Summary
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) is caused by loss-of-function mutations in CCM1, CCM2, or CCM3 genes of endothelial cells. It is characterized by pericyte deficiency. However, the role of pericytes in CCMs is not yet clarified. We found pericytes in Cdh5CreERT2;Ccm1fl/fl (Ccm1ECKO) mice had a high expression of PDGFRβ. The inhibition of pericyte function by CP-673451 aggravated the CCM lesion development. RNA-sequencing analysis revealed the molecular traits of pericytes, such as highly expressed ECM-related genes, especially Fn1. Furthermore, KLF4 coupled with phosphorylated SMAD3 (pSMAD3) promoted the transcription of fibronectin in the pericytes of CCM lesions. RGDS peptide, an inhibitor of fibronectin, decreased the lesion area in the cerebella and retinas of Ccm1ECKO mice. Also, human CCM lesions had abundant fibronectin deposition, and pSMAD3- and KLF4-positive pericytes. These findings indicate that pericytes are essential for CCM lesion development, and fibronectin intervention may provide a novel target for therapeutic intervention in such patients.
Subject areas: Neuroscience, Neuroanatomy, Clinical neuroscience
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
We presented the first evidence that blockage of pericytes could aggravate CCMs
-
•
We evaluated the genetic profiles of pericytes in Ccm1ECKO mice
-
•
We further showed that inhibition of fibronectin could prohibit the development of CCMs
Neuroscience; Neuroanatomy; Clinical neuroscience
Introduction
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) affects 0.5% of the world’s population.1 Approximately 80% of cases are sporadic, and 20% of cases are familial; about 5% of familial CCM patients also suffer from retinal CCM lesions. The loss-of-function mutations in CCM1, CCM2, or CCM3 genes of endothelial cells (ECs) result in CCM lesions.1,2,3
CCM is characterized by reduced pericyte coverage and impaired endothelial-pericyte interaction.4,5,6 Notably, increased pericyte coverage and normalization of EC-pericyte interaction rescue the CCM phenotype.4,5,7 A recent study shows that platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGFRβ) signaling mediates the EC-pericyte interaction during angiogenesis.8,9 Knockout or blockage of PDGFRβ caused a loss of pericytes and dysfunction in the tight junction of ECs,10,11 enlarged the capillaries, and decreased the vessel branching points.12 The decrease in pericytes also promotes the development of arteriovenous malformation.13 However, whether inhibition of pericyte function aggravates CCM lesions is yet to be elucidated.
Fibronectin (FN) is a critical regulator of vascular remodeling and angiogenesis.14,15,16 Its expression is barely detectable in normal adult vasculature,17 whereas the fibronectin-rich matrix is found in immature or impaired vessels.15,18,19,20 Overexpressed fibronectin induces capillary dilation,21,22,23 whereas fibronectin antagonist significantly decreases the lumen volume.16 In addition, pericytes are a major source of fibronectin.24,25 The increased deposition of fibronectin was detected in CCM lesions.18,23,26 Therefore, fibronectin secreted by pericytes might contribute to the pathology of CCMs.
In addition, fibronectin produced by perivascular cells is regulated through transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling.27,28 The activated TGF-β phosphorates Smad2 and Smad3. Phosphorylated Smad2 (pSmad2) and pSmad3 form a compound that regulates the transcription of target genes (including Fn1) via interaction with other transcription factors.29,30 Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) is a vital transcription factor that induces the expression of fibronectin.31,32,33 Klf4-knockout in perivascular cells decreases fibronectin production.32 Of interest, KLF4 might act as a co-transcription factor with pSmad2/3 in pericytes to promote the transcription of fibronectin. TGF-β/Smad34 and KLF435 are highly expressed in the ECs of CCM lesions. However, data showing the expression levels and interaction between Smad3 and KLF4 in pericytes of CCM lesions are insufficient.
Therefore, we hypothesized that inhibition of pericyte function could aggravate CCM lesions, KLF4 could interact with TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway to regulate the production of fibronectin in CCM pericytes, and disrupted fibronectin function could rescue CCM diseases. The present study aimed to identify the essential role of pericytes in the development of CCMs. These findings could improve our understanding of the disease pathobiology and yield a novel treatment for CCMs.
Results
Relative expression of PDGFRβ was increased in CCM1ECKO mice
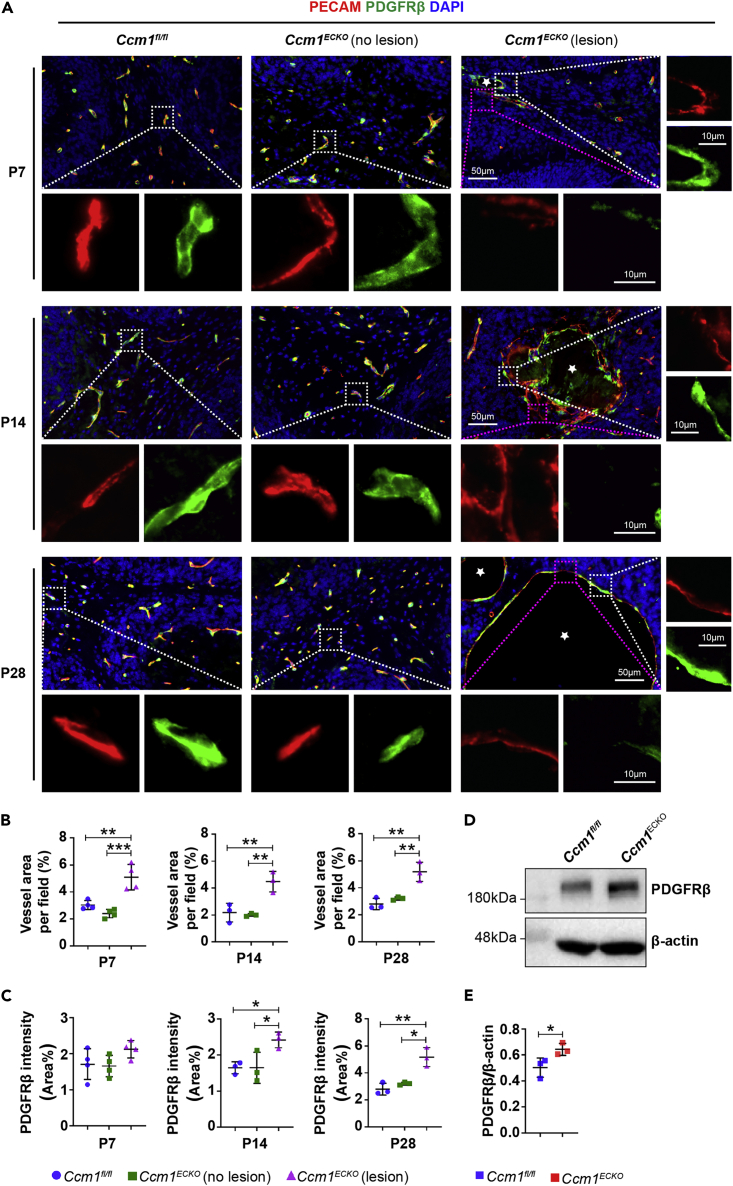
The CCM lesions consisted of dilated and irregular structures of microvessels, poorly covered by pericytes. The unaffected blood vessels adjacent to CCM lesions had a normal appearance and were covered by pericytes similar to those in control animals (Figure 1A). The quantification of immunofluorescence (IF) staining showed that the vascular area of CCM lesions was increased (Figure 1B), accompanied with the upregulation of PDGFRβ (Figure 1C) in CCM1ECKO mice at age P14. Western blot (WB) analysis revealed that the relative expression of PDGFRβ in cerebellar microvessels with a diameter less than 10 μm was higher in Ccm1ECKO mice than in Ccm1fl/fl mice at age P14 (Figures 1D and 1E). These results suggested that PDGFRβ was highly expressed in pericytes to partially compensate for the loss of pericytes in CCM lesions.
Figure 1.
Reduced pericyte coverage in Ccm1ECKO mice
(A) Representative IF images of PECAM and PDGFRβ in the cerebella of Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice at different time points. Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) were enlarged vascular lesions (asterisks). The white box regions represented ECs covered by pericytes, whereas the purple box regions showed the ECs without pericyte coverage. Scale bar: 50 μm, 10 μm in higher-magnification images.
(B) Quantification of vascular area as shown in (A) at different time points.
(C) Quantification of the expression of PDGFRβ as shown in (A) at different time points.
(D and E) WB analysis showed that the level of PDGFRβ increased significantly in cerebellar microvessels of Ccm1ECKO mice at P14. n = 3 or 4 mice per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for B and C, unpaired Student’s t-test for E.
Structural remodeling of pericytes in CCM lesions
The immunostaining results showed more complex processes of pericytes were in CCM lesions (Figure S1A), which became mesh or ensheathed (Figure S1B). Conversely, the non-affected perivascular cells adjacent to CCM lesions had a thin-strand appearance and were distributed along the vessel axis, similar to those in control animals (Figures S1A and S1B). These findings suggested that pericytes might remodel their shape in CCM lesions.
Interrupting pericyte function exacerbated CCM lesions
To investigate the function of pericytes in CCM lesions, mice were administered CP-673451 (a specific inhibitor of pan-PDGFRβ)36,37 (Figure S2A). The expression of PDGFRβ was downregulated in the cerebellar microvessels of CP-673451-treated mice (Figures S2B–S2D), whereas the level of PDGFRα was not downregulated (Figures S2B, S2E, and S2F). In addition, the expression of desmin, another marker of pericyte, also decreased in retinal vessels of CP-673451-treated mice (Figures S2G and S2H).
