Abstract
Leishmaniasis is a tropical disease that leads to various clinical phenotypes. This study aimed to investigate protein expression changes in metacyclic and amastigote-like stages of L. tropica isolated from Iranian cutaneous leishmaniasis patients. Isolated samples were cultured and species type identified using PCR–RFLP technique. The promastigotes were grown in RPMI1640 media and differentiated to metacyclic and amastigote-like forms, followed by the extracted proteins of both successive stages carried out for proteomics and bioinformatics analysis. Using SWATH-MS quantitative proteomics technique, a total 176 and 155 distinct proteins were identified in metacyclic and axenic amastigote stages, respectively. Of these, 65 proteins were altered significantly (p-value < 0.05 and fold change ≥ 2) between studied stages. Several gene ontology (GO) categories were enriched for biological process during conversion of metacyclic promastigotes into amastigote-like, which “metabolic process” (GO: 0044281, P-Value: 6.52e-5), and “translation” (GO: 0006412, p-value: 5.01e–14) were disclosed as the top category in up and down-regulated proteins, respectively. Also, the KEGG pathway analysis indicated “metabolic pathways” and “ribosome” term as the most important pathways in up and down-regulated proteins, respectively. According to protein interaction network analysis, enolase (ENOL) has been detected as main hub proteins during differentiation, followed by Putative NADH-dependent fumarate reductase (LmjF.35.1180) and 40S ribosomal protein S2 (LmjF.32.0450). Overall, protein changes possibly play important roles in L. tropica biology. Anabolic pathways were down-regulated, whereas catabolic pathways were up-regulated during L. tropica differentiation. These protein expression changes could provide parasite survival in host macrophages, and could use as novel potential drug and vaccine targets for leishmaniasis.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords: Leishmaniasis, Leishmania tropica, Proteomics, SWATH-MS
Introduction
Parasites of the genus leishmania cause a wide range of disease called leishmaniasis from cutaneous lesions to fatal visceral leishmaniasis. Leishmania species are affecting 12 million people worldwide with 0.9–1.6 million new cases each year (Desjeux 1996, 2001). These parasites have a dimorphic life cycle including extracellular and flagellated promastigote in sndfly and an intracellular and non-motile amastigote form within the infected macrophages of vertebrate hosts. Each of promastigote and amastigote forms are adapted to residue in the different environment include midgut of the sandflies and hydrolytic environment of the phagolysosomes for a long time, respectively. Differentiation from promastigote to the amastigote accompanied by several morphological and biochemical changes which basically depends on the expression of stage-specific proteins (Bente et al. 2003). There is no vaccine for leishmaniasis and the control of these protozoa relies only on chemotherapy. The first-line of treatment relies on pentavalent antimony (SbV) compounds and drug resistant parasites has emerged worldwide (Kedzierski et al. 2009) such as Iran. L. major and L. tropica are the causative agents for cutaneous leishmaniasis in Iran and some of the neighboring countries (Ahmadi et al. 2013; Ashrafmansouri et al. 2015). Since the parasites regulate gene expression mainly at post-transcriptional stages, “Omics” approach including genomics, proteomics (Jardim et al. 2018; Sundar and Singh 2018), metabolomics (Atan et al. 2018) along with bioinformatics analysis (Dashatan et al. 2018) is thought to yield critical insight into the mechanisms of stage differentiation, parasite biology, species differences, virulence and drug resistance (Amiri-Dashatan et al. 2018, 2020a; Menezes et al. 2013; Moreira et al. 2014). In the field of the molecular differences between procyclic, metacyclic and amastigote forms, several investigation was reported the proteome of promastigotes and amastigotes forms of L. major, L. infantum, L. donovani and L. Mexicana. Most of these reports have used 2DE map to detect global differences of Leishmania species life stages (Amiri-Dashatan et al. 2020b; Ashrafmansouri et al. 2019), which may be due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) affect charged amino acids (Rosenzweig et al. 2008). Therefore, gel free approaches provide a valuable resource to higher proteome coverage and more precise quantitative information. Sequential window acquisition of all theoretical mass spectrometry (SWATH-MS) approach is a recently developed label free quantitative method, in which data independent acquisition is coupled with peptide spectral library match (Paape et al. 2010; Zhu et al. 2009). So far, proteomic studies to define the protein changes and pathways underlying in metacyclic and amastigote-like stages of L. tropica have not been reported. Identification of altered proteins during parasite development can help to introducing potential novel therapeutic targets and vaccine production for leishmaniasis. To the best of our knowledge, SWATH-based comparative proteomic analysis is the first report in Iran on the quantitative comprehensive studies regarding the proteomic profiles of metacyclic and amastigote-like of L.tropica. Therefore, in this study, we have employed label-free quantitative proteomics approach (SWATH) to identify differentially regulated proteins between metacyclic and amastigote-like forms in Iranian isolates of L. tropica by proteomic and bioinformatics approach.
Materials and methods
Sample collection
A total of 5 Leishmania tropica isolates were collected from patients in Bam city of Kerman province which is endemic region for cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L. tropica. In addition, age, gender, lesion site and diameter of lesion matched participated in our study. We utilized five Iranian isolates of L.tropica, whom their cutaneous leishmaniasis newly diagnosed. This study was approved by Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Ethical code: IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1398.040). Informed consent was received from all participating patients in the present study. The identities of the isolates performed by using PCR–RFLP technique, in which the internal transcribed-spacer-1 (ITS1) region of the parasites’ ribosomal-RNA gene amplified, followed by HaeIII digestion of the resulting amplicons, as described previously. To carry out the PCR, we used the primers L1TSR (5ʹ-CTGGATCATTTTCCGATG-3ʹ) and L 5.8 (5ʹ-TGATACCACTTATCGCACTT-3ʹ) as the forward and reverse primers, respectively. Therefore, metacyclic and amastigote-like samples pooled separately and SWATH analysis performed in three replicates. The fold changes in current study calculated between groups.
Cell culture and differentiation of L. topica
Primary isolates initially were grown on Novy-Nicolle-Mc Neal (NNN) medium and for mass culture, parasites were transferred to RPMI1640 medium (Gibco, Germany) supplemented with %10 FCS (Gibco, Germany), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin (Gibco, Germany) in 25 °C. Promastigotes were cultured with repeated medium for 6–10 days for achievement the metacyclic promastigotes form. During this time, the numbers of parasites were counted with light microscope. The parasites of stationary phase were then divided into the two aliquots. The content of one aliquot contain 107 metacyclic cell/ml were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C and washed three times with sterile PBS (pH: 7.4) and collected in -70˚C for the protein extraction. The other aliquot was used to achieve amastigote-like parasites. To generate amastigote-like form, the cell’s environment condition was changed. Briefly, metacyclic promastigotes were placed in RPMI1640 and Schneider's Drosophila medium (pH: 3.5–4.4) supplemented with 20–25% FCS (Gibco, Germany), 200 U/ml penicillin, and 200 µg/ml streptomycin (Gibco, Germany) and maintained at 35 °C with 5% CO2 for 96- 120 h. The cells were monitored daily for observation of lack of flagella and spherical form of cells using Giemsa staining with an optical microscope. The 107 cells/ml verified amastigote-like cells by observing cell roundness, aflagellated and immobile forms; were collected in − 70˚C for the protein extraction.
