Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to explore the distribution differences of common risk factors between coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke in China.
Setting
The China National Stroke Screening Survey is a cluster sampling survey based on a nationwide general community population, adopting multistage stratified sampling method and covering all 31 provinces in China mainland.
Participants
A total number of 725 707 people aged 40 years and above were included in the study.
Primary and secondary outcome measures
The basic demographic information, lifestyle behaviour, physical examination, traditional risk factors, family history of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and CVD events were collected. Risk factors of CHD and stroke were explored and analysed in the whole investigated population to identify the common risk factors. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to analyse the distribution difference of risk factors between CHD and stroke.
Results
There were 13 variables associated with CHD and stroke, in which 11 variables revealed differences in the distribution between CHD and stroke. Family history of stroke (OR: 2.30; 95% CI 2.15 to 2.45), men (OR: 1.92; 95% CI 1.80 to 2.05), rural areas (OR: 1.70; 95% CI 1.60 to 1.80), transient ischaemic attack (OR: 1.41; 95% CI 1.30 to 1.54) and hypertension (OR: 1.28; 95% CI 1.19 to 1.38) indicated significantly stronger association with stroke, while family history of CHD (OR: 0.25; 95% CI 0.23 to 0.27), atrial fibrillation (OR: 0.60; 95% CI 0.51 to 0.71), diabetes (OR: 0.76; 95% CI 0.71 to 0.81), dyslipidaemia (OR: 0.76; 95% CI 0.72 to 0.81), smoking (OR: 0.79; 95% CI 0.73 to 0.85) and overweight/obesity (OR: 0.90; 95% CI 0.86 to 0.93) had closer relationship with CHD.
Conclusions
The distribution of risk factors for CHD and stroke were substantial differences. More specific prevention and control measures should be formulated according to the distribution differences of risk factors related to CVD.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease, Stroke, Cardiac Epidemiology, EPIDEMIOLOGY, PUBLIC HEALTH
Strengths and limitations of this study.
The China National Stroke Screening Survey is a nationwide cross-sectional study based on general community population.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke had many common risk factors, while the distribution of specific risk factors between CHD and stroke were substantial differences.
More specific prevention and control measures should be formulated according to the distribution differences of risk factors related to cardiovascular disease.
Introduction
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in China and worldwide.1 2 Previous studies have shown the significant regional and ethnic differences in the incidence and mortality of CVD.3–6 For example, coronary heart disease (CHD) is the leading cause of death in most Western countries, while stroke is more common in China.4–6 The distributional differences of specific risk factors for different CVD types may be an important reason for this phenomenon. To clarify the relationship between different risk factors and the first manifestation of CVD can help us better understand the pathophysiological mechanism of different CVD as well as the potential benefits of controlling these risk factors.
Many previous studies have considered the CHD and stroke as a whole to explore common risk factors of both.7–9 Only a few studies investigated the differences of risk factors between CHD and stroke in a same cohort,10–14 some of which just enrolled male or female populations,10 11 or only reported the difference of a single risk factor12 or conducted based on a small sample size.14 There is still lack of large sample size, representative population-based research about whether differences exist in the distribution of risk factors between CHD and stroke. The China National Stroke Screening Survey (CNSSS) is a nationwide cross-sectional study based on general community population. By analysing the data collected from the CNSSS, this study aimed to explore the specific common risk factors of CHD and stroke and whether there are differences in the distribution of these specific risk factors between CHD and stroke.
Materials and methods
Study design
The CNSSS is a cluster sampling survey based on a nationwide general community population, adopting multistage stratified sampling method and covering all 31 provinces in China mainland. The initial stages of CNSSS had been described in our previous publications.15–19
The CNSSS used a third-stage stratified cluster sampling method. In the first stage, 128 prefecture-level cities were selected by 31 provinces according to the different proportion of the Sixth National Population Census of China in 2010. In the second stage, one urban street and one rural town were selected from each prefecture-level city, respectively. In the third stage, an urban community and a rural village were selected from each urban street and rural town. All residents aged 40 years or older were surveyed during the primary screening, and the response rate of each place was required to be no less than 85%. Ultimately, 828 764 subjects from 256 communities and villages participated in the survey, each of whom signed a written informed consent.
Data collection
A questionnaire survey which conducted by trained staff was performed based on the population aged 40 and above in the sampled communities and towns by adopting the unified epidemiological survey scale of CVD. The project developed a data reporting information platform, in which the information of the paper questionnaire was reported uniformly by trained staff of each subcentre. The following variables were analysed for the present study: (1) basic demographic information: sex, age and place of residence; (2) lifestyle behaviours: smoking, alcohol consumption and exercise; (3) physical examination: blood pressure, height, weight, body mass index (BMI); (4) traditional risk factors: hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidaemia, atrial fibrillation (AF), transient ischaemic attack (TIA), family history of CHD or stroke, (5) CVD events: CHD, stroke.
