The title charge-neutral complex is a low-spin complex with a moderately distorted pseudo-octahedral coordination environment of the metal ion. As a result of their asymmetric shape, the molecules stack into chains, which eventually pack into layers and, finally, into a three-dimensional network connected by weak C—H⋯N, C—H⋯C hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, spin-crossover, spin transition, energy frameworks
Abstract
The unit cell of the title compound, [FeII(C17H12BrN6O)2]·2MeOH, consists of a charge-neutral complex molecule and two independent molecules of methanol. In the complex molecule, the two tridentate ligand molecules 2-[5-(3-bromo-4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine coordinate to the FeII ion through the N atoms of the pyrazole, pyridine and triazole groups, forming a pseudo-octahedral coordination sphere around the central ion. In the crystal, neighbouring asymmetric molecules are linked through weak C—H(pz)⋯π(ph) interactions into chains, which are then linked into layers by weak C–H⋯N/C interactions. Finally, the layers stack into a three-dimensional network linked by weak interlayer C—H⋯π interactions between the methoxy groups and the phenyl rings. The intermolecular contacts were quantified using Hirshfeld surface analysis and two-dimensional fingerprint plots, revealing the relative contributions of the contacts to the crystal packing to be H⋯H 34.2%, H⋯C/C⋯H 25.2%, H⋯Br/Br⋯H 13.2%, H⋯N/N⋯H 12.2% and H⋯O/O⋯H 4.0%. The average Fe—N bond distance is 1.949 Å, indicating the low-spin state of the FeII ion. Energy framework analysis at the HF/3–21 G theory level was performed to quantify the interaction energies in the crystal structure.
1. Chemical context
A broad class of coordination compounds exhibiting spin-state switching between low- (total spin S = 0) and high-spin states (total spin S = 2) is represented by FeII complexes based on tridentate bisazolepyridine ligands (Halcrow, 2014 ▸; Suryadevara et al., 2022 ▸; Halcrow et al., 2019 ▸). In the case of asymmetric ligand design, where one of the azole groups carries a hydrogen on a nitrogen heteroatom and acts as a Brønsted acid, deprotonation can produce neutral complexes that can be either high-spin (Schäfer et al., 2013 ▸) or low-spin (Shiga et al., 2019 ▸) or exhibit temperature-induced transitions between the spin states of the central atom (Seredyuk et al., 2014 ▸), depending on the ligand field strength. The periphery of the molecule, i.e. ligand substituents, also plays an important role in the behaviour, determining the way in which molecules are packed in the lattice and their interactions with each other, and therefore further influencing the spin state adopted by the central atom. As we have recently demonstrated, the dynamic rearrangement of the methoxy group between the bent and extended configurations can lead to a highly hysteretic spin transition via a supramolecular blocking mechanism (Seredyuk et al., 2022 ▸).
Having interest in spin-transition 3d-metal complexes formed by polydentate ligands (Bartual-Murgui et al., 2017 ▸; Bonhommeau et al., 2012 ▸; Valverde-Muñoz et al., 2020 ▸), we report here on our current structural exploration of a new complex [FeII L 2] based on an asymmetric deprotonable ligand with two substituents on the phenyl group, L = 2-[5-(3-bromo-4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine.
2. Structural commentary
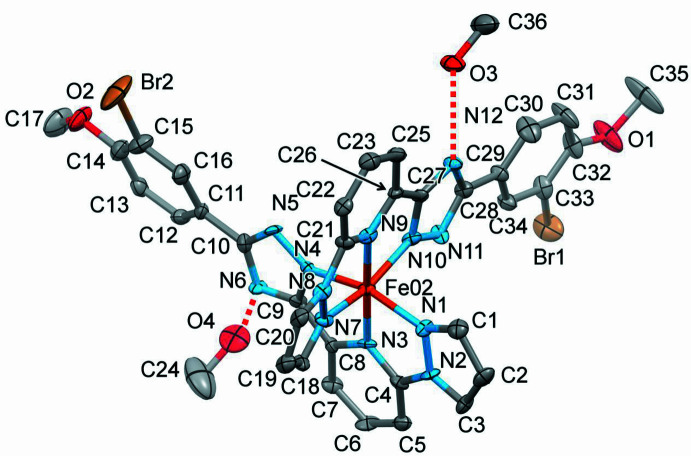
The title complex has a asymmetric molecule with divergent phenyl groups. The ligand molecules are almost planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.330 Å), including the methoxy substituents, which also lie in the plane of the aromatic groups [atoms C17 and C35 are 0.514 (1) and 0.116 (1) Å, respectively, away from the planes passing through their respective ligand molecules]. The two independent methanol molecules form O—H⋯N hydrogen bonds with the triazole (trz) rings of the ligand molecules (Fig. 1 ▸, Table 1 ▸). The central FeII ion of the complex has a distorted octahedral N6 coordination environment formed by the nitrogen donor atoms of two tridentate ligands (Fig. 1 ▸).
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dashed lines.
Table 1. Geometry (Å, °) of hydrogen bonds and C⋯N interactions in the title compound.
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C29–C34 rings, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17⋯N6i | 3.201 (16) | |||
| O3—H3A⋯N12 | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.820 (12) | 160 |
| O4—H4⋯N6 | 0.84 | 2.06 | 2.855 (11) | 158 |
| C1—H1⋯O4ii | 0.95 | 2.22 | 3.128 (14) | 161 |
| C18—H18⋯O3iii | 0.95 | 2.27 | 3.192 (14) | 163 |
| C35—H35A⋯C30iv | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.233 (16) | 121 |
| C3—H3⋯N5iii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.301 (13) | 148 |
| C7—H7⋯O4 | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.310 (11) | 148 |
| C22—H22⋯N11ii | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.317 (13) | 166 |
| C20—H20⋯N11ii | 0.95 | 2.55 | 3.389 (13) | 148 |
| C5—H5⋯N5iii | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.440 (12) | 161 |
| C17—H17A⋯O4i | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.451 (17) | 159 |
| C34—H34⋯C20v | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.535 (15) | 159 |
| C25—H25⋯O3 | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.542 (13) | 150 |
| C18—H18⋯C36iii | 0.95 | 2.88 | 3.65 (2) | 138 |
| C2—H2⋯C31vi | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.639 (15) | 143 |
| C2—H2⋯C32vi | 0.95 | 2.89 | 3.656 (15) | 139 |
| C2—H2⋯C30vi | 0.95 | 2.86 | 3.734 (11) | 154 |
| C2—H2⋯Cg2vi | 0.95 | 2.57 | 3.501 (11) | 168 |
| C19—H19⋯Cg1vi | 0.95 | 2.74 | 3.681 (11) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
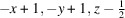 ; (ii)
; (ii)
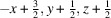 ; (iii)
; (iii)
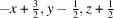 ; (iv)
; (iv)
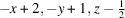 ; (v)
; (v)
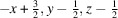 ; (vi)
; (vi)
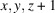 .
.
The average bond length, <Fe—N> = 1.949 Å, is typical for low-spin complexes with an N6 coordination environment (Gütlich & Goodwin, 2004 ▸). The average trigonal distortion parameters Σ = Σ1 12(|90 − φ i|), where φ i is the angle N–Fe–N′ (Drew et al., 1995 ▸), and Θ = Σ1 24(|60 − θ i|), where θ i is the angle generated by superposition of two opposite faces of an octahedron (Chang et al., 1990 ▸) are 93.3 and 298.8°, respectively. The values reveal a deviation of the coordination environment from an ideal octahedron (where Σ = Θ = 0) but is, however, in the expected range for bisazolepyridines and similar ligands (see below). The calculated continuous shape measure (CShM) value relative to the ideal Oh symmetry is 2.24 (Kershaw Cook et al., 2015 ▸). The volume of the [FeN6] coordination polyhedron is 9.536 Å3.