Protein extraction and SWATH-MS analysis
The 1 × 10 7 cells/ml (each of metacyclic and amastigote-like forms) were dissolved in lysis buffer (containing 8MUrea, DTT, Tris–Hcl, Glycerol, Tween–20 and 1 × protease inhibitor cocktail) and incubated for 2 h at room temperature. The cell extract was centrifuged at 15,000 g for 15 min at 4 °C to remove the cell debris. Protein concentration of supernatant was measured using Bradford assay. The soluble protein extracts were precipitated according to PhenoSwitch Bioscience laboratory protocol and stored at − 70 °C in single use aliquots. LC–MS/MS was performed at PhenoSwitch Bioscience, laboratory in Sherbrooke, Canada, using ABSciex Triple TOF 5600 instrument (ABSciex, Foster City, CA, USA) equipped with an electrospray interface with a 25 μm i.d. capillary and coupled to an EksigentμUHPLC (Eksigent, Redwood City, CA, USA). All experiments were carried out in three replicates. Proteins fold with differences in greater than 2 and p-value < 0.05 were detected as significant altered proteins between metacyclic promastigotes and axenic amastigotes of L. tropica.
Gene ontology enrichment and pathway analysis
To better TriTryp database (The Kinetoplastid Genomics Resource) (http://tritrypdb.org/tritrypdb/) was applied for gene ontology enrichment analysis. TriTrypDB is an integrated database providing access to genome-scale datasets for kinetoplastid parasites, and supporting a variety of complex queries driven by research and development needs (Aslett et al. 2009). The differentially regulated proteins between metacyclic promastigote and axenic amastigote stages were selected for Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway, and enriched based on biological process, molecular function and cellular component. Pathway analysis of differentially regulated proteins was performed using STRING database (http://string-db.org) (Mering et al. 2003).
Protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis
All proteins which had significantly different expressions (up-regulated, down-regulated) in amastigote-like form compared with metacyclic stage were selected for protein–protein interaction network construction. Analyzing the network properties of protein-expression data might reveal the organizational pattern of protein expression in disease, which might in turn help us to identify new potential drug targets. Protein- protein interaction network was constructed by using STRING database, was visualized using the Cytoscape 3.6.0 software (Shannon et al. 2003). CytoHubba plugin in Cytoscape were selected for high degree (hub) proteins in obtained network. Molecular Complex Detection (MCODE) used to analyze the characteristics of the networks. The MCODE algorithm is used to find densely connected regions (modules) and then to recognize seed nodes as a complex with the highest weighted vertex in each module (Bader and Hogue 2003).
Results
Protein changes in metacyclic promastigotes and axenic amastigotes of L. tropica by SWATH-MS
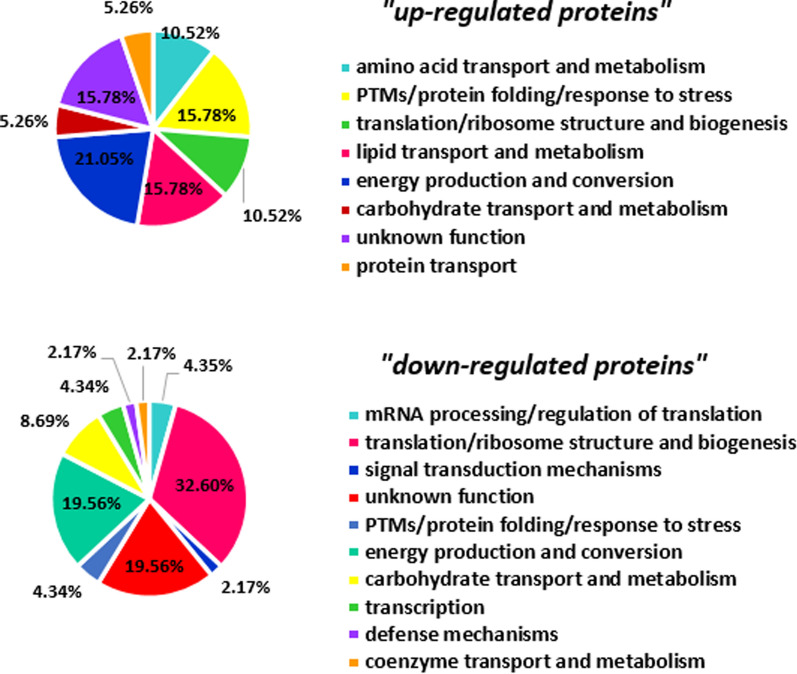
The significant differentially expressed proteins (fold change > 2 & p-value < 0.05) in the two developmental stages (metacyclic promastigotes and axenic amastigotes) were selected by statistical analysis. As shown in Fig. 1, a total 176 and 155 distinct proteins were identified in metacyclic and axenic amastigote stage, respectively. A total of 65 common proteins were differentially expressed in the two successive stages as up-regulated and down-regulated proteins, and detailed properties of them present in Table 1. It should be noted that 29 and 30 proteins were also expressed with fold change less than 2 in metacyclic and amastigote-like stages, respectively (Fig. 1). Among differential proteins, 19 and 46 proteins up-regulated and down-regulated during differentiation of L. tropica isolates, respectively (Fig. 1). One of the differential expressed proteins is hypothetical and its functions in Leishmania still remain to be elucidated. Further database mining indicated that the differentially expressed proteins could be classified into 18 groups based on cluster of orthologous groups of proteins (COG) function classification (Fig. 2). The COGs classification in the two developmental stages revealed that the up-regulated proteins were foremost involved in energy production and conversion cluster and down-regulated proteins were more involved in translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis.
Fig. 1.
The number of protein profile, differential and uniquely protein expression between metacyclic promastigotes and axenic amastigotes of Iranian L. tropica isolates (U: uniquely expression; FC: Fold Change; up-reg: up-regulated; down-reg: down-regulated)
Table 1.
