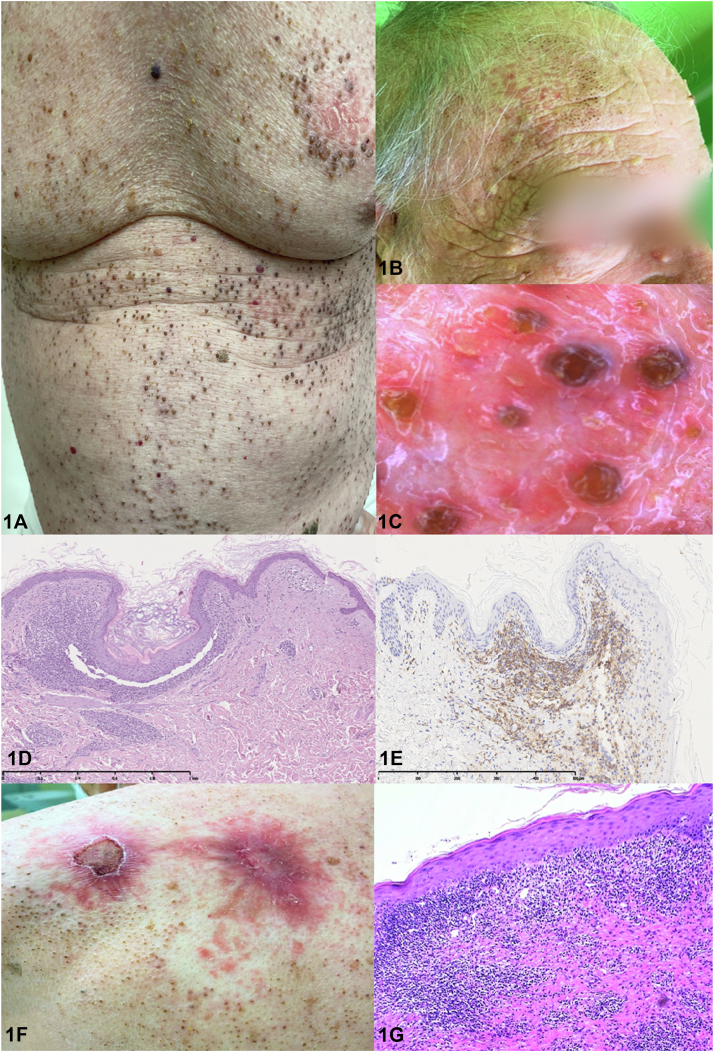
A 68-year-old White man presented with a 2-year history of asymptomatic, widespread comedones associated with patchy alopecia of the scalp and eyebrows and total alopecia of axillary and pubic hairs (Fig 1, A to C). Histopathology of a comedonal area demonstrated a dilated, follicular infundibulum with keratotic plugging and a perifollicular band-like CD4-predominant atypical T-lymphocytic infiltrate leading to the detachment and infiltration of the follicles (Fig 1, D and E). Subsequently, erythematous, erosive plaques started to develop on the trunk and limbs of the patient (Fig 1, F), the histopathology of which showed a more extensive, diffused, epidermotropic infiltrate containing CD4-predominant T lymphocytes with sparse medium- to large-sized lymphocytes (Fig 1, G).
Fig 1.
Question 1: What is the most likely diagnosis?
-
A.
Solar comedones (Favre-Racouchot syndrome)
-
B.
Extensive nevus comedonicus
-
C.
Comedonal folliculotropic mycosis fungoides
-
D.
Graham Little–Piccardi–Lassueur syndrome
-
E.
Dowling-Degos disease
Answers:
-
A.
Solar comedones (Favre-Racouchot syndrome) – Incorrect. Solar comedones, also known as Favre-Racouchot syndrome, involve only the skin around the temporal and periorbital areas in patients aged >50 years. Occasionally, they may also involve the malar and retroauricular areas, earlobes, and neck, but not the trunk. Histopathology shows solar elastosis and dilated pilosebaceous infundibulum filled with lamellar keratin in the absence of inflammatory infiltrate.
-
B.
Extensive nevus comedonicus – Incorrect. Nevus comedonicus is an uncommon abnormality of the pilosebaceous unit, which is congenital but may also appear late in adulthood. It may be localized or have extensive involvement; the latter shows unilateral or sometimes bilateral predominance. Histopathology shows multiple keratin-filled epidermal invaginations without inflammatory infiltrate.
-
C.
Comedonal folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) – Correct. Follicular lesions, including comedones, are the typical presentation of FMF. However, widespread comedones as the sole and initial manifestation of FMF is exceedingly rare.1,2 Histopathology shows comedo-like lesions with a dilated, follicular infundibulum with keratotic plugging and a perifollicular, atypical CD4+ lymphocytic infiltrate leading to infiltration of the follicle (Fig 1, D and E). Polymerase chain reaction test for the T-cell receptor gene may reveal monoclonality, as was the case in our patient.
-
D.
Graham Little–Piccardi–Lassueur syndrome – Incorrect. Graham Little syndrome is a rare variant of lichen planopilaris, which is characterized by progressive patchy scarring alopecia of the scalp, nonscarring alopecia of the axilla and groin, and a follicular lichen planus eruption on the body that affects middle-aged postmenopausal women.3 Histopathology includes follicles and cysts surrounded by a lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate in the absence of atypical lymphocytes. Contrary to the case of our patient, neither infiltrate nor plaque-like lesions with epidermotropic infiltrate were present.
