Abstract
Mycoplasmas may be associated with rheumatoid arthritis in various animal hosts. In humans, mycoplasma arthritis has been recorded in association with hypogammaglobulinemia. Mycoplasma fermentans is one mycoplasma species considered to be involved in causing arthritis. To clarify which mycoplasmal compounds contribute to the inflammatory, bone-destructive processes in arthritis, we used a well-defined lipopeptide, 2-kDa macrophage-activating lipopeptide (MALP-2) from M. fermentans, as an example of a class of macrophage-activating compounds ubiquitous in mycoplasmas, to study its effects on bone resorption. MALP-2 stimulated osteoclast-mediated bone resorption in murine calvaria cultures, with a maximal effect at around 2 nM. Anti-inflammatory drugs inhibited MALP-2-mediated bone resorption by about 30%. This finding suggests that MALP-2 stimulates bone resorption partially by stimulating the formation of prostaglandins. Since interleukin-6 (IL-6) stimulates bone resorption, we investigated IL-6 production in cultured calvaria. MALP-2 stimulated the liberation of IL-6, while no tumor necrosis factor was detectable. Additionally, MALP-2 stimulated low levels of NO in calvaria cultures, an effect which was strongly increased in the presence of gamma interferon, causing an inhibition of bone resorption. MALP-2 stimulated the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts isolated from long bones of newborn rats and cultured on dentine slices without affecting their number. In bone marrow cultures, MALP-2 inhibited the formation of osteoclasts. It appears that MALP-2 has two opposing effects: it increases the bone resorption in bone tissue by stimulation of mature osteoclasts but inhibits the formation of new ones.
Mycoplasmas are wall-less bacteria which are mostly harmless commensals but can also be associated with clinical symptoms from nongonococcal urethritis (12) to rheumatoid arthritis. One species, Mycoplasma arthritidis, has been studied particularly well with respect to its arthritogenic properties (47). It releases a superantigen whose structure has been elucidated and whose functional domains were identified (4). However, other mycoplasma species, which do not produce or release superantigens, may also be associated with rheumatoid arthritis in various animal hosts such as chickens (30), swine (17), goats (40, 41), or cattle (34). In human adults and occasionally children, mycoplasma arthritis has been recorded in association with hypogammaglobulinemia (9, 35). In a classical paper, M. fermentans was also considered to be a causative agent of arthritis (49); this finding has recently been supported by modern analytical tools (43).
Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory disorder with infiltration of leukocytes and increases of local concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines (2, 3, 33) followed by degradation of the joint cartilage. With progression of the disease, cytokines may activate bone cells and induce bone resorption, resulting in local bone loss. Additionally, various bacterial components have been shown to interact directly with bone cells and cause changes in bone remodelling (29).
It is less clear which mycoplasmal compounds contribute to the inflammatory, bone-destructive processes in mycoplasma-associated arthritis. According to a recent report, high-molecular-weight components from M. hyorhinis and M. arthritidis cause bone resorption in bone organ cultures (32). In many aspects, this material resembled the mycoplasma-derived high-molecular-weight material (MDHM) which was isolated from M. fermentans by virtue of its macrophage-stimulatory activity (25) and which turned out to be a mixture of lipopeptides (26). It has been previously observed that mycoplasmas, like other microorganisms, produce components which activate macrophages (10, 18, 20, 38) and that they induce inflammation under various natural or experimental conditions (13, 16, 19, 42). In continuation of previous work on MDHM, a well-defined lipopeptide, named 2-kDa macrophage-activating lipopeptide (MALP-2), was isolated from M. fermentans and purified. Its structure was elucidated and further supported by chemical synthesis (26). The synthetic MALP-2 has the structure S-[2,3-bispalmitoyloxypropyl]-cysteinyl-GNNDESNISFKEK. MALP-2 activates peritoneal macrophages to release nitric oxide (NO) at picomolar concentrations. Macrophages stimulated with MDHM, of which MALP-2 is a component, also produce interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and IL-1 (25, 28), and MALP-2 causes leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model because of its capacity to stimulate chemokine release (6).
In this study, we investigated whether MALP-2 would also stimulate bone resorption. The data demonstrate that this lipopeptide, which is but one example of a class of macrophage-activating compounds ubiquitous in mycoplasmas (11, 18, 27, 38), is active in causing bone resorption in cultured murine calvaria and in increasing the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts isolated from rat bone but not in increasing the number of osteoclasts in the bone marrow culture.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials.
