Abstract
Background
As an essential component of the BR (brassinosteroid) signaling pathway, BSK (BR-signalling kinases) plays a vital role in plant growth, development, and stress regulation. There have been sporadic reports on the functions of members of this family in monocotyledonous model plant rice, but few reports have been reported on the phylogenetic analysis and gene expression profiling of the family genes.
Results
In this study, a total of 6 OsBSK members were identified at the genomic level by bioinformatics methods, distributed on four rice chromosomes. Through the evolution analysis of 74 BSK proteins from 22 species, it was found that BSKs originated from higher plants, were highly conserved, and could be divided into six subgroups. Among them, OsBSKs belonged to four subgroups or two significant groups. OsBSK family gene promoters contained a large number of light, abscisic acid (ABA), and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) response-related elements. At the same time, the qRT-PCR test also showed that the genes of this family were involved in response to a variety of hormones, biotic and abiotic stress treatments, and expression patterns of the family gene can be roughly divided into two categories, which were similar to the tissue expression patterns of genes in different growth stages. OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK3 were mostly up-regulated. OsBSK2, OsBSK4, and OsBSK5 were mostly down-regulated or had little change in expression.
Conclusions
This study revealed the origin and evolution of the BSK family and the farm-out of BSKs in rice growth, development, and stress response. It provides the theoretical reference for in-depth analysis of BR hormone, signal transduction, and molecular breeding design for resistance.
Keywords: Oryza sativa L., OsBSKs, Gene family, qRT-PCR, Evolution
Background
As the sixth class of hormones, brassinosteroid (BR) is a steroid hormone regulating plant growth and stress response [1, 2]. BR is widely present in various tissues and organs of plants, with varying contents of distribution in pollen, roots, stems, and leaves, indicating that BR can play an essential role in plant growth and development, such as seed germination, fibrous root formation, leaf morphogenesis, and flower organ differentiation [3]. Nawaz et al. point out that exogenous spraying of BR can not only enhance the drought resistance and salt resistance of plants but also reduce the incidence of rice blast, phytophthora root rot of soybean, and Fusarium verticillioides [4]. At the same time, it has also been fully proved at the molecular genetic level that the BR plays a vital role in regulating plant growth and development and stress. For example, the receptor BRI1 (Brassinosteroid insensitive 1) in the BR signaling pathway can regulate cell water uptake; the co-receptor BAK1 (BRI1 associated receptor kinase 1) has been proved to regulate plant height through expression level in Oryza sativa L.; BIN2 (BR-insensitive 2) can respond to cold stress; BZR1(Brassinazole resistant 1) can promote light response by regulating light signal-related genes [5–7]. In addition, some studies suggest that the BR signaling pathway may have emerged after the evolutionary divergence of vascular plants [8], and the components of the BR signaling pathway are remarkably conserved in the plant kingdom [9]. Therefore, the related research on plant BR hormone has essential theoretical and practical significance for producing different crops.
BSK(BR-signalling kinases) is a crucial component linking other components, which receives the signal from the BR receptor BRI1 and co-receptor BAK1 and then transmits the signal down to BIN2. BRI1 phosphorylates BSK and activates it. In this step, the leading site of BRI1 phosphorylates BSK is S230, and activated BSK then phosphorylates and activates BSU1 (BRI1 suppressor 1) [10, 11]. BSKs are plant-specific receptor-like cytoplasmic kinases belonging to a subfamily of the RLCK-XII superfamily, containing a TPR (Tetratricopeptide repeats) domain and a kinase PKc (Putative kinase catalytic) domain. Among them, the TPR domain has a binding function and can interact with other proteins [12]. The kinase PKc domain plays a vital role in plant cells’ differentiation, reproduction, and apoptosis. Studies have shown that Arabidopsis bsk3 mutant reduced sensitivity to BR signaling, and other bsk single mutations have no significant effect on BR signaling; quadruple mutants bsk3,4,7,8 and pentuple mutants bsk3,4,6,7,8 all showed lower sensitivity to BR signaling [13]. The response of Arabidopsis BR to mild nitrogen deficiency in the formation of the root structure is mainly regulated by BSK3 [14], and it is likely to regulate the signal in the form of a scaffold protein [15]. Arabidopsis BSKs can also, independent of BR signaling, interact with bacterial flagellin Flg22 (Flagellin peptide 22) and other multiple immune factors and participate in plant PTI (pattern-triggered immunity) responses [16–19]. In O. sativa L., studies have also found that BSKs not only can positively regulate rice BR signaling but also positively regulate rice immune resistance [20, 21]. OsBSK2 can regulate granulotype independently of the BR signaling pathway [22]. The above studies show that BSKs have functional redundancy in the BR signaling transduction, and their family members may play different roles in different biological processes.