Definition of CVDs and risk factors
Stroke was diagnosed by a combination of self-reported history, medical records and the judgement of professional doctors according to WHO criteria. The diagnosis of CHD included history of angina pectoris, myocardial infarction as well as previous history of coronary artery bypass grafting or stent implantation and be confirmed by a specialist. Blood pressure, fasting blood sugar, fasting blood lipids and BMI were measured on site for all survey subjects.19 20 Hypertension was diagnosed by self-reported history of hypertension, or current use of antihypertensive drugs within 2 weeks or elevated blood pressure (systolic pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic pressure ≥90 mm Hg) in the onsite measurement.16 Diabetes was diagnosed by self-report history of diabetes, or current use of hypoglycaemic drugs or fasting blood glucose ≥7.0 mmol/L in the onsite measurement.17 Dyslipidaemia was diagnosed by self-reported history of dyslipidaemia, or current use of lipid-lowering drugs or the detection of one or more of the following status (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL, triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL, High density lipoprotein <40 mg/dL) in the onsite measurement.17 AF was diagnosed by self-reported history of AF, or previous ECG support or the detection of AF indicated in ECG in the onsite measurement.18 BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in metres squared. Overweight was defined as 24 ≤BMI <28, and obesity was defined as BMI ≥28.16 Smoking was defined as one cigarette per day for at least 3 consecutive months. Regular drinking was defined as drinking at least three times per week with the consumption of alcohol more than 100 g. Lack of exercise was defined as weekly exercise less than three times the intensity of moderate and above exercise ≥30 min. Exercise lack is defined as moderate or higher intensity exercise no less than three times per week, no less than 30 min each time.
Quality control
The National Health and Family Planning Commission had established a special project office responsible for the quality control, organisation and coordination of the project. First, this study conducted a unified training for all personnel involved in questionnaire survey, physical examination and data entry. The training course was divided into two steps below: the provincial training was responsible by the project office, and the training of participating units in the province was managed by provincial units. In the onsite survey, each subcentre had a trained staff, usually a neurologist, responsible for the review and reporting of data. Second, the data reporting information platform could realise automatic control of the system, systematic checking of necessary items and questionnaires with unfinished or incomplete items could not be submitted successfully. Third, epidemiologists and statistical experts were organised by the project office to analyse the data reported by the subcentres, who were responsible for checking abnormal data and returning to the subcentres for one-by-one review.
Patient and public involvement
Patients were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting or dissemination plans of our research.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was carried out in two steps. First, risk factors of CHD and stroke were explored and analysed in the whole investigated population to identify the common risk factors. Second, people with both CHD and stroke were excluded as well as those neither with CHD nor with stroke, we just took the samples only with CHD and the samples only with stroke as our analysis population, then taking CVD as dependent variables (stroke was defined as 1, whereas CHD was defined as 0) and the common risk factors as independent variables, multivariate logistic regression analysis was carried out to study the distribution difference of the common risk factors between CHD and stroke.
Descriptive analysis was performed for baseline information. Categorical variables were expressed as n (%), and continuous variables were presented in the form of mean±SD. 2 test and t test were used for univariate analysis of categorical variables and continuous variables, and the differences were statistically significant with p<0.1. Binary, logistic regression was used for multivariate analysis, the OR and 95% CI were calculated by backward stepwise regression, and the difference was statistically significant with p<0.05. SPSS V.19.0 was used for all statistical analyses (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois).
Results
Basic information
A total of 828 764 permanent residents in general communities aged 40 and above completed the survey from May 2014 to April 2015. Of these, we excluded data from project areas with a response rate less than 85%, incomplete baseline information and abnormal data. Finally, 725 707 people were included in the study. The average age was 57.23±11.40 years, with men accounting for 46.73% and the rural population accounting for 52.55% of the total. All variables had sex difference except BMI. To be specific, the rates of smoking and drinking of men were significantly higher than those of women, whereas there was an opposite relationship in other variables. Furthermore, except hypertension, all variables revealed geographical difference. The proportion of smoking and drinking in rural areas was higher than that in urban areas, and the proportion of other variables in urban areas was higher than that in rural areas (table 1).
Table 1.
