Abstract
The organizational aspects of the educational process of training air traffic controllers are analyzed. A critical assessment is given to the results of cooperation between education and aviation air traffic services. The data of a survey of students are presented, revealing the positive and negative aspects of the cooperation of the education system with civil aviation structures, in particular, the impact of the teacher's work experience on the quality of the educational process, as well as the rooted approach to the development of curricula. The dynamics of growth and decrease in the level of assimilation of educational material by students is shown, depending on the methodology of the teacher's current monitoring of progress.
Keywords: Organizational, Civil aviation, Training, controller, ICAO, Traffic
Organizational; Civil aviation; Training; Controller; ICAO; Traffic.
1. Introduction
Civil aviation is characterized by continuous improvement in the design of aircraft, their flight performance, the infrastructure of airfield and air service systems. These distinctive aspects oblige to develop and improve the educational process for the training of aviation specialists in a consistent manner by updating the composition, content and volume of educational materials, educational, methodological and technical support, including pedagogical technology and skill.
It is known that the organizational, economic, managerial and other activities of civil aviation operators providing international air transportation are carried out on the basis of ICAO standards and recommendations developed under the Chicago Convention (Doc 7300, ICAO, 2006). One of the parties in the activities of ICAO is the implementation of a policy in the field of training specialists for civil aviation, the principles of which are determined by the following four fundamental factors (ICAO Policy in the field of civil aviation training, 2016):
-
1.
TRAINAIR PLUS program.
-
2.
Recognition by ICAO of civil aviation training activities.
-
3.
Training programs for civil aviation specialists developed by ICAO.
-
4.
Cooperation and partnership agreements.
The main goal of the ICAO personnel policy is to achieve high performance in the field of flight safety. The Investing in Human Resources section of the ICAO document (Doc 10004, ICAO, 2014) on the Global Aviation Safety Plan (GASP) 2014–2016 notes: “The successful implementation of the GASP objectives depends largely on the recruitment and retention of qualified personnel and continuous investment in the implementation of measures aimed at developing and improving the professional skills of aviation personnel. Such investments will improve training and education programs to ensure that aviation professionals have the necessary skills to safely operate the international aviation system at a time of significant growth and change. An example is the adoption of ICAO regulations for the introduction of more systematic training methods such as evidence-based competency training.” Further in the same document, in paragraph c) "Implementation of training and education programs" states: "States implement comprehensive programs for the training and education of their technical personnel. Various initiatives, including the Trainair PLUS ICAO program, enable high-quality training for current and future generations of aviation professionals in a cost-effective manner.”
Further, in the development of Dos 10004 for 2017–2019, Dos 10004 for 2020–2022 was put into use. This document lists KE-4 Qualified Technicians (page I-3-2) as one of the Important Critical Elements (CEs) for ensuring safety. The relevance of the issue of training highly qualified personnel will always be present, because. The development of air technology does not stand still.
A critical reflection on the ICAO personnel policy gives grounds to believe that it provides for the creation of a single educational and methodological platform for all member countries in order to eliminate differences in the final results of the educational process and thereby ensure the growth of flight safety indicators and equal rights for aviation personnel in the labor market.
Promotion of the ICAO directive personnel policy by civil aviation authorities, in particular, for the training of air traffic controllers, is carried out on the basis of the relevant documents (Doc 7192 A-1, ICAO; Doc 7192 D-3, ICAO, 1998; Doc 7192 F-1, ICAO; Doc 9941, ICAO, 2011), the provisions of which are put into practice by member countries, based on their economic capabilities.
The role of the personnel policy of ICAO has increased even more in light of the growth in the use of various types of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). In this regard, it is important to refer to the Aviation System Block Upgrades (ASBU) of ICAO. The concept of using ASBUs is described in the ICAO document (Doc 9750-AN/963, ICAO, 2016). The vision is to modernize the aviation system based on existing mid-term ATM modernization plans and the realities of limited access to advanced technological improvements in many regions of the developing world.