There have been many reports on the BR signaling pathway and the function of signal components [9, 23], but there are relatively few studies on the function of BSK genes. In rice, studies on the evolution and diverse functions of the OsBSK gene family have not been reported. This study started with the monocotyledonous model plant rice, and 6 BSK family members were identified at the genome level. The evolution analysis of different species found that BSKs originated from higher plants and were highly conserved. Furthermore, qRT-PCR was used to clarify the expression profiles of BSK genes in response to hormones, biotic, and abiotic stress, revealing their functional diversity. This study provides a theoretical basis for the origin and evolution of BSKs, reveals the role of BSKs in rice growth and development and response to stress, and provides a reference for the in-depth analysis of the BR signaling transduction pathway and application in crop production.
Results
Identification of the OsBSK gene family
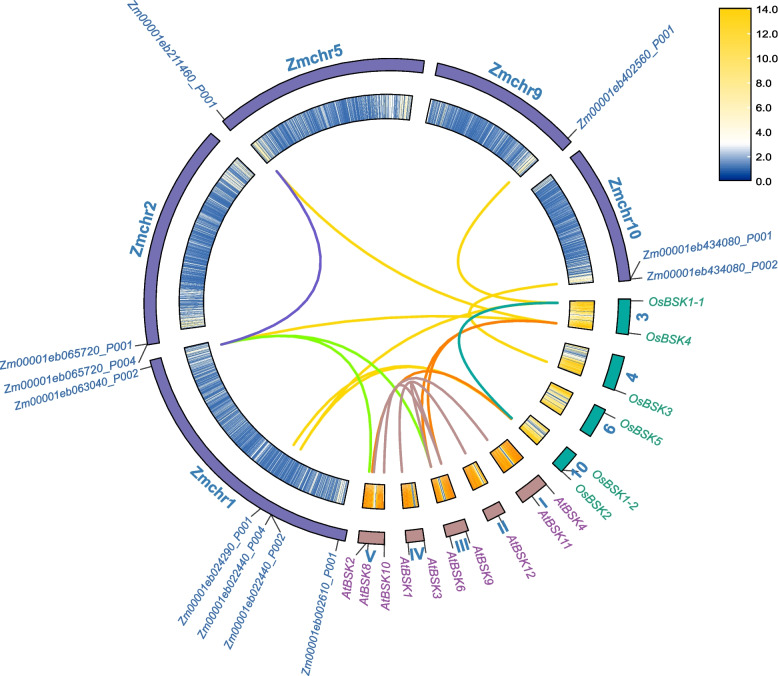
A total of 6 OsBSK genes were identified at the rice genome level (Table 1), referred to previous literature named OsBSK1–1 ~ OsBSK5 [20], encoding amino acid chain lengths between 359 ~ 806 aa, molecular weights between 40.3 ~ 91.1 KDa, isoelectric points between 5.33 and 7.91. OsBSK5 had the largest molecular weight and the lowest isoelectric point among them. As shown in Fig. 1, 6 OsBSK genes were located on chromosomes 3, 4, 6, and 10 of the 12 rice chromosomes, respectively. OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK4 were located on chromosome 3 together, and OsBSK1–2 and OsBSK2 were located on chromosome 10, relatively close. Subcellular localization prediction showed that most OsBSKs had nuclear and cytoplasmic localization.
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of the OsBSK genes
| Gene Name | Rice Genome Gene Number |
Coding Regions/bp | Amino Acid/aa | Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight/kDa | Isoelectric Point | Subcellular Localization Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OsBSK1–1 | LOC_Os03g04050 | 1596 | 532 | C2604H4075N743O785S32 | 59.4 | 6.05 | Nuc/Mit |
| OsBSK1–2 | LOC_Os10g39670 | 1569 | 523 | C2559H4033N731O761S30 | 58.2 | 7.91 | Nuc/Mit |
| OsBSK2 | LOC_Os10g42110 | 1539 | 513 | C2492H3924N686O750S22 | 56.2 | 5.94 | Cyt/Nuc |
| OsBSK3 | LOC_Os04g58750 | 1077 | 359 | C1766H2769N485O547S22 | 40.3 | 5.45 | Nuc/Cyt |
| OsBSK4 | LOC_Os03g61010 | 1467 | 489 | C2398H3741N673O716S23 | 54.2 | 6.20 | Mit/Cyt |
| OsBSK5 | LOC_Os06g06760 | 2418 | 806 | C3963H6357N1143O1245S3 | 91.1 | 5.33 | Nuc/Cyt |
Nuc Nuclear, Cyt Cytoplasmic, Mit Mitochondrial
Fig. 1.
