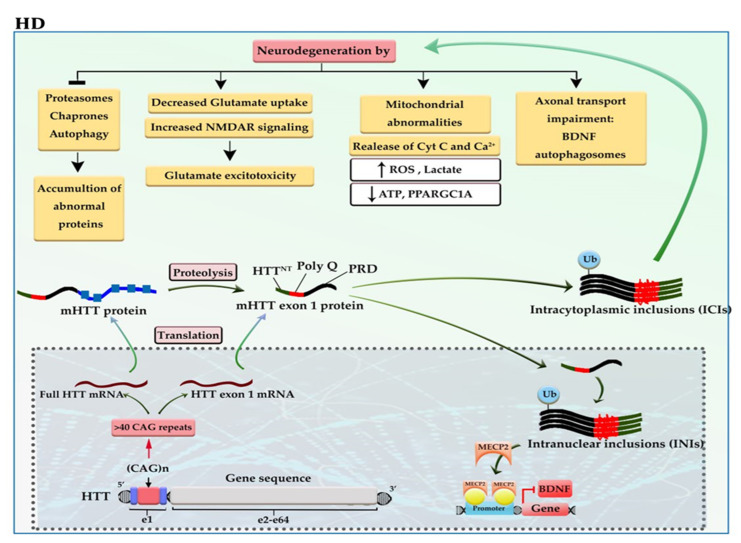
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of the selected mechanisms in the pathogenesis of HD. HTT gene, located at 4p16, has 64 exons and a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the exon 1 region. The CAG repeats in the coding sequence of mutant HTT (mHTT) produce mHTT exon 1 protein. mHTT exon 1 protein enters the nucleus. The gradual aggregation of mHTT exon 1 oligomers leads to the formation of large inclusions in the cytoplasm and nucleus of neural cells. The intracytoplasmic inclusions (ICIs) have various toxic effects on neural cells and can exacerbate the aggregation of mHTT exon 1 protein. Whereas the polyQ tract of intranuclear inclusions (INIs) recruits MECP2 to the promoter of BDNF, downregulating the expression of BDNF. BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; Cyt-c: cytochrome c; mHTT: mutant huntingtin; NMDAR: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; ROS: reactive oxygen species.