Abstract
Background:
Chronic testicular pain due to genitofemoral neuropathy often becomes refractory to conservative medical therapy. Neurostimulation is a potentially useful treatment option, should the neuropathic pain remain refractory to more invasive procedures such as orchiectomy. We provide a case report of spinal cord stimulation (SCS) for successful treatment of genitofemoral neuropathy and have also reviewed the literature to find similar cases which required a similar treatment paradigm.
Case Description:
A 42-year-old male underwent SCS for refractory testicular and groin pain. SCS through a four-column, 2 × 8 contact neurostimulator paddle lead, was implanted in the mid-thoracic-9 (T9) vertebral level, providing > 50% testicular pain relief with a decrease in visual analog scale scores from 8–10/10 to 3–4/10. The patient required one adjustment to the stimulation parameters at the time of the 6 weeks follow-up visit due to over-stimulation. He then continued to experience >50% resolution in pain 9 months later. A review of the literature yielded only two similar cases that successfully utilized SCS for treatment of chronic testicular pain.
Conclusion:
SCS should be considered as a possible treatment option for patients with chronic testicular pain localized to the genitofemoral nerve distribution.
Keywords: Genitofemoral, Orchalgia, Spinal cord stimulation, Testicular pain

INTRODUCTION
Chronic testicular pain, or orchalgia, although typically idiopathic, may also be associated with genitofemoral neuropathy.[1,7] Chronic testicular region pain accounts for 2.5–5% of all urologic consultations and affects approximately 100,000 males in the United States per year.[1] Treatment options include conservative therapy (e.g., with analgesics), nerve blocks, or surgery for refractory pain.[3,7] If pain persists and becomes neuropathic, therapies are more limited. We report a case of a 42-year-old male with genitofemoral neuropathic pain who responded with >50% pain relief after spinal cord stimulation (SCS). We also conducted a review of the literature for similar cases and treatment protocols.
CASE REPORT
A 42-year-old male presented with a 3.5-year history of chronic right groin and testicular pain (refractory genitofemoral neuropathy characterized by constant and dull burning sensations) after a gunshot injury to the groin. The pain failed to resolve with several anti-inflammatory and pain medications: ibuprofen, gabapentin, ketorolac, and opioids (e.g., hydromorphone, oxycodone, morphine, and fentanyl). The patient initially benefitted from a genitofemoral nerve block, a right ilioinguinal nerve block, and a right spermatic cord block. As his pain then became refractory to these treatment modalities, and his MR studies of the thoracic and lumbar spine were negative for causative pathology, he underwent a trial of genitofemoral SCS. His visual analog scale (VAS) scores before the SCS trial ranged from 8 to 10/10.
SCS for genitofemoral neuropathy
For the SCS trial, two percutaneous 16-contact, midline cylindrical leads were temporarily implanted, and positional adjustments were made until the patient reported adequate capture of the typical painful areas. The optimal level of stimulation was at the mid-T9 level. The SCS trial lasted for 1 week, at which point he reported >50% reduction in both right groin and testicular pain, with his VAS score decreasing to 3/10. He also noted improvement in sleep, mobility, and functional activity. He underwent permanent SCS placement with a 4-column, 2 × 8-contact epidural paddle lead (at mid-T9 through a laminotomy at T10) [Figure 1]. A paddle SCS lead was in the posterior midline with the tip of the lead at the bottom of T8. In addition, a neurostimulator pulse generator was placed in the patient’s right flank. The operation was uneventful. SCS parameters were set immediately following the procedure: pulse width of 400 microseconds (μs), frequency of 40 Hertz (Hz), and current of 5.5 milliamperes (mA). The patient’s postoperative pain medications remained unchanged with acetaminophen and duloxetine.
Figure 1:
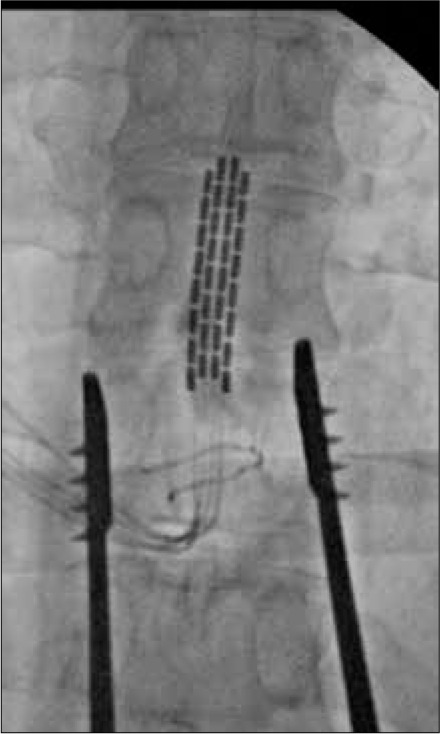
Intraoperative radiograph of midline thoracic-9 implantation of the epidural 4-column spinal cord stimulation paddle lead.