Chromosomal location and collinearity of BSK genes in Oryza sativa Japonica, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Zea mays. The blue, cyan, and purple lines indicate the collinearity of Z. mays, O. sativa Japonica, and A. thaliana, respectively. The yellow, orange, and green lines indicate the collinearity of Z. mays and O. sativa Japonica, A. thaliana and O. sativa Japonica, Z. mays and A. thaliana, respectively
Evolution of the BSK gene family in plant
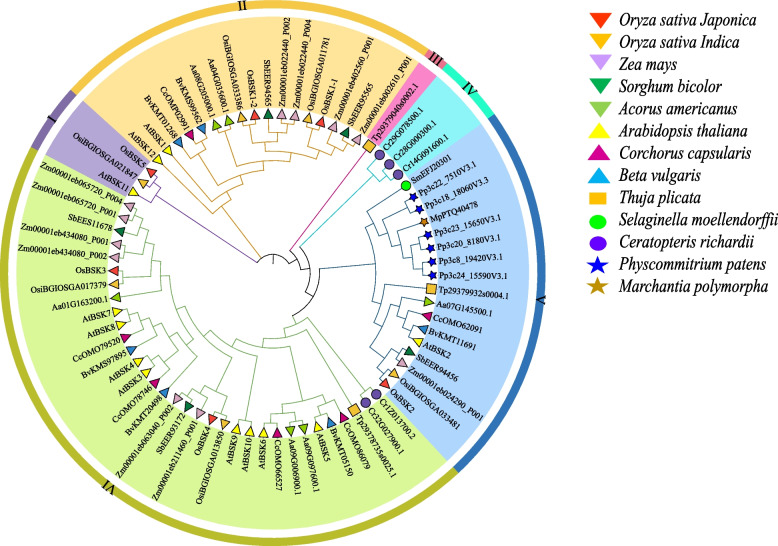
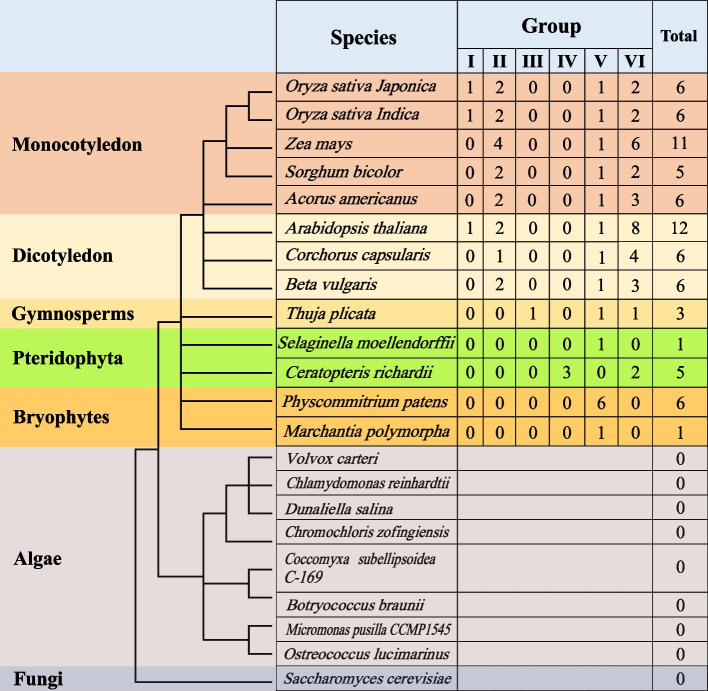
As shown in Fig. 2, we isolated 13 species containing members of BSKs out of 22, all of which were higher plants. A total of 74 BSK proteins in these species were divided into six subgroups according to their evolutionary relationship. The V subgroup and the VI subgroup were located in the same evolutionary branch, and the evolutionary relationship was relatively close. Species of the same phylum were roughly equally distributed in different subgroups. Compared with other species, the BSK proteins in the two bryophytes Physcommitrium patens and Marchantia polymorpha were all located in subgroup V, indicating that this subgroup may be the early evolutionary form of the family. We identified six BSK members in O. sativa Indica. As shown in Fig. 2, these members could find member proteins with highly similar amino acid sequences in OsBSKs, but there was no member similar to the amino acid sequence of OsBSK5 except the homology in O. sativa Indica. The members of OsBSKs were divided into four subgroups. Subgroup I only had OsBSK5, subgroup II included OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2, subgroup V only had OsBSK2, and subgroup VI included OsBSK3 and OsBSK4. Furthermore, combined with the evolution analysis of the rice BSK family, we could also divide them into two groups: OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK5 were in the same group; OsBSK2, OsBSK3, and OsBSK4 were in the same group, of which OsBSK2 should be the origin of the rice BSK family. According to the structure and identification results of the phylogenetic tree, we counted the number of BSK members for each species, as shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 2.
The phylogenetic tree of BSK proteins in plant. Consisting of a total of 74 BSK proteins from 13 species, divided into 6 subgroups
Fig. 3.
Species phylogenetic tree and number of BSK genes
The results showed that BSK family members existed in bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms, and angiosperms and were more abundant in angiosperms, with more than five members in each species. However, these genes were still subjected to purifying selection and were evolutionarily conserved. In this study, no family member was found in algae and fungi, and only the PKc and TPR domain existed independently. Therefore, we speculated that BSK genes originated from higher plants, and the two specific conserved domains evolved gradually from a single PKc or TPR domain with the evolution of the plant.