The ASBU concept was initiated by ICAO with the aim of integrating unmanned aerial systems into controlled and uncontrolled airspace, which increases the likelihood of potential conflict cases. This can be explained by the steady growth in sales of UAVs and income from their commercial services, about which there is enough information on the Internet resources. This fact necessitates the development of air traffic control systems and, accordingly, the process of training personnel.
Thus, based on the foregoing, it should be noted that with the development of aviation technology and the revision of the rules and regulations of flights, the educational process should be in the focus of special attention. The ICAO recommendations regarding the training of aviation personnel are largely of a directive and general methodological nature. However, the educational process taking place in the environment of an audience or a specialized class requires a detailed search and application of new approaches that contribute to the growth of the quality of training. In this regard, conducting a study to identify educational reserves to improve the quality of training for air traffic services is always one of the urgent tasks. At the same time, we should not forget that the future specialist should not be a biological module of the air traffic service system, but be a specialist able to accumulate knowledge and experience, analyze his decisions and actions, and be able to generate new solutions for new and unforeseen events.
A special place in the system of training aviation specialists is occupied by the process of training aviation dispatchers, who are a kind of managers of processes related to the organization, management and control of aircraft movement in the airspace.
The training of air traffic controllers is characterized by a distinctive feature associated with strict observance of the norms and rules for servicing both domestic and international flights. This feature justifies the need to pay increased attention to the volume, composition and content of professional knowledge, because any unaccounted for necessary educational element can lead to various air incidents in the future, up to aviation accidents.
Currently, according to scientific publications, quite a lot of attention is paid to the development of the educational system for the training of aviation specialists. In the light of the research and development of civil aviation personnel potential, there are a large number of scientific and technical publications and documents that reflect the problems and tasks to be solved. In terms of this, the development of aviation specialist training programs remains relevant due to the globalization of economies. At the same time, various ranges of achievements are observed. Some states, due to the insufficient level of provision of the aviation sector of the economy with specialists, began to intensify educational activities. As an example, we can cite information from the publication (Malagas et al., 2017), which describes in sufficient detail the directions for the development and improvement of the system for training aviation specialists in Greece. The Republic of Uzbekistan does not remain aloof from these problems, in which organizational measures are being taken to increase the economic efficiency of air transport structures, including the training of aviation specialists.
A comprehensive analysis of scientific sources and their systematization seems to be an independent study, therefore, based on the objectives of this study, it is advisable to dwell on some of them, which are closest to the specifics of the training of air traffic controllers.
Scientific work is devoted to the issues of performance improvement education based on the education of tolerance between the teacher and the student, which allows you to remove various kinds of barriers that negatively affect academic performance. In this regard, the authors propose a model for the formation of tolerance. The results of this article are undoubtedly valuable and are of a universal nature, which allows them to be used to organize and conduct the educational process in many theoretical and practical disciplines of education, including the training of air traffic controllers. The special value of these lies in the creation of a tolerant climate in the educational process, which allows, to a certain extent, to exclude psychological tension from the audience, which, as a rule, leads to premature fatigue and weakening of attention. This result is certainly important for the educational process of training air traffic controllers, because. On the part of personnel consumers, special attention is paid to the psychological qualities of air traffic controllers, because labor activity takes place in an environment with a high psychological load. Therefore, in these specialists, already at the stages of training, it is necessary to develop a stable psyche against the background of tolerant training.
Regarding the human factor in ensuring air traffic safety, there is a publication (Arcúrio et al., 2018). The content of the publication is related to ergonomics, in the aspect of which the reliability of a person is considered, characterized as the result of various cognitive processes. Overall, the study is in the context of aviation security, from an ergonomics point of view, and with the aim of reducing the frequency of human factors and errors at airport security checkpoints. The results of this article are of interest in terms of ensuring the safety of the work of air traffic controllers, which is largely determined by their readiness to work in an environment of advanced means of monitoring the air situation. In this case, the training of air traffic controllers should take into account ergonomic aspects, which will have a positive effect on reducing the share of the human factor in the occurrence of aviation incidents. Unfortunately, in the training materials for the training of air traffic controllers, ergonomics issues are poorly covered.