3. Supramolecular features
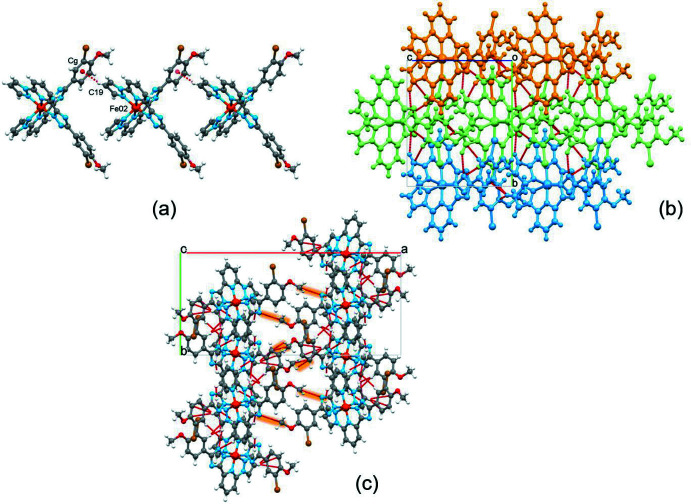
As a result of their asymmetric shape, neighbouring complex molecules fit into each other and interact through a weak C—H(pz)⋯π(ph) intermolecular contact between the pyrazole (pz) and phenyl (ph) groups respectively (Table 1 ▸). The mono-periodic supramolecular chains formed extend along the c-axis direction with a stacking periodicity of 10.6434 (3) Å (equal to cell parameter c; Fig. 2 ▸ a). Through weak intermolecular C—H(pz, py)⋯ N/C(pz, trz) interactions in the range 3.128 (14)–3.734 (11) Å (Table 1 ▸), neighbouring chains are linked into corrugated layers in the bc plane (Fig. 2 ▸ b,c). The layers stack with interlayer interactions limited to C—H⋯N(trz) and C—H⋯π(ph) contacts involving the methyl groups (Fig. 2 ▸ c). The voids between the layers are occupied by methanol molecules, which also participate in bonding between neighbouring layers (see Table 1 ▸ for the complete list of intermolecular interactions).
Figure 2.
(a) Mono-periodic supramolecular chain formed by stacking of molecules of the title compound. (b) Di-periodic layers formed by supramolecular chains. For a better representation, each chain has a different colour. (c) Highlighted interactions of neighbouring layers in the three-dimensional supramolecular network of the title complex. The red dashed lines correspond to contacts below the sum of the van der Waals radii. The methanol molecules are not shown for clarity.
4. Hirshfeld surface and 2D fingerprint plots
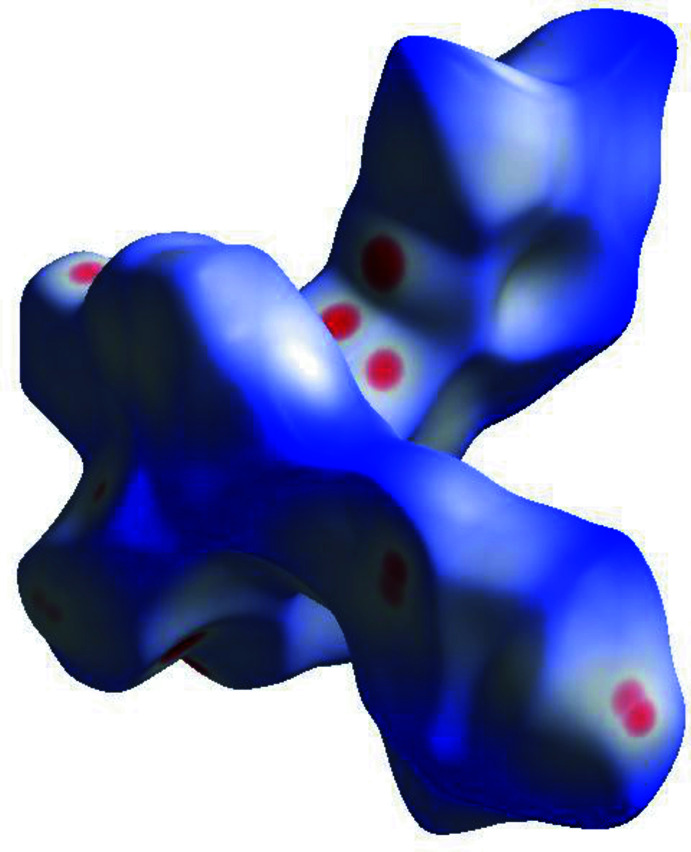
Hirshfeld surface analysis was performed and the associated two-dimensional fingerprint plots were generated using CrystalExplorer (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸), with a standard resolution of the three-dimensional d norm surfaces plotted over a fixed colour scale of −0.2869 (red) to 2.4335 (blue) a.u. (Fig. 3 ▸). The pale-red spots represent short contacts and negative d norm values on the surface corresponding to the interactions described above. The overall two-dimensional fingerprint plot is illustrated in Fig. 4 ▸. The Hirshfeld surfaces mapped over d norm are shown for the H⋯H, H⋯C/C⋯H, H⋯Br/Br⋯H, H⋯N/N⋯H and H⋯O/O⋯H contacts together with the two-dimensional fingerprint plots associated with their relative contributions to the Hirshfeld surface. At 34.2%, the largest contribution to the overall crystal packing is from H⋯H interactions, which are located in the middle region of the fingerprint plot. H⋯C/C⋯H contacts contribute 25.2%, and the H⋯Br/Br⋯H contacts contribute 13.2% to the Hirshfeld surface and both result in a pair of characteristic wings. The H⋯N/N⋯H contacts, represented by a pair of sharp spikes in the fingerprint plot, make a 12.2% contribution to the Hirshfeld surface. Finally, H⋯O/O⋯H contacts, which account for 4.0% of the contribution, are mostly distributed in the middle part of the plot.
Figure 3.
A projection of d norm mapped on the Hirshfeld surface, showing the intermolecular interactions within the molecule. Red areas represent regions where contacts are shorter than the sum of the van der Waals radii, blue areas represent regions where contacts are larger than the sum of van der Waals radii, and white areas are regions where contacts are close to the sum of van der Waals radii.
Figure 4.
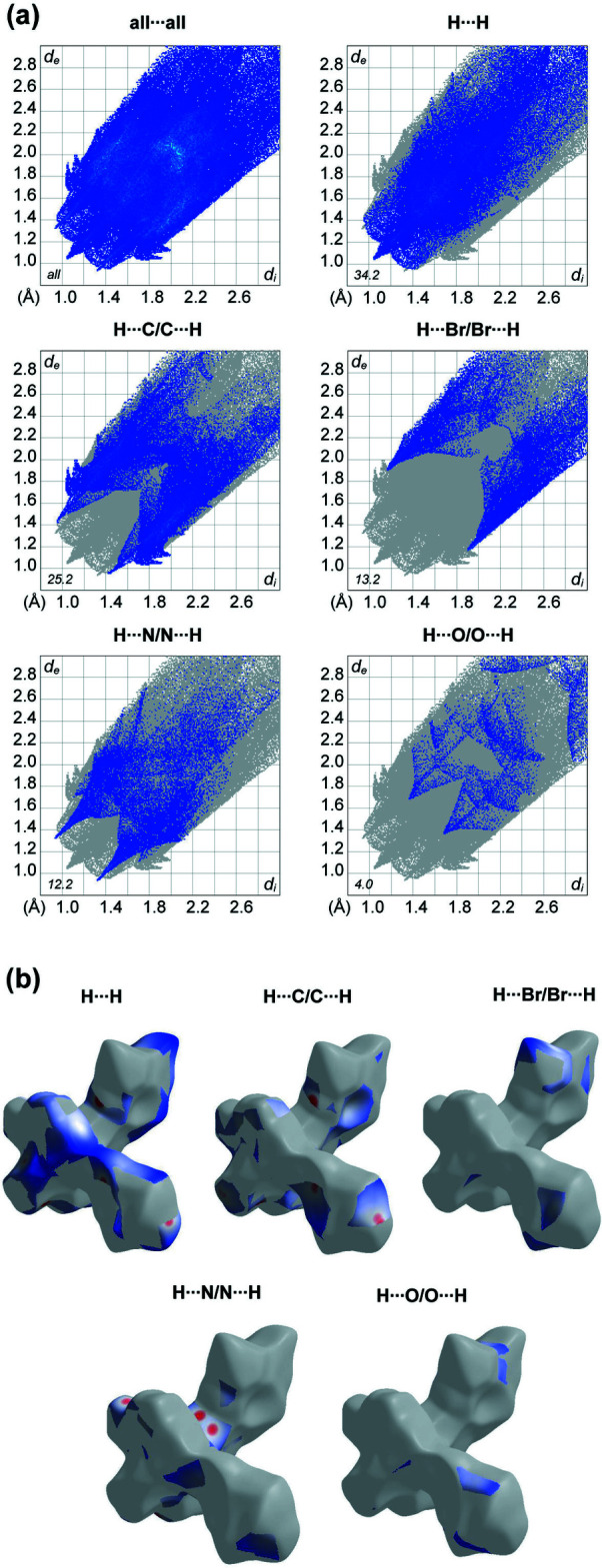
(a) The overall two-dimensional fingerprint plot and those decomposed into specified interactions. (b) Hirshfeld surface representations with the function d norm plotted onto the surface for the different interactions.