In addition, the conserved domains of BSKs in various species except PKc and TPR were analyzed (Table 2), and almost all of the tested species contained PLN00113, which belongs to the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase. STYKc was a phosphotransferase that occurs in conserved domains of three species. PLN03088 (SGT1) appeared in the conserved domains of Thuja plicata and Beta vulgaris, is a suppressor of the G2 allele of skp1, and could interact with RAR1 and HSP90 to participate in plant disease resistance responses [24].
Table 2.
Conserved domains of various species
| Classes | Species | Auxiliary Domainsa |
|---|---|---|
| Bryophytes | Physcommitrium patens | STYKc |
| Pteridophyta | Ceratopteris richardii | PLN00113 |
| Gymnosperms | Thuja plicata | PLN00113, PLN03088 |
| Monocotyledon | Acorus americanus | STYKc, PLN00113 |
| Oryza sativa Indica | STYKc, PLN00113 | |
| Sorghum bicolor | PLN00113 | |
| Zea mays | PLN00113 | |
| Dicotyledon | Arabidopsis thaliana | PLN00113 |
| Beta vulgaris | PLN00113, PLN03088 | |
| Corchorus capsularis | STYKc, PLN00113 |
a The domains are located outside of the Pkc domain and TPR domain
Analysis of OsBSK gene structure and their encoded protein structure
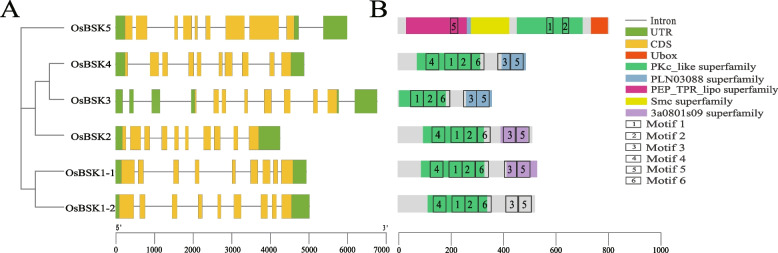
Analysis of the intron and exon structure of the OsBSK family genes (Fig. 4-A) showed that the number of exons in each gene of the OsBSK family was 8–10. The OsBSK2, OsBSK4, and OsBSK3 genes in the same group had different numbers of exons. The first two genes had ten exons, and the latter had eight exons; other OsBSK genes belonging to the same group had nine exons, and the OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 genes had similar structures.
Fig. 4.
OsBSK gene structure, domains, and motifs in Oryza sativa Japonica. A OsBSK gene structure. B OsBSK domains and motifs. Motifs are arranged in the corresponding domains according to their position in the protein
As shown in Fig. 4-B, The OsBSK family all contained PKc (PF07714) and TPR (PF13414) domains, the PKc domain was located at the C-terminal of the protein, and the TPR domain was located at the N-terminal of the protein. However, the positions of PKc and TPR domains in OsBSK5 protein were opposite to other protein domains. Through protein conserved sequence analysis, six motifs were found in the OsBSK family, and motif1 was highly conserved. Combined with protein domain analysis, motif1 and motif2 were conserved motifs in the PKc domain, and motif5 belonged to conserved motifs in the TPR domain. The secondary structure of OsBSK family proteins showed that the extension chain and helical structure were intertwined, and they together constituted the N-terminus of OsBSK proteins, but its C-terminus only had a helical structure. OsBSK5 protein had the most significant proportion of α-helices. Studies had shown that a TPR motif contained two antiparallel α-helices [25], so it was speculated that OsBSK5 had more α-helix structures because it contained more TPR motifs. OsBSK3 protein had the least number of motifs, which had also been confirmed in the tertiary structure of OsBSK proteins.
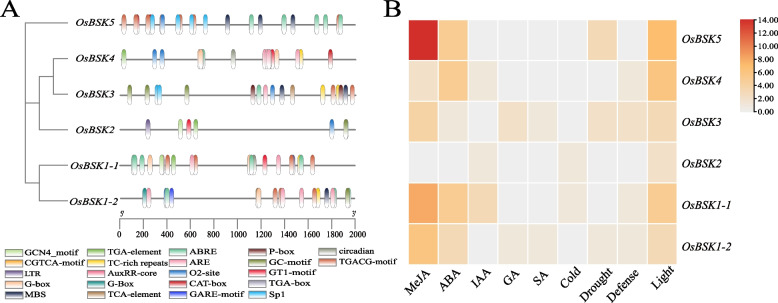
Cis-elements analysis of OsBSK gene promoters
As shown in Fig. 5, the gene promoter sequence contained many light-responsive related elements, such as TGA-element, G-BOX, GT1-motif, and Sp1. Among the hormones, the number of acting elements of methyl jasmonate (MeJA) and abscisic acid (ABA) was more, and the acting elements of salicylic acid (SA), gibberellin (GA), and auxin were less. Anaerobic-related cis-elements ARE, drought-related cis-elements MBS, and low temperature-related cis-elements LTR were also found in abiotic stress. The number of growth and development-related elements was relatively small, such as O2-site, CAT-box, GCN4_motif, and circadian. It indicated that the OsBSK genes were involved in light response and the regulation of growth metabolism and were regulated by various hormones. However, it was worth noting that the types and numbers of tested cis-elements on the OsBSK2 gene promoter were significantly less than those of other family members, and only this gene promoter had no cis-elements related to ABA response, which provided support for our previous speculation that OsBSK2 was the origin of the OsBSK family.
