Abstract
Sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene transfer for active accumulation of iodide in tumor cells is a powerful theranostic strategy facilitating both diagnostic and therapeutic application of radioiodide. In glioblastoma (GBM), the blood-brain barrier (BBB) presents an additional delivery barrier for nucleic acid nanoparticles. In the present study, we designed dual-targeted NIS plasmid DNA complexes containing targeting ligands for the transferrin receptor (TfR) and the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), thus providing the potential for active transport across the BBB followed by targeting of tumor cells. In vitro125I transfection studies confirmed TfR- and EGFR-dependent transfection efficiency and NIS-specific iodide uptake of dual-targeted polyplexes. In vivo gene transfer in mice bearing orthotopic U87 GBM xenografts was assessed at 48 h after intravenous polyplex injection by positron emission tomography (PET) imaging using 18F-labeled tetrafluoroborate (TFB) as tracer. The tumoral 18F-TFB uptake of mice treated with dual-targeted polyplexes (0.56% ± 0.08% ID/mL) was significantly higher compared with mice treated with EGFR-mono-targeted (0.33% ± 0.03% ID/mL) or TfR-mono-targeted (0.27% ± 0.04% ID/mL) polyplexes. In therapy studies, application of 131I induced a superior therapeutic effect of the dual-targeted therapy, demonstrated by a significant delay in tumor growth and prolonged survival.
Keywords: sodium iodide symporter, NIS, radioiodine, blood-brain barrier, EGFR, transferrin receptor, tumor-specific targeting, nanocarrier, pDNA delivery, gene transfer, gene therapy, polyplexe, glioblastoma
Graphical abstract
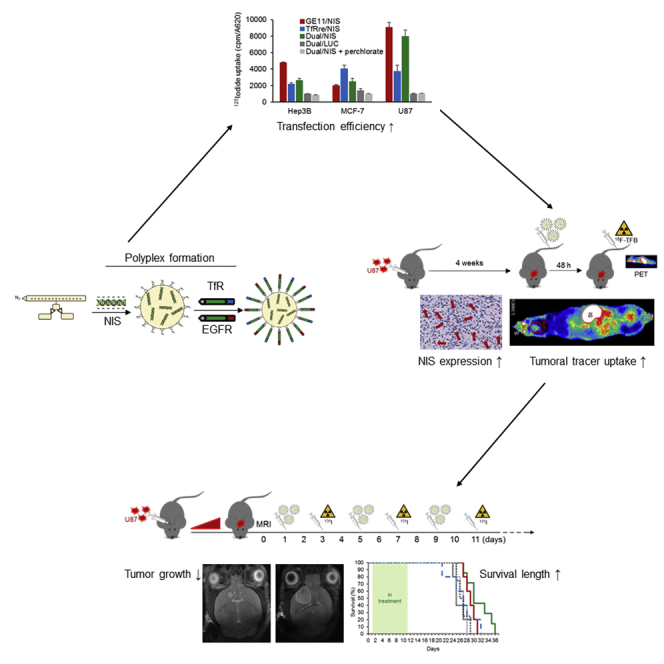
Targeted lipopolyplexes represent promising new vehicles for the tumor-specific delivery of therapeutic genes, such as the theranostic sodium iodide symporter (NIS). Spellerberg et al. established specific and highly efficient EGFR-targeted polyplexes, able to actively cross the blood-brain barrier by transferrin receptor targeting, for an effective NIS gene therapy of glioblastoma.
Introduction
Cloning of the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene in 1996 provided a powerful tool for cytoreductive gene therapy. As an intrinsic plasma glycoprotein, NIS imports iodide into thyroid follicular cells by an active transport mechanism.1 The use of NIS as a theranostic gene has been applied for over 80 years in the management of differentiated thyroid cancer.2 Functional NIS expression allows the accumulation of radionuclides such as 123I, 124I, 99mTc, or 18F-tetrafluoroborate (TFB), which facilitates non-invasive diagnostic imaging through scintigraphic or positron emission tomography (PET) imaging techniques and provides the possibility of dosimetric calculations. In addition to serving as a reporter gene, NIS allows the application of therapeutic radionuclides (131I, 188Re) that facilitate cytotoxic destruction of tumor tissue through the radionuclide trapping activity of NIS-expressing cells and the bystander effect induced by the crossfire effect of beta emission.3,4 The extensive clinical experience with radioiodide imaging and treatment in differentiated thyroid cancer patients is now being translated to non-thyroidal cancers. Our initial studies focused on prostate cancer using adenovirus-mediated human NIS gene delivery in vivo.5,6,7 Since then, our group has focused on the optimization and expansion of NIS-based gene therapy, establishing modified viruses, mesenchymal stem cells, and targeted polyplexes as effective gene delivery vehicles for systemic application. To date, we have successfully introduced NIS into hepatocellular carcinoma, neuroblastoma, colorectal cancer liver metastases, anaplastic thyroid carcinoma, and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30 In these studies, high levels of NIS transgene expression resulted in a delay in tumor growth and prolonged survival in in vivo 131I or 188Re therapy trials. These pilot studies formed the backdrop for refocusing these technologies for the potential treatment of glioblastoma (GBM), a therapeutically challenging and aggressive tumor.
GBM is the most common and a highly aggressive primary brain tumor. Current GBM therapy involves surgical resection, external beam radiation, and temozolomide; however, theses approaches remain largely palliative.31 Due to its aggressive nature, patient survival is, on average, less than 15 months after diagnosis, with a survival of more than 3 years considered as long-term survival.32,33 One of the challenges that make GBM notoriously difficult to target is the blood-brain barrier (BBB), which limits the effectiveness of systemic therapies. The BBB is characterized by tight junctions between the endothelial cells in brain capillaries, low vesicular transport, high metabolic activity, and an extensive variety of efflux pumps.34 This environment represents an active and highly restrictive barrier that protects the central nervous system and provides the basis for optimal neuronal function. Most biotechnologically produced therapeutics are not able to cross the BBB.35 In high-grade gliomas and brain metastases, the blood-brain-tumor barrier (BBTB) can be compromised in its integrity and might be more leaky compared with the intact BBB. Nevertheless, the BBTB presents an additional barrier for systemic treatment of brain tumors.36 By reengineering pharmaceutical compounds to make them suitable for receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT), a well-known mechanism for crossing the BBB, the active uptake from blood into brain becomes possible.37 The transferrin receptor (TfR) is expressed on brain endothelial cells to import iron conjugated with transferrin and is one of the major targeting receptors for RMT. Synthetic non-viral gene delivery systems can be functionalized with a specific TfR ligand for BBB penetration to introduce the NIS gene therapy as a therapy concept to GBM.38,39,40
The gene shuttle system used here involves nanosized polyplexes that are chemically designed for the site-specific delivery of plasmid DNA (pDNA). The polyplexes include sequence-defined cationic lipo-oligoaminoamides (OAAs) required for stable pDNA complexation through electrostatic interaction.41 Due to their novel design incorporating an azido functional group, ligands containing dibenzocyclooctyne (DBCO) can be added for potential functionalization via copper-free click reaction. In addition to the masking of positive charges using monodisperse polyethylene glycol (PEG), the surface functionalization by addition of peptidic ligands is used for targeting purposes.42 In earlier studies, we have convincingly demonstrated the enormous potential of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted polyplexes for tumor-specific delivery.12,13,19,20,23,24 Based on EGFR overexpression as a histopathological hallmark in GBM43,44 in our most recent study, we have already shown successful GBM targeting using EGFR-mono-targeted polyplexes that led to a significant increase in tumoral iodide uptake as shown by in vivo PET imaging, and a sharp decrease in tumor growth that was accompanied by a significant prolongation of survival in the therapy group.45 The present study evaluated a combinatorial strategy to generate a dual-targeted gene transfer vehicle. It was designed to overcome the BBB through inclusion of the ligand TfRre, a 12-amino-acid small protease-resistant retro-enantio peptide that binds the TfR,40 thereby facilitating transport across the BBB, which was recently applied as a targeting agent for pDNA and siRNA delivery by Benli-Hoppe et al.46 The combination of this technology with EGFR targeting using the allosteric EGFR-specific ligand GE11 led to enhanced targeting and therapeutic potential. We monitored vector biodistribution and transfection efficiency by non-invasive imaging in an orthotopic GBM mouse model and subsequently demonstrated the potential therapeutic efficacy of our novel dual-targeted NIS polyplexes after 131I application.
Results
EGFR and TfR expression in adult GBMs
We explored the pathophysiologic context of EGFR and TfR expression in a GBM subtype-specific manner by searching The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset for genes encoding for EGFR and TfR.47 Interestingly, EGFR and TfR expression in GBM is upregulated in about one-third (EGFR) and about half (TfR) of the GBMs compared with levels found in non-tumor brain tissue (Figures S1A and S1B). EGFR is expressed in GBM in a subtype-specific manner, being enriched in the classical subtype while no subtype-specific expression can be seen for the TfR gene (Figures S1C and S1D).
Polyplex formation and characterization
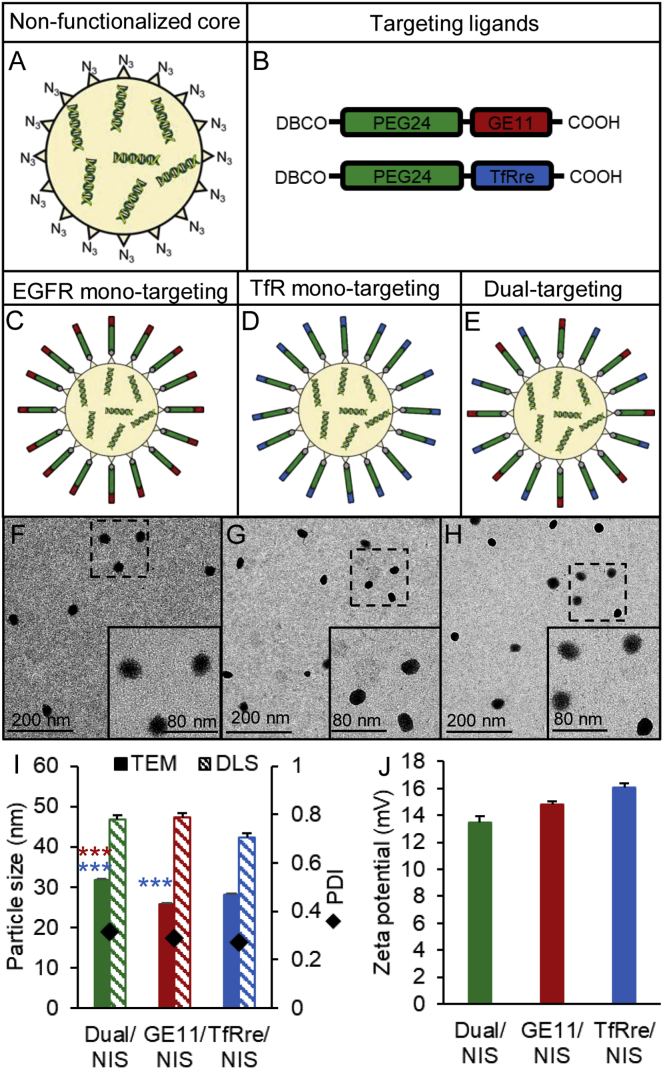
NIS polyplexes (Figure 1) were formed with 10 μg/mL pDNA by first complexing with the T-shaped lipo-OAA 1252 into nanoparticles (Figures 1A),41 followed by surface modification with shielding and targeting reagents DBCO-PEG24-GE11 and/or DBCO-PEG24-TfRre (Figure 1B) using azido/DBCO click chemistry as previously described.46,48 For surface shielding, a monodisperse PEG moiety with 24 oxyethylene units (PEG24) was introduced and the GE11 peptide was applied for EGFR targeting and the TfRre peptide for TfR targeting. In this manner, either mono-targeted NIS polyplexes (GE11/NIS, TfRre/NIS) (Figures 1C and 1D) or dual-targeted polyplexes containing both ligands (Dual/NIS) (Figure 1E) were prepared. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images were taken of Dual/NIS (Figure 1F), GE11/NIS (Figure 1G), and TfRre/NIS (Figure 1H) polyplexes. Polyplexes were generally spherical (Figures 1F–1H) and sizes as measured by TEM revealed a range of 25–32 nm (Figure 1I). The characterization by dynamic light scattering (DLS) yielded approximate dimensions of 42–48 nm (size by numbers) and the polydispersity indexes (PDIs), an indicator of the heterogeneity of particle sizes, were all below 0.3, reflecting a narrow and uniform size distribution (Figure 1I). Zeta potential measurements were assessed by DLS to determine surface charge of polyplexes. A slightly positive surface charge is desired to meet the balancing act between sufficient cellular uptake and no aggregation with biomacromolecules. All formulation displayed a zeta potential of 13–17 mV (Figure 1J).