MALP-2 was synthesized as described previously (26). It was kept as a stock solution in 10 mM octylglucoside and 45% 2-propanol. When added to the incubation medium, the stock solution of MALP-2 (18 μM) was first diluted 1:25 with 25 mM n-octyl-β-d-glucopyranoside (Sigma, Buchs, Switzerland) and then with medium to the final concentration. Vehicle solution was added to the control calvaria. Bovine serum albumin (radioimmunoassay grade) and the prostaglandin inhibitors indomethacin and flurbiprofen were obtained from Sigma; hydrocortisone, NADPH, and NG-monomethyl-l-arginine (LMMA) were obtained from Fluka, Buchs, Switzerland; nitrate reductase from Aspergillus species was obtained from Roche Diagnostic, Rotkreuz, Switzerland; fetal bovine serum (FBS) was obtained from Biological Industries, Inotech, Dottikon, Switzerland. Calcitonin was donated by Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, Switzerland; 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol was donated by Hoffmann-LaRoche, Basel, Switzerland; recombinant mouse gamma interferon-γ (IFN-γ) was a generous gift from G. R. Adolf, Bender & Co. GmbH (Vienna, Austria).
Calvarium culture.
Culture conditions similar to those described previously (7) were used. Briefly, calvarium explants from 4- to 5-day-old ddy mice, bred in our breeding facilities, were obtained aseptically. The bones were divided into two halves along the median suture. The calvarium halves were preincubated in 1 ml of alpha minimal essential medium (α-MEM) supplemented with 1% penicillin, 1% streptomycin, and 0.1% bovine serum albumin in 12-well tissue culture plates on a rocking platform at 37°C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2–95% air. After 24 h, the medium was changed; one half of the bone preparation was used as a control, and the other half was treated. After a culture period of 48 to 72 h, the medium was collected and the bones were demineralized in 4 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid. The calcium in medium and trichloroacetic solution was determined. The blank value obtained from medium incubated without calvaria was subtracted. Bone resorption was calculated by the amount of calcium released into the medium as the percentage of total calcium (bone and medium). Data are presented in this manner in Fig. 3 and 4. The effect of the test substances is given as the difference between treated and control bone and is presented in Fig. 1 and 2.
FIG. 3.
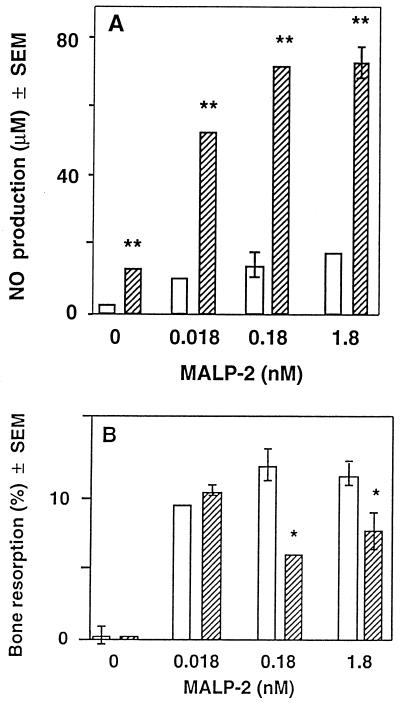
Effect of IFN-γ on NO production and MALP-2-induced bone resorption in murine calvaria. After 24 h of preincubation, the calvarium pairs were cultured for 48 h in the presence of MALP-2. One half was (hatched bars) and the other half was not (open bars) treated with IFN-γ (200 U/ml). NO production (A) and bone resorption (B) are given as means ± SEM of five calvarium halves. SEMs smaller than the symbols are not drawn. ∗ and ∗∗, significantly different from value for untreated half; P < 0.05 and P < 0.001, respectively.
FIG. 4.
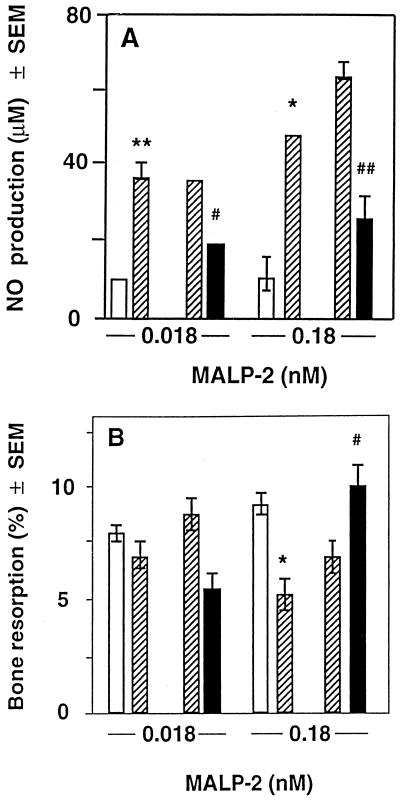
Effects of inhibitors of NO production on bone resorption. Two groups of calvarium pairs were investigated after preincubation as for Fig. 3. In one group, the effect of IFN-γ on pairs treated with MALP-2 (open bars) and MALP-2 and plus IFN-γ (200 U/ml) (hatched bars) was investigated. In the second group, the effect of 0.1 mM LMMA on calvarium pairs treated with MALP-2 plus IFN-γ (200 U/ml) (hatched bars) and MALP-2, IFN-γ, and 100 μM LMMA (solid bars) was investigated. NO production (A) and bone resorption (B) are given as means ± SEM of five halves. SEMs smaller than the symbols are not drawn. ∗ and ∗∗, significantly different from value for MALP-2 alone; P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. # and ##, significantly different from value for MALP-2 and IFN-γ; P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively.
