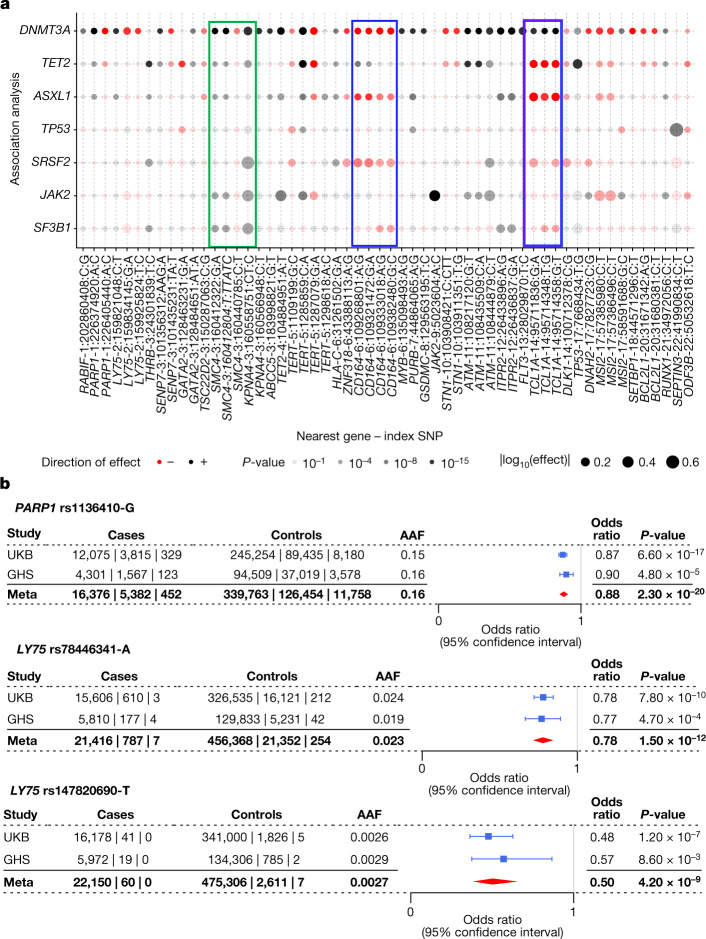
Fig. 2. Germline effect size comparisons across CHIP and Forest plots of PARP1 and LY75 missense variants.
a, Using results from CHIP gene-specific association analyses, effect sizes of index SNPs are compared across CHIP subtypes. SNPs were chosen as those that were independent on the basis of clumping and thresholding (with some refinement based on our conditionally independent variant list) and genome-wide significant in at least one association with CHIP or a CHIP subtype. Certain loci showed notably different effects across CHIP subtypes, as seen at the CD164 locus, which was associated with DNMT3A CHIP and ASXL1 CHIP but not TET2 CHIP, and the TCL1A locus, which was associated with increased risk of DNMT3A CHIP but reduced risk of other CHIP subtypes (blue rectangles). b, Forest plots are shown reflecting the protective associations of a PARP1 missense variant (rs1136410-G) and two LY75 missense variants (rs78446341-A, rs147820690-T) with our DNMT3A CHIP phenotype in the UKB and GHS cohorts. Centre points represent odds ratios as estimated by approximate Firth logistic regression, with errors bars representing 95% confidence intervals. P-values are uncorrected and reflect two-sided tests. Numbers below the cases and controls columns represent counts of individuals with homozygote reference, heterozygote and homozygous alternative genotypes, respectively.