Figure 1.
Polyplex characterization
The sequence-defined cationic lipo-OAA containing an N-terminal azido group complexed NIS pDNA (N/P ratio of 12) to build an azido bearing core (A). Structures are shown of PEGylated DBCO agents containing the GE11 peptide to target tumoral EGFR or TfRre peptide to target transferrin receptors (B). Ligands were added with 0.25 equiv to build EGFR mono-targeted (C) or TfR mono-targeted polyplexes (D). For dual-targeted polyplexes, 0.125 equiv of DBCO-PEG24-GE11 and 0.125 equiv of DBCO-PEG24-TfRre were used (E). TEM images are shown of DBCO-PEG24-Dual/NIS (F), DBCO-PEG24-GE11/NIS (G) and DBCO-PEG24-TfRre/NIS polyplexes (H) revealing spherical shapes and narrow size distribution. One representative image of each group is shown (scale bar, 200 μm; close-up, 80 μm). TEM measurements revealed a size of 25–32 nm and DLS measurements a size of 42–48 nm (size by numbers) with a uniform size distribution (PDI ≤ 0.3) (I) and a positive surface charge below 20 mV (J) (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001). Results are reported as mean ± SEM (n = 3).
Polyplex-mediated NIS gene transfer in vitro
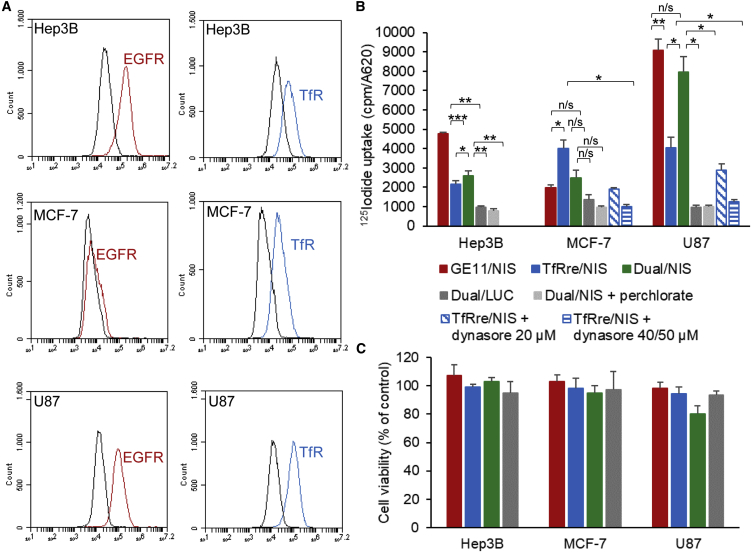
Cell-surface EGFR and TfR expression levels were determined on the human hepatocellular cancer cell line Hep3B, human breast cancer cell line MCF-7, and human GBM cell line U87 by flow cytometry. Hep3B cells showed positive EGFR expression and a minor level of TfR expression, and the MCF-7 cells expressed very low levels of EGFR and a high density of TfR. The U87 cells showed high expression levels for both receptors (Figure 2A). Cell transfection studies were performed using GE11/NIS polyplexes for EGFR-targeted transfection, TfRre/NIS polyplexes for TfR-targeted transfection, Dual/NIS polyplexes for dual-targeted transfection, and Dual/LUC polyplexes as negative control containing a non-NIS-expressing plasmid. Results of the 125I uptake studies indicated that transfection efficiency of the polyplexes correlates with levels of cell surface receptor expression. EGFR-positive Hep3B cells showed 6.1-fold higher iodide uptake 24 h after GE11/NIS polyplex treatment compared with background levels, while TfRre/NIS polyplex treatment resulted in 2.5-fold uptake levels (Figure 2B). Respective outcomes were observed using TfR-positive MCF-7 cells. No efficient transfection was observed using GE11/NIS polyplexes, but 125I uptake was 4.4-fold increased after transfection with TfRre/NIS polyplexes (Figure 2B). U87 cells, expressing both surface receptors, showed 9.5-fold increased 125I uptake after GE11/NIS polyplex treatment and a 3.8-fold increase after TfRre/NIS polyplex transfection. The treatment with GE11/NIS led to a 2.4-fold increased iodide uptake compared with TfRre/NIS (Figure 2B). Dual/NIS polyplexes showed high transfection efficiency in U87 cells with a 7.9-fold increased iodide uptake and moderate transfection efficiency in Hep3B cells with a 3.5-increased iodide uptake (Figure 2B). Using luciferase (LUC)-coding polyplexes (Dual/LUC) or adding the NIS-specific inhibitor perchlorate iodide uptake resulted in background levels. To further validate the TfR-dependent transfection efficiency, TfR-positive MCF-7 and U87 cells were simultaneously treated with increasing concentrations of the dynamin inhibitor dynasore and TfRre/NIS polyplexes. Dynamin is essential for clathrin-dependent coated vesicle formation. A decrease of radioiodide uptake was shown at 20 μM dynasore with a complete inhibition of radioiodide uptake activity at 40 μM on MCF-7 and 50 μM on U87 cells (Figure 2B). All results were normalized to cell survival, and polyplex treatment of cells had no impact on cell survival (Figure 2C).
Figure 2.
Polyplex-mediated NIS gene transfer in vitro
Cell surface receptor expression of EGFR and TfR was measured by flow cytometry. A specific antibody monitored the expression levels of human EGFR and TfR on Hep3B, MCF-7, and U87 cells compared with isotype controls (A). 125I cell transfection studies (n = 3 for each cell line) showed EGFR- and TfR-specific transfection efficiency of targeted polyplexes (GE11/NIS, TfRre/NIS) (B). Dual/NIS polyplexes showed transfection efficiency in Hep3B and U87 cells (B). Background radiation levels after control transfection with LUC-coding polyplexes (Dual/LUC) or the addition of NIS-specific inhibitor perchlorate proved NIS dependency of iodide uptake (B). Treatment with the dynamin inhibitor dynasore resulted in a dose-dependent inhibition of the transfection of MCF-7 and U87 cells using TfRre/NIS polyplexes demonstrating the TfR dependency of transfection with TfR-targeted polyplexes. Total inhibition was reached by the concentration of 40 μM on MCF-7 and 50 μM on U87 cells (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01). Cell viability of Hep3B, MCF-7, and U87 was not affected by polyplex treatment (C). Results are reported as mean ± SEM.