Fig. 5.
OsBSK elements and number statistics heatmap A The distribution of elements in OsBSK. B Heatmap of the number of OsBSK elements classified by role. Different colors represent different numbers of cis-elements
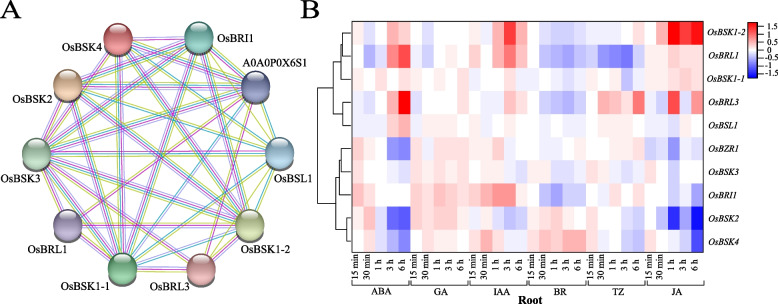
Analysis of proteins interaction with BSK
String prediction (Fig. 6-A) showed protein interaction among the five OsBSK (except OsBSK5). There were ten nodes and 35 groups of interaction relationships in the relationship network, among which OsBSK3 interacted with nine other proteins. In the interaction network, the five OsBSK members could interact with receptor kinases such as BRI1, BRL1, and BRL3; they could also interact with BSU1 family member BSL1. It was worth mentioning that A0A0P0X6S1 is the Os07g0503400 protein in japonica rice varieties, and the function of this protein was unknown. Yuan et al. have confirmed that there is a protein interaction between OsBSK2 and OsBSK3 in regulating grain size in rice, confirming our prediction [26]. As shown in Fig. 6-B, the expression of genes predicted to have protein interactions in the roots of rice seedlings treated with different hormones also proved the possibility of their interactions. For example, OsBSK1–2, OsBRL1, and OsBRI1 had the same expression pattern after BR hormone treatment, indicating that they may interact in responding to BR hormone. The prediction results of phosphorylation sites showed that all family members had sites 39–71, and the number of threonines was significantly more than that of serine and tyrosine.
Fig. 6.
Protein interaction network prediction and gene expression heatmap. A Lines represent interaction relationships, where cyan, pink, gray, and green lines represent from curated databases, experimentally determined, protein homology, and textmining. B Gene expression heatmap with predicted protein interactions in rice seedling roots treated with ABA, GA, IAA, BR, trans-zeatin(TZ), and JA. Different colors represent different expression values
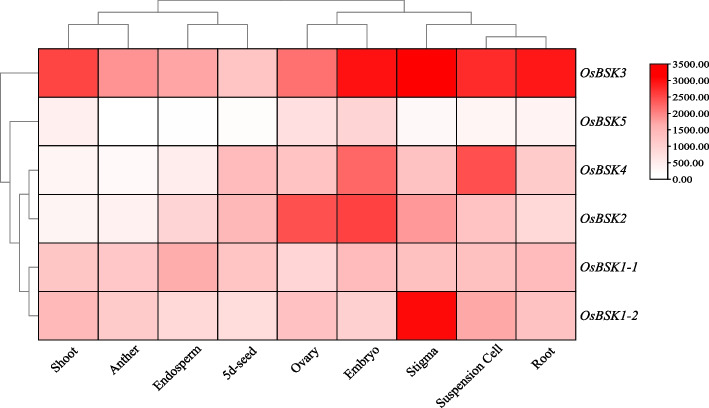
Tissue expression profiles of OsBSK genes throughout the growth period
The expression of OsBSK genes in different tissues during the whole growth period (Fig. 7) showed that OsBSK genes were expressed to different degrees in different developmental stages in O. sativa L.. Among them, OsBSK3 was highly expressed during the whole growth period, and OsBSK5 was low expressed during the whole growth period. The expression of OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 was similar, and the expression of OsBSK2 and OsBSK4 was similar. It could be seen that the expression of genes belonging to the same category in evolution was also roughly similar in the whole growth period.
Fig. 7.