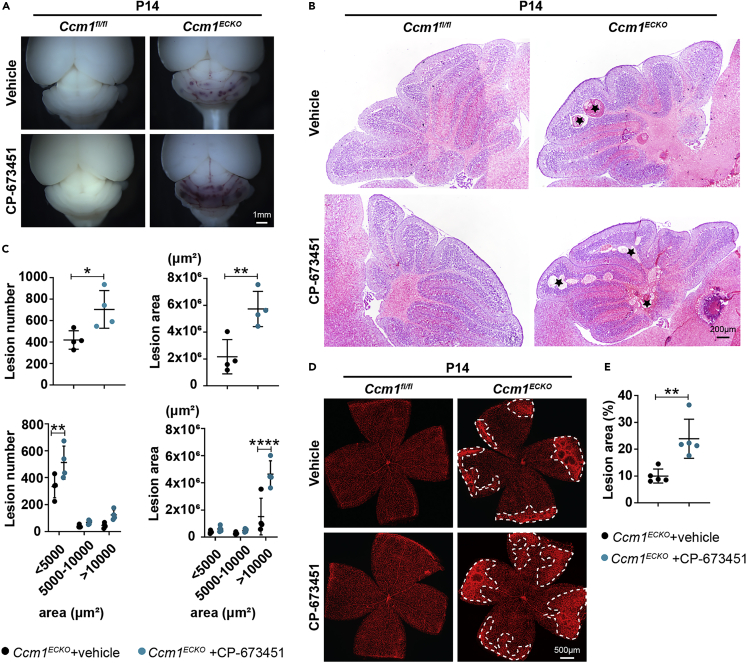
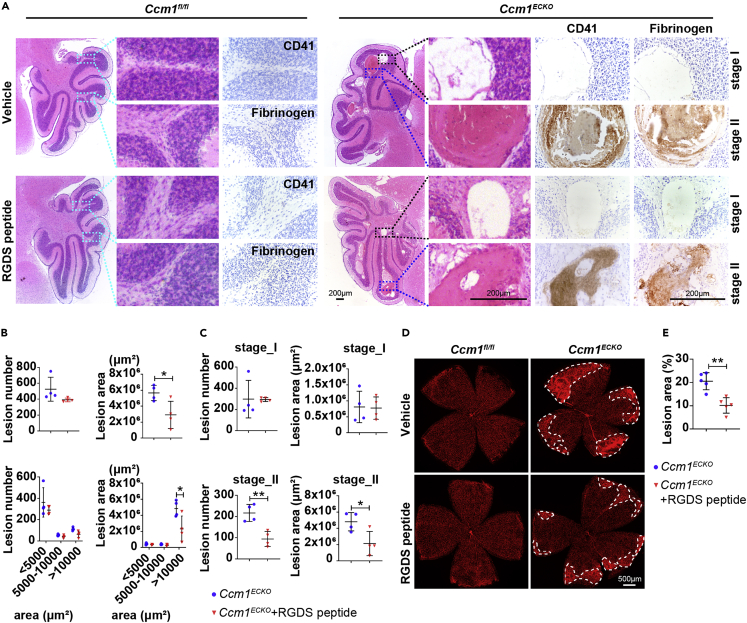
Subsequently, we found the cerebellar CCM lesions were increased in CP-673451-treated CCM1ECKO mice at age P14 (Figures 2A and 2B). The histological quantification of cerebellar lesions demonstrated that lesion numbers and areas increased significantly in CP-673451-treated Ccm1ECKO mice (Figure 2C). Specifically, CCM lesions were classified into 3 categories based on the area of < 5000 μm2, 5000–10000 μm2, or > 10000 μm2.38 Quantification results showed that the lesion numbers increased in area < 5000 μm2, and enlarged lesions were mainly focused in area >10000 μm2 (Figure 2C). In addition, the whole-mount staining of mouse retinas revealed that the area of lesions increased markedly in CP-673451-treated Ccm1ECKO mice at age P14 (Figures 2D and 2E). These data indicated that interrupting the function of pericytes exacerbated CCM lesions in both cerebella and retinas, and pericytes were involved in CCM development.
Figure 2.
Interruption of pericyte function exacerbated lesion burden in the cerebella and retinas of Ccm1ECKO mice
(A and B) Stereomicroscopic images and hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining showed abundant CCM lesions in the cerebella of CP-673451-treated Ccm1ECKO mice. Representative images of CCM lesions (asterisks) were shown in (B).
(C) Semiquantitative results of cerebellar CCM lesions as shown in (B).
(D) Representative confocal microscopy images of retina in Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1ECKO mice treated with vehicle or CP-673451. The whole-mount staining of the mouse retina was performed with isolectin B4. The white dotted line marked CCM lesions.
(E) Large and complicated CCM lesion area in retinas of Ccm1ECKO mice treated with CP-673451. n = 4 or 5 mice per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Scale bar: 1 mm in A; 200 μm in B; 500 μm in D. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test for upper panels of C and E, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for bottom panels of C.
Gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of pericytes in Ccm1ECKO mice
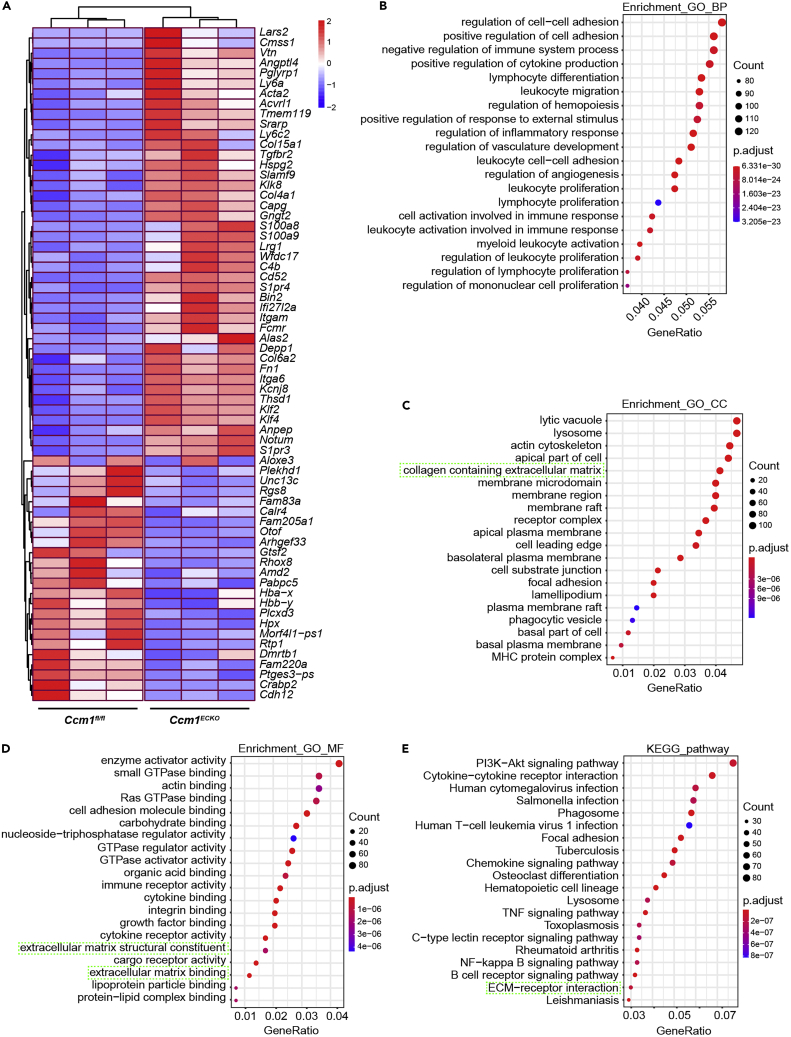
To investigate the genetic profiles of pericytes in CCMs, we isolated pericytes from Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice for RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). The real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) results showed that enriched pericytes had good purity and had not contamination from other cells (Figure S3). The RNA-seq analysis identified 2277 differentially expressed genes (DEGs), including 1557 upregulated and 720 downregulated DEGs. A heatmap was utilized to display the top DEGs, including 42 upregulated genes and 24 downregulated genes ranked by P-value (Figure 3A). These DEGs were subjected to GO enrichment and KEGG pathway analyses.
Figure 3.
Bulk RNA-seq analysis of pericytes in Ccm1ECKO mice
(A) The heatmap displayed the top DEGs in pericytes of Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1ECKO mice. Each block represented a single gene. The red block indicated the upregulated genes, and the blue block implied the downregulated genes.
(B–D) The top 20 GO enrichment analyses related to BP, CC, and MF. The cyan dotted box marked the pathway related to ECM.
(E) Top 20 KEGG pathways. The cyan dotted box displayed the pathway related to ECM-receptor interaction.
The analysis of 2277 distinct DEGs for the enrichment in GO database revealed the top 20 GO enriched pathways with the lowest adjusted P-values according to biological process (BP), cell component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The GO enrichment analysis of BP was related to the regulation of cell-cell adhesion, positive regulation of cell adhesion, and negative regulation of the immune system (Figure 3B). In the CC group, the upregulated genes were enriched in the lytic vacuole, lysosome, and actin cytoskeleton (Figure 3C). The additional GO enrichment analysis of MF revealed that the enzyme activator activity, small GTPase binding, and actin-binding were significantly enriched in pericytes purified from Ccm1ECKO mice (Figure 3D). KEGG analysis identified PI3K-Akt signaling, cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, and human cytomegalovirus infection pathways (Figure 3E). Notably, both GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses were associated with extracellular matrix (ECM) for highly expressed genes (Figures 3C–3E). Therefore, it could be inferred that ECM produced by pericytes might contribute to the pathogenesis of CCM lesions.
Ligand/receptor interactions between pericytes and ECs in CCM lesions
The expression data of the brain microvascular ECs from Ccm1 conditional knockout mice and Ccm1fl/fl mice, accessible through GEO: GSE12396839 and GEO: GSE85657,40 were integrated into the analysis with our expression data of pericytes (GEO: GSE213244). The current analysis results demonstrated that 515 ligand/receptor complexes, including TGFβ-TGFβR, Dll/Jag-Notch, and ECM-integrin were involved in the crosstalk between pericytes and ECs in CCM lesions (Table S1). Typically, the interactions of ligand/receptor complexes included 268 “EC_ligand and pericyte_receptor” (145 cell adhesion interactions, 47 secreted protein-to-receptor interactions, 36 cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions, 33 ECM-to-receptor interactions, and 7 secreted protein-to-ECM interactions) and 299 “pericyte_ligand and EC_receptor” (132 cell adhesion interactions, 52 secreted protein-to-receptor interactions, 44 cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions, 69 ECM-to-receptor interactions, and 2 secreted protein-to-ECM interactions) (Figures S4A-S4C). Notably, the chord diagram showed fibronectin was a critical communication molecule between pericytes and ECs (Figure S4D).
Pericytes increased fibronectin deposition in CCM lesions
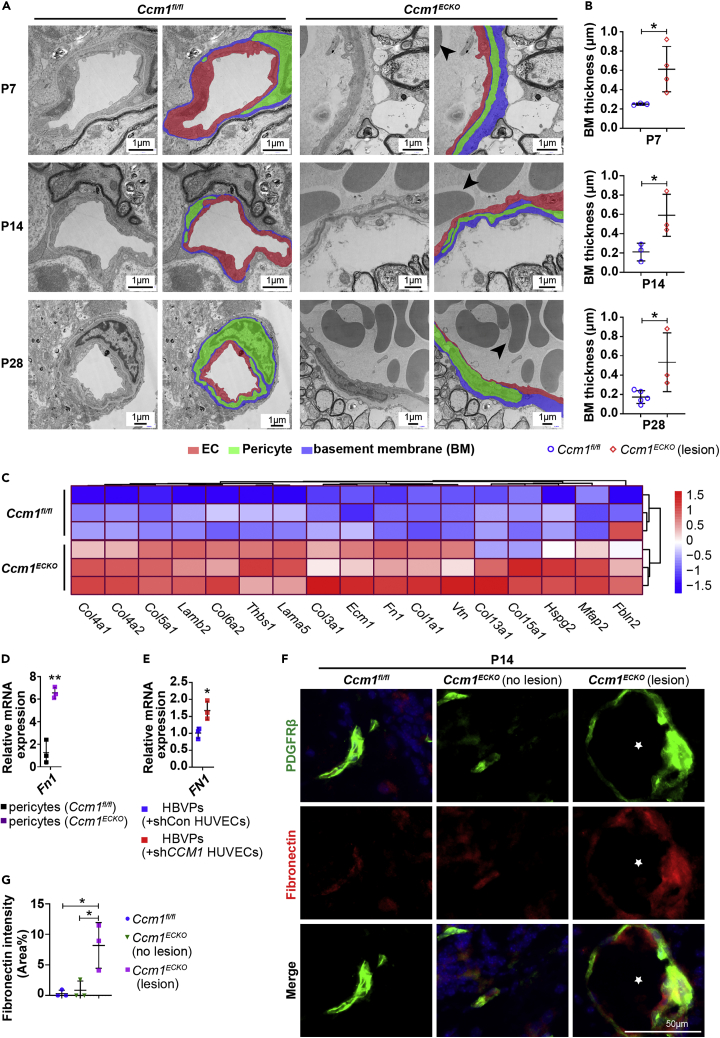
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was performed to further investigate the ECM structure in CCMs. The most notable characteristic was significant basal membrane (BM) thickness for CCM lesions (Figure 4A). The quantification revealed that BM was thicker in CCM lesions than that in normal vessels at different time points (Figure 4B). RNA-seq analysis indicated that ECM-related genes were upregulated in pericytes of Ccm1ECKO mice (Figure 4C). The pericytes synthesize various ECM proteins, such as fibronectin, versican, aggrecan, and many collagens.41 Fibronectin is expressed during development, especially in vascular morphogenesis, and vascular injury.42,43,44 Pericytes are expressed ten times more fibronectin than ECs.45 Furthermore, RNA-seq analysis results revealed that the fibronectin mRNA level was upregulated in pericytes and downregulated in Ccm1 conditional knockout ECs (Table 1). RT-qPCR assays showed that the expression levels of Fn1 were upregulated in pericytes both in vivo and in vitro (Figures 4D and 4E). The immunostaining results demonstrated that fibronectin was abundant in CCM lesions, and most of it was colocalized with pericytes. Conversely, the non-affected blood vessels adjacent to CCM lesions had minimal deposition of fibronectin, which was similar to the control vessels (Figures 4F and 4G). These data suggested that pericytes increased the deposition of fibronectin in CCM lesions.