Systemic NIS gene transfer in vivo
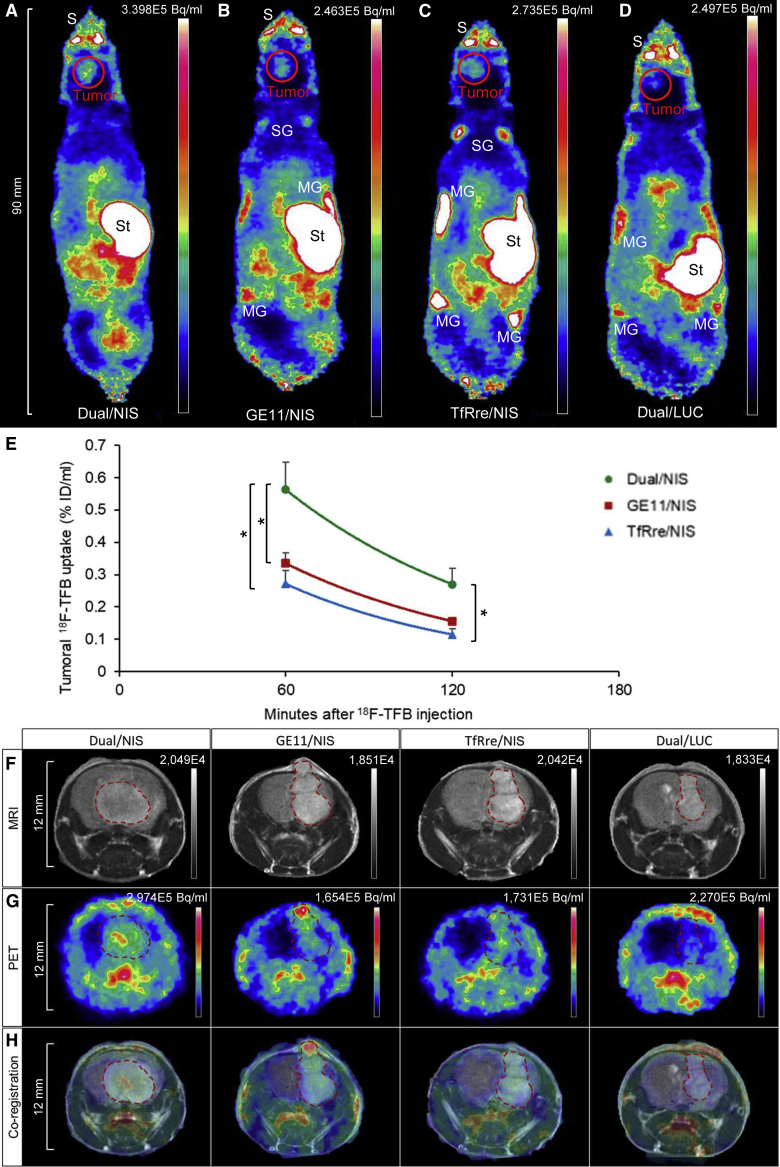
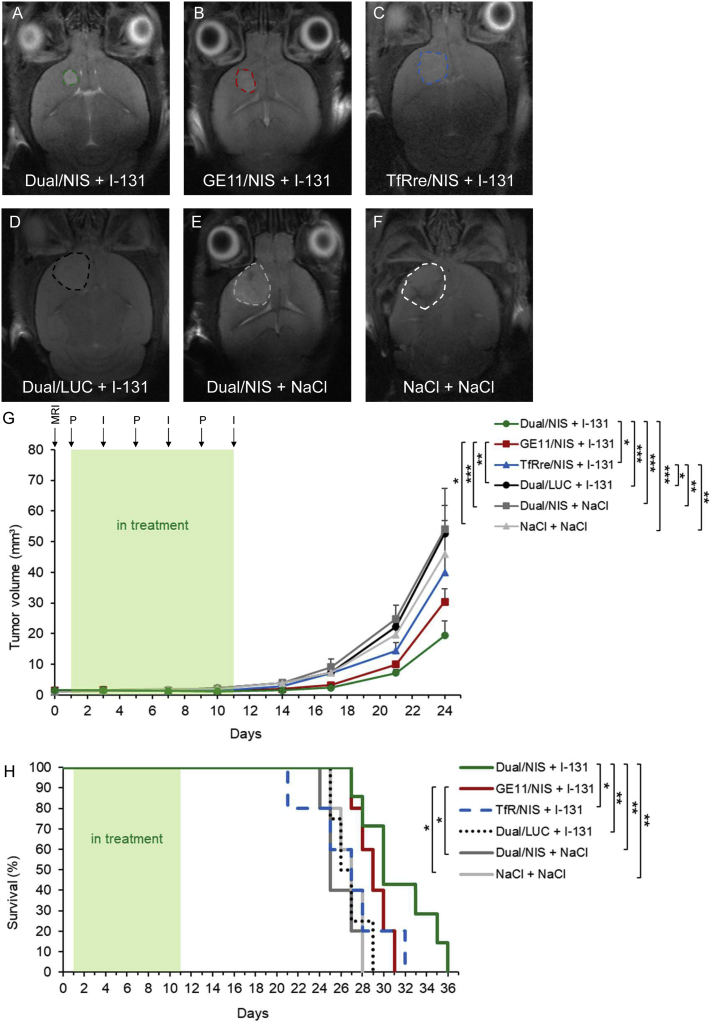
Functional tumoral NIS expression was assessed in an orthotopic GBM (U87) xenograft mouse model after systemic polyplex injection. Mice received polyplexes 23–26 days after intracranial U87 cell inoculation and, 48 h later, high-resolution PET imaging was performed using in-house-synthesized 18F-labeled TFB as tracer. Robust tumoral radionuclide uptake was found in mice treated with Dual/NIS (Figure 3A), GE11/NIS (Figure 3B), and TfRre/NIS polyplexes (Figure 3C), as shown by strong signals in the brain area. The strongest signal was seen in the group that received dual-targeted polyplexes (Figure 3A). No tumoral 18F-TFB uptake above background levels was measured in mice that were injected with LUC-coding polyplexes as control (Dual/LUC) (Figure 3D). Due to physiological NIS expression, the salivary glands, stomach, and mammary glands normally accumulate NIS substrates. In the quantitative analysis, tumors of mice that received dual-targeted NIS polyplexes showed a significantly higher tracer uptake of 0.56% ± 0.08% ID/mL compared with tumors from mice injected with GE11/NIS polyplexes, which exhibited an uptake of 0.33% ± 0.03% ID/mL, or injected with TfRre/NIS polyplexes, revealing an uptake of 0.27% ± 0.04% ID/mL (Figure 3E). Magnetic resonance (MR) (Figure 3F) and PET images (Figure 3G) of axial tumor slices are shown, and their co-registration (Figure 3H) displayed the high congruence of PET signal localization in the tumor area assessed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Figure 3.
Polyplex-mediated NIS gene transfer in vivo
U87 GBM-bearing mice were treated with polyplexes and 48 h later 18F-TFB PET imaging was performed by serial scanning over 120 min. Tumoral tracer uptake was significantly higher in mice treated with Dual/NIS polyplexes (n = 6) (A) compared with GE11/NIS (n = 6) (B) or TfRre/NIS (n = 5) polyplexes (C). Mice treated with GE11/NIS showed a trend toward higher tumoral tracer accumulation compared with mice administered with TfRre/NIS (B and C). No tumoral tracer uptake above background levels was measured in mice injected with Dual/LUC polyplexes (n = 3) (D). One representative image is shown for each group. Quantitative analysis is presented as the percentage of the injected dose per milliliter tumor (E) (∗p ≤ 0.05). Axial MR images (F) and axial PET images (G) of GBMs are shown and co-registered (H) to demonstrate signal localization in the tumor area. One representative tumor slice is shown for each group. Results are reported as mean ± SEM. Tumor signal is encircled in red. (S, nasal secretion, snout; St, stomach; SG, salivary glands; MG, mammary glands).
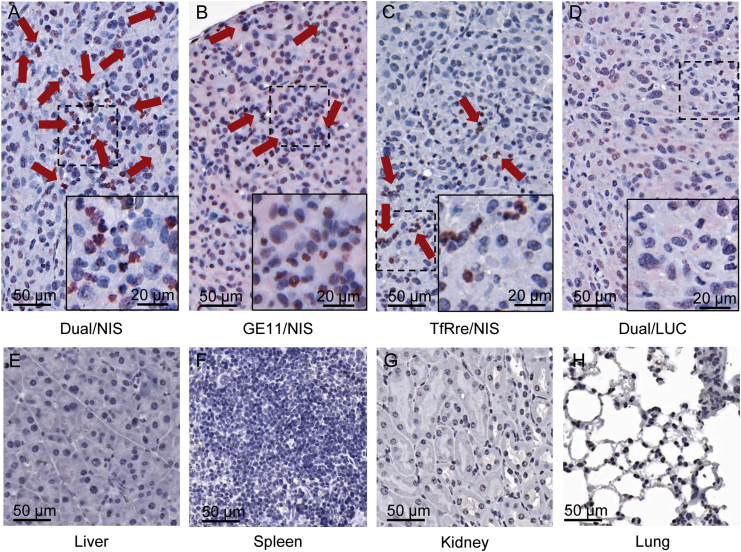
Ex vivo analysis of NIS protein expression by immunohistochemistry
After tissue preparation, tumor sections were analyzed by immunohistochemical staining using an anti-NIS monoclonal antibody. Tumor sections derived from mice that received Dual/NIS (Figure 4A), GE11/NIS (Figure 4B), or TfRre/NIS (Figure 4C) polyplexes showed NIS-expressing tumor cells throughout the tumor sections (red), with the dual-targeted polyplex-treated tumors showing a trend toward higher number and expanded areas of NIS protein expression. Quantitative analysis of four visual fields per tumor revealed 3.73% ± 1.46% NIS-expressing cells in tumor sections of mice that received Dual/NIS polyplexes, 1.75% ± 0.24% in tumor sections of GE11/NIS-treated mice, and 0.58% ± 0.28% in tumor sections of TfRre/NIS-injected mice. In addition to membrane-associated NIS-specific immunoreactivity, NIS staining was also seen in the cytoplasm resulting from NIS protein that is not properly targeted to the membrane after NIS transfection of tumor cells. Immunohistochemical staining of tumor sections from control animals that received Dual/LUC polyplexes showed no NIS-specific immunoreactivity (Figure 4D). In tissue sections of control organs (liver, Figure 4E; spleen, Figure 4F; kidney, Figure 4G; and lung, Figure 4H) of mice treated with Dual/NIS polyplexes, no NIS expression was detected.
Figure 4.
Ex vivo analysis of NIS protein expression
Immunohistochemical staining of NIS protein in GBM xenografts embedded in paraffin showed positive NIS expression (red) in mice treated with targeted NIS polyplexes (A–C). GBM sections of mice treated with Dual/NIS polyplexes revealed a trend toward higher amounts of NIS positive cells (A) compared with mice injected with GE11/NIS (B) or TfRre/NIS polyplexes (C). No positive NIS staining in tumors of mice that received Dual/LUC as control polyplexes (D). Liver (E), spleen (F), kidney (G), and lung (H) sections of a mouse treated with Dual/NIS did not show any NIS expression. One representative image with 20× original magnification is shown for each group (scale bar, 50 μm). A 40× original magnification was chosen for the close-up (scale bar, 20 μm).
131I therapy studies in vivo
Based on the results of the imaging studies, GBM-bearing mice were then injected intravenously (i.v.) with Dual/NIS (n = 7), GE11/NIS (n = 5) or TfRre/NIS (n = 5) followed by intraperitoneal 131I application (55.5 MBq) 48 h later. This application cycle was repeated three times at 4-day intervals. In parallel, control groups received LUC-coding Dual/LUC polyplexes plus 131I, Dual/NIS polyplexes followed by saline, or saline only. Tumor growth was monitored by high-resolution MRI twice a week. All three therapy groups showed a significant delay in tumor growth compared with control groups, with the dual-targeted NIS polyplex therapy group showing the most prominent tumor growth inhibition (Figure 5A, day 21 of therapy trial is shown) compared with mice treated with GE11/NIS polyplexes (Figure 5B; non-significant) or mice injected with TfRre/NIS polyplexes (Figure 5C, significant, ∗p ≤ 0.05). All control groups showed an aggressive tumor growth (Dual/LUC + 131I, Figure 5D; Dual/NIS + NaCl, Figure 5E; and NaCl + NaCl, Figure 5F). The significant delay of tumor growth (Figure 5G) resulted in a significant extension of survival of the Dual/NIS + 131I and GE11/NIS + 131I group (Figure 5H) with a trend toward survival advantage of mice treated with Dual/NIS polyplexes followed by 131I compared with animals that received GE11/NIS polyplexes followed by 131I. The slight delay in tumor growth in mice administered with TfRre/NIS + 131I had no impact on survival time. On day 29, the last control mouse was sacrificed based on the animal welfare protocol, while 40% of the GE11/NIS and 57% of the Dual/NIS therapy group were still alive. We did not observe any unexpected toxicities that may have been induced by polyplex treatment or radioiodide effects on nearby non-cancerous brain tissue.
Figure 5.