Expression profiles of OsBSK genes in the whole growth period. Different colors represent different expression values
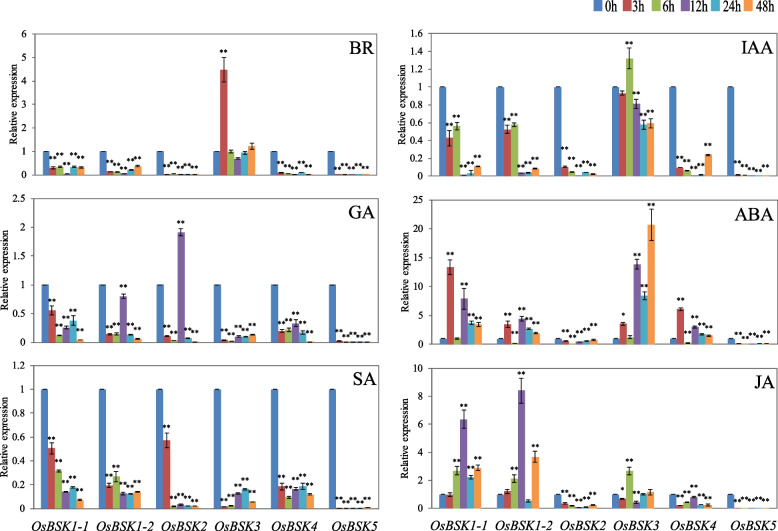
Expression analysis of OsBSK genes response to hormones
As shown in Fig. 8, the expression patterns of OsBSK family members in rice seedlings treated with the six hormones could be roughly divided into two categories. OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK3 were up-regulated by at least two hormones; OsBSK2, OsBSK4, and OsBSK5 were up-regulated by one hormone at most. After SA hormone treatment, all OsBSK genes were down-regulated; after BR, IAA, and GA hormone treatment, only one OsBSK gene was up-regulated, and the rest were down-regulated; after ABA and JA hormones, more than half of the OsBSK members were up-regulated. Among the six family members, OsBSK5 had no expression changes in the six hormone treatments; OsBSK3 could be up-regulated by ABA, JA, IAA, and BR hormones; OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 could also be up-regulated by ABA and JA hormones.
Fig. 8.
Expression analysis of OsBSK genes after hormones treatment with BR, IAA, GA, ABA, SA, and JA. (Significant differences: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01)
Expression analysis of OsBSK genes under biotic and abiotic stress
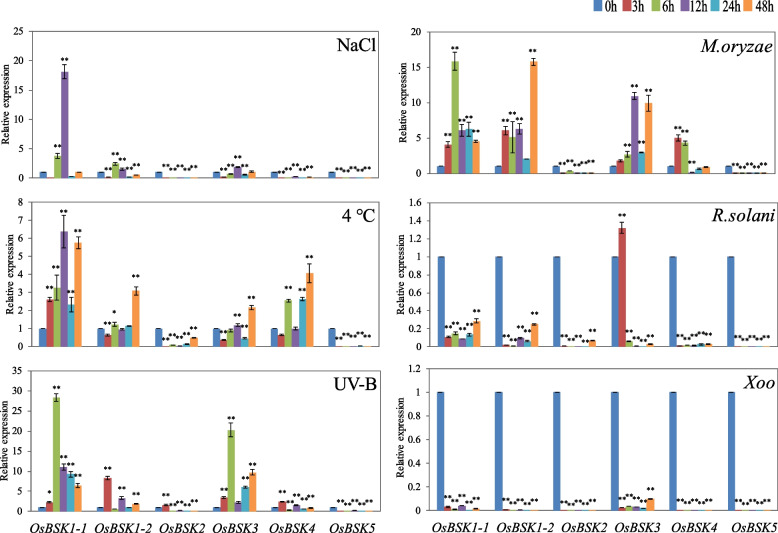
As shown in Fig. 9, in the rice seedlings treated with abiotic stress such as NaCl, 4 °C, and UV-B radiation, the expression of BSK family members changed significantly, but the overall change trend was similar. OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK3 could be up-regulated by the three treatments tested. OsBSK4 could be up-regulated by 4 °C and UV-B radiation and down-regulated by NaCl treatment. OsBSK2 and OsBSK5 showed no change or little change.
Fig. 9.
Expression profiles of OsBSK genes response to various stresses with NaCl, 4 °C, UV-B, M. oryzae, R. solani, and Xoo. (Significant differences: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01)
As shown in Fig. 9, the OsBSK family members differed greatly in response to inoculation of different pathogens such as Magnaporthe oryzae, Rhizoctonia solani, and Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. In the rice seedlings inoculated with M. oryzae, the overall expressions of OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2 and OsBSK3 were up-regulated, while the expressions of OsBSK2 and OsBSK5 were down-regulated, and OsBSK4 showed a noticeable change of up-regulation and then down-regulation. In the rice seedlings inoculated with R. solani, except for OsBSK3, which was up-regulated after 3 h of treatment, the other family member genes were down-regulated at different periods. In the rice seedlings inoculated with Xoo, the expression of all BSK family members was down-regulated at different periods.