Figure 4.
Abnormal deposition of fibronectin in CCM lesions
(A) Representative TEM images of cerebellar vessels in Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1ECKO mice. ECs were labeled in red. Pericytes were labeled in green. The basement membrane was labeled in blue. Large amounts of erythrocytes were stacked in CCM lesions (arrowheads). Scale bar: 1 μm.
(B) Quantification of basal membrane thickness in normal vessels and CCM lesions in (A).
(C) Heatmap of DEGs related to ECM in pericytes of Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice. Upregulated and downregulated genes were marked in red and blue, respectively.
(D) Relative mRNA expression levels (fold-change) of Fn1 in pericytes isolated from Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice.
(E) Relative expression levels (fold change) of FN1 in HBVPs co-cultured with shCCM1 HUVECs.
(F) Representative IF images of fibronectin. Abundant fibronectin was deposited in CCM lesions (asterisks), most of which were merged with PDGFRβ compared to the controls. Scale bar: 50 μm.
(G) Quantification of fibronectin expression in (F). n = 3–5 mice per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t-test for B, D, E, and G.
Table 1.
Log2 fold-change (Log2FC) of Fn1 expression in pericytes and ECs
Anti-fibronectin restricted the development of CCM lesions
Accumulated fibronectin has a potential role in producing vascular malformation.22,23 The inhibition of fibronectin through RGDS peptide (a special fibronectin inhibitor) decreases angiogenesis.46,47 Therefore, the inhibition of fibronectin might have therapeutic effects on patients with CCMs by disrupting angiogenesis. In RGDS peptide-treated Ccm1ECKO mice (Figure S5A), the reduced CCM lesion burden was observed on the surface of the cerebella and retinas (Figures S5B and S5C). The histological quantification of cerebellar lesions demonstrated that RGDS peptide decreases the lesion areas, mainly focusing on area > 10000 μm2, but did not reduce the number of lesions (Figures 5A and 5B). Furthermore, CCM lesions could be sorted into two stages in H&E staining: Stage I represented the lesions with only an enlarged vascular cavity; and stage II was cavernous lesions comprising a thrombus. Immunohistochemistry assays identified key molecular signatures of thrombus such as fibrinogen and CD41. We found that fibrinogen and CD41 positive clots could be seen in stage II lesions, whereas stage I lesions lacked fibrinogen and CD41 positive clots (Figure 5A). The distribution analysis of cerebellar lesions showed that the number and areas of stage II lesions in RGDS peptide-treated mice decreased significantly (Figure 5C). Moreover, the RGDS peptide reduced the number of retinal filopodia and vascular junction density in Ccm1ECKO mice at age P8 (Figures S5D and S5F) and the lesion areas of retinas at age P14 (Figures 5D and 5E). Nonetheless, no significant difference was observed in the retinal outgrowth between Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1ECKO mice treated with or without RGDS peptide (Figures S5E and S5G). Taken together, these data suggested that inhibition of fibronectin restricted the development of CCMs possibly through the anti-angiogenic effect.
Figure 5.
Blockage of fibronectin could rescue CCM lesions
(A) Representative images of H&E and immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining of Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1ECKO mice at age P14 treated with vehicle or RGDS peptide. The cyan boxes marked the staining of fibrinogen and CD41 which were negative in cerebellum of Ccm1fl/fl mice. The blue boxes marked CCM lesions with thrombus which was fibrinogen and CD41 positive; the black boxes indicated CCM lesions without thrombus which was fibrinogen and CD41 negative. Scale bar: 200 μm.
(B and C) The semiquantitative results of total CCM lesion number and area of cerebella in (A). The number and area of CCM lesions were quantified according to the area of < 5000 μm2, 5000–10000 μm2, or > 10000 μm2 (B), and according to CCM lesions with (stage II) or without thrombus (stage I) (C).
(D) Representative confocal microscopy images of the retina in Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice. The whole-mount staining of retinas was performed using isolectin B4. The white dotted line marked CCM lesions. Scale bar: 500 μm.
(E) Quantification of retinal lesion area in Ccm1ECKO mice treated with or without RGDS peptide. n = 4 or 5 mice per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, unpaired Student’s t-test for upper panels of B, C, and E, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for bottom panels of B.
Fibronectin also induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT),48,49,50 and intervention of fibronectin attenuates EMT.48,51 EMT is closely related to endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) with highly similar mechanisms.52 EndMT plays a critical role in the onset and progression of CCMs.34,53 Therefore, we attempted to explore whether inhibition of fibronectin prohibited CCM development via prevention of EndMT processes of ECs. The current results revealed that RGDS peptide treatment partially downregulated the levels of Snail1 and N-cadherin in the conditional CCM1 knockdown HUVECs that are markers of EndMT (Figures S5H and S5I). In summary, this study preliminarily demonstrated that the inhibition of fibronectin rescued CCM development, possibly via the prohibition of EndMT processes.
KLF4 interacted with pSMAD3 to promote the production of fibronectin in the pericytes of CCM lesions
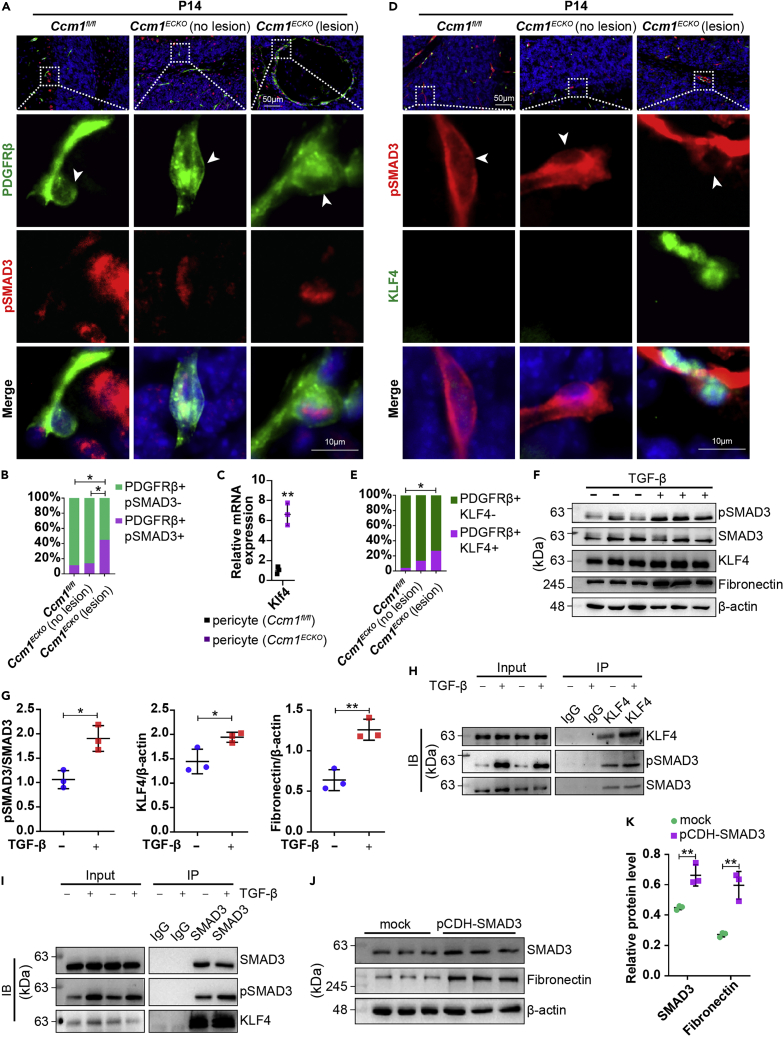
CCM1-silenced ECs overexpressed TGF-β (Figures S6A and S6B), which could act on perivascular cells.8 The results also showed that pSMAD3 was detected in large numbers of pericytes of CCM lesions, whereas only a small number of pSMAD3-positive pericytes were detected in the normal vessels (Figure 6A). The quantification of IF staining demonstrated a high proportion of pSMAD3-positive pericytes in CCM lesions (Figure 6B). The accumulating evidence implied that SMAD3 was activated in pericytes of CCM lesions.
Figure 6.
KLF4 cooperated with pSMAD3 to promote the production of fibronectin
(A) Representative IF images of PDGFRβ and pSMAD3. White boxed regions in the upper panels represented the typical regions shown at high magnifications on the lower panels. Arrowhead labeled the pericyte cell bodies. Scale bar: 50 μm, 10 μm in higher-magnification images.
(B) The quantitative results showed that PDGFRβ and pSMAD3-positive pericytes increased in CCM lesions (n = 3 mice).
(C) Relative expression levels (fold change) of Klf4 in pericytes of Ccm1ECKO and Ccm1fl/fl mice at P14.
(D) Representative IF images of PDGFRβ and KLF4. White boxed regions in the upper panels represented the typical regions shown at high magnifications on the lower panels. Arrowhead labeled the pericyte cell bodies. Scale bar: 50 μm, 10 μm in higher-magnification images.
(E) The quantitative results showed increased PDGFRβ- and KLF4-positive pericytes in CCM lesions (n = 4 mice).
(F and G) WB analysis of pSMAD3, KLF4, and fibronectin in human brain vessel pericytes treated with vehicle or 10 ng/mL TGF-β for 4 hours. The expression levels of pSMAD3, KLF4, and fibronectin increased.
(H and I) HBVPs were treated with 10 ng/mL TGF-β for 4 hours. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-KLF4 (H) or anti-SMAD3 (I) as indicated. The precipitates were analyzed by WB.
(J and K) WB analysis showed that SMAD3 and fibronectin expression was upregulated in pericytes after transfection with pCDH-SMAD3 lentivirus for 48 h. n = 3 per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, chi-square test for B and E, unpaired Student’s t-test for C, G and K.
KLF4 plays a critical role in CCM pathogenesis.54 The relative expression of Klf4 was upregulated in pericytes purified from Ccm1ECKO mice (Figure 6C). KLF4-positive pericytes were observed in blood vessels of CCM lesions, but rarely detected in the non-affected blood vessels adjacent to CCM lesions and in control vessels (Figures 6D and 6E).
