Figure 4. CSK inhibition is highly associated with atrial fibrillation in individual case safety reports gathered in the international pharmacovigilance database, VigiBase.
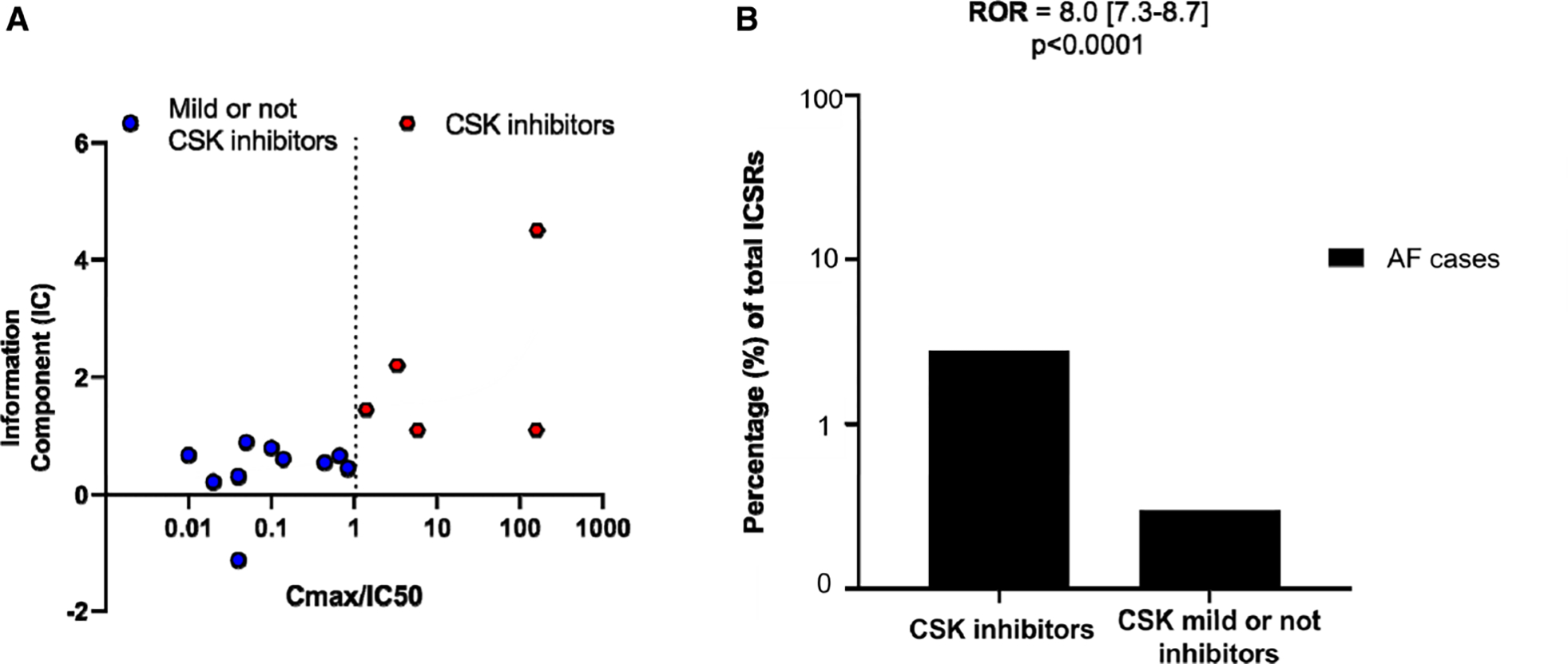
A, Data are Cmax/CSK IC50 against atrial fibrillation information component (a Bayesian disproportionality estimator) for 16 kinase inhibitors that are reported to inhibit CSK with various potency (IC50s range from 2.2 nmol/L to 66 μmol/L; Table V in the Data Supplement) out of all kinase inhibitors approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration as anticancer drugs. CSK inhibitors are defined as Cmax/CSK IC50>1, and mild or not CSK inhibitors have Cmax/IC50<1. B, ROR for AF cases over total number of ICSRs on CSK inhibitors compared with the non-CSK inhibitors (mild or not CSK inhibitors). AF indicates atrial fibrillation; CSK, C-terminal Src kinase; ICSR, individual case safety reports; and ROR, reporting odds ratio.