A scientific article (Silva and Vladimirs, 2017) provides reasonably well-founded information about the human factor regarding the activities of air traffic controllers. It states that the source of the activity of the air traffic controller is the flow of events that are associated with unpredicted changes in airspace conditions. Based on the analysis of the causes of aviation incidents, the occurrence of errors associated with the provision of incorrect conflicting instructions is argued. Violations of instructions and normative documents are indicated as the dominant reason. This can naturally be explained by the level of preparedness of air traffic controllers.
The scientific article Shamsiev (2021a) provides a critical analysis of the method of developing programs in the training disciplines of air traffic controllers. Big shortcomings are revealed that negatively affect the adequacy of graduates' knowledge for future professional activities. Recommendations are given to eliminate negative organizational and methodological factors through the use of existing aviation documents that regulate the composition of the knowledge of aviation specialists.
To date, many aspects of the aviation specialist training system remain unaffected or little studied, although some of them lie on the surface. In this context, there are facts when scientific and technological achievements in the field of management regarding economies remain out of sight of specialists involved in the development and improvement of organizational and management systems in the field of civil aviation, including the training of aviation specialists. Taking this into account, it is advisable to strive to take into account the possibility of using new management solutions for sectors of the economy in the aviation sector. In particular, the article Shamsiev (2021b) describes one of the possibilities for improving the process of training air traffic controllers based on the digitalization of methodological support. This path is the most effective, as it allows you to significantly expand the audience of students and perform the necessary actions to obtain the necessary knowledge, both in the classroom and remotely.
The results outlined below are one of the fragments that can partially, but tangibly eliminate the existing shortcomings in the field of aviation education.
The main purpose of this article is to identify and analyze some organizational factors that at first glance are of little importance, but to a certain extent have a positive or negative impact on student performance.
As the final results of the study, it is supposed to develop solutions that help eliminate the existing negative factors that reduce the efficiency and quality of training of air traffic controllers. Due to the fact that the research materials are largely based on observations of the educational process of training air traffic controllers in Uzbekistan, its conclusions are more positional in nature.
2. Materials and methods
The features of this study in the field of training aviation specialists for civil aviation of the Republic of Uzbekistan are the following:
-
1.
The article was prepared based on the results of the work carried out by prof. Z.Z. Shamsiev within the framework of the research plan agreed with the Center "Uzaeronavigation" of the Republic of Uzbekistan.
-
2.
The study is devoted to improving the educational process of training aviation dispatchers for civil aviation.
-
3.
Scientific work is not funded. It is conducted on an initiative basis in compliance with ethical standards.
As a methodological research tool, preference is given to the statistical method, in which, to the extent necessary, critical conclusions of students who perceive the situation most vividly were used, since they are consumers of knowledge, which fully explains their incredible observation and interest in analyzing events in the education system.
In general, the process of training air traffic controllers is characterized by the presence of visible and invisible factors that positively or negatively affect the level and quality of knowledge of graduates. Some of them fundamentally reduce the effectiveness of mastering educational materials. Some of them are the reason leading to the lack of the required volume, composition, content and strength of the acquired knowledge among graduates, and the inadequacy of their workplace. In most cases, the dominant case is that the range of theoretical knowledge is weakly or inadequately supported by the range of practical knowledge and skills. One of the reasons for the existence of this fact is the weak connection between the educational process and production, due to the weak proximity of the curriculum to the requirements of civil aviation regulations relating to air traffic control. When evaluating the effectiveness of the educational process, one should not lose sight of the student's personal characteristics, methodological capabilities and the skill of the teacher.