131I therapy studies in vivo
GBM-bearing mice were included in therapy trial once tumor volume reached ≥1mm³, confirmed by MRI on day 0. Mice were treated with three cycles of i.v. injection of polyplexes on days 1, 5, and 9 followed by i.p. injection of 55.5 MBq 131I 48 h later (respectively days 3, 7, and 11). Tumor volume was monitored twice a week by MRI. Exemplary MR images of tumor sizes on day 21 of the therapy trial from each group are shown: Dual/NIS + 131I (n = 7) (A), GE11/NIS + 131I (n = 5) (B), TfRre + 131I (n = 5) (C), Dual/LUC + 131I (n = 4) (D), Dual/NIS + NaCl (n = 5) (E), and NaCl + NaCl (n = 5) (F). Tumors are encircled. Injection of Dual/NIS, GE11/NIS, and TfRre/NIS polyplexes followed by 131I led to significant delay in tumor growth compared with the negative control groups Dual/LUC + 131I, Dual/NIS + NaCl, or saline only (G). Administration of Dual/NIS + 131I revealed a trend toward a delay in tumor growth compared with GE11/NIS + 131I and a significant delay compared with TfRre + 131I (G) (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001). Therapy mice treated with Dual/NIS + 131I showed a significant extension of survival compared with TfRre/NIS + 131I and all three negative control groups. Administration of GE11/NIS + 131I led to a significant extension compared with injection of Dual/NIS + NaCl and NaCl + NaCl (∗∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01). Results are reported as mean ± SEM.
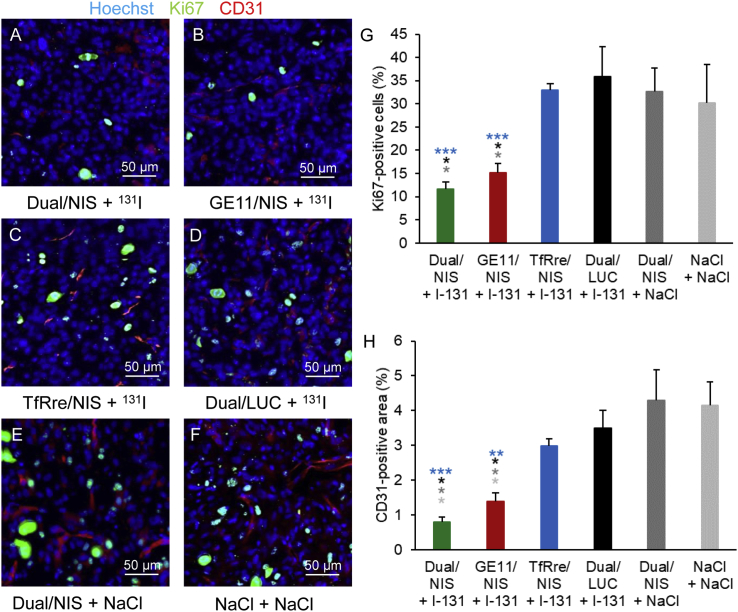
The results were further validated by staining of proliferation status and blood vessel density (Figures 6A–6F). The two therapy groups Dual/NIS and GE11/NIS showed a significantly lower number of Ki67-positive cells (Figure 6G) and a significantly smaller area of CD31 positivity (Figure 6H) compared with TfRre/NIS and negative control groups.
Figure 6.
Ex vivo analysis of cell proliferation index and blood vessel density of therapy tumors
Frozen tissue sections from GBM of the therapy study were prepared and stained for Ki67 (green) for cell proliferation index and CD31 (red) for blood vessel density. Hoechst (blue) was used for nuclei staining. The two therapy groups Dual/NIS (A) and Ge11/NIS (B) followed by 131I showed significantly fewer Ki67-positive cells and significantly smaller CD31-positive area compared with TfRre/NIS + 131I (C) and negative control groups: Dual/LUC + 131I (D), Dual/NIS + NaCl (E), NaCl only (F). Quantitative analysis for cell proliferation index (G) and blood vessel density (H) are shown (∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p ≤ 0.01, ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001). One representative picture of each group is shown at 20× magnification (scale bar, 50 μm). Results are reported as mean ± SEM (for each group n = 4).
Discussion
The BBB represents a major challenge in developing effective therapeutics for brain diseases. This is true not only for neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s, Huntington’s, and Parkinson’s diseases, but also for brain malignancies, such as GBM. Brain microvascular endothelial cells supported by pericytes, astrocytes, tight junctions, neurons, and the basement membrane ensure the blockage of all large molecules and 98% of small molecules into the brain at sufficient therapeutic levels.35 During GBM development, tumor neo-vasculature is formed and neo-capillaries exhibit small fenestrations. Therefore, the permeability of the BBTB is altered and small nanocarriers may pass through such areas. With further tumor growth, inter-endothelial gaps are formed and the BBTB is progressively disrupted, compromising the vascular integrity.49 However, it is suggested that initially occurring GBM cells and residual tumor cells infiltrating to brain parenchyma are populated behind an intact BBB and are barely reached by passive targeting.50 These invasive tumor cells and tumor-associated stromal cells are drivers of tumor recurrence, highlighting the urgent need for active BBB transfer of therapeutic compounds to treat early-stage tumors and reach invasive cell populations.51,52
In the past decade, nanoparticles have become a major research focus based on their flexible composition, allowing them to be tailor made for site-specific drug delivery. Polyplexes (i.e., complexes of pDNA with synthetic sequence-defined cationic subunits), as used in the present study, enable the chemical evolution of a precisely defined medicine.46
Targeted delivery of nucleic acid polyplexes is a complicated process involving multiple extracellular and intracellular barriers.36 Physiochemical characteristics of polyplexes can affect biological distribution, cellular uptake, penetration into biological barriers, and resultant therapeutic effects, highlighting the importance of size, surface charge, and shape of the nanoparticles. Optimally designed polyplexes show a size of around 20–75 nm to ensure sufficient blood circulation and escape from the removal processes found in lung, liver, spleen, and kidney and also allow efficient tissue penetration.53 Larger particles and agglomerates above 2 μm are captured by pulmonary capillary vessels leading to toxicity issues.54 In our studies, TEM images showed homogeneous and spherical nanoparticles for Dual/NIS, GE11/NIS, and TfRre/NIS in the range of 25–32 nm. The characterization by DLS showed a size range between 42 and 48 nm and a low PDI (≤0.3) confirming a narrow size distribution. The apparent discrepancy in size, identified by TEM and DLS, was previously observed and can be explained by fixation/dehydration for TEM and the high sensitivity of DLS for minor fractions of aggregates. No NIS-positive cells were detected off target in liver, spleen, kidney, or lung tissue by immunohistochemical staining. To avoid self-aggregation and aggregation with biomacromolecules, a monodisperse PEG moiety with 24 oxyethylene units was introduced for surface shielding, which was previously shown to be suitable for the in vivo targeting of related polyplexes.22,55,56 Positively charged nanoparticles are more easily internalized than neutral and negatively charged nanoparticles. They are also more efficiently taken up by proliferating cells. Interestingly, cationic nanoparticles were found to specifically attach to tumor vasculature due to negatively charged glycoproteins on the luminal side of tumor endothelium.57,58 Therefore, a slightly positive surface charge (<20 mV) is desired.54 DLS characterization of Dual/NIS, GE11/NIS and TfRre/NIS polyplexes displayed a zeta potential of 13–17 mV.
The polyplexes encapsulated an expression plasmid for the sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene. NIS is a well-characterized iodide symporter and implemented as standard care in the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer for more than 80 years. It is a self-protein, originated in thyrocytes, with no cell toxicity or immunogenicity. NIS actively accumulates a wide range of substrates, such as 123I,124I, 99mTc, TFB, 131I, and 188Re.59 Therefore, NIS polyplexes are part of nanotheranostics facilitating diagnostic and monitoring features, such as γ-scintigraphy, single-photon emission computed tomography, and PET, as well as the application of beta-emitting radionuclides for a therapeutic purpose. The lack of iodide organification in non-thyroid cancer resulting in a potentially limited half-life of radioiodide in the tumor cells has been raised in the past as an argument against effective NIS gene therapy of non-thyroidal tumors. However, extensive subsequent preclinical studies, including our own, have convincingly demonstrated that the level of radionuclide accumulation reached in the tumor, the duration of 131I retention, and the distribution of NIS transgene expression is sufficient to elicit a significant therapeutic effect of 131I in a variety of tumor entities, including clinically highly aggressive tumor models.17,19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,45 In this context, interesting studies by Castillo-Rivera et al. have demonstrated that the tumor microenvironment may play a role in regulation of NIS function and localization of NIS at the plasma membrane, thereby affecting the efficacy of NIS gene therapy approaches, which will have to be explored further in preclinical tumor models.60
In our current study, we took advantage of the imaging function of NIS expression using three-dimensional 18F-TFB PET offering to visualize NIS-expressing cells with high resolution and sensitivity. The 18F-labeled TFB represents a novel PET-based tracer that can deliver clear images with an excellent target-to-background ratio.59 A well-delineated tumor signal in the PET images displayed high congruence with localization of the tumor area using MR images. A potential disadvantage of 18F-TFB may be a lack of reliable radiation dosimetry extrapolation of radioiodide treatment due to the short half-life of the agent and especially the different pharmacokinetics of 18F-TFB compared with iodide.59,61
A further notable characteristic of nanoparticles is the ability to enhance its bioavailability by the conjugation of specific targeting ligands onto the surface of the polyplexes.53 In the present study, we used the well-characterized ligand GE11 for EGFR targeting and the TfRre peptide for TfR targeting. Both ligands proved to be highly specific and effective in single targeting experiments.12,13,19,20,23,40,45,46
In in vitro cell transfection, we showed EGFR- and TfR-dependent transfection efficiency. GE11/NIS polyplexes showed high transfection efficiency in EGFR-positive Hep3B and U87 cells, while there was an only minor iodide uptake in EGFR-negative MCF-7 cells. Similar specificity was observed when using the TfRre/NIS peptide: high transfection efficiency was seen in the TfR-positive MCF-7 and U87 cells, while a low transfection efficiency was found in the low-TfR-expressing Hep3B cells. The results of U87 cell transfection using GE11/NIS and TfRre/NIS indicate an advantageous transfection efficacy of GE11 polyplexes compared with TfRre polyplexes. Dual-targeted polyplexes showed high transfection efficiency in U87 cells and moderate transfection efficiency in Hep3B cells, suggesting that, in the context of the dual targeting approach, the main effect of tumor cell transfection may arise from the EGFR targeting by the GE11 ligand. For all three cell lines, transfection resulted in only background levels when using LUC-coding control polyplexes or in the presence of the NIS-specific inhibitor perchlorate, thus demonstrating that iodide uptake is indeed NIS mediated.