TGF-β-treated HBVPs remarkably increased the expression levels of pSMAD3 and KLF4 (Figures 6F, 6G, and S6C–S6F). Moreover, the co-IP results revealed that pSMAD3 could be pulled down by KLF4, and KLF4 could be pulled down by pSMAD3 (Figures 6H and 6I). In addition, HBVPs expressed remarkable fibronectin after stimulation with TGF-β (Figures 6F and 6G) or transfection with pCDH-SMAD3 lentivirus (Figures 6J and 6K). Taken together, these findings suggested that KLF4 interacted with pSMAD3 to promote the transcription of fibronectin in the pericytes of CCM lesions.
Human CCM lesions had abundant fibronectin and pSMAD3- and KLF4-positive pericytes
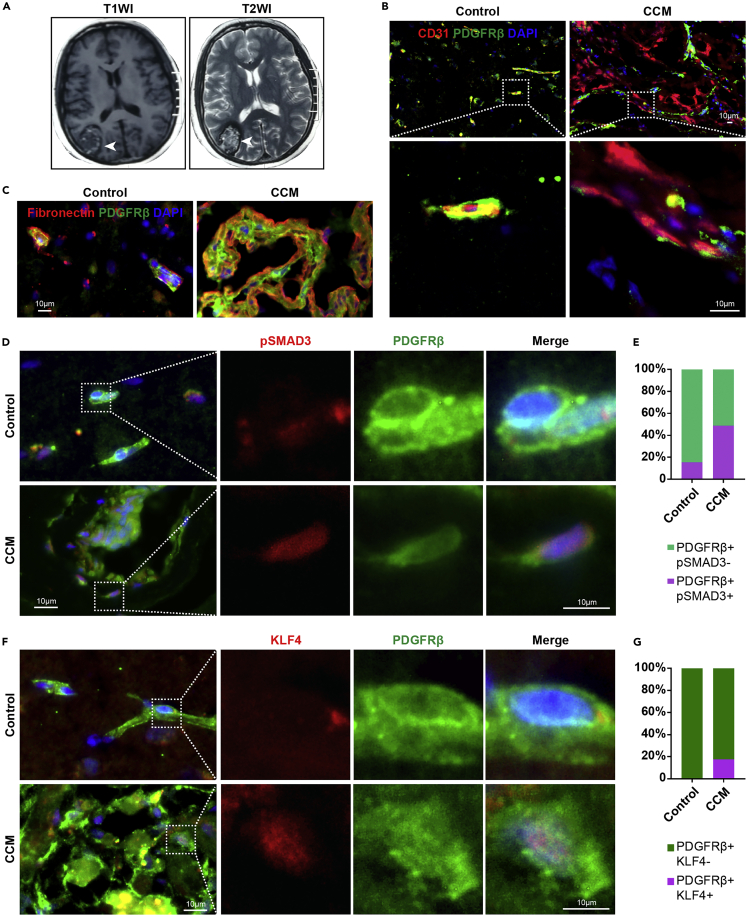
Next, we detected the expression levels of fibronectin, KLF4, and pSMAD3 in lesions surgically excised from human CCMs (Figure 7A) and control subjects. In control subjects, almost all vessels had intact pericyte coverage but were structurally defective with decreased pericyte coverage in human CCM lesions (Figure 7B). In human CCM lesions, pericytes became amorphous and had a high expression of fibronectin, which was rare in the microvessels of control subjects (Figure 7C). We also confirmed the presence of pSMAD3-positive pericytes (Figures 7D and 7E) and KLF4-positive pericytes (Figures 7F and 7G) in human CCM lesions. Overall, these data suggested that the deposition of abundant fibronectin and abnormal pericytes expressed KLF4 and pSMAD3 as a common pathological mechanism of CCMs.
Figure 7.
Human CCM lesions had abundant fibronectin, and KLF4- and pSMAD3-positive pericytes
(A) Representative T1-weighted (left panel) and T2-weighted (right panel) magnetic resonance images of human CCM lesions (n = 2).
(B) Representative IF images of CD31 and PDGFRβ in control subjects and human CCMs.
(C) Representative IF images of fibronectin and PDGFRβ. Abundant fibronectin accumulated in human CCMs.
(D and E) Representative IF images of PDGFRβ and pSMAD3. Human CCM lesions had predominant pSMAD3-positive pericytes (n = 2). White box regions in the left panels represent the typical regions at high magnifications on the right.
(F and G) Representative IF images show KLF4-positive pericytes in human CCM lesions (n = 2). White box regions in the left panels represent the typical regions at high magnifications on the right. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Scale bar: 10 μm in B-D, and F.
Discussion
PDGFRβ is used to identify pericytes, but also labels fibroblasts and vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs).8 Pericytes are located in microvessels with a diameter less than 10 μm, whereas fibroblasts and vSMCs are distributed in larger vessels with a diameter more than 10 μm.8,55 Based on the vascular size, we could easily identify PDGFRβ expression in pericytes, rather than in fibroblasts and vSMCs in large vessels. In this study, we found that PDGFRβ was significantly upregulated in cerebellar microvessels of Ccm1ECKO mice, indicating that increased PDGFRβ was derived from pericytes rather than fibroblasts and vSMCs.
Pericytes in CCM lesions became mesh or ensheathed, accompanied by the generation of complex processes. The neighboring pericytes might offset the pericyte loss and promote pericyte-EC communication.56 Supposedly, pericytes in the CCM lesions remodel the conformation, analogous to the structural remodeling of pericytes in other cerebrovascular diseases.57,58 As a result of structural remodeling, the expression of PDGFRβ increased progressively.58 Together, Yildirim et al.59 and our results demonstrated that PDGFRβ expression was higher in CCM lesions than in normal vessels. However, we also found that partial ECs lacked pericyte coverage in CCM lesions, which could be attributed to the significantly increased lesion vascular areas caused by proliferation and clonal expansion of ECs.60 These data indicate that increased expression of PDGFRβ and remodeling of processes partially improve the pericyte coverage.4,56,61 Therefore, pericytes might play a critical role in the pathogenesis of CCM.
Previous studies demonstrated that CP-673451 reduced the pericyte coverage by blocking the function of PDGFRβ, which in turn induces a substantial depletion of pericytes or make pericytes detach from the microvessels.62,63 In this study, we showed that CP-673451 significantly downregulated the expression of PDGFRβ and desmin, but did not decrease the level of PDGFRα expressed by fibroblasts and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Furthermore, the cerebellar and retinal CCM lesions were increased in CP-673451-treated Ccm1ECKO mice. Thus, the current findings revealed that the inhibition of pericyte function by PDGFRβ inhibitor caused pericyte loss that exacerbated the development of CCMs.
The current and previous results18,23,26 demonstrated that CCM lesions had increased deposition of fibronectin. Specifically, CCM-deficient ECs produce less fibronectin,64 whereas pericytes produce more fibronectin in CCM lesions. Furthermore, after specific deletion of CCM3 in mural cells, pericytes could also produce abundant fibronectin.26 Therefore, pericytes in CCM lesions might be the primary source of fibronectin.
Fibronectin could be upregulated by stimulated SMAD3 and KLF4.31,32,65 Either loss of Smad365 or conditional ablation of KLF432 reduces the level of fibronectin. These data suggested that pSMAD3 and KLF4 could play a synergistic role in the production of fibronectin. The in vivo results showed that pericytes were pSMAD3- and KLF4-positive in CCM lesions. Furthermore, the in vitro results revealed that KLF4 interacted with pSMAD3 and the complex regulated the expression of fibronectin in pericytes. Therefore, we speculated that fibronectin produced in pericytes of CCM lesions is co-regulated by pSMAD3 and KLF4.
Fibronectin is a critical matrix component associated with sprouting angiogenesis.66 It is essential for tip cell migration67 and filopodia formation.68 Blocking fibronectin disrupts angiogenesis.69 CCM is a vascular malformation characterized by excessive branching angiogenic sprouts70 and abundant fibronectin. Thus, we hypothesized whether fibronectin contributed to the pathogenesis of CCMs and whether anti-fibronectin therapy might rescue the development of CCMs. RGDS peptide is a specific tetrapeptide contained in the fibronectin sequence but not in the vitronectin, collagen, or laminin, and a specific inhibitor of fibronectin.71,72,73,74 Reportedly, synthetic RGDS peptide can inhibit integrin by competing with fibronectin.75 In our study, RGDS peptide disrupted filopodia formation, decreased the vascular junction density of Ccm1ECKO mice, limited the cerebellar and retinal CCM lesion development, and suppressed EndMT. In addition, the downregulation of integrin β1, a fibronectin receptor, rescues the phenotypes caused by genetic mutations in CCM-1 or CCM-2.23,76 Taken together, the intervention of fibronectin inhibited angiogenesis and alleviated EndMT process possibly via disrupted interaction between fibronectin and integrin, thus rescuing the development of CCMs.
Furthermore, the local organization of thrombi promotes the development of CCM diseases.77 Reportedly, the inhibition of fibronectin prevents thrombus formation.78,79 We also demonstrated that the numbers and areas of thrombus-containing CCM lesions were decreased in RGDS peptide-treated Ccm1ECKO mice. Hence, the inhibition of fibronectin rescues CCM disease progression via its antithrombotic activity. Local thrombi also resulted in repeated microhemorrhages in CCM diseases.77 Conversely, antithrombotic therapy could benefit patients with CCMs by decreasing the risk of intracranial hemorrhage and focal neurological deficit.80
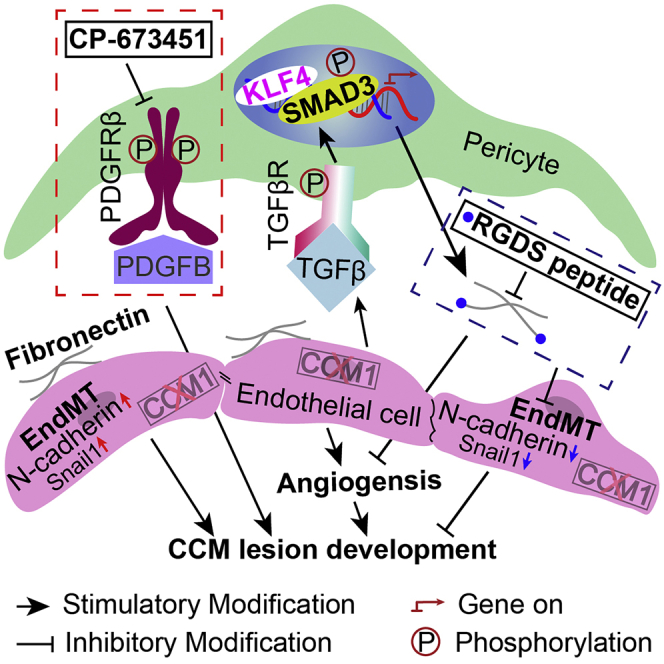
In conclusion, the current study revealed that the inhibition of pericyte function by blocking PDGFRβ significantly exacerbates CCM progression in Ccm1ECKO mice. Fibronectin produced in pericytes of CCM lesions could be co-regulated by pSMAD3 and KLF4. Then, the intervention of fibronectin rescued the development of CCM via anti-angiogenic effect and alleviation of EndMT process in the conditional CCM1 knockdown ECs. Thus, our findings of fibronectin intervention, including RGDS peptide, may provide a novel target for therapeutic intervention in patients with CCMs.