Figure 1 shows a Conditional hypothetical model of the “Ideal” educational process, when all indicators are good, given that the technical and methodological support also meets the standards and requirements.
Figure 1.
Conditional hypothetical model of a “Ideal” educational process.
A feature of this model is that the influence of any impact caused by external or internal factors can change the state of this ideal model for better or worse. Any deviation of indicators in a negative direction, as a rule, affects the quality of education, which can be expressed by low knowledge of graduates and an increase in the likelihood of being unemployed. At the same time, the inefficiency of the educational process can be expressed in a variety of options and contents, and at the same time in large numbers.
In this context, it would be correct to note the relevance of developing a “Ideal” educational process standard for each area of education, despite the fact that there is an appropriate state educational standard (SES). SES, if you give it an accurate assessment, it is a policy document that declares the general requirements for the knowledge of a graduate, the composition and content of academic disciplines, the volume of academic hours. These indicators are more remote from the objectively required values.
Along with the above omissions, the documents lack a methodological mechanism for achieving the required quality of a graduate's knowledge. Further, on the basis of the SES, curricula of educational subjects are compiled, which have imperfections. On the basis of curricula, appropriate educational and methodological complexes are developed, concentrating educational and methodological material, as well as information about the technical and information resources used. In general, the documents do not provide a system standard for a “Ideal” educational process, which would allow an objective assessment of its quality.
Educational practice shows that, in general, students can be conditionally divided into two categories, and those that occupy any intermediate states. Students of the first category, when the educational material is relevant and presented with effective teaching methods and means, actively and motivatedly acquire knowledge. Students of the second category, for various reasons, show weak motivation and low activity.
The level of educational-methodical and educational-technical support meets the requirements of the State Educational Standard.
3. Results
-
−
graduates have the required knowledge, skills and competencies to perform the profession of air traffic controller;
-
−
graduates have no problems finding employment, if there are no other reasons, for example, the absence of a job vacancy.
Portrait of a student audience:
-
−
students have a strong motivation to get an education and work in their specialty;
-
−
students are constantly in search of new knowledge;
-
−
there is an active direct and feedback between the teacher and students;
-
−
students successfully complete theoretical training and practical classes in air traffic control in accordance with the training/training program.
Teacher portrait:
-
−
the teacher is active with students and has pedagogical skills and practical skills in the field of air traffic management;
-
−
the teaching material of the teacher has a novelty and is relevant to the future professional activity of students;
-
−
other positive qualities of a teacher that contribute to improving the effectiveness of teaching.
The attitude towards learning among students of the intermediate state is difficult to explain, and it is associated with a separate study that has a socio-psychological focus.
The study of the organizational aspects of the educational process is to some extent based on the hypothetical “Ideal” model, since taking this model as a standard, it is possible to assess the real state of the current educational process and formulate the correct conclusions based on the results. Thus, the existing options for motivating the acquisition of knowledge reveal in general terms a positive and negative picture of the process of training air traffic controllers. Based on the above, it is necessary to improve and develop the educational process. Weak motivation does not give a full return. There are many reasons for poor student performance. They may be associated with social and psychological factors that require separate studies, and they are the subject of research in the science of social psychology.
When studying the issues of improving the quality of training of air traffic controllers, first of all, attention was paid to the administrative method of providing or replenishing the education system with faculty. This factor is the most decisive, because teachers are the bearers of knowledge that are passed on to students.
As a rule, the teaching staff of universities in Uzbekistan is mainly replenished by graduates immediately after their graduation from the university. Such specialists, of course, do not have real production experience. They, in the course of their teaching activities, improve and replenish the baggage of theoretical and practical knowledge through short-term internships at enterprises and institutions for advanced training and retraining, as well as through research work in doctoral studies and the defense of PhD or DSc dissertations. All these types of development and improvement, for all their attractiveness, have a drawback in terms of their proximity to real processes. Although they have theoretical knowledge, practical knowledge and skills acquired on simulators, etc., this knowledge lacks the following qualitative indicators:
-
a)
they have not been tested and formalized in real practice;
-
b)
the form of internships is often formal or introductory;
-
c)
the knowledge and experience gained during the internship period were not subjected to verification, load and responsibility for making any practical decisions related to the implementation of real production tasks, etc.