General characteristics of the CNSSS
| Characteristics | Total, n (%) | Sex, n (%) | Region, n (%) | P value for sex | P value for region | ||
| Female | Male | Urban | Rural | ||||
| Age, years | 57.23±11.40 | 57.40±11.38 | 57.03±11.41 | 57.26±11.50 | 57.20±11.30 | <0.001 | 0.029 |
| 40~ | 224 173 (30.89) | 115 964 (30.00) | 108 209 (31.91) | 106 788 (31.01) | 117 385 (30.78) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 50~ | 213 000 (29.35) | 115 023 (29.76) | 97 977 (28.89) | 101 240 (29.40) | 111 760 (29.31) | ||
| 60~ | 172 780 (23.81) | 93 393 (24.16) | 79 387 (23.41) | 79 411 (23.06) | 93 369 (24.48) | ||
| 70~ | 86 475 (11.92) | 46 161 (11.94) | 40 314 (11.89) | 42 716 (12.41) | 43 759 (11.47) | ||
| 80~ | 29 279 (4.03) | 16 018 (4.14) | 13 261 (3.91) | 14 188 (4.12) | 15 091 (3.96) | ||
| Height, cm | 162.96±8.12 | 158.26±6.31 | 168.31±6.48 | 163.95±7.91 | 162.06±8.20 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Weight, kg | 63.63±10.04 | 59.94±8.87 | 67.83±9.63 | 64.69±9.99 | 62.66±9.98 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.91±3.04 | 23.92±3.20 | 23.90±2.85 | 24.02±3.00 | 23.81±3.07 | 0.130 | <0.001 |
| <18.5 | 16 308 (2.25) | 10 052 (2.60) | 6256 (1.84) | 6913 (2.01) | 9395 (2.46) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 18.5~24 | 380 043 (52.37) | 201 371 (52.09) | 178 672 (52.68) | 174 900 (50.79) | 205 143 (53.79) | ||
| 24~28 | 264 385 (36.43) | 136 843 (35.40) | 127 542 (37.61) | 131 176 (38.09) | 133 209 (34.93) | ||
| ≥28 | 64 971 (8.95) | 38 293 (9.91) | 26 678 (7.87) | 31 354 (9.11) | 33 617 (8.81) | ||
| Smoking | 47 997 (6.61) | 4163 (1.08) | 43 834 (12.92) | 20 223 (5.87) | 27 774 (7.28) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Regular drinking | 24 939 (3.44) | 2148 (0.56) | 22 791 (6.72) | 11 574 (3.36) | 13 365 (3.50) | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| Lack of exercise | 59 712 (8.23) | 33 104 (8.56) | 26 608 (7.85) | 31 722 (9.21) | 27 990 (7.34) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 121 281 (16.71) | 65 681 (16.99) | 55 600 (16.39) | 57 538 (16.71) | 63 743 (16.71) | <0.001 | 0.955 |
| Diabetes | 39 752 (5.48) | 22 283 (5.76) | 17 469 (5.15) | 21 770 (6.32) | 17 982 (4.72) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 113 159 (15.59) | 62 817 (16.25) | 50 342 (14.84) | 56 793 (16.55) | 56 186 (14.73) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AF | 2783 (0.38) | 1636 (0.42) | 1147 (0.34) | 1433 (0.42) | 1350 (0.35) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| TIA | 13 284 (1.83) | 8199 (2.12) | 5085 (1.50) | 6707 (1.95) | 6577 (1.72) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 13 077 (1.80) | 7947 (2.06) | 5130 (1.51) | 8070 (2.34) | 5007 (1.31) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Family history of stroke | 30 103 (4.15) | 16 987 (4.39) | 13 116 (3.87) | 15 553 (4.52) | 14 550 (3.82) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; CNSSS, China National Stroke Screening Survey; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Common risk factors of CHD and stroke
In the univariate factor analysis, all 14 variables were associated with CHD and stroke (table 2). After adjusting for other risk factors, 13 variables (except alcohol consumption) were associated with CHD and stroke. There was a negative correlation of men and rural population with CHD, while hypertension, family history of CHD, dyslipidaemia, AF, TIA, smoking, diabetes, family history of stroke, age, lack of exercise, overweight/obesity and alcohol consumption were positively correlated with CHD. Besides, all the 13 risk factors were positively correlated with stroke (table 3). According to the OR value from high to low, figure 1 shows the distribution of risk factors of CHD and stroke.
Table 2.