The differential expressed proteins in L. tropica metacyclic and amastigote-like stages
| FC AT/MT | Uniprot IDs | Protein name | Gene name | Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated proteins list during metacyclic conversion into amastigote-like form of L. tropica | ||||
| 12.91 | E9ACW0 | Putative heat shock protein DNAJ | LMJF_27_2400 | DIVHELPVPLEAFYCGK |
| 7.53 | E9ADS8 | Putative lipophosphoglycan biosynthetic protein | LMJF_29_0760 (LPG3) | MLDILVNSLYTNR |
| 2.05 | E9AF45 | Kinetoplastid membrane protein 11 | LMJF_35_2210 (KMPII-1) | FAELLEQQK, LDRLDEEFNRK, EHSEHFK |
| 3.83 | Q4Q1M0 | Chaperonin HSP60, mitochondrial | LMJF_36_2030 | IQSIHSLLPALNHVVR, TGVTIVR,KIQSIHSLLPALNHVVR, AVAAVATTLGPK |
| 7.28 | Q4Q1R4 | Putative universal minicircle sequence binding protein | LMJF_36_1610 (UMSBP1) | CGEAGHMSR |
| 41.32 | Q4Q1Y2 | Putative 40S ribosomal protein S18 | LMJF_36_0940 | SLTLIPDHFQHIVR,FKIPDWFLNR,TEHLSSSMVDTRAGTLTAEELEKIAEIIADPAK, HAYGLR |
| 13.02 | Q4Q3V3 | Succinyl-CoA:3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase | LMJF_33_2340 | SGNLVFR, QTGGQIIR, GPGGAMDLVASGSR |
| 21.18 | Q4Q5P6 | Putative 26S proteasome regulatory subunit | LMJF_32_0390 | VAGLLLGR, HTNDEAIATFLAAIAR |
| 22.5 | Q4Q822 | Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex | LMJF_28_2420 | GLVVPVIR, LGLMSPFVK, NLIEDPAR |
| 6.68 | Q4Q931 | Putative 40S ribosomal protein S33 | LMJF_28_2420 (S33-1) | ENDMLSLMETER, GNVTQVR, LMAEAGSPDYNR |
| 78.77 | Q4Q9X6 | ATP synthase subunit beta | LMJF_25_1170 | IFNVLGDAIDQR, VAQSALTMAEYFR, GHGGFSVFAGVGER,FTQANSEVSALLGR, TVIIMELINNVAK |
| 3.0 | Q4QAB9 | Uncharacterized protein | LMJF_24_2110 | ALENPVNLDK, MEFVIDR, NEAAFQDVGIEYYR |
| 20.39 | Q4QD34 | Phosphoglycerate kinase | LMJF_20_0100 (PGKC) | SALPTIQK, EGGSCILMSHLGRPK, VLGAGYAGYLMEK |
| 2.73 | Q4QDF0 | Glycosomal malate dehydrogenase | LMJF_19_0710 (Gmdh) | RDPALAELAK, GSATLSMAEAGAR,VQVAGTEVVK, DPALAELAK, LLGVSLLDGLR |
| 5.04 | Q4QGX4 | Putative pretranslocation protein,alpha subunit | LMJF_11_1050 | QANWLMSLKPMLAVLPEIEKPR |
| 6.15 | Q4QJF1 | ATPase alpha subunit | LMJF_05_0500 | VDAGAPNIVSR, SPVNYNLLTGFK, FVALFNQK, VVNPLGHEVPVGL, AVDTMIPIGR |
| 2.0 | Q9U0V9 | Possible 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase | LMJF_23_0690 (L7836.03) | LDDFTFPCLFAK, KHPDFGK |
| 14.28 | E9ACG7 | Putative delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase | LMJF_03_0200 | YGLTGAVFSR, GAFEFQGQK, CTGAVVGQQPFGGSR, GYFVEPTIIETK |
| 9.32 | E9AFE7 | Putative cystathione gamma lyase | LMJF_35_3230 | NNLHGGMLWFEVK, VGITDGFVR, NNLHGGMLWFEVK, NNLHGGMLWFEVK |
| Down-regulated proteins list during metacyclic conversion into amastigote-like form of L. tropica | ||||
| 8.28 | O62591 | Probable eukaryotic initiation factor 4A | LMJF_01_0770 | HNLIQGLVLSPTR, VLVTTDLVAR,HNLIQGLVLSPTR, ESLTLEGIK |
| 28.72 | Q4FX73 | 40S ribosomal protein S3a | LMJF_35_0400 | NVLSDALVR, FTVQEVQGR, EWYDVVAPANFEK |
| 4.81 | Q4QEB3 | GMP reductase | LMJF_17_0725 (GMPR) | IGVGPGSICITR, LIVGAAIGVK, GPLAPILK |
| 2.47 | Q4QG98 | 60S ribosomal protein L18 | LMJF_13_0560 (RPL18-A) | GVDLTGISK, AAPIAVVVGDVLDDVR |
| 2.84 | E9AD27 | Putative calpain-like cysteine peptidase | LMJF_27_0500 | SIFLPLNTFLK, AELQRAVLKAQNAK, NATAIQDLEEALNDR |
| 26.07 | E9AD53 | Putative small GTP-binding protein Rab1 | LMJF_27_0760 | LLLIGDSGVGK, DFADSLGIPFLETSAK |
| 3.47 | E9ADF9 | Putative glycosomal phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase | LMJF_27_1810 | VAYPLEHIPGALTHAVAGHPNNVIFLTNDAFGVMPPVAR, NLTAPELVQWALK, GALCVL SYAK, KGDVTVFFGLSGTGK, GVFNIEGGCYAK |
| 17.39 | E9ADX3 | Tryparedoxin | LMJF_29_1150 (TXN2) | MPWLALPFEDRK |
| 3.17 | E9AE57 | Putative fumarate hydratase | LMJF_29_1960 | HGGFYLGSIGGPAAILAK, YFAHQAR, YVEEVEVFGR |
| 2.12 | E9AEB3 | ATP-dependent 6-phosphofructokinase | pfk | TAIELSR, TIDNDLAFSHR, FGGTILGSSR,HLHFNPSETSIGIVTCGGICPGLNDVIR, EMVDTLVR |
| 67.7 | E9AEL4 | Putative ATP-dependent DEAD-box RNA helicase | LMJF_35_0370 | TASFVIPVLEK, VHILVATPGR, GFEKPSPVQEEAIPVALQGK, HIPGLEVMVTTGGTTLR, ELALQTAQVTK, NVNFEEYALR |
| 4.36 | E9AEU1 | Putative NADH-dependent fumarate reductase | LMJF_35_1180 | LGGNSLLECVVFGK, AATILQK, ATSGINAWGTR, LALIGGGTGVAPMLQIVR, LIGCPEANVMATLK |
| 6.1 | E9AF23 | 40S ribosomal protein S6 | LMJF_35_2010 | LFNLSR, GAIGFNTFR, RGAIGFNTFR,RVQLQDYR, VGDQPIEGVTDTTAPR |
| 2.83 | E9AFK3 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L23 | LMJF_35_3790 | VLNAVIIR, ISTHAPAIV, NLYVISVK |
| 36.1 | Q4Q090 | 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-independent phosphoglycerate mutase | PGAM | VALQGASLVDDALK, MFVTMDR, SAEITEAAIEALK, VALQGASLVDDALK |
| 2.64 | Q4Q124 | Adenosylhomocysteinase | LMJF_36_3910 | AGVFFLPK, VAALHLAHVGAK, DISLAEWGR, EHVEIKPQVDR, VKDISLAEWGR, FDNLYGCR |
| 7.9 | Q4Q1D2 | 40S ribosomal protein S24 | S24E-2 | TTGFGLIYDDLASLK |