5. Energy framework analysis
The energy framework (Spackman et al., 2021 ▸), calculated using the wave function at the HF/3-21G theory level, including the electrostatic potential forces (E ele), the dispersion forces (E dis) and the total energy diagrams (E tot), are shown in Fig. 5 ▸. The cylindrical radii, adjusted to the same scale factor of 100, are proportional to the relative strength of the corresponding energies. The major contribution to the intermolecular interactions is due to the dispersion forces (E dis), reflecting the dominating interactions in the lattice of the neutral asymmetric molecules. The topology of the energy framework resembles the topology of the interactions within and between the layers described above. The calculated values E tot are in the range 65.2–87.6 kJ mol−1 for intrachain and intralayer interactions, whereas for the interlayer interactions they are within 7.7–23.4 kJ mol−1. The colour-coded interaction mappings within a radius of 3.8 Å of a central reference molecule for the title compound together with full details of the various contributions to the total energy (E tot) are given in the supporting information.
Figure 5.
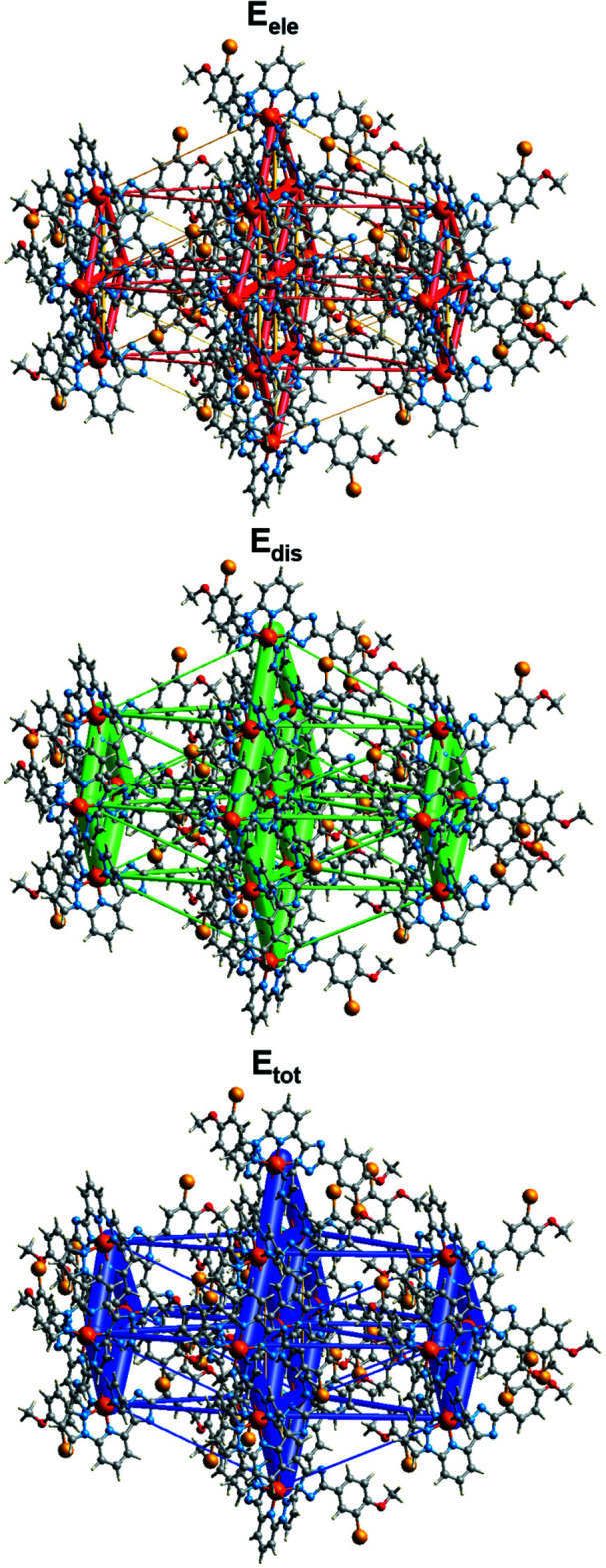
The calculated energy frameworks, showing the electrostatic potential forces (E ele), dispersion forces (E dis) and total energy (E tot) diagrams. Tube size is set at 100 scale, cut-off is 5 kJ mol−1.
6. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.42, last update February 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) reveals several similar neutral FeII complexes with a deprotonable azole group, for example, derivatives of a pyrazole-pyridine-tetrazole (IGERIX and LUTGEO; Gentili et al., 2015 ▸; Senthil Kumar et al., 2015 ▸) and a pyrazole-pyridine-benzimidazole (XODCEB; Shiga et al., 2019 ▸). There are also related complexes based on phenanthroline-tetrazole, such as QIDJET (Zhang et al., 2007 ▸) and phenanthroline-benzimidazole (DOMQUT; Seredyuk et al., 2014 ▸). Schematic structures of the complexes are shown in Fig. S1 in the supporting information. The Fe—N distances of these complexes in the low-spin state are 1.933–1.959 Å, while in the high-spin state they are in the range 2.179–2.184 Å. The values of the trigonal distortion and CShM(Oh ) change correspondingly, and in the low-spin state they are systematically lower than in the high-spin state. Table 2 ▸ collates the structural parameters of the complexes and of the title compound.
Table 2. Computed distortion indices (Å,°) for the title compound and similar complexes reported in the literature.
| CSD refcode | Spin state | <Fe—N> | Σ | Θ | CShM(Oh ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title compound | LS | 1.949 | 93.3 | 298.8 | 2.24 |
| IGERIX a | HS | 2.179 | 149.7 | 553.2 | 6.06 |
| IGERIX01 a | LS | 1.986 | 105.6 | 350.6 | 2.85 |
| LUTGEO b | LS | 1.933 | 85.0 | 309.6 | 2.10 |
| XODCEB c | LS | 1.950 | 87.4 | 276.6 | 1.93 |
| DOMQIH d | LS | 1.962 | 83.8 | 280.7 | 2.02 |
| QIDJET01 e | LS | 1.970 | 90.3 | 341.3 | 2.47 |
| QIDJET e | HS | 2.184 | 145.5 | 553.3 | 5.88 |
| DOMQUT d | LS | 1.991 | 88.5 | 320.0 | 2.48 |
| DOMQUT02 d | HS | 2.183 | 139.6 | 486.9 | 5.31 |
7. Synthesis and crystallization
The synthesis of the title compound is identical to that reported recently for a similar complex (Seredyuk et al., 2022 ▸). It was produced by layering in a standard test tube. The layering sequence was as follows: the bottom layer contains a solution of [Fe(L 2)](BF4)2 prepared by dissolving L = 2-[5-(3-bromo-4-methoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-6-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine (100 mg, 0.252 mmol) and Fe(BF4)2·6H2O (43 mg, 0.126 mmol) in boiling acetone, to which chloroform (5 ml) was then added. The middle layer was a methanol–chloroform mixture (1:10, 10 ml), which was covered by a layer of methanol (10 ml), to which 100 µl of NEt3 was added dropwise. The tube was sealed, and black cubic single crystals appeared in 3–4 weeks (yield ca 60%). Elemental analysis calculated for C36H32Br2FeN12O4: C, 47.39; H, 3.54; N, 18.42. Found: C, 47.11; H, 3.74; N, 18.40.
8. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 3 ▸. The highest and lowest remaining electron density peaks are located 1.01 and 0.88 Å, respectively, from the Br2 atom. H atoms were refined as riding [C—H = 0.95–0.98 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2–1.5U eq(C)]. O-bound H atoms were refined with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O).