FIG. 1.
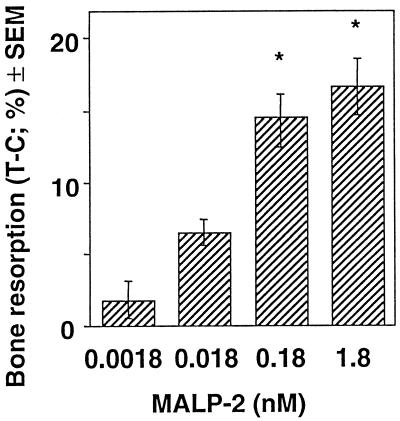
Effect of MALP-2 on calcium release by murine calvaria. Pairs of calvarium halves were preincubated for 24 h in α-MEM containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin and then cultured for 72 h in the presence or absence of increasing amounts of MALP-2. Bone resorption is presented as the difference in the percentage of calcium release between the treated half (T) and the control half (C). Values are means ± SEM of 15 calvarium pairs. ∗, significantly different from control (no MALP-2) value; P < 0.001.
FIG. 2.
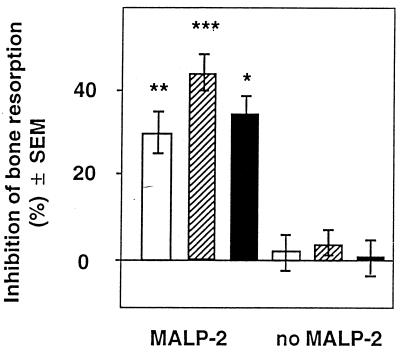
Effects of inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis on MALP-2-mediated bone resorption. Both halves of calvarium pairs were preincubated as described for Fig. 1 and then treated with either MALP-2 or vehicle without MALP-2 (no MALP-2). Indomethacin (open bars), hydrocortisone (hatched bars), and flurbiprofen (solid bars) at a concentration of 10−6 M were added to one half of the calvarium pairs, and the bones were incubated for 72 h. Values are means ± SEM of 10 pairs (MALP-2) and 5 pairs (no MALP-2). ∗, ∗∗, and ∗∗∗, significantly different from control (no inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis) value; P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001, respectively.
Isolation of osteoclasts and pit assay.
Femurs and tibia from 1-day-old rats were dissected and cureted with a scalpel in Eagle's minimal essential medium containing Earle's salt with 15 mM instead of 25 mM bicarbonate and 10% fetal calf serum (incubation medium) (1). The cell suspension was collected, and after the bone fragments had settled, the supernatant was transferred to a new tube. Aliquots of 0.4 ml were layered on four dentine slices (0.5 by 0.5 cm) which had been preincubated with medium. Six rats were needed for 44 slices. After incubation for 40 min at 37°C in 5% CO2–95% air, nonadherent cells were washed off with phosphate-buffered saline. The slices were transferred to 24-well cell culture dishes and incubated for 24 h in 0.5 ml of incubation medium containing either no addition, vehicle, or MALP-2. At the end of the incubation, the cells were fixed with a mixture of 3 vol of acetone and 2 vol of 38 mM citrate buffer (pH 5.4) and stained for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) with kit 386-A from Sigma. After the TRAP-positive multinucleated cells (more than two nuclei) were counted, the dentine slices were sonicated in 70% isopropanol twice for 15 s each time, cleaned with a brush, dried, and sputter coated with gold (SCD 004 sputter coater; Balzers Process Systems, Balzers, Liechtenstein). The number of resorption pits on each dentine slice was enumerated by using a light microscope with light from the side.
Bone marrow culture.