| 2.8 | Q4Q1F5 | Dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex | LTITPIPMPALSPTMEK, WFQHFHDAMENPLSLLL | |
| 2.49 | Q4Q1X7 | Putative 40S ribosomal protein S10 | LMJF_36_0980 | FFFTEGVIACK |
| 7.71 | Q4Q230 | Uncharacterized protein | LMJF_36_0480 | KSPIMSK, LMDQSLPVYDDVVTGVGR |
| 2.59 | Q4Q2H7 | Putative vacuolar ATP synthase catalytic subunit A | LMJF_34_3670 | ITWNYIR, NIVTFYEEAQR, TCLVANTSNMPVAAR, EEELQEIVQLVGK |
| 7.61 | Q4Q3U8 | Putative heat shock protein | LMJF_33_2390 | YNLHFNPQHPLIR, GLLPDWLR, EELTANLGTIAGSGSK |
| 2.74 | Q4Q4U1 | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase | GCVL-2 | ALTGGVEYLFK, AAQLGLK, AVGTEDGFVK |
| 3.42 | Q4Q5P0 | 40S ribosomal protein S2 | LMJF_32_0450 | GTGIVAAPVPK, THGNLIMATFYALR |
| 8.42 | Q4Q6E1 | Putative vacuolar-type proton translocating pyrophosphatase 1 | LMJF_31_1220 | QFQDPEVAEGR |
| 3.81 | Q4Q9H4 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L7 | KILQLLR, AVEPYIAYGYPSLATVR | |
| 35.55 | Q4Q9M4 | Succinate–CoA ligase [ADP-forming] subunit alpha, mitochondrial | LMJF_25_2130 | VIVQGMTGK, VVGGVSPK, VIVQGMTGK, AGTFHTK |
| 3.93 | Q4Q9R2 | Polyprenol reductase | EnCR | DLGPQIGYR, ELESMFVHK, FSHPTMPMR |
| 2.22 | Q4Q9V1 | GTP-binding nuclear protein | LMJF_25_1420 | LILVGDGGTGK, SNYNFEKPFVWLAK, VCDNIPIVLVGNK |
| 5.74 | Q4Q9Y0 | Putative cytochrome c oxidase VII | LMJF_25_1130 | IPNPFAYSFK, VWAPATTLAEYR |
| 5.22 | Q4QAG8 | Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit, mitochondrial | LMJF_24_1630 | AITMEILAGR, LGANSLLDIVVFGK, GEGGYLVNSEGER, SPVWNSNLIEALELR |
| 18.71 | Q4QAX6 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L17 | LMJF_24_0040 | HVQVDQAAR, SVVAMMSLLK |
| 2.0 | Q4QEI9 | Elongation factor 1-alpha | LMJF_17_0080 | IGGIGTVPVGR, GITIDIALWK, FESPKSVFTIIDAPGHR, SVFTIIDAPGHR, EHALLAFTLGVK, STATGHLIYK |
| 7.48 | Q4QEM2 | Paraflagellar rod protein 2C | LMJF_16_1425 | AQLLEHLVELVADKFR, TLGQLVYK |
| 14.07 | Q4QEX4 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L21 | LMJF_16_0460 | GVGVIINKPVR, TGIVWNVTPR, VGDYVDVVADSAVR |
| 33.52 | Q4QF62 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 | LMJF_15_1203 | AVHIDVDQATLAFVMESVTGR, ASPSQADVEAICK |
| 23.38 | Q4QF80 | Tryparedoxin peroxidase | TRYP1 | GLFIIDPHGMLR |
| 6.15 | Q4QFF2 | Putative ribonucleoprotein p18, mitochondrial | LMJF_15_0280 | FCAMMDLMEEMQHR, FCAMMDLMEEMQHR, NCPPDLETYNATLQK |
| 19.25 | Q4QFG2 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L13a | LMJF_15_0200 | APSDVFVR, HRPEIIVIDLK, HRPEIIVIDLKDHVLGR, CEQLNIAGTEIR |
| 2.34 | Q4QFL8 | Enolase | ENOL | HIDEPLPILMEAIEK, LPVPCFNVINGGK |
| 181.11 | Q4QFP8 | Putative small myristoylated protein-3 | SMP-3 | ISFEANPIAK, DNGNGLLFR |
| 5.92 | Q4QG31 | 40S ribosomal protein S4 | RS4 | LRECLPLLVIIR, AVIVTGGANR, ECLPLLVIIR,DLNNLQVTVPK, MNVIQER,DASGAEFATR |
| 3.49 | Q4QGA9 | Uncharacterized protein | LMJF_13_0450 | SPEFDAIYEQQQK |
| 2.77 | Q4QGC5 | Tubulin alpha chain | LMJF_13_0280 | LIGQVVSSLTASLR, IHFVLTSYAPVVSAEK, EIVDLALDR, QLFNPEQLVSGK, AVCMIANSTAIAEVFAR |
| 2.59 | Q4QGN9 | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase | PGI | AVLHVALR, HFVALSTNTEK, PSNSILVNALTPR, QVNLEETIFIIASK |
| 22.93 | Q4QIP1 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L7a | LMJF_07_0500 | APLAVVTGLQEVTR, WPTFVTMQR,TATCVALTDVNAEDEATLK |
The list of differential expression proteins based on fold change > 2 and p-value < 0.05 during developmentally process from metacyclic promastigotes to amastigotes like in Iranian L. tropica isolates
FC fold change, AT amastigote of L. tropica, MT metacyclic of L. tropica
Fig. 2.
COG (clusters of orthologous groups) function classification coverage of the protein sequence. A total of 8 and 10 groups of all up-regulated & down-regulated of differentially expressed proteins were clustered by orthologous groups, respectively. PTM: post-translational modification
Gene ontology findings
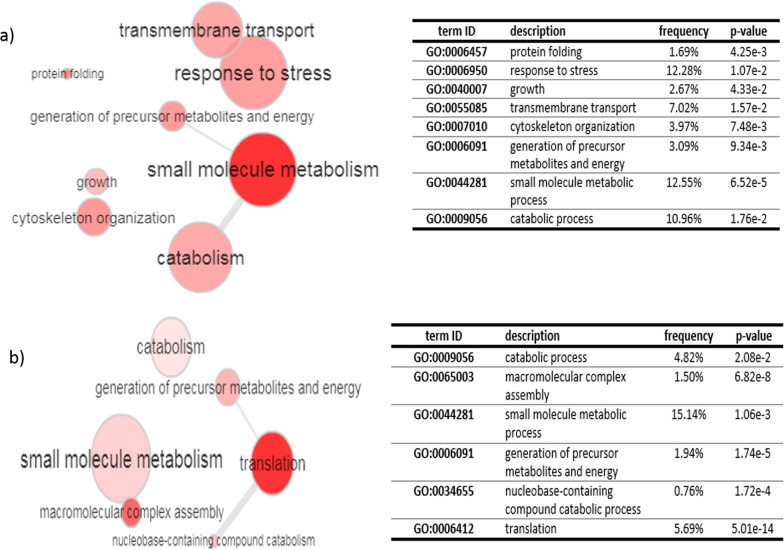
Gene ontology (GO) analysis of total 65 significant differentially expressed proteins (up/down regulated proteins) was performed based on biological process by the kinetoplastid genomics resource database (TriTrypDB). According to gene ontology analysis of up-regulated proteins, the metabolic process (GO: 0044281), response to stress (GO: 0006950) and catabolic process (GO: 0009056) with 12.55%, 12.28% and 10.96%, had the highest frequency among other biological processes, respectively (Fig. 3a). Most of the down-regulated proteins were involved in metabolic process (1.06e-3) and translation (5.01e–14) (Fig. 3b). Total 81 and 60 proteins were uniquely expressed in metacyclic and axenic amastigote stage, respectively. Gene ontology enrichment analysis of metacyclic-specific proteins indicating that translation and response to stress had the high frequency in biological process enrichment. In addition, translation was the significant GO term in biological process of amastigote-specific expressed proteins.