Table 3. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | [Fe(C17H12BrN6O)2]·2CH4O |
| M r | 912.40 |
| Crystal system, space group | Orthorhombic, P n a21 |
| Temperature (K) | 180 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 27.4318 (10), 12.6723 (4), 10.6434 (3) |
| V (Å3) | 3699.9 (2) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.63 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.3 × 0.26 × 0.04 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Xcalibur, Eos |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2022 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.772, 1.000 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 14160, 6227, 4361 |
| R int | 0.061 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.595 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.057, 0.125, 1.03 |
| No. of reflections | 6227 |
| No. of parameters | 502 |
| No. of restraints | 7 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 1.25, −0.62 |
| Absolute structure | Flack x determined using 1444 quotients [(I +)−(I −)]/[(I +)+(I −)] (Parsons et al., 2013 ▸) |
| Absolute structure parameter | −0.009 (8) |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053Isup4.cdx
Includes energy framework data and schematic structures of similar neutral Fe(II) complexes. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053sup3.pdf
CCDC reference: 2215273
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Author contributions are as follows: Conceptualization, KZ and MS; methodology, KZ; formal analysis, IOF; synthesis, SOM; single-crystal measurements, SS; writing (original draft), MS; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), TYS, MS; visualization and calculations, KZ, VMA; funding acquisition, MS, IOF, VMA.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| [Fe(C17H12BrN6O)2]·2CH4O | Dx = 1.638 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 912.40 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Cell parameters from 3167 reflections |
| a = 27.4318 (10) Å | θ = 2.2–25.7° |
| b = 12.6723 (4) Å | µ = 2.63 mm−1 |
| c = 10.6434 (3) Å | T = 180 K |
| V = 3699.9 (2) Å3 | Plate, clear dark red |
| Z = 4 | 0.3 × 0.26 × 0.04 mm |
| F(000) = 1840 |
Data collection
| Xcalibur, Eos diffractometer | 6227 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-ray tube, Enhance (Mo) X-ray Source | 4361 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.061 |
| Detector resolution: 16.1593 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.8° |
| ω scans | h = −29→32 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2022) | k = −15→9 |
| Tmin = 0.772, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −11→12 |
| 14160 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0468P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.125 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.03 | Δρmax = 1.25 e Å−3 |
| 6227 reflections | Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3 |
| 502 parameters | Absolute structure: Flack x determined using 1444 quotients [(I+)-(I-)]/[(I+)+(I-)] (Parsons et al., 2013) |
| 7 restraints | Absolute structure parameter: −0.009 (8) |
| Primary atom site location: dual |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.93947 (6) | 0.18179 (10) | 0.18738 (16) | 0.0755 (6) | |
| Br2 | 0.58117 (5) | 0.86423 (9) | 0.16575 (14) | 0.0533 (4) | |
| Fe1 | 0.74880 (4) | 0.51357 (9) | 0.66488 (14) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.9850 (3) | 0.3512 (6) | 0.0344 (7) | 0.046 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.5033 (3) | 0.7175 (7) | 0.0845 (8) | 0.059 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.7925 (3) | 0.4642 (7) | 0.7986 (7) | 0.021 (2) | |
| N2 | 0.7854 (3) | 0.3616 (6) | 0.8310 (6) | 0.0190 (19) | |
| N3 | 0.7331 (2) | 0.3663 (5) | 0.6688 (8) | 0.0169 (16) | |
| N4 | 0.6980 (3) | 0.5090 (7) | 0.5358 (7) | 0.019 (2) | |
| N5 | 0.6735 (3) | 0.5777 (6) | 0.4591 (7) | 0.021 (2) | |
| N6 | 0.6424 (3) | 0.4144 (6) | 0.4290 (7) | 0.021 (2) | |
| N7 | 0.7030 (3) | 0.5599 (6) | 0.7956 (7) | 0.0179 (19) | |
| N8 | 0.7095 (3) | 0.6637 (6) | 0.8297 (7) | 0.0203 (19) | |
| N9 | 0.7639 (2) | 0.6605 (5) | 0.6733 (7) | 0.0157 (16) | |
| N10 | 0.8015 (3) | 0.5208 (7) | 0.5376 (7) | 0.0167 (19) | |
| N11 | 0.8252 (3) | 0.4538 (7) | 0.4581 (7) | 0.020 (2) | |
| N12 | 0.8561 (3) | 0.6197 (6) | 0.4353 (7) | 0.020 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.8232 (4) | 0.5020 (9) | 0.8838 (9) | 0.022 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.836027 | 0.571689 | 0.884392 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | 0.8342 (4) | 0.4225 (8) | 0.9744 (9) | 0.027 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.854203 | 0.429649 | 1.046766 | 0.032* | |
| C3 | 0.8103 (3) | 0.3351 (8) | 0.9362 (9) | 0.022 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.810827 | 0.267895 | 0.975646 | 0.027* | |
| C4 | 0.7534 (3) | 0.3030 (8) | 0.7529 (8) | 0.020 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.7444 (3) | 0.1970 (8) | 0.7604 (8) | 0.020 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.760428 | 0.153348 | 0.819944 | 0.024* | |
| C6 | 0.7104 (3) | 0.1564 (7) | 0.6761 (9) | 0.026 (2) | |
| H6 | 0.703580 | 0.082904 | 0.675727 | 0.032* | |
| C7 | 0.6865 (3) | 0.2219 (8) | 0.5934 (8) | 0.023 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.662303 | 0.194369 | 0.538543 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 0.6979 (3) | 0.3278 (8) | 0.5907 (8) | 0.018 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.6790 (3) | 0.4128 (8) | 0.5154 (7) | 0.016 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.6407 (4) | 0.5181 (8) | 0.3985 (8) | 0.020 (2) | |
| C11 | 0.6061 (3) | 0.5658 (8) | 0.3117 (8) | 0.021 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.5688 (4) | 0.5087 (9) | 0.2563 (10) | 0.042 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.566690 | 0.435012 | 0.271727 | 0.051* | |
| C13 | 0.5339 (4) | 0.5569 (9) | 0.1775 (13) | 0.049 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.508661 | 0.515389 | 0.141389 | 0.059* | |
| C14 | 0.5360 (4) | 0.6632 (9) | 0.1525 (11) | 0.034 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.5737 (3) | 0.7203 (9) | 0.2037 (9) | 0.029 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.6080 (4) | 0.6728 (8) | 0.2824 (9) | 0.026 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.633427 | 0.714686 | 0.316951 | 0.031* | |
| C17 | 0.4597 (5) | 0.6610 (12) | 0.0437 (14) | 0.085 (6) | |
| H17A | 0.436960 | 0.710675 | 0.004257 | 0.128* | |
| H17B | 0.443970 | 0.628133 | 0.116611 | 0.128* | |
| H17C | 0.468752 | 0.606305 | −0.017004 | 0.128* | |
| C18 | 0.6699 (4) | 0.5218 (9) | 0.8754 (9) | 0.027 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.656975 | 0.452322 | 0.872907 | 0.033* | |