Postoperative course following SCS implantation
Six weeks after the permanent SCS was implanted, the patient continued to report >50% pain relief, VAS scores remained stable at 3/10, and he was able to return to work. At the 6 week follow-up visit, the patient reported over-stimulation symptoms; therefore, the stimulation parameters were adjusted to a pulse width of 340 μs, frequency of 40 Hz, and current of 6.1 mA. At the 9 months follow-up, the patient continued to report >50% pain relief with VAS scores in the 3–4/10 range.
DISCUSSION
The first-line treatment for chronic testicular pain is conservative medical therapy that often proves inadequate with success rates ranging from only 4.2% to 15.2%.[1,7] Other invasive procedures have been developed for refractory genitofemoral neuropathies including: botulinum toxin injections, spermatic cord blocks, varicocelectomy, epididymectomy, vasovasostomy, orchiectomy, and/or microsurgical denervation of the spermatic cord.[3,7] The present patient failed multiple conservative treatment modalities.
Two prior cases of SCS successfully treating chronic testicular pain
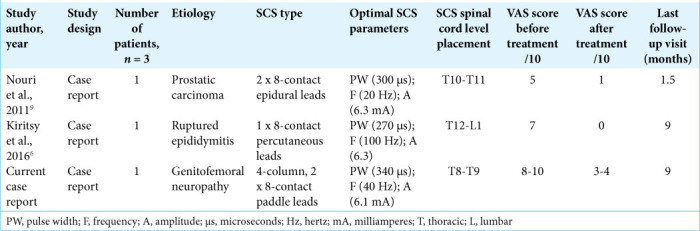
A literature review including PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Ovid EMBASE databases yielded just two prior reports of successful utilization of SCS for chronic testicular pain.[6,9] In 2011, Nouri and Brish reported a 57-year-old patient with a history of malignancy-related orchalgia refractory to opioids, ilioinguinal nerve blocks, iliohypogastric nerve blocks, and ganglion impar nerve blocks, who underwent SCS placement resulting in >80% pain reduction with a decrease in VAS scores from 5/10 to 1/10 at 6 weeks follow-up [Table 1].[9] In 2016, Kiritsy and Siefferman reported a 59-year-old male with bilateral intractable testicular pain due to ruptured epididymitis, who failed various medical interventions (e.g., left spermatic cord stripping and nerve blocks) and underwent SCS; 3 weeks postoperatively, he had 100% pain relief that lasted for 9 months [Table 1].[6]
Table 1:
Individual study characteristics and outcomes for SCS patients with testicular pain
Testicular pain as a complication of SCS
Huang et al. reported two cases of acute, neuropathic testicular and scrotal pain following a percutaneous SCS trial.[4] One case was resolved with corticosteroids and stimulator activation, while the other became refractory, and the SCS had to be removed.[4]
Types of testicular pain
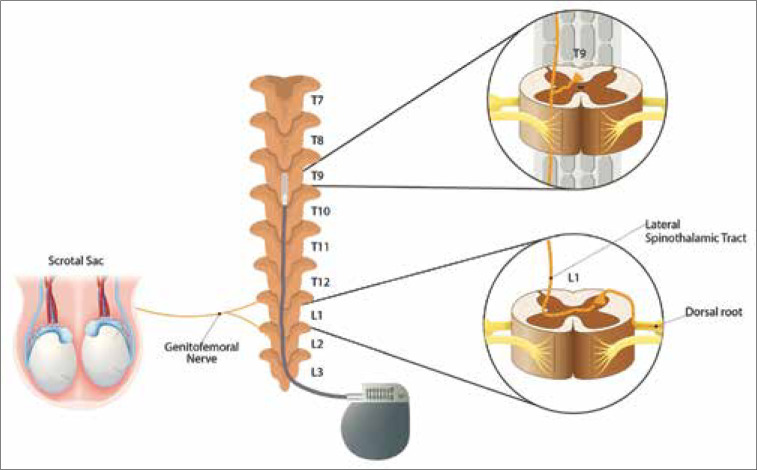
There are two proposed types of testicular pain: nociceptive and neuropathic.[7] SCS initiates orthodromic neurotransmission to supraspinal centers and antidromic effects directly to the spinal cord, leading to effective modulation of chronic pain [Figure 2]. Two contemporary mechanisms for nociceptive pain include segmental and supraspinal effects.[5,10] When SCS is applied over the dorsal spinal cord, segmental effects lead to antidromic activation of primary afferents that result in reduction of neurotransmission in reflex pathways mediated in pain modulation.[5] In the supraspinal mechanism, SCS provides pain relief at supraspinal centers such as the thalamus, periaqueductal gray of the midbrain, and medulla.[10]
Figure 2:
Possible mechanism of spinal cord stimulation modulating pain relief in a patient with the right-sided genitofemoral neuropathy. A four-column, 2 × 8 contact simulator was implanted in the mid-T9 vertebral level.