Bone marrow cultures were done as described elsewhere (44). Tibias and fermurs were aseptically dissected from 6- to 8-week-old male ddy strain mice. The bone marrow cavity was flushed out with 1 ml of α-MEM, using a sterile 25-gauge needle. The marrow cells were collected, and 7.5 × 105 cells were cultured in 24-well tissue culture dishes (Falcon; Becton Dickinson, Winiger AG, Wohlen, Switzerland) in 0.5 ml of α-MEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 10 nM 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in an atmosphere of 5% CO2–95% air. The vitamin D metabolite is required to support the formation of TRAP-positive multinucleated cells. After 3 days, 0.4 ml of the old medium was replaced with fresh medium. At day 6, the cells were fixed with a 3:2 mixture of acetone and 38 mM citrate buffer (pH 5.4). The osteoclast-like cells were stained for TRAP by using kit 386-A from Sigma. The TRAP-positive cells with three and more nuclei were counted, and the result was expressed as number per well.
Determination of calcium.
Calcium was analyzed colorimetrically, using methylthymol blue as the indicator (Ca-Kit; bioMérieux Suisse s.a., Geneva, Switzerland).
Determination of NO production.
NO produced by cells decays to nitrite and nitrate. The nitrate was reduced to nitrite with nitrate reductase (25). Thus, an aliquot of 100 μl of supernatant was mixed with 10 μl of solution containing 20 m U of nitrate reductase and NADPH at a concentration of 110 μM and incubated for a 10 min at 37°C. Then Griess solution consisting of a freshly made 1:1 mixture of 0.1% naphthylethylenediamine-2HCl in water and 1% sulfanilamide in 5% H3PO4 was added, and the absorbancy was determined at 490 nm (24).
Production of IL-6 and TNF-α by calvaria.
Calvarium halves were incubated in the presence of 0.18 nM MALP-2 for 3 h (TNF-α) and 6 h (IL-6). The media were collected, and the cytokines were determined. IL-6 was determined in a capture enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the IL-6-specific monoclonal antibody MM600C (mouse immunoglobulin G1κ; Endogen, Cambridge, Mass.) as a capture antibody, and a biotinylated monoclonal antibody from clone 6B4 (46) (a kind gift from J. van Snick, Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, Brussels, Belgium) was used for determination. To calculate IL-6 concentrations in the samples, an authentic standard preparation of mouse recombinant IL-6 (Boehringer, Mannheim, Germany) was used for comparison. TNF-α was determined by a cytotoxicity assay using a TNF-α-sensitive L929 cell clone (C5F6) (a generous gift from C. Galanos, Freiburg, Germany) as target cells (46). Cells were plated at a density of 5 × 104 cells/well in 96-well microtiter plates and incubated for 3 h at 37°C in humidified 7.5% CO2 in air. After exposure to TNF-α for 20 h in the presence of actinomycin D (4 μg/ml), viability of the C5F6 cells was determined by staining the surviving cells with crystal violet. TNF-α activity was calibrated by using a standard preparation of mouse recombinant TNF-α (Boehringer). The detection limit was 5 pg/ml.
Statistics.
The effect on calvaria was investigated by comparing the treated half of the calcium with the control half. The results were analyzed by pair analysis using Student's t test. Results for the isolated osteoclasts (Fig. 5) and bone marrow culture (Table 1) were analyzed by analysis of variance (Students-Newman-Keuls multiple-comparison test). Results are presented as means ± standard errors of the means (SEM).
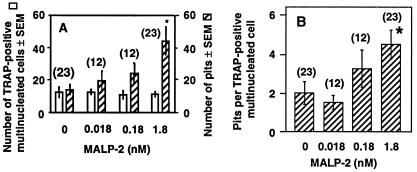
FIG. 5.
Effect of MALP-2 on the bone-resorbing activity of isolated osteoclasts. Rat osteoclasts adhering to dentine slices were incubated for 24 h in the presence of vehicle (0 nM MALP-2) and various concentrations of MALP-2. The number of TRAP-positive multinucleated cells (osteoclasts; open bars) and of pits (hatched bars) (A) and the ratio of pits to TRAP-positive mononuclear cells (B) are given as means ± SEM of n (given in parentheses) slices. ∗, significantly different from value for 0 nM MALP-2; P < 0.05.
TABLE 1.
Effect of MALP-2 on the formation of osteoclasts
| MALP-2 concn (nM) | No. of multinucleated TRAP-positive cellsa |
|---|---|
| 0 | |
| Medium only | 46 ± 5 |
| Vehicle | 37 ± 8 |
| 0.0018 | 31 ± 7b |
| 0.018 | 26 ± 4b |
| 0.18 | 17 ± 5bc |
Mean ± SEM of four culture dishes.
Significantly different from medium-only value.