Fig. 3.
Gene ontology enrichment analysis of differentially expressed proteins based on biological process enrichment during conversion of metacyclic promastigotes into the amastigote like of Iranian isolates of L. tropica by TriTrypDB (kinetoplastid Genomics Resource): a up-regulated proteins and (b) down-regulated proteins. The circles color and size are corresponded on the p-value and frequency, respectively. The dark circles are related to high significance (low p-value) and large sizes are also related to higher frequency
Pathway analysis
Protein expression changes (up/down regulated proteins) were also selected for KEGG pathway analysis. The pathway enrichment analysis was performed using the STRING online database. The pathway enrichment analysis revealed that the most critical pathway of up- and down-regulated proteins involved in L. tropica metacyclic into the amastigote-like differentiation included metabolic pathways and ribosome, carbon metabolism and glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, respectively (Table 2, 3).
Table 2.
The KEGG pathways of up-regulated proteins during conversion of L. tropica metacyclic into the amastigote-like
| Pathway ID | pathway description | Gene No. | FDR | Matching proteins (IDs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 | Metabolic pathways | 7 | 0.0017 | LmjF.03.0200,LmjF.05.0510,LmjF.19.0710,LmjF.20.0100,LmjF.23.0690, LmjF.25.1170,LmjF.28.2420 |
| 1110 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 4 | 0.0211 | LmjF.19.0710,LmjF.20.0100,LmjF.23.0690,LmjF.28.2420 |
| 1200 | Carbon metabolism | 3 | 0.0251 | LmjF.19.0710,LmjF.20.0100,LmjF.28.2420 |
| 20 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 2 | 0.0364 | LmjF.19.0710,LmjF.28.2420 |
| 280 | Valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation | 2 | 0.0364 | LmjF.23.0690,LmjF.33.2340 |
FDR false discovery rate, KEGG kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
Table 3.
The KEGG pathways of down-regulated proteins during conversion of L. tropica metacyclic into the amastigote-like
| Pathway ID | Pathway description | Gene NO | FDR | Matching proteins (IDs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3010 | Ribosome | 11 | 4.13E–10 | LmjF.07.0510, LmjF.13.1230, LmjF.15.0200, LmjF.15.1207, LmjF.16.0460, LmjF.24.0040, LmjF.32.0450,LmjF.35.0420,LmjF.35.3800,LmjF.36.0990,LmjF.36.2870 |
| 1200 | Carbon metabolism | 9 | 1.76E–08 | LmjF.12.0530, LmjF.14.1160, LmjF.24.1630, LmjF.27.1810, LmjF.29.1960, LmjF.29.2510, LmjF.32.3310,LmjF.36.2660,LmjF.36.6650 |
| 10 | Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | 7 | 2.19E–08 | LmjF.12.0530, LmjF.14.1160, LmjF.27.1810, LmjF.29.2510, LmjF.32.3310, LmjF.36.2660, LmjF.36.6650 |
| 1110 | Biosynthesis of secondary metabolites | 11 | 2.19E–08 | LmjF.12.0530, LmjF.14.1160, LmjF.17.0725, LmjF.24.1630, LmjF.25.1770, LmjF.27.1810, LmjF.29.1960,LmjF.29.2510,LmjF.32.3310,LmjF.36.2660,LmjF.36.6650 |
| 1100 | Metabolic pathways | 14 | 2.51E–07 | LmjF.12.0530, LmjF.14.1160, LmjF.15.1040, LmjF.17.0725, LmjF.24.1630, LmjF.25.1770, LmjF.27.1810, LmjF.29.1960, LmjF.29.2510, LmjF.32.3310, LmjF.34.3670, LmjF.36.2660, LmjF.36.3910,LmjF.36.6650 |
| 20 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 5 | 6.25E–06 | LmjF.24.1630,LmjF.27.1810,LmjF.29.1960,LmjF.32.3310,LmjF.36.2660 |
| 620 | Pyruvate metabolism | 4 | 0.000217 | LmjF.27.1810,LmjF.29.1960,LmjF.32.3310,LmjF.36.2660 |
| 190 | Oxidative phosphorylation | 3 | 0.0185 | LmjF.24.1630,LmjF.31.1220,LmjF.34.3670 |
| 1230 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | 3 | 0.037 | LmjF.14.1160,LmjF.29.2510,LmjF.36.6650 |
| 30 | Pentose phosphate pathway | 2 | 0.0395 | LmjF.12.0530,LmjF.29.2510 |
| 260 | Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 2 | 0.0395 | LmjF.32.3310,LmjF.36.6650 |
FDR false discovery rate
Protein–protein interaction network analysis
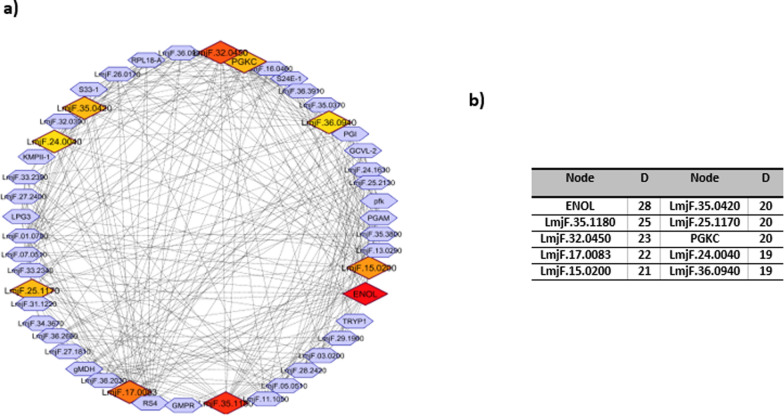
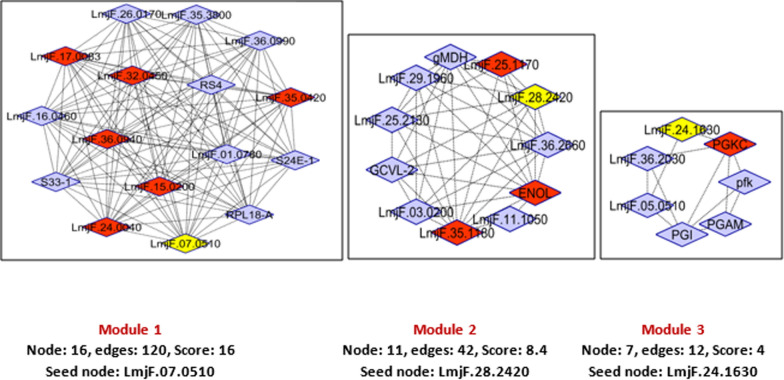
The PPI network of the significant differentially expressed proteins (between metacyclic and amastigote like stages of L. tropica) was constructed, in which including 53 nodes and 323 edges (Fig. 4a). Nodes represent the proteins from our list and others that directly interact with them. Connections contain direct interaction partners and interconnections. In order to simplify the connection patterns, interactions for the nodes with the greatest degrees (hubs) was selected. Centrality analysis based on node degree by CytoHubba (as cytoscape plugin) revealed the top 10 great number of close interconnections that can be seen with darker/different color (Fig. 4a). The hub nodes were included ENOL, LmjF.35.1180, LmjF.32.0450, LmjF.17.0083, LmjF.15.0200, LmjF.35.0420, LmjF.25.1170, PGKC, LmjF.24.0040 and LmjF.36.0940 (Fig. 4b). Further analysis of complex region of network by MCODE revealed 3 modules for the network. The seed nodes (yellow nodes in each module) of each module were included LmjF.07.0510, LmjF.28.2420 and LmjF.24.1630. The orange nodes (6, 3 and 1 node numbers in modules 1, 2 and 3, respectively) are the hub proteins that present in modules (Fig. 5).