The TfR is abundant in the endothelial cells lining brain vasculature and has been shown to be a suitable receptor for transcytosis.37 The biodistribution of radiolabeled transferrin-conjugated liposomes for 5-fluorouracil delivery was previously investigated in rats and brain uptake was increased by 13 times compared with non-conjugated liposomes.62 Pardridge et al. demonstrated BBB transfer of a tritium engineered humanized monoclonal antibody against the human TfR1 (3H-hTfRMAb), which cross-reacted with the primate TfR, in a primate model. The brain uptake at 2 h after i.v. injection of 3H-hTfRMAb was 1.1% ID/100 g. Capillary depletion analysis showed that the majority of the vascular bond antibody had passaged across the BBB into brain parenchyma by 2 h after administration.39 The TfR-targeting peptide TfRre used in our present study was initially identified by phage display, interacts with the receptor at a binding site different from that of transferrin to avoid competition, and, in order to increase metabolic stability, a retro-enantio version of the peptide was used.40 Prades et al. showed the capacity of TfRre to travel through the BBB using an in vitro cellular transwell model. Various types of cargo have been attached to the N-terminal region of the peptide, and the capacity of the constructs to cross the cellular BBB model was evaluated. Further validation of the penetration of the cargo-peptide constructs was performed in living mice using intravital two-photon microscopy and confirmed by ex vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy of sectioned brain slices.40
Successful NIS gene therapy of GBM mediated by EGFR-mono-targeted GE11 polyplexes was recently shown by our group.45 Building on these results, we refined the surface functionalization by adding the TfR-targeting peptide TfRre to facilitate active transport of the NIS polyplexes across the BBB. EGFR-amplified GBM cells can be highly invasive, and, therefore, they are partly detected in areas with an intact BBB,44 emphasizing the promising concept of combining the GE11 peptide with the TfRre peptide for sequential targeting.
Quantitative analysis of PET imaging revealed a significantly higher tumoral tracer uptake in mice treated with dual-targeted polyplexes compared with groups injected with mono-targeted GE11 or TfRre polyplexes. Immunohistochemical staining confirmed tumoral NIS protein expression in the groups treated with Dual/NIS, GE11/NIS, or TfRre/NIS, with the highest number of NIS-positive cells and expanded areas of NIS-specific immunostaining in tumor sections of mice treated with dual-targeted polyplexes.
The results obtained from the imaging studies were mirrored by the outcome of the therapy study. Mice treated with Dual/NIS, GE11/NIS, or TfRre/NIS polyplexes followed by 131I 48 h later showed a significant delay in tumor growth compared with negative controls (Dual/LUC + 131I, Dual/NIS + NaCl, NaCl only). Dual-targeted polyplexes led to a significantly slower tumor growth compared with TfR-targeted polyplexes and a trend toward slower tumor growth compared with EGFR-targeted polyplexes. The delay in tumor growth also led to a prolonged survival for Dual/NIS- and GE11/NIS-treated mice. The slightly decreased tumor growth in the TfR-targeted polyplex-treated group had no impact on survival time, thus matching the lowest in vivo transfection efficiency as demonstrated by the non-invasive PET imaging studies. In accordance with these findings, mice treated with Dual/NIS and GE11/NIS polyplexes followed by 131I showed fewer proliferating cells as determined by Ki67 staining and reduced blood vessel density assessed by CD31 staining measured at the end of the therapy study, suggesting a long-term antiangiogenic effect of 131I. An important aspect of any kind of GBM treatment is the side effects affecting healthy neighboring brain tissue. This is indeed an important issue in the context of 131I therapy due to the well-known bystander effect associated with NIS-mediated radioiodide therapy resulting from the crossfire effect of the beta emitter 131I with a path length of 2.4 mm, as demonstrated in our previous work.14,16,63,64 In our therapy series, we have not observed any unexpected toxicities. The dimension of serious side effects by damaging healthy tissue should be assessed in future studies, including large animal studies. The beneficial effect of the dual targeting strategy may further arise in part from additional targeting of TfR on tumor cells, also known to be widely expressed in GBM tumor cells,65,66 thereby simultaneously targeting two receptors, the EGFR as well as the TfR, resulting in enhanced particle uptake by receptor crosslinking and triggering enhanced endocytosis and particle uptake into the lysosome.24,67 Therefore, the dual-targeted polyplexes address concurrently two major obstacles in optimizing GBM treatment strategies, actively crossing the BBB and addressing tumor heterogeneity.
However, TfR-mono-targeted polyplexes can potentially act as both a BBB crossing and a glioma-targeting nanocarrier, but they showed the lowest tumoral tracer uptake in PET imaging despite high TfR expression in U87 cells, suggesting that, in the context of the dual targeting approach, the TfRre peptide worked mainly as a BBB shuttle and the GE11 peptide was indeed required for a solid antitumoral effect. Although the U87 mouse model is a widely used GBM mouse xenograft model for proof-of-principle studies, it does not faithfully represent BBTB characteristics of the majority of GBM patients due to a relatively large extent of BBTB disruption.68 In order to have a more accurate prediction of clinical outcome of novel therapeutic strategies, mouse models using patient-derived GBM cells better mimic the invasive and infiltrative nature of human GBM.69 Also, genetically engineered mouse models, which allow de novo tumor formation, more accurately provide functional tight junction proteins, transporters, or extracellular matrix (ECM) components that are essential in BBB development and biology.70 For a more robust and quantitative analysis of the superior efficacy of cascade-targeting polyplexes in the context of NIS gene therapy, further experiments have to be performed in tumor models that more reliably reflect the invasive nature of GBM with a reproducible BBB. Optionally, other well-described BBB ligands might be evaluated,36 which, however, is beyond the scope of the current study.
In conclusion, this novel approach of dual targeting of TfR and EGFR for polyplex-mediated NIS gene delivery to GBM combines two crucial dual approaches: sequential targeting of two cascades in the context of site-specific drug delivery resulting in increased NIS gene expression in the tumor lesion, in synergy with the theranostic function of NIS enhancing safety by molecular imaging of biodistribution and gene expression levels and allowing targeted NIS-based radioiodide therapy. Our results highlight the potential of the efficient dual-targeted NIS lipopolyplexes as a promising concept for future clinical translation of the NIS gene therapy in the field of nanotheranostics.
Materials and methods
Cell lines
The human GBM cell line U87 (CLS 300367, Cell Line Service, Eppelheim, Germany) was cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; 1 g/L glucose; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) supplemented with 1% (v/v) minimum essential Eagle’s medium (MEM) non-essential amino acids (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). The human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 (American Type Culture Collection [ATCC] HTB-22) was grown in MEM (Sigma-Aldrich) and 1% (v/v) L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich), 1% (v/v) sodium pyruvate (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 5 μg/mL insulin (Sigma-Aldrich) were added. The human hepatocellular cancer cell line Hep3B (HB-8064; ATCC, Manassas, VA, UDA) was cultured in DMEM (1 g/L glucose; Sigma-Aldrich) supplemented with 1% (v/v) MEM non-essential amino acids (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1% (v/v) sodium pyruvate (Thermo Fisher Scientific), and 1% (v/v) L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich). We added 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS Superior, Sigma-Aldrich) and 1% (v/v) penicillin/streptomycin (Sigma-Aldrich) to all media. All cells were maintained at 37°C, 5% CO2, and a relative humidity of 95%. The culture medium was replaced every 48 h and cells were passaged at 70% confluency.
Plasmid, carrier, and DBCO-agent synthesis
The synthesis and optimization of the human NIS cDNA was performed by GENEART (Regensburg, Germany) based on the plasmid pCpG-hCMV-Luc. The establishment of the expression vector pCpG-hCMV-NIS has been described in detail previously.12 The production and purification of the plasmids pNIS-DNA and pCMVLuc (encoding a Photinus pyralis LUC under control of the cytomegalovirus promoter) was operated by Plasmid Factory (Bielefeld, Germany). The T-shaped lipo-OAA 1252 was synthesized via standard Fmoc SPPS as described previously.41 The EGFR- and TfR-targeting agents containing PEG24 as shielding domain and one DBCO unit as attachment site for orthogonal click reaction were synthesized as described previously.46,48
Polyplex formation
The final pDNA concentration was 10 μg/mL for in vitro experiments and 200 μg/mL for in vivo studies. The amount of OAA was calculated at N/P 12 (protonatable nitrogen/phosphate ratio). The solvent was 20 mM HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich) buffer with 5% (w/v) glucose (Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) at pH 7.4 (HBG buffer). pDNA and OAA were diluted in HBG buffer to the same volume. The pDNA solution was mixed in OAA solution by pipetting rapidly 10 times, followed by 30 min incubation at room temperature to form core polyplexes. Ligands for post-modification were diluted in HBG buffer with an equivalence of 0.25. For the dual-targeted polyplexes, the equivalence of 0.25 was composed of 0.125 equiv GE11 and 0.125 equiv TfRre. The total volume of the diluted ligand was one-quarter of the volume of the OAA-pDNA mixture. The ligand was added to the core polyplex solution by pipetting rapidly 10 times, followed by further incubation for 4 h at room temperature.
Particle imaging by TEM
Polyplexes (pDNA concentration 10 μg/mL) were formed in water instead of HBG. The preparation of carbon-coated copper grids (Ted Pella, USA, 300 mesh, 3.0-mm OD) and the staining procedure was performed as described previously.46 All grids were analyzed with a JEOL JEM-1100 (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) electron microscope at 80 kV acceleration voltage.
Particle size and zeta potential measurements
Particle size and zeta potential of polyplexes were measured by DLS on a Zetasizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments, Worcestershire, UK). Polyplexes were formed in 100 μL of HBG buffer with a final pDNA concentration of 10 μg/mL, and 700 μL HBG was added before zeta potential measurement. Detailed measurement parameters were described previously.46 Results are presented by analysis of size by numbers.
Flow cytometry analysis
Flow cytometry was performed to analyze EGFR and TfR expression levels on cell surfaces. U87, MCF-7, and Hep3B were trypsinized and 8 × 105 cells each were washed and resuspended in 100 μL of PBS containing 10% (v/v) FBS (fluorescence-activated cell sorting [FACS] buffer). For EGFR expression, an antibody for human EGFR detection (monoclonal mouse immunoglobulin [Ig] G1, clone H11; Dako, Glostrup, Denmark, catalog no. [cat.] M3563) or a negative isotype control antibody (abcam, Cambridge, UK) was added at a dilution of 1:200 and the samples were incubated for 1 h on ice. Afterward, the cells were washed with FACS buffer and stained with an Alexa Fluor 488 antibody at a dilution of 1:400 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 1 h on ice. For TfR expression, an FITC-labeled antibody for human CD71 detection (monoclonal mouse IgG1k, clone Ber-T9, Milli-Mark, Millipore Corporation, Temecula, CA; cat. FCMAB207F) or an FITC-labeled negative isotype control antibody (abcam) was added at a dilution of 1:10 and an incubation time of 1 h on ice. Propidium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich) was utilized at a dilution of 1:100 to exclude dead cells. BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer (BD Bioscience, Franklin Lakes, NJ) was used for analysis, and appropriate gating was conducted for exclusion of aggregated or fragmented cells.
125I uptake assay
U87, MCF-7, and Hep3B cells were seeded in six-well plates and grown to 60%–70% confluency. Medium was changed to serum-, antibiotic-, and supplement-free medium, and 200 μL/well polyplex solution was added with a pDNA concentration of 10 μg/mL. DBCO-PEG-Dual/NIS, DBCO-PEG-GE11/NIS, and DBCO-PEG-TfRre/NIS were added as targeting polyplexes, and DBCO-PEG-Dual/LUC was added as negative control. Cells were incubated for 4 h at 37°C, and subsequently the medium was replaced by normal growth medium. Cells were maintained overnight, and, 24 h after transfection, NIS-mediated 125I uptake was evaluated as described previously.7 The NIS-specific inhibitor perchlorate (1 mM potassium perchlorate; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was added as an additional control. The dynamin inhibitor dynasore (Merck) was added in different concentrations (20, 40, and 50 μM) 30 min prior to the cell treatment with TfRre/NIS polyplexes. Results are normalized to cell survival and specified as counts per minute (cpm/A620).
