Abstract
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), an infectious acute respiratory disease caused by a newly emerging RNA virus, is a still-growing pandemic that has caused more than 6 million deaths globally and has seriously threatened the lives and health of people across the world. Currently, several drugs have been used in the clinical treatment of COVID-19, such as small molecules, neutralizing antibodies, and monoclonal antibodies. In addition, several vaccines have been used to prevent the spread of the pandemic, such as adenovirus vector vaccines, inactivated vaccines, recombinant subunit vaccines, and nucleic acid vaccines. However, the efficacy of vaccines and the onset of adverse reactions vary among individuals. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are crucial regulators of viral infections and antiviral immune responses and are heavily involved in COVID-19 pathologies. During novel coronavirus infection, circRNAs not only directly affect the transcription process and interfere with viral replication but also indirectly regulate biological processes, including virus-host receptor binding and the immune response. Consequently, understanding the expression and function of circRNAs during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection will provide novel insights into the development of circRNA-based methods. In this review, we summarize recent progress on the roles and underlying mechanisms of circRNAs that regulate the inflammatory response, viral replication, immune evasion, and cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection, and thus highlighting the diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in the treatment of COVID-19 and future research directions.
Keywords: COVID-19, circRNAs, inflammatory response, biological regulator, vaccine
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious acute respiratory disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (1). As of 18 July 2022, the cumulative number of cases reported globally is now over 500 million, and the cumulative number of deaths exceeds 6 million. The rapid spread of the provirus strain of SARS-CoV-2 has seriously threatened the lives and health of people across the world, and it certainly caught most of the population completely off-guard and forever changed their lives (2). In times of global pandemic, there is an urgent need for prophylactic vaccines and therapeutic drugs to protect individuals from COVID-19 and to help abate the growing epidemic (1). Currently, several drugs have been used in the clinical treatment of COVID-19, including small molecules (SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors), neutralizing antibodies (casirivimab and imdevimab), and monoclonal antibodies (tocilizumab) (3–6). In addition, some vaccines have been used to prevent the spread of the pandemic, such as adenovirus vector vaccines (VAXZEVRIA, COVISHIELD™), inactivated vaccines (inactivated COVID-19 vaccine (Vero Cell), CoronaVac), recombinant subunit vaccines (COVOVAX™), and nucleic acid vaccines (COMIRNATY®). However, the efficacy of vaccines and the onset of adverse reactions vary among individuals (7). Therefore, it is desperately important to develop safe and effective drugs and vaccines to prevent, diagnose and treat COVID-19.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a large class of abundant, stable and ubiquitous noncoding RNA molecules having a covalently closed loop structure generated from back-splicing of pre-mRNA transcripts. By acting as microRNA (miRNA) sponges, RNA-binding protein sponges, regulating transcription and translating to proteins, circRNAs have recently shown huge capabilities as gene regulators at transcriptional or post-transcriptional levels in the pathogenesis of various diseases, such as viral infections. Accumulating evidence indicates that circRNAs are crucial regulators of viral infections and antiviral immune responses and are heavily involved in COVID-19 pathologies (8–20). During novel coronavirus infection, circRNAs not only directly affect the transcription process and interfere with viral replication but also indirectly regulate biological processes, such as virus-host receptor binding and the immune response (21). However, the characteristics and functional mechanisms of circRNAs in COVID-19 remain unclear. This review focuses on the roles of circRNAs in regulation of the inflammatory response, viral replication, immune evasion, and cytokines induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection, exploring the underlying regulatory mechanisms, and thus highlighting the prospects and challenges in circRNA applications.
Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 and regulation of related circRNAs
Structure and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are the largest, enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus belonging to the Coronaviridae family (22, 23) and have been divided into four genera: α-coronavirus, β-coronavirus, γ-coronavirus, and δ-coronavirus. Additionally, β-coronavirus is further subdivided into four different lineages: A, B, C, and D (24, 25). Genetic sequence analysis has revealed that SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-1 can be classified into the B lineage, while the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) with lower homology belongs to the C lineage (26, 27). Furthermore, these CoVs possess cis-acting secondary RNA structures flanked by 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions, which are essential for RNA synthesis (28). At the 5’-terminal region, two-thirds of the genomic RNA constitutes two open reading frames (ORF1a and ORF1b), which are involved in encoding nonstructural proteins (nsps) in the viral life cycle. One-third of the genome RNAs of the 3’-end are involved in encoding structural proteins, including spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins, as well as eight accessory proteins (28–30). Although SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 share a large number of similarities in cytopathic effects on host cells, there are fundamental differences in their structures and modes of replication due to sequence divergence. The S protein mediates attachment of the virus to host cell surface receptors and is the first and essential step in CoV infection. However, both SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 enter host cells by using membrane-bound angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a primary receptor, while MERS-CoV enters host cells by binding to the dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) receptor (31). Furthermore, in addition to relying on cell-surface transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2), SARS-CoV-1 entry into host cells also relies on the assistance of cysteine cathepsin B (CatB) and cysteine cathepsin L (CatL), while the invasion of SARS-CoV-2 depends only on TMPRSS2 (32, 33). Moreover, several studies have found that SARS-CoV-1 mainly enters cells by binding to the ACE2 receptor in the lower respiratory tract tissue of the host, whereas SARS-CoV-2 mainly replicates in the upper respiratory tract epithelium (34, 35).
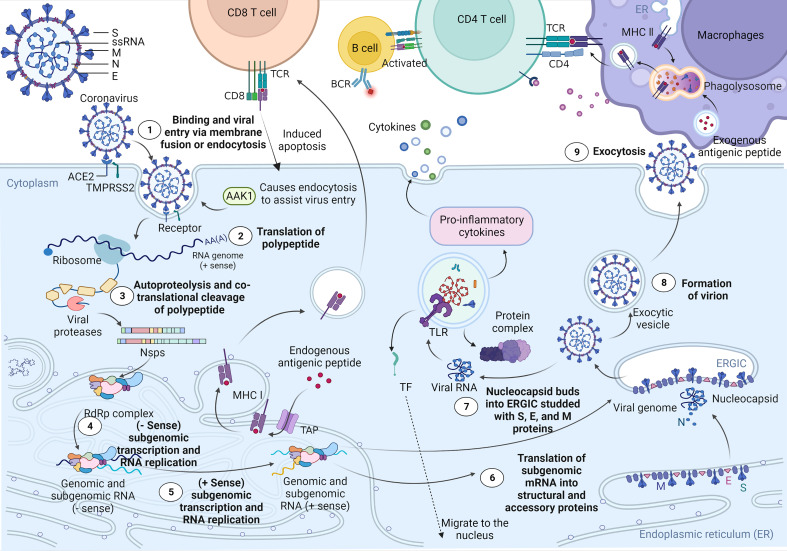
Recent studies have shown that ciliated bronchial epithelial cells and type II alveolar cells are the primary targets of SARS-CoV-2 (36). As shown in Figure 1 , when SARS-CoV-2 attaches to host cells, its S1 protein binds to the ACE2 receptor on the surface of the host cells. At the same time, the master regulator of endocytosis, AP2-associated kinase 1 (AAK1), triggers endocytosis for smooth virus entry into host cells. However, loss of AAK1 leads to interruption of virus particle assembly and entry of the virus into susceptible host cells (36). After entering cells, SARS-CoV-2 hijacks the endogenous transcriptional machinery of host cells to replicate and disseminate within the host. First, the RNA of SARS-CoV-2 encodes 2 long polyproteins and 4 structural proteins, of which the polyproteins are hydrolysed by proteases to generate short nsps, which promote viral replication and induce rapid cellular decay (37, 50). The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-mediated antigen presentation is an ubiquitous process by which cells present endogenous proteins to CD8+ T lymphocytes during immune surveillance and response and plays a critical role in antiviral immunity. A recent study by Yoo J et al. showed that the MHC class I pathway is targeted by SARS-CoV-2 (39). Moreover, the induction of the MHC class I pathway is inhibited by SARS-CoV-2 infection. MHC class I contributes towards antiviral immunity by facilitating the presentation of viral antigens to CD8 cytotoxic T cells. Consequently, activated CD8 cytotoxic T cells specifically eliminate virus-infected cells (40–43). In addition, the ability of B lymphocytes to capture external antigens and present them as peptide fragments, loaded on MHC class II molecules, to CD4+ T cells is a crucial part of the adaptive immune response. The ability to activate CD4+ T cells is restricted to antigen-presenting cells that are endocytosed and processed in lysosomes for presentation on MHC class II molecules, which can transduce signals required for B-cell activation. Moreover, MHC class II antigen presentation by B lymphocytes is a multistep process involving in the presentation of MHC II-peptide complexes to CD4+ T cells (44–47). Although the host’s innate immune system works against the virus particles in this process, a small number of viruses still escape, and the RNAs released by these viruses are captured and identified by toll-like receptors (TLRs). Subsequently, activated TLRs further induce cellular autoimmunity, resulting in a series of immune response processes, such as protein complex formation, transcription factor (TF) migration to the nucleus, and proinflammatory cytokine expression (48, 49, 51). Furthermore, several recent studies have demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 not only directly damages lung tissue but also triggers a cytokine storm, which leads to a sharp increase in cytokines and hyperactivation of immune cells, causing diffuse alveolar damage and exacerbating respiratory failure in patients and even potentially causing uncontrollable systemic inflammatory responses (SIRS) (52).
Figure 1.
Cell entry mechanism and life cycle of SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 virions consist of structural proteins, including spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins. When in contact with host cells, the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 specifically interacts with cellular receptors [such as angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)] and host factors [such as the cell surface serine protease TMPRSS2 and major endocytosis regulator AP2-related protein kinase 1 (AAK1)] to promote viral uptake and fusion at the cellular or endosomal membranes (37, 38). Following entry, viral genomic RNA is released into the cytoplasm and translated into polypeptides, which are subsequently hydrolysed and cotranslationally cleaved by proteases to generate nonstructural proteins (nsps). nsps further form RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) complexes in the endoplasmic reticulum. Subsequently, the RdRP complex is involved in the transcription and RNA replication of the - sense subgenome and the + sense subgenome. Translation of the −sense and +sense subgenomes further enables the synthesis of structural and accessory proteins at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. At the same time, the nucleocapsid buds into an ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) filled with S, E, and M proteins. Finally, virions are secreted from infected cells via exocytosis. As a result, MHC class I contributes towards antiviral immunity by facilitating the presentation of viral antigens to CD8 cytotoxic T cells. Moreover, the ability of antigen-presenting cells to capture external antigens and present them as peptide fragments, loaded on MHC class II molecules, which can transduce signals required for B-cell activation, to CD4+ T cells is a crucial part of the adaptive immune response (39–47). In addition, the RNA released by the virus is captured and recognized by the pattern recognition receptor Toll-like receptor (TLR) located on the endosomal membrane. Subsequently, TLR activates and induces further self-immunity of cells, resulting in the formation of protein complexes, the migration of transcription factors (TFs) to the nucleus, and the expression of proinflammatory cytokines (48, 49).
