Summary
Ribosome synthesis begins in the nucleolus with 90S pre-ribosome construction, but little is known about how the many different snoRNAs that modify the pre-rRNA are timely guided to their target sites. Here, we report a role for Cms1 in such a process. Initially, we discovered CMS1 as a null suppressor of a nop14 mutant impaired in Rrp12-Enp1 factor recruitment to the 90S. Further investigations detected Cms1 at the 18S rRNA 3′ major domain of an early 90S that carried H/ACA snR83, which is known to guide pseudouridylation at two target sites within the same subdomain. Cms1 co-precipitates with many 90S factors, but Rrp12-Enp1 encircling the 3′ major domain in the mature 90S is decreased. We suggest that Cms1 associates with the 3′ major domain during early 90S biogenesis to restrict premature Rrp12-Enp1 binding but allows snR83 to timely perform its modification role before the next 90S assembly steps coupled with Cms1 release take place.
Keywords: ribosome assembly, pre-rRNA, snoRNA, H/ACA, 90S pre-ribosome, yeast, suppressor, pseudouridylation, RNA modification
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Cms1 is a suppressor of nop14 mutants impaired in Rrp12-Enp1 recruitment to the 90S
-
•
Cms1 associates with early 90S to restrict premature Rrp12-Enp1 recruitment
-
•
Cms1 allows timely pseudouridylation by snR83 at the exposed 3′ major domain
Lau et al. report a role for Cms1 in coordinating local pre-rRNA pseudouridylation by the H/ACA snoRNA snR83 on the early 90S pre-ribosome. During this process, Cms1 associates with the 18S rRNA 3′ major domain to restrict premature Rrp12-Enp1 binding.
Introduction
Eukaryotic ribosome synthesis is a highly energy-consuming process that occurs along a cascade of numerous assembly, modification, and maturation steps from the nucleolus to the cytoplasm. There, the small 40S and large 60S ribosomal subunits are supplied for protein synthesis. In yeast, four ribosomal RNAs (18S, 5.8S, 25S, and 5S rRNA), 79 ribosomal proteins, about 70 different small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and approximately 200 assembly factors hierarchically enter and dynamically participate in this enormous assembly line (Ben-Shem et al., 2011; Klinge et al., 2012; Kressler et al., 2010).
Following transcription by RNA polymerase I, a large rRNA precursor, called 35S pre-rRNA in yeast, is produced. This is composed of two external transcribed spacers (5′-ETS and 3′-ETS) and two internal transcribed spacers (ITS1 and ITS2) separating the mature 18S, 5.8S, and 25S rRNAs (Granneman and Baserga, 2004; Henras et al., 2015). The 5S rRNA is synthesized separately by RNA polymerase III before assembling into pre-ribosomal particles. The first steps of ribosome assembly are initiated while pre-rRNA synthesis is taking place. These include modification of pre-rRNA base and ribose moieties, RNA folding and processing, and recruitment of early ribosomal proteins and assembly factors (Venema and Tollervey, 1999; Zhang et al., 2016). This eventually yields the 90S pre-ribosome (also known as the small subunit processome), the first stable intermediate amenable to high-resolution structural analysis (Cheng et al., 2019; Kornprobst et al., 2016; Singh et al., 2021). During this nucleolar phase, pre-60S assembly also begins on the nascent 35S pre-rRNA. Cleavages within ITS1, at either site A2 (occurring co-transcriptionally) or site A3 (occurring post-transcriptionally), separate the 40S and 60S subunit biogenesis routes until the small and large subunits have reached their maturity in the cytoplasm (Henry et al., 1994; Lebaron et al., 2013; Lygerou et al., 1996).
When 90S biogenesis begins co-transcriptionally in the nucleolus, the emerging 5′-ETS already binds several 90S modules, such as UTP-A, UTP-B, and the U3 snoRNP. As the pre-rRNA continues to grow in the 18S rRNA region, more 90S factors (e.g., Utp20) and modules (e.g., Noc4-Nop14-Emg1-Enp1-Rrp12, UTP-C, Bms1-Rcl1, Mpp10-Sas10-Imp3-Imp4, Utp7-Sof1-Utp14) become successively integrated before the archetypal 90S has formed (Chaker-Margot et al., 2015; Cheng et al., 2019; Hunziker et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2016). At a certain point, the 90S undergoes a dramatic transition, which involves shedding of most of the 90S factors until the primordial pre-40S (Dis-C) emerges (Cheng et al., 2020; Du et al., 2020). However, Dis-C still carries the U3 snoRNA and a few residual 90S factors, including the helicase Dhr1. Their final removal and recruitment of the next set of pre-40S factors occur in the pre-40S maturation steps that follow (Cheng et al., 2020; Sardana et al., 2015).
The 90S carries only a single snoRNA, the U3 snoRNA, which, together with Nop56, Nop58, Snu13, and Nop1, constitutes a typical C/D box small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein (snoRNP) (Chaker-Margot et al., 2017; Hunziker et al., 2016; Kornprobst et al., 2016). However, U3 is not involved in pre-rRNA methylation (see below) but has a structural role in the 90S. In this case, the 5′ single-stranded region of the U3 snoRNA anneals at distinct regions in the 5′-ETS and 18S rRNA. These contacts help to organize the nascent pre-RNA, and also keep the 18S rRNA immature at distinct sites (Beltrame and Tollervey, 1992; Hughes, 1996; Sharma and Tollervey, 1999).
However, there exist many other snoRNAs in eukaryotic cells, which guide numerous covalent pre-rRNA modifications during ribosome synthesis (Dunbar and Baserga, 1998; Jaafar et al., 2021; Venema and Tollervey, 1999). These snoRNAs form snoRNPs that belong to either the C/D box (such as U3) or the H/ACA box particles (Kiss et al., 2006; Watkins and Bohnsack, 2012). The C/D box snoRNPs catalyze 2′-O-ribose methylation, with Nop1/fibrillarin as the methyltransferase and Nop58, Nop56, and Snu13 as further core factors. The H/ACA snoRNPs mediate pseudouridylation, with Cbf5 acting as a pseudouridine synthase and Gar1, Nhp2, and Nop10 as its core factors (Duan et al., 2009; Lapinaite et al., 2013; Li and Ye, 2006; Lin et al., 2011). Many of the known rRNA modifications are thought to occur quite early during ribosome assembly, when the pre-rRNA is not yet compactly folded or target sites are masked by assembly factors. Although the mechanistic details of these processes remain largely unknown, it is conceivable that a stepwise assembly of 90S might grant the many different snoRNPs access to their modification sites, which number approximately 100 in yeast rRNA and 200 in human, with many conserved in evolution (Sharma and Lafontaine, 2015; Sloan et al., 2017).
Since little is known about snoRNA-mediated modification during early ribosome formation and its coupling with downstream assembly steps, we sought to investigate this mechanism, which is assumed to be coordinated. We observed such a coupling with our initial discovery that Cms1, a poorly characterized ribosome biogenesis factor, suppresses a specific nop14 mutant defective in Noc4 module assembly. Further characterization of Cms1 showed that it is associated with a specific box H/ACA snoRNA, snR83, which guides pseudouridylation at two specific uridines in the 3′ major domain of the 18S rRNA. Based on these insights, we propose a model in which Cms1 could coordinate snR83-guided modification within the 3′ major domain, coupled with the stepwise assembly of the Noc4 module in the same region of the 90S pre-ribosome.
Results
The Nop14-N motif connects the Noc4 module and Rcl1-Bms1 in the 90S pre-ribosome
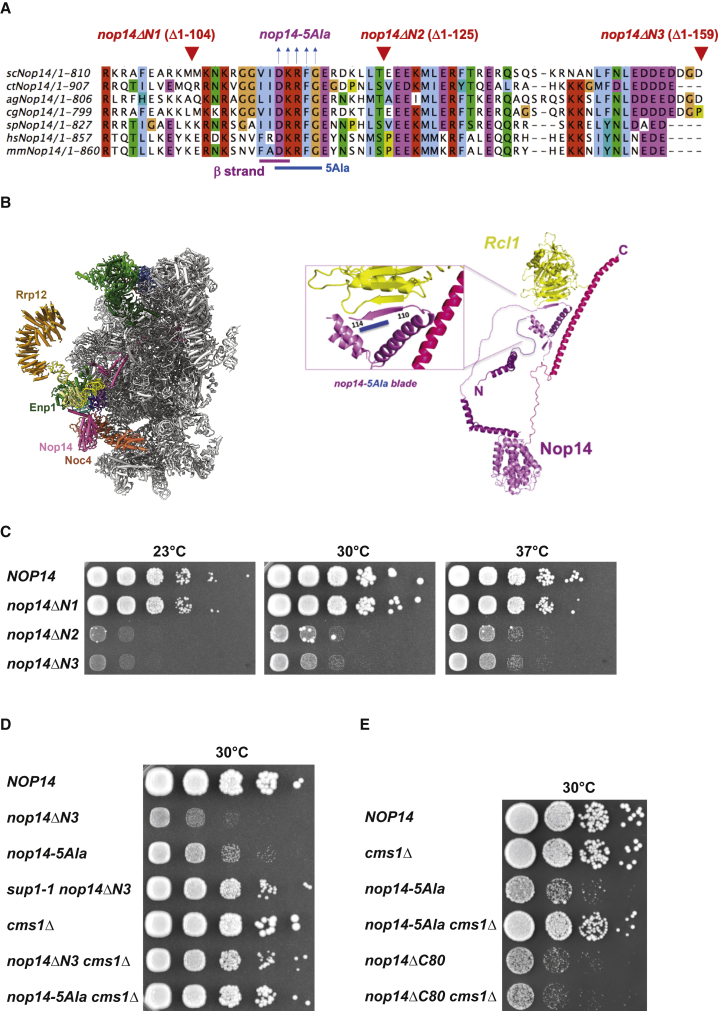
Analysis of 90S pre-ribosome structures from evolutionarily distant organisms such as yeast, Chaetomium thermophilum, and human revealed a conserved interaction between the Noc4 module (Noc4-Nop14-Emg1-Enp1-Rrp12) and the Rcl1-Bms1 heterodimer, mediated by a short β strand in the Nop14 N-terminal extension (residues 110–114 in yeast) that contacts another β strand in Rcl1 (Figures 1A and 1B). This observation prompted us to investigate the role of the extended Nop14 N terminus by performing a deletion analysis in yeast. Whereas Nop14 N-terminal residues 1–104 (nop14ΔN1) could be removed without impairing growth, deleting farther into the β-strand (residues 1–125, nop14ΔN2) generated a slow-growth phenotype that was not exacerbated in the nop14ΔN3 mutant lacking residues 1–159 (Figure 1C). To demonstrate that the strong inhibition of growth observed for the two longer nop14 N-terminal deletions was caused by the removal of the interacting β-strand residues 110–114, five “alanine scan” mutations (nop14-5Ala) were introduced into this part of Nop14 (Figures 1A and 1D). As anticipated, the nop14-5Ala mutant showed a strong growth defect, albeit slightly less pronounced than the nop14ΔN2 deletion (Figure 1D).
Figure 1.
A short β strand in the Nop14 N-terminal extension performs a crucial role in ribosome biogenesis
(A) Multiple sequence alignment of the highly conserved region of the Nop14 N-terminal extension, performed with orthologs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (sc), Chaetomium thermophilum (ct), Homo sapiens (hs), Mus musculus (mm), Ashbya gossypii (ag), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (sp), and Candida glabrata (cg). The positions of the yeast Nop14 deletions are indicated above the alignment; nop14ΔN1 lacks residues 1–104, nop14ΔN2 lacks residues 1–125, and nop14ΔN3 lacks residues 1–159. The β strand in the Nop14 N terminus, which has been mutated with five alanine residues (nop14-5Ala), is also indicated.
(B) Cryo-EM structure of C. thermophilum 90S, highlighting the Noc4 module with the Nop14 subunit (magenta) poking, with its N- and C-terminal extensions, into the 90S (left; figure adapted from Cheng et al., 2019). Extracted from this 90S structure (PDB: 6RXU, updated) are ctNop14 (right), composed of a central α-helical domain with N- and C-terminal extensions, and Rcl1 (yellow), which binds to the β strand (residues 110–114) in the Nop14 N terminus. The magnified view (inset) shows in detail this Nop14-N β strand bound to another β strand in Rcl1. The region containing the alanine scan mutation (5Ala) is indicated by a blue line.
