Fig. 5.
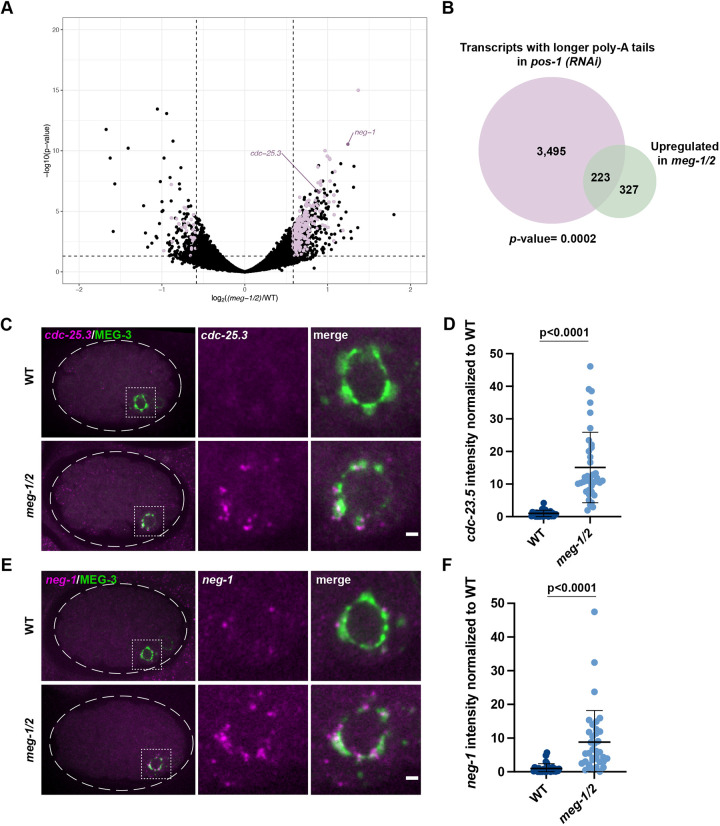
meg-1/2 are required for the turnover of a subset of POS-1 targets. (A) RNA-seq from two independent experiments comparing meg-1 meg-2 (RNAi) and wild-type embryos identified 230 downregulated and 550 upregulated genes (±1.5 fold change). Purple dots correspond to genes significantly down/upregulated in meg-1 meg-2 embryos that also exhibited longer poly-A tails in pos-1(RNAi) embryos (Elewa et al., 2015). (B) A total of 223 genes upregulated in meg-1 meg-2 embryos overlap with genes with poly-A tails extended in pos-1(RNAi) embryos. P=0.0002 (Fisher's exact test; Materials and Methods). (C,E) Photomicrographs of cdc-25.3 and neg-1 smFISH in embryos expressing the P granule marker MEG-3::GFP. Inset shows P4. cdc-25.3 and neg-1 are turned over less efficiently in meg-1 meg-2 P4 blastomeres. Dashed white line indicates embryo boundary. Dashed square indicates P4. (D,F) Intensity of cdc-25.3 and neg-1 in P4 normalized to wild type. In situs for cdc-25.3 and neg-1 were done in the same embryos in two independent experiments in which mutant and control animals were processed in parallel. Wild type n=29; meg-1/2 n=38. Data are mean±s.d. Unpaired two-tailed t-test was used to make comparisons between genotypes. Scale bars: 1 µm.