Significantly different from vehicle value.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In calvarium cultures, MALP-2 stimulated bone resorption in a dose-dependent manner, as was determined from the release of calcium into the medium. The maximum effect was observed at a MALP-2 concentration of 0.18 to 1.8 nM (Fig. 1). Calcitonin, which inhibits the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts (8, 31), decreased MALP-2-induced calcium release by 67 and 96% at concentrations of 0.1 and 1.0 nM, respectively (not shown). These results indicate an osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.
It was previously shown that MDHM, consisting of a mixture of mycoplasmal lipopeptides including MALP-2, could induce the synthesis of arachidonate metabolites (28) and NO (25) in cultures of peritoneal macrophages. Both compounds are known to influence bone metabolism (15, 45) and could therefore mediate the response to MALP-2 in our system.
We therefore studied the effects on MALP-2-mediated bone resorption of various anti-inflammatory drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis. There was an inhibition of about 30% (Fig. 2). The low bone resorption in the absence of MALP-2 was not influenced by these inhibitors, which suggests that MALP-2 stimulates bone resorption at least partially by stimulating the formation of prostaglandins.
We then ascertained whether MALP-2 would stimulate NO production also in the calvarium system. NO is an important mediator of bone resorption. At low concentrations, it seems to stimulate bone resorption (45); at high concentrations, however, it inhibits bone resorption by inducing apoptosis of osteoclast precursor cells and by directly inhibiting the activity of mature osteoclasts. Inflammatory cells produce IFN-γ, which stimulates the production of NO. IFN-γ thus protects against the bone loss through stimulating NO production (14, 22, 23, 36, 45).
In our studies, treatment of calvarium halves with MALP-2 slightly increased the synthesis of NO (Fig. 3A), but the low concentration of NO did not seem to influence bone resorption, since the latter was not diminished by LMMA, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (not shown). IFN-γ stimulated NO production, even in the absence of MALP and to a higher extent in the presence of MALP (Fig. 3A). We investigated whether the higher concentrations of NO-produced in the presence of IFN-γ would inhibit bone resorption. Indeed, at 0.18 and 1.8 nM MALP-2, the addition of IFN-γ decreased bone resorption, but it had no effect at 0 and 0.018 nM MALP-2 (Fig. 3B). When the NO production stimulated by 0.18 nM MALP-2 and IFN-γ was inhibited by LMMA (Fig. 4A), bone resorption returned to the same level as that found when no IFN-γ was present (Fig. 4B). This indicates that the inhibition of bone resorption is due to NO and not to the direct effect of IFN-γ on bone resorption. At 0.018 nM MALP-2, IFN-γ had no significant effect on bone resorption, as observed in Fig. 3B. Thus, under our experimental conditions, we did not find that low concentrations of NO-stimulated bone resorption, as was demonstrated by van't Hof and Ralston (45). However, in agreement with other data (21, 45), higher levels of IFN-γ-stimulated NO production inhibited bone resorption, which suggests that IFN-γ produced by inflammatory cells may also reduce the MALP-2-induced bone resorption in vivo.
We then tested whether MALP-2 would also activate the bone-resorbing activity of osteoclasts isolated from bones of newborn rats. The number of osteoclasts (TRAP-positive multinucleated cells) was not changed by the treatment with MALP-2, but the number of resorption pits (lacunae) was increased dose dependently (Fig. 5A). Consequently, the ratio of the number of pits divided by the number of osteoclasts was increased, indicating that MALP-2 stimulated the bone-resorbing activity of the osteoclasts (Fig. 5B) and did not influence the number of osteoclasts.
It has been demonstrated that osteoblasts can produce IL-6, a cytokine that stimulates bone resorption. Thus, parathyroid hormone-stimulated bone resorption is partially mediated through the IL-6 production by osteoblasts (22). We therefore investigated whether MALP-2 could stimulate IL-6 in cultured calvaria as it does in peritoneal macrophages (21, 25). Indeed, the IL-6 production of calvaria was increased from <3 ng/ml in the absence of MALP-2 to 45.6 ng/ml (mean ± SEM of five calvarium halves) in the presence of 0.18 nM MALP-2. The calvaria did not produce any detectable TNF-α, and MALP-2 did not influence the production of this cytokine.
The effect of MALP-2 on the generation of osteoclasts was investigated by culturing bone marrow cells. In this culture, hemopoietic precursor cells develop in the presence of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol to osteoclast-like cells expressing osteoclastic properties (44). They stain positive for TRAP, bind calcitonin, and resorb bone when cultured on bone slices. As seen in Table 1, MALP-2 did not stimulate the formation of TRAP-positive multinucleated cells. On the contrary, it inhibited the formation of these cells. These data and those in Fig. 5 suggest that MALP-2 has two opposing effects, although at different sites: it increases bone resorption in bone tissue by stimulating the mature osteoclasts, and it inhibits the formation of new osteoclasts in the bone marrow.