Differential expression of related circRNAs
Increasing studies have shown that circRNAs can be used as biomarkers and therapeutic targets in multiple viral diseases, as their abnormal levels may be considered to indicate the stage of pathology and prognosis (53, 54). CircRNAs encoded by viruses might play an important role in host-virus interactions by regulating viral and host gene expression. The study of changes in the expression levels of circRNAs will help us to further understand the mechanism of CoV entry into host cells and how to prevent and treat any secondary symptoms. CircRNAs encoded by CoVs are essential components of the CoV transcriptome and have the potential ability to encode circRNAs exerting different functions in host cells. The dynamic expression of these circRNAs may regulate host gene expression at different times to influence virus pathogenicity. For example, Cai Z et al. (15) identified 28754, 720, and 3437 virus-encoded circRNAs from Calu-3 cells infected with MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1, and SARS-CoV-2, respectively. Moreover, the expression levels of MERS-CoV-encoded circRNAs were significantly higher than those encoded by SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 circRNAs. The results revealed that the expression level of certain circRNAs was increased in the late stage of viral infection compared to the early stage. Interestingly, another study came to a different conclusion. Yang S et al. (17) predicted 351, 224, and 2764 circRNAs derived from SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, respectively. Moreover, 75 potential SARS-CoV-2 circRNAs were identified from RNA samples extracted from SARS-CoV-2-infected Vero E6 cells. These results suggest that virus-encoded circRNAs have strong cell and tissue specificity and play critical roles in autoimmune diseases and viral pathogenesis.
Currently, multiple studies based on bioanalysis have found a variety of dynamically expressed host-encoded circRNAs associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Yang M et al. (16) found 42 host-encoded circRNAs that were significantly dysregulated, of which 17 were upregulated and 25 were downregulated in SARS-CoV-2-infected human lung epithelial cells. Dysregulated circRNAs can regulate mRNA stability, immunity, and cell death by binding specific proteins and indirectly regulate gene expression by absorbing their targeted miRNAs. Notably, this result is consistent with that obtained by Zhang X et al. (18) who demonstrated that the proportion of differentially expressed (DE) circRNAs was very low (4/35056, 0.01%) at 6 hpi and was significantly increased (1567/46569, 3.4%) at 24 hpi in MERS-CoV-infected vs. mock-infected Calu-3 cells. Moreover, 1267 DE circRNAs were identified when comparing MERS-CoV-infected samples at 6 and 24 hpi. These results suggest that the DE circRNAs have potential biological functions during CoV infection, especially in the late stage of CoV infection. Additionally, Wu Y et al. (11) identified 570 DE circRNAs, of which 155 were upregulated and 415 were downregulated, in the peripheral blood of COVID-19 patients. Further analysis showed that these circRNAs could negatively affect the normal physiological activities of the body by regulating host cell immunity and inflammation, substance and energy metabolism, cell cycle progression and apoptosis. Collectively, both virus-encoded circRNAs and host-encoded circRNAs are progressively expressed during virus infection, thereby affecting the infection process, but the specific roles and mechanisms remain unclear. As shown in Supplementary Table 1 , we summarize the key viral and host cell circRNAs and role in COVID-19, SARS and MERS pathogenesis to provide a theoretical basis for further understanding the changes in the expression level of CoV-associated circRNAs and their roles in pathogenesis and virus replication.
Potential mechanisms of circRNAs in SARS-COV-2 infection
Sponging of miRNAs by circRNAs affects viral replication
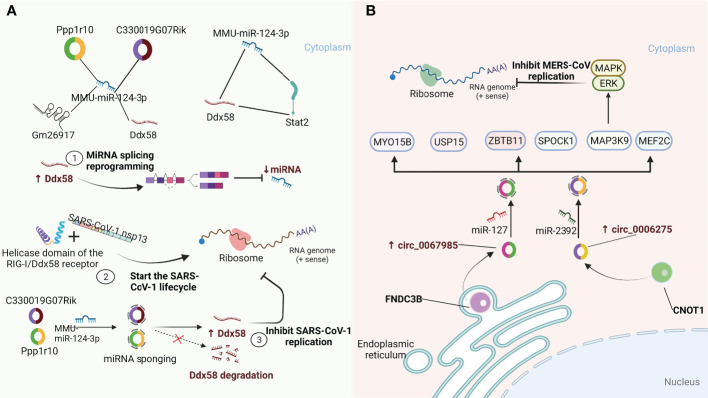
CircRNAs are highly evolutionarily conserved across species with cell-specific and tissue-specific characteristics (57–60). As an integral part of the competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network, circRNAs containing miRNA-responsive elements can regulate downstream target gene expression by acting as microRNA (miRNA) sponges to quickly bind the respective miRNAs and release the inhibitory effect of miRNAs on messenger RNA (mRNA) translation. Remarkably, circRNAs containing miRNA-responsive elements can act as miRNA sponges through the ceRNA network to prevent miRNA-mediated regulation of target genes (61, 62). Moreover, the sponge functions of circRNAs have been confirmed to be more efficient than those of linear miRNAs and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) transcripts (63, 64). A recent study by Arora S et al. (65) identified a ceRNA network consisting of one miRNA (MMU-miR-124-3p), one lncRNA (Gm26917), one TF (Stat2), one mRNA (Ddx58), and two circRNAs (Ppp1r10, C330019G07Rik) in SARS-CoV-1-infected cells. As shown in Figure 2A , the RIG-I/Ddx58 receptor in the ceRNA network has a helicase domain that interacts with SARS-CoV-1 nsp13 and initiates the viral life cycle. In addition, Ddx58 is involved in the mRNA splicing process and miRNA biogenesis, and its upregulation leads to reprogramming of miRNA splicing events, thereby downregulating the miRNA expression. Overexpression of miR-124-3p leads to the degradation of Ddx58, resulting in a reduction in viral replication. Furthermore, miR-124-3p has been shown to modulate TLR-mediated innate immune responses by targeting Stat3 and reducing IL-6 and TNF-α expression (66). These results suggest that miR-124-3p may also play a similar role in regulating Stat2 to affect the viral life cycle. Importantly, in this ceRNA regulatory network, two circRNAs (Ppp1r10 and C330019G07Rik) play vital regulatory roles as sponges of miR-124-3p to hinder the degradation of Ddx58, which in turn affects the replication of SARS-CoV-1. In addition, Zhang X et al. (18) found that host circRNAs mainly function as sponges of miRNAs to affect MERS-CoV replication. As shown in Figure 2B , hsa_circ_0067985 is derived from the gene FNDC3B and acts as a sponge of hsa-miR-1275, and hsa_circ_0006275 is derived from the gene CNOT1 and serves as a sponge of hsa-miR-2392, both of which are significantly upregulated in MERS-CoV infection and thus regulate the expression of representative downstream targets, including MAP3K9, MYO15B, SPOCK1, MEF2C, USP15, and ZBTB11. Collectively, these results provide new insights into the regulation of circRNAs and their related signalling pathways as host-targeted antiviral strategies against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Figure 2.
CircRNAs function as miRNA sponges to influence viral replication. (A) A quintuple ceRNA network exists in SARS-CoV-1 infection that includes one miRNA (MMU-miR-124-3p), one lncRNA (Gm26917), one TF (Stat2), one mRNA (Ddx58) and two circRNAs (Ppp1r10, C330019G07Rik). They form a closed 3-node miRNA feed-forward loop and a 4-node ceRNA network, respectively. Upregulation of Ddx58 leads to reprogramming of miRNA splicing events, resulting in downregulation of miRNA expression. Meanwhile, the helicase domain of the RIG-I/Ddx58 receptor can interact with SARS-CoV-1 nonstructural protein 13 (NSP13) to initiate the viral life cycle. Furthermore, Ppp1r10 and C330019G07Rik act as sponges for miR-124-3p, inhibiting miR-124-3p expression, which in turn impedes Ddx58 degradation and further inhibits SARS-CoV-1 replication (65). (B) circ_0067985 derived from the FNDC3B gene and circ_0006275 derived from the CNOT1 gene serve as miR-127 and miR-2392 sponges, respectively, to regulate the downstream expression of MAP3K9, MYO15B, SPOCK1, MEF2C, USP15 and ZBTB11. Of these, the upstream regulator of the MAPK pathway, MAP3K9, further regulates the downstream ERK/MAPK pathway to inhibit MERS-CoV replication (18).
CircRNAs in regulation of the immune response in SARS-CoV-2 infection by affecting cytokines
CircRNAs can effectively prevent the virus from damaging the body by mediating the immune response process of the host-virus interaction (67). A study by Li X et al. (9) found that NF90/NF110 produced from human interleukin-enhanced binding factor 3 (ILF3) directly regulate back-splicing and coordinate with circRNA production in response to viral infection. The nuclear export of NF90/NF110 upon viral infection contributed in part to a decrease in circRNA production. Moreover, NF90/NF110-circRNP accumulation in the cytoplasm may influence the host immune response. The findings also indicated that circRNAs compete with viral mRNAs for binding to NF90/NF110, and circRNAs may act as a molecular reservoir of NF90/NF110 for a prompt immune response upon viral infection (9, 68). In addition, Chen YG et al. (69) found that circRNAs composed of self-splicing introns can bind to the receptor retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) to effectively activate immune signal transduction in the context of viral infection. A recent study also indicated that the overexpressed hsa_circ_0000479 in COVID-19 patients may regulate the expression of IL-6 and RIG-I by sponging hsa-miR-149-5p (55). Additionally, regulation of immune responses by circRNAs generally involves the transduction of signalling pathways and the production of cytokines. A recent comprehensive protein transcription analysis indicated that epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB), hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), mammalian leukaemia target of rapamycin (mTOR) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) signalling pathways, among others, were markedly modulated during the course of SARS-CoV-2 infection (70). The parental genes of DE circRNAs enriched in these pathways are associated with numerous antiviral signalling pathways, such as interferon (IFN), chemokines, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and RIG-I-like receptors (58), indicating that circRNAs play regulatory roles in cell signal transduction and immune-inflammatory response during SARS-CoV-2 infection.