As for passing advanced training courses, it must be admitted that teachers gain methodological experience and knowledge on them, which serve as the basis for the formation of skills. It is in this segment of the educational process that there is a significant discrepancy between the knowledge gained at the university and the requirements of the future workplace.
The above-mentioned gap in the university staffing system is to a certain extent eliminated by integrating the educational process and production by involving leading industry specialists in the educational process, which is expressed more part-time, less often on a permanent basis, and moreover, after their retirement.
Strengthening the training of air traffic controllers by attracting specialists from air traffic services (ATS) structures, although it has undeniable relevance, due to a number of reasons, for example, due to their lack of methodological experience, does not give them the opportunity to effectively realize their potential to improve the quality of education and maximize satisfaction and approximation of the transferred knowledge to the requirements of the workplace.
Observations of the teaching activities of industry professionals have shown that they provide materials mainly based on personal experience and, of course, experience gained in a particular area of the aircraft flight services system. This involuntarily affects the composition and content of the transferred knowledge. At the same time, they do not pay enough or generally do not pay attention to the systematic construction of training materials and their structuring, taking into account the teaching methodology. They are unconsciously satisfied that the student audience with great attention and interest perceives concrete and living information from the production activities of the police department. The presence of this fact in the educational process was confirmed by the results of a survey conducted among students (Table 1).
Table 1.
The results of a survey of students on the assessment of the methodological skills of teachers of the department and specialists of internal affairs services, invited part-time.
| No |
The content of the questions asked to students during the survey | The form of involving a teacher in the educational process of the university |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| University lecturer | Specialist from the structures of the Department of Internal Affairs, working part-time | ||
| 1 | Which of the teachers conducts lectures more professionally and methodologically correctly? |
|
− |
| 2 | Which of the teachers conducts practical and training sessions more professionally and methodologically correctly? | − |
|
| 3 | Which of the teachers gives more real information about the practice? | − |
|
The questions were related to the classes devoted to the organization and maintenance of air traffic, air navigation, flight safety, radio exchange between the pilot and air traffic controller and simulator training.
The survey revealed the following dominant facts.
First fact. Specialists from the departments of internal affairs are characterized by the fact that, when conducting theoretical classes, they are involuntarily more inclined to transfer information from their personal experience, while breaking away from the general context of the academic discipline. Sometimes the process of transferring theoretical materials comes down to recommendations to memorize some fragment of the material, without a proper explanation of its nature and connection with the links of professional functions. This is explained, as mentioned above, by their lack of a sufficient methodological basis for constructing a logical sequence and structuring lecture materials.
Second fact. The pedagogical activity of the specialist, connected with the conduct of practical classes, including training on simulator complexes, showed a diametrically opposite picture. Here, students highly appreciate their work, because. production experts teach how things should be in reality, including special cases from their practice, demonstrating their practical experience with specific air traffic services tasks. Specialists have solid knowledge that is related to their functions at work.
Third fact. Specialists of the internal affairs services provide students with lively and relevant information within the framework of the classes, because by the nature of their official duties they are carriers of new events and new information.
The current state of the issue under consideration brings to the surface an urgent task related to the feasibility of creating an effective educational platform that allows for defect-free training of specialists with the achievement of rational use of the academic time resource.
At first glance, the task submitted for consideration seems trivial due to the presence today of an incredibly large number of scientific and methodological works that reasonably recommend various educational technologies, the use of which brings social and economic benefits. It is the great variety of educational methods and technologies that fundamentally complicates their choice.