Fig. 4.
Whole Connected Component of the PPI Network of differential expressed proteins that were visualized by Cytoscape software. a The nodes are layout by degree value (darker to bright brown nodes corresponded to hub proteins). b The hub proteins along with their degree (D)
Fig. 5.
The modules of whole PPI network. The hub proteins of our analyses are presented in modules 1, 2 and 3 that are shown in orange color. Seed nodes in each module are also shown by yellow color
Discussion
In this study, we aimed to identify differentially expressed proteins between metacyclic and amastigote-like stages of Iranian isolates of L. tropica. To this end, we applied a quantitative proteomic approach for the first time to profile protein expression in metacyclic and amastigote-like form of L. tropica. To date, several transcriptomic and proteomic analyses have been reported about Leishmania stages. Rosenzweig et al. (Rosenzweig et al. 2008), (Lahav et al. 2011), and Saxena et al. (Saxena et al. 2007) are examples of these investigations that have studied of Leishmania promastigote to amastigote differentiation. A total of 176 and 155 proteins were detected in metacyclic and amastigote-like forms, respectively. Among these, 65 proteins were significantly differentially expressed between studied stages that 46 and 19 proteins were down/up-regulated in amastigote-like form, respectively. According to GO classification, the DEPs were included in various pathways (Fig. 2) that offers their vital roles in the metabolism, infectivity, virulence and pathogenicity of parasite.
Among the down-regulated proteins in our study, E9AD27, has been identified as a common protein between L. major, L. tropica and L. infantum isolates in Iranian patients (Hajjaran et al. 2015). At present study, another protein (Q4QFL8) has also decreased in amastigote-like form vs metacyclic form of L. tropica. This protein also reported as a differentially expressed protein between meglumine antimoniate sensitive and resistant in promastigote of L. tropica isolated from Iranian anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis patients (Hajjaran et al. 2012). Energy production and conversion function, protein folding/response to stress and lipid metabolism were the highest rank among the up-regulated proteins in amastigote-like stage in our results. The energy production and conversion cluster were included dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase component of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, ATP synthase subunit beta, glycosomal malate dehydrogenase and ATPase alpha subunit proteins. Malate dehydrogenase enzyme activity links amino acid metabolism with carbohydrate metabolism pathway that led to energy production (Martin et al. 1976). According to the previous investigations, catabolic pathways that led to provide energy were also up-regulated during the Leishmania differentiation. Specifically, tri-carboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and respiratory chain activity were reported with highly expression in amastigote-like stage (Rosenzweig et al. 2008). Malate dehydrogenase is another up-regulated protein relate to energy production that required for performing the gluconeogenesis process in amastigote forms that is essential for amastigote proliferation within host macrophages (Naderer et al. 2006). In the present study, ATP synthase subunit beta protein up-regulated in amastigote-like and this may be essential for parasite differentiation. We found that lipid transport and metabolism involved proteins including succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase, conserved hypothetical protein and possible 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase also up-regulated in amastigote-like form. Succinyl-CoA: 3-ketoacid-coenzyme A transferase is a Key enzyme for ketone body catabolism that amastigote form uses these sources for energy production in absence of glucose in macrophage environment. In general, amastigote forms provide their required energy through fatty acid oxidation by elevated TCA enzymes activity and differentiating parasites shift from glucose to fatty and amino acid oxidation and from glycolysis to gluconeogenesis (Atan et al. 2018; Hart and Coombs 1982; Paape et al. 2010). In our study, the proteins involved in protein folding and response to stress increased, which is consistent with the results of previous studies. Nugent et al. reported HSP60 and HSP70 proteins in study of L. Mexicana differentiation (Nugent et al. 2004). Recent proteomic studies have also reported that proteins involved in stress response differentially expressed between promastigotes and amasigotes stages of L. donovani (Bente et al. 2003) and L. infantum (El Fakhry et al. 2002). In addition, the up-regulated response to stress activity possibly means that amastigote form struggles with the oxidative stress to survive inside the host cells. We found that the kinetoplastid membrane protein (KMP)-11 was up-regulated during metacyclic differentiation into amastigote form. KMP-11 as a hydrophobic protein, is involved in the interaction of pathogen-host, which its expression has been reported into be increased is increased in amastigote stage (Jardim et al. 1995). According to Mukhopadhyay et al. results, the expression of KMP-11 was decreased along with parasite virulence as a function of the time of the subculture in L. donovani (Mukhopadhyay et al. 1998). It was also reported in several independent experiments that the isolation of a Sb (III) resistant L. infantum cell line always correlated with a high decrease in the KMP-11 protein (El Fadili et al. 2009). In this study, based on gene ontology analysis, translation/ribosome structure and biogenesis category was the most significant cluster among the down-regulated proteins, which included several ribosomal proteins In summary, our results were in agreement with other in-vivo studies indicate that abundance of translation machinery proteins, translational activity and protein synthesis decreased in parasites undergoes differentiation from promastigote to amastigote (Lahav et al. 2011; Mazareb et al. 1999; Mottram and Coombs 1985). Decreased expression of mRNA processing/ replication related proteins seems during metacyclic into amastigote differentiation present beneficial since amastigotes growth and energy consumption are also slower rather than promastigotes (Mukkada et al. 1985). In addition, the down-regulation of anabolic processes involved proteins such as translational activity and glycolytic pathways and the up-regulation of catabolic functions including lipid and amino acid metabolism in amastigote-like stage were in keeping with the previous studies. Tubulin alpha chain was described as one of the down-regulated proteins in this study. This protein is a fundamental component of the cytoskeleton which is responsible for cell shape and is involved in cell division, ciliary and flagellar motility and intracellular transport. The down-regulation of this proteins