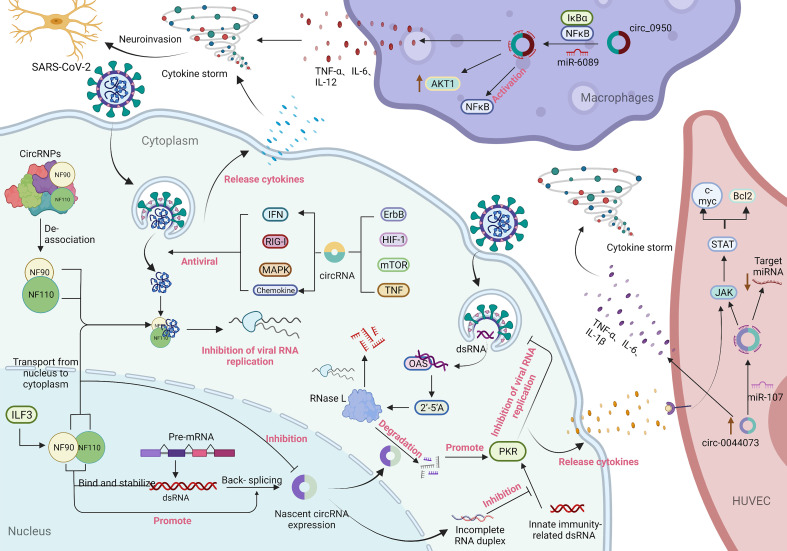
Cytokines are small molecular polypeptides or glycoproteins synthesized and secreted by a variety of cell types, participating in many physiological processes including the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses. Cytokines have been shown to act as immunomodulators involved in autocrine, paracrine and endocrine signaling, and play important roles in the immune response to host-viral infection (71, 72). Moreover, viral infection can lead to the production of cytokines that have a crucial role in control of the immune response and anti-viral defence, as well as in the capacity of target cells to support virus replication (73). Several recent studies have found that SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers an autoimmune response by activating certain immune factors, such as 2’-5’ oligoadenylate synthase (OAS1-3), interferon-inducible protein (Ifit1-3), and the T helper cell type 1 (Th1) chemokines CXCL9/10/11, and reducing the transcription of ribosomal proteins (74). A previous study showed that the activation of OAS requires the participation of viral genome dsRNA, which combines to generate 2’-5’ oligoadenylate (2’-5’A). Furthermore, 2’-5’A exerts antiviral effects by significantly increasing the activity of RNase L to degrade viral RNA and interfere with viral protein synthesis (75). Liu CX et al. (76) found that endogenous circRNAs tend to form imperfect short (16–26 bp) RNA duplexes and act as inhibitors of dsRNA-activated Protein Kinase R (PKR) associated with innate immunity. Moreover, circRNAs can be globally degraded by the endonuclease RNase L to activate the PKR antiviral pathway. As shown in Figure 3 , these results indicate that circRNAs may modulate the immune circRNAs may modulate the immune response in SARS-CoV-2 infection by affecting cytokines.
Figure 3.
Immune response involving circRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 infection and the potential mechanism of circRNAs in inflammation. During virus infection, nuclear factor 90 (NF90) and its 110 (NF110) isoform produced by interleukin-enhanced binding factor 3 (ILF3) bind to viral mRNA to inhibit virus replication through two pathways: transport from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and decoupling from the circRNA-protein complex (CircRNPs) in the cytoplasm. Among them, the transport of NF90/NF110 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm can reduce the expression of circRNAs. In contrast, the binding of NF90/NF110 to dsRNA formed during pre-mRNA processing can not only stabilize the RNA duplex but also promote reverse splicing to form circRNA (57). 2’-5’ Oligoadenylate (2’-5’A) is generated by the combination of 2’-5’ oligoadenylate synthase (OAS) and viral genome dsRNA and plays an antiviral effect by significantly increasing the activity of RNase L to degrade viral RNA and interfere with viral protein synthesis. Endogenous circRNAs often form incomplete RNA duplexes and act as inhibitors of PKR activation by dsRNAs associated with innate immunity. Meanwhile, circRNAs can be globally degraded by the endonuclease RNase L to activate the PKR antiviral pathway (77). In addition, parental genes enriched for differentially expressed circRNAs in signalling pathways that are significantly regulated upon SARS-CoV-2 infection are associated with multiple antiviral signalling pathways (16, 74, 78). The generation of a cytokine storm is related to the overproduction of proinflammatory cytokines mediated by circRNAs. In macrophages, circ_09505 acts as a sponge of miR-6089 through the IκBα/NFκB signalling pathway, on the one hand, promoting the expression of AKT1 in macrophages and the activation of NF-κB, and on the other hand, promoting the production of the proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 (79). Furthermore, circ_0044073 in HUVSMCs and HUVECs functions as a miR-107 sponge to downregulate the expression levels of target mRNAs, while activation of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway enhanced the expression of the downstream proteins Bcl2 and c-myc. Moreover, circ_0044073 significantly upregulated the levels of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α (80). In addition, the occurrence of a cytokine storm disrupts the balance of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, thereby invading the patient’s nervous system (81, 82).
Potential mechanism of action of circRNAs in inflammation
Inflammation involves a set of biologic mechanisms that evolved in multicellular organisms to contain invasive pathogens and resolve injuries by activating innate and adaptive immune responses, which require a balance between sufficient cytokine production to eliminate pathogens and avoidance of a hyperinflammatory response that causes collateral damage (77). Remarkably, cytokine storm is closely associated with overproduction of a series of proinflammatory cytokines and poor prognosis, which is related to inflammatory signalling in the pathway regulated by circRNAs, as shown in Figure 3 . A study by Yang J et al. (83) demonstrated that the expression of circ_09505 in arthritic (RA) mice was positively correlated with the life cycle of macrophages. Circ_09505 sponges miR-6089 to promote the expression of AKT1 and activate nuclear factor-kB (NF-κB) in macrophages through the IκBα/NFκB signalling pathway, thereby promoting macrophage inflammation. Furthermore, circ_09505 functions as a sponge of miR-6089 in macrophages to promote the production of proinflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12. Numerous studies have demonstrated that activation of the NF-κB pathway plays a pivotal regulatory role in the development of SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation (84–88). Collectively, these findings may provide novel insights into the mechanism underlying circRNAs in the regulation of the IκBα/NFκB signalling pathway as a potential therapeutic target for the initial symptoms of inflammation in COVID-19 patients.
Additionally, a study by Shen L et al. (79) found that circ_0044073 was upregulated in chronic inflammation of the arterial vessel wall and promoted the proliferation of human vascular cells by acting as a sponge for miR-107. The study further found that overexpressed circ_0044073 in vascular cells reduced the expression levels of miR-107 target mRNAs and activated the JAK/STAT signalling pathway, thereby enhancing the expression of downstream proteins, such as Bcl2 and c-myc. The JAK/STAT pathway has been shown to be activated downstream of various cytokines during cytokine storms and that is involved in promoting inflammation, proliferation, migration, and adhesion of vascular cells (80). Furthermore, circ_0044073 can significantly increase the levels of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. These findings suggested that SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the balance between proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory mechanisms by promoting the occurrence of a cytokine storm via the specific regulations of circRNAs pathways, which in turn leads to cardiovascular inflammation in patients with COVID-19.
Regulatory roles of circRNAs in immune evasion
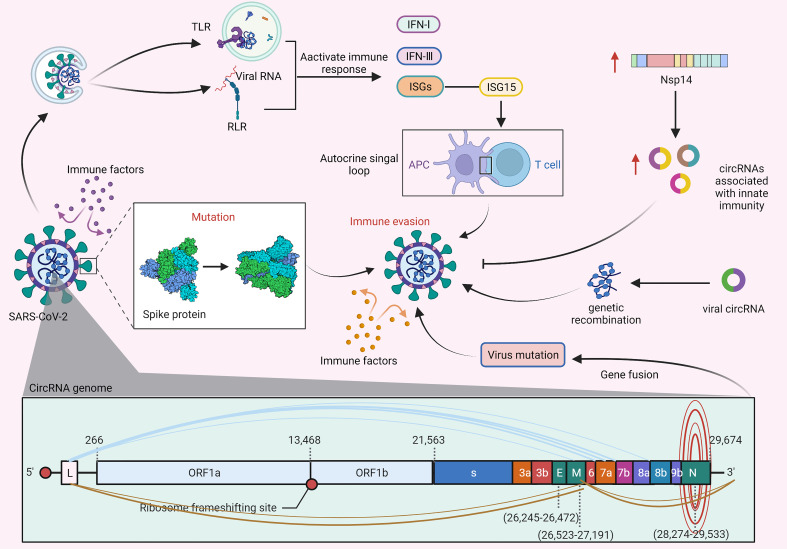
The innate immune response can effectively prevent the virus from invading the host. However, the virus has evolved the ability to evade the host immune response. As shown in Figure 4 , viral nucleic acid intermediates and released genomic RNAs during the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 can be recognized by TLRs and RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), thereby activating the body’s immune pathways to produce immune factors, such as IFN-I, IFN-III, and numerous ISGs. ISGs have general antiviral effects, however, the proviral effects of ISG15 may lead to the generation of autocrine loops that ultimately induce viral drug resistance by amplifying and prolonging their secretion (89, 94). In addition, a study by Arora S et al. (65) demonstrated that SARS-CoV-1 may reprogram splicing events by inducing the cytoplasmic translocation of DROSHA (an enzyme involved in miRNA biogenesis) to generate another circRNA that can act as a sponge for miR-124-3p and hinder its degradation of Ddx58, thereby evading ISG-mediated antiviral effects (90). Furthermore, SARS-CoV-1 can enhance viral replication by confiscating the helicase in Ddx58 independent of interferon-related pathways.
Figure 4.
CircRNAs regulate immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2. During SARS-CoV-2 proliferation, genomic RNAs are recognized by TLR receptors and pattern recognition receptors (RLRs) and subsequently activate immune responses. The proviral action of the immune factor ISG15 leads to the generation of an autocrine loop, which amplifies and prolongs autocrine signalling and ultimately induces viral drug resistance (89, 90). Furthermore, the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 can prevent the virus from being cleared by immune factors, and mutation of the S protein will further enhance the ability of the virus to evade immune responses (91, 92). In addition, the expression of viral nsp14 can upregulate the levels of circRNAs related to innate immunity, thereby inhibiting viral replication and immune evasion (93). Likewise, viral circRNAs may be involved in the mechanism of genome recombination, resulting in mutation of virions leading to immune evasion. There are various types of gene fusions in the circRNA genome of SARS-CoV-2, which may cause the virus to mutate and evade immunity.
Several recent studies have found that SARS-CoV-2 can further evade immune responses by mutating its S protein on the basis of its S protein shielding immune factor clearance, which can greatly promote the spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the population (91, 95). Recent studies have shown that circRNAs play a key role in the immune evasion and replication of SARS-CoV-2. For example, Zaffagni M et al. (92, 96) found that SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 mediates the effects of viral infection on the host cell transcriptome. Nsp14 altered the splicing of more than 1000 genes and resulted in a dramatic increase in the number of circRNAs that were linked to innate immunity. Furthermore, a recent study by Hassanin A et al. (97) indicated that viral circRNAs are involved in the mechanism of genome recombination, which may cause virion mutation leading to immune evasion. In addition, a study by Yang S et al. (17, 98) found that abundant and diverse circRNAs are generated by SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV and represent a novel type of circRNA that differs from circRNAs encoded by DNA genomes, and forward splice junctions (FSJs) representing noncanonical “splicing” events were detected in these circRNA genome sequences. Furthermore, the study also reported the existence of alternative back-splicing events in SARS-CoV-2 circRNAs that share either 5’ or 3’ breakpoints. Several studies have reported that gene fusion is closely related to the occurrence and development of various diseases, and thus, fused genes may be potential drug targets. Accordingly, atypical fusions in the SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome may provide conditions for the generation of viral mutation as well as viral survival and immune evasion in infected tissues.