(C) Dot-spot growth analysis of the indicated yeast strains containing the various Nop14 N-terminal deletions, lacking residues 1–104 (nop14ΔN1), residues 1–125 (nop14ΔN2), or residues 1–159 (nop14ΔN3), in comparison to the isogenic wild-type strain. Cells were grown for 3 days at 23°C, 30°C, or 37°C.
(D) Dot-spot growth analysis of wild-type yeast W303 (NOP14) and the indicated nop14ΔN3 and nop14-5Ala mutants, either as single mutants or combined with the sup1-1 suppressor (nop14ΔN3 derived). Growth was analyzed on YPD plates at 30°C for 3 days.
(E) Dot-spot growth analysis of wild-type NOP14 and the indicated cms1Δ, nop14-5Ala, and nop14ΔC80 single mutants and nop14-5Ala cms1Δ and nop14ΔC80 cms1Δ double mutants. Growth was analyzed on YPD plates at 30°C for 3 days.
CMS1 gene disruption rescues nop14 N-terminal deletion mutants
We observed that the two slow-growing nop14 N-terminal deletion mutants, when plated at high cell density, occasionally produced a few faster-growing colonies (Figure 1C and data not shown). To ascertain whether these are extragenic suppressors, we performed genetic tests (Figures S1A–S1C). Notably, when one of these suppressors (called sup1-1) was backcrossed to an isogenic nop14ΔN3 initial strain, the resulting diploid exhibited a loss of suppressor activity, but after sporulation and tetrad analysis, a 2:2 segregation of fast- versus slow-growing colonies was observed (Figures S1A and S1B). These genetic data suggest that sup1-1 carries a single recessive mutation responsible for the extragenic suppressor activity that restores growth of the nop14 N-terminal mutants.
To identify the suppressor gene locus, the genome of the sup1-1 yeast strain was sequenced. This uncovered a meaningful T nucleotide insertion in the nonessential CMS1 gene, causing a Ser68Phe substitution in the Cms1 protein (full-length Cms1 has 291 amino acids), with a subsequent frameshift into a short open reading frame (ORF) before a stop codon (Figure S1D). We assumed that this C-terminally truncated Cms1 in the sup1-1 strain is nonfunctional, and hence a cms1-null-like phenotype might be responsible for the suppression of the nop14 N-deletion mutants. To obtain experimental evidence for this, the CMS1 gene was disrupted in the nop14ΔN3 and nop14-5Ala strains, which in both cases restored cell growth to a large, but not full, extent (Figure 1D). However, another slow-growing mutant, nop14ΔC80, lacking the long C-terminal α helix that pokes into the 90S at another site (see Figure 1B), was not suppressed by cms1Δ (Figure 1E). Together, these data show that the CMS1 gene disruption specifically suppresses nop14 N-terminal mutations.
CMS1 encodes a poorly characterized but conserved protein (human homolog CMSS1; Figure S2A) that was initially found as a high-copy suppressor of MCM10 (Wang and Wu, 2001). However, based on other analyses, it was implicated in 90S ribosome biogenesis (Grandi et al., 2002; Hunziker et al., 2019; van Leeuwen et al., 2020; Gavin et al., 2002; Sturm et al., 2017). Cms1 exhibits a helicase fold, but it is likely inactive as a helicase owing to the absence of classical ATPase/helicase motifs (e.g., Walker A, DEAD box) and a second RecA-like domain (Figures S2B and S2C).
Based on our genetic and structural data, we wondered if a mutation in the pairing Rcl1 β strand could be suppressed by cms1Δ as well. To examine this, we replaced a charged loop emerging from this Rcl1 β strand with a neutral glycine-serine (GGGGS) loop. Notably, this Rcl1 GGGGS loop mutant exhibited a slow-growing phenotype that could be suppressed by cms1Δ (Figure S3A).
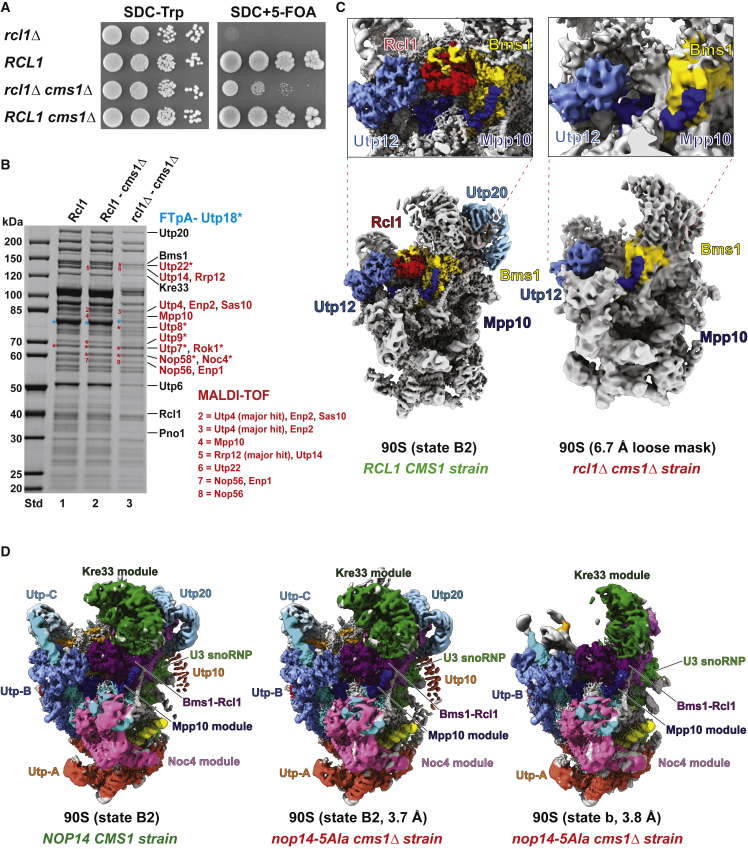
Prompted by these findings, we tested whether a complete chromosomal deletion of either NOP14 or RCL1, both of which are essential genes in yeast, could be suppressed by cms1Δ. Whereas the cms1-null allele did not rescue nop14Δ (data not shown), the rcl1Δ cms1Δ double-gene-disruption strain was viable, although cells grew very slowly (Figure 2A). This observation is consistent with a recent systematic bypass suppression analysis of essential yeast genes, including RCL1, which yielded a similar result (van Leeuwen et al., 2020).
Figure 2.
Biochemical and structural analysis of 90S particles isolated from the viable rcl1Δ cms1Δ and nop14-5Ala cms1 suppressor strains
(A) Complete chromosomal deletion of RCL1, which is lethal in yeast, can be rescued by cms1Δ. Dot-spot growth analysis of wild type (RCL1 CMS1), single cms1Δ and cms1Δ mutants, and the double-disruption rcl1Δ cms1Δ suppressor strains. The shuffle strains were grown on 5-FOA plates at 30°C for 4 days.
(B) Affinity purification of FTpA-Utp18 from wild type (RCL1 CMS1), single cms1Δ mutant, and double-disruption strain rcl1Δ cms1Δ.
(C) Cryo-EM analysis of 90S pre-ribosomal particles, isolated from the double-disruption rcl1Δ cms1Δ strain via the 90S bait protein FTpA-Utp18. Note that there is no electron density for Rcl1 (shown in red in the wild-type 90S) in the mutant 90S particles, but Bms1 (yellow) could be well discerned at its authentic position, together with other typical 90S substructures. For comparison, the cryo-EM structure of an intact yeast 90S particle in state B2 (EMD-11358) is shown in a related orientation. The overall resolution of the 90S from the rcl1Δ cms1Δ strain is 6.7 Å (using a loose mask from cryoSPARC).
(D) Cryo-EM analysis of 90S pre-ribosomal particles isolated from the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor strain via the 90S bait protein FTpA-Utp18. In total, two 90S particles, state B2 (middle) and state b (right), could be classified from the dataset, which are highly similar to published 90S particles state B2 (EMD-11358) and b (EMD-8859), respectively. Notably, Utp20 is missing in the 90S state b. For comparison, the cryo-EM structure of an intact yeast 90S particle in state B2 (EMD-11358) is shown in a related orientation (left). All structures are color coded to indicate the different 90S modules.
Cryo-EM structure of the 90S particles isolated from cms1Δ suppressors
Since the cms1Δ gene disruption not only rescued the nop14-5Ala mutant, but also allowed yeast cells to live without the essential RCL1, we sought to gain insight into the structure of 90S particles from these different suppressors. Affinity purification of Utp18 (UTP-B factor) from the rcl1Δ cms1Δ suppressor revealed co-enrichment of many 90S factors, but Rcl1, Bms1, and a few other factors such as Utp20, Utp22, and Utp14 were absent or present in low abundance (Figure 2B). Moreover, the free pool of the UTP-B module was diminished. Subsequent cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis of these suppressor-derived 90S particles showed a cavity at the expected position of Rcl1. However, adjacent to this hole, Rcl1’s partner Bms1 was still present at its authentic position (Figures 2C and S3B–S3E). In addition, several other typical 90S substructures, such as the 5′-ETS with its attached UTP-A, UTP-B, and U3 snoRNP modules, were readily identified on these unusual 90S particles. In contrast, another area corresponding to the 5′ rRNA domain, including Utp20, was either not as clearly visible or not resolved at all, suggesting that this subpart of the 90S is in a more immature, and therefore still more dynamic, state, which is not yet correctly folded and/or rigidly integrated into the 90S structure (Figures 2C and S3B–S3E). Thus, quite unexpectedly, ribosome biogenesis can take place without the essential Rcl1 under cms1Δ-suppressing conditions. However, such 90S pre-ribosomes are biochemically less stable and structurally immature or not correctly assembled in distinct regions, providing an explanation for the slow-growth phenotype of the rcl1Δ cms1Δ strain.
Cryo-EM analysis of the 90S particles purified from the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor revealed two major populations; one was similar to the 90S wild-type B2 state (Cheng et al., 2020), whereas the other exhibited a more immature appearance, with flexible central and 5′ domains (Figures 2D and S3F). Since the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor does not exhibit optimal cell growth compared with wild-type yeast (see Figure 1D), this could explain the existence of these two different 90S classes.
90S pre-ribosomes from the nop14-5Ala mutant retain Cms1 instead of Rrp12-Enp1
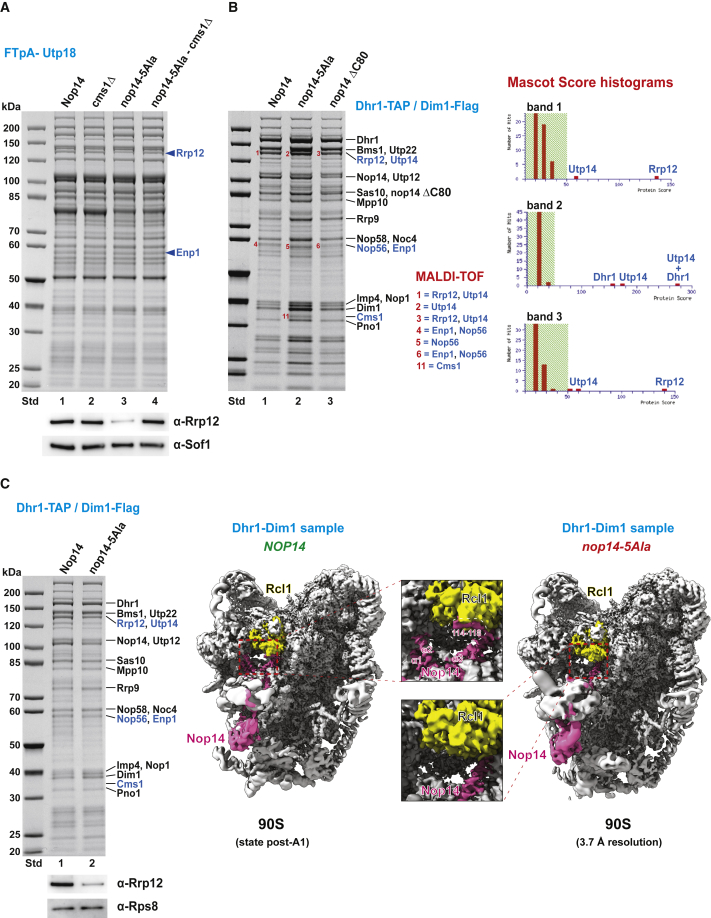
To investigate whether the nop14-5Ala mutation causes disruption to the assembly of the Noc4 module, we isolated 90S particles from the mutant strain via FTpA-Utp18 and identified the co-precipitated factors. Although the overall pattern of co-enriched 90S factors was similar compared with that of wild-type particles, the Rrp12 band, together with its direct binding partner Enp1, was markedly decreased in the nop14-5Ala strain, which could be confirmed by western blotting using α-Rrp12 antibodies (Figure 3A). However, this defect was corrected in the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor strain, where co-enrichment of Rrp12-Enp1 was restored in the FTpA-Utp18 preparation (Figures 3A and S4 and Table S1). Thus, disrupting CMS1 in nop14-5Ala cells not only improved cell growth, but also induced recovery from arrested pre-ribosome maturation with reappearance of Rrp12-Enp1 in the suppressor-derived 90S particles.
