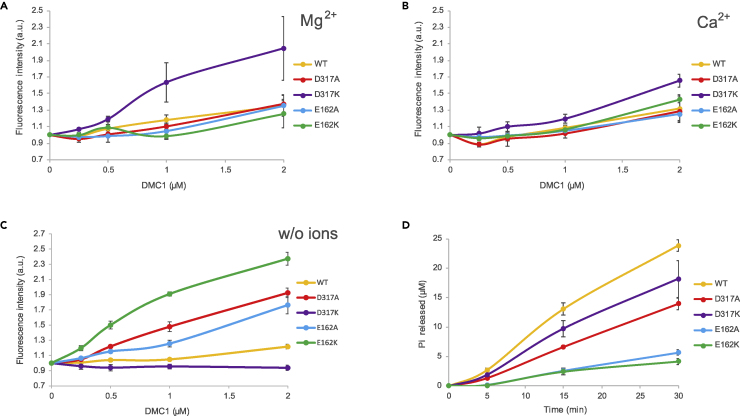
Figure 4.
ATP binding and hydrolysis of human DMC1 mutants
(A) ATP binding of human DMC1 variants measured as a change of the fluorescence emission intensity of TNP-ATP upon binding to DMC1 in the presence of ATP (1 mM) and 1-mM MgCl2 (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(B) ATP binding of human DMC1 variants measured as a change of the fluorescence emission intensity of TNP-ATP upon binding to DMC1 in the presence of ATP (1 mM) and 1-mM CaCl2 (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(C) ATP binding of human DMC1 variants measured as a change of the fluorescence emission intensity of TNP-ATP upon binding to DMC1 in the presence of ATP (1 mM) and absence of bivalent ion (mean ± SD; n = 3).
(D) ATP hydrolysis of DMC1 variants (2 μM) analyzed using the colorimetric phosphate detection assay in the presence of 90-mer ssDNA (6.3-μM nucleotides) and MgCl2 (1 mM) (mean ± SD; n = 3).