Figure 1.
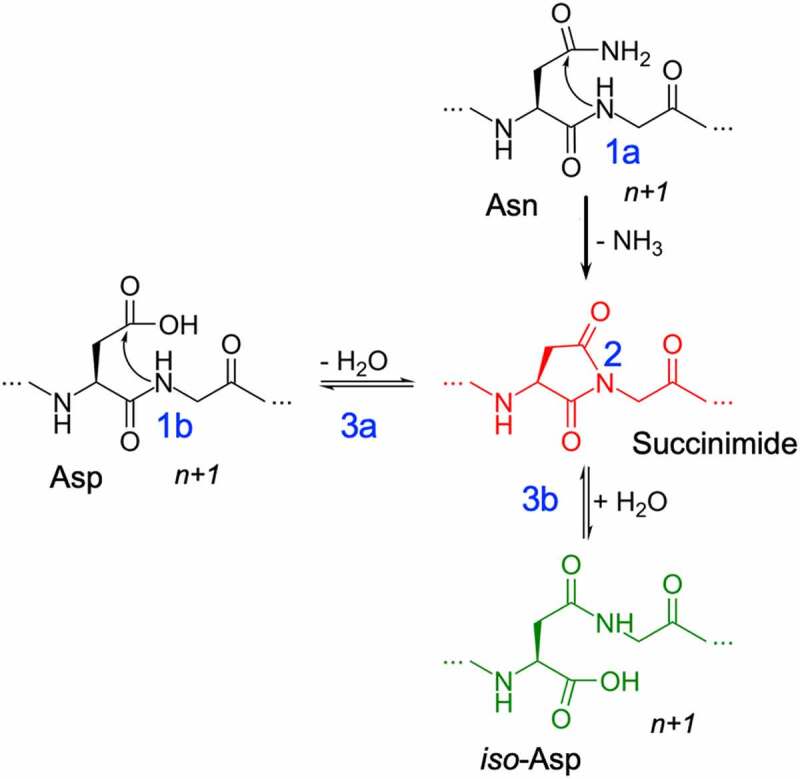
Deamidation (1a) and Isomerization (1b) reaction mechanisms showing deprotonation (1) of the n + 1 amide leading to the formation of succinimide intermediate (2) and hydrolysis of succinimide (3) into aspartic acid (3a) or iso-aspartic acid (3b).