Consider, using a simple example, the possibility of using a well-known method of increasing the efficiency of the educational process and activating students' attention to the next educational material.
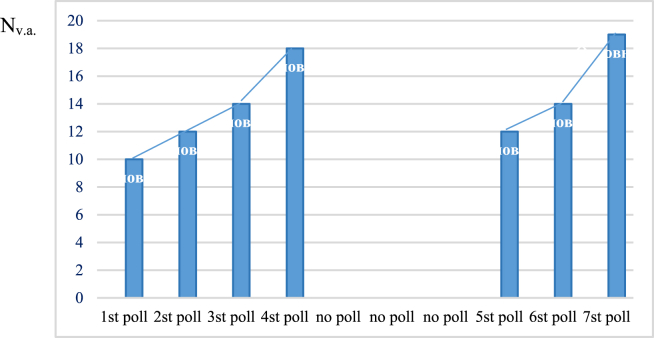
In terms of ensuring the logical connection of the lecture materials with the materials of the previous lecture, the teacher, starting to present the next material, as a rule, repeats the main and defining parts of the previous lecture in order to build a technology for presenting the current material on their basis. Given this rule, a short-term survey of students was conducted before the start of the lecture in order to draw their attention to the continuity of the materials covered with the materials of the current lecture. The survey involved 20 students. The survey was conducted in the form of a test, which had one correct answer and 3 incorrect answers. During the survey, the question was raised about the composition of the tasks of air traffic control. The survey on the same test was carried out continuously at 4 lectures in a row. Statistics showed an increase in correct answers Nv.a. from 10 to 18 (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Graph of student progress depending on the intensity of ongoing monitoring.
Further, the survey at the next three lectures was terminated. On the part of the teacher, the necessary materials of the previous lecture were recalled in order to maintain continuity. Unexpectedly for the students, the survey on the same questions was resumed at the next 8th lecture using the same test. Number of correct answers Nv.a. during the first survey, it fell from 18 to 12, and then rose to 19. This phenomenon can be explained by the fact that some students subconsciously considered that the teacher would not return to this test and therefore weakened their attention to air traffic control tasks - knowledge of air traffic control tasks movement faded into the background. A distinctive feature of the survey was that the students were not made aware of the results. It turns out that some students had a superficial memorization, did not attach much importance to this topic, etc.
This fact is the object of the theory of knowledge in philosophical science. Without going into the essence of this phenomenon in detail, it should be noted that the student must have the qualities to memorize firmly and forever. In current classes, the previously presented materials should be in the field of their attention, so that the integrity and completeness of knowledge are formed throughout the training, and so that after graduation they can immediately take a workplace.
In this process, as shown by the results of the survey, the teacher must show some activity, have a certain methodology of influence, so that students are maximally focused on the perception and memorization of educational material. In part of the foregoing, it is appropriate to pay serious attention to the observance of the systematically phased formation of mental actions. In the aspect of this, the question arises: - Does the teaching staff of higher educational institutions take into account these aspects of educational technology when conducting lectures and practical classes? There is no unequivocal answer to this question; one can simply state evasive answers: “Not always”, “Possibly”, etc.
4. Main results
-
1.
Based on the study of the process of training air traffic controllers, the following main factors have been identified that have both positive and negative effects on the effectiveness of the process of training air traffic controllers.
-
2.
The integration of education and air traffic services structures can significantly increase the level of practical knowledge and skills, however, the lack of methodological experience of industry specialists involved in the educational process in combination leads to a decrease in student performance in terms of acquiring theoretical knowledge.
-
3.
Approximation of the knowledge of university graduates to the requirements of air traffic services structures through the integration of education and aviation structures is carried out without due attention to the methodological preparedness of invited specialists, because there is no solution to the issue of the specialist's interest in additional time and labor costs for acquiring methodological knowledge and skills.
-
4.