Role of SCS for neuropathic testicular pain
SCS is a relatively less invasive modality versus surgery for chronic orchalgia (e.g., SCS trial versus orchiectomy). However, perioperative complications occur in 0.7–38% of SCS cases and may be due to: device failure such as lead migration and over/under stimulation; biologic factors such as infection and seroma; and even complications of SCS placement itself.[2,8] Although there are limited data supporting SCS’ application in chronic orchalgia, it should be considered as a treatment option where surgery has failed.
CONCLUSION
SCS is a valuable treatment modality for patients with chronic orchalgia, especially when the pain distribution can be adequately localized to the genitofemoral nerve region.
Footnotes
How to cite this article: Mamaril-Davis JC, Joshi N, Palsma R, Aguilar-Salinas P, Walter CM, Hashim S, et al. Spinal cord stimulation for genitofemoral neuropathy: A case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol Int 2022;13:533.
Contributor Information
James Christopher Mamaril-Davis, Email: jmamarildavis@arizona.edu.
Neil Joshi, Email: neiljoshi@arizona.edu.
Ryan Palsma, Email: rppalsma@arizona.edu.
Pedro Aguilar-Salinas, Email: paguilar@arizona.edu.
Christina M. Walter, Email: chrismw@arizona.edu.
Shamam Hashim, Email: shamamhashim@emil.arizona.edu.
Martin Weinand, Email: mweinand@arizona.edu.
Declaration of patient consent
Institutional Review Board (IRB) permission obtained for the study.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Journal or its management. The information contained in this article should not be considered to be medical advice; patients should consult their own physicians for advice as to their specific medical needs.
REFERENCES
- 1.Calixte N, Brahmbhatt J, Parekattil S. Chronic testicular and groin pain: Pathway to relief. Curr Urol Rep. 2017;18:83. doi: 10.1007/s11934-017-0722-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cameron T. Safety and efficacy of spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of chronic pain: A 20-year literature review. J Neurosurg. 2004;100:254–67. doi: 10.3171/spi.2004.100.3.0254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chaudhari R, Sharma S, Khant S, Raval K. Microsurgical denervation of spermatic cord for chronic idiopathic orchialgia: Long-term results from an institutional experience. World J Mens Health. 2019;37:78–84. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.180035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang M, Desai VR, Ho D, Simpson RK. Acute neuropathic orchalgia and scrotalgia after percutaneous spinal cord stimulator lead placement: Two cases with an unusual complication. Cureus. 2017;9:e1003. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hunter JP, Ashby P. Segmental effects of epidural spinal cord stimulation in humans. J Physiol. 1994;474:407–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kiritsy MP, Siefferman JW. Spinal cord stimulation for intractable testicular pain: Case report and review of the literature. Neuromodulation. 2016;19:889–92. doi: 10.1111/ner.12487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Siref LE. StatPearls. Treasure Island: StatPearls Publishing LLC; 2022. Chronic Testicular Pain and Orchalgia. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mekhail NA, Mathews M, Nageeb F, Guirguis M, Mekhail MN, Cheng J. Retrospective review of 707 cases of spinal cord stimulation: Indications and complications. Pain Pract. 2011;11:148–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2010.00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nouri KH, Brish EL. Spinal cord stimulation for testicular pain. Pain Med. 2011;12:1435–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4637.2011.01210.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vallejo R, Bradley K, Kapural L. Spinal cord stimulation in chronic pain: Mode action. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2017;42:S53–60. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]