Prospects of the clinical application of circRNAs in COVID-19
CircRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for COVID-19 detection
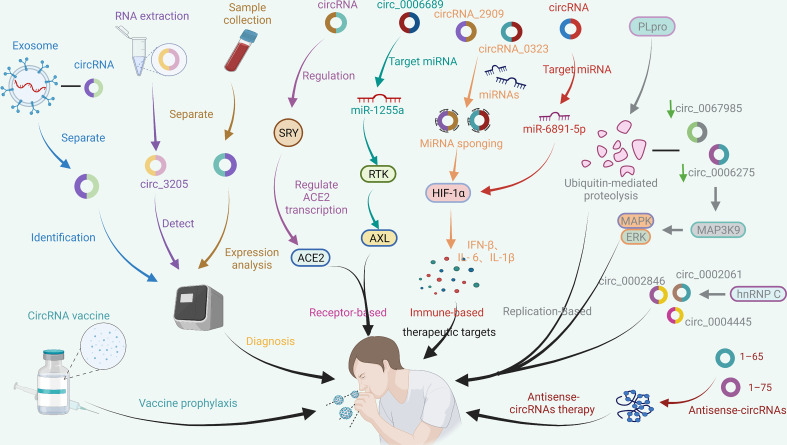
CircRNAs are resistant to RNase R degradation and have a longer half-life, and their expression patterns are affected by viral infection. Several studies have demonstrated that circRNAs are abundant in the circulatory system of COVID-19 patients and may be reliable biomarkers of disease progression or prognosis (15–17). A study by Wu Y et al. (11) found that 114 DE circRNAs in SARS-CoV-2-infected peripheral blood were associated with exosomes, which could not only promote infection but also activate the body’s immune response (99, 100). Moreover, recent studies have demonstrated that exosomes may be a key factor in the recurrence of COVID-19 (101). Importantly, since exosomes can reflect the pathological state of the cells from which they originate, they can be used as diagnostic markers of various diseases. Thus, identification and isolation of exosome-related circRNAs may be helpful for the diagnosis of COVID-19.
In addition, a recent study found that virus-encoded circRNAs in SARS-CoV-2 infection downregulated genes related to cholesterol, alcohol, sterol, and fatty acid metabolic processes and upregulated genes associated with cellular responses to oxidative stress at the later stage of virus infection (15). Barbagallo D et al. (56) found that circ_3205 encoded by SARS-CoV-2 serves as a sponge of hsa-miR-298, thereby targeting downstream KCNMB4 and PRKCE mRNAs to promote the development of COVID-19. Furthermore, circ_3205 was only expressed in positive samples, and its expression was positively correlated with S protein mRNA and SARS-CoV-2 viral load, suggesting that circ_3205 could be used as a diagnostic marker for COVID-19. More importantly, the dysregulation of circRNAs may reflect physiological and pathological changes in each human body. For example, host circRNAs formed by nonsequential back-splicing in SARS-CoV-2-infected Calu-3 cells are widely and abundantly expressed in human lung epithelial cells compared to normal Calu-3 cells (16, 102). Zhang X et al. (18) found that differential expression of circRNAs in the circRNA-miRNA–mRNA network leads to the disturbance of a series of biological processes in MERS-CoV-infected Calu-3 and HFL cells. Overall, it is suggested that monitoring the expression level of circRNAs may provide a new reference index for diagnosis and prognosis determination in COVID-19 patients (103).
CircRNAs as potential therapeutic targets for COVID-19
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, a wealth of studies have shown that angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a recognized receptor for SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells. Therefore, regulating the ACE2 gene promoter to interfere with the transcription and production of ACE2 may be a new approach to preventing the virus from binding to host cells to prevent COVID-19. Previous studies have shown that sex-determining region Y (SRY) can inhibit ACE2 promoter activity, thus increasing angiotensinogen, renin, and ACE gene promoter activity (104). Furthermore, a recent study by Wang D et al. (105) indicated that there are 24 common transcription factor binding sites in the conserved region of the ACE2 gene promoter, including SRY, HNF-1, IRF, AP-1, YY1, and c-Jun. Previous studies have revealed that SRY transcripts mainly exist in the form of circRNA molecules, which account for more than 90% of all SRY transcripts (106, 107). Moreover, recent studies have also demonstrated that circRNAs can participate in the regulation of SRY-box transcription factors through the ceRNA network thereby regulating the expression of downstream target genes (108–110). Remarkably, several studies have found significant gender differences in the incidence of COVID-19, with males having significantly higher rates than females. Consequently, circRNAs may affect the transcription process of ACE2 by regulating SRY-related genes, thus mediating the infection of SARS-CoV-2 to the host. However, no research has focused on circRNAs involved in the regulation of ACE2 through modulation of the SRY gene. In addition, recent studies have revealed that AXL receptor tyrosine kinase (AXL), a founding member of the TAM family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), is a novel candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 to invade host cells. AXL can specifically interact with the N-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 genome to mediate its entry into host cells without the involvement of ACE2, suggesting that AXL may be a potential target for future treatment of COVID-19 (111). Notably, a recent study has found that hsa_circ_0006689 regulates the transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathway by targeting hsa-miR-1255a (112), indicating that hsa_circ_0006689 may participate in the invasion of SARS-CoV-2 by mediating the expression of AXL. Taken together, circRNAs may be therapeutic targets against COVID-19 by regulating the binding of SARS-CoV-2 to relevant host receptors.
Immunity induced by a viral infection can protect cellular functions, resist viral invasion, clear viruses, and clear infections. However, excessive activation of immune responses may cause serious damage to the host (113). For example, over-recruitment of immune cells and uncontrolled proinflammatory cytokines can lead to systemic inflammation that can cause extensive damage to tissues and organs. Numerous studies have shown that TNF and IL-1β can stimulate the production of IL-6, which can serve as a biomarker of disease severity and a prognostic indicator of cytokine storm (114, 115). Interestingly, IL-6 is involved in the activation of the NF-kB pathway, and subsequently, NF-kB positively regulates HIF-1α, which in turn enhances the regulatory effect of HIF-1α on the expression of downstream proinflammatory factors. Meanwhile, HIF-1α plays a key role in the synthesis of IL-1β (116–120). A recent study by Tian M et al. (121) found that the ORF3a protein of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19 can promote the production of HIF-1α, which regulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-β, IL-6, and IL-1β, to promote virus replication and infection. Noticeably, Yang YW et al. (122) found that two circRNAs (circ_2909 and circ_0323) could promote the expression of HIF-1α and inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) by acting as sponges for miRNAs. Furthermore, Demirci YM et al. (123) reported DE miRNAs during SARS-CoV-2 infection and found that ORF3a protein is a viral target of human miRNAs. The study further found that among 2498 miRNAs with predicted targets, 2448 had more targets in circRNAs. Therefore, regulatory network of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA contributes to regulating the expression of downstream HIF-1 pathway genes and that may become a new approach to treating COVID-19.
Currently, CoVs have evolved to the point where they can evade a complex system of sensors and signalling molecules to suppress host immunity. Papain-like protease (PLpro) is an enzyme in CoVs that regulates viral spread and innate immune responses (124, 125). Several recent studies have demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2-PLpro is a multifunctional enzyme with deubiquitination and de-ISG activities via regulating multiple signalling pathways, such as STING, NF-κB, and TGF-β, to block immune responses (126), suggesting that PLpro can serve as an important therapeutic target against COVID-19. Remarkably, previous studies have indicated that MERS-CoV-PLpro has deubiquitination activity and participates in the proteolysis of viral polyproteins during viral replication (127, 128). A study by Zhang X et al. (18) found that ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis was significantly disturbed after MERS-CoV infection, and DE circRNAs related to ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis could affect MERS-CoV replication by regulating downstream target genes. For example, knockout of hsa_circ_0067985 or hsa_circ_0006275 significantly reduced the expression of MAP3K9, thereby regulating the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/MAPK pathway associated with MERS-CoV replication (129). In addition, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C (hnRNP C) is an upstream regulator of multiple proviral circRNAs and can bind and obscure Alu on pre-mRNA and protect against Alu exonation to regulate circRNA biogenesis (130, 131). A recent study by Zhang X et al. (19) found that hnRNP C was able to regulate MERS-CoV replication by targeting the CRK-mTOR signalling pathway. Furthermore, this study also confirmed that hnRNP C is a key modulator of the expression of MERS-CoV-perturbed circRNAs, such as hsa_circ_0002846, hsa_circ_0002061 and hsa_circ_0004445, and the data further demonstrated that hnRNP C regulates the expression of these circRNAs through direct physical binding. The correlation analysis of circRNAs and their parental genes as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 is summarized in Supplementary Table 2 , which suggests that circRNAs play a key role in the occurrence of COVID-19.
Discussion
In summary, circRNAs are emerging as important players in regulating virus-mediated infection and subsequent disease status. With the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing technology and bioinformatics, it has been demonstrated that a large number of circRNAs are DE in COVID-19 patients and that circRNAs play a key role in the process of virus-host interaction. On the one hand, the host directly regulates immune response factors during virus infection via circRNAs and indirectly regulates the expression of downstream target genes through the ceRNA network to inhibit virus replication. On the other hand, viruses trigger molecular expression through host-encoded and self-encoded circRNAs, generating new circRNAs that interfere with the host’s innate immune response and that may create a suitable microenvironment for the virus to replicate or mutate in cells. Moreover, conserved circRNAs are widely involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Furthermore, these circRNAs act as key targeted therapies for SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, including blocking the binding of the virus to host receptors, inducing host-specific immune responses, interfering with gene transcription, and hindering protein translation. Current studies clearly show that circRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and closely involved in the process of SARS-CoV-2 infection, which paves the way for further studies on how circRNAs regulate host-virus dynamics in CoV-involved diseases. However, the lack of research on clinical effectiveness has greatly increased the challenges in the clinical application of circRNAs.