Replenishment of the teaching staff of the university by inviting graduates immediately after graduation to teaching activities leads to a big drawback due to the lack of real production experience. Here the question is appropriate: - How correct is this approach in terms of replenishment or training of the teaching staff? At the same time, doctoral studies absolutely do not provide for an internship at an enterprise. The future teacher is deprived of practical skills acquired in real conditions of production or service. Can the teaching information of a teacher be considered convincing if it has not been tested in practice? The teacher's information will be based on his spatial representations. It will look unconvincing, which invisibly and systematically reduces the level of education, and in the future negatively affects the employment of a graduate.
-
5.
Conducting theoretical and practical classes must necessarily be based on methodologically successful approaches to teaching and knowledge control.
5. Conclusion
The study of individual aspects of the educational process of training air traffic controllers showed that despite the large number of scientific papers devoted to the development of effective methods and methods for organizing, conducting and managing educational processes, there are areas that require additional study so that graduates receive a decent education that allows them to successfully find a job.
It should be noted that the materials of the article are based on the data of the educational process of training aviation dispatchers of the Republic of Uzbekistan. Therefore, the author believes that some provisions and results are positional in nature, which may not correspond to the educational processes of other universities.
Declarations
Author contribution statement
Zair Shamsiev, Doctor of Sciences: Conceived and designed the experiments; Performed the experiments; Analyzed and interpreted the data; Contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools or data; Wrote the paper.
Funding statement
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Data availability statement
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Declaration of interest's statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
No additional information is available for this paper.
References
- Arcúrio Michelle S.F., Nakamura Eliane S., Armborst Talita. Human factors and errors in security aviation: an ergonomic perspective. J. Adv. Transport. 2018:9. Hindawi. Article ID 5173253. [Google Scholar]
- Doc 10004 ICAO . 2014. Flight Safety. Global Aviation Safety Plan: 2014-2016. [Google Scholar]
- Doc 7192 A-1 ICAO. Training Guide. Part A-1. General Provisions.
- Doc 7192 D-3 ICAO . 1998. Training Guide. Part. Flight Operations Officer/Controller. [Google Scholar]
- Doc 7192 F-1 ICAO. Training Guide. Part F-1. Meteorological Support for Air Traffic Controllers and Pilots.
- Doc 7300 ICAO . Vol. 9. 2006. Convention on International Civil Aviation. Montreal. [Google Scholar]
- Doc 9750-AN/963. ICAO . fifth ed. 2016. Global Air Navigation Plan 2016-2030. [Google Scholar]
- Doc 9941 ICAO . 2011. Training Development Guide Competency Based Training Methodology.https://www.afeonline.com/shop/icao-doc-9941.html access mode://Internet. [Google Scholar]
- ICAO Policy in the Field of Civil Aviation Specialists Training. 2016. https://docplayer.com/49770264-Politika-ikao-v-oblasti-podgotovki-specialistov-grazhdanskoy-aviacii-25-maya-2016-goda.html Electronic resource - access mode://Internet. [Google Scholar]
- Malagas Konstantinos, et al. Higher education aviation programs in Greece: a missed opportunity or a challenge to meet? J. Aero. Technol. Manag. 2017;9(4):510. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsiev Z.Z. Methodology for convergence of the training program with the professional activities of aviation specialists. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aero. 2021;8(1) [Google Scholar]
- Shamsiev Z.Z. Digitalization of educational and methodological support for the training of aviation dispatchers. Int. J. Aviat. Aeronaut. Aero. 2021;8(3) https://commons.erau.edu/ijaaa/vol8/iss3/6 Retrieved from. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Andersone, Vladimirs Šestakovs. Accordance to Obtain a Certain Level of Professional Qualities. Vol. 5. Transport and Aerospace Engineering; 2017. Some theoretical aspects of the air traffic controller training group formation; pp. 43–47.https://www.degruyter.com/view/j/tae ISSN 2255-9876 (online) ISSN 2255-968X (print) [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
No data was used for the research described in the article.