Figure 3.
Characterization of 90S particles from the nop14-5Ala mutant and its cms1Δ suppressor
(A) FTpA-Utp18 was affinity purified from the wild type (lane 1), the single mutants cms1Δ (lane 2) and nop14-5Ala (lane 3), and the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ double mutant (suppressor, lane 4). Equivalent amounts of the final eluates were analyzed on a 4%–12% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie blue (top) and analyzed by western blotting using anti-Rrp12 and anti-Sof1 (90S marker) antibodies (bottom). An independent series of FTpA-Utp18 affinity purifications from wild type and the same mutant strains is shown in Figure S4, from which the final eluates were further analyzed by semiquantitative mass spectrometry (Table S1), but also used for RNA analysis (see also Figure 6). The experiment was repeated four times, yielding in all cases similar outcomes.
(B) Dhr1-Dim1 split-tag affinity purification of particles in the 90S → pre-40S transition from the wild type (NOP14, lane 1), the nop14-5Ala mutant (lane 2), and the nop14ΔC80 mutant (lane 3). The final eluates were analyzed on a 4%–12% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie blue. Bands numbered 1–11 were excised from the gel and identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Shown on the right are Mascot score histograms (probability-based MOWSE algorithm; scores greater than 50 were regarded as statistically significant) for the individual excised bands 1–3; 90S factors are identified above the red bars. The Mascot score is a statistical score for how well the experimental data match the database sequences.
(C) Cryo-EM structure comparison of 90S pre-ribosomes in the post-A1 state purified from wild-type NOP14 (left) and nop14-5Ala cells (right), both isolated via Dhr1-Dim1 split tags. Rcl1 and Nop14 are colored in yellow and pink, respectively. The Rcl1-Nop14 interaction region from both structures is shown in detail as insets in the middle. The Nop14 N-terminal helices (α1–α2) and its short Rcl1 interaction strand (residues 114–116) can be seen in the wild-type but not the mutant 90S particle. Analysis of both Dhr1-Dim1 eluates by SDS-PAGE/Coomassie staining and western blotting using anti-Rrp12 and anti-Rps8 antibodies is shown on the left.
Although significant levels of Cms1 were not detected in wild-type 90S pre-ribosomes purified via FTpA-Utp18, they were approximately 8-fold greater if such particles were isolated from the nop14-5Ala mutant (Figure S4B), providing a biochemical explanation for our initial genetic findings. In addition to Cms1, another nonessential factor, Nop6, was co-enriched approximately 4-fold in nop14-5Ala-derived 90S particles (Figure S4B). Interestingly, NOP6 has also been found to be a null suppressor, but in contrast to Cms1, it rescued the nonviable phenotype of two other Noc4 module-null strains, noc4Δ and emg1Δ (also termed nep1Δ) (van Leeuwen et al., 2020; Schilling et al., 2012). Thus, vulnerable mutations in Noc4 module subunits or in the Bms1-Rcl1 heterodimer can be suppressed by disrupting CMS1 or NOP6, which both are nonessential factors implicated in the early 90S assembly pathway (see the discussion).
Based on these findings, we wondered if Cms1 could still be identified in pre-ribosomal particles from the nop14-5Ala mutant that developed further into the primordial pre-40S stage. This suspicion was strengthened by the finding that the particular dual 90S/pre-40S factor that marks this conversion, Dim1 (Cheng et al., 2020), was strongly enriched in the FTpA-Utp18 preparation from the nop14-5Ala mutant, in contrast to wild-type cells (Figure S4B). Indeed, 90S-to-pre-40S transition particles isolated from nop14-5Ala cells via the Dhr1-Dim1 bait combination exhibited Cms1 as a Coomassie-stainable band, but Rrp12 and Enp1 remained in lower abundance (Figures 3B and 3C). Cryo-EM analysis of this eluate revealed post-A1 90S particles that were devoid of the nop14-5Ala motif at the Rcl1 site, but the preceding Nop14 N-terminal helices α1 and α2 also could not be discerned (Figure 3C, right).
To reveal the pre-ribosome assembly intermediates, which pile up in the nop14-5Ala mutant, we performed sucrose gradient centrifugation of the different Dhr1-Dim1 eluates to separate 90S and pre-40S particles. Interestingly, in the case of the mutant, the pool of pre-40S still containing Cms1 was significantly increased, whereas in the wild-type preparation the 90S pool dominated (Figure S4C). Thus, mutations in the critical Nop14 N-terminal β strand hinder Cms1 from detaching in time during pre-ribosome biogenesis, causing this early 90S factor to remain attached to assembly intermediates that entered the 90S-to-pre-40S transition stage (see the discussion).
Cms1 co-precipitates many 90S assembly factors except Rrp12-Enp1
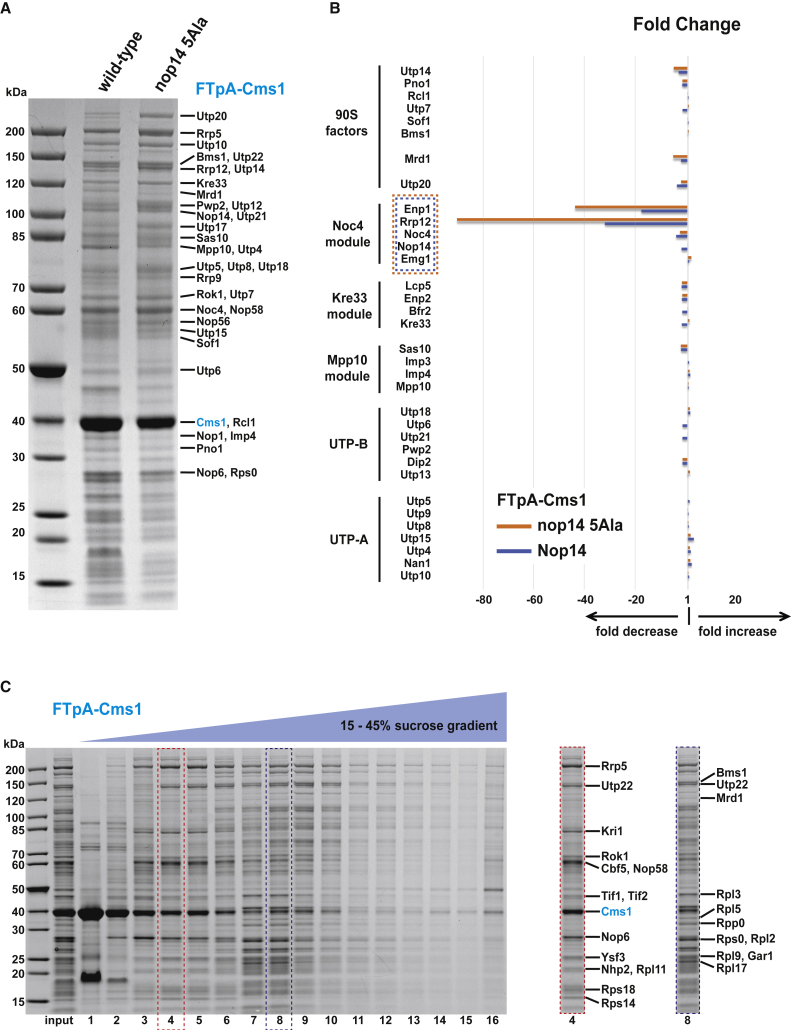
To determine the relationship between Cms1 and biogenesis of the Noc4 module, we considered isolating Cms1 from yeast cells under wild-type (i.e., physiological) as well as nop14-5Ala mutant conditions. However, since Cms1 is nonessential, it was important to demonstrate its functionality while modified with an affinity tag. We assumed that a tagged Cms1 is functional if suppressor activity toward nop14-5Ala is lost. In applying this test, only N-terminal, and not C-terminal, tagging yielded a functional Cms1 bait (data not shown). Hence, we continued with affinity purification of ProtA-TEV-Flag-Cms1 (FTpA-Cms1) from wild-type and nop14-5Ala mutant cells (Figure 4A). In both preparations, Cms1 was efficiently purified in an overstoichiometric ratio compared with the other co-enriched bands, pointing to different Cms1 pools. Mass spectrometry identified the Cms1-co-precipitated bands as classical 90S factors (e.g., UTP-A, UTP-B, Bms1-Rcl1, Kre33, Mpp10-Sas10, and the C/D box core factors Nop58, Nop56, Nop1), factors suggested to act in the upstream 90S assembly pathway (e.g., Mrd1, Kri1, Rok1, Nop6), and, interestingly, core factors of the H/ACA snoRNPs (e.g., Cbf5, Gar1, Nhp2) that catalyze snoRNA-guided pseudouridylation (Figure 4A and Table S2). Consistent with this pattern, Utp20, which associates later in the 90S assembly pathway (Cheng et al., 2020), was less co-enriched in the Cms1 preparation. Finally, when comparing the co-enrichment of the five Noc4 module factors by semiquantitative mass spectrometry, we observed that Rrp12 and Enp1 were distinctly lower in abundance than the other three members (Noc4, Nop14, and Emg1) in the wild type and, even more so, in the nop14-5Ala mutant (Figure 4B, Table S2). Thus, Enp1 and Rrp12 are specifically reduced from early 90S assembly intermediates if affinity purified via Cms1, pointing to Cms1 having an influence on stepwise Noc4 module assembly.
Figure 4.
Affinity purification of the FTpA-Cms1 from NOP14 wild-type and nop14-5Ala mutant cells
(A) FTpA-Cms1 was affinity purified from the wild type (NOP14) and the nop14-5Ala mutant, and final eluates were analyzed on a 4%–12% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie blue. The bands labeled on the right were excised and identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and colored according to their presence in the major 90S modules. The experiment was repeated several times with similar outcomes.
(B) Semiquantitative mass spectrometry analysis of the FTpA-Cms1 eluates derived from NOP14 (blue) and nop14-5Ala (orange) strains shown in (A). The label-free iBAQ (intensity-based absolute quantification) values for the co-enriched 90S factors were normalized to Pwp2, which was set as equal for both preparations, before comparing the fold decrease or increase in abundance of a given factor relative to Pwp2. Enp1 and Rrp12 are particularly lower in abundance than the other Noc4 module factors (Nop14, Noc4, and Emg1) in the Cms1 preparation from wild-type cells, and even more so in the preparation from the nop14-5Ala mutant. The whole dataset of iBAQ values from the semiquantitative mass spectrometry analysis is shown in Table S2.
(C) Sucrose gradient centrifugation of affinity-purified FTpA-Cms1. The final eluate of affinity-purified FTpA-Cms1 (input) from wild-type cells was loaded onto a 15%–45% sucrose gradient and the collected fractions 1–16 were analyzed on a 4%–12% gradient SDS-polyacrylamide gel and stained with Coomassie blue. Fractions 4 (subcomplexes) and 8 (90S-like particles) are separately displayed on the right, and the bands indicated were identified by mass spectrometry.
We next analyzed affinity-purified Cms1 by sucrose gradient centrifugation to verify its presence in 90S particles, but also to detect a possible association with smaller complexes. As anticipated, a pool of Cms1 present in fractions 8–10 of the gradient co-sedimented with 90S-factor-containing pre-ribosomal particles, but Cms1 also segregated broadly in the upper part of the gradient (Figure 4C). The presence of Cms1 in fractions 4 and 5 was of particular interest, because this part of the gradient contained components of the “upstream” 90S assembly pathway, such as Kri1, Rok1, and Nop6, and H/ACA snoRNA core factors (e.g., Cbf5, Nhp2). Thus, Cms1 appears to be present not only in pre-ribosomal particles but also in smaller complexes, which might include H/ACA snoRNPs (see below).
