Figure 5.
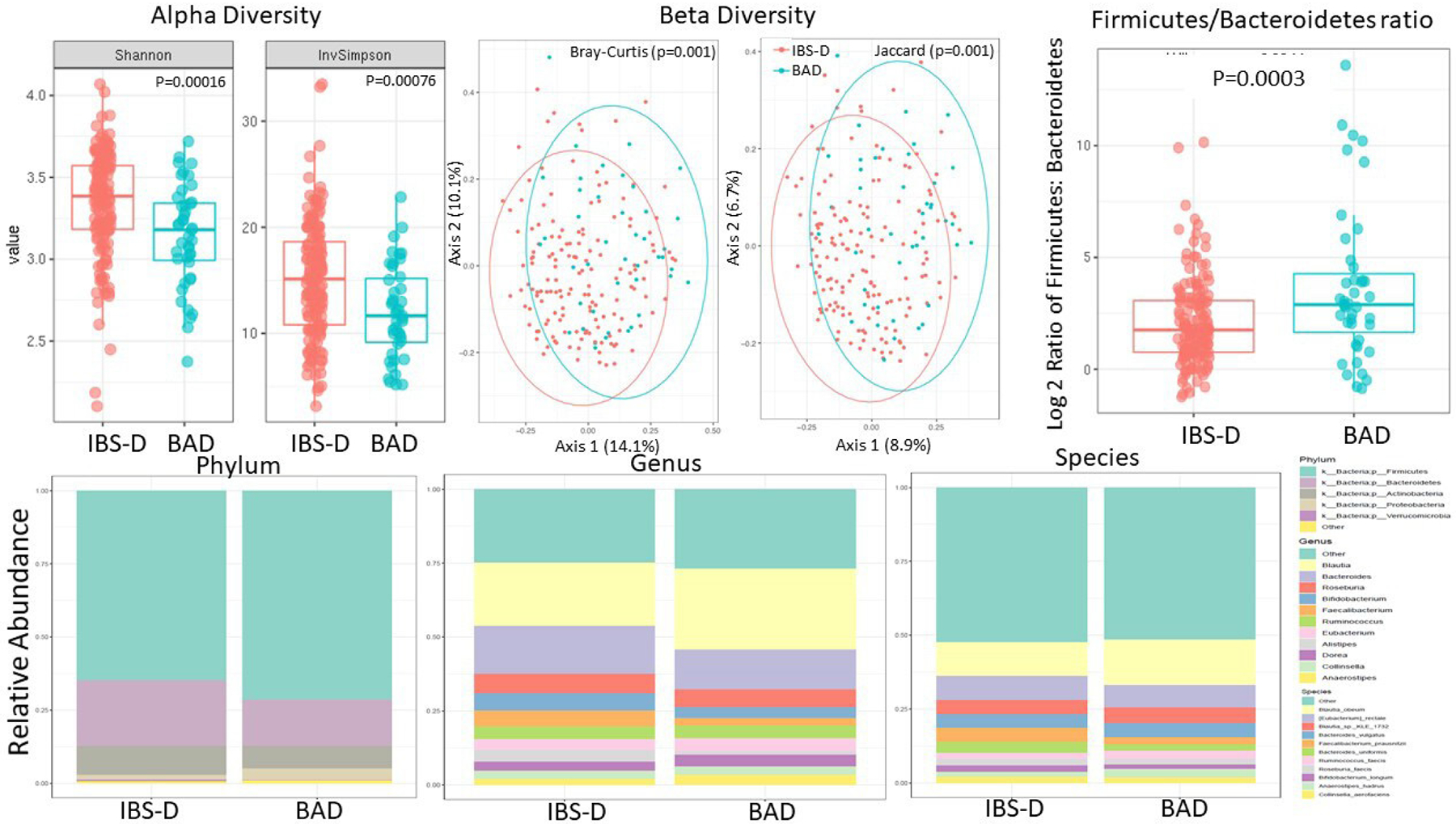
Upper panel: alpha diversity and beta diversity and Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio are significantly different in patients with IBS-D without ABAM compared with patients with BAD. Lower panel: differences in microbiome composition at the phylum, genus and species levels in patients with IBS-D without ABAM compared with patients with BAD. Data based on SHOTGUN metagenomics. Note the reduced alpha diversity in patients with BAD and the different compositional profile based on beta diversity among the two groups. ABAM, abnormal bile acid metabolism; BAD, bile acid diarrhoea; IBS-D, irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhoea.