Univariate analysis of risk factors for CHD and stroke
| Characteristics | CHD, n (%) | Stroke, n (%) | ||||||
| Yes | No | χ2 | P value | Yes | No | χ2 | P value | |
| Total | 10 654 | 715 053 | 15 989 | 709 718 | ||||
| Sex (male) | 4125 (28.72) | 335 023 (46.85) | 279.078 | <0.001 | 8110 (50.72) | 331 038 (46.64) | 104.502 | <0.001 |
| Region (rural) | 4379 (41.10) | 376 985 (52.72) | 568.386 | <0.001 | 8515 (53.26) | 372 849 (52.53) | 3.256 | 0.071 |
| Age | 4657.234 | <0.001 | 6926.216 | <0.001 | ||||
| 40~ | 687 (6.45) | 223 486 (31.25) | 913 (5.71) | 223 260 (31.46) | ||||
| 50~ | 2324 (21.81) | 210 676 (29.46) | 3539 (22.13) | 209 461 (29.51) | ||||
| 60~ | 4209 (39.51) | 168 571 (23.57) | 6644 (41.55) | 166 136 (23.41) | ||||
| 70~ | 2767 (25.97) | 83 708 (11.71) | 3915 (24.49) | 82 560 (11.63) | ||||
| 80~ | 667 (6.26) | 28 612 (4.00) | 978 (6.12) | 28 301 (3.99) | ||||
| BMI | 2767.767 | <0.001 | 2261.651 | <0.001 | ||||
| <18.5 | 207 (1.94) | 16 101 (2.25) | 322 (2.01) | 15 986 (2.25) | ||||
| 18.5~24 | 3420 (32.10) | 376 623 (52.67) | 5875 (36.74) | 374 168 (52.72) | ||||
| 24~28 | 4588 (43.06) | 259 797 (36.33) | 6841 (42.79) | 257 544 (36.29) | ||||
| ≥28 | 2439 (22.89) | 62 532 (8.75) | 2951 (18.46) | 62 020 (8.74) | ||||
| Smoking | 2628 (24.67) | 45 369 (6.34) | 5705.550 | <0.001 | 4416 (27.62) | 43 581 (6.14) | 11 679.211 | <0.001 |
| Regular drinking | 1551 (14.56) | 23 388 (3.27) | 4030.177 | <0.001 | 2484 (17.81) | 22 455 (3.16) | 7212.358 | <0.001 |
| Lack of exercise | 4269 (40.07) | 55 443 (7.75) | 14 518.060 | <0.001 | 6013 (37.61) | 53 699 (7.57) | 18 687.903 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 8614 (80.85) | 112 667 (15.76) | 31 958.204 | <0.001 | 13 182 (82.44) | 108 099 (15.23) | 50 750.234 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 3565 (33.46) | 36 187 (5.06) | 16 353.881 | <0.001 | 4118 (25.75) | 35 634 (5.02) | 12 983.573 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 6883 (64.60) | 106 276 (14.86) | 19 734.787 | <0.001 | 8982 (56.18) | 104 177 (14.68) | 20 458.912 | <0.001 |
| AF | 397 (3.73) | 2386 (0.33) | 3162.834 | <0.001 | 387 (2.42) | 2396 (0.34) | 1775.677 | <0.001 |
| TIA | 1409 (13.23) | 11 875 (1.66) | 7812.480 | <0.001 | 2504 (15.66) | 10 780 (1.52) | 17 402.607 | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 2762 (25.92) | 10 315 (1.44) | 35 557.668 | <0.001 | 1808 (11.31) | 11 269 (1.59) | 8348.822 | <0.001 |
| Family history of stroke | 3061 (28.73) | 27 042 (3.78) | 16 434.360 | <0.001 | 6069 (37.96) | 24 034 (3.39) | 47 002.257 | <0.001 |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Table 3.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for CHD and stroke
| Characteristics | CHD | Stroke | ||
| OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Sex (male) | 0.63 (0.59 to 0.66) | <0.001 | 1.18 (1.14 to 1.23) | <0.001 |
| Region (rural) | 0.73 (0.70 to 0.76) | <0.001 | 1.17 (1.13 to 1.21) | <0.001 |
| Age | 1.54 (1.51 to 1.57) | <0.001 | 1.52 (1.50 to 1.55) | <0.001 |
| BMI | 1.16 (1.13 to 1.20) | <0.001 | 1.03 (1.00 to 1.05) | 0.034 |
| Smoking | 1.79 (1.68 to 1.90) | <0.001 | 1.45 (1.39 to 1.52) | <0.001 |
| Lack of exercise | 1.37 (1.31 to 1.43) | <0.001 | 1.35 (1.30 to 1.40) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 5.83 (5.49 to 6.18) | <0.001 | 9.09 (8.65 to 9.55) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 1.76 (1.68 to 1.84) | <0.001 | 1.30 (1.25 to 1.36) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 2.03 (1.94 to 2.13) | <0.001 | 1.44 (1.38 to 1.49) | <0.001 |
| AF | 1.98 (1.76 to 2.24) | <0.001 | 1.28 (1.13 to 1.44) | <0.001 |
| TIA | 1.97 (1.85 to 2.11) | <0.001 | 2.92 (2.77 to 3.08) | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 4.89 (4.63 to 5.17) | <0.001 | 1.09 (1.03 to 1.16) | 0.004 |
| Family history of stroke | 1.60 (1.52 to 1.68) | <0.001 | 4.33 (4.16 to 4.50) | <0.001 |
| Regular drinking | 1.10 (1.03 to 1.18) | 0.007 | …… | …… |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Figure 1.