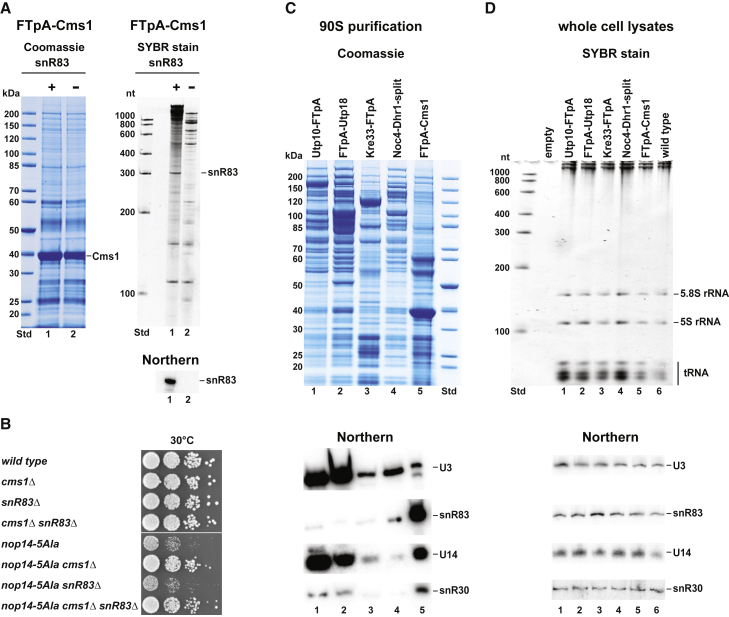
H/ACA snoRNA snR83 is specifically enriched in Cms1-precipitated early 90S
To identify snoRNAs that co-enrich with Cms1, we analyzed the co-precipitated RNAs extracted from the affinity-purified Cms1 by polyacrylamide-urea gel electrophoresis and SYBR green staining. This revealed a few snoRNA candidates in the lower molecular weight region of the gel, including a prominent band of approximately 300 nt that could correspond to the H/ACA snoRNA snR83, according to its theoretical size of 306 nt (Figure 5A). This assumption was experimentally verified by northern analysis and by chromosomal disruption of the SNR83 gene (snR83Δ), the latter causing the disappearance of the 300 nt band from the polyacrylamide-urea gel (Figure 5A). snR83 is an H/ACA snoRNA known to guide pseudouridylation at two sites, U1290 within helix H35 and U1415 within helix H40 (Schattner et al., 2004; Torchet et al., 2005), which are both located in the 18S rRNA 3′ major domain. Subsequent genetic tests in yeast, however, did not generate a synergistic growth defect when the nonessential snR83Δ was combined with cms1Δ (Figure 5B).
Figure 5.
H/ACA snR83 is co-precipitated by Cms1 but not by other typical 90S factors
(A) Affinity purification of FtpA-Cms1 from SNR83 (lane 1, plasmid-based FtpA-Cms1 expressed in cms1Δ strain) and snR83Δ-disrupted cells (lane 2, plasmid-based FtpA-Cms1 expressed in cms1Δ snR83Δ strain), followed by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining (left). For RNA analysis, RNA extracted from the Cms1 eluate was separated on a polyacrylamide gel, and co-enriched small RNAs were visualized by SYBR green staining (right), or detected by northern blotting using a probe for snR83, which is shown below the SYBR-stained gel.
(B) Dot-spot growth analysis of yeast strains on SDC-leu plates at 30°C after 2 days of incubation carrying the indicated wild-type and single- and double-chromosomal knockout alleles.
(C) Affinity purification of FTpA-Cms1 and different 90S particles (FTpA-Utp10, FTpA-Utp18, Kre33-FTpA, pA-Noc4-FT-Dhr1) followed by SDS-PAGE analysis with Coomassie staining (top) and northern blotting using specific probes for U3, snR83, U14, and snR30 (bottom). All yeast strains were grown in YPD medium, but Cms1 was shifted from SDC-leu to YPD medium for 6 h.
(D) Total RNA analysis extracted from whole-cell lysates of the corresponding affinity-tagged strains shown in (C) and analyzed by RNA gel electrophoresis, and SYBR green staining (top) and northern blotting using specific probes for U3, snR83, U14, and snR30 (bottom).
To determine whether snR83 is present in classical 90S pre-ribosomal particles, we performed a northern analysis of the RNA extracted from the Cms1 eluate, with comparison with other established 90S preparations. We found that snR83 was specifically enriched in the Cms1-derived particles, but only a little of this H/ACA snoRNA was present in other 90S particles affinity purified via Utp10, Utp18, or Noc4-Dhr1 (Figures 5C and 5D). However, as anticipated, these particles contained other 90S-typical snoRNAs such as U3 or U14.
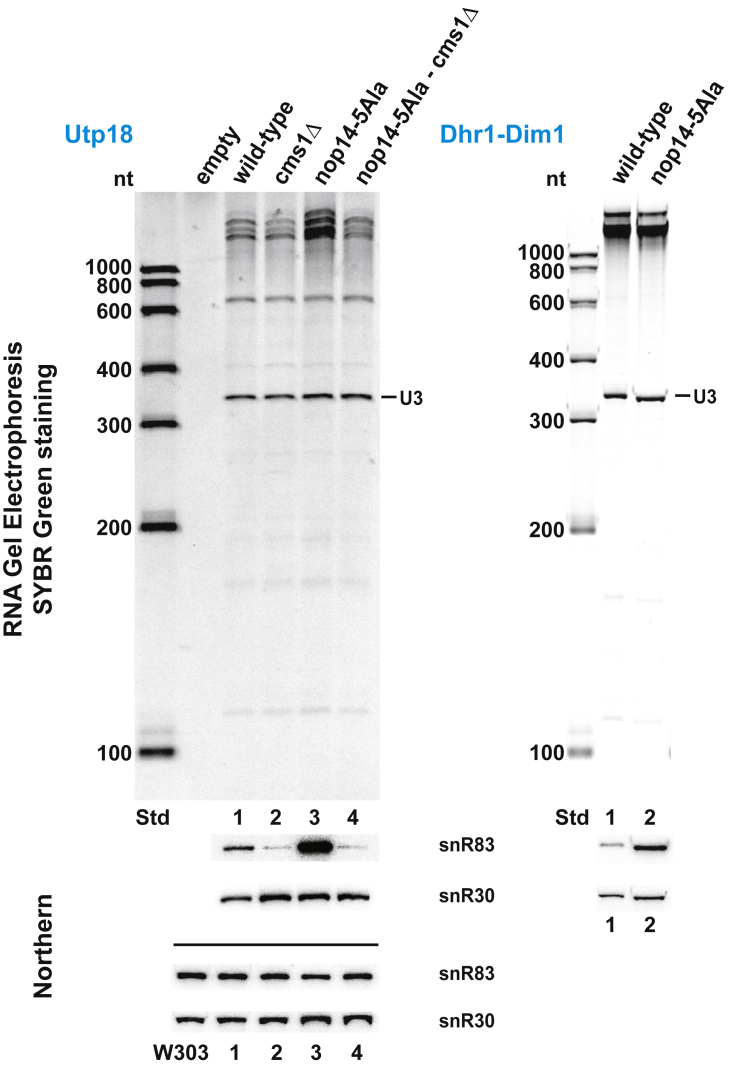
To determine whether the association of snR83 with early 90S particles is affected by mutations in factors investigated in this study, we affinity purified FtpA-Utp18 from strains cms1Δ, nop14-5Ala, and nop14-5Ala cms1Δ as well as the wild type, and compared the patterns of co-precipitated 90S factors and snoRNAs (Figure 6). This showed that wild-type 90S particles contained little snR83, the amount of which was further diminished in the cms1Δ strain. In contrast, nop14-5Ala-derived 90S particles exhibited high accumulation of snR83, which, however, completely returned to background levels in the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor strain. In contrast to snR83, other co-precipitated snoRNAs, such as snR30 and U3, did not significantly differ in abundance among the various 90S preparations (Figure 6, left). Moreover, we observed that snR83 was still co-enriched in the Dhr1-Dim1 preparation when isolated from nop14-5Ala but not wild-type cells (Figure 6, right). Thus, snR83 enrichment in 90S particles derived from the nop14-5Ala mutant correlates with Cms1 accumulation but also reduction in Rrp12-Enp1, whereas the opposite is true for the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor strain, which exhibits a strong decline in snR83 in favor of an Rrp12-Enp1 association. However, we did not observe that the slow growth of the nop14-5Ala strain was suppressed by the snR83Δ disruption (Figure 5B).
Figure 6.
H/ACA snoRNA snR83 is enriched in matured 90S particles derived from the nop14-5Ala mutant
RNA analysis of the final eluates of affinity-purified FTpA-Utp18 from wild-type, cms1Δ, nop14-5Ala, and nop14-5Ala cms1Δ double-disruption strains (left) and split-tag affinity-purified Dhr1-Dim1 from wild type and nop14-5Ala mutant (right). The extracted RNA was analyzed by RNA gel electrophoresis (top) and northern blotting (bottom). For SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining of these eluates, see Figure S4. The RNA was first separated on a polyacrylamide gel, and co-enriched small RNAs were visualized by SYBR green staining (the prominent U3 snoRNA is indicated) before northern blotting was performed using specific probes for snR83 and snR30. For comparison, total RNA was also extracted from whole-cell lysates of the FTpA-Utp18-expressing wild-type, cms1Δ, nop14-5Ala, and nop14-5Ala cms1Δ strains, as well as from the isogenic and unmodified W303, followed by northern analysis using the same snR83 and snR30 probes (shown below the eluate northern).
Cms1 crosslinks to H32-H34 of the 18S rRNA 3′ major domain
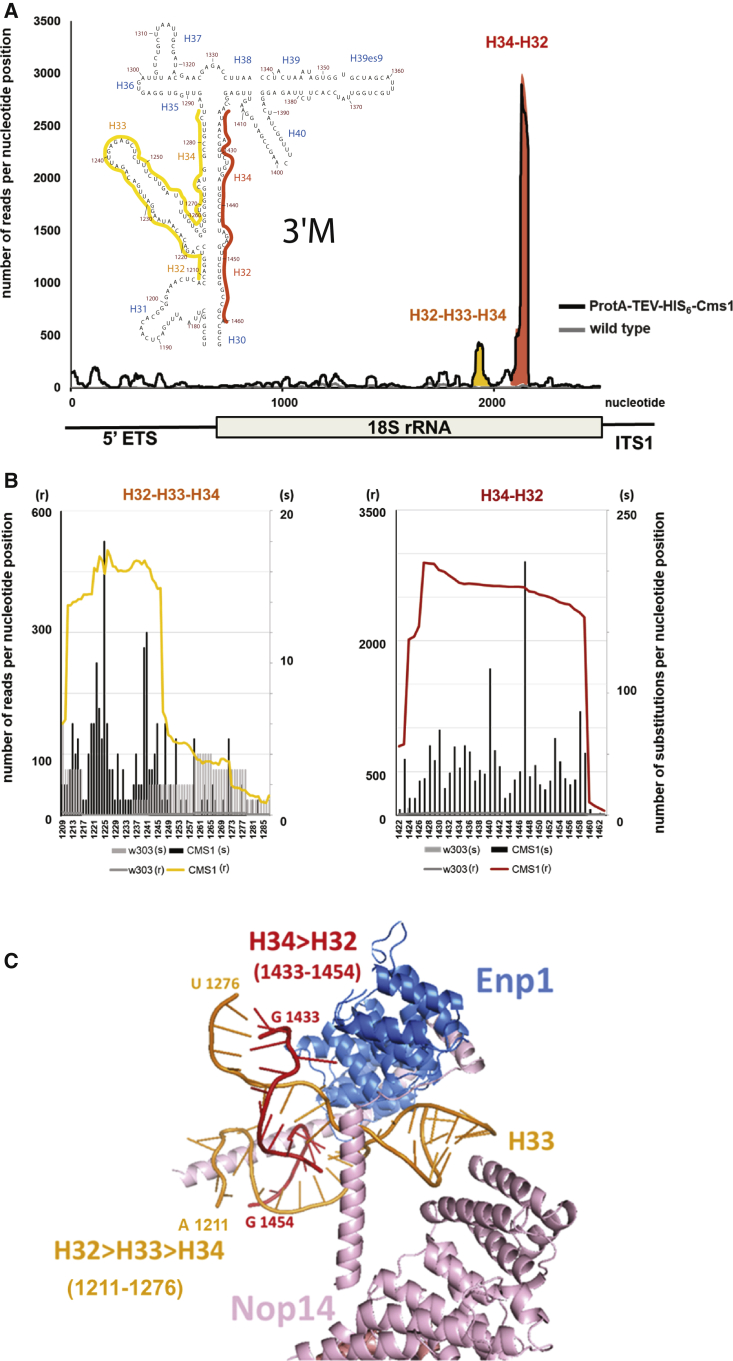
Since disrupting the CMS1 gene in the nop14-5Ala strain restored Rrp12-Enp1 recruitment to the 90S, we hypothesized that Cms1 associates at a 90S site where Rrp12 and Enp1 are normally engaged, thereby hindering premature incorporation of these two Noc4 module factors. To determine whether this occurs by direct binding of Cms1 to Nop14, we tested in vitro for such an interaction, but could not find supporting evidence (data not shown). Hence, we performed in vivo UV cross-linking of Cms1 to RNA using the CRAC method (Granneman et al., 2009) to test whether the functional ProtA-TEV-His6-Cms1 construct has direct contact with the pre-rRNA, possibly mediated by the RNA-helicase-like domain of Cms1. Notably, ProtA-TEV-His6-Cms1 was specifically cross-linked to the 3′ major domain of the 18S rRNA at two specific sites, with the highest peak corresponding to the descending H34-H32 strand and a second smaller peak assigned to the ascending H32-H34 strand and intercalated helix H33 (Figures 7A and 7B). Furthermore, the occurrence of several highly recurring mutations in the cloned and sequenced Cms1 CRAC products indicated a direct contact between Cms1 and specific RNA bases in this region of the 18S rRNA (Figure 7B). Thus, Cms1 is positioned along H32-H34 of the 3′ major domain, which is also the region in the 90S cryo-EM structure where Enp1 and Nop14, two members of the Noc4 module, are located (Figure 7C).