| C19 | 0.6568 (4) | 0.6007 (9) | 0.9651 (9) | 0.028 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.634576 | 0.593789 | 1.033020 | 0.033* | |
| C20 | 0.6829 (4) | 0.6878 (8) | 0.9327 (9) | 0.022 (2) | |
| H20 | 0.682436 | 0.753910 | 0.974832 | 0.026* | |
| C21 | 0.7426 (3) | 0.7227 (8) | 0.7576 (8) | 0.019 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.7510 (4) | 0.8292 (8) | 0.7670 (9) | 0.024 (2) | |
| H22 | 0.734218 | 0.871698 | 0.826391 | 0.029* | |
| C23 | 0.7855 (3) | 0.8719 (7) | 0.6848 (9) | 0.028 (2) | |
| H23 | 0.792262 | 0.945451 | 0.686681 | 0.033* | |
| C25 | 0.8098 (4) | 0.8074 (8) | 0.6009 (9) | 0.024 (2) | |
| H25 | 0.833605 | 0.836305 | 0.545977 | 0.029* | |
| C26 | 0.7993 (3) | 0.7007 (8) | 0.5971 (8) | 0.015 (2) | |
| C27 | 0.8201 (3) | 0.6167 (8) | 0.5207 (8) | 0.017 (2) | |
| C28 | 0.8572 (3) | 0.5168 (9) | 0.3993 (8) | 0.022 (2) | |
| C29 | 0.8908 (3) | 0.4756 (8) | 0.3034 (9) | 0.021 (2) | |
| C30 | 0.9141 (4) | 0.5434 (9) | 0.2193 (8) | 0.028 (3) | |
| H30 | 0.908122 | 0.617120 | 0.223076 | 0.034* | |
| C31 | 0.9464 (4) | 0.5030 (10) | 0.1295 (9) | 0.029 (3) | |
| H31 | 0.962898 | 0.550064 | 0.074511 | 0.034* | |
| C32 | 0.9544 (4) | 0.3969 (10) | 0.1196 (9) | 0.034 (3) | |
| C33 | 0.9309 (4) | 0.3287 (9) | 0.2023 (10) | 0.037 (3) | |
| C34 | 0.8993 (4) | 0.3676 (9) | 0.2928 (9) | 0.029 (3) | |
| H34 | 0.883359 | 0.320139 | 0.348246 | 0.035* | |
| C35 | 1.0089 (5) | 0.4170 (10) | −0.0556 (11) | 0.062 (4) | |
| H35A | 1.026381 | 0.372877 | −0.116380 | 0.093* | |
| H35B | 1.032148 | 0.463288 | −0.012460 | 0.093* | |
| H35C | 0.984662 | 0.460036 | −0.099718 | 0.093* | |
| O3 | 0.8946 (3) | 0.8132 (7) | 0.3501 (8) | 0.054 (2) | |
| H3A | 0.889770 | 0.749515 | 0.368323 | 0.080* | |
| C36 | 0.9355 (6) | 0.8495 (13) | 0.4134 (18) | 0.101 (6) | |
| H36A | 0.964669 | 0.816116 | 0.378324 | 0.151* | |
| H36B | 0.932720 | 0.831820 | 0.502734 | 0.151* | |
| H36C | 0.937869 | 0.926235 | 0.403763 | 0.151* | |
| O4 | 0.6173 (3) | 0.2092 (6) | 0.3391 (7) | 0.040 (2) | |
| H4 | 0.620155 | 0.274742 | 0.348513 | 0.059* | |
| C24 | 0.5796 (4) | 0.1885 (10) | 0.2562 (11) | 0.054 (4) | |
| H24A | 0.581928 | 0.115298 | 0.227028 | 0.082* | |
| H24B | 0.581953 | 0.236323 | 0.184082 | 0.082* | |
| H24C | 0.548314 | 0.199154 | 0.298680 | 0.082* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0982 (11) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.1007 (13) | 0.0159 (8) | 0.0583 (11) | −0.0030 (9) |
| Br2 | 0.0659 (8) | 0.0299 (7) | 0.0640 (8) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0228 (9) | 0.0170 (8) |
| Fe1 | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0113 (7) | 0.0179 (6) | −0.0009 (6) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0006 (8) |
| O1 | 0.048 (5) | 0.041 (6) | 0.050 (5) | 0.001 (4) | 0.030 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
| O2 | 0.048 (5) | 0.050 (6) | 0.077 (6) | −0.010 (5) | −0.044 (4) | 0.030 (5) |
| N1 | 0.023 (5) | 0.016 (5) | 0.023 (5) | −0.008 (4) | 0.003 (4) | 0.001 (4) |
| N2 | 0.028 (5) | 0.011 (5) | 0.019 (4) | −0.001 (4) | 0.007 (3) | 0.007 (4) |
| N3 | 0.027 (4) | 0.011 (4) | 0.013 (4) | −0.003 (3) | 0.008 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
| N4 | 0.028 (5) | 0.015 (5) | 0.013 (4) | 0.001 (4) | 0.000 (3) | −0.001 (4) |
| N5 | 0.021 (5) | 0.010 (5) | 0.031 (5) | −0.005 (4) | −0.001 (4) | 0.009 (4) |
| N6 | 0.025 (5) | 0.015 (5) | 0.022 (5) | −0.002 (4) | −0.004 (4) | 0.000 (4) |
| N7 | 0.024 (5) | 0.010 (5) | 0.020 (4) | −0.002 (4) | 0.008 (4) | 0.004 (4) |
| N8 | 0.030 (5) | 0.009 (5) | 0.022 (5) | 0.002 (4) | 0.001 (4) | −0.007 (4) |
| N9 | 0.026 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.013 (4) | −0.001 (3) | −0.008 (4) | −0.002 (4) |
| N10 | 0.015 (4) | 0.016 (5) | 0.018 (4) | 0.000 (4) | −0.004 (3) | 0.002 (4) |
| N11 | 0.027 (5) | 0.014 (5) | 0.017 (5) | −0.005 (4) | 0.005 (4) | −0.010 (4) |
| N12 | 0.024 (5) | 0.010 (5) | 0.026 (5) | −0.004 (4) | 0.004 (4) | −0.003 (4) |
| C1 | 0.019 (6) | 0.013 (6) | 0.034 (6) | −0.003 (5) | −0.003 (5) | −0.002 (5) |
| C2 | 0.033 (6) | 0.022 (7) | 0.025 (6) | 0.008 (6) | −0.006 (5) | 0.001 (5) |
| C3 | 0.029 (6) | 0.018 (6) | 0.020 (5) | 0.011 (5) | −0.005 (4) | 0.005 (4) |
| C4 | 0.025 (6) | 0.018 (6) | 0.015 (5) | −0.001 (5) | −0.004 (4) | 0.001 (4) |
| C5 | 0.027 (6) | 0.013 (6) | 0.020 (5) | 0.003 (5) | 0.003 (4) | 0.007 (4) |
| C6 | 0.034 (5) | 0.020 (5) | 0.026 (6) | −0.005 (5) | 0.007 (6) | 0.001 (6) |
| C7 | 0.028 (6) | 0.024 (7) | 0.018 (5) | 0.000 (5) | −0.005 (4) | −0.005 (5) |
| C8 | 0.018 (5) | 0.013 (6) | 0.022 (5) | −0.003 (5) | 0.004 (4) | −0.006 (4) |
| C9 | 0.021 (6) | 0.016 (6) | 0.009 (5) | 0.001 (5) | −0.002 (4) | 0.000 (4) |
| C10 | 0.025 (6) | 0.018 (7) | 0.018 (5) | 0.001 (5) | −0.002 (4) | 0.003 (4) |
| C11 | 0.022 (6) | 0.021 (6) | 0.021 (5) | −0.005 (5) | −0.002 (4) | 0.003 (5) |
| C12 | 0.039 (8) | 0.023 (7) | 0.064 (8) | −0.007 (6) | −0.007 (6) | 0.015 (6) |
| C13 | 0.039 (6) | 0.042 (8) | 0.066 (8) | −0.014 (6) | −0.033 (7) | 0.012 (8) |
| C14 | 0.026 (5) | 0.041 (7) | 0.035 (6) | −0.002 (5) | −0.009 (5) | 0.021 (6) |
| C15 | 0.026 (6) | 0.031 (7) | 0.028 (6) | 0.001 (5) | −0.002 (5) | 0.013 (5) |
| C16 | 0.026 (6) | 0.021 (6) | 0.031 (6) | −0.003 (5) | −0.007 (5) | −0.001 (5) |
| C17 | 0.069 (10) | 0.081 (12) | 0.105 (11) | −0.027 (9) | −0.065 (9) | 0.032 (9) |
| C18 | 0.031 (7) | 0.018 (7) | 0.032 (6) | 0.000 (6) | 0.001 (5) | 0.004 (5) |
| C19 | 0.039 (7) | 0.028 (7) | 0.017 (5) | 0.006 (6) | 0.009 (5) | 0.000 (5) |
| C20 | 0.027 (6) | 0.019 (6) | 0.019 (5) | 0.009 (5) | 0.007 (4) | 0.003 (5) |
| C21 | 0.022 (6) | 0.015 (6) | 0.019 (5) | −0.005 (5) | −0.006 (4) | 0.003 (4) |
| C22 | 0.026 (6) | 0.023 (6) | 0.023 (5) | 0.001 (5) | −0.005 (4) | −0.005 (5) |
| C23 | 0.046 (6) | 0.009 (5) | 0.028 (6) | −0.002 (5) | −0.001 (6) | −0.002 (5) |
| C25 | 0.030 (6) | 0.018 (6) | 0.023 (5) | −0.007 (5) | 0.001 (4) | 0.005 (5) |
| C26 | 0.013 (5) | 0.014 (6) | 0.020 (5) | −0.002 (5) | −0.002 (4) | 0.002 (4) |
| C27 | 0.021 (5) | 0.021 (6) | 0.010 (5) | −0.007 (5) | 0.003 (4) | −0.001 (4) |
| C28 | 0.016 (5) | 0.025 (7) | 0.023 (6) | 0.002 (5) | 0.000 (4) | 0.002 (5) |
| C29 | 0.018 (5) | 0.025 (7) | 0.020 (5) | 0.005 (5) | 0.000 (4) | −0.004 (5) |
| C30 | 0.030 (6) | 0.030 (7) | 0.026 (5) | −0.008 (6) | 0.004 (5) | −0.011 (5) |
| C31 | 0.020 (6) | 0.038 (8) | 0.028 (6) | −0.007 (6) | 0.003 (4) | −0.001 (5) |
| C32 | 0.033 (7) | 0.041 (8) | 0.028 (6) | 0.010 (6) | 0.001 (5) | −0.005 (5) |
| C33 | 0.050 (7) | 0.028 (7) | 0.033 (7) | 0.007 (6) | 0.004 (6) | −0.008 (5) |
| C34 | 0.025 (6) | 0.031 (7) | 0.032 (6) | −0.004 (6) | 0.012 (5) | −0.001 (5) |
| C35 | 0.072 (10) | 0.057 (11) | 0.056 (8) | −0.007 (9) | 0.038 (8) | −0.005 (8) |
| O3 | 0.067 (6) | 0.023 (5) | 0.070 (6) | −0.009 (5) | 0.009 (5) | 0.013 (4) |
| C36 | 0.058 (11) | 0.065 (13) | 0.179 (18) | −0.023 (10) | −0.015 (12) | 0.025 (12) |