Cell viability assay
At 24 h after transfection, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reagent (commercially available, Sigma-Aldrich) was applied followed by an incubation time of 1 h at 37°C. Ten percent dimethyl sulfoxide in isopropanol with an incubation time of 15 min at room temperature was used for cell lysis. The measurement was performed on a Sunrise microplate absorbance reader (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland) at a wavelength of 620 nm. Cell viability is presented as percentage of control (HBG).
Establishment of orthotopic U87 xenografts
U87 cells were intracranially implanted in 6- to 7-week-old female CD-1 nu/nu mice (Charles River, Sulzfeld, Germany) using a stereotactic head holder (David Kopf Instruments, Tujunga, CA) as described in detail previously.45 Animals were maintained with access to mouse chow and water ad libitum and under specific-pathogen-free conditions. More than 15% weight loss or signs of ill health (impairment of breathing, drinking, eating, or cleaning behavior) led to sacrifice. All experimental protocols were authorized by the regional governmental commission for animals (Regierung von Oberbayern) and meet the requirements of the German Animal Welfare Act.
18F-TFB synthesis
For synthesis of 18F-TFB, the protocol published by Khoshnevisan et al. was followed.71 Briefly, 18F− in H2O (starting activity 6 GBq), trapped on a preconditioned (first 0.9% NaCl [5 mL], then H2O [10 mL]) quaternary methyl ammonium (QMA) ion exchange column (Sep-Pak Light, Accell Plus QMA Carbonate, Waters, Wilmslow, UK), was eluted with 0.9% NaCl (0.5 mL) and dried under an argon stream at 95°C and azeotropic distillation with acetonitrile (MeCN; Merck) (3 × 0.5 mL) was performed. 15-Crown-5 (24 mg) (Sigma-Aldrich) in MeCN (0.5 mL) and boron trifluoride diethyl etherate (BF3·OEt2; Sigma-Aldrich) (1 μL) in MeCN (0.5 mL) were added and the mixture was heated to 80°C for 10 min. After quenching with H2O (8 mL), the reaction mixture was passed over preconditioned (H2O, 20 mL; acetone, 20 mL; air, 20 mL) neutral alumina (Sep-Pak Plus, Alumina N Cartridges, Waters, Wilmslow, UK) and QMA (preconditioning see above) cartridges in tandem. QMA cartridges were washed with H2O (4 mL) and, afterward, the product was eluted from the QMA cartridge using 0.9% NaCl (0.5 mL). Quality check was performed using radio thin-layer chromatography (TLC) on a neutral alumina stationary phase (TLC aluminum sheets aluminum oxide 60 F254 neutral [type E] pre-coated, Merck) with methanol (100%) (J.T.Baker, Avantor, Radnor, PA, USA) as mobile phase. The TLC plates were scanned using a radioTLC imaging scanner (Mini-Scan, Eckert & Ziegler Radiopharma, Wilmington, MA, USA). The yield was 14.2% ± 1.2% with a purity of 97.5% ± 0.95%.
Tumoral 18F-TFB uptake in vivo
Between 25 and 30 days after i.c. U87 cell inoculation, mice were i.v. injected with polyplexes (DBCO-PEG-Dual/NIS for dual-targeted NIS gene transfer, DBCO-PEG-GE11/NIS and DBCO-PEG-TfRre/NIS for mono-targeted NIS gene transfer, and DBCO-PEG-Dual/LUC as negative control). The pDNA dose was 2.5 mg/kg in a total volume of 250 μL, and HBG was the solvent. Based on the regimen of our previous study,45 48 h later, mice received 10 MBq of in-house-synthesized 18F-TFB as an NIS PET tracer via the tail vein. NIS-mediated 18F-TFB accumulation in GBM areas was determined by small-animal PET/MRI (nanoScan, Mediso, Budapest, Hungary). Serial scanning was performed 60 and 120 min after 18F-TFB application. Our previous study61 showed a good tracer washout from blood and a high accumulation in the tumor at 60 min. The 120-min time point served to obtain the tracer efflux. Results were assessed using Nucline Acquisition Software (Mediso) and were analyzed with Inveon Research Workplace (SIEMENS Preclinical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany). Ten days before imaging, L-thyroxine (LT4; 5 mg/mL, Sigma-Aldrich) was added to the drinking water of the mice to downregulate thyroidal NIS expression, and, at the same time, the mouse chow was changed to a low-iodine diet (≤0.015 mg/kg iodine) to reduce competition between the NIS substrates I− and TFB (ssniff Spezialdiäten, Soest, Germany).
Tumor volume was assessed by MRI during the scan. The tumor area of each slice was encircled and the size was provided in square millimeters. The average tumor area and tumor height were calculated: Aaverage (mm2) = Atotal (mm2)/Nnumber of sections containing tumor; H (mm) = Nnumber of sections containing tumor ∗ Tslice thickness (mm). This was followed by the calculation of the tumor volume: Vtumor (mm³) = Aaverage (mm2) ∗H (mm). Only mice bearing a GBM with a size of >30 mm³ were considered for the PET imaging analysis. There was no significant difference in the mean tumor sizes between the experimental groups: mice that received DBCO-PEG-Dual/NIS had a mean tumor size of 69.3 ± 11.8 mm³, the group that was injected with DBCO-PEG-GE11/NIS had a mean tumor volume of 70.0 ± 13.5 mm³, and DBCO-PEG-TfRre-treated mice were bearing tumors with a mean size of 61.4 ± 10.9 mm³.
Tissue preparation
After anesthesia and thorax incision, mice were perfused transcardially with 1× PBS followed by a 4% formaldehyde solution (paraformaldehyde [PFA]). Brain, liver, spleen, kidney, and lungs were explanted and fixed in 4% PFA for 48 h at room temperature and stored in 1× PBS at 4°C until paraffin embedding.
Ex vivo immunohistochemical NIS protein staining
Paraffin-embedded tissues were rehydrated and incubated with a primary mouse monoclonal NIS-specific antibody (Merck Millipore; cat. MAB3564, dilution 1:500) for 60 min at room temperature. Subsequently, a biotin-SP-conjugated goat antimouse IgG antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch; West Grove, PA; dilution 1:200) was applied for 20 min, followed by peroxidase-conjugated streptavidin (Jackson ImmunoResearch; dilution 1:300) for a further 20 min. The detailed protocol was described previously.72 Scanning of stained sections was performed with the Pannoramic MIDI digital slide scanner and pictures were taken using Caseviewer software (3DHISTECH, Budapest, Hungary). Four visual fields (20× magnification) per tumor were chosen and analyzed with ImageJ software (NIH, Bethesda, MD) for quantification.
131I therapy studies
Starting 5 days after i.c. U87 cell implantation, tumor growth was assessed twice a week by high-resolution MRI. A tumor volume of ≥1 mm³ was defined as inclusion parameter (day 0). Therapy trials were started 24 h later with a polyplex injection via the tail vein followed by an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 55.5 MBq 131I (Rotop Pharmaka, Dresden, Germany) 48 h later. A therapeutic dose of 55.5 MBq 131I (1.5 mCi) was used, initially chosen empirically based on radiation safety issues, tolerability, and efficacy, and was continuously used in our studies for the purpose of comparability. Based on a table of dose conversion factors that allows for allometric adaption from preclinical animal models to humans based on body surface area (BSA) formulated by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the mouse dose of 55.5 MBq translates to 13.9 GBq (372 mCi) for a 75-kg human being, which lies within the dosimetrically determined dose range (300–600 mCi) in patients with advanced metastasized differentiated thyroid cancer.59,73 The therapy trial was repeated three times; i.v. polyplex injections were performed on days 1, 5, and 9 and i.p. 131I injections were performed on days 3, 7, and 11. Therapy mice received DBCO-PEG-Dual/NIS, DBCO-PEG-GE11/NIS, or DBCO-PEG-TfRre/NIS followed by 131I. Control mice were treated with DBCO-PEG-Dual/LUC followed by 131I or with DBCO-PEG-Dual/NIS followed by saline (NaCl), or with NaCl i.v. followed by NaCl i.p., respectively. Greater than fifteen percent weight loss; impairment of breathing, drinking, eating, or cleaning behavior; and self-isolation from the group were defined as endpoint criteria. Once at least one of those endpoint criteria was met, the mice were sacrificed.
MRI was performed as described previously.45 Briefly, MRI was acquired with a small-animal 7T preclinical scanner (Agilent Discovery MR901 magnet and gradient system, Bruker AVANCE III HD electronics running ParaVision software release 6.0.1). A birdcage quadrature volume resonator (RAPID Biomedical, Rimpar, Germany) was used for 300-MHz radiofrequency (RF) transmission, and a rigid-housing two channel surface receiver coil array (RAPID Biomedical) was placed over the mouse’s head. Animals were screened for tumor growth with a T2-weighted rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement (RARE) sequence. Seven slices with a thickness of 1 mm were generated, and images were exported in a Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) format for analysis with the DICOM viewer RadiAnt (Medixant, Poznan, Poland). ROIs were visually determined. The tumor volume was calculated as described above.
Indirect immunofluorescence assay
The brains of therapy and control mice were prepared as described in the section “tissue preparation.” At 48 h after post-fixation in PFA, the organs were left in 30% sucrose for at least 24 h at 4°C. Afterward, tissue was embedded in Cryomatrix (Leica) for freezing. Frozen tumor sections were stained with an antibody against Ki67 (abcam, cat. ab15580, dilution 1:200) for cell proliferation and CD31 (BD Pharmingen, Heidelberg, Germany, cat. 550274, dilution 1:50) for blood vessel density as described previously.24 Scanning was performed with the Pannoramic MIDI digital slide scanner and pictures were taken using Caseviewer software (3DHISZTECH Ltd.). Four visual fields (20× magnification) per tumor were chosen and analyzed with ImageJ software (NIH) for quantification.