-
E.
Dowling-Degos disease – Incorrect. Dowling-Degos disease usually arises in the third or fourth decade of life and is characterized by reticulated hyperpigmentation in intertriginous areas, lentigo-like brown macules, comedo-like lesions on the back and neck, and pitted perioral scars. Histopathology shows increased pigmentation of the basal layer and downward elongation of the rete ridges, as well as follicular hyperkeratosis with thinning of the underlying suprapapillary epithelium in absence of atypical lymphocytes.
Question 2: Which of the following skin signs is considered the harbinger of progression to a more aggressive course in the setting of FMF?
-
A.
Pustules
-
B.
Alopecia of eyebrows
-
C.
Epidermotropic plaque lesions
-
D.
Comedones
-
E.
Pruritus
Answers:
-
A.
Pustules – Incorrect. Sparse pustules are not uncommon in FMF. Indeed, the underlying infiltration of atypical lymphocytes may induce a distortion of follicles with a reactive proliferation of keratinocytes, dilating the keratin-stuffed infundibulum. Therefore, it may manifest clinical comedogenic aspects and folliculitis-like features induced by secondary infection with Staphylococcus aureus.
-
B.
Alopecia of eyebrows – Incorrect. Involvement of the eyebrows is highly characteristic in FMF and may present as an early disease manifestation as well as a useful clue in the differential diagnosis. However, it is, as such, not associated with an aggressive course.
-
C.
Epidermotropic plaque lesions – Correct. Plaque lesions that show denser perifollicular and extensively confluent or diffused infiltrates containing medium- to large-sized tumor cells are considered to be indicative of an aggressive course and poor survival in the early stage of the disease.4 The development of epidermotropic plaques in our patient after a longstanding comedonal eruption was seen as a sign of poor prognosis.
-
D.
Comedones – Incorrect. Comedones are an expression of follicular involvement in FMF without any prognostic sign.
-
E.
Pruritus – Incorrect. Pruritus has a high frequency (almost 80%) in patients with FMF. However, its relationship with the aggressiveness of the disease is a controversial issue. Recent studies suggests that pruritus has no effect on survival or disease progression.4
Question 3: Which is the best treatment for this patient?
-
A.
Narrowband UV-B phototherapy
-
B.
Topical and systemic steroids
-
C.
Mogamulizumab
-
D.
Pegylated interferon alpha-2a + isotretinoin
-
E.
Mechlorethamine gel
Answers:
-
A.
Narrowband UV-B phototherapy – Incorrect. Narrowband UV-B phototherapy is not useful in diagnosing FMF, as the UV-B rays penetrate the superficial dermis but cannot reach the deep adnexal neoplastic component.
-
B.
Topical and systemic steroids – Incorrect. Although both topical and systemic steroids are useful in the initial stages of mycosis fungoides, they are not applicable in the more advanced stages of the disease following the presentation of extensive cutaneous lesions. This was the case in our patient, whose stage is IB: T2b, N0, M0,and B0.
-
C.
Mogamulizumab – Incorrect. Mogamulizumab is a humanized antibody against chemokine receptor type 4 that was recently approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for refractory or relapsed mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. No data are available for its use in treating FMF.
-
D.
Pegylated interferon alpha-2a + isotretinoin – Correct. This is the combination treatment that we have chosen for this patient. In addition to pegylated interferon alpha-2a, we have decided to use oral isotretinoin as this drug tends to normalize follicular keratinization, which prevents the formation of new comedo-like lesions, thus reducing the secretion of the sebaceous glands and has antiinflammatory properties.5 Currently, our patient has partially benefited from this therapy; his hair has regrown and the comedo-like components have decreased with good compliance.
-
E.
Mechlorethamine gel – Incorrect. Mechlorethamine gel is an alkylant agent used to treat the early stages of mycosis fungoides in patients who have received previous skin treatment. Our patient showed extensive comedonal cutaneous lesions with plaques in the setting of stage IB. Therefore, the use of a topical treatment was not feasible.
Conflicts of interest
None disclosed.
Footnotes
Funding sources: None.
IRB approval: Not applicable.
References
- 1.Torres T., Velho G., Alves R., Selores M. Widespread comedones as the sole clinical manifestation of follicular mycosis fungoides. Eur J Dermatol. 2010;20:534–535. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2010.0988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Errichetti E., Chiacchio R., Piccirillo A. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides presenting as non-inflammatory scarring scalp alopecia associated with comedo-like lesions. Int J Dermatol. 2016;55:e40–e41. doi: 10.1111/ijd.12976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Iamsumang W., Rutnin S., Suchonwanit P. Comedone-like lesions as a manifestation of lichen planopilaris beyond the scalp: a case report with dermoscopic features and literature review. Case Rep Dermatol. 2021;13:106–113. doi: 10.1159/000512711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van Santen S., Jansen P.M., Quint K.D., Vermeer M.H., Willemze R. Plaque stage folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: histopathologic features and prognostic factors in a series of 40 patients. J Cutan Pathol. 2020;47:241–250. doi: 10.1111/cup.13615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Del Guzzo C.A., Jariwala N.N., Haun P.L., et al. Pilot study of a novel therapeutic approach for refractory advanced stage folliculotropic mycosis fungoides. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100 doi: 10.2340/00015555-3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]