It remains to be elucidated which cells in the bone tissue are the target of MALP-2. Macrophages in the calvaria may be activated by the lipopeptide, and the products released by these cells may stimulate bone resorption. However, such a mechanism seems unlikely, since we were unable to detect any MALP-2-stimulated TNF-α production in calvaria. Macrophages also are probably not involved in the activation of isolated osteoclasts. Their number in isolated osteoclast preparations is too small to induce an effect. The osteoblasts may be the target of MALP-2. They may also be the cells which produce NO, since it has been demonstrated that osteoblasts release NO when stimulated with lipopolysaccharide, TNF-α, or IL-1, and in particular when these stimulators act in concert with IFN-γ (5, 37, 39). The IL-6 produced in the presence of MALP-2 originates also probably from osteoblasts. As mentioned above, these cells have been demonstrated to produce IL-6 (22). In bone marrow culture, which is an intricate system where many factors can be produced, MALP-2 may activate hemopoietic cells to release inhibitors of osteoclast formation. NO may be such an inhibitor. The molecule has been shown to be apoptotic for osteoclast progenitor cells (45).
It is still a matter of debate whether mycoplasmas, in order to cause joint inflammation, must be present as live organisms at this site. If the presence of substances like MALP-2 in the joints is sufficient to cause inflammation, one could envisage that MALP, or mycoplasmal lipoproteins in general, are transported there as immunocomplexes, since lipoproteins are dominant antigens and antibody is frequently detected in the sera of arthritis patients (11). Another vehicle to transport live mycoplasmas to the joints could be neutrophils, which phagocytose but do not kill mycoplasmas. This possibility has been discussed elsewhere (48).
In conclusion, the results demonstrate that MALP-2 increases bone resorption in calvaria and in isolated osteoclasts, suggesting that it stimulates the bone-resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. The formation of osteoclasts is reduced in bone marrow culture. Thus, in vivo MALP-2 may induce local bone loss by stimulating the bone-resorbing activity of mature osteoclasts. However, this effect may be weakened by the inhibition of the osteoclast generation and by the formation of NO. Target cells of MALP-2 may be osteoblasts stimulating the osteoclasts and hemopoietic cells. However, the osteoclasts may also be directly affected by MALP-2.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank I. Ryf for correcting the English and J. Scriven for editing this manuscript, C. Galanos, Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology, Freiburg, Germany, for cell line L929, clone C5F6, and T. Hirsch for performing the TNF and IL-6 assays. We are grateful to R. Süßmuth and G. Jung for a generous supply of synthetic MALP-2 and to Novartis Pharma AG, Basel, and Hoffmann-LaRoche, Basel, Switzerland, for supplying calcitonin and 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol, respectively.
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (grant 31-049256.96) and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Mu 672/2-3).
REFERENCES
- 1.Arnett T R, Spowage M. Modulation of the resorptive activity of rat osteoclasts by small changes in extracellular pH near the physiological range. Bone. 1996;18:277–279. doi: 10.1016/8756-3282(95)00486-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Badolato R, Oppenheim J J. Role of cytokines, acute-phase proteins, and chemokines in the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996;26:526–538. doi: 10.1016/s0049-0172(96)80041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Brennan F M, Zachariae C O, Chantry D, Larsen C G, Turner M, Maini R N, Matsushima K, Feldmann M. Detection of interleukin 8 biological activity in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and production of interleukin 8 mRNA by isolated synovial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990;20:2141–2144. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cole B C, Knudtson K L, Oliphant A, Sawitzke A D, Pole A, Manohar M, Benson L S, Ahmed E, Atkin C L. The sequence of the Mycoplasma arthritidis superantigen, MAM: identification of functional domains and comparison with microbial superantigens and plant lectin mitogens. J Exp Med. 1996;183:1105–1110. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Damoulis P D, Hauschka P V. Cytokines induce nitric oxide production in mouse osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;201:924–931. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Deiters U, Muhlradt P F. Mycoplasmal lipopeptide MALP-2 induces the chemoattractant proteins MIP-1α, MCP-1, and MIP-2 and promotes leukocyte infiltration in mice. Infect Immun. 1999;67:3390–3398. doi: 10.1128/iai.67.7.3390-3398.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Felix R, Fleisch H, Frandsen P L. Effect of Pasteurella multocidatoxin on bone resorption in vitro. Infect Immun. 1992;60:4984–4988. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.4984-4988.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Friedman J, Raisz L G. Thyrocalcitonin: inhibitor of bone resorption in tissue culture. Science. 1965;150:1465–1467. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3702.1465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Furr P M, Taylor-Robinson D, Webster A D. Mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas in patients with hypogammaglobulinaemia and their role in arthritis: microbiological observations over twenty years. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994;53:183–187. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.3.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Herbelin A, Ruuth E, Delorme D, Michel-Herbelin C, Praz F. Mycoplasma argininiTUH-14 membrane lipoproteins induce production of interleukin-1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor alpha by human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1994;62:4690–4694. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.10.4690-4694.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hoffman R W, O'Sullivan F X, Schafermeyer K R, Moore T L, Roussell D, Watson-McKown R, Kim M F, Wise K S. Mycoplasma infection and rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of their relationship using immunoblotting and an ultrasensitive polymerase chain reaction detection method. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1219–1228. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199707)40:7<1219::AID-ART5>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Horner P J, Gilroy C B, Thomas B J, Naidoo R O, Taylor-Robinson D. Association of Mycoplasma genitalium with acute non-gonococcal urethritis. Lancet. 1993;342:582–585. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91411-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Howard C J, Anderson J C, Gourlay R N, Taylor-Robinson D. Production of mastitis in mice with human and bovine ureaplasmas (T-mycoplasmas) J Med Microbiol. 1975;8:523–529. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kasten T P, Collin-Osdoby P, Patel N, Osdoby P, Krukowski M, Misko T P, Settle S L, Currie M G, Nickols G A. Potentiation of osteoclast bone-resorption activity by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:3569–3573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kawaguchi H, Pilbeam C C, Harrison J R, Raisz L G. The role of prostaglandins in the regulation of bone metabolism. Clin Orthop. 1995;313:36–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kennedy S, Ball H J. Pathology of experimental ureaplasma mastitis in ewes. Vet Pathol. 1987;24:302–307. doi: 10.1177/030098588702400403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kobisch M, Friis N F. Swine mycoplasmoses. Rev Sci Tech. 1996;15:1569–1605. doi: 10.20506/rst.15.4.983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kostyal D A, Butler G H, Beezhold D H. A 48-kilodalton Mycoplasma fermentansmembrane protein induces cytokine secretion by human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1994;62:3793–3800. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.3793-3800.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lindsey J R, Cassell H. Experimental Mycoplasma pulmonis infection in pathogen-free mice. Models for studying mycoplasmosis of the respiratory tract. Am J Pathol. 1973;72:63–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Loewenstein J, Rottem S, Gallily R. Induction of macrophage-mediated cytolysis of neoplastic cells by mycoplasmas. Cell Immunol. 1983;77:290–297. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lowik C W, Nibbering P H, van de Ruit M, Papapoulos S E. Inducible production of nitric oxide in osteoblast-like cells and in fetal mouse bone explants is associated with suppression of osteoclastic bone resorption. J Clin Investig. 1994;93:1465–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI117124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lowik C W, van der Pluijm G, Bloys H, Hoekman K, Bijvoet O L, Aarden L A, Papapoulos S E. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-like protein (PLP) stimulate interleukin-6 production by osteogenic cells: a possible role of interleukin-6 in osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;162:1546–1552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90851-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.MacIntyre I, Zaidi M, Alam A S, Datta H K, Moonga B S, Lidbury P S, Hecker M, Vane J R. Osteoclastic inhibition: an action of nitric oxide not mediated by cyclic GMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Migliorini P, Corradin G, Corradin S B. Macrophage NO2−production as a sensitive and rapid assay for the quantitation of murine IFN-gamma. J Immunol Methods. 1991;139:107–114. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90357-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Muhlradt P F, Frisch M. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of a Mycoplasma fermentans-derived substance that activates macrophages to release nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin-6. Infect Immun. 1994;62:3801–3807. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.9.3801-3807.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Muhlradt P F, Kiess M, Meyer H, Sussmuth R, Jung G. Isolation, structure elucidation, and synthesis of a macrophage stimulatory lipopeptide from Mycoplasma fermentans acting at picomolar concentration. J Exp Med. 1997;185:1951–1958. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.11.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muhlradt P F, Kiess M, Meyer H, Sussmuth R, Jung G. Structure and specific activity of macrophage-stimulating lipopeptides from Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1998;66:4804–4810. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.10.4804-4810.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Muhlradt P F, Schade U. MDHM, a macrophage-stimulatory product of Mycoplasma fermentans, leads to in vitro interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor, and prostaglandin production and is pyrogenic in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1991;59:3969–3974. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3969-3974.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nair S P, Meghji S, Wilson M, Reddi K, White P, Henderson B. Bacterially induced bone destruction: mechanisms and misconceptions. Infect Immun. 1996;64:2371–2380. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.7.2371-2380.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Narat M, Bencina D, Kleven S H, Habe F. The hemagglutination-positive phenotype of Mycoplasma synoviaeinduces experimental infectious synovitis in chicken more frequently than does the hemagglutination-negative phenotype. Infect Immun. 