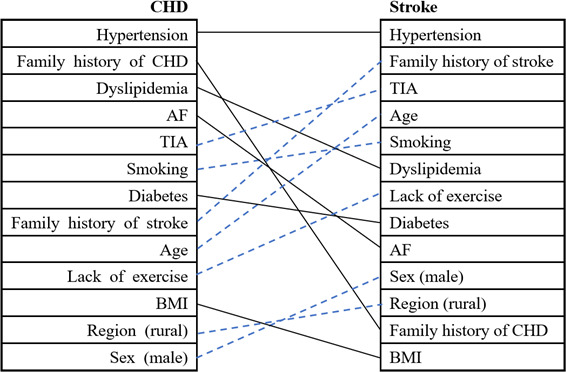
The rank of common risk factors of CHD and stroke based on OR value. The solid line indicates that the ranking of risk factors goes down, while the dotted line indicates that the ranking goes up. AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Distribution differences of common risk factors between CHD and stroke
After the exclusion of 1988 patients with both CHD and stroke, there were 8666 patients with CHD and 14 001 patients with stroke separately. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, CVD was taken as the dependent variable (stroke was defined as 1, whereas CHD was defined as 0) and the 13 common risk factors were taken as independent variables. The results showed that 11 of 13 risk factors (except age and lack of exercise) revealed differences in the distribution between CHD and stroke (table 4). The risk factors with OR >1 were more frequently detected in patients with stroke, and others with OR <1 may be more frequently detected in patients with CHD. The family history of stroke, men, rural area, TIA and hypertension were more closely associated with stroke, while the family history of CHD, AF, diabetes, dyslipidaemia, smoking and overweight/obesity indicated stronger relationship with CHD. Figure 2 displayed the distribution differences of risk factors for stroke and CHD.
Table 4.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of common risk factors distribution between CHD and stroke
| Characteristics | OR | 95% CI | P value |
| Family history of stroke | 2.30 | 2.15 to 2.45 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male) | 1.92 | 1.80 to 2.05 | <0.001 |
| Region (rural) | 1.70 | 1.60 to 1.80 | <0.001 |
| TIA | 1.41 | 1.30 to 1.54 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.28 | 1.19 to 1.38 | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.90 | 0.86 to 0.93 | <0.001 |
| Smoking | 0.79 | 0.73 to 0.85 | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.76 | 0.72 to 0.81 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 0.76 | 0.71 to 0.81 | <0.001 |
| AF | 0.60 | 0.51 to 0.71 | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 0.25 | 0.23 to 0.27 | <0.001 |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Figure 2.
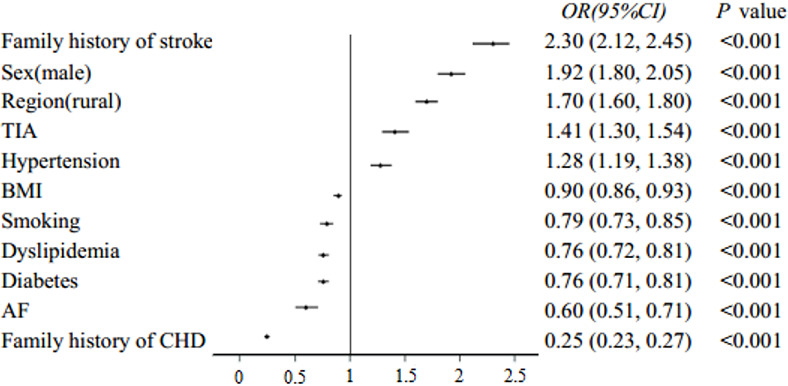
The forest plots of distribution differences of common risk factors between CHD and stroke. The risk factors with OR >1 indicates a closer association with stroke, and others with OR <1 indicates a closer association with CHD. AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
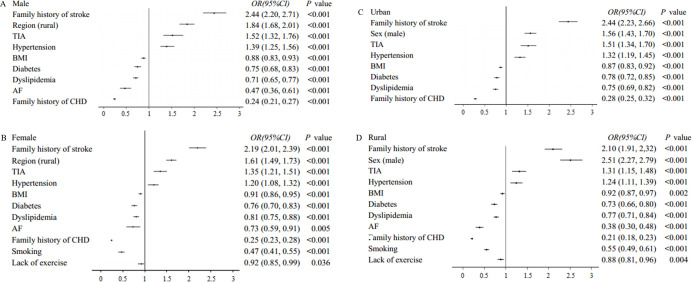
Subgroup analysis by gender and region showed that the distribution differences of risk factors between CHD and stroke also existed in different gender and region groups (figure 3). The risk factors that were more closely related to stroke were the same across different genders or regions (table 5, table 6). Smoking and lack of exercise were more closely related to CHD than stroke in the female population but not in the male population (table 5). AF and lack of exercise were more closely related to CHD than stroke in rural area but not in urban area (table 6).
Figure 3.
Subgroup analysis of distribution differences based on sex and region. The risk factors with OR >1 indicates a closer association with stroke, and others with OR 1 indicates a closer association with CHD.AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Table 5.