Limitations of the study
The CCM lesions are dilated vascular malformations. Therefore, using the method to isolate the proposed microvessels might lose a part of CCM lesional vasculatures, mainly in the larger lesions. It might affect the assessment of CCM vasculatures. Furthermore, CCM is considered a hyperpermeability disease. However, we did not analyze the change in hyperpermeability in Ccm1ECKO mouse model after inhibiting the function of pericytes. In addition, the role of RGDS peptide-mediated signals in anti-angiogenesis and anti-EndMT remains to be explored.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| goat-anti-PECAM | R&D systems | Cat# AF3628; RRID: AB_2161028 |
| rabbit anti-CD31 | Abcam | Cat# ab28364; RRID: AB_726362 |
| rabbit anti-PDGFRβ | Abcam | Cat# ab69506; RRID: AB_1269704 |
| goat anti-PDGFRβ | R&D systems | Cat# AF1042; RRID: AB_2162633 |
| goat anti-PDGFRα | R&D systems | Cat# AF1062; RRID: AB_2236897 |
| rabbit anti-Fibronectin | Abcam | Cat# ab268020 |
| rabbit anti-Smad3 (phospho S423+S425) | Abcam | Cat# ab52903; RRID: AB_882596 |
| goat anti-KLF4 | R&D systems | Cat# AF3158; RRID: AB_2130245 |
| rabbit anti-desmin | Abcam | Cat# ab15200; RRID: AB_301744 |
| isolectin B4 | Vector Laboratories | Cat# DL-1207; RRID: AB_2336415 |
| rat anti-PDGFRβ-biotin | Thermo Fisher Scientific | Cat# 14-1402-82; RRID: AB_467493 |
| rabbit anti-Fibrinogen | ABclonal | Cat# A19685 |
| rabbit anti-CD41 | ABclonal | Cat# A11490; RRID: AB_2861582 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-Puro | Provided by Dr. Yupeng Cheng (Tianjin Medical University, China) | N/A |
| short hairpin RNAs of CCM1 | Provided by Dr. Yuzheng Zhang (Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, China) | N/A |
| non-specific short hairpin RNAs | Provided by Dr. Yuzheng Zhang (Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, China) | N/A |
| Biological samples | ||
| Human brain CCM tissues | First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University | N/A |
| Human brain epilepsy tissues | First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University | N/A |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| CP-673451 | Selleck | Cat# S1536 |
| RGDS peptide | MCE | Cat# HY-12290 |
| Human TGF-β1 | Absin | Cat# abs04204 |
| Deposited data | ||
| Raw and analyzed data | This paper | GEO: GSE213244 |
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
| Human umbilical vein endothelial cells | Provided by Dr. Xiaohong Wang (Tianjin Medical University, China) | N/A |
| Human brain vascular pericytes | ScienCell | Cat# 1200 |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| Cdh5CreERT2/+ | Dr. Xiangjian Zheng, Tianjin Medical University | N/A |
| Ccm1fl/fl | Dr. Xiangjian Zheng, Tianjin Medical University | N/A |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| FN1 Forward: GTCCCCTGGGGTCACCTAT | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| FN1 Reverse: TCCTGTTATCTGGGCCCGA | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| Fn1 Forward: TTGAGAACCTGAATCCTGGCC | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| Fn1 Reverse: TATTCTGTCCCAGGCAGGAGA | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| Klf4 Forward: GTGCCCCGACTAACCGTTG | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| Klf4 Reverse: GTCGTTGAACTCCTCGGTCT. | Tsingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. | N/A |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| pCDH-CMV-MCS-SMAD3-EF1-Puro | This paper | N/A |
| short hairpin RNAs of CCM1 | This paper | N/A |
| non-specific short hairpin RNAs | This paper | N/A |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| Image J | ImageJ Software | https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html |
| GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 | GraphPad | https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/ |
| SPSS 20.0 | IBM Co. | https://www.ibm.com |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Dr. Changbin Shi (changbinshi@hotmail.com).
Materials availability
This study did not generate new unique reagents.
Experimental model and subject detail
Patients
This study included 2 patients with CCMs and 2 with epilepsy as control, undergoing surgical excision of CCM and epilepsy lesions to identify the clinical indications unrelated to this study. The diagnosis of CCM was established based on the evidence of typical histopathological criteria in every case. Clinical information for CCM and epilepsy patients were as follows: patient 1, female, 55 years old, CCM; patient 2, female, 43 years old, CCM; patient 3, female, 33 years old, epilepsy, and patient 4, male, 22 years old, epilepsy. The study was approved by the first affiliated hospital of Harbin Medical University Institutional Review Board. All participants gave informed consent for the processing of a portion of their surgical specimens for research purpose.
Experimental animals
All mice experiments were conducted in compliance with animal procedure protocols and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees of the Harbin Medical University and Tianjin Medical University, China.
Cdh5CreERT2 transgenic mice and Ccm1fl/fl mice have been described previously.34,81 Briefly, newborn offspring from a Cdh5CreERT2; Ccm1fl/fl (Ccm1ECKO) × Ccm1fl/fl intercross were injected with 75 μL of 4-hydroxy tamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich, H6278; 0.5 mg/mL solubilized in 5% ethanol-corn oil mixture) by intraperitoneal injection at postnatal day 2 (P2) to induce Cre activity. The phenotypes of Ccm1ECKO mice were analyzed at P7, P14, or P28, respectively. Among all the genetic experiments, tamoxifen-injected littermate animals were used as control, and both male and female animals were used. Mice aged P14 were used in all the experiments unless indicated otherwise.
Ccm1fl/fl or Ccm1ECKO mice were injected either vehicle control or PDGFRβ inhibitor CP-673451 (30 mg/kg body weight, Selleck, S1536) intraperitoneally from P5–P7 daily and P9–P13 every alternate day. Subsequently, mice were harvested at P14. Ccm1fl/fl or Ccm1ECKO mice were also intraperitoneally injected with vehicle control or a specific fibronectin inhibitor RGDS peptide (5 mg/kg body weight, MCE, HY-12290) from P5–P7 daily and P9–P13 every alternate day. Then, the mice were collected at P8 or P14.
All mice used in this study were maintained on a C57BL/6 background. A total of 123 animals were enrolled. Mice of both sexes were randomized and assigned to each group. Raw data, including exact animal numbers in each group (for different experiments), were included in the Table S2.
Cell culture
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were cultured in an endothelial cell medium (ScienCell, 1001) containing 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (ScienCell, 0025). Human brain vascular pericytes (HBVPs) (ScienCell, 1200) were grown in pericyte media (ScienCell, 1201) supplemented with 2% FBS. The cells were incubated in humidified air containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C and used between P4 and P8.
Method details
H&E staining
The brain samples of mice were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin or optimum cutting temperature (OCT) compound. Next, the paraffin-embedded or OCT-embedded tissue blocks were serially cut into 8-μm-thick sections. The brain sections were stained by H&E according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Biosharp, BL700A, BL700B). The images were acquired using a Nikon microscope (Nikon, DS-Ri2).
IF and IHC staining
Antigen retrieval was performed by heating the tissue sections (8-μm-thick sections) in an improved citrate antigen retrieval solution (pH 6.0) (Beyotime, P0083) for 15 minutes (min). The non-special antigen was blocked by 1% (w/v) bovine serum albumin (BSA), 10% (v/v) normal donkey serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch Inc., 017-000-121), and 0.3% Triton X-100 (Solarbio, T8200) in phosphate-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST) at room temperature for 2 hours. Subsequently, the tissue sections were incubated with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. For IF staining, the sections were incubated with species-specific Alexa Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:500). The tissue sections were rewashed in PBST at room temperature (5 min/time, four times). Then, the slides were mounted using an antifade solution containing 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (Vector Laboratories, H-2000). For IHC staining, the sections were incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies, then developed by 3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) tablet (Sigma-Aldrich, D5905), and counterstained with hematoxylin.
The immunostaining was performed in triplicate. IF staining was performed with littermate tissues processed simultaneously under the same conditions. The images were acquired with a Nikon microscope (Nikon, DS-Ri2). The following primary antibodies were used for IF staining: goat-anti-PECAM (1:200, R&D systems, AF3628), rabbit anti-CD31 (1:100, Abcam, ab28364), rabbit anti-PDGFRβ (1:100, Abcam, ab69506), goat anti-PDGFRβ (1:100, R&D systems, AF1042), goat anti-PDGFRα (1:100, R&D systems, AF1062), rabbit anti-Fibronectin (1:100, Abcam, ab268020), rabbit anti-Smad3 (phospho S423+S425) (1:100, Abcam, ab52903), goat anti-KLF4 (1:100, R&D systems, AF3158), rabbit anti-Desmin (1:100, Abcam, ab15200), rabbit anti-Fibrinogen (1:100, ABclonal, A19685), rabbit anti-CD41 (1:100, ABclonal, A11490).
Retinal whole-mount IF staining
The fixation of eyes, dissection, and staining of retinas in mice has been described previously.82 Briefly, the mouse eyes were fixed in 2% PFA at 4 °C overnight. On the following day, the eyes were washed four times in PBS for 5 min each. The retinas were dissected into four quadrants and blocked/permeabilized in 1% BSA with 0.3% Triton X-100 at 4 °C overnight. After washing four times for 5 min each in Pblec buffer (1% Triton X-100, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, and 0.1 mM MnCl2 in PBS; pH 6.8), the retinas were incubated overnight in biotinylated isolectin B4 (1:50, Vector Laboratories, DL1207) with or without rabbit anti-desmin (1:100, Abcam, ab15200). On the next day, the retinas were washed and incubated with suitable species-specific Alexa Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies (1:500) at room temperature for 1.5 hours. Then, the retinas were washed and mounted onto microscope glass slides with Dako fluorescence mounting medium (Dako, S3023).
Immunostaining was performed in triplicate. All IF staining was performed on littermate tissues processed simultaneously under the same conditions. The images were acquired using a confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Axio-Imager LSM-800).
Isolated cerebellar microvasculature and purified pericytes
We isolated cerebellar microvessels with a diameter less than 10 μm using sucrose solution and by gradient certification according to the methods described previously.83 Briefly, P14 cerebella were homogenized by a tissue scissor and a loose-fitting pestle Dounce homogenizer in cold sucrose buffer (0.3 M sucrose, 5 mM HEPES, pH 7.4). The supernatant and the layer of myelin on the top of the pellet were collected by centrifugation of the cerebellar homogenate at 1000 ×g twice at 4 °C for 10 min each and discarded. The pellet was resuspended in sucrose buffer, and the large vasculature was separated from microvessels by centrifugation at 40 ×g at 4 °C for 5 min. The supernatant was clarified by centrifugation at 350 ×g at 4 °C for 10 min. Finally, the micro-vasculatures were enriched in the pellets (Figures S7A and S7B).
The microvascular pellets were digested into single-cell suspension by 1 mg/mL collagenase/dispase (Roche, 10269638001) and 0.5 μL/mL benzonase (Merck Millipore, E1014) in Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium (DMEM) (Corning, 10-017-CV) at 37 °C for 5–10 min. After erythrocytes were lysed on ice for 5 min, the single cell suspension was incubated with a complex of anti-biotin microbeads (Miltenyi Biotec, 130-090-485) and conjugated with rat anti-PDGFRβ-biotin antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 14-1402-82) at 4 °C for 45 min. Then, the supernatant containing pericyte-PDGFRβ antibody-magnetic microbead complexes was passed through MS column (Miltenyi Biotec, 130-042-201) to collect the pericytes. Finally, the purified pericytes were performed RNA-seq analysis.