| O4 | 0.044 (5) | 0.021 (5) | 0.053 (5) | 0.003 (4) | −0.018 (4) | −0.012 (4) |
| C24 | 0.060 (9) | 0.047 (10) | 0.056 (9) | 0.012 (8) | −0.019 (7) | −0.022 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C33 | 1.883 (11) | C11—C12 | 1.384 (14) |
| Br2—C15 | 1.879 (11) | C11—C16 | 1.392 (13) |
| Fe1—N1 | 1.964 (8) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—N3 | 1.916 (7) | C12—C13 | 1.412 (14) |
| Fe1—N4 | 1.958 (8) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| Fe1—N7 | 1.964 (8) | C13—C14 | 1.374 (14) |
| Fe1—N9 | 1.909 (6) | C14—C15 | 1.375 (13) |
| Fe1—N10 | 1.982 (8) | C15—C16 | 1.396 (13) |
| O1—C32 | 1.364 (12) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| O1—C35 | 1.430 (13) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| O2—C14 | 1.342 (11) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| O2—C17 | 1.462 (14) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.359 (10) | C18—H18 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.328 (12) | C18—C19 | 1.429 (14) |
| N2—C3 | 1.354 (11) | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C4 | 1.418 (12) | C19—C20 | 1.360 (14) |
| N3—C4 | 1.324 (11) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C8 | 1.363 (11) | C21—C22 | 1.373 (13) |
| N4—N5 | 1.370 (11) | C22—H22 | 0.9500 |
| N4—C9 | 1.344 (12) | C22—C23 | 1.398 (13) |
| N5—C10 | 1.340 (12) | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| N6—C9 | 1.361 (11) | C23—C25 | 1.382 (13) |
| N6—C10 | 1.354 (12) | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| N7—N8 | 1.376 (10) | C25—C26 | 1.384 (13) |
| N7—C18 | 1.334 (12) | C26—C27 | 1.455 (13) |
| N8—C20 | 1.352 (11) | C28—C29 | 1.472 (13) |
| N8—C21 | 1.404 (11) | C29—C30 | 1.395 (14) |
| N9—C21 | 1.329 (11) | C29—C34 | 1.393 (13) |
| N9—C26 | 1.365 (11) | C30—H30 | 0.9500 |
| N10—N11 | 1.364 (11) | C30—C31 | 1.399 (12) |
| N10—C27 | 1.331 (12) | C31—H31 | 0.9500 |
| N11—C28 | 1.341 (12) | C31—C32 | 1.367 (15) |
| N12—C27 | 1.341 (11) | C32—C33 | 1.393 (15) |
| N12—C28 | 1.359 (12) | C33—C34 | 1.385 (14) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9500 | C34—H34 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.426 (13) | C35—H35A | 0.9800 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C35—H35B | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.350 (14) | C35—H35C | 0.9800 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | O3—H3A | 0.8400 |
| C4—C5 | 1.369 (12) | O3—C36 | 1.387 (16) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C36—H36A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.392 (13) | C36—H36B | 0.9800 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C36—H36C | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.376 (13) | O4—H4 | 0.8400 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | O4—C24 | 1.384 (12) |
| C7—C8 | 1.379 (13) | C24—H24A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.440 (13) | C24—H24B | 0.9800 |
| C10—C11 | 1.456 (13) | C24—H24C | 0.9800 |
| N1—Fe1—N7 | 88.4 (3) | O2—C14—C13 | 125.4 (10) |
| N1—Fe1—N10 | 93.7 (3) | O2—C14—C15 | 116.5 (10) |
| N3—Fe1—N1 | 79.1 (3) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.1 (10) |
| N3—Fe1—N4 | 80.0 (3) | C14—C15—Br2 | 120.5 (7) |
| N3—Fe1—N7 | 97.6 (3) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.2 (10) |
| N3—Fe1—N10 | 102.9 (3) | C16—C15—Br2 | 118.3 (8) |
| N4—Fe1—N1 | 159.1 (4) | C11—C16—C15 | 121.9 (9) |
| N4—Fe1—N7 | 93.0 (3) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.1 |
| N4—Fe1—N10 | 92.3 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.1 |
| N7—Fe1—N10 | 159.4 (3) | O2—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| N9—Fe1—N1 | 98.3 (3) | O2—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N9—Fe1—N3 | 176.0 (4) | O2—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N9—Fe1—N4 | 102.5 (3) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| N9—Fe1—N7 | 79.3 (3) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N9—Fe1—N10 | 80.2 (3) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C32—O1—C35 | 118.7 (10) | N7—C18—H18 | 125.0 |
| C14—O2—C17 | 117.1 (10) | N7—C18—C19 | 110.1 (10) |
| N2—N1—Fe1 | 113.6 (6) | C19—C18—H18 | 125.0 |
| C1—N1—Fe1 | 140.1 (8) | C18—C19—H19 | 127.3 |
| C1—N1—N2 | 105.3 (8) | C20—C19—C18 | 105.4 (9) |
| N1—N2—C4 | 116.2 (7) | C20—C19—H19 | 127.3 |
| C3—N2—N1 | 111.9 (8) | N8—C20—C19 | 107.8 (9) |
| C3—N2—C4 | 131.9 (8) | N8—C20—H20 | 126.1 |
| C4—N3—Fe1 | 120.6 (6) | C19—C20—H20 | 126.1 |
| C4—N3—C8 | 119.6 (8) | N9—C21—N8 | 109.7 (8) |
| C8—N3—Fe1 | 119.6 (6) | N9—C21—C22 | 123.9 (9) |
| N5—N4—Fe1 | 138.5 (7) | C22—C21—N8 | 126.3 (9) |
| C9—N4—Fe1 | 114.6 (6) | C21—C22—H22 | 121.6 |
| C9—N4—N5 | 106.8 (8) | C21—C22—C23 | 116.7 (9) |
| C10—N5—N4 | 105.0 (8) | C23—C22—H22 | 121.6 |
| C10—N6—C9 | 101.7 (8) | C22—C23—H23 | 120.0 |
| N8—N7—Fe1 | 113.0 (6) | C25—C23—C22 | 120.1 (9) |
| C18—N7—Fe1 | 141.1 (7) | C25—C23—H23 | 120.0 |
| C18—N7—N8 | 105.5 (8) | C23—C25—H25 | 120.1 |
| N7—N8—C21 | 116.6 (7) | C23—C25—C26 | 119.8 (9) |
| C20—N8—N7 | 111.1 (8) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.1 |
| C20—N8—C21 | 132.2 (8) | N9—C26—C25 | 119.7 (8) |
| C21—N9—Fe1 | 121.0 (6) | N9—C26—C27 | 109.8 (8) |
| C21—N9—C26 | 119.5 (8) | C25—C26—C27 | 130.5 (9) |
| C26—N9—Fe1 | 119.4 (6) | N10—C27—N12 | 113.6 (9) |
| N11—N10—Fe1 | 138.0 (7) | N10—C27—C26 | 116.2 (8) |
| C27—N10—Fe1 | 114.5 (6) | N12—C27—C26 | 130.3 (9) |
| C27—N10—N11 | 107.5 (8) | N11—C28—N12 | 115.1 (9) |
| C28—N11—N10 | 103.3 (8) | N11—C28—C29 | 121.5 (10) |
| C27—N12—C28 | 100.4 (8) | N12—C28—C29 | 123.3 (9) |
| N1—C1—H1 | 125.1 | C30—C29—C28 | 121.0 (10) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 109.9 (10) | C34—C29—C28 | 120.6 (9) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 125.1 | C34—C29—C30 | 118.4 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 127.1 | C29—C30—H30 | 119.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 105.9 (9) | C29—C30—C31 | 120.2 (11) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 127.1 | C31—C30—H30 | 119.9 |
| N2—C3—H3 | 126.5 | C30—C31—H31 | 119.5 |
| C2—C3—N2 | 106.9 (9) | C32—C31—C30 | 120.9 (10) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.5 | C32—C31—H31 | 119.5 |
| N3—C4—N2 | 109.9 (8) | O1—C32—C31 | 124.6 (10) |
| N3—C4—C5 | 123.8 (8) | O1—C32—C33 | 116.2 (11) |
| C5—C4—N2 | 126.3 (8) | C31—C32—C33 | 119.2 (10) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.7 | C32—C33—Br1 | 120.2 (8) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 116.5 (9) | C34—C33—Br1 | 119.3 (9) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.7 | C34—C33—C32 | 120.5 (11) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C29—C34—H34 | 119.6 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.6 (9) | C33—C34—C29 | 120.7 (10) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.7 | C33—C34—H34 | 119.6 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 | O1—C35—H35A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.5 (9) | O1—C35—H35B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 | O1—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| N3—C8—C7 | 119.8 (9) | H35A—C35—H35B | 109.5 |