Subgroup analysis of distribution differences by gender
| Characteristics | Women | Men | ||
| OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Family history of stroke | 2.19 (2.01 to 2.39) | <0.001 | 2.44 (2.20 to 2.71) | <0.001 |
| Region (rural) | 1.61 (1.49 to 1.73) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.68 to 2.01) | <0.001 |
| TIA | 1.35 (1.21 to 1.51) | <0.001 | 1.52 (1.32 to 1.76) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.20 (1.08 to 1.32) | <0.001 | 1.39 (1.25 to 1.56) | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.91 (0.86 to 0.95) | <0.001 | 0.88 (0.83 to 0.93) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 0.76 (0.70 to 0.83) | <0.001 | 0.75 (0.68 to 0.83) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.81 (0.75 to 0.88) | <0.001 | 0.71 (0.65 to 0.77) | <0.001 |
| AF | 0.73 (0.59 to 0.91) | 0.005 | 0.47 (0.36 to 0.61) | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 0.25 (0.23 to 0.28) | <0.001 | 0.24 (0.21 to 0.27) | <0.001 |
| Smoking | 0.47 (0.41 to 0.55) | <0.001 | …… | …… |
| Lack of exercise | 0.92 (0.85 to 0.99) | 0.036 | …… | …… |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Table 6.
Subgroup analysis of distribution differences by region
| Characteristics | Rural | Urban | ||
| OR (95% CI) | P value | OR (95% CI) | P value | |
| Sex (male) | 2.51 (2.27 to 2.79) | <0.001 | 1.56 (1.43 to 1.70) | <0.001 |
| Family history of stroke | 2.10 (1.91 to 2.32) | <0.001 | 2.44 (2.23 to 2.66) | <0.001 |
| TIA | 1.31 (1.15 to 1.48) | <0.001 | 1.51 (1.34 to 1.70) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.24 (1.11 to 1.39) | <0.001 | 1.32 (1.19 to 1.45) | <0.001 |
| BMI | 0.92 (0.87 to 0.97) | 0.002 | 0.87 (0.83 to 0.92) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 0.77 (0.71 to 0.84) | <0.001 | 0.75 (0.69 to 0.82) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 0.73 (0.66 to 0.80) | <0.001 | 0.78 (0.72 to 0.85) | <0.001 |
| Family history of CHD | 0.21 (0.18 to 0.23) | <0.001 | 0.28 (0.25 to 0.32) | <0.001 |
| Lack of exercise | 0.88 (0.81 to 0.96) | 0.004 | …… | …… |
| Smoking | 0.55 (0.49 to 0.61) | <0.001 | …… | …… |
| AF | 0.38 (0.30 to 0.48) | <0.001 | …… | …… |
AF, atrial fibrillation; BMI, body mass index; CHD, coronary heart disease; TIA, transient ischaemic attack.
Discussion
The CNSSS is a large sample size, nationwide community population-based cluster sampling survey, which can reflect the distribution of CVD and risk factors in real world. This study showed that CHD and stroke had many common risk factors, while the distribution of these risk factors between CHD and stroke was substantial differences.
Necessity of comprehensive screening and prevention of CVD in China
As revealed in the present study, there were substantial similarities in the association of risk factors with CHD and stroke, including hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidaemia, AF, TIA, smoking, overweight/obesity, lack of exercise, family history of CVD, age, sex and region. An enormous amount of studies has confirmed that these traditional risk factors are related to CVD,7 21 although the pathophysiological mechanisms leading to CVD are not identical. At present, China has a large number of high-risk groups of CVD, including 244.5 million hypertension, 113.9 million diabetes, 358.3 million dyslipidaemia and 7.7 million AF.22–25 In order to reduce the disease burden caused by CVD, the Chinese government launched the screening and prevention programmes for CHD and stroke,19 26 respectively. Since CHD and stroke have many common risk factors, we believe that it is necessary to carry out comprehensive screening and prevention of CVD. We found that hypertension is the most important risk factor for both CHD and stroke. Although the latest survey shows that the awareness rate, treatment rate and control rate of hypertension in China have been improved, but compared with the developed countries is still very low.21 22 These results suggest that interventions for hypertension are still a top priority for CVD prevention in China.
Heterogeneity of risk factor distribution
The distribution of most risk factors involved in this study was significantly different between CHD and stroke. Family history of CVD was the most different risk factor for CHD and stroke among all risk factors. Men were more closely associated with stroke, while women were more closely associated with CHD. Geographically, stroke was more likely in rural population and CHD more likely in urban population. Among the risk factors that can be intervened, AF, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, smoking, overweight/obesity were more closely related to CHD, while TIA and hypertension were more closely related to stroke.