indicated that the cytoskeleton organization and motility repressed in amastigote stage inside macrophage cells in mammalian host. Some uncharacterized proteins also were detected as differentially expressed proteins between studied stages that further studies are required to identify function and involved biological processes by them. In order to confirm some of the proteins identified in this study by techniques such as western blotting, we encountered limitations in the supply of the desired antibodies that were not performed. Furthermore, further in vivo and in vitro investigations are needed to identify more accurate roles of each detected proteins in differentiation, infectivity and virulence of Leishmania. Herein, we also investigated PPI network of differentially expressed proteins via bioinformatics approach. Since PPI network analysis is a powerful approach in categorization and ranking of the drug target candidate and potential biomarker for a certain disease (Chávez-Fumagalli et al. 2018; Dashatan et al. 2018; Flórez et al. 2010), here the PPI network of the significant different regulated proteins are constructed (Fig. 4). Topological analysis of the networks leads to rank of the nodes based on their centrality properties in network (Dashatan et al. 2018; Jeong et al. 2001). By degree centrality value using Cytohubba plugin in Cytoscape software, the top 10 node selected as important hub proteins. The hub proteins can be recommended for new potential drug targets in disease. According to results, ENOL has highest degree and this protein can be thought of as a potential drug target. Enolase described as an important enzyme in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis as two important cellular pathways. Glycolysis play important roles in ATP supply and gluconeogenesis is crucial for the virulence and viability of Leishmania parasite. ENOL protein plays also an important role in cell morphology and vesicle trafficking by cytoskeleton system. Furthermore, enolase enzyme is available in secretome and leishmanial parasite surface. Based on the surface enolase, plasminogen receptor can probably play a role in virulence and invasiveness of parasites (Avilán et al. 2011; Dashatan et al. 2018). It must be pointed out that further investigations are required using western blotting or real time PCR to validate the results of this study. In the present study, another hub protein with a role in energy metabolism is phosphoglycerate kinase (PGKC) and LmjF.25.1170 (ATP synthase subunit beta). Among other hub proteins, LmjF.32.0450, LmjF.17.0083, LmjF.15.0200, LmjF.35.0420, LmjF.24.0040 and LmjF.36.0940 involved in translation and are as constituents of ribosome. Therefore, manipulation and controlling of translation process in L. tropica could be as an approach in differentiation of parasite and also as a potential drug target to cutaneous leishmaniasis therapy. The other detected hub protein was LmjF.35.1180, NADH-fumarate reductase. NADH-fumarate reductase enzyme is an important component in the intermediate metabolism in the Leishmania parasite and absent in mammalian cells, furthermore, it could be a potential drug target for leishmaniasis. Module is a part of a network with closely part of proteins, which having specific biological function (Newman 2006). In this study, we demonstrated three modules in PPI network. Functional enrichment analysis of these modules showed that ATP synthesis, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, biosynthesis of amino acids, pentose phosphate pathway, TCA cycle, translation and gene expression are the main affected pathways by differentially expressed proteins. We also categorized the modules based on the presence of hub proteins in them to get a better molecular view of parasite differentiation. The module number 1 contained the largest number of hub proteins that recognized as a hub module. The hub module proteins play possibly a more important role in parasite biology including metacyclic into amastigote differentiation. The proteins of module 1 involved in the translation and gene expression pathway, therefore, it can be concluded that the protein synthesis process is the most important pathway altered during parasite differentiation. In the current study, further analysis of modules by MCODE revealed seed nodes in modules that included LmjF.07.0510, LmjF.28.2420 and LmjF.24.1630. These seed nodes can serve as candidate drug and vaccine for cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by L. tropica.
In conclusions, this study presents an initial attempt at making comparisons between the global protein expression patterns of two distinct life stages (metacyclic and amastigote) of L. tropica species in Iranian isolates. There are very limited data on protein profile of L. tropica, furthermore, we showed that protein expression profiles modulated different in two successive developmentally forms of L. tropica using a quantitative proteomics approach (SWATH-MS). Also, several important proteins signatures introduced in sand-fly and mammalian host of L. tropica such as parasite biology, infectivity and pathogenesis factors, and survival in macrophage cells, which would be useful to identify potential drug targets. However, many investigations are needed to better understand the role of each differential expressed proteins to clarify molecular mechanisms of parasite differentiation. Finally, quantitative proteomics approach plays a crucial role in introducing metabolic pathways related to stage-specific of Leishmania parasite.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Proteomics Research Center in Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Abbreviations
- SWATH-MS
Sequential window acquisition of all theoretical fragment ion spectra mass spectrometry
- L
Leishmania
- ITS1
Intrnal transcribed-spacer-1
- NNN
Novy-nicolle-mc neal
- MCODE
Molecular complex detection
- COG
Cluster of orthologs groups
- GO
Gene ontology
- PPI
Protein–protein interaction
- PCR–RFLP
Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- FC
Fold change
- 2DE
Two dimensional electrophoresis
- PTM
Post translational modification
- FCS
Fetal calf serum
- KEGG
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- TCA
Tricarboxylic acid
- KMP-11
Kinetoplastid membrane protein-11
Author contributions
All authors conceived and designed the study; MA and NAD participated in experimental work, collection and analysis of data and drafted the manuscript; NA provided the expertise and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors interpreted the data, revised and approved the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Data of this study are included in the article and the primary data can be provided from the corresponding author.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Ethical code: IR.SBMU.MSP.REC.1398.040). Informed consent was received from all participating patients in the present study.
Consent for publication
All the authors consented to the publication of this article.