1998;66:6004–6009. doi: 10.1128/iai.66.12.6004-6009.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nicholson G C, Moseley J M, Sexton P M, Mendelsohn F A, Martin T J. Abundant calcitonin receptors in isolated rat osteoclasts. Biochemical and autoradiographic characterization. J Clin Investig. 1986;78:355–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI112584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Novak J F, Hayes J D, Jr, McMaster J H. Mycoplasma-mediated bone resorption in bone organ cultures. Microbios. 1995;81:241–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ostergaard M, Stoltenberg M, Lovgreen-Nielsen P, Volck B, Jensen C H, Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging-determined synovial membrane and joint effusion volumes in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: comparison with the macroscopic and microscopic appearance of the synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:1856–1867. doi: 10.1002/art.1780401020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pfutzner H, Sachse K. Mycoplasma bovis as an agent of mastitis, pneumonia, arthritis and genital disorders in cattle. Rev Sci Tech. 1996;15:1477–1494. doi: 10.20506/rst.15.4.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Poggio T V, Orlando N, Galanternik L, Grinstein S. Microbiology of acute arthropathies among children in Argentina: Mycoplasma pneumoniae and hominis and Ureaplasma urealyticum. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1998;17:304–308. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199804000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ralston S H, Ho L P, Helfrich M H, Grabowski P S, Johnston P W, Benjamin N. Nitric oxide: a cytokine-induced regulator of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10:1040–1049. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650100708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ralston S H, Todd D, Helfrich M, Benjamin N, Grabowski P S. Human osteoblast-like cells produce nitric oxide and express inducible nitric oxide synthase. Endocrinology. 1994;135:330–336. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.1.7516867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rawadi G, Roman-Roman S. Mycoplasma membrane lipoproteins induced proinflammatory cytokines by a mechanism distinct from that of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1996;64:637–643. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.2.637-643.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Riancho J A, Salas E, Zarrabeitia M T, Olmos J M, Amado J A, Fernandez-Luna J L, Gonzalez-Macias J. Expression and functional role of nitric oxide synthase in osteoblast-like cells. J Bone Miner Res. 1995;10:439–446. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650100315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rodriguez J L, Gutierrez C, Brooks D L, Damassa A J, Oros J, Fernandez A. A pathological and immunohistochemical study of goat kids undergoing septicaemic disease caused by Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capricolum, Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri and Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides (large colony type) Zentbl Veterinaermed Reihe B. 1998;45:141–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1998.tb00777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rodriguez J L, Poveda J B, Gutierrez C, Acosta B, Fernandez A. Polyarthritis in kids associated with Mycoplasma putrefaciens. Vet Rec. 1994;135:406–407. doi: 10.1136/vr.135.17.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Rollins S, Colby T, Clayton F. Open lung biopsy in Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986;110:34–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sohaeverbeke T, Gilroy C B, Bebear C, Dehais J, Taylor-Robinson D. Mycoplasma fermentans in joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other joint disorders. Lancet. 1996;347:1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)91065-x. . (Letter.) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Takahashi N, Yamana H, Yoshiki S, Roodman G D, Mundy G R, Jones S J, Boyde A, Suda T. Osteoclast-like cell formation and its regulation by osteotropic hormones in mouse bone marrow cultures. Endocrinology. 1988;122:1373–1382. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-4-1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.van't Hof R J, Ralston S H. Cytokine-induced nitric oxide inhibits bone resorption by inducing apoptosis of osteoclast progenitors and suppressing osteoclast activity. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12:1797–1804. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1997.12.11.1797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vink A, Coulie P G, Wauters P, Nordan R P, Van Snick J. B cell growth and differentiation activity of interleukin-HP1 and related murine plasmacytoma growth factors. Synergy with interleukin 1. Eur J Immunol. 1988;18:607–612. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Washburn L R, Ramsay J R. Experimental induction of arthritis in LEW rats and antibody response to four Mycoplasma arthritidis strains. Vet Microbiol. 1989;21:41–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(89)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Webster A D, Furr P M, Hughes-Jones N C, Gorick B D, Taylor-Robinson D. Critical dependence on antibody for defence against mycoplasmas. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988;71:383–387. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Williams M H, Brostoff J, Roitt I M. Possible role of Mycoplasma fermentans in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1970;2:277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91328-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]