RNA-seq and data analysis
Total RNA was extracted from pericytes using TRIzol® reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 15596018) according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and genomic DNA was digested using DNase I (TaKaRa). The RNA quality was determined on a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent) and quantified using the ND-2000 (NanoDrop Technologies). Only high-quality RNA sample (OD260/280 = 1.8–2.2, OD260/230 ≥ 2.0, RIN ≥ 6.5, 28S:18S ≥ 1.0, >10 μg) was used to construct the sequencing library. The RNA purification, reverse transcription, library construction, and sequencing were performed at Majorbio Biopharm Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China) using Illumina HiSeq 10X (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The distinct DEGs were analyzed on the free Majorbio Cloud Platform (www.cloud.majorbio.com). DEGs with |log2FC| >1 and P-value ≤0.05(DESeq284 / EdgeR85 with Q-value ≤0.05 and DEGs with |log2FC| >1 and Q value ≤0.05 (DESeq2 or EdgeR) / Q-value ≤0.001(DEGseq) were considered to be significantly expressed genes. The heatmaps for DEGs were constructed using pheatmap package of R language, and the clustering distance in heatmap was based on the method proposed by Minkowski.86 In addition, GO enrichment analysis was performed to identify the significantly enriched DEGs at Bonferroni-corrected P-value ≤0.05 compared to the whole-transcriptome background. GO functional enrichment and KEGG pathways were analyzed using the clusterProfiler package of R language.87
The bulk RNA-seq data of brain microvascular ECs in Ccm1fl/fl and Ccm1,conditional knockout mice were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) data with accession number GEO: GSE12396839 and GEO: GSE85657.40 The expression file of pericytes was accessible through GEO: GSE213244. We conducted an integrative analysis of RNA-seq data of pericytes and ECs in CCM lesions to infer pericyte-EC communication from their transcriptomic data. The ligand-receptor pairs88 were used to infer pericyte-EC communication from their transcriptomic data. A chord diagram was utilized to display the ligand and receptor genes of pericyte-EC interaction ranked by |log2FC| >1. The chord diagram was visualized using circlize package of R language.89
TEM
Mice were perfused with PBS and 4% PFA under deep anesthesia. The cerebella were pre-fixed in electron microscopy fixative (2% PFA, 2,5% glutaraldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, 1042390250), 2% sucrose, 2 mmol/L CaCl2 in PBS (pH 7.4) at 4 °C for 4–6 hours and sliced into 1 mm × 1 mm × 1 mm sections under the stereomicroscope. These cubes were post-fixed in new electron microscopy fixative at 4 °C overnight. Then, the tissues were dehydrated in graded acetone (30%, 50%, 70%, and 95% acetone in water) at 4 °C for 15 min each, followed by that in 100% acetone at twice for 10 min each at room temperature. Subsequently, the dehydrated tissues were embedded in the epoxy resin overnight, and the blocks were polymerized at 70 °C. The sections were cut into 70-nm-thick slices on a vibrating blade microtome (Leica, EM UC6), placed on copper grids, and stained with uranyl acetate for 15 min and lead citrate for 10 min. The images were captured by TEM (Hitachi, H-7650).
Plasmid construction, lentivirus production, and transduction of HBVPs
The coding sequences of human SMAD3 were synthesized and inserted into the lentiviral vector pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-Puro. Briefly, the vector particles were transfected into HEK293T cells together with helper plasmid psPAX2 and pMD2.G by polyethyleneimine (PEI) (Sigma-Aldrich, 919012) and Opti-MEM (Gibco, A4124802), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After 6 hours of incubation, the medium was replaced. The supernatant was collected after 48 hours, sterilized through a 0.45-μm filter, mixed with PEG 8000 solution, incubated at 4 °C overnight, and concentrated by centrifugation at 3330 ×g for 1 hour. The concentrated lentivirus particles were resuspended in PBS and stored at −80 °C.
HBVPs were seeded in 6-well plates and cultured in pericyte media containing 2% FBS. At 70% confluency, HBVPs were transfected with pCDH-CMV-MCS-SMAD3-EF1-Puro (pCDH-SMAD3) lentivirus or mock lentivirus. After 6 hours of incubation, the transfection mixture was replaced with fresh pericyte media containing 2% FBS. The experiments were conducted 48 hours after lentivirus transfection.
HUVECs treated by RGDS peptide
HUVECs transfected with specific short hairpin RNAs of CCM1 (shCCM1) or non-specific short hairpin RNAs (shCon) were incubated in an endothelial cell medium containing RGDS peptide (250 μg/mL) or PBS for 24 hours. The experiments were performed 24 hours after treatment with RGDS peptide.
HBVPs treated with TGF-β
HBVPs were seeded in 6-well plates and cultured using pericyte media containing 2% FBS. At 70% confluency, HBVPs were incubated in a serum-free medium for 24 hours, followed by treatment with recombinant TGF-β1 (Absin, abs04204) or PBS. The experiments were performed at different time points after treatment with TGF-β.
Construction of HUVECs and HBVPs co-culture model
The co-culture model was established as described previously.90 Briefly, about 2 × 104 HBVPs were seeded in pericyte media on the surface of the membrane of the inverted hanging insert (Merck Millipore, MCHT06H48). After incubation for 6 hours, the hanging inserts were reverted on the 6-well plate and incubated in pericyte media containing 2% FBS at 37°C Overnight. The following day, about 1.5×105 shCCM1 or shCon-transfected HUVECs were plated on the inside of inserts. The day that HUVECs were plated in the insert was defined as day 0. The RT-qPCR analysis of FN1 was performed on day 5.
RT-qPCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol® Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 15596018). Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized using the StarScript II First-strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (GenStar, A212-02), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, RT-qPCR was performed using ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech Co, Q711-02/03) in the LightCycler rapid thermal cycler system (Applied Biosystems). All RT-qPCRs were performed in triplicate. The relative mRNA expression level was calculated as follows: relative mRNA expression = 2ˆ[-(△Ctsample-△Ctcontrol)].
The primers were as follows: FN1 Forward: GTCCCCTGGGGTCACCTAT; FN1 Reverse: TCCTGTTATCTGGGCCCGA; Fn1 Forward: TTGAGAACCTGAATCCTGGCC; Fn1 Reverse: TATTCTGTCCCAGGCAGGAGA; Klf4 Forward: GTGCCCCGACTAACCGTTG; Klf4 Reverse: GTCGTTGAACTCCTCGGTCT.
Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP)
Co-IP was performed as described previously.91 HBVPs were cultured in 10-cm dish with serum-free medium for 24 hours before treatment with 10 ng/mL of TGF-β for 4 hours. The cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (1% (v/v) NP-40, 50mM Tris (pH=8.0), and 150 mM NaCl in distilled water) consisting of 1× proteinase inhibitor and 1× phosphatase inhibitor (Roche, 04906837001) on ice for 30 min. The supernatants were collected by centrifugation of cells lysates at 13523 ×g at 4 °C for 20 min and incubated with anti-KLF4 or anti-SMAD3 antibodies at 4 °C overnight. On the following day, Protein G beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 10003D) were added to cell supernatants to crosslink the antibody-protein complexes at 4 °C for 6 hours. The bead-antibody-protein complexes were washed four times (4 °C, 10 min/each) with RIPA buffer consisting of 1× proteinase and phosphatase inhibitors. The bead-antibody-protein complexes were pulled down with a magnet (Thermo Fisher Scientific, 12321D). The bead-antibody-protein complexes were mixed with 100 μL of 1× loading buffer and boiled at 95 °C for 10 min. The eluted protein fraction was analyzed by WB.
WB analysis
Samples of cerebellar microvascular pellets or cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 1× proteinase inhibitors (Roche, 04693116001). The proteins were separated by 8–12% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels and transferred to nitrocellulose (NC) membrane. Then, the membrane was blocked with 10% skimmed milk-PBST, probed with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight, and subsequently incubated with horseradish peroxide-conjugated secondary antibody. Finally, the blots were developed with enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) (NCM Biotech, P10300), and the signals were acquired on a MiniChemi610 imaging system (Beijing Sage Creation Science Co., Ltd).
The following primary antibodies were used: rabbit anti-PDGFRβ (1:1000, CST, 3169), goat anti-PDGFRα (1:100, R&D systems, AF1062), rabbit anti-TGFβ (1:1000, KleanAB, p100446), rabbit anti-Smad3 (phospho S423+s425) (1:1000, Abcam, ab52903), rabbit anti-Smad3 (1:1000, CST, 9513), rabbit anti-Fibronectin (1:1000, Abcam, ab268020), rabbit anti-KLF4 (1:1000, CST, 12173), and rabbit anti-β-Actin (1:1000, ABclonal, AC026).
Quantification and statistical analysis
Imaging analysis and quantification
Quantitative analysis was performed using Image J software (https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/download.html). At least three brain tissue slices were selected from each animal for quantification of staining images, and the interval of slices was 100 μm, and at least three mice in each group were taken. We defined areas containing the non-affected blood vessels adjacent to CCM lesions as no lesion area and areas containing CCM lesions as lesion areas. Vascular area per field was calculated by the area of PECAM-positive staining divided by the tissue area of the brain section per high-power field. The intensity of PDGFRβ or fibronectin was measured as the area of PDGFRβ or fibronectin-positive staining divided by the tissue area of the brain section per high-power field. The number of KLF4-positive or pSMAD3-positive pericytes was determined by counting the KLF4-positive or pSMAD3-positive nuclei in PDGFRβ-positive cells. The proportion of KLF4-positive or pSMAD3-positive fraction of pericytes was determined by counting the number of KLF4-positive or pSMAD3-positive pericytes present in PDGFRβ-positive cells. The number of filopodia was normalized to the standard length (100 μm) of the angiogenic front.92 The retinal lesion area is expressed as the percentage of lesion area against the total area of the retinal vasculature. The relative quantification of WB films was reflected as the ratio of the mean gray value of the target band over the mean gray value of β-actin.
Statistical analysis
Data analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA) and SPSS 20.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA) software. The data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The statistical significance was assessed by two-tailed Student’s t-test between two groups. One way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed for the multiple groups. Tukey’s method was used for pairwise comparisons between groups. The comparison of proportion was performed using chi-square test and Bonferroni’s method. P-values < 0.05 indicated statistical significance.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Shida Wang (Harbin Veterinary Research Institute of CAAS, China) for providing technical support for transmission electron microscopy, Professor Xiaohong Wang (Department of Pharmacology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tianjin Medical University, China) for generously providing HUVECs, Professor Yuzheng Zhang (Research Center for Translational Medicine, Shanghai East Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, China) for generously providing shCCM1 and shCon plasmid, Professor Yupeng Cheng (Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tianjin Medical University, China) for generously providing pCDH-CMV-MCS-EF1-Puro, psPAX2, and pMD2.G plasmid, and Doctor Jing Liu (Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Tianjin Medical University, China) for help with solving technical confusion. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81771276 and 82071298), Key Project of Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (ZD2016015), and the Foundation for High-Level Returned Overseas Talents of Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China to C.B.S.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, X.J.Z. and C.B.S.; Methodology, Z.F.D., J.W.L., Y.L., R.W., H.L.Y., Z.Y.X., S.T.W., X.Y., D.B.L., D.D.Z., G.F.L., Y.W.W., C.Y.M., and W.Z.D.; Formal Analysis, Z.F.D., J.W.L., Y.L., R.W., H.L.Y., Z.Y.X., S.T.W., X.Y., D.B.L., D.D.Z., G.F.L., Y.W.W., C.Y.M., and W.Z.D.; Investigation, Z.F.D.; Data curation, Z.F.D.; Writing – Original Draft, Z.F.D.; Writing – Review and Editing, X.J.Z. and C.B.S.; Visualization, Z.F.D.; Supervision, X.J.Z. and C.B.S.; Project Administration, X.J.Z. and C.B.S.; Funding Acquisition, X.J.Z. and C.B.S.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Published: December 22, 2022
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105642.