The heterogeneity of the relationship between specific risk factors and different types of CVD may be related to the pathophysiological mechanisms of these risk factors in different types of CVD. As expected, we found that hypertension is more related to stroke, while dyslipidaemia is more related to CHD, which is consistent with previous studies.11 13 14 The possible reasons are that hypertension increases the risk of ischaemic stroke and haemorrhagic stroke at the same time, while dyslipidaemia shows the opposite effect.21 On the pathophysiological mechanism, the strong association between hypertension and stroke might be explained by the relationship between hypertension and cerebral small vessel disease or AF.13 27 Conversely, the relationship of different lipid subtypes with ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke is different. Hypercholesterolemia increases the risk of ischaemic stroke but reduces the risk of haemorrhagic stroke. Higher level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) seems to be associated with lower risk of haemorrhagic stroke; however, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level seems to be positively associated with risk of intracerebral haemorrhage.28 29 In addition, diabetes and smoking were associated with ischaemic stroke, but not predictive of haemorrhagic stroke.11 This may be the reason why they are more closely related to CHD. Contrary to expectations, AF is more closely associated with CHD than stroke. The possible reason is that CHD increases the risk of AF, while stroke does not increase the risk of AF.30 31
Elucidating the underlying mechanism for the heterogeneity of specific risk factor distribution on CVD types requires further work. Only a few studies focused on the differences of risk factors between CHD and stroke in a same cohort in the past.10–13 There was a great heterogeneity among these studies, for example, the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study included only women, and sample size is small,11 the Physicians’ Health Study included only men,10 the Rotterdam study just compared gender differences in one area of the population,12 the European Prospective Investigation of Cancer (EPIC)-Norfolk Study included only three risk factors (LDL-c, systolic blood pressure and smoking).13 Findings in our study were consistent with those reported in EPIC-Norfolk Study and Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. The EPIC-Norfolk Study suggested that hypertension was intimately associated with stroke, and dyslipidaemia showed stronger relationship with CHD.13 Meanwhile, Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study revealed that BMI, smoking, diabetes, family history of CHD and hypercholesterolemia were associated with CHD, while hypertension was related to stroke.11 Unlike our results, the Physicians’ Health Study indicated no difference in the distribution of risk factors such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, smoking and physical exercise between CHD and stroke.10 Contrary to our results, the Rotterdam study showed that women were more likely to have stroke, while men had higher risk of CHD.12 The reason for this huge difference may be the different race, age and occupation backgrounds included in different studies. Besides, the geographical environment and climate of different countries may also play an important role.32 Different countries should formulate corresponding prevention and control measures for CVD according to the prevalence and distribution of risk factors in their own countries.
Implications
Our results could suggest that differences may exist in the efficacy of improving specific risk factors across CVD types. The heterogeneity in the association between particular risk factors and specific CVD types demonstrated in the current study could improve the selection of high-risk patients for population-based screening programmes. For example, for women with a family history of CHD, more attention should be paid to the prevention of CHD, and for men with a family history of stroke, more stroke should be prevented. In addition, the results of this study are helpful for clinical studies to select appropriate endpoint indicators. Heterogeneity in the definitions of composite endpoints may lead to different results and conclusions on the efficacy of study interventions and could lead to overestimation or underestimation of the effect on specific CVD types. The specific types of CVD events may vary depending on the risk factors for clinical intervention. In the study of lipid lowering, the risk of CHD should be paid more attention, while the study of blood pressure lowering should pay more attention to the risk of stroke.
There are several limitations in this study. First, the judgement of CVD events was mainly based on self-reported history. In order to reduce the recall bias, each CVD event should be confirmed by a specialist in cardiology or neurology to make the diagnosis as accurate as possible. Second, this study was a cross-sectional survey that can only indicate the correlation between risk factors and CVD, without the ability to reflect the causal relationship. However, this study has a large sample size and is based on a nationwide cluster sampling survey, which can explain the relationship between specific risk factors and CVD types to a certain extent.
Conclusion
Although CHD and stroke had many common risk factors, the distribution of these risk factors between CHD and stroke were substantial differences. More specific prevention and control measures should be formulated according to the distribution differences of risk factors related to CVD.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants of the CNSSS and all the colleagues from 256 sub-centerscentres in 31 provinces who worked very hard to ensure the accuracy of the data.
