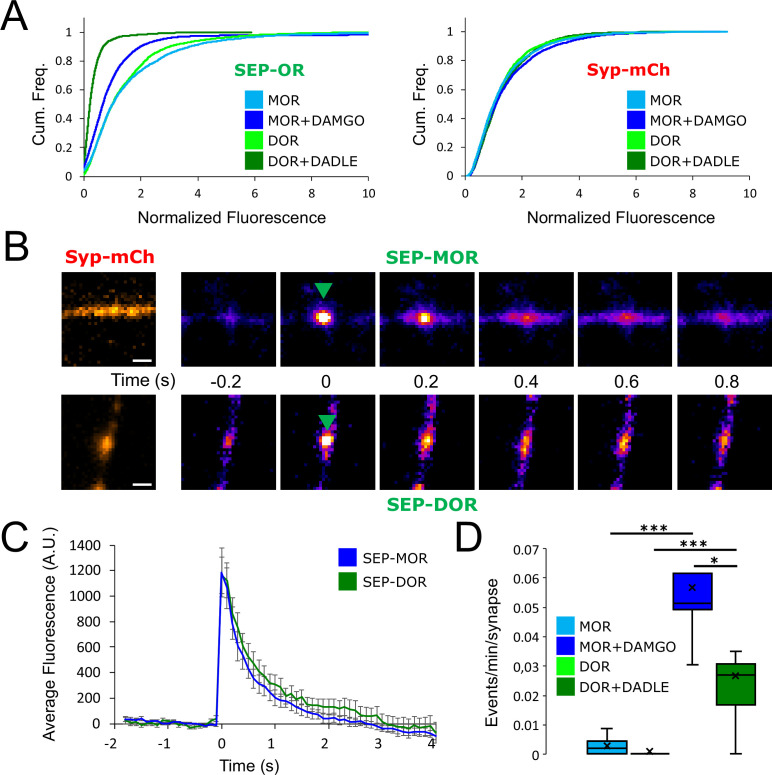
Figure 5. DOR is less efficiently recycled to the plasma membrane compared to MOR.
(A) Eighteen hr of incubation with DADLE 10 μm (n=2934 synapses) induces a marked loss of surface SEP-DOR in axons compared to the untreated control (n=3,376 synapses). The loss is more pronounced than what is observed after chronic treatment of SEP-MOR with DAMGO (replotted from Figure 1G). Syp-mCh fluorescence control remains similar across conditions. (B) Representative examples of surface insertion of SEP-tagged opioid receptors. Neurons were incubated for 20 min with either DAMGO 10 μM (for SEP-MOR) or DADLE 10 μM (for SEP-DOR), and imaged at 10 Hz using oblique illumination. Insertion events appear as bursts of fluorescence (green arrow). Scale bar is 1 μm. (C) Average fluorescence intensity profile at the site of insertion for SEP-MOR (n=59 events) and SEP-DOR (n=49 events), for events imaged as described in B. Error bars represent SEM. (D) Whisker plots of the normalized frequency of surface insertion events for neurons imaged as described in B. Frequency of recycling events was increased for both MOR (n=5 acquisitions) and DOR (n=8 acquisitions) compared to the no agonist pretreatment condition (MOR n=6 acquisitions, DOR n=8 acquisitions). *, *** represent p<0.05, 0.001, respectively. See also Figure 5—source data 1.