Figure 7.
In vivo RNA-protein cross-linking (CRAC) reveals Cms1 binding to the H32-H34 region of the 3′ major domain
(A) Actively growing yeast cells (strain W303) expressing ProtA-TEV-His6-Cms1 or untagged Cms1 were exposed to UV light. Cross-linked RNAs, after trimming and linker ligation, were amplified by RT-PCR and subjected to Illumina-Solexa sequencing. Sequence reads were aligned with the 5′-ETS and 18S rRNA region (for alignment with the entire 35S pre-rRNA sequence [RDN37-1]) and are displayed in the histogram. For the ProtA-TEV-His6-Cms1 sample, the major peak (red) corresponds to the descending strand of H34 > 32, and a second peak (orange) to the ascending strand of H32 > H33 > H34. Also shown is the secondary structure of the 3′ major domain (from H32 to H40), with the Cms1 CRAC nucleotides in the H32-H33-H34 region labeled with an orange line and those in the H34 > H32 region marked with a red line (using the RiboVision v.1.15 tool). The CRAC experiment was repeated twice and yielded reproducible results.
(B) Expanded views of the Cms1 CRAC peaks corresponding to H32-H33-H34 (orange; 1,209–1,285 nt) and H34-H32 (red; 1,422–1,460 nt), with the number of reads (r) per nucleotide position indicated on the y axis and the nucleotide position in the 35S pre-rRNA on the x axis. The numbers of substitutions (s) found in the cloned and sequenced Cms1 CRAC products are displayed in the same graph (Cms1, black lines; mock W303, gray lines). For Cms1, the highest substitutions (>100) were found at C1456 and C1440 (H34 > H32).
(C) Mapping of the Cms1 CRAC hits within the yeast 90S cryo-EM structure (PDB: 6ZQC). Only the area of the 3′ major domain with bound Enp1 and Nop14, the H34 > H32 descending strand (positions 1,454–1,433; red), and the H32 > H33 > H34 ascending strand (positions 1,211–1,276; orange) are shown. Note that the entire H32-34 region is in close proximity to direct points of contact with Nop14 and Enp1.
As Cms1 is conserved in evolution (see Figure S2A), we inspected the sites of Cms1-RNA cross-linking found for yeast in the other known 90S cryo-EM structures from C. thermophilum and H. sapiens. The human map (Singh et al., 2021) revealed in molecular detail how the entire Noc4-Nop14-Emg1-Enp1-Rrp12 module interacts with the 3′ major domain in a highly conserved constellation, with Enp1 (called BYSL in human) being wedged by H32-H33-H34 (also seen in the yeast and ct maps), and the RRP12 α solenoid encircling H35-H40 (Figure S5). Thus, it is feasible that Cms1 positioned along H32-H34 might hinder the initial recruitment of Enp1-Rrp12, but allow snR83 to interact with the 3′ major domain during early 90S assembly (see the discussion). However, Cms1 appears to have no major role in the snR83-guided rRNA modifications, as the pseudouridylation status of U1290 was not and that of U1415 was only slightly affected by the cms1Δ deletion (Figure S6).
Discussion
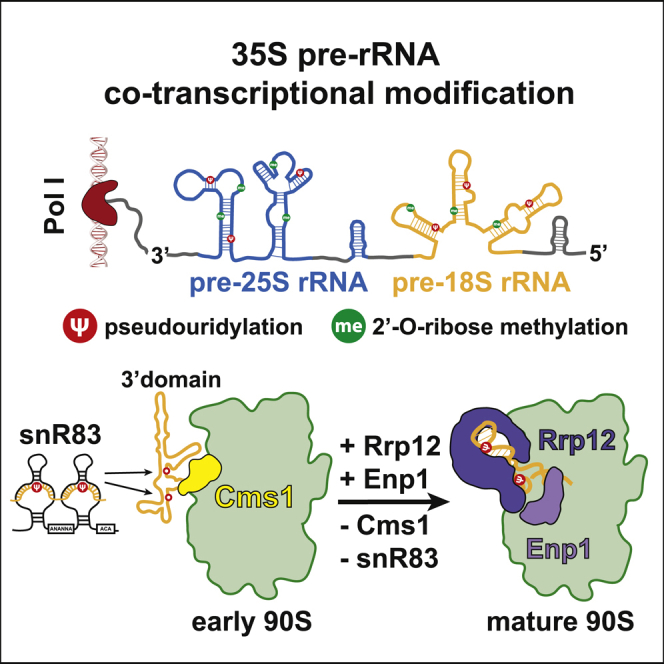
In this study, we report that the Noc4 module assembles stepwise at the 3′ major domain of the 90S pre-ribosome, which could be a means to coordinate local pre-rRNA modification by an H/ACA snoRNA before 90S assembly is completed. We discovered this interdependent assembly while studying nop14 N-terminal mutants whose growth defects were suppressed by a loss-of-function mutation in the nonessential CMS1, which encodes a poorly characterized 90S assembly factor. One of the mutants used, nop14-5Ala, was precisely constructed to locally impair the interaction between Nop14 and adjacent Rcl1, which is a member of the Bms1-Rcl1 heterodimer. In vivo, this nop14-5Ala mutant created a distinct 90S biogenesis defect with disturbed Rrp12-Enp1 assembly into the Noc4 module, which could be caused by Cms1 occupying an overlapping binding site on the early 90S. However, by deleting Cms1 from the genome, this defect could be rescued and cell growth restored.
We speculate that the extended flexible Nop14 N terminus, before it is fixed at the Rcl1 site, is available for other interactions, including a link to snR83, and in this way could coordinate development of the 3′ major domain at an early stage of pre-ribosome assembly (Figure S7). Thus, a hitherto unacknowledged role of Rcl1 in 90S biogenesis could be to ultimately make contact with the N-terminal Nop14 β strand, thereby terminating its putative “upstream” interactions and allowing full assembly of the Noc4 module. Notably, both Cms1 and snR83 remain bound on pre-ribosomes when isolated from the nop14-5Ala mutant even until reaching the 90S-to-pre-40S transition stage, leading to an accumulation of early nucleolar pre-40S particles (Figure S4C). However, from then on, further maturation could be slowed down, because downstream pre-40S factors (e.g., Slx9, Ltv1, Rio2, or Tsr1) might not effectively join (Ameismeier et al., 2018; Campbell and Karbstein, 2011; Schafer et al., 2003). This could also affect nuclear export of the nascent 40S, because some of these factors are involved in recruiting the nuclear export machinery (Fischer et al., 2015; Zemp et al., 2009; Seiser et al., 2006; Moriggi et al., 2014).
Based on these data, we speculate how Cms1 could facilitate snR83 recruitment to the 3′ major domain in coordination with other early 90S assembly steps (Figure S7). Via its inactive helicase domain, Cms1 might exert a specific RNA-binding activity toward the H32-34 region of the 3′-major domain, thereby competing with Enp1-Rrp12 binding at a related site. This could help snR83 to access its two substrate RNA nucleotides, which after Rrp12-Enp1 recruitment to the 90S appear to be less accessible (Figure S7 and Video S1). However, also in the absence of Cms1, snR83 can still modify its two target uridines, showing that Cms1 has no direct role in this modification reaction. At present, it remains unclear whether Cms1 physically interacts with snR83 or one of its H/ACA core factors, but we observe that whenever Cms1 is associated with 90S, snR83 is present, and vice versa, if Cms1 release is disturbed (like in the nop14-5Ala mutant), snR83 dissociation is affected. Thus, Cms1 and snR83 are part of an early 90S factor network in the 3′ major domain that could coordinate 90S assembly and couple this with local pseudouridylation, before these early 90S factors dissociate and enable Rrp12-Enp1 to enter the H35-H40 region (Figure S7). Notably, both a human Cms1 (CMSS1; Figure S2A) and an snR83 homolog (called ACA4) exist; the latter is known to pseudouridylate the conserved U1347 (corresponding to U1290 in yeast) within H35 of the human 18S rRNA (Kiss et al., 2004). Thus, during human 90S biogenesis, pre-rRNA modification in the 3′ major domain and progressive Noc4 module assembly might also be coordinated.
Limitations of the study
Some of the conclusions drawn from this study are derived from data based on pre-ribosomal particles isolated from mutant cells, which might be part of the physiological but only arrested pathway. However, they could also represent dead-end assembly intermediates. Moreover, we interpreted our results largely based on a linear 90S maturation pathway, but it is possible that this assembly line has parallel and/or alternative segments. Another limitation of this study concerns our failure to solve the structure of Cms1-derived 90S particles by high-resolution cryo-EM. We attribute this to the highly flexible and uncompacted folded states of these early biogenesis intermediates, leaving the question of how Cms1 and snR83 are attached to the 3′ major domain unresolved. Finally, the exact role of the nonessential snR83 in snoRNA-guided pseudouridylation at the 3′ major domain of the 18S rRNA is not clear, but since both H/ACA snoRNA and its target site(s) are conserved over 1 billion years of evolution, this points to an important function.