Footnotes
Contributors: LD W and YM X contributed to research design and the revision of this manuscript, responsible for the overall content as the guarantor; YP L contributed to research design, data collection and writing of this manuscript; L Y, Y S, YS L, J L and SH S contributed to data collection and processing; AR W, L Z, Y G, CS T contributed to data collection and the revision of the manuscript; all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding: This study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1311303), the Non-profit Central Research Institute Fund of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences (2020-PT310-01) and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by Henan Association for Science and Technology (2022HYTP048).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement
Data are available upon reasonable request. The data are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding authors.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University (2021-KY-0067-001). Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
- 1. Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2020;76:2982–3021. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators . Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Neurol 2021;20:795–820. 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators . Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 2020;396:1204–22. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Irawati S, Wasir R, Floriaan Schmidt A, et al. Long-Term incidence and risk factors of cardiovascular events in Asian populations: systematic review and meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies. Curr Med Res Opin 2019;35:291–9. 10.1080/03007995.2018.1491149 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2021 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 2021;143:e254-e743. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Zhao D, Liu J, Wang M, et al. Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in China: current features and implications. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019;16:203–12. 10.1038/s41569-018-0119-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Goff DC, Lloyd-Jones DM, Bennett G, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart association Task force on practice guidelines. Circulation 2014;129:S49-73. 10.1161/01.cir.0000437741.48606.98 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Yang X, Li J, Hu D, et al. Predicting the 10-year risks of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in Chinese population: the China-PAR project (prediction for ASCVD risk in China). Circulation 2016;134:1430–40. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Pylypchuk R, Wells S, Kerr A, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk prediction equations in 400 000 primary care patients in New Zealand: a derivation and validation study. Lancet 2018;391:1897–907. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30664-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Glynn RJ, Rosner B. Comparison of risk factors for the competing risks of coronary heart disease, stroke, and venous thromboembolism. Am J Epidemiol 2005;162:975–82. 10.1093/aje/kwi309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Leening MJG, Cook NR, Franco OH, et al. Comparison of cardiovascular risk factors for coronary heart disease and stroke type in women. J Am Heart Assoc 2018;7:e007514. 10.1161/JAHA.117.007514 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Leening MJG, Ferket BS, Steyerberg EW, et al. Sex differences in lifetime risk and first manifestation of cardiovascular disease: prospective population based cohort study. BMJ 2014;349:g5992. 10.1136/bmj.g5992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Stoekenbroek RM, Boekholdt SM, Luben R, et al. Heterogeneous impact of classic atherosclerotic risk factors on different arterial territories: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Eur Heart J 2016;37:880–9. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv630 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Simons LA, Simons J, Friedlander Y, et al. A comparison of risk factors for coronary heart disease and ischaemic stroke: the Dubbo study of Australian elderly. Heart Lung Circ 2009;18:330–3. 10.1016/j.hlc.2009.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Guan T, Ma J, Li M, et al. Rapid transitions in the epidemiology of stroke and its risk factors in China from 2002 to 2013. Neurology 2017;89:53–61. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004056 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Fu W, Cao S, Liu B, et al. Association of general and central adiposity with blood pressure among Chinese adults: results from the China national stroke prevention project. J Hypertens 2018;36:2406–13. 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001852 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Longde W, Ling Y, Yang H, et al. Fixed-Dose combination treatment after stroke for secondary prevention in China: a national community-based study. Stroke 2015;46:1295–300. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007384 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Wang X, Fu Q, Song F, et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation in different socioeconomic regions of China and its association with stroke: results from a national stroke screening survey. Int J Cardiol 2018;271:92–7. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.05.131 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Chao B-H, Yan F, Hua Y, et al. Stroke prevention and control system in China: CSPPC-Stroke program. Int J Stroke 2021;16:265–72. 10.1177/1747493020913557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Wang X, Li W, Song F, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis detected by ultrasonography: a national cross-sectional study. J Am Heart Assoc 2018;7. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008701. [Epub ahead of print: 05 04 2018]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart association Task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 2019;140. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wang Z, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al. Status of hypertension in China: results from the China hypertension survey, 2012-2015. Circulation 2018;137:2344–56. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032380 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American diabetes association: national cross sectional study. BMJ 2020;369:m997. 10.1136/bmj.m997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Pan L, Yang Z, Wu Y, et al. The prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of dyslipidemia among adults in China. Atherosclerosis 2016;248:2–9. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Wang Z, Chen Z, Wang X, et al. The disease burden of atrial fibrillation in China from a national cross-sectional survey. Am J Cardiol 2018;122:793–8. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2018.05.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lu J, Xuan S, Downing NS, et al. Protocol for the China peace (patient-centered Evaluative assessment of cardiac events) million persons project pilot. BMJ Open 2016;6:e010200. 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Sörös P, Whitehead S, Spence JD, et al. Antihypertensive treatment can prevent stroke and cognitive decline. Nat Rev Neurol 2013;9:174–8. 10.1038/nrneurol.2012.255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Glasser SP, Mosher A, Howard G, et al. What is the association of lipid levels and incident stroke? Int J Cardiol 2016;220:890–4. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.06.091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wang X, Dong Y, Qi X, et al. Cholesterol levels and risk of hemorrhagic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 2013;44:1833–9. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.001326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Jabre P, Jouven X, Adnet F, et al. Atrial fibrillation and death after myocardial infarction: a community study. Circulation 2011;123:2094–100. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.990192 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. January CT, Wann LS, Alpert JS, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American heart association Task force on practice guidelines and the heart rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;64:e1–76. 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Hadley MB, Vedanthan R, Fuster V. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease: a window of opportunity. Nat Rev Cardiol 2018;15:193–4. 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.207 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request. The data are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding authors.