Discussion
Identification and evolutionary analysis of the OsBSK family
In this study, six OsBSK gene family members were identified at the rice genome level, divided into four subgroups: subgroup I, subgroup II, subgroup V, and subgroup VI. Furthermore, we combined the evolutionarily related subgroups into two groups, namely OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK5 as a group, and OsBSK2, OsBSK3, and OsBSK4 as a group. The multi-species phylogenetic analysis showed that BSK genes were generally more abundant in angiosperms, but no BSK genes were found in algae and fungi. It was speculated that this family of genes might originate from higher plants, which was mutually proved with the previous speculation that the BR signaling pathway appeared after the evolutionary divergence of vascular plants [8]. We found PKc and TPR single domains in algae and fungi and speculated that proteins containing only PKc or TPR domains in lower plants, coexisting PKc and TPR domains evolved in higher plants as plants evolved, the BSK family emerged and evolved in angiosperms, and underwent purification selection and were highly evolutionarily conserved. Even so, there are differences in BSKs in O. sativa Japonica and O. sativa Indica, for example, OsBSK2 [27].
In addition, according to the evolution analysis of different species, we speculated that subgroup V was the origin of family members in different species. OsBSK2 located in subgroup V may be the origin of OsBSKs. In our analysis of cis-elements in the promoters of OsBSK family genes, we found that only OsBSK2 has no ABA-inducible elements, and the types and numbers of elements were the least, which can also provide support for our inferred view that OsBSK2 was the origin of the family.
Expression and function analysis of OsBSK genes
The protein interaction prediction analysis found that, except for OsBSK5, which was a low expression in the whole growth period, the other family members not only interacted with each other but also interacted with the upstream and downstream components of the BR signaling pathway, which was consistent with the OsBSK2 can directly interact with the BR receptor kinase OsBRI1 [22]. Indicating OsBSKs may play an essential role in the BR signaling pathway. Research has shown that Arabidopsis bsk3 mutation could alleviate the inhibitory effect of exogenous BR on root growth, and bsk5 mutation increased drought resistance and improved sensitivity to salt stress and ABA hormone [11, 28]. However, BSK3, 5, and 8 have functional redundancy. Arabidopsis mutant bsk3, 4, 7, 8 and mutant bsk3, 4, 6, 7, 8 can reduce the degree of leaf curl and increase leaf inclination [13]. We speculated that OsBSK3 or OsBSK4, which were classified in the same subgroup as the genes mentioned above, may have the same function. Previous studies has shown that OsBSK1–2 is a significant positive regulator of rice plant immunity [20]. Because the gene structure and protein structure of OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 were highly similar, we speculated that these two genes might have similar functions. Meanwhile, OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 were up-regulated under salt stress and belonged to the same subgroup evolutionarily as ZmBSK1 [29, 30]. We speculated that OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 also played an active role in the drought tolerance of rice plants. OsBSK2 was expressed explicitly in ovary and embryo growth stages and was in the same subgroup as AtBSK2 with known functions. We speculated that it was involved in the development of plant zygote and germ and stress responses of salt and high-temperature [31–33]. Recent studies have shown that this gene is involved in rice grain size [22], which also confirmed our inference.
In the analysis of cis-elements in the promoters of rice BSK genes, we found many light-responsive elements, MeJA-inducible elements, and ABA-inducible elements, indicating that hormones and light can regulate genes of this family. The expression analysis of BSK family genes in rice seedlings treated with hormonal, biotic, and abiotic stresses by qRT-PCR showed that the gene expression was in good agreement with the promoter prediction, especially the members of subgroups II and VI. In addition, the expression of OsBSK2 in rice treated with ABA did not change significantly, which may be related to the absence of ABA-inducible elements in the promoter sequence of this gene.
Furthermore, we classified the expression patterns of 6 OsBSK genes and found that those treated with the hormone, biotic, and abiotic stress were the same and could be roughly divided into two groups: the majority induced up-regulated expression group and the expression down-regulated or no expression group. The former included OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK3, which can be up-regulated by ABA, JA, UV-B, low temperature, and M. oryzae; The latter included OsBSK2, OsBSK4, and OsBSK5, most of which were down-regulated or unchanged in expression analysis except OsBSK4 which could be up-regulated by ABA, low temperature and M. oryzae. Meanwhile, in the analysis of tissue expression profile during the whole growth period of rice, we found that OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2 belonged to the same branch, and OsBSK2 and OsBSK4 belonged to the same branch, except for OsBSK3 with high expression and OsBSK5 with low or no expression. The abovementioned patterns of hormones and stress were generally consistent with the tissue expression patterns during the growth period. OsBSK1–1 and OsBSK1–2, both of which belonged to the second subgroup, had the same expression pattern during the whole growth period, hormone, and stress treatment, making us more convinced of the conservation of family gene evolution.