STAR★Methods
Key resources table
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Rrp12 | Moriggi et al., 2014 | N/A |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Sof1 | Jansen et al., 1993 | N/A |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-Rps8 | Dieci et al., 2005 | N/A |
| Goat polyclonal anti-Rabbit-IgG (H + L) - Horseradish Peroxidase conjugated | Biorad | Catalog # 170-6515; Lot # 350000928 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| E. coli DH5α | Taylor et al., 1993 | N/A |
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| Flag peptide (DYKDDDDK) | CASLO | N/A |
| TEV protease | Parks et al., 1994 | N/A |
| SIGMAFAST | Sigma-Aldrich | S8830 |
| SYBR Green II RNA gel stain | Sigma–Aldrich | S9305 |
| RiboLock RNase inhibitor | Thermo Scientific | EO0381 |
| RNace-IT | Agilent Technologies | 400720 |
| RNasin | Promega | N2615 |
| TSAP | Promega | M9910 |
| T4 PNK | NEB | M0201 |
| T4 RNA ligase 2 truncated | NEB | M0242 |
| T4 RNA ligase | NEB | M0204 |
| Proteinase K | NEB | P8107 |
| Superscript III | Invitrogen | 18080093 |
| RNase H | NEB | M0297 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| ANTI-FlagM2 Affinity Gel | Sigma–Aldrich | A2220 |
| HIS-Select Nickel Affinity Gel | Sigma–Aldrich | P6611 |
| IgG–Sepharose 6 Fast Flow | GE Healthcare | 17096902 |
| Deposited data | ||
| Raw and analyzed data | This paper | Mendeley: https://doi.org/10.17632/8xdscd7r35.1. |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, sup1-1 whole-genome sequencing; short-read | This paper | SRA: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/ERX9848983 |
| RAW files of mass spectrometry data (Table S1) | This paper | ProteomeXChange:10.6019/PXD037562 |
| RAW files of mass spectrometry data (Table S2) | This paper | ProteomeXChange:10.6019/PXD037619 |
| 90S state rcl1Δ cms1Δ cryo-EM density (FTpA-Utp18) | This paper | EMD-34284 |
| 90S state nop14-5Ala cms1Δ cryo-EM density (FTpA-Utp18, state: B2) | This paper | EMD-34285 |
| 90S state nop14-5Ala cms1Δ cryo-EM density (FTpA-Utp18, state: b) | This paper | EMD-34286 |
| 90S state nop14-5Ala cryo-EM density (Dhr1-Dim1) | This paper | EMD-34283 |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| S. cerevisiae: Strain background: W303 ade2-1 ,trp1-1, leu2-3,112, his3-11,15, ura3-1, can1-100 | Thomas and Rothstein, 1989 | W303 |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, [pRS316 NOP14], W303 | This paper | Nop14 shuffle |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, [pRS316 NOP14], cms1::hphNT1, W303 | This paper | Nop14 shuffle, cms1Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, [pRS316 NOP14], cms1::hphNT1, snR83::kanMX6, W303 | This paper | Nop14 shuffle, cms1Δ, snR83Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, [pRS316 NOP14], [pRS315 FTpA-UTP18], W303 | This paper | Nop14 shuffle, FTpA-Utp18 |
| S. cerevisiae: nop14::natNT2, [pRS316 NOP14], DHR1-TAP::HIS3, DIM1-Flag::natNT2, W303 | This paper | Nop14 shuffle, Dhr1-TAP, Dim1-Flag |
| S. cerevisiae: cms1::hphNT1, W303 | This paper | cms1Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: cms1::hphNT1, snR83::natNT2, W303 | This paper | cms1Δ, snR83Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: rcl1::natNT2, [pRS316 RCL1], cms1::hphNT1, W303 | This paper | Rcl1 shuffle, cms1Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: rcl1::natNT2, [pRS316 RCL1], W303 | This paper | Rcl1 shuffle |
| S. cerevisiae: FTpA-CMS1-LEU2, snR83::natNT2, W303 | This paper | FTpA-Cms1, snR83Δ |
| S. cerevisiae: FTpA-CMS1-LEU2, W303 | This paper | FTpA-Cms1 |
| S. cerevisiae: NOC4-TAP::HIS3, DHR1-Flag::natNT2, W303 | Cheng et al. 2020 | Noc4-TAP, Dhr1-Flag |
| S. cerevisiae: KRE33-FTpA::HIS3, W303 | Cheng et al., 2019 | Kre33-FTpA |
| S. cerevisiae: TAP-Flag-UTP18::natNT2, W303 | Thoms et al., 2015 | TAP-Flag-Utp18 |
| S. cerevisiae: UTP10-FTpA::natNT2, W303 | Kornprobst et al., 2016 | Utp10-FTpA |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| 5′-rApp/AGATCGGAAGAGCGGTTCAG/ddC/-3′ | Granneman et al., 2011 | L3 linker |
| 5′-InvddT/ACACrGrArCrGrCrUrCrUrUrCrCr GrArUrCrUr NrNrNrNrGrCrGrCrArGrC-3′ |
Thoms et al., 2015 | L5 Ac |
| 5′-InvddT/ACACrGrArCrGrCrUrCrUrUrCr CrGrArUrCrUr NrNrNrNrUrArArGrC-3′ |
Thoms et al., 2015 | L5 Aa |
| 5′-GCTGAACCGCTCTTCCGAT-3′ | Granneman et al., 2011 | L3 RT oligo |
| 5′-AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACA CTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT-3′ |
Granneman et al., 2011 | P5 PCR oligo |
| 5′-CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGAT CGGTCTCGGCATTCCTGCTGAACCG CTCTTCCGATCT-3′ |
Granneman et al., 2011 | P3 PCR oligo |
| 5′-TTATGGGACTTGTT-3′ | Sharma and Tollervey, 1999 | anti-U3 |
| 5′-TCACTCAGACATCCTAGG-3′ | Allmang et al., 1999 | anti-U14 |
| 5′-ATGTCTGCAGTATGGTTTTAC-3′ | Fath et al., 2000 | anti-snR30 |
| 5′-TATGAACACAATTGTTGTAGT-3′ | This paper | anti-snR83 |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| Plasmid: PADH1-NOP14-TADH1, URA3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS416 Nop14 |
| Plasmid: PRCL1-RCL1-TADH1, URA3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS316 Rcl1 |
| Plasmid: PUTP18-FTpA-UTP18-TADH1, LEU2, ARS/CEN, AmpR | Thoms et al., 2015 | YCplac111-FTpA-Utp18 |
| Plasmid: PCMS1-FTpA-CMS1-TADH1, LEU2, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS315 FTpA-Cms1 |
| Plasmid: PCMS1-HTpA-CMS1-TADH1, LEU2, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS315 HTpA-Cms1 |
| Plasmid: PADH1-NOP14-TADH1, HIS3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS413 Nop14 |
| Plasmid: PADH1-NOP14-TADH1, TRP1, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS414 Nop14 |
| Plasmid: PADH1-nop14 ΔN3-TADH1, HIS3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS413 nop14ΔN3 (ΔN 1–159) |
| Plasmid: PADH1-nop14 5Ala-TADH1, HIS3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS413 nop14-5Ala |
| Plasmid: PADH1-nop14 5Ala-TADH1, TRP1, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS414 nop14-5Ala |
| Plasmid: PADH1-nop14 ΔC80-TADH1, HIS3, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS413 nop14ΔC80 |
| Plasmid: PADH1-nop14 ΔC80-TADH1, TRP1, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS414 nop14ΔC80 |
| Plasmid: PRCL1-RCL1-TADH1, TRP1, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS314 Rcl1 |
| Plasmid: PRCL1-rcl1 GGGGS loop-TADH1, TRP1, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS314 rcl1 GGGGS loop |
| Plasmid: PCMS1-CMS1-TADH1, LEU2, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | pRS315 Cms1 |
| Plasmid: PGAL1-10-CMS1-TADH1, LEU2, ARS/CEN, AmpR | This paper | YCplac111 pGAL Cms1 |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| ClustalOMEGA | EMBL-EBI (Madeira et al., 2022) |
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo |
| Jalview | Waterhouse et al., 2009 | https://www.jalview.org |
| pyCRAC | Webb et al., 2014 | https://sandergranneman.bio.ed.ac.uk/pycrac-software |
| USCF Chimera | Pettersen et al., 2004 | http://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera |
| Coot | Emsley and Cowtan, 2004 | https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/personal/pemsley/coot/ |
| MaxQuant | Cox and Mann, 2008 | https://www.maxquant.org |
| EPU | Thermo Fisher | https://www.thermofisher.com/de/de/home/electron-microscopy/products/software-em-3d-vis/epu-software.html |
| MotionCor2 | Zheng et al., 2017 | https://emcore.ucsf.edu/cryoem-software |
| CTFFIND4 | Rohou and Grigorieff, 2015 | http://grigoriefflab.janelia.org/ctffind4 |
| cryoSPARC | Punjani et al., 2017 | https://cryosparc.com/ |
| GCTF | Zhang, 2016 | https://www.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/kzhang/ |
| Gautomatch | Zhang, 2017 | https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/research/locally-developed-software/zhang-software/ |
| Relion V3.1 | Kimanius et al., 2016 | https://www3.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/relion/index.php?title=Main_Page |
| PHENIX | Adams et al., 2010 | https://www.phenix-online.org |
| ChimeraX | Goddard et al., 2018 | https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ |
| Other | ||
| Quantifoil holey carbon R3/3 with 3 nm continuous | Quantifoil Micro Tools GmbH | https://www.emsdiasum.com/microscopy/products/grids/quantifoil.aspx |
Resource availability
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Ed Hurt (ed.hurt@bzh.uni-heidelberg.de).
Materials availability
All unique/stable reagents (plasmids and yeast strains) generated in this study are available from the lead contact without restriction.
Experimental model and subject details
Yeast strains
Yeast cells were grown in different media and different temperatures as outlined in the Method details section. The genotypes of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains used are listed in the Key resources table.
Bacterial strains
The E. coli DH5a strain (Thermo Fisher Scientific) used for plasmid constructions was grown under standard conditions at 37°C.
Method details
Yeast strains
All yeast strains generated and used in this study are listed in the Key resources table. Genomic tagging and gene disruptions were performed as previously described (Janke et al., 2004; Longtine et al., 1998). Genomic manipulations were verified by western blotting using antibodies against tagged proteins, colony PCR, and/or sequencing.
Identification of candidate mutations by high-throughput DNA sequencing
Preparation of genomic DNA from yeast strains, high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics identification of mutations was carried out as previously described (Thoms et al., 2018). Results were viewed with the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) software (Thorvaldsdóttir et al., 2013), and the presence of the nop14ΔN3 allele in the sup1-1 suppressor strain was verified. This sequence analysis revealed only one significant mutation in the sup1-1 genome compared to the genomes of two isogenic reference strains (PRJEB56518). The identified mutation corresponds to a one-nucleotide insertion in the CMS1 ORF, leading to a frameshift mutation and a premature stop codon (see Figure S1D).
Tandem affinity purification of pre-ribosomal particles
Yeast strains expressing tagged bait proteins, used for single-bait or split-bait tandem affinity purifications, were cultured at 30°C and harvested during the logarithmic growth phase (OD600 nm ≈ 2.0). Cells were lysed mechanically using a cryogenic cell mill (Retsch MM400) and for two liter of cell powder 15mL of lysis buffer, containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 5% glycerol, 0.1% NP-40, and 1 mM DTT, supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (SIGMAFAST), was used. The lysate was cleared twice by centrifugation (4,600xg for 10 min at 4°C followed by 35,000xg for 20 min at 4°C) and the supernatant was loaded onto 500 μL IgG Sepharose 6 Fast Flow resin (GE Healthcare) for at least 2 h at 4°C. The beads were washed twice, in batch mode (20 mL) and by gravity flow (10 mL), with purification buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 5% glycerol, 0.01% NP-40, and 1 mM DTT. Bound proteins were eluted by TEV protease cleavage for 1 h at 16°C. For the second affinity purification step, the TEV eluate was transferred to 50 μL Flag-agarose beads (Anti-Flag M2 Affinity Gel, Sigma–Aldrich) and incubated for 1 h at 4°C. The beads were washed (7 mL), and bound proteins were eluted with purification buffer containing Flag peptide (final concentration 300 μg/mL). For cryo-EM analysis the elution buffer contained 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 2% glycerol, 0.01% NP-40 and 1 mM DTT. Final eluates were either analyzed by SDS-PAGE on 4–12% polyacrylamide gels (NuPAGE, Invitrogen) followed by colloidal Coomassie staining (Roti Blue, Roth), or were further separated by sucrose gradient centrifugation. Fractions from the sucrose gradient were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (see below).
RNA extraction and northern analysis
RNA obtained from affinity-purified pre-ribosomes was extracted from the Flag eluates using phenol–chloroform followed by precipitation with ethanol. For detection of snoRNAs, RNA samples were separated on 8% polyacrylamide–8 M urea gels followed by staining with the fluorescent dye SYBR Green (Sigma–Aldrich, S9305). For northern blot analysis, the RNA was transferred onto a nylon membrane (GE Healthcare) and UV-crosslinked. The 5'-32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes used for northern analysis are listed in the Key resources table.