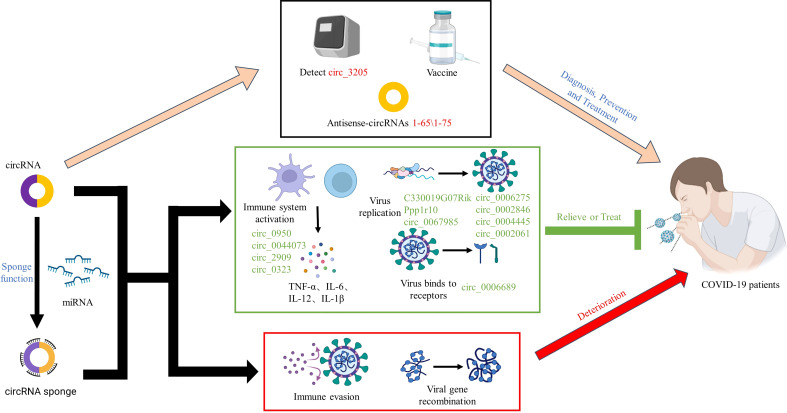
By far, the new mutated strain of SARS-CoV-2, Omicron, has once again caused a global panic. At this stage, vaccination is the most promising way to end the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the efficacy of vaccines and the onset of adverse reactions vary among individuals. Information on COVID-19 vaccines that have been certified for emergency use by the WHO and are in the process of being evaluated is summarized in Table 1 (132–149). Traditional vaccines and nucleic acid vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 have been extensively developed. Among them, an mRNA vaccine was the first to be officially approved by the FDA for use in the COVID-19 pandemic due to its advantages of rapid production, low cost, and rapid response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, in the face of rapidly mutating virus strains, alternative vaccines with high efficacy, high design flexibility, and fast production have not yet been developed. With the development of RNA vaccines, improving RNA stability has become a huge challenge. Fortunately, prior to this challenge, circRNAs showed great potential. Unlike linear mRNA, circRNA is highly stable and has a long half-life because its covalently closed-loop structure protects it from exonuclease-mediated degradation (150–152). However, only a few endogenous circRNAs have been demonstrated to serve as templates for protein translation, but several studies have shown that m6A modifications introduced into the ribosomal entry site (IRES) or 5’-untranslated region via artificial engineering can promote the extensive translation of circRNAs (110, 153–155). Recently, Liang Qu et al. (10) rapidly synthesized a highly stable circRNA-RBD vaccine (a circRNA vaccine that encodes the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein trimer) through in vitro transcription and found that the vaccine was capable of inducing potent and sustained anti-SARS-CoV-2-RBD neutralizing antibodies and Th1-biased T-cell responses in mice. Furthermore, the production of highly active neutralizing antibodies of the corresponding Beta variant was successfully induced in mice by using the circRNA vaccine encoding the RBD variant (K417N-E484K-501Y). Moreover, the latest research results have revealed that circRNA-RBD-Delta can elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the Delta and Omicron variants compared to the circRNA-RBD-Omicron vaccine, which only induces effective neutralizing antibodies against Omicron. In addition, Seephetdee C et al. (20) found that SARS-CoV-2 circRNA vaccine VFLIP-X induces humoral and cellular immune responses that provide broad immune responses against emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants in mice. The results showed that circRNA vaccines can not only effectively prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection but can also quickly adapt to emerging SARS-CoV-2 mutant strains. Additionally, compared with the preparation method for conventional inactivated vaccines, which requires obtaining virus strains and then expanding and culturing live viruses, circRNA technology allows rapid development of new vaccines by only obtaining virus sequences or mutated sequences. CircRNA vaccines have the advantages of strong stability, immunogen coding ability, self-adjuvant, rapid mass production in vitro, and no needed nucleotide modification. CircRNAs can also be used to express nanobodies or ACE2 decoys to neutralize SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus (10). Recently, Breuer J et al. (156) found that artificial circRNAs can bypass the cellular RNA sensors and that are not recognized by the innate immune system. Moreover, the antisense circRNAs 1–65 and 1–75 designed by Pfafenrot C et al. (14) significantly inhibited viral replication by specifically targeting specific 5’-UTR regions and sgRNAs of the SARS-CoV-2 genome. The potential applications of circRNAs for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of COVID-19 are shown in Figure 5 , which indicates that circRNAs have very good application prospects in the fight against SARS-CoV-2 variant viruses, and circRNA vaccines and artificial circRNAs can be used as new vaccines and therapeutic platforms in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Table 1.
Status of COVID-19 vaccines within WHO Emergency Use Listing (EUL)/Prequalification (PQ).
| Vaccine | WHO EUL Holder | National Regulatory System (NRA) of record | Recommendation issued | Suitable age | Type of vaccine | Working principle | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COMIRNATY® | BioNTech Manufacturing GmbH | European Medicines Agency | aged 5 years and older | Nucleic acid vaccine | mRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | broken down shortly after vaccination myocarditis pericarditiserythema multiformeAllergic reactions | (132) | |
| Food and Drug Administration | 16-Jul-21 | |||||||
| VAXZEVRIA | AstraZeneca AB / SK Bioscience Co. Ltd | European Medicines Agency | 15-Feb-21 | aged 18 years and older | Adenovirus vector vaccine | Adenovirus recombinantly containing a gene for the production of SARS-CoV-2 spike-in protein | Thrombosis in combination with thrombocytopenia(TTS),Guillain-Barré syndromeangioedema,capillary leak syndrome,Allergic reactions | (133) |
| European Medicines Agency | 15-Apr-21 | |||||||
| Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare | 09-Jul-21 | |||||||
| AstraZeneca AB | Therapeutic Goods Administration | 09-Jul-21 | ||||||
| Health Canada | ||||||||
| COFEPRIS (DP) ANMAT (DS) | ||||||||
| COVISHIELD™ | Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd | Central Drugs Standard Control Organization | 15-Feb-21 | aged 18 years and older | Adenovirus vector vaccine | Adenovirus recombinantly containing a gene for the production of SARS-CoV-2 spike-in protein | Thrombosis in combination with thrombocytopenia TTS),Allergic reactions | (134) |
| Ad26.COV2-S [recombinant] | Janssen–Cilag International NV | European Medicines Agency | 12-Mar-21 | aged 18 years and older | Adenovirus vector vaccine | encoding a full-length and stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome [TTS], capillary leak syndrome, and Guillain-Barré syndrome | (135) |
| SPIKEVAX | Moderna Biotech | European Medicines Agency | 30-Apr-21 | aged 12 years and older | Nucleic acid vaccine | mRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | broken down shortly after vaccination,erythema multiforme,Allergic reactions | (136) |
| ModernaTX, Inc | Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) | |||||||
| Food and Drug Administration | ||||||||
| Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccine (Vero Cell) | Beijing Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd. (BIBP) | National Medicinal Products Association | 18 to 59 years of age | Inactivated vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (137) | |
| CoronaVac | Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd | National Medical Products Administration | 01-Jun-21 | 18 to 59 years of age | Inactivated vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (138) |
| COVAXIN® | Bharat Biotech International Ltd | Central Drugs Standard Control Organization | 03-Nov-21 | aged 18 years and older | Inactivated vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | Headaches,Fever | (139) |
| COVOVAX™ | Serum Institute of India Pvt. Ltd | Central Drugs Standard Control Organization | aged 18 years and older | Recombinant subunit vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (140) | |
| NUVAXOVID™ | Novavax CZ a.s. | European Medicines Agency | aged 18 years and older | Recombinant subunit vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (140) | |
| Sputnik V | Russian Direct Investment Fund | Russian NRA | / | aged 18 years and older | Adenovirus vector vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | Localised pain, weakness, headaches and joint pain | (141) |
| Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (Vero Cell) | Wuhan Institute of Biological Products Co Ltd | National Medicinal Products Association | / | 18 to 59 years of age | Inactivated vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (142) |
| Ad5-nCoV | CanSinoBIO | National Medicinal Products Association | / | / | Recombinant subunit vaccine | Adenovirus recombinantly containing a gene for the production of SARS-CoV-2 spike-in protein | local injection site reactions,Headache, Drowsiness and Muscle aches | (143) |
| CoV2 preS dTM-AS03 vaccine | SANOFI | European Medicines Agency | / | / | Adjuvanted soluble protein vaccines | robust induction of antibody responses | local injection site reactions,Headaches,Fever | (144) |
| SCB-2019 | Clover Biopharmaceuticals | National Medicinal Products Association | / | / | Recombinant subunit vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (145) |
| Recombinant Novel Coronavirus Vaccine (CHO Cell) | Zhifei Longcom, China | National Medicinal Products Association | / | / | Recombinant subunit vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | local injection site reactions | (146) |
| Zorecimeran (INN) concentrate and solvent for dispersion for injection; Company code: CVnCoV/CV07050101 | Curevac | European Medicines Agency | / | / | Nucleic acid vaccine | mRNA-based vaccine encapsulated in lipid nanoparticle (LNP) | Headache, fatigue, chills and pain at the injection site | (147) |
| EpiVacCorona | Vector State Research Centre of Viralogy and Biotechnology | Russian NRA | / | / | Adenovirus vector vaccine | The immune system is stimulated to neutralize the virus by peptides-short fragments of viral protein | / | (148) |
| SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine, Inactivated (Vero Cell) | IMBCAMS, China | National Medicinal Products Association | / | 18 to 59 years of age | Inactivated vaccine | The antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 can be produced after vaccination | Redness and swelling at the injection site, induration and fever at the injection site | (142) |
| Soberana 01, Soberana 02 Soberana Plus Abdala | BioCubaFarma - Cuba | CECMED | / | / | Conjugate protein vaccines | SARS-CoV-2 spike protein conjugated chemically to meningococcal B or tetanus toxoid or Aluminum | / | (149) |
Figure 5.
Potential application of circRNAs in the treatment of COVID-19. CircRNAs are a new class of regulatory factors that mediate host–virus interactions. The identification and isolation of exosome-associated circRNAs, virus-encoded circRNAs, and significantly DE circRNAs after SARS-CoV-2 infection may be helpful in the diagnosis of COVID-19. In addition, circRNAs may serve as potential therapeutic targets against COVID-19 by indirectly regulating the expression of host receptors, such as ACE2 and AXL, that bind to SARS-CoV-2; HIF-1α and other signalling pathways related to the immune response; and multiple signalling pathways related to SARS-CoV-2 replication. Additionally, vaccines based on circRNAs and antisense circRNAs have shown initial effectiveness in preventing and inhibiting SARS-CoV-2. The coloured arrows in the figure are only for the convenience of differentiation and have no special meaning.
In general, circRNAs are highly resistant to RNAse R due to their unique ring structure and are more conservative and stable than lncRNAs and miRNAs. CircRNAs can exist stably in cells or tissues and have become the star molecules in the field of ncRNA. Furthermore, circRNAs have the potential to be molecular markers of viral infectious diseases, which can provide a scientific basis for early diagnosis of diseases and the search for potential therapeutic targets. Taking circRNAs as an entry point to study the interaction between viral infection and the host will help clarify the function of circRNAs and thus the pathogenic mechanism of coronaviruses. Therefore, circRNAs may prove to be helpful as diagnostic markers and therapeutic agents against COVID-19.