| N3—C8—C9 | 109.1 (8) | H35A—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 131.1 (9) | H35B—C35—H35C | 109.5 |
| N4—C9—N6 | 112.4 (8) | C36—O3—H3A | 109.5 |
| N4—C9—C8 | 116.6 (8) | O3—C36—H36A | 109.5 |
| N6—C9—C8 | 130.8 (9) | O3—C36—H36B | 109.5 |
| N5—C10—N6 | 114.0 (9) | O3—C36—H36C | 109.5 |
| N5—C10—C11 | 120.6 (9) | H36A—C36—H36B | 109.5 |
| N6—C10—C11 | 125.3 (9) | H36A—C36—H36C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 122.3 (10) | H36B—C36—H36C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 116.3 (9) | C24—O4—H4 | 109.5 |
| C16—C11—C10 | 121.4 (9) | O4—C24—H24A | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.1 | O4—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 121.9 (10) | O4—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.1 | H24A—C24—H24B | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 | H24A—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.6 (10) | H24B—C24—H24C | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 | ||
| Br1—C33—C34—C29 | −177.7 (8) | C3—N2—C4—N3 | 172.4 (9) |
| Br2—C15—C16—C11 | −177.8 (7) | C3—N2—C4—C5 | −8.0 (16) |
| Fe1—N1—N2—C3 | −169.9 (6) | C4—N2—C3—C2 | −178.2 (9) |
| Fe1—N1—N2—C4 | 8.8 (10) | C4—N3—C8—C7 | −4.9 (13) |
| Fe1—N1—C1—C2 | 165.1 (8) | C4—N3—C8—C9 | 175.6 (8) |
| Fe1—N3—C4—N2 | 0.4 (10) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −2.0 (13) |
| Fe1—N3—C4—C5 | −179.2 (7) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 2.7 (14) |
| Fe1—N3—C8—C7 | −179.9 (7) | C6—C7—C8—N3 | 0.7 (14) |
| Fe1—N3—C8—C9 | 0.5 (10) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −179.8 (9) |
| Fe1—N4—N5—C10 | −176.2 (7) | C7—C8—C9—N4 | 179.9 (9) |
| Fe1—N4—C9—N6 | 177.2 (6) | C7—C8—C9—N6 | 3.8 (17) |
| Fe1—N4—C9—C8 | 0.5 (10) | C8—N3—C4—N2 | −174.6 (7) |
| Fe1—N7—N8—C20 | −170.3 (6) | C8—N3—C4—C5 | 5.7 (14) |
| Fe1—N7—N8—C21 | 7.5 (9) | C9—N4—N5—C10 | 0.7 (10) |
| Fe1—N7—C18—C19 | 167.7 (8) | C9—N6—C10—N5 | 0.4 (11) |
| Fe1—N9—C21—N8 | −1.0 (10) | C9—N6—C10—C11 | −177.5 (9) |
| Fe1—N9—C21—C22 | −178.6 (7) | C10—N6—C9—N4 | 0.1 (10) |
| Fe1—N9—C26—C25 | 178.7 (7) | C10—N6—C9—C8 | 176.3 (10) |
| Fe1—N9—C26—C27 | −0.7 (10) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 176.6 (10) |
| Fe1—N10—N11—C28 | 180.0 (7) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −177.1 (9) |
| Fe1—N10—C27—N12 | 179.3 (6) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.4 (19) |
| Fe1—N10—C27—C26 | −0.1 (10) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.3 (15) |
| O1—C32—C33—Br1 | −3.1 (13) | C12—C13—C14—O2 | −176.3 (11) |
| O1—C32—C33—C34 | 179.6 (10) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (19) |
| O2—C14—C15—Br2 | −5.6 (14) | C13—C14—C15—Br2 | 176.3 (9) |
| O2—C14—C15—C16 | 176.0 (10) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −2.1 (17) |
| N1—N2—C3—C2 | 0.3 (11) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.6 (16) |
| N1—N2—C4—N3 | −6.1 (11) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.9 (16) |
| N1—N2—C4—C5 | 173.6 (9) | C17—O2—C14—C13 | 6.0 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 2.4 (12) | C17—O2—C14—C15 | −171.9 (11) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | −2.2 (11) | C18—N7—N8—C20 | 3.1 (10) |
| N2—C4—C5—C6 | 178.2 (8) | C18—N7—N8—C21 | −179.0 (8) |
| N3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.2 (14) | C18—C19—C20—N8 | 0.6 (12) |
| N3—C8—C9—N4 | −0.6 (11) | C20—N8—C21—N9 | 172.9 (9) |
| N3—C8—C9—N6 | −176.7 (8) | C20—N8—C21—C22 | −9.5 (16) |
| N4—N5—C10—N6 | −0.7 (11) | C21—N8—C20—C19 | −179.8 (9) |
| N4—N5—C10—C11 | 177.2 (8) | C21—N9—C26—C25 | −5.5 (12) |
| N5—N4—C9—N6 | −0.5 (10) | C21—N9—C26—C27 | 175.1 (8) |
| N5—N4—C9—C8 | −177.3 (8) | C21—C22—C23—C25 | −1.0 (14) |
| N5—C10—C11—C12 | −173.9 (9) | C22—C23—C25—C26 | 1.0 (14) |
| N5—C10—C11—C16 | 4.5 (15) | C23—C25—C26—N9 | 2.3 (13) |
| N6—C10—C11—C12 | 3.9 (15) | C23—C25—C26—C27 | −178.5 (9) |
| N6—C10—C11—C16 | −177.7 (9) | C25—C26—C27—N10 | −178.9 (9) |
| N7—N8—C20—C19 | −2.3 (11) | C25—C26—C27—N12 | 1.9 (17) |
| N7—N8—C21—N9 | −4.4 (11) | C26—N9—C21—N8 | −176.6 (7) |
| N7—N8—C21—C22 | 173.2 (9) | C26—N9—C21—C22 | 5.7 (14) |
| N7—C18—C19—C20 | 1.4 (12) | C27—N10—N11—C28 | 0.4 (10) |
| N8—N7—C18—C19 | −2.7 (11) | C27—N12—C28—N11 | −0.9 (11) |
| N8—C21—C22—C23 | −179.6 (8) | C27—N12—C28—C29 | 179.4 (8) |
| N9—C21—C22—C23 | −2.4 (14) | C28—N12—C27—N10 | 1.1 (10) |
| N9—C26—C27—N10 | 0.4 (11) | C28—N12—C27—C26 | −179.6 (9) |
| N9—C26—C27—N12 | −178.8 (9) | C28—C29—C30—C31 | 179.4 (8) |
| N10—N11—C28—N12 | 0.3 (11) | C28—C29—C34—C33 | 179.8 (9) |
| N10—N11—C28—C29 | −180.0 (8) | C29—C30—C31—C32 | 2.1 (15) |
| N11—N10—C27—N12 | −1.0 (10) | C30—C29—C34—C33 | 1.1 (15) |
| N11—N10—C27—C26 | 179.6 (8) | C30—C31—C32—O1 | 179.6 (9) |
| N11—C28—C29—C30 | 162.3 (9) | C30—C31—C32—C33 | −1.4 (15) |
| N11—C28—C29—C34 | −16.3 (14) | C31—C32—C33—Br1 | 177.8 (8) |
| N12—C28—C29—C30 | −18.0 (15) | C31—C32—C33—C34 | 0.6 (16) |
| N12—C28—C29—C34 | 163.4 (9) | C32—C33—C34—C29 | −0.4 (16) |
| C1—N1—N2—C3 | 1.2 (10) | C34—C29—C30—C31 | −1.9 (14) |
| C1—N1—N2—C4 | 180.0 (8) | C35—O1—C32—C31 | −3.0 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—N2 | −1.6 (11) | C35—O1—C32—C33 | 178.0 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C29–C34 rings, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17···N6i | 3.201 (16) | |||
| O3—H3A···N12 | 0.84 | 2.02 | 2.820 (12) | 160 |
| O4—H4···N6 | 0.84 | 2.06 | 2.855 (11) | 158 |
| C1—H1···O4ii | 0.95 | 2.22 | 3.128 (14) | 161 |
| C18—H18···O3iii | 0.95 | 2.27 | 3.192 (14) | 163 |
| C35—H35A···C30iv | 0.98 | 2.62 | 3.233 (16) | 121 |
| C3—H3···N5iii | 0.95 | 2.45 | 3.301 (13) | 148 |
| C7—H7···O4 | 0.95 | 2.46 | 3.310 (11) | 148 |
| C22—H22···N11ii | 0.95 | 2.39 | 3.317 (13) | 166 |
| C20—H20···N11ii | 0.95 | 2.55 | 3.389 (13) | 148 |
| C5—H5···N5iii | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.440 (12) | 161 |
| C17—H17A···O4i | 0.98 | 2.52 | 3.451 (17) | 159 |
| C34—H34···C20v | 0.95 | 2.63 | 3.535 (15) | 159 |
| C25—H25···O3 | 0.95 | 2.69 | 3.542 (13) | 150 |
| C18—H18···C36iii | 0.95 | 2.88 | 3.65 (2) | 138 |
| C2—H2···C31vi | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.639 (15) | 143 |
| C2—H2···C32vi | 0.95 | 2.89 | 3.656 (15) | 139 |
| C2—H2···C30vi | 0.95 | 2.86 | 3.734 (11) | 154 |
| C2—H2···Cg2vi | 0.95 | 2.57 | 3.501 (11) | 168 |
| C19—H19···Cg1vi | 0.95 | 2.74 | 3.681 (11) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z−1/2; (ii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x+3/2, y−1/2, z+1/2; (iv) −x+2, −y+1, z−1/2; (v) −x+3/2, y−1/2, z−1/2; (vi) x, y, z+1.