Supplemental information
Data and code availability
-
•
Bulk RNA-seq data have been deposited at GEO and are publicly available as of the date of publication. Accession numbers are listed in the key resources table.
-
•
This paper does not report original code.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
References
- 1.Revencu N., Vikkula M. Cerebral cavernous malformation: new molecular and clinical insights. J. Med. Genet. 2006;43:716–721. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2006.041079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Flemming K.D., Lanzino G. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation: What a Practicing Clinician Should Know. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020;95:2005–2020. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Labauge P., Denier C., Bergametti F., Tournier-Lasserve E. Genetics of cavernous angiomas. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:237–244. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(07)70053-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Oldenburg J., Malinverno M., Globisch M.A., Maderna C., Corada M., Orsenigo F., Conze L.L., Rorsman C., Sundell V., Arce M., et al. Propranolol Reduces the Development of Lesions and Rescues Barrier Function in Cerebral Cavernous Malformations: A Preclinical Study. Stroke. 2021;52:1418–1427. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.029676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhou H.J., Qin L., Jiang Q., Murray K.N., Zhang H., Li B., Lin Q., Graham M., Liu X., Grutzendler J., Min W. Caveolae-mediated Tie2 signaling contributes to CCM pathogenesis in a brain endothelial cell-specific Pdcd10-deficient mouse model. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:504. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20774-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schulz G.B., Wieland E., Wüstehube-Lausch J., Boulday G., Moll I., Tournier-Lasserve E., Fischer A. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation-1 Protein Controls DLL4-Notch3 Signaling Between the Endothelium and Pericytes. Stroke. 2015;46:1337–1343. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Jenny Zhou H., Qin L., Zhang H., Tang W., Ji W., He Y., Liang X., Wang Z., Yuan Q., Vortmeyer A., et al. Endothelial exocytosis of angiopoietin-2 resulting from CCM3 deficiency contributes to cerebral cavernous malformation. Nat. Med. 2016;22:1033–1042. doi: 10.1038/nm.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Armulik A., Genové G., Betsholtz C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev. Cell. 2011;21:193–215. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Huang H. Pericyte-Endothelial Interactions in the Retinal Microvasculature. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:E7413. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kitahara H., Kajikawa S., Ishii Y., Yamamoto S., Hamashima T., Azuma E., Sato H., Matsushima T., Shibuya M., Shimada Y., Sasahara M. The Novel Pathogenesis of Retinopathy Mediated by Multiple RTK Signals is Uncovered in Newly Developed Mouse Model. EBioMedicine. 2018;31:190–201. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nikolakopoulou A.M., Zhao Z., Montagne A., Zlokovic B.V. Regional early and progressive loss of brain pericytes but not vascular smooth muscle cells in adult mice with disrupted platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shiraya T., Araki F., Ueta T., Fukunaga H., Totsuka K., Arai T., Uemura A., Moriya K., Kato S. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates the Retinal Vascular Abnormalities in Anti-PDGFR-beta Antibody-Induced Pericyte Depletion Mouse Models. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:977. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58039-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Winkler E.A., Birk H., Burkhardt J.K., Chen X., Yue J.K., Guo D., Rutledge W.C., Lasker G.F., Partow C., Tihan T., et al. Reductions in brain pericytes are associated with arteriovenous malformation vascular instability. J. Neurosurg. 2018;129:1464–1474. doi: 10.3171/2017.6.JNS17860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Uemura A., Kusuhara S., Wiegand S.J., Yu R.T., Nishikawa S.i. Tlx acts as a proangiogenic switch by regulating extracellular assembly of fibronectin matrices in retinal astrocytes. J. Clin. Invest. 2006;116:369–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI25964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Milner R., Hung S., Erokwu B., Dore-Duffy P., LaManna J.C., del Zoppo G.J. Increased expression of fibronectin and the alpha 5 beta 1 integrin in angiogenic cerebral blood vessels of mice subject to hypobaric hypoxia. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008;38:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.01.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chiang H.Y., Korshunov V.A., Serour A., Shi F., Sottile J. Fibronectin is an important regulator of flow-induced vascular remodeling. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009;29:1074–1079. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.181081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Tucker R.P., Saupe F., Gasser I., Cseh B., Orend G. Fibronectin and tenascin-C: accomplices in vascular morphogenesis during development and tumor growth. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011;55:511–525. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.103243eo. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kiliç T., Pamir M.N., Küllü S., Eren F., Ozek M.M., Black P.M. Expression of structural proteins and angiogenic factors in cerebrovascular anomalies. Neurosurgery. 2000;46:1179–1191. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200005000-00032. discussion 1191-1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhou Q., Zheng J.W., Yang X.J., Wang Y.A., Ye W.M., Zhu H.G., Zhang Z.Y. Fibronectin: characterization of a somatic mutation in Sturge-Weber syndrome (SWS) Med. Hypotheses. 2009;73:199–200. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2009.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rangel-Castilla L., Russin J.J., Martinez-Del-Campo E., Soriano-Baron H., Spetzler R.F., Nakaji P. Molecular and cellular biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a review of current concepts and future trends in treatment. Neurosurg. Focus. 2014;37:E1. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mitsuhashi Y., Odermatt B.F., Schneider B.V., Schnyder U.W. Immunohistological evaluation of endothelial markers and basement membrane components in port-wine stains. Dermatol. 1988;176:243–250. doi: 10.1159/000248712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Comi A.M., Hunt P., Vawter M.P., Pardo C.A., Becker K.G., Pevsner J. Increased fibronectin expression in sturge-weber syndrome fibroblasts and brain tissue. Pediatr. Res. 2003;53:762–769. doi: 10.1203/01.PDR.0000058921.54071.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Faurobert E., Rome C., Lisowska J., Manet-Dupé S., Boulday G., Malbouyres M., Balland M., Bouin A.P., Kéramidas M., Bouvard D., et al. CCM1-ICAP-1 complex controls beta1 integrin-dependent endothelial contractility and fibronectin remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 2013;202:545–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201303044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bogush M., Heldt N.A., Persidsky Y. Blood Brain Barrier Injury in Diabetes: Unrecognized Effects on Brain and Cognition. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2017;12:593–601. doi: 10.1007/s11481-017-9752-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Laredo F., Plebanski J., Tedeschi A. Pericytes: Problems and Promises for CNS Repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019;13:546. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wang K., Zhang H., He Y., Jiang Q., Tanaka Y., Park I.H., Pober J.S., Min W., Zhou H.J. Mural Cell-Specific Deletion of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation 3 in the Brain Induces Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020;40:2171–2186. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sweeney M., Foldes G. It Takes Two: Endothelial-Perivascular Cell Cross-Talk in Vascular Development and Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018;5:154. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Meng X.M., Nikolic-Paterson D.J., Lan H.Y. TGF-beta: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016;12:325–338. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Derynck R., Zhang Y.E. Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature. 2003;425:577–584. doi: 10.1038/nature02006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cunha S.I., Magnusson P.U., Dejana E., Lampugnani M.G. Deregulated TGF-beta/BMP Signaling in Vascular Malformations. Circ. Res. 2017;121:981–999. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.309930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xu D., Chen P.P., Zheng P.Q., Yin F., Cheng Q., Zhou Z.L., Xie H.Y., Li J.Y., Ni J.Y., Wang Y.Z., et al. KLF4 initiates sustained YAP activation to promote renal fibrosis in mice after ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021;42:436–450. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0463-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Murgai M., Ju W., Eason M., Kline J., Beury D.W., Kaczanowska S., Miettinen M.M., Kruhlak M., Lei H., Shern J.F., et al. KLF4-dependent perivascular cell plasticity mediates pre-metastatic niche formation and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2017;23:1176–1190. doi: 10.1038/nm.4400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Boriushkin E., Zhang H., Becker M., Peachey J., Shatat M.A., Adams R.H., Hamik A. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates developmental angiogenesis through disruption of the RBP-J-NICD-MAML complex in intron 3 of Dll4. Angiogenesis. 2019;22:295–309. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9657-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Maddaluno L., Rudini N., Cuttano R., Bravi L., Giampietro C., Corada M., Ferrarini L., Orsenigo F., Papa E., Boulday G., et al. EndMT contributes to the onset and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations. Nature. 2013;498:492–496. doi: 10.1038/nature12207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cuttano R., Rudini N., Bravi L., Corada M., Giampietro C., Papa E., Morini M.F., Maddaluno L., Baeyens N., Adams R.H., et al. KLF4 is a key determinant in the development and progression of cerebral cavernous malformations. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016;8:6–24. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201505433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Konotop G., Bausch E., Nagai T., Turchinovich A., Becker N., Benner A., Boutros M., Mizuno K., Krämer A., Raab M.S. Pharmacological Inhibition of Centrosome Clustering by Slingshot-Mediated Cofilin Activation and Actin Cortex Destabilization. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6690–6700. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sugg K.B., Korn M.A., Sarver D.C., Markworth J.F., Mendias C.L. Inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor signaling prevents muscle fiber growth during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. FEBS Lett. 2017;591:801–809. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cardoso C., Arnould M., De Luca C., Otten C., Abdelilah-Seyfried S., Heredia A., Leutenegger A.L., Schwaninger M., Tournier-Lasserve E., Boulday G. Novel Chronic Mouse Model of Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Stroke. 2020;51:1272–1278. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.027207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Koskimäki J., Girard R., Li Y., Saadat L., Zeineddine H.A., Lightle R., Moore T., Lyne S., Avner K., Shenkar R., et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of cerebral cavernous malformation across multiple species and genotypes. JCI Insight. 2019;4:e126167. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.126167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lopez-Ramirez M.A., Fonseca G., Zeineddine H.A., Girard R., Moore T., Pham A., Cao Y., Shenkar R., de Kreuk B.J., Lagarrigue F., et al. Thrombospondin1 (TSP1) replacement prevents cerebral cavernous malformations. J. Exp. Med. 2017;214:3331–3346. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Davis G.E., Senger D.R. Endothelial extracellular matrix: biosynthesis, remodeling, and functions during vascular morphogenesis and neovessel stabilization. Circ. Res. 2005;97:1093–1107. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000191547.64391.e3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Murphy P.A., Jailkhani N., Nicholas S.A., Del Rosario A.M., Balsbaugh J.L., Begum S., Kimble A., Hynes R.O. Alternative Splicing of FN (Fibronectin) Regulates the Composition of the Arterial Wall Under Low Flow. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021;41:e18–e32. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lee J., Kim K.E., Choi D.K., Jang J.Y., Jung J.J., Kiyonari H., Shioi G., Chang W., Suda T., Mochizuki N., et al. Angiopoietin-1 guides directional angiogenesis through integrin alphavbeta5 signaling for recovery of ischemic retinopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:203ra127. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chiu C.H., Chou C.W., Takada S., Liu Y.W. Development and fibronectin signaling requirements of the zebrafish interrenal vessel. PLoS One. 2012;7:e43040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Mandarino L.J., Sundarraj N., Finlayson J., Hassell H.R. Regulation of fibronectin and laminin synthesis by retinal capillary endothelial cells and pericytes in vitro. Exp. Eye Res. 1993;57:609–621. doi: 10.1006/exer.1993.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Nicosia R.F., Bonanno E., Smith M. Fibronectin promotes the elongation of microvessels during angiogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 1993;154:654–661. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041540325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Aguzzi M.S., Facchiano F., Ribatti D., Gaeta R., Casadio R., Rossi I., Capogrossi M.C., Facchiano A. A novel RGDS-analog inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;321:809–814. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.07.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li C.L., Yang D., Cao X., Wang F., Hong D.Y., Wang J., Shen X.C., Chen Y. Fibronectin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via activation of calpain. Oncol. Lett. 2017;13:3889–3895. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.5896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu Y., Li J., Zeng S., Zhang Y., Zhang Y., Jin Z., Liu S., Zou X. Bioinformatic Analyses and Experimental Verification Reveal that High FSTL3 Expression Promotes EMT via Fibronectin-1/alpha5beta1 Interaction in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021;8:762924. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.762924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Câmara J., Jarai G. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in primary human bronchial epithelial cells is Smad-dependent and enhanced by fibronectin and TNF-alpha. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2010;3:2. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-3-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chen Y., Chen L., Hong D., Chen Z., Zhang J., Fu L., Pan D., Zhang Y., Xu Y., Gan S., et al. Baicalein inhibits fibronectin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by decreasing activation and upregulation of calpain-2. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:341. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1572-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Krizbai I.A., Gasparics Á., Nagyőszi P., Fazakas C., Molnár J., Wilhelm I., Bencs R., Rosivall L., Sebe A. Endothelial-mesenchymal transition of brain endothelial cells: possible role during metastatic extravasation. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Takada S., Hojo M., Tanigaki K., Miyamoto S. Contribution of Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition to the Pathogenesis of Human Cerebral and Orbital Cavernous Malformations. Neurosurgery. 2017;81:176–183. doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyx078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhou Z., Tang A.T., Wong W.Y., Bamezai S., Goddard L.M., Shenkar R., Zhou S., Yang J., Wright A.C., Foley M., et al. Cerebral cavernous malformations arise from endothelial gain of MEKK3-KLF2/4 signalling. Nature. 2016;532:122–126. doi: 10.1038/nature17178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jones H.E., Abrams K.A., Siegenthaler J.A. Techniques for visualizing fibroblast-vessel interactions in the developing and adult CNS. Neurophotonics. 2022;9:021911. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.9.2.021911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hartmann D.A., Underly R.G., Grant R.I., Watson A.N., Lindner V., Shih A.Y. Pericyte structure and distribution in the cerebral cortex revealed by high-resolution imaging of transgenic mice. Neurophotonics. 2015;2:041402. doi: 10.1117/1.NPh.2.4.041402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Berthiaume A.A., Grant R.I., McDowell K.P., Underly R.G., Hartmann D.A., Levy M., Bhat N.R., Shih A.Y. Dynamic Remodeling of Pericytes In Vivo Maintains Capillary Coverage in the Adult Mouse Brain. Cell Rep. 2018;22:8–16. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Berthiaume A.A., Hartmann D.A., Majesky M.W., Bhat N.R., Shih A.Y. Pericyte Structural Remodeling in Cerebrovascular Health and Homeostasis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:210. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yildirim O., Bicer A., Ozkan A., Kurtkaya O., Cirakoglu B., Kilic T. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor ligand and receptor in cerebral arteriovenous and cavernous malformations. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010;17:1557–1562. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2010.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Detter M.R., Snellings D.A., Marchuk D.A. Cerebral Cavernous Malformations Develop Through Clonal Expansion of Mutant Endothelial Cells. Circ. Res. 2018;123:1143–1151. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Olson L.E., Soriano P. PDGFRbeta signaling regulates mural cell plasticity and inhibits fat development. Dev. Cell. 2011;20:815–826. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Chintalgattu V., Rees M.L., Culver J.C., Goel A., Jiffar T., Zhang J., Dunner K., Jr., Pati S., Bankson J.A., Pasqualini R., et al. Coronary microvascular pericytes are the cellular target of sunitinib malate-induced cardiotoxicity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:187ra69. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Franco M., Roswall P., Cortez E., Hanahan D., Pietras K. Pericytes promote endothelial cell survival through induction of autocrine VEGF-A signaling and Bcl-w expression. Blood. 2011;118:2906–2917. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-01-331694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schwefel K., Spiegler S., Kirchmaier B.C., Dellweg P.K.E., Much C.D., Pané-Farré J., Strom T.M., Riedel K., Felbor U., Rath M. Fibronectin rescues aberrant phenotype of endothelial cells lacking either CCM1, CCM2 or CCM3. FASEB J. 2020;34:9018–9033. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902888R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zonneville J., Safina A., Truskinovsky A.M., Arteaga C.L., Bakin A.V. TGF-beta signaling promotes tumor vasculature by enhancing the pericyte-endothelium association. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:670. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4587-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Chen T., Dong J., Zhou H., Deng X., Li R., Chen N., Luo M., Li Y., Wu J., Wang L. Glycation of fibronectin inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis by uncoupling VEGF receptor-2-c-Src crosstalk. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020;24:9154–9164. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Usuelli M., Meyer T., Mezzenga R., Mitsi M. VEGF and VEGFR2 bind to similar pH-sensitive sites on fibronectin, exposed by heparin-mediated conformational changes. J. Biol. Chem. 2021;296:100584. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Summerbell E.R., Mouw J.K., Bell J.S.K., Knippler C.M., Pedro B., Arnst J.L., Khatib T.O., Commander R., Barwick B.G., Konen J., et al. Epigenetically heterogeneous tumor cells direct collective invasion through filopodia-driven fibronectin micropatterning. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eaaz6197. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Zhou X., Rowe R.G., Hiraoka N., George J.P., Wirtz D., Mosher D.F., Virtanen I., Chernousov M.A., Weiss S.J. Fibronectin fibrillogenesis regulates three-dimensional neovessel formation. Genes Dev. 2008;22:1231–1243. doi: 10.1101/gad.1643308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wüstehube J., Bartol A., Liebler S.S., Brütsch R., Zhu Y., Felbor U., Sure U., Augustin H.G., Fischer A. Cerebral cavernous malformation protein CCM1 inhibits sprouting angiogenesis by activating DELTA-NOTCH signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:12640–12645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000132107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rehmann M.S., Luna J.I., Maverakis E., Kloxin A.M. Tuning microenvironment modulus and biochemical composition promotes human mesenchymal stem cell tenogenic differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2016;104:1162–1174. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Droppelmann C.A., Gutiérrez J., Vial C., Brandan E. Matrix metalloproteinase-2-deficient fibroblasts exhibit an alteration in the fibrotic response to connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 because of an increase in the levels of endogenous fibronectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:13551–13561. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M807352200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jia J., Jeon E.J., Li M., Richards D.J., Lee S., Jung Y., Barrs R.W., Coyle R., Li X., Chou J.C., et al. Evolutionarily conserved sequence motif analysis guides development of chemically defined hydrogels for therapeutic vascularization. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eaaz5894. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Mabry K.M., Schroeder M.E., Payne S.Z., Anseth K.S. Three-Dimensional High-Throughput Cell Encapsulation Platform to Study Changes in Cell-Matrix Interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2016;8:21914–21922. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b11359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.He Q.Q., Ren S., Xia Z.C., Cheng Z.K., Peng N.F., Zhu Y. Fibronectin Facilitates Enterovirus 71 Infection by Mediating Viral Entry. J. Virol. 2018;92 doi: 10.1128/JVI.02251-17. e02251–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Renz M., Otten C., Faurobert E., Rudolph F., Zhu Y., Boulday G., Duchene J., Mickoleit M., Dietrich A.C., Ramspacher C., et al. Regulation of beta1 integrin-Klf2-mediated angiogenesis by CCM proteins. Dev. Cell. 2015;32:181–190. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Snellings D.A., Hong C.C., Ren A.A., Lopez-Ramirez M.A., Girard R., Srinath A., Marchuk D.A., Ginsberg M.H., Awad I.A., Kahn M.L. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation: From Mechanism to Therapy. Circ. Res. 2021;129:195–215. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Chen S., Peng Z., Wang Y., Wu J., An R., Miao R., Zhao M., Peng S. Development and activity evaluation of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing antithrombotic conjugate. J. Mol. Struct. 2019;1198:126816. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.07.063. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Matuskova J., Chauhan A.K., Cambien B., Astrof S., Dole V.S., Piffath C.L., Hynes R.O., Wagner D.D. Decreased plasma fibronectin leads to delayed thrombus growth in injured arterioles. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006;26:1391–1396. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000216282.58291.c6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Zuurbier S.M., Hickman C.R., Tolias C.S., Rinkel L.A., Leyrer R., Flemming K.D., Bervini D., Lanzino G., Wityk R.J., Schneble H.-M., et al. Long-term antithrombotic therapy and risk of intracranial haemorrhage from cerebral cavernous malformations: a population-based cohort study, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:935–941. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30231-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Corada M., Nyqvist D., Orsenigo F., Caprini A., Giampietro C., Taketo M.M., Iruela-Arispe M.L., Adams R.H., Dejana E. The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway modulates vascular remodeling and specification by upregulating Dll4/Notch signaling. Dev. Cell. 2010;18:938–949. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Connor K.M., SanGiovanni J.P., Lofqvist C., Aderman C.M., Chen J., Higuchi A., Hong S., Pravda E.A., Majchrzak S., Carper D., et al. Increased dietary intake of omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces pathological retinal angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2007;13:868–873. doi: 10.1038/nm1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Bales K.R., O'Neill S.M., Pozdnyakov N., Pan F., Caouette D., Pi Y., Wood K.M., Volfson D., Cirrito J.R., Han B.H., et al. Passive immunotherapy targeting amyloid-beta reduces cerebral amyloid angiopathy and improves vascular reactivity. Brain. 2016;139:563–577. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Love M.I., Huber W., Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014;15:550. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Robinson M.D., McCarthy D.J., Smyth G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kolde R. 2019. pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R package version 1.0. 12. R Packag. version 1.0 8. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Yu G., Wang L.G., Han Y., He Q.Y. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS. 2012;16:284–287. doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhang Y., Liu T., Wang J., Zou B., Li L., Yao L., Chen K., Ning L., Wu B., Zhao X., Wang D. Cellinker: a platform of ligand-receptor interactions for intercellular communication analysis. Bioinformatics. 2021;37:2025–2032. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Gu Z., Gu L., Eils R., Schlesner M., Brors B. circlize Implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics. 2014;30:2811–2812. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Stone N.L., England T.J., O'Sullivan S.E. A Novel Transwell Blood Brain Barrier Model Using Primary Human Cells. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019;13:230. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Han M., Li A.Y., Meng F., Dong L.H., Zheng B., Hu H.J., Nie L., Wen J.K. Synergistic co-operation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B with activator protein 1 in angiotensin II-induced angiotensinogen gene activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS J. 2009;276:1720–1728. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.06902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yamamoto H., Ehling M., Kato K., Kanai K., van Lessen M., Frye M., Zeuschner D., Nakayama M., Vestweber D., Adams R.H. Integrin beta1 controls VE-cadherin localization and blood vessel stability. Nat. Commun. 2015;6:6429. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
-
•
Bulk RNA-seq data have been deposited at GEO and are publicly available as of the date of publication. Accession numbers are listed in the key resources table.
-
•
This paper does not report original code.
-
•
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.