Author contributions
XG, DF, YL and ML conceived the idea, analysis of literature, and writing of the manuscript; XG, XD and NC collected and read the literature and revised the article; MZ and ML read through and corrected the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 81800434], Grant of Sichuan Province Science and Technology Agency Grant [2019YJ0487].
Acknowledgments
Figures were created with ©BioRender - biorender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
| COVID-19 | coronavirus disease 2019 |
| RNAse R | ribonuclease R |
| SARS-CoV-2 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 |
| CoVs | coronaviruses |
| PKR | Protein Kinase R |
| RNase L | ribonuclease L |
| NF90 | nuclear factor 90 |
| NF110 | nuclear factor 110 |
| Calu-3 | human lung adenocarcinoma cells |
| SARS-CoV-1 | severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1 |
| MERS-CoV | middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| nsps | nonstructural proteins |
| S | spike |
| E | envelope |
| M | membrane |
| N | nucleocapsid |
| ACE2 | angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| DPP4 | dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| TMPRSS2 | transmembrane serine protease 2 |
| CatB | cathepsin B |
| CatL | cathepsin L |
| AAK1 | AP2-associated kinase 1 |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| TF | transcription factor |
| SIRs | systemic inflammatory responses |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| ncRNAs | non-coding RNAs |
| hpi | hours post-infection |
| ecircRNA | exonic circRNA |
| ciRNA | intronic circRNA |
| EIciRNA | exon-intronic circRNA |
| ceRNA | competing endogenouse RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| lncRNA | long noncoding RNA |
| mRNA | messenger RNA |
| HFL-I | human embryonic lung fibroblast cell |
| ILF3 | human interleukin-enhanced binding factor 3 |
| dsRNA | double-stranded RNA |
| CircRNPs | circRNA-protein complexes |
| RIG-I | retinoic acid inducible gene-I |
| HIF-1 | hypoxia-inducible factor-1 |
| mTOR | mammalian leukemia target of pamycin |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ISG | interferon-stimulated gene |
| IFN | interferon |
| OAS1-3 | 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthase |
| Ifit1-3 | interferon-inducible protein |
| Th1 | T helper cell type 1 |
| 2'-5'A | 2'-5' oligoadenylate |
| PKR | Protein Kinase R |
| RA | arthritic |
| HUVSMCs | human vascular smooth muscle cells |
| HUVECs | human vascular endothelial cells |
| RLRs | RIG-I-like receptors |
| FSJs | forward splicing junctions |
| SRY | sex-determining region Y |
| AXL | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor-kB |
| NOS2 | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| PLpro | papain-like protease |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| RBD | receptor-binding domain |
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.980231/full#supplementary-material
References
- 1. Aleem A, Akbar Samad AB, Slenker AK. Emerging variants of SARS-CoV-2 and novel therapeutics against coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC; (2022). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Torjesen I. Covid-19: Delta variant is now UK's most dominant strain and spreading through schools. BMJ (Clin Res ed) (2021) 373:n1445. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n1445 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Jorgensen SCJ, Kebriaei R, Dresser LD. Remdesivir: Review of pharmacology, pre-clinical data, and emerging clinical experience for COVID-19. Pharmacotherapy (2020) 40(7):659–71. doi: 10.1002/phar.2429 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Gupta A, Gonzalez-Rojas Y, Juarez E, Crespo Casal M, Moya J, Falci DR, et al. Early treatment for covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody sotrovimab. N Engl J Med (2021) 385(21):1941–50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107934 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Lan SH, Lai CC, Huang HT, Chang SP, Lu LC, Hsueh PR. Tocilizumab for severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob agents. (2020) 56(3):106103. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Tomazini BM, Maia IS, Cavalcanti AB, Berwanger O, Rosa RG, Veiga VC, et al. Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: The CoDEX randomized clinical trial. Jama (2020) 324(13):1307–16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Christie A, Brooks JT, Hicks LA, Sauber-Schatz EK, Yoder JS, Honein MA. Guidance for implementing COVID-19 prevention strategies in the context of varying community transmission levels and vaccination coverage. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2021) 70(30):1044–7. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7030e2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Awan FM, Yang BB, Naz A, Hanif A, Ikram A, Obaid A. The emerging role and significance of circular RNAs in viral infections and antiviral immune responses: possible implication as theranostic agents. RNA Biol (2021) 18(1):1–15. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1790198 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Li X, Liu CX, Xue W, Zhang Y, Jiang S, Yin QF, et al. Coordinated circRNA biogenesis and function with NF90/NF110 in viral infection. Mol Cell (2017) 67(2):214–27.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Qu L, Yi Z, Shen Y, Lin L, Chen F, Xu Y, et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell (2022) 185(10):1728–44.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wu Y, Zhao T, Deng R, Xia X, Li B, Wang X. A study of differential circRNA and lncRNA expressions in COVID-19-infected peripheral blood. Sci Rep (2021) 11(1):7991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86134-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Chen YG, Chen R, Ahmad S, Verma R, Kasturi SP, Amaya L, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification controls circular RNA immunity. Mol Cell (2019) 76(1):96–109.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Yan L, Chen YG. Circular RNAs in immune response and viral infection. Trends Biochem Sci (2020) 45(12):1022–34. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Pfafenrot C, Schneider T, Müller C. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus proliferation by designer antisense-circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res (2021) 49(21):12502–16. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1096 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Cai Z, Lu C, He J, Liu L, Zou Y, Zhang Z, et al. Identification and characterization of circRNAs encoded by MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Briefings Bioinf (2021) 22(2):1297–308. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa334 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Yang M, Qi M, Xu L, Huang P, Wang X, Sun J, et al. Differential host circRNA expression profiles in human lung epithelial cells infected with SARS-CoV-2. Infect Genet Evol J Mol Epidemiol evol. Genet Infect Dis. (2021) 93:104923. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yang S, Zhou H, Liu M, Jaijyan D, Cruz-Cosme R, Ramasamy S, et al. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV encode circular RNAs of spliceosome-independent origin. J Med virol. (2022) 94(7):3203–22. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Zhang X, Chu H, Wen L, Shuai H, Yang D, Wang Y, et al. Competing endogenous RNA network profiling reveals novel host dependency factors required for MERS-CoV propagation. Emerg Microbes Infect (2020) 9(1):733–46. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1738277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Zhang X, Chu H. hnRNP c modulates MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replication by governing the expression of a subset of circRNAs and cognitive mRNAs. Emerg Microbes Infect (2022) 11(1):519–31. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2032372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Seephetdee C, Bhukhai K, Buasri N, Leelukkanaveera P, Lerdwattanasombat P, Manopwisedjaroen S, et al. A circular mRNA vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X spike confers a broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by mouse sera. Antiviral Res (2022) 204:105370. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Zhou Z, Sun B, Huang S, Zhao L. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis (2019) 10(7):503. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1744-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Rahman N, Basharat Z. Virtual screening of natural products against type II transmembrane serine protease (TMPRSS2), the priming agent of coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Molecules (2020) 25(10):2271. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Cheever FS, Daniels JB, Pappenheimer AM, Bailey OT. A murine virus (JHM) causing disseminated encephalomyelitis with extensive destruction of myelin. J Exp Med (1949) 90(3):181–210. doi: 10.1084/jem.90.3.181 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Yang Y, Xiao Z, Ye K, He X, Sun B, Qin Z, et al. SARS-CoV-2: characteristics and current advances in research. Virol J (2020) 17(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01369-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Fehr AR, Perlman S. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton NJ) (2015) 1282:1–23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhou P, Yang X-L, Wang X-G, Hu B, Zhang L, Zhang W, et al. Discovery of a novel coronavirus associated with the recent pneumonia outbreak in humans and its potential bat origin. bioRxiv preprint server Biol (2020) 22:914952. doi: 10.1101/2020.01.22.914952 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Cascella M, Rajnik M, Aleem A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL: StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC; (2022). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lu R, Wang Y, Wang W, Nie K, Zhao Y, Su J, et al. Complete genome sequence of middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) from the first imported MERS-CoV case in China. Genome announc (2015) 3(4):e00818–15. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00818-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wu A, Peng Y, Huang B, Ding X, Wang X, Niu P, et al. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe (2020) 27(3):325–8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. van Boheemen S, de Graaf M, Lauber C, Bestebroer TM, Raj VS, Zaki AM, et al. Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. mBio (2012) 3(6):e00473–12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00473-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS, Li F. Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus. J Virol (2020) 94(7):e00127-20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00127-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gierer S, Bertram S, Kaup F, Wrensch F, Heurich A, Krämer-Kühl A, et al. The spike protein of the emerging betacoronavirus EMC uses a novel coronavirus receptor for entry, can be activated by TMPRSS2, and is targeted by neutralizing antibodies. J virol. (2013) 87(10):5502–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00128-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Shang J, Wan Y, Luo C, Ye G, Geng Q, Auerbach A. Cell entry mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2020) 117(21):11727–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2003138117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Leung GM, Hedley AJ, Ho LM, Chau P, Wong IO, Thach TQ, et al. The epidemiology of severe acute respiratory syndrome in the 2003 Hong Kong epidemic: an analysis of all 1755 patients. Ann Internal Med (2004) 141(9):662–73. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-141-9-200411020-00006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Wölfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Müller MA, et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature (2020) 581(7809):465–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2196-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Richardson P, Griffin I, Tucker C, Smith D, Oechsle O, Phelan A, et al. Baricitinib as potential treatment for 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease. Lancet (London England) (2020) 395(10223):e30–1. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30304-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Owen DR, Allerton CMN. An oral SARS-CoV-2 m(pro) inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science (2021) 374(6575):1586–93. doi: 10.1126/science.abl4784 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. V'Kovski P, Kratzel A, Steiner S, Stalder H. Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2. Nat Rev Microbiol (2021) 19(3):155–70. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Yoo JS, Sasaki M. SARS-CoV-2 inhibits induction of the MHC class I pathway by targeting the STAT1-IRF1-NLRC5 axis. Nat Commun (2021) 12(1):6602. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26910-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Rha MS, Jeong HW, Ko JH, Choi SJ, Seo IH, Lee JS, et al. PD-1-Expressing SARS-CoV-2-Specific CD8(+) T cells are not exhausted, but functional in patients with COVID-19. Immunity (2021) 54(1):44–52.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.12.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Saini SK, Hersby DS, Tamhane T. SARS-CoV-2 genome-wide T cell epitope mapping reveals immunodominance and substantial CD8(+) T cell activation in COVID-19 patients. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(58):eabf7550. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf7550 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Aschman T, Schneider J, Greuel S, Meinhardt J, Streit S, Goebel HH, et al. Association between SARS-CoV-2 infection and immune-mediated myopathy in patients who have died. JAMA Neurol (2021) 78(8):948–60. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Poluektov Y, George M, Daftarian P, Delcommenne MC. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 specific CD4(+) and CD8 (+) T cell responses using MHC class I and II tetramers. Vaccine (2021) 39(15):2110–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Taher I, Almaeen A, Ghazy A, Abu-Farha M, Mohamed Channanath A, Elsa John S, et al. Relevance between COVID-19 and host genetics of immune response. Saudi J Biol Sci (2021) 28(11):6645–52. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.07.037 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Sáez JJ, Lennon-Duménil AM, Yuseff MI. Studying MHC class II presentation of immobilized antigen by b lymphocytes. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton NJ). (2019) 1988:419–37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9450-2_29 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Obermair FJ, Renoux F, Heer S. High-resolution profiling of MHC II peptide presentation capacity reveals SARS-CoV-2 CD4 T cell targets and mechanisms of immune escape. Sci Adv (2022) 8(17):eabl5394. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl5394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Hyun YS, Lee YH, Jo HA, Baek IC, Kim SM, Sohn HJ, et al. Comprehensive analysis of CD4(+) T cell response cross-reactive to SARS-CoV-2 antigens at the single allele level of HLA class II. Front Immunol (2021) 12:774491. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.774491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Hur S. Double-stranded RNA sensors and modulators in innate immunity. Annu Rev Immunol (2019) 37:349–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042718-041356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Fung SY, Yuen KS. A tug-of-war between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and host antiviral defence: lessons from other pathogenic viruses. Emerg Microbes Infect (2020) 9(1):558–70. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1736644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Meyer B, Chiaravalli J, Gellenoncourt S. Characterising proteolysis during SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies viral cleavage sites and cellular targets with therapeutic potential. Nat Commun (2021) 12(1):5553. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25796-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Upton JW, Chan FK. Staying alive: cell death in antiviral immunity. Mol Cell (2014) 54(2):273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Hui DSC, Zumla A. Severe acute respiratory syndrome: Historical, epidemiologic, and clinical features. Infect Dis Clinics N Am (2019) 33(4):869–89. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2019.07.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Du WW, Fang L, Yang W, Wu N, Awan FM, Yang Z, et al. Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ (2017) 24(2):357–70. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2016.133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Zhang Z, Yang T, Xiao J. Circular RNAs: Promising biomarkers for human diseases. EBioMedicine (2018) 34:267–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Firoozi Z, Mohammadisoleimani E. Hsa_circ_0000479/Hsa-miR-149-5p/RIG-I, IL-6 axis: A potential novel pathway to regulate immune response against COVID-19. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol (2022) 2022:2762582. doi: 10.1155/2022/2762582 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Barbagallo D, Palermo CI, Barbagallo C, Battaglia R, Caponnetto A, Spina V, et al. Competing endogenous RNA network mediated by circ_3205 in SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS (2022) 79(2):75. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04119-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Barrett SP, Wang PL, Salzman J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. eLife (2015) 4:e07540. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07540 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol (2014) 32(5):453–61. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2890 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PloS Genet (2013) 9(9):e1003777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T, Epstein I, Tushev G, et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci (2015) 18(4):603–10. doi: 10.1038/nn.3975 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature (2013) 495(7441):384–8. doi: 10.1038/nature11993 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell (2011) 146(3):353–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature (2013) 495(7441):333–8. doi: 10.1038/nature11928 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Thomas LF, Sætrom P. Circular RNAs are depleted of polymorphisms at microRNA binding sites. Bioinf (Oxford England) (2014) 30(16):2243–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Arora S, Singh P, Dohare R, Jha R, Ali Syed M. Unravelling host-pathogen interactions: ceRNA network in SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). Gene (2020) 762:145057. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Qin Z, Wang PY, Su DF, Liu X. miRNA-124 in immune system and immune disorders. Front Immunol (2016) 7:406. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Cadena C, Hur S. Antiviral immunity and circular RNA: No end in sight. Mol Cell (2017) 67(2):163–4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.07.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Wang M, Yu F, Wu W, Zhang Y, Chang W, Ponnusamy M, et al. Circular RNAs: A novel type of non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral immunity. Int J Biol Sci (2017) 13(12):1497–506. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.22531 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Chen YG, Kim MV, Chen X, Batista PJ, Aoyama S, Wilusz JE, et al. Sensing self and foreign circular RNAs by intron identity. Mol Cell (2017) 67(2):228–38.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.022 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Appelberg S, Gupta S, Svensson Akusjärvi S, Ambikan AT, Mikaeloff F, Saccon E, et al. Dysregulation in Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 signaling identified by proteo-transcriptomics of SARS-CoV-2 infected cells. Emerg Microbes Infect (2020) 9(1):1748–60. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1799723 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Fajgenbaum DC, June CH. Cytokine storm. (2020) 383(23):2255–73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2026131 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Coperchini F, Chiovato L, Croce L, Magri F, Rotondi M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev (2020) 53:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Alcami A. Viral mimicry of cytokines, chemokines and their receptors. Nat Rev Immunol (2003) 3(1):36–50. doi: 10.1038/nri980 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Lieberman NAP, Peddu V. In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age. PLoS Biol (2020) 18(9):e3000849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Hertzog PJ. Overview. type I interferons as primers, activators and inhibitors of innate and adaptive immune responses. immunology and cell biology. Immunol Cell Biol (2012) 90(5):471–3. doi: 10.1038/icb.2012.15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Liu CX, Li X, Nan F, Jiang S, Gao X, Guo SK, et al. Structure and degradation of circular RNAs regulate PKR activation in innate immunity. Cell (2019) 177(4):865–80.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Chousterman BG, Swirski FK, Weber GF. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin Immunopathol (2017) 39(5):517–28. doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0639-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Fagone P, Ciurleo R, Lombardo SD, Iacobello C, Palermo CI, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Transcriptional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection dismantles pathogenic pathways activated by the virus, proposes unique sex-specific differences and predicts tailored therapeutic strategies. Autoimmun Rev (2020) 19(7):102571. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102571 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Shen L, Hu Y, Lou J, Yin S, Wang W, Wang Y, et al. CircRNA−0044073 is upregulated in atherosclerosis and increases the proliferation and invasion of cells by targeting miR−107. Mol Med Rep (2019) 19(5):3923–32. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Wang R, Zhang Y, Xu L, Lin Y, Yang X, Bai L, et al. Protein inhibitor of activated STAT3 suppresses oxidized LDL-induced cell responses during atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein e-deficient mice. Sci Rep (2016) 6:36790. doi: 10.1038/srep36790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. García-Howard M, Herranz-Aguirre M, Moreno-Galarraga L, Urretavizcaya-Martínez M, Alegría-Echauri J, Gorría-Redondo N, et al. Case report: Benign infantile seizures temporally associated with COVID-19. Front Pediatr (2020) 8:507. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. McClelland S, Dubé CM, Yang J, Baram TZ. Epileptogenesis after prolonged febrile seizures: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic opportunities. Neurosci Letters (2011) 497(3):155–62. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.02.032 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Yang J, Cheng M, Gu B, Wang J, Yan S, Xu D. CircRNA_09505 aggravates inflammation and joint damage in collagen-induced arthritis mice via miR-6089/AKT1/NF-κB axis. Cell Death Dis (2020) 11(10):833. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03038-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Khan S, Shafiei MS, Longoria C, Schoggins JW. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway. Elife (2021) 10. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68563 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Wu Y, Ma L, Cai S, Zhuang Z, Zhao Z, Jin S. RNA-Induced liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein facilitates NF-κB hyper-activation and inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther (2021) 6(1):167. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00575-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Ma Q, Li R, Pan W, Huang W, Liu B, Xie Y, et al. Phillyrin (KD-1) exerts anti-viral and anti-inflammatory activities against novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronavirus 229E (HCoV-229E) by suppressing the nuclear factor kappa b (NF-κB) signaling pathway. Phytomedicine (2020) 78:153296. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153296 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Neufeldt CJ, Cerikan B, Cortese M, Frankish J, Lee JY, Plociennikowska A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a pro-inflammatory cytokine response through cGAS-STING and NF-κB. Commun Biol (2022) 5(1):45. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02983-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Giron LB, Peluso MJ, Ding J, Kenny G, Zilberstein NF, Koshy J, et al. Markers of fungal translocation are elevated during post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 and induce NF-κB signaling. JCI Insight (2022) 7(18):e164813. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.160989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Li G, Fan Y. Coronavirus infections and immune responses. (2020) 92(4):424–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Shapiro JS, Schmid S, Aguado LC, Sabin LR, Yasunaga A, Shim JV, et al. Drosha as an interferon-independent antiviral factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2014) 111(19):7108–13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319635111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Weisblum Y, Schmidt F. Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants. Elife (2020) 9:e61312. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61312 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Zaffagni M, Harris JM, Patop IL, Pamudurti NR, Nguyen S, Kadener S. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 mediates the effects of viral infection on the host cell transcriptome. bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology. bioRxiv [Preprint] (2022) 2021.07.02.450964. doi: 10.1101/2021.07.02.450964 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Ogando NS, Zevenhoven-Dobbe JC, van der Meer Y, Bredenbeek PJ, Posthuma CC. The enzymatic activity of the nsp14 exoribonuclease is critical for replication of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. (2020) 94(23):93. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01246-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol (2001) 1(2):135–45. doi: 10.1038/35100529 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Guan H, Wang Y, Perčulija V, Saeed A, Liu Y, Li J, et al. Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein provides insights into evolution of unique coronavirus spike proteins. J Virol (2020) 94(22):e01301–20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01301-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Zaffagni M, Harris JM, Patop IL, Pamudurti NR, Nguyen S, Kadener S. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 mediates the effects of viral infection on the host cell transcriptome. (2022) 11:e71945. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Hassanin A, Rambaud O, Klein D. Genomic bootstrap barcodes and their application to study the evolution of sarbecoviruses. Viruses (2022) 14(2):440. doi: 10.3390/v14020440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Yang S, Zhou H. Circular RNA profiling reveals abundant and diverse circRNAs of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV origin. bioRxiv [Preprint] (2020) 2020.12.07.415422. doi: 10.1101/2020.12.07.415422 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Liu Z, Zhang X, Yu Q, He JJ. Exosome-associated hepatitis c virus in cell cultures and patient plasma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun (2014) 455(3-4):218–22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Kerr CH, Dalwadi U, Scott NE. Transmission of cricket paralysis virus via exosome-like vesicles during infection of drosophila cells. Sci Rep (2018) 8(1):17353. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35717-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Elrashdy F, Aljaddawi AA, Redwan EM. On the potential role of exosomes in the COVID-19 reinfection/reactivation opportunity. J Biomol Struct Dyn (2021) 39(15):5831–42. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1790426 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Sun J, Ye F, Wu A, Yang R, Pan M, Sheng J, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the intensive early stage responses of host cells to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Front Microbiol (2020) 11:593857. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.593857 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y, Zhang J, Huang L, Zhang C, et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med (2020) 8(4):420–2. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(20)30076-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Milsted A, Underwood AC, Dunmire J, DelPuerto HL, Martins AS, Ely DL, et al. Regulation of multiple renin-angiotensin system genes by sry. J Hypertens (2010) 28(1):59–64. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328332b88d [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Wang D LD. Bioinformatics analysis of ACE2 gene promoter Region,SARS-CoV-2 key receptor. J Natural Sci Hunan Normal Univ (2020) 43(5):30. doi: 10.7612/j.issn.2096-5281.2020.05.005 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, et al. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene sry in adult mouse testis. Cell (1993) 73(5):1019–30. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90279-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Granados-Riveron JT, Aquino-Jarquin G. Does the linear sry transcript function as a ceRNA for miR-138? the sense of antisense. F1000Research (2014) 3:90. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.3872.2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Li S, Liu J, Liu S, Jiao W, Wang X. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles prevent the development of osteoarthritis via the circHIPK3/miR-124-3p/MYH9 axis. J Nanobiotechnol (2021) 19(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00940-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Zhang W, Zhang H, Zhao X. circ_0005273 promotes thyroid carcinoma progression by SOX2 expression. Endocr-related Cancer (2020) 27(1):11–21. doi: 10.1530/erc-19-0381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Zhang P, Li J. Down-regulation of circular RNA hsa_circ_0007534 suppresses cell growth by regulating miR-219a-5p/SOX5 axis in osteosarcoma. J Bone Oncol (2021) 27:100349. doi: 10.1016/j.jbo.2021.100349 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Bohan D, Van Ert H. Phosphatidylserine receptors enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS Pathog (2021) 17(11):e1009743. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009743 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Wei Y LWY, Fan RG, Hou W, Wen SJ, Lin YK. Preliminary study on the molecular mechanism of circRNA hsa-circ-0006689 in systemic lu-pus erythematosus. J Guangxi Med Univ (2021) 38(3):486–92. doi: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2021.03.011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Getts DR, Chastain EM, Terry RL, Miller SD. Virus infection, antiviral immunity, and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev (2013) 255(1):197–209. doi: 10.1111/imr.12091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Xue M, Del Bigio MR. Intracortical hemorrhage injury in rats : relationship between blood fractions and brain cell death. Stroke (2000) 31(7):1721–7. doi: 10.1161/01.str.31.7.1721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Masuda K, Kishimoto T. Regulation of IL-6 in immunity and diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol (2016) 941:79–88. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0921-5_4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. van den Berg DF, Te Velde AA. Severe COVID-19: NLRP3 inflammasome dysregulated. Front Immunol (2020) 11:1580. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01580 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Hariharan A, Hakeem AR. The role and therapeutic potential of NF-kappa-B pathway in severe COVID-19 patients. Inflammopharmacology (2021) 29(1):91–100. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Kircheis R, Haasbach E, Lueftenegger D, Heyken WT, Ocker M, Planz O. NF-κB pathway as a potential target for treatment of critical stage COVID-19 patients. Front Immunol (2020) 11:598444. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.598444 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Cai X, Huang Y, Zhang X, Wang S, Zou Z, Wang G, et al. Cloning, characterization, hypoxia and heat shock response of hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) from the small abalone haliotis diversicolor. Gene (2014) 534(2):256–64. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Sheu SY, Hong YW, Sun JS, Liu MH, Chen CY, Ke CJ. Radix scrophulariae extracts (harpagoside) suppresses hypoxia-induced microglial activation and neurotoxicity. BMC complement Altern Med (2015) 15:324. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0842-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. Tian M, Liu W, Li X, Zhao P, Shereen MA, Zhu C, et al. HIF-1α promotes SARS-CoV-2 infection and aggravates inflammatory responses to COVID-19. Signal Transduct Target Ther (2021) 6(1):308. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00726-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Yang YW, Meng X, Meng YY, Tang HK, Cheng MH, Zhang ZQ, et al. ceRNA regulatory network of FIH inhibitor as a radioprotector for gastrointestinal toxicity by activating the HIF-1 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids (2021) 25:173–85. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.05.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Demirci YM, Saçar Demirci MD. Circular RNA-MicroRNA-MRNA interaction predictions in SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Integr Bioinf (2021) 18(1):45–50. doi: 10.1515/jib-2020-0047 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Harcourt BH, Jukneliene D, Kanjanahaluethai A, Bechill J, Severson KM, Smith CM, et al. Identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replicase products and characterization of papain-like protease activity. J virol. (2004) 78(24):13600–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.24.13600-13612.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Lim KP, Ng LF, Liu DX. Identification of a novel cleavage activity of the first papain-like proteinase domain encoded by open reading frame 1a of the coronavirus avian infectious bronchitis virus and characterization of the cleavage products. J virol. (2000) 74(4):1674–85. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.4.1674-1685.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Mahmoudvand S, Shokri S. Interactions between SARS coronavirus 2 papain-like protease and immune system: A potential drug target for the treatment of COVID-19. Scand J Immunol (2021) 94(4):e13044. doi: 10.1111/sji.13044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Bailey-Elkin BA, Knaap RC, Johnson GG, Dalebout TJ, Ninaber DK, van Kasteren PB, et al. Crystal structure of the middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) papain-like protease bound to ubiquitin facilitates targeted disruption of deubiquitinating activity to demonstrate its role in innate immune suppression. J Biol Chem (2014) 289(50):34667–82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.609644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Ratia K, Saikatendu KS, Santarsiero BD, Barretto N, Baker SC, Stevens RC, et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus papain-like protease: structure of a viral deubiquitinating enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci United States America. (2006) 103(15):5717–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510851103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Kindrachuk J, Ork B, Hart BJ, Mazur S. Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (2015) 59(2):1088–99. doi: 10.1128/aac.03659-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Di Liddo A, de Oliveira Freitas Machado C, Fischer S, Ebersberger S, Heumüller AW, Weigand JE, et al. A combined computational pipeline to detect circular RNAs in human cancer cells under hypoxic stress. J Mol Cell Biol (2019) 11(10):829–44. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjz094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Zarnack K, König J, Tajnik M, Martincorena I, Eustermann S, Stévant I, et al. Direct competition between hnRNP c and U2AF65 protects the transcriptome from the exonization of alu elements. Cell (2013) 152(3):453–66. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.12.023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Meißner T. MMW fortschritte der medizin. (2021) 163(14):64. doi: 10.1007/s15006-021-0196-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Sprute R, Schumacher S, Pauls M, Pauls W, Cornely OA. Delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity reaction to vaxzevria (ChAdOx1-s) vaccine against SARS-CoV-2. Drugs RD (2021) 21(4):371–4. doi: 10.1007/s40268-021-00358-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Knoll MD, Wonodi C. Oxford-AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine efficacy. Lancet (London England) (2021) 397(10269):72–4. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32623-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Sadoff J, Le Gars M, Shukarev G, Heerwegh D, Truyers C, de Groot AM, et al. Interim results of a phase 1-2a trial of Ad26. COV2.S Covid-19 Vaccine (2021) 384(19):1824–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2034201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Hammerschmidt SI, Thurm C, Bošnjak B, Bernhardt G. Robust induction of neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 delta variant after homologous spikevax or heterologous vaxzevria-spikevax vaccination. (2022) 52(2):356–9. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Wang H, Zhang Y, Huang B, Deng W, Quan Y, Wang W, et al. Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate, BBIBP-CorV, with potent protection against SARS-CoV-2. Cell (2020) 182(3):713–21.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Sharma O, Sultan AA, Ding H, Triggle CR. A review of the progress and challenges of developing a vaccine for COVID-19. frontiers in immunology. Front Immunol (2020) 11:585354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.585354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Thiagarajan K. What do we know about india's covaxin vaccine? BMJ (2021) 373:n997. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Chung YH, Beiss V, Fiering SN, Steinmetz NF. COVID-19 vaccine frontrunners and their nanotechnology design. ACS Nano (2020) 14(10):12522–37. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07197 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Jones I, Roy P. Sputnik V COVID-19 vaccine candidate appears safe and effective. Lancet (London England) (2021) 397(10275):642–3. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(21)00191-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Akova M, Unal S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (inactivated, vero cell): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials (2021) 22(1):276. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05180-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Wu S, Huang J, Zhang Z, Wu J, Zhang J, Hu H, et al. Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an aerosolised adenovirus type-5 vector-based COVID-19 vaccine (Ad5-nCoV) in adults: preliminary report of an open-label and randomised phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis (2021) 21(12):1654–64. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00396-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Francica JR, Flynn BJ, Foulds KE, Noe AT, Werner AP, Moore IN, et al. Vaccination with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and AS03 adjuvant induces rapid anamnestic antibodies in the lung and protects against virus challenge in nonhuman primates. bioRxiv preprint server Biol (2021). doi: 10.1101/2021.03.02.433390 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Ambrosino D, Han HH, Hu B, Liang J, Clemens R, Johnson M, et al. Immunogenicity of SCB-2019 coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine compared with 4 approved vaccines. J Infect Dis (2022) 225(2):327–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab574 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Liu H, Zhou C, An J, Song Y, Yu P, Li J, et al. Development of recombinant COVID-19 vaccine based on CHO-produced, prefusion spike trimer and alum/CpG adjuvants. Vaccine (2021) 39(48):7001–11. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.10.066 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Baker N, Dolgin E. Coronapod: CureVac disappoints in COVID vaccine trial. Nature (2021). doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-01694-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Hadj Hassine I. Covid-19 vaccines and variants of concern: A review. Rev Med Virol (2021) 32(4):e2313. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Aguilar-Guerra TL, Fajardo-Díaz EM. Cuba's national regulatory authority & COVID-19: Olga lidia jacobo-casanueva MS director, center for state control of medicines and medical devices (CECMED). MEDICC Rev (2021) 23(3-4):9–14. doi: 10.37757/mr2021.v23.n3.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Patiño C, Haenni AL, Urcuqui-Inchima S. NF90 isoforms, a new family of cellular proteins involved in viral replication? Biochimie (2015) 108:20–4. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.10.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet (2019) 20(11):675–91. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, Sas-Chen A, Ulitsky I, Yarden Y. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res (2016) 44(3):1370–83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153. Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell (2017) 66(1):9–21.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.02.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154. Wesselhoeft RA, Kowalski PS, Anderson DG. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nat Commun (2018) 9(1):2629. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05096-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155. Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang Y, et al. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N(6)-methyladenosine. Cell Res (2017) 27(5):626–41. doi: 10.1038/cr.2017.31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156. Breuer J, Barth P, Noe Y, Shalamova L, Goesmann A, Weber F, et al. What goes around comes around: Artificial circular RNAs bypass cellular antiviral responses. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids (2022) 28:623–35. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.04.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.