Fig. B.2.
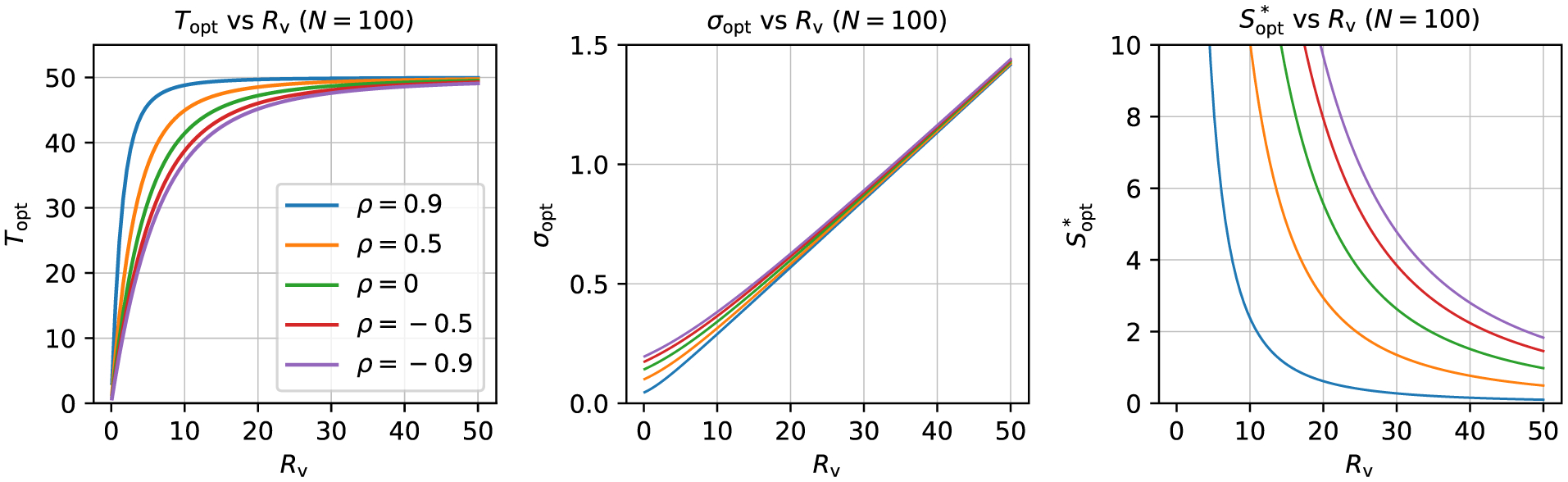
Visualizations of the information in the formula (B.5). Given N = 100 total samples, what is the optimal number to partition as trials? The answer depends strongly on the variability ratio Rv: for very low Rv, the optimal number of trials is relatively low; as Rv increases, Topt approaches N∕2 (where Topt = Sopt). The behavior is similar across correlation values, with ρ primarily affecting the rate at which Topt reaches N∕2. The middle and right panels show how the optimal uncertainty σopt and minimal subject sample size change as functions of Rv and ρ.