Cryo-electron microscopy and image processing
3.5 μL of affinity-purified FTpA-Utp18 or Dhr1-TAP-Dim1-Flag final eluates derived from the rcl1Δ cms1Δ double gene disruption strain, nop14-5Ala cms1Δ suppressor strain or nop14-5Ala mutant strain was directly applied to pre-coated (2 nm) R3/3 holey-carbon-supported copper grids (Quantifoil). The grids were then blotted for 2–3 s at 4°C and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane using an FEI Vitrobot Mark IV. Data collection was carried out on a FEI Titan Krois cryo-electron microscope operating at 300 keV. All data were collected with a pixel size of 1.045 Å and within a defocus range of −0.8 to −2.5 μm using a K2 Summit direct electron detector under low-dose conditions, with a total dose of 44 e−/Å2. Original image stacks were dose-weighted, aligned, summed, and drift-corrected using MotionCor2 (Zheng et al., 2017). Contrast-transfer function (CTF) parameters and resolutions were estimated for each micrograph using CTFFIND4 and GCTF, respectively (Zhang, 2016; Rohou and Grigorieff, 2015). Micrographs with an estimated resolution of less than 5 Å and an astigmatism of less than 5% were manually screened for contamination or carbon rupture.
For the cryo-EM dataset 1 collected from the sample (FTpA-Utp18 eluate) derived from the rcl1Δ cms1Δ double gene disruption strain, a total number of 42,744 particles were picked from 495 good micrographs using Gautomatch (Zhang, 2017). The picked particles were immediately classified into six classes in cryoSPARC (Punjani et al., 2017) with the 90S pre-ribosome as a reference. Only one class (16,024 particles) showed the classical 90S shape in high resolution. This class was picked and refined to its final state using cryoSPARC homogenous refinement. Maps and models were visualized and figures created with ChimeraX (Pettersen et al., 2004).
For the dataset 2 collected from the sample (FTpA-Utp18 eluate) derived from the nop14-5Ala cms1Δ strain, a total number of 559,976 particles were picked from 5,731 good micrographs using Gautomatch (Zhang, 2017). Particle extraction was carried out in Relion 3.1. The extracted particles were imported into cryoSPARC (Punjani et al., 2017), followed by 2D classification and 3D heterogeneous refinement. As a result, a total number of 154,021 particles showed the typical 90S features and were imported back to Relion (Kimanius et al., 2016) to perform the final 3D classification. Finally, two of the six classes, which showed the classic 90S structure, could be refined to high resolution, of which one class closely resembled the reported state b and accounted for 22,056 particles (Chaker-Margot et al., 2017), while the other class was identical to the reported state B2 and accounted for 33,340 particles (Cheng et al., 2020). The final 3D refinement, including postprocessing, local resolution filtering of the final reconstructions, was carried out in Relion.
For the dataset 3 collected from the sample (Dhr1-Dim1 eluate) derived from nop14-5Ala mutant strain, a total number of 412,761 particles were picked from 5,268 good micrographs using Gautomatch (Zhang, 2017). After particle extraction in Relion, all particles were directly imported into cryoSPARC (Punjani et al., 2017). Heterogeneous refinement was carried out using state Dis-C as initial reference to classify all particles into six classes (Cheng et al., 2020). Finally, two of the six classes, which showed the Dis-C and post-A1 shape states, respectively, were imported back to Relion (Kimanius et al., 2016). Extensive 3D classification was carried out for both classes using the Relion 3D classification module. Finally, a total number of 14,298 particles resembled the reported state Dis-C (Cheng et al., 2020), however, with still partial Utp20 binding. The other 66,762 particles were identical to the reported state Dis-C (Cheng et al., 2020). In the case of 90S pre-ribosome, after classification, a total number of 18,800 particles resembled the reported state post-A1, however, with differences in the Rcl1 and Nop14 interaction region. The final 3D refinement, including postprocessing, local resolution filtering of the final reconstructions, was carried out in Relion (Kimanius et al., 2016).
Since the final reconstructions were either highly similar to the reported structures or were in low resolution, we used these published structural models to perform rigid-body fitting into the corresponding reconstructions (Cheng et al., 2020; Chaker-Margot et al., 2017). The missing Utp20 and Rcl1 in dataset 1 and the missing Nop14-Rcl1 interaction in dataset 3 were simply manually removed in Coot (Emsley and Cowtan, 2004). Maps and models were visualized and figures created with ChimeraX (Goddard et al., 2018).
Sucrose gradient centrifugation
Flag eluates from tandem affinity purifications were loaded onto a 10–40% (w/v) or 15–45% (w/v) linear sucrose gradient with buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 100 mM NaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.003% NP-40, and 1 mM DTT, and then centrifuged for 16 h at 129,300 g at 4°C. After centrifugation, fractions of equal volume were precipitated with 10% trichloroacetic acid, resuspended in sample buffer and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by staining with colloidal Coomassie (Roti Blue, Roth).
Mass spectrometry
Precipitated proteins from Flag eluates or fractions from sucrose gradients were analyzed by semiquantitative mass spectrometry at FingerPrints Proteomics (University of Dundee, UK) based on 1D nLC–ESI-MS/MS. Prominent bands from Coomassie-stained gels were individually excised and identified by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry.
CRAC analysis
The crosslinking and cDNA analysis (CRAC) of Cms1 was performed as previously described with only minor changes (Granneman et al., 2009, 2011), using a W303 strain as the control and a W303 cms1Δ strain with His6-TEV-ProtA-Cms1 expressed from a plasmid. Yeast cells were harvested during logarithmic growth (OD260 nm = 0.6–0.8) and UV-irradiated using a Megatron UV chamber (1.6 J/cm2). The reverse-transcribed and amplified cDNA from Cms1 and control samples was sequenced using the Illumina MiSeq sequencing platform and analyzed using the PyCRAC software package, which is available at https://sandergranneman.bio.ed.ac.uk/pycrac-software. The 5' linkers used contained a region of random nucleotides designed for removal of duplicate reads generated throughout the PCR amplification (Thoms et al., 2015). The obtained reads were mapped against the yeast 35S rDNA reference.
Pseudouridylation analysis
The pseudouridylation analysis was performed according to Kiss and Jády (Kiss and Jády, 2004).
Quantification and statistical analysis
Cryo-electron data were processed with RELION and cryoSPARC and further analyzed as described in the Method details. The raw semiquantitative mass spectrometry data shown in Tables S1 and S2 were analyzed using MaxQuant software (Cox and Mann, 2008), and for MALDI-TOF data the MASCOT Score (Matrix Science Inc.) was used. No statistical analysis was used in this study.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the ERC (ADG 741781 GLOWSOME to E.H. and ADG 885711 Human-Ribogenesis to R.B.), the DFG (BE 1814/15-1 to R.B.), and by the Canton of Fribourg (D.K.). We thank Dr. Laurent Falquet (Bioinformatics Core Facility, University of Fribourg) for bioinformatics analysis of the high-throughput sequencing data of the sup1-1 suppressor genome. We further thank Dr. Mercedes Dosil (Centro de Investigación del Cáncer, Universidad de Salamanca, Spain) for providing the anti-Rrp12 yeast polyclonal antibody.
Author contributions
M.K., B.L., O.B.-G., and E.H. conceived the study. M.K. and B.L. performed the genetic analysis. M.K., B.L., and O.B.-G. performed the biochemical analysis. J.C. and R.B. performed the cryo-EM analysis. D.K. analyzed the suppressor genome data. B.J. and T.K. performed the pseudouridylation assays. E.H. and B.L. wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Published: November 22, 2022
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111684.
Contributor Information
Roland Beckmann, Email: beckmann@genzentrum.lmu.de.
Ed Hurt, Email: ed.hurt@bzh.uni-heidelberg.de.
Supplemental information
Data and code availability
-
-
The accession codes for the cryo-EM densities in this paper are: EMD-34284 (FTpA-Utp18: state rcl1Δ cms1Δ), EMDB: EMD-34285 (FTpA-Utp18: state B2 nop14-5Ala cms1Δ), EMD-34286 (FTpA-Utp18: state b nop14-5Ala cms1Δ) and EMD-34283 (Dhr1-Dim1: state B2 nop14-5Ala). All the original data for SDS-PAGE stained by Coomassie blue and for northern blotting have been deposited with Mendeley and can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.17632/8xdscd7r35.1.
-
-
All sequencing data from sequencing data of the suppressor strains have been deposited in the Short Read Archive (SRA) under the project number PRJEB56518 and the DOI is listed in the key resources table.
-
-
All mass spectrometry Thermo Fisher RAW files and complete MaxQuant protein identification results have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al., 2022) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD037562 and 10.6019/PXD037562 (Table S1) and PXD037619 and 10.6019/PXD037619 (Table S2).
-
-
This paper does not report original code.
-
-
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request
References
- Adams P.D., Afonine P.V., Bunkoczi G., Chen V.B., Davis I.W., Echols N., Headd J.J., Hung L.W., Kapral G.J., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allmang C., Kufel J., Chanfreau G., Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Tollervey D. Functions of the exosome in rRNA, snoRNA and snRNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1999;18:5399–5410. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.19.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameismeier M., Cheng J., Berninghausen O., Beckmann R. Visualizing late states of human 40S ribosomal subunit maturation. Nature. 2018;558:249–253. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltrame M., Tollervey D. Identification and functional analysis of two U3 binding sites on yeast pre-ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1992;11:1531–1542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05198.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shem A., Garreau de Loubresse N., Melnikov S., Jenner L., Yusupova G., Yusupov M. The structure of the eukaryotic ribosome at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 2011;334:1524–1529. doi: 10.1126/science.1212642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M.G., Karbstein K. Protein-protein interactions within late pre-40S ribosomes. PLoS One. 2011;6:e16194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaker-Margot M., Barandun J., Hunziker M., Klinge S. Architecture of the yeast small subunit processome. Science. 2017;355:eaal1880. doi: 10.1126/science.aal1880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaker-Margot M., Hunziker M., Barandun J., Dill B.D., Klinge S. Stage-specific assembly events of the 6-MDa small-subunit processome initiate eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015;22:920–923. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J., Baßler J., Fischer P., Lau B., Kellner N., Kunze R., Griesel S., Kallas M., Berninghausen O., Strauss D., et al. Thermophile 90S pre-ribosome structures reveal the reverse order of Co-transcriptional 18S rRNA subdomain integration. Mol. Cell. 2019;75:1256–1269.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J., Lau B., La Venuta G., Ameismeier M., Berninghausen O., Hurt E., Beckmann R. 90S pre-ribosome transformation into the primordial 40S subunit. Science. 2020;369:1470–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.abb4119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J., Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1367–1372. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieci G., Bottarelli L., Ottonello S. A general procedure for the production of antibody reagents against eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Protein Pept. Lett. 2005;12:555–560. doi: 10.2174/0929866054395860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Y., An W., Zhu X., Sun Q., Qi J., Ye K. Cryo-EM structure of 90S small ribosomal subunit precursors in transition states. Science. 2020;369:1477–1481. doi: 10.1126/science.aba9690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan J., Li L., Lu J., Wang W., Ye K. Structural mechanism of substrate RNA recruitment in H/ACA RNA-guided pseudouridine synthase. Mol. Cell. 2009;34:427–439. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunbar D.A., Baserga S.J. The U14 snoRNA is required for 2'-O-methylation of the pre-18S rRNA in Xenopus oocytes. RNA. 1998;4:195–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emsley P., Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath S., Milkereit P., Podtelejnikov A.V., Bischler N., Schultz P., Bier M., Mann M., Tschochner H. Association of yeast RNA polymerase I with a nucleolar substructure active in rRNA synthesis and processing. J. Cell Biol. 2000;149:575–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer U., Schäuble N., Schütz S., Altvater M., Chang Y., Boulos Faza M., Panse V.G. A non-canonical mechanism for Crm1-export cargo complex assembly. Elife. 2015;4 doi: 10.7554/eLife.05745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin A.-C., Bösche M., Krause R., Grandi P., Marzioch M., Bauer A., Schultz J., Rick J.M., Michon A.M., Cruciat C.M., et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature. 2002;415:141–147. doi: 10.1038/415141a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard T.D., Huang C.C., Meng E.C., Pettersen E.F., Couch G.S., Morris J.H., Ferrin T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 2018;27:14–25. doi: 10.1002/pro.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandi P., Rybin V., Bassler J., Petfalski E., Strauss D., Marzioch M., Schäfer T., Kuster B., Tschochner H., Tollervey D., et al. 90S pre-ribosomes include the 35S pre-rRNA, the U3 snoRNP, and 40S subunit processing factors but predominantly lack 60S synthesis factors. Mol. Cell. 2002;10:105–115. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00579-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman S., Baserga S.J. Ribosome biogenesis: of knobs and RNA processing. Exp. Cell Res. 2004;296:43–50. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman S., Kudla G., Petfalski E., Tollervey D. Identification of protein binding sites on U3 snoRNA and pre-rRNA by UV cross-linking and high-throughput analysis of cDNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:9613–9618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901997106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granneman S., Petfalski E., Tollervey D. A cluster of ribosome synthesis factors regulate pre-rRNA folding and 5.8S rRNA maturation by the Rat1 exonuclease. EMBO J. 2011;30:4006–4019. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henras A.K., Plisson-Chastang C., O'Donohue M.F., Chakraborty A., Gleizes P.E. An overview of pre-ribosomal RNA processing in eukaryotes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2015;6:225–242. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry Y., Wood H., Morrissey J.P., Petfalski E., Kearsey S., Tollervey D. The 5' end of yeast 5.8S rRNA is generated by exonucleases from an upstream cleavage site. EMBO J. 1994;13:2452–2463. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J.M. Functional base-pairing interaction between highly conserved elements of U3 small nucleolar RNA and the small ribosomal subunit RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1996;259:645–654. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker M., Barandun J., Buzovetsky O., Steckler C., Molina H., Klinge S. Conformational switches control early maturation of the eukaryotic small ribosomal subunit. Elife. 2019;8:e45185. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker M., Barandun J., Petfalski E., Tan D., Delan-Forino C., Molloy K.R., Kim K.H., Dunn-Davies H., Shi Y., Chaker-Margot M., et al. UtpA and UtpB chaperone nascent pre-ribosomal RNA and U3 snoRNA to initiate eukaryotic ribosome assembly. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:12090. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaafar M., Contreras J., Dominique C., Martín-Villanueva S., Capeyrou R., Vitali P., Rodríguez-Galán O., Velasco C., Humbert O., Watkins N.J., et al. Association of snR190 snoRNA chaperone with early pre-60S particles is regulated by the RNA helicase Dbp7 in yeast. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:6153. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26207-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janke C., Magiera M.M., Rathfelder N., Taxis C., Reber S., Maekawa H., Moreno-Borchart A., Doenges G., Schwob E., Schiebel E., Knop M. A versatile toolbox for PCR-based tagging of yeast genes: new fluorescent proteins, more markers and promoter substitution cassettes. Yeast. 2004;21:947–962. doi: 10.1002/yea.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R., Tollervey D., Hurt E.C. A U3 snoRNP protein with homology to splicing factor PRP4 and Gb domains is required for ribosomal RNA processing. EMBO J. 1993;12:2549–2558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05910.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimanius D., Forsberg B.O., Scheres S.H., Lindahl E. Accelerated cryo-EM structure determination with parallelisation using GPUs in RELION-2. Elife. 2016;5 doi: 10.7554/eLife.18722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Jády B.E. Functional characterization of 2'-O-methylation and pseudouridylation guide RNAs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2004;265:393–408. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-775-0:393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A.M., Jády B.E., Bertrand E., Kiss T. Human box H/ACA pseudouridylation guide RNA machinery. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;24:5797–5807. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.13.5797-5807.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Fayet E., Jády B.E., Richard P., Weber M. Biogenesis and intranuclear trafficking of human box C/D and H/ACA RNPs. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2006;71:407–417. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinge S., Voigts-Hoffmann F., Leibundgut M., Ban N. Atomic structures of the eukaryotic ribosome. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012;37:189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornprobst M., Turk M., Kellner N., Cheng J., Flemming D., Koš-Braun I., Koš M., Thoms M., Berninghausen O., Beckmann R., Hurt E. Architecture of the 90S pre-ribosome: a structural view on the birth of the eukaryotic ribosome. Cell. 2016;166:380–393. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressler D., Hurt E., Bassler J. Driving ribosome assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1803:673–683. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapinaite A., Simon B., Skjaerven L., Rakwalska-Bange M., Gabel F., Carlomagno T. The structure of the box C/D enzyme reveals regulation of RNA methylation. Nature. 2013;502:519–523. doi: 10.1038/nature12581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebaron S., Segerstolpe A., French S.L., Dudnakova T., de Lima Alves F., Granneman S., Rappsilber J., Beyer A.L., Wieslander L., Tollervey D. Rrp5 binding at multiple sites coordinates pre-rRNA processing and assembly. Mol. Cell. 2013;52:707–719. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.10.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Ye K. Crystal structure of an H/ACA box ribonucleoprotein particle. Nature. 2006;443:302–307. doi: 10.1038/nature05151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Lai S., Jia R., Xu A., Zhang L., Lu J., Ye K. Structural basis for site-specific ribose methylation by box C/D RNA protein complexes. Nature. 2011;469:559–563. doi: 10.1038/nature09688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longtine M.S., McKenzie A., Demarini D.J., Shah N.G., Wach A., Brachat A., Philippsen P., Pringle J.R. Additional modules for versatile and economical PCR-based gene deletion and modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1998;14:953–961. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(199807)14:10<953::AID-YEA293>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygerou Z., Allmang C., Tollervey D., Séraphin B. Accurate processing of a eukaryotic precursor ribosomal RNA by ribonuclease MRP in vitro. Science. 1996;272:268–270. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5259.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madeira F., Pearce M., Tivey A.R.N., Basutkar P., Lee J., Edbali O., Madhusoodanan N., Kolesnikov A., Lopez R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:W276–W279. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriggi G., Nieto B., Dosil M. Rrp12 and the Exportin Crm1 participate in late assembly events in the nucleolus during 40S ribosomal subunit biogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2014;10:e1004836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T.D., Leuther K.K., Howard E.D., Johnston S.A., Dougherty W.G. Release of proteins and peptides from fusion proteins using a recombinant plant-virus proteinase. Anal. Biochem. 1994;216:413–417. doi: 10.1006/abio.1994.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Riverol Y., Bai J., Bandla C., García-Seisdedos D., Hewapathirana S., Kamatchinathan S., Kundu D.J., Prakash A., Frericks-Zipper A., Eisenacher M., et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: a Hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D543–D552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersen E.F., Goddard T.D., Huang C.C., Couch G.S., Greenblatt D.M., Meng E.C., Ferrin T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004;25:1605–1612. doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punjani A., Rubinstein J.L., Fleet D.J., Brubaker M.A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:290–296. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohou A., Grigorieff N. CTFFIND4: fast and accurate defocus estimation from electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 2015;192:216–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.08.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardana R., Liu X., Granneman S., Zhu J., Gill M., Papoulas O., Marcotte E.M., Tollervey D., Correll C.C., Johnson A.W. The DEAH-box helicase Dhr1 dissociates U3 from the pre-rRNA to promote formation of the central pseudoknot. PLoS Biol. 2015;13:e1002083. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer T., Strauss D., Petfalski E., Tollervey D., Hurt E. The path from nucleolar 90S to cytoplasmic 40S pre-ribosomes. EMBO J. 2003;22:1370–1380. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schattner P., Decatur W.A., Davis C.A., Ares M., Jr., Fournier M.J., Lowe T.M. Genome-wide searching for pseudouridylation guide snoRNAs: analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:4281–4296. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling V., Peifer C., Buchhaupt M., Lamberth S., Lioutikov A., Rietschel B., Kötter P., Entian K.D. Genetic interactions of yeast NEP1 (EMG1), encoding an essential factor in ribosome biogenesis. Yeast. 2012;29:167–183. doi: 10.1002/yea.2898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiser R.M., Sundberg A.E., Wollam B.J., Zobel-Thropp P., Baldwin K., Spector M.D., Lycan D.E. Ltv1 is required for efficient nuclear export of the ribosomal small subunit in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 2006;174:679–691. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.062117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma K., Tollervey D. Base pairing between U3 small nucleolar RNA and the 5' end of 18S rRNA is required for pre-rRNA processing. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999;19:6012–6019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.9.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S., Lafontaine D.L.J. 'View from A bricge': a new perspective on eukaryotic rRNA base modification. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015;40:560–575. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S., Vanden Broeck A., Miller L., Chaker-Margot M., Klinge S. Nucleolar maturation of the human small subunit processome. Science. 2021;373:eabj5338. doi: 10.1126/science.abj5338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloan K.E., Warda A.S., Sharma S., Entian K.D., Lafontaine D.L.J., Bohnsack M.T. Tuning the ribosome: the influence of rRNA modification on eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis and function. RNA Biol. 2017;14:1138–1152. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1259781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm M., Cheng J., Baßler J., Beckmann R., Hurt E. Interdependent action of KH domain proteins Krr1 and Dim2 drive the 40S platform assembly. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:2213. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02199-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R.G., Walker D.C., McInnes R.R. E. coli host strains significantly affect the quality of small scale plasmid DNA preparations used for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:1677–1678. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas B.J., Rothstein R. Elevated recombination rates in transcriptionally active DNA. Cell. 1989;56:619–630. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms M., Mitterer V., Kater L., Falquet L., Beckmann R., Kressler D., Hurt E. Suppressor mutations in Rpf2-Rrs1 or Rpl5 bypass the Cgr1 function for pre-ribosomal 5S RNP-rotation. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:4094. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06660-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoms M., Thomson E., Baßler J., Gnädig M., Griesel S., Hurt E. The exosome is recruited to RNA substrates through specific adaptor proteins. Cell. 2015;162:1029–1038. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorvaldsdóttir H., Robinson J.T., Mesirov J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013;14:178–192. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torchet C., Badis G., Devaux F., Costanzo G., Werner M., Jacquier A. The complete set of H/ACA snoRNAs that guide rRNA pseudouridylations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA. 2005;11:928–938. doi: 10.1261/rna.2100905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen J., Pons C., Tan G., Wang J.Z., Hou J., Weile J., Gebbia M., Liang W., Shuteriqi E., Li Z., et al. Systematic analysis of bypass suppression of essential genes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020;16:e9828. doi: 10.15252/msb.20209828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., Tollervey D. Ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1999;33:261–311. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J.W., Wu J.R. Overexpression of a novel gene, Cms1, can rescue the growth arrest of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mcm10 suppressor. Cell Res. 2001;11:285–291. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterhouse A.M., Procter J.B., Martin D.M.A., Clamp M., Barton G.J. Jalview Version 2--a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1189–1191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins N.J., Bohnsack M.T. The box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs: key players in the modification, processing and the dynamic folding of ribosomal RNA. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2012;3:397–414. doi: 10.1002/wrna.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb S., Hector R.D., Kudla G., Granneman S. PAR-CLIP data indicate that Nrd1-Nab3-dependent transcription termination regulates expression of hundreds of protein coding genes in yeast. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R8. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemp I., Wild T., O'Donohue M.F., Wandrey F., Widmann B., Gleizes P.E., Kutay U. Distinct cytoplasmic maturation steps of 40S ribosomal subunit precursors require hRio2. J. Cell Biol. 2009;185:1167–1180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200904048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K. Gctf: real-time CTF determination and correction. J. Struct. Biol. 2016;193:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2015.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K. MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology; 2017. Gautomatch.https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/download/gautomatch-053/ [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Wu C., Cai G., Chen S., Ye K. Stepwise and dynamic assembly of the earliest precursors of small ribosomal subunits in yeast. Genes Dev. 2016;30:718–732. doi: 10.1101/gad.274688.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng S.Q., Palovcak E., Armache J.P., Verba K.A., Cheng Y., Agard D.A. MotionCor2: anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods. 2017;14:331–332. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
-
-
The accession codes for the cryo-EM densities in this paper are: EMD-34284 (FTpA-Utp18: state rcl1Δ cms1Δ), EMDB: EMD-34285 (FTpA-Utp18: state B2 nop14-5Ala cms1Δ), EMD-34286 (FTpA-Utp18: state b nop14-5Ala cms1Δ) and EMD-34283 (Dhr1-Dim1: state B2 nop14-5Ala). All the original data for SDS-PAGE stained by Coomassie blue and for northern blotting have been deposited with Mendeley and can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.17632/8xdscd7r35.1.
-
-
All sequencing data from sequencing data of the suppressor strains have been deposited in the Short Read Archive (SRA) under the project number PRJEB56518 and the DOI is listed in the key resources table.
-
-
All mass spectrometry Thermo Fisher RAW files and complete MaxQuant protein identification results have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al., 2022) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD037562 and 10.6019/PXD037562 (Table S1) and PXD037619 and 10.6019/PXD037619 (Table S2).
-
-
This paper does not report original code.
-
-
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request