In the expression profile of the tested hormones, ABA treatment induced up-regulation of 4 OsBSK genes, JA treatment induced up-regulation of 3 OsBSK genes, BR and IAA only up-regulated the OsBSK3 gene, and SA treatment down-regulated the expression of all family genes. The OsBSK3 gene was the most sensitive to exogenous BR and was up-regulated, consistent with previous results [21]. The above results indicated that BSK family members had both divisions and cooperation in response to different hormones and were involved in regulating plant growth, development, and stress. On the one hand, the responses of BSKs to the two hormones SA and JA were very different, which not only indicated that this family of genes may be involved in the defense response of plants to pathogens but also suggested that there may be different responses to different types of pathogens, such as biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Our study also supported the inference that this family member induced distinctly different expression patterns upon infection by M. oryzae, R. solani, and Xoo. On the other hand, the BSK family was identified as a BR family, which had a more comprehensive response to the ABA hormone. Our study also supported this result. That is, different abiotic stresses in the test can cause the expression of family members to different degrees. Some BSK family genes in Arabidopsis can also be significantly changed by ABA, salt, cold, and high-temperature treatments [33]. Recently, studies at the genetic level have also shown that ZmBSK1 plays an essential regulatory role in plant responses to drought and salt stress [29, 30].
Conclusions
At the rice genome level, six members of the OsBSK family have been identified, which originated from higher plants and were highly conserved. These six genes can be divided into four subgroups or two major groups according to the conserved protein domain. The hormone and stress expression profiles of OsBSK family genes from the qRT-PCR assay had a certain relationship with their promoter cis-elements, and they also had a good similarity with the gene expression patterns during the growth period. The expression patterns of BSK family members in rice seedlings treated with six hormones (ABA, JA, SA, BR, IAA, and GA), three abiotic stress (NaCl, 4 °C, and UV-B radiation), and three pathogens (M. oryzae, R. solani, and Xoo) treatments were similar. Most of OsBSK1–1, OsBSK1–2, and OsBSK3 were up-regulated; most of OsBSK2, OsBSK4, and OsBSK5 were down-regulated or changed little.
Methods
Materials and treatment
Hormone and stress expression profiling analysis took the O. sativa Japonica variety “Kongyu 131” as the test material. Subsequent treatment was carried out when the rice in the culture medium grew to three leaves and one heart. At 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h after treatment, the rice leaves were quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at − 70 °C for later use. Rice seeds were sterilized with 10% NaClO for 30 min, rinsed with distilled water three times, and germinated in the dark at 26 °C for 2 d. The seeds with the same bud length were selected and placed in the EP tube with the bottom cut off on the floating plate. The IRRI formula nutrient solution was changed every 3 d [34]. In the artificial climate room, the light intensity was 1200 μmol‧m− 2‧s− 1, the light time was 12 h/d, and the day and night temperatures were 28 °C/25 °C, respectively. Different hormones were sprayed on leaves at the concentrations of 0.5 mol/L IAA, 0.2 mol/L GA, 0.1 mol/L ABA, 0.001 mol/L BR, 0.2 mol/L SA, and 0.1 mol/L JA, respectively. For abiotic stress treatment, the hydroponic seedlings were placed in a constant temperature incubator at 4 °C, in a 150 mM NaCl solution, and under an 80 W UV lamp for 1 h before normal cultivation to complete low temperature, salt, and UV treatments. Appropriate inoculation methods were used for pathogen treatment. M. oryzae (strain 1391) was inoculated by spraying method, R. solani (strain YN-7) was inoculated by embedding method, and Xoo (strain XOOJ18) was inoculated by leaf clipping method. Each treatment was repeated three times.
Identification of gene family members
The protein sequence alignment was performed in the NCBI database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) according to the published protein sequences of Arabidopsis BSK. Meanwhile, the typical PKc and TPR domains were searched in the Rice Genome Database (http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/index.htm). Aligned and identified in the NCBI, SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/) and Pfam (http://xfam.org/) databases to remove redundant proteins [35, 36].
The gene accession number, coding sequence length, and amino acid number were from the Rice Genome Database, and the molecular formula, molecular weight, and isoelectric point were from Expasy (http://web.expasy.org/cgi-bin/protaparam/protparam). Subcellular localization analysis was performed using Expasy, and chromosomal localization, gene density, and collinearity of genes were analyzed and visualized by TBtools software [37].
Phylogenetic analysis of proteins
According to the published Arabidopsis BSK protein sequences, other species downloaded from the EnsemblPlants (https://plants.ensembl.org/index.html) and Phytozome (https://phytozome-next.jgi.doe.gov/) [38] databases were compared and screened by TBtools software and the NCBI website. The BSK family members of 13 species, including bryophytes(Physcommitrium patens、Marchantia polymorpha), pteridophytes(Selaginella moellendorffii 