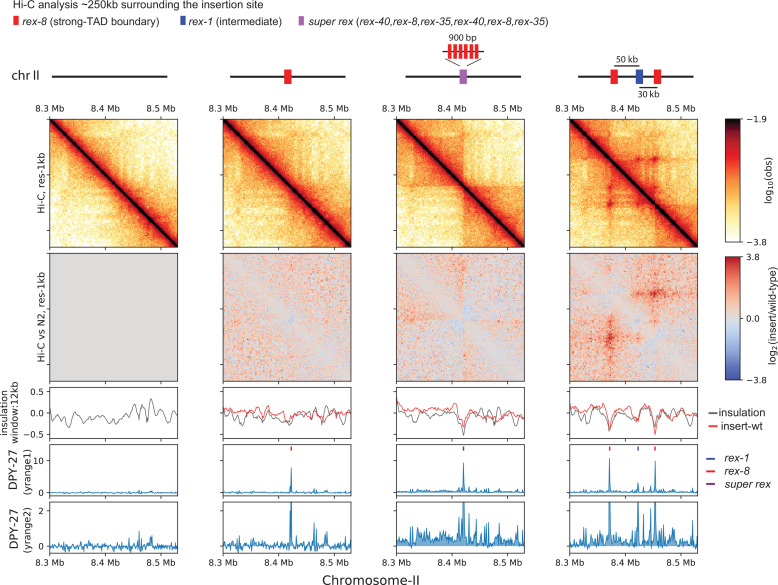
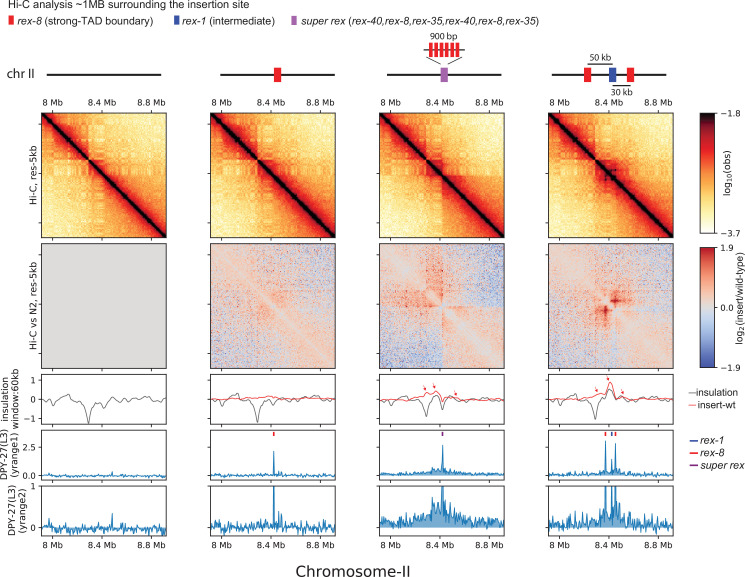
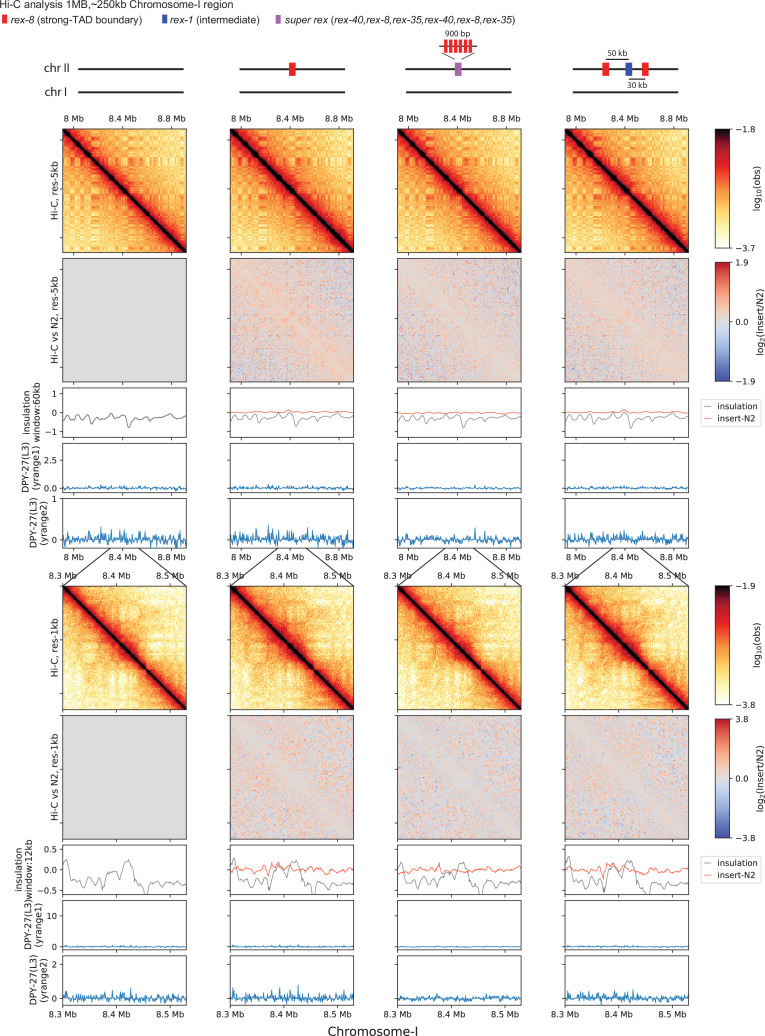
Figure 6. Ectopic insertion of rex elements that lead to condensin dosage compensation (DC) spreading form loop-anchored topologically associating domains (TADs).
Snapshot of a region on chromosome-II where recruitment elements on the X-chromosome (rex) sites are inserted. Shown are four different conditions in L3 stage: wild-type, single rex-8 insertion at one site, six concatenated strong rex (super rex) insertion at the same site and insertion of rex-8, rex-1, and rex-8 at a distance from each other spanning ~80 kb. Two different y-range cutoffs for ChIP-seq data are provided to highlight the level of condensin DC spreading in each strain. Log2ratio Hi-C plots or subtraction of insulation score (insertion-wild type) plots are generated using wild-type data mapped to the corresponding insertion genome in comparison.