Statistics
In vitro experiments were performed at least in triplicate and results are shown as mean ± SEM, mean fold change ± SEM, and percentage for survival plots. Two-tailed Student’s t test was used to prove statistical significance. Results of imaging studies are presented as percentage of injected dose per milliliter of tumor, and two-tailed Student’s t test was used to prove statistical significance. For therapy studies, differences in tumor growth were tested by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Fisher’s least significant difference (LSD). Mouse survival is presented in a Kaplan-Meier plot, and statistical significance was tested by log rank. Statistical significance was defined as a p value of <0.05 (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Markus Mittelhäuser, Sandra Sühnel, Sybille Reder, and Jakob Allmann (Department of Nuclear Medicine, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany) for their assistance and support in performing the imaging and therapy studies. We are grateful to Olga Seelbach and her team (Comparative Experimental Pathology, Institute of Pathology, School of Medicine, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany) for preparation of paraffin-embedded slides. We want to acknowledge Susanne Kempter (Department of Physics, LMU Munich, Munich, Germany) for TEM measurements. We owe thanks to Dr. Stefan Stangl (Center of Translational Cancer Research, Klinikum rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich, Munich, Germany) for his help in establishing the orthotopic GBM mouse model in our group. Furthermore, we are grateful for the permission of Prof. Dr. Julia Mayerle, Dr. Yvonne Regel, and Dr. Ujjwal Mahajan to use their laboratory equipment, and we thank Sissy M. Jhiang (Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA) for supplying the full-length human NIS cDNA. This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the Collaborative Research Center SFB 824 to C.S. (project C8), K.S. (project Z2), and F.S. (project Z3), as well as within the Priority Program SPP1629 to C.S. and P.J.N., and by the DFG research project WA 1648/7-1 to E.W., and by a grant from the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung to C.S. (2021.094.1). Ö.Ö. appreciates receiving a YLSY fellowship granted by the Turkish Ministry of Education as support to his PhD study. R.E.K. and R.G. are supported by the DFG (GL691/2; SFB824), the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung, the Anni-Hofmann Stiftung, and the Verein zur Förderung von Wissenschaft und Forschung an der Medizinischen Fakultät der LMU München (WiFoMed). R.G. acknowledges funding by DFG grant INST 409/223-1 FUGG. This work was performed as partial fulfillment of the doctoral thesis of RS at the Faculty of Chemistry and Pharmacy of the LMU Munich.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, R.S., M.E., R.E.K., R.G., E.W., P.J.N., and C.S.; methodology, R.S., T.B.-H., C.K., M.E., R.E.K., K.S., G.M., E.W., P.J.N., and C.S.; investigation, R.S., T.B.-H., Ö.Ö., M.H., and N.S.; formal analysis, R.S., T.B.-H., and Ö.Ö.; resources, F.S., W.A.W., R.G., K.S., and G.M.; writing – original manuscript, R.S.; writing – review and editing, T.B.-H., C.K., M.H., N.S., Ö.Ö., K.S., G.M., M.E., F.S., R.E.K., R.G., W.A.W. E.W., P.J.N., and C.S.; funding acquisition, F.S., E.W., P.J.N., and C.S., supervision, E.W. and C.S.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2022.10.013.
Supplemental information
Data availability
Data are available on request from the authors.
References
- 1.Dai G., Levy O., Carrasco N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature. 1996;379:458–460. doi: 10.1038/379458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Spitzweg C., Morris J.C. Gene therapy for thyroid cancer: current status and future prospects. Thyroid. 2004;14:424–434. doi: 10.1089/105072504323150732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guo R., Zhang M., Xi Y., Ma Y., Liang S., Shi S., Miao Y., Li B. Theranostic studies of human sodium iodide symporter imaging and therapy using 188Re: a human glioma study in mice. PLoS one. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hingorani M., Spitzweg C., Vassaux G., Newbold K., Melcher A., Pandha H., Vile R., Harrington K. The biology of the sodium iodide symporter and its potential for targeted gene delivery. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2010;10:242–267. doi: 10.2174/156800910791054194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spitzweg C., Dietz A.B., O'Connor M.K., Bergert E.R., Tindall D.J., Young C.Y., Morris J.C. In vivo sodium iodide symporter gene therapy of prostate cancer. Gene Ther. 2001;8:1524–1531. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Spitzweg C., O'Connor M.K., Bergert E.R., Tindall D.J., Young C.Y., Morris J.C. Treatment of prostate cancer by radioiodine therapy after tissue-specific expression of the sodium iodide symporter. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6526–6530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Spitzweg C., Zhang S., Bergert E.R., Castro M.R., McIver B., Heufelder A.E., Tindall D.J., Young C.Y., Morris J.C. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) promoter-driven androgen-inducible expression of sodium iodide symporter in prostate cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2136–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Grünwald G.K., Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Schwenk N., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Schwaiger M., Zach C., Göke B., Holm P.S., Spitzweg C. Sodium iodide symporter (NIS)-mediated radiovirotherapy of hepatocellular cancer using a conditionally replicating adenovirus. Gene Ther. 2013;20:625–633. doi: 10.1038/gt.2012.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Grünwald G.K., Vetter A., Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Schwenk N., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Schwaiger M., Zach C., Wagner E., Göke B., et al. EGFR-targeted adenovirus dendrimer coating for improved systemic delivery of the theranostic NIS gene. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids. 2013;2:e131. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2013.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grünwald G.K., Vetter A., Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Schwenk N., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Schwaiger M., Zach C., Wagner E., Göke B., et al. Systemic image-guided liver cancer radiovirotherapy using dendrimer-coated adenovirus encoding the sodium iodide symporter as theranostic gene. J. Nucl. Med. 2013;54:1450–1457. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.115493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Klutz K., Russ V., Willhauck M.J., Wunderlich N., Zach C., Gildehaus F.J., Göke B., Wagner E., Ogris M., Spitzweg C. Targeted radioiodine therapy of neuroblastoma tumors following systemic nonviral delivery of the sodium iodide symporter gene. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009;15:6079–6086. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Klutz K., Schaffert D., Willhauck M.J., Grünwald G.K., Haase R., Wunderlich N., Zach C., Gildehaus F.J., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Göke B., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted (131)I-therapy of liver cancer following systemic delivery of the sodium iodide symporter gene. Mol. Ther. 2011;19:676–685. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Dohmen C., Wunderlich N., Knoop K., Zach C., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Gildehaus F.J., Ziegler S., Fürst S., et al. Image-guided tumor-selective radioiodine therapy of liver cancer after systemic nonviral delivery of the sodium iodide symporter gene. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011;22:1563–1574. doi: 10.1089/hum.2011.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Wunderlich N., Zach C., Anton M., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Göke B., Spitzweg C. Sodium iodide symporter (NIS)-mediated radionuclide ((131)I, (188)Re) therapy of liver cancer after transcriptionally targeted intratumoral in vivo NIS gene delivery. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011;22:1403–1412. doi: 10.1089/hum.2010.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Knoop K., Kolokythas M., Klutz K., Willhauck M.J., Wunderlich N., Draganovici D., Zach C., Gildehaus F.J., Böning G., Göke B., et al. Image-guided, tumor stroma-targeted 131I therapy of hepatocellular cancer after systemic mesenchymal stem cell-mediated NIS gene delivery. Mol. Ther. 2011;19:1704–1713. doi: 10.1038/mt.2011.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Knoop K., Schwenk N., Dolp P., Willhauck M.J., Zischek C., Zach C., Hacker M., Göke B., Wagner E., Nelson P.J., Spitzweg C. Stromal targeting of sodium iodide symporter using mesenchymal stem cells allows enhanced imaging and therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013;24:306–316. doi: 10.1089/hum.2012.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Knoop K., Schwenk N., Schmohl K., Müller A., Zach C., Cyran C., Carlsen J., Böning G., Bartenstein P., Göke B., et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated, tumor stroma-targeted radioiodine therapy of metastatic colon cancer using the sodium iodide symporter as theranostic gene. J. Nucl. Med. 2015;56:600–606. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.146662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Müller A.M., Schmohl K.A., Knoop K., Schug C., Urnauer S., Hagenhoff A., et al. Hypoxia-targeted 131I therapy of hepatocellular cancer after systemic mesenchymal stem cell-mediated sodium iodide symporter gene delivery. Oncotarget. 2016;7:54795–54810. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schmohl K.A., Dolp P., Schug C., Knoop K., Klutz K., Schwenk N., Bartenstein P., Nelson P.J., Ogris M., Wagner E., Spitzweg C. Reintroducing the sodium-iodide symporter to anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 2017;27:1534–1543. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmohl K.A., Gupta A., Grünwald G.K., Trajkovic-Arsic M., Klutz K., Braren R., Schwaiger M., Nelson P.J., Ogris M., Wagner E., et al. Imaging and targeted therapy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using the theranostic sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene. Oncotarget. 2017;8:33393–33404. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Urnauer S., Klutz K., Grünwald G.K., Morys S., Schwenk N., Zach C., Gildehaus F.J., Rödl W., Ogris M., Wagner E., Spitzweg C. Systemic tumor-targeted sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma mediated by B6 peptide polyplexes. J. Gene Med. 2017;19:e2957. doi: 10.1002/jgm.2957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Urnauer S., Morys S., Krhac Levacic A., Müller A.M., Schug C., Schmohl K.A., et al. Sequence-defined cMET/HGFR-targeted polymers as gene delivery vehicles for the theranostic sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene. Mol. Ther. 2016;24:1395–1404. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Urnauer S., Müller A.M., Schug C., Schmohl K.A., Tutter M., Schwenk N., et al. EGFR-targeted nonviral NIS gene transfer for bioimaging and therapy of disseminated colon cancer metastases. Oncotarget. 2017;8:92195–92208. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Urnauer S., Schmohl K.A., Tutter M., Schug C., Schwenk N., Morys S., Ziegler S., Bartenstein P., Clevert D.A., Wagner E., Spitzweg C. Dual-targeted NIS polyplexes-a theranostic strategy toward tumors with heterogeneous receptor expression. Gene Ther. 2019;26:93–108. doi: 10.1038/s41434-019-0059-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tutter M., Schug C., Schmohl K.A., Urnauer S., Schwenk N., Petrini M., Lokerse W.J.M., Zach C., Ziegler S., Bartenstein P., et al. Effective control of tumor growth through spatial and temporal control of theranostic sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene expression using a heat-inducible gene promoter in engineered mesenchymal stem cells. Theranostics. 2020;10:4490–4506. doi: 10.7150/thno.41489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tutter M., Schug C., Schmohl K.A., Urnauer S., Kitzberger C., Schwenk N., Petrini M., Zach C., Ziegler S., Bartenstein P., et al. Regional hyperthermia enhances mesenchymal stem cell recruitment to tumor stroma: implications for mesenchymal stem cell-based tumor therapy. Mol. Ther. 2021;29:788–803. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Schug C., Gupta A., Urnauer S., Steiger K., Cheung P.F.Y., Neander C., Savvatakis K., Schmohl K.A., Trajkovic-Arsic M., Schwenk N., et al. A novel approach for image-guided (131)I therapy of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using mesenchymal stem cell-mediated NIS gene delivery. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019;17:310–320. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schug C., Kitzberger C., Sievert W., Spellerberg R., Tutter M., Schmohl K.A., Eberlein B., Biedermann T., Steiger K., Zach C., et al. Radiation-induced amplification of TGFB1-induced mesenchymal stem cell-mediated sodium iodide symporter (NIS) gene (131)I therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:5997–6008. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-4092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schug C., Sievert W., Urnauer S., Müller A.M., Schmohl K.A., Wechselberger A., et al. External beam radiation therapy enhances mesenchymal stem cell-mediated sodium-iodide symporter gene delivery. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018;29:1287–1300. doi: 10.1089/hum.2018.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Schug C., Urnauer S., Jaeckel C., Schmohl K.A., Tutter M., Steiger K., Schwenk N., Schwaiger M., Wagner E., Nelson P.J., Spitzweg C. TGFB1-driven mesenchymal stem cell-mediated NIS gene transfer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2019;26:89–101. doi: 10.1530/ERC-18-0173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Weller M., van den Bent M., Tonn J.C., Stupp R., Preusser M., Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E., Henriksson R., Le Rhun E., Balana C., Chinot O., et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:e315–e329. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pearson J.R.D., Regad T. Targeting cellular pathways in glioblastoma multiforme. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017;2 doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 world health organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Daneman R., Prat A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015;7 doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a020412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pardridge W.M. The blood-brain barrier: bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx. 2005;2:3–14. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.2.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vetter V.C., Wagner E. Targeting nucleic acid-based therapeutics to tumors: challenges and strategies for polyplexes. J. Control Release. 2022;346:110–135. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pardridge W.M. Drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:1959–1972. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2012.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wiley D.T., Webster P., Gale A., Davis M.E. Transcytosis and brain uptake of transferrin-containing nanoparticles by tuning avidity to transferrin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:8662–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1307152110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pardridge W.M., Boado R.J., Patrick D.J., Ka-Wai Hui E., Lu J.Z. Blood-brain barrier transport, plasma pharmacokinetics, and neuropathology following chronic treatment of the rhesus monkey with a brain penetrating humanized monoclonal antibody against the human transferrin receptor. Mol. Pharm. 2018;15:5207–5216. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Prades R., Oller-Salvia B., Schwarzmaier S.M., Selva J., Moros M., Balbi M., Grazú V., de La Fuente J.M., Egea G., Plesnila N., et al. Applying the retro-enantio approach to obtain a peptide capable of overcoming the blood-brain barrier. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015;54:3967–3972. doi: 10.1002/anie.201411408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Berger S., Krhač Levačić A., Hörterer E., Wilk U., Benli-Hoppe T., Wang Y., Öztürk Ö., Luo J., Wagner E. Optimizing pDNA lipo-polyplexes: a balancing act between stability and cargo release. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22:1282–1296. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c01779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wang Y., Luo J., Truebenbach I., Reinhard S., Klein P.M., Höhn M., et al. Double click-functionalized siRNA polyplexes for gene silencing in epidermal growth factor receptor-positive tumor cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020;6:1074–1089. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Verhaak R.G.W., Hoadley K.A., Purdom E., Wang V., Qi Y., Wilkerson M.D., Miller C.R., Ding L., Golub T., Mesirov J.P., et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer cell. 2010;17:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Eskilsson E., Røsland G.V., Solecki G., Wang Q., Harter P.N., Graziani G., Verhaak R.G.W., Winkler F., Bjerkvig R., Miletic H. EGFR heterogeneity and implications for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2018;20:743–752. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Spellerberg R., Benli-Hoppe T., Kitzberger C., Berger S., Schmohl K.A., Schwenk N., Yen H.Y., Zach C., Schilling F., Weber W.A., et al. Selective sodium iodide symporter (NIS) genetherapy of glioblastoma mediatedby EGFR-targeted lipopolyplexes. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2021;23:432–446. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Benli-Hoppe T., Göl Öztürk Ş., Öztürk Ö., Berger S., Wagner E., Yazdi M. Transferrin receptor targeted polyplexes completely composed of sequence-defined components. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021;43 doi: 10.1002/marc.202100602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Bowman R.L., Wang Q., Carro A., Verhaak R.G., Squatrito M. GlioVis data portal for visualization and analysis of brain tumor expression datasets. Neuro. Oncol. 2017;19:139–141. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/now247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Truebenbach I., Zhang W., Wang Y., Kern S., Höhn M., Reinhard S., Gorges J., Kazmaier U., Wagner E. Co-delivery of pretubulysin and siEG5 to EGFR overexpressing carcinoma cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2019;569 doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schlageter K.E., Molnar P., Lapin G.D., Groothuis D.R. Microvessel organization and structure in experimental brain tumors: microvessel populations with distinctive structural and functional properties. Microvasc. Res. 1999;58:312–328. doi: 10.1006/mvre.1999.2188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sarkaria J.N., Hu L.S., Parney I.F., Pafundi D.H., Brinkmann D.H., Laack N.N., Giannini C., Burns T.C., Kizilbash S.H., Laramy J.K., et al. Is the blood-brain barrier really disrupted in all glioblastomas? A critical assessment of existing clinical data. Neuro. Oncol. 2018;20:184–191. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lemée J.M., Clavreul A., Menei P. Intratumoral heterogeneity in glioblastoma: don't forget the peritumoral brain zone. Neuro. Oncol. 2015;17:1322–1332. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lemée J.M., Clavreul A., Aubry M., Com E., de Tayrac M., Eliat P.A., Henry C., Rousseau A., Mosser J., Menei P. Characterizing the peritumoral brain zone in glioblastoma: a multidisciplinary analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2015;122:53–61. doi: 10.1007/s11060-014-1695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhao M., van Straten D., Broekman M.L.D., Préat V., Schiffelers R.M. Nanocarrier-based drug combination therapy for glioblastoma. Theranostics. 2020;10:1355–1372. doi: 10.7150/thno.38147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Jo D.H., Kim J.H., Lee T.G., Kim J.H. Size, surface charge, and shape determine therapeutic effects of nanoparticles on brain and retinal diseases. Nanomedicine. 2015;11:1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2015.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang S., Reinhard S., Li C., Qian M., Jiang H., Du Y., Lächelt U., Lu W., Wagner E., Huang R. Antitumoral cascade-targeting ligand for IL-6 receptor-mediated gene delivery to glioma. Mol. Ther. 2017;25:1556–1566. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.04.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kos P., Lächelt U., He D., Nie Y., Gu Z., Wagner E. Dual-targeted polyplexes based on sequence-defined peptide-PEG-oligoamino amides. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015;104:464–475. doi: 10.1002/jps.24194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang H.-X., Zuo Z.-Q., Du J.-Z., Wang Y.-C., Sun R., Cao Z.-T., Ye X.-D., Wang J.-L., Leong K.W., Wang J. Surface charge critically affects tumor penetration and therapeutic efficacy of cancer nanomedicines. Nano Today. 2016;11:133–144. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Luo J., Schmaus J., Cui M., Hörterer E., Wilk U., Höhn M., Däther M., Berger S., Benli-Hoppe T., Peng L., Wagner E. Hyaluronate siRNA nanoparticles with positive charge display rapid attachment to tumor endothelium and penetration into tumors. J. Control Release. 2021;329:919–933. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Spitzweg C., Nelson P.J., Wagner E., Bartenstein P., Weber W.A., Schwaiger M., Morris J.C. The sodium iodide symporter (NIS): novel applications for radionuclide imaging and treatment. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 2021;28 doi: 10.1530/ERC-21-0177. T193–t213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Castillo-Rivera F., Ondo-Méndez A., Guglielmi J., Guigonis J.M., Jing L., Lindenthal S., Gonzalez A., López D., Cambien B., Pourcher T. Tumor microenvironment affects exogenous sodium/iodide symporter expression. Transl. Oncol. 2021;14 doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kitzberger C., Spellerberg R., Morath V., Schwenk N., Schmohl K.A., Schug C., Urnauer S., Tutter M., Eiber M., Schilling F., et al. The sodium iodide symporter (NIS) as theranostic gene: its emerging role in new imaging modalities and non-viral gene therapy. EJNMMI Res. 2022;12:25. doi: 10.1186/s13550-022-00888-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Soni V., Kohli D.V., Jain S.K. Transferrin coupled liposomes as drug delivery carriers for brain targeting of 5-florouracil. J. Drug Target. 2005;13:245–250. doi: 10.1080/10611860500107401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Willhauck M.J., Sharif Samani B.R., Gildehaus F.J., Wolf I., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Stark H.J., Göke B., Morris J.C., Spitzweg C. Application of 188rhenium as an alternative radionuclide for treatment of prostate cancer after tumor-specific sodium iodide symporter gene expression. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007;92:4451–4458. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-0402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Willhauck M.J., Sharif-Samani B., Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R., Wunderlich N., Göke B., Morris J.C., Spitzweg C. Functional sodium iodide symporter expression in breast cancer xenografts in vivo after systemic treatment with retinoic acid and dexamethasone. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008;109:263–272. doi: 10.1007/s10549-007-9646-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Recht L., Torres C.O., Smith T.W., Raso V., Griffin T.W. Transferrin receptor in normal and neoplastic brain tissue: implications for brain-tumor immunotherapy. J. Neurosurg. 1990;72:941–945. doi: 10.3171/jns.1990.72.6.0941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yukawa H., Tsukamoto R., Kano A., Okamoto Y., Tokeshi M., Ishikawa T., et al. Quantum dots conjugated with transferrin for brain tumor cell imaging. J. Cell Sci. Ther. 2013;04 [Google Scholar]
- 67.Moody P.R., Sayers E.J., Magnusson J.P., Alexander C., Borri P., Watson P., Jones A.T. Receptor crosslinking: a general method to trigger internalization and lysosomal targeting of therapeutic receptor:ligand complexes. Mol. Ther. 2015;23:1888–1898. doi: 10.1038/mt.2015.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brighi C., Reid L., Genovesi L.A., Kojic M., Millar A., Bruce Z., White A.L., Day B.W., Rose S., Whittaker A.K., Puttick S. Comparative study of preclinical mouse models of high-grade glioma for nanomedicine research: the importance of reproducing blood-brain barrier heterogeneity. Theranostics. 2020;10:6361–6371. doi: 10.7150/thno.46468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Huszthy P.C., Daphu I., Niclou S.P., Stieber D., Nigro J.M., Sakariassen P., Miletic H., Thorsen F., Bjerkvig R. In vivo models of primary brain tumors: pitfalls and perspectives. Neuro. Oncol. 2012;14:979–993. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Simeonova I., Huillard E. In vivo models of brain tumors: roles of genetically engineered mouse models in understanding tumor biology and use in preclinical studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014;71:4007–4026. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1675-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Khoshnevisan A., Jauregui-Osoro M., Shaw K., Torres J.B., Young J.D., Ramakrishnan N.K., Jackson A., Smith G.E., Gee A.D., Blower P.J. [(18)F]tetrafluoroborate as a PET tracer for the sodium/iodide symporter: the importance of specific activity. EJNMMI Res. 2016;6:34. doi: 10.1186/s13550-016-0188-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Spitzweg C., Baker C.H., Bergert E.R., O'Connor M.K., Morris J.C. Image-guided radioiodide therapy of medullary thyroid cancer after carcinoembryonic antigen promoter-targeted sodium iodide symporter gene expression. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007;18:916–924. doi: 10.1089/hum.2007.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Trujillo M.A., Oneal M.J., McDonough S., Qin R., Morris J.C. A steep radioiodine dose response scalable to humans in sodium-iodide symporter (NIS)-mediated radiovirotherapy for prostate cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012;19:839–844. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.