Geometry (Å, °) of hydrogen bonds and C···N interactions in the title compound.
| D–H···A | D–H | D···A | H···A | D–H···A | Symmetry operation |
| C17···N6 | - | 3.20 (2) | - | - | 1-x,1-y,-1/2+z |
| O3-H···N12 | 0.84 (1) | 2.82 (1) | 2.02 (1) | 159.5 (5) | x,y,z |
| O4-H···N6 | 0.84 (1) | 2.86 (1) | 2.06 (2) | 158.0 (5) | x,y,z |
| C1-H···O4 | 0.95 (1) | 3.13 (1) | 2.22 (1) | 160.6 (5) | 1.5-x,1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C18-H···O3 | 0.95 (1) | 3.19 (1) | 2.27 (1) | 162.6 (5) | 1.5-x,-1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C35-H···C30 | 0.95 (1) | 3.23 (2) | 2.62 (2) | 121.0 (5) | 2-x,1-y,-1/2+z |
| C3-H···N5 | 0.95 (1) | 3.30 (1) | 2.46 (2) | 148.4 (5) | 1.5-x,-1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C7-H···O4 | 0.95 (1) | 3.31 (1) | 2.46 (1) | 148.4 (5) | x,y,z |
| C22-H···N11 | 0.95 (1) | 3.32 (1) | 2.39 (1) | 165.6 (5) | 1.5-x,1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C20-H···N11 | 0.95 (1) | 3.39 (1) | 2.55 (2) | 147.6 (5) | 1.5-x,1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C5-H···N5 | 0.95 (1) | 3.44 (1) | 2.53 (2) | 160.7 (5) | 1.5-x,-1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C17-H···O4 | 0.95 (1) | 3.45 (2) | 2.52 (2) | 159.1 (5) | 1-x,1-y,-1/2+z |
| C34-H···C20 | 0.95 (1) | 3.53 (2) | 2.63 (1) | 159.1 (5) | 1.5-x,-1/2+y,-1/2+z |
| C25-H···O3 | 0.95 (1) | 3.54 (1) | 2.69 (1) | 149.6 (5) | x,y,z |
| C18-H···C36 | 0.95 (1) | 3.65 (2) | 2.88 (1) | 138.0 (5) | 1.5-x,-1/2+y,1/2+z |
| C2–H···C31 | 0.95 (1) | 3.64 (2) | 2.84 (1) | 143.0 (5) | x,y,1+z |
| C2-H···C32 | 0.95 (1) | 3.66 (2) | 2.89 (2) | 139.0 (5) | x,y,1+z |
| C2–H···C30 | 0.95 (1) | 3.73 (1) | 2.86 (1) | 154.4 (5) | x,y,1+z |
Funding Statement
Funding for this research was provided by: Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine (grant No. 22BF037-03, 22BF037-04).
References
- Bartual-Murgui, C., Piñeiro-López, L., Valverde-Muñoz, F. J., Muñoz, M. C., Seredyuk, M. & Real, J. A. (2017). Inorg. Chem. 56, 13535–13546. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bonhommeau, S., Lacroix, P. G., Talaga, D., Bousseksou, A., Seredyuk, M., Fritsky, I. O. & Rodriguez, V. (2012). J. Phys. Chem. C, 116, 11251–11255.
- Chang, H. R., McCusker, J. K., Toftlund, H., Wilson, S. R., Trautwein, A. X., Winkler, H. & Hendrickson, D. N. (1990). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112, 6814–6827.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Drew, M. G. B., Harding, C. J., McKee, V., Morgan, G. G. & Nelson, J. (1995). J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. pp. 1035–1038.
- Gentili, D., Demitri, N., Schäfer, B., Liscio, F., Bergenti, I., Ruani, G., Ruben, M. & Cavallini, M. (2015). J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 7836–7844.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gütlich, P. & Goodwin, H. A. (2004). Top. Curr. Chem. 233, 1–47.
- Halcrow, M. A. (2014). New J. Chem. 38, 1868–1882.
- Halcrow, M. A., Capel Berdiell, I., Pask, C. M. & Kulmaczewski, R. (2019). Inorg. Chem. 58, 9811–9821. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kershaw Cook, L. J., Mohammed, R., Sherborne, G., Roberts, T. D., Alvarez, S. & Halcrow, M. A. (2015). Coord. Chem. Rev. 289–290, 2–12.
- Parsons, S., Flack, H. D. & Wagner, T. (2013). Acta Cryst. B69, 249–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2022). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Schäfer, B., Rajnák, C., Šalitroš, I., Fuhr, O., Klar, D., Schmitz-Antoniak, C., Weschke, E., Wende, H. & Ruben, M. (2013). Chem. Commun. 49, 10986. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Senthil Kumar, K., Šalitroš, I., Heinrich, B., Fuhr, O. & Ruben, M. (2015). J. Mater. Chem. C. 3, 11635–11644.
- Seredyuk, M., Znovjyak, K., Valverde-Muñoz, F. J., da Silva, I., Muñoz, M. C., Moroz, Y. S. & Real, J. A. (2022). J. Am. Chem. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c05417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Seredyuk, M., Znovjyak, K. O., Kusz, J., Nowak, M., Muñoz, M. C. & Real, J. A. (2014). Dalton Trans. 43, 16387–16394. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shiga, T., Saiki, R., Akiyama, L., Kumai, R., Natke, D., Renz, F., Cameron, J. M., Newton, G. N. & Oshio, H. (2019). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 58, 5658–5662. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spackman, P. R., Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2021). J. Appl. Cryst. 54, 1006–1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suryadevara, N., Mizuno, A., Spieker, L., Salamon, S., Sleziona, S., Maas, A., Pollmann, E., Heinrich, B., Schleberger, M., Wende, H., Kuppusamy, S. K. & Ruben, M. (2022). Chem. Eur. J. 28, e202103853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Valverde–Muñoz, F., Seredyuk, M., Muñoz, M. C., Molnár, G., Bibik, Y. S. & Real, J. A. (2020). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59, 18632–18638. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W., Zhao, F., Liu, T., Yuan, M., Wang, Z. M. & Gao, S. (2007). Inorg. Chem. 46, 2541–2555. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053Isup4.cdx
Includes energy framework data and schematic structures of similar neutral Fe(II) complexes. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022010179/dj2053sup3.pdf
CCDC reference: 2215273
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report