Competing interests
The authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- Ahmadi N, Modiri M, Mamdohi S. First survey of cutaneous leishmaniasis in Borujerd county, western Islamic Republic of Iran. East Mediterr Health J. 2013;19(10):847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiri-Dashatan N, Koushki M, Rezaei Tavirani M, Ahmadi N. Proteomic-based Studies on Leishmania. J Mazand Univ Med Sci. 2018;28(163):173–190. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri-Dashatan N, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Ahmadi N. A quantitative proteomic and bioinformatics analysis of proteins in metacyclogenesis of Leishmania tropica. Acta Trop. 2020;202:105227. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiri-Dashatan N, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Zali H, Koushki M, Ahmadi N. Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins in Leishmania major metacyclogenesis. Microbial Pathog. 2020;149:104557. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafmansouri M, Sarkari B, Hatam G, Habibi P, Khabisi SA. Utility of Western blot analysis for the diagnosis of cutaneous Leishmaniasis. Iran J Parasitol. 2015;10(4):599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafmansouri M, Sadjjadi FS, Seyyedtabaei S, Haghighi A, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Ahmadi N. Comparative two-dimensional gel electrophoresis maps for amastigote-like proteomes of Iranian Leishmania tropica and Leishmania major Isolates. Galen Medical Journal. 2019;8:1520. doi: 10.31661/gmj.v8i0.1520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslett M, Aurrecoechea C, Berriman M, Brestelli J, Brunk BP, Carrington M, Depledge DP, Fischer S, Gajria B, Gao X. TriTrypDB: a functional genomic resource for the Trypanosomatidae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009;38(supp1):D457–D462. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atan NAD, Koushki M, Ahmadi NA, Rezaei-Tavirani M. Metabolomics-based studies in the field of Leishmania/leishmaniasis. Alexandria J Med. 2018;54:383. [Google Scholar]
- Avilán L, Gualdrón-López M, Quiñones W, González-González L, Hannaert V, Michels PA, Concepción J-L. Enolase: a key player in the metabolism and a probable virulence factor of trypanosomatid parasites—perspectives for its use as a therapeutic target. Enzyme Res. 2011;2011:1. doi: 10.4061/2011/932549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader GD, Hogue CW. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003;4(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bente M, Harder S, Wiesgigl M, Heukeshoven J, Gelhaus C, Krause E, Clos J, Bruchhaus I. Developmentally induced changes of the proteome in the protozoan parasite Leishmania donovani. Proteomics. 2003;3(9):1811–1829. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200300462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chávez-Fumagalli MA, Schneider MS, Lage DP, Tavares GdSV, Mendonça DVC, Santos TTdO, Pádua RM, Machado-de-Ávila RA, Leite JPV, Coelho EAF. A computational approach using bioinformatics to screening drug targets for Leishmania infantum Species. Evidence-Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:1. doi: 10.1155/2018/6813467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cv M, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt S, Bork P, Snel B. STRING: a database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31(1):258–261. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dashatan NA, Tavirani MR, Zali H, Koushki M, Ahmadi N. Prediction of Leishmania Major Key Proteins via Topological Analysis of Protein-Protein Interaction Network. Galen Med J. 2018;7:e1129. doi: 10.22086/gmj.v0i0.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjeux P. Leishmaniasis: public health aspects and control. Clin Dermatol. 1996;14(5):417–423. doi: 10.1016/0738-081x(96)00057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjeux P. Worldwide increasing risk factors for leishmaniasis. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2001;190(1):77–79. doi: 10.1007/s004300100085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Fadili K, Drummelsmith J, Roy G, Jardim A, Ouellette M. Down regulation of KMP-11 in Leishmania infantum axenic antimony resistant amastigotes as revealed by a proteomic screen. Exp Parasitol. 2009;123(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2009.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Fakhry Y, Ouellette M, Papadopoulou B. A proteomic approach to identify developmentally regulated proteins in Leishmania infantum. Proteomics. 2002;2(8):1007–1017. doi: 10.1002/1615-9861(200208)2:8<1007::AID-PROT1007>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flórez AF, Park D, Bhak J, Kim B-C, Kuchinsky A, Morris JH, Espinosa J, Muskus C. Protein network prediction and topological analysis in Leishmania major as a tool for drug target selection. BMC Bioinformat. 2010;11(1):484. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjaran H, Azarian B, Mohebali M, Hadighi R, Assareh A, Vaziri B. Comparative proteomics study on meglumine antimoniate sensitive and resistant Leishmania tropica isolated from Iranian anthroponotic cutaneous leishmaniasis patients. East Mediterr Health J. 2012;18(2):165. doi: 10.26719/2012.18.2.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjaran H, Bazargani MM, Mohebali M, Burchmore R, Salekdeh GH, Kazemi-Rad E, Khoramizadeh MR. Comparison of the proteome profiling of iranian isolates of Leishmania tropica, L. major and L. infantum by two-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) and mass-spectrometry. Iranian J Parasitol. 2015;10(4):530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D, Coombs GH. Leishmania mexicana: energy metabolism of amastigotes and promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1982;54(3):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardim A, Funk V, Caprioli R, Olafson R. Isolation and structural characterization of the Leishmania donovani kinetoplastid membrane protein-11, a major immunoreactive membrane glycoprotein. Biochem J. 1995;305(1):307–313. doi: 10.1042/bj3050307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardim A, Hardie DB, Boitz J, Borchers CH. Proteomic profiling of Leishmania donovani promastigote subcellular organelles. J Proteome Res. 2018;17(3):1194–1215. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási A-L, Oltvai ZN. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature. 2001;411(6833):41. doi: 10.1038/35075138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedzierski L, Sakthianandeswaren A, Curtis JM, Andrews PC, Junk PC, Kedzierska K. Leishmaniasis: current treatment and prospects for new drugs and vaccines. Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(5):599–614. doi: 10.2174/092986709787458489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahav T, Sivam D, Volpin H, Ronen M, Tsigankov P, Green A, Holland N, Kuzyk M, Borchers C, Zilberstein D. Multiple levels of gene regulation mediate differentiation of the intracellular pathogen Leishmania. FASEB J. 2011;25(2):515–525. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-157529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E, Simon MW, Schaefer III FW, Mukkada AJ. Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in four human species of Leishmania: a comparative survey. J Protozool. 1976;23(4):600–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazareb S, Fu ZY, Zilberstein D. Developmental regulation of proline transport in Leishmania donovani. Exp Parasitol. 1999;91(4):341–348. doi: 10.1006/expr.1998.4391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes JPBd, Almeida TFd, Petersen ALdOA, Guedes CES, Mota M, Lima JGB, Palma LC, Buck GA, Krieger MA, Probst CM. Proteomic analysis reveals differentially expressed proteins in macrophages infected with Leishmania amazonensis or Leishmania major. Microbes Infect. 2013;15(8–9):579–591. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreira W, Légaré D, Racine G, Roy G, Ouellette M. Proteomic analysis of metacyclogenesis in Leishmania infantum wild-type and PTR1 null mutant. EuPA Open Proteom. 2014;4:171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Mottram JC, Coombs GH. Leishmania mexicana: enzyme activities of amastigotes and promastigotes and their inhibition by antimonials and arsenicals. Exp Parasitol. 1985;59(2):151–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay S, Sen P, Majumder HK, Roy S. Reduced expression of lipophosphoglycan (LPG) and kinetoplastid membrane protein (KMP)-11 in Leishmania donovani promastigotes in axenic culture. J parasitol. 1998;1:644–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukkada AJ, Meade JC, Glaser TA, Bonventre PF. Enhanced metabolism of Leishmania donovani amastigotes at acid pH: an adaptation for intracellular growth. Science. 1985;229(4718):1099–1101. doi: 10.1126/science.4035350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naderer T, Ellis MA, Sernee MF, De Souza DP, Curtis J, Handman E, McConville MJ. Virulence of Leishmania major in macrophages and mice requires the gluconeogenic enzyme fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006;103(14):5502–5507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509196103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman ME. Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices. Phys Rev e: Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2006;74(3 Pt 2):036104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.74.036104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nugent PG, Karsani SA, Wait R, Tempero J, Smith DF. Proteomic analysis of Leishmania mexicana differentiation. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004;136(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2004.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paape D, Barrios-Llerena ME, Le Bihan T, Mackay L, Aebischer T. Gel free analysis of the proteome of intracellular Leishmania mexicana. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2010;169(2):108–114. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig D, Smith D, Opperdoes F, Stern S, Olafson RW, Zilberstein D. Retooling Leishmania metabolism: from sand fly gut to human macrophage. FASEB J. 2008;22(2):590–602. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9254com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A, Lahav T, Holland N, Aggarwal G, Anupama A, Huang Y, Volpin H, Myler P, Zilberstein D. Analysis of the Leishmania donovani transcriptome reveals an ordered progression of transient and permanent changes in gene expression during differentiation. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2007;152(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2006.11.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundar S, Singh B. Understanding Leishmania parasites through proteomics and implications for the clinic. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018;15(5):371–390. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1468754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W, Smith JW, Huang C-M (2009) Mass spectrometry-based label-free quantitative proteomics. BioMed research international 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data of this study are included in the article and the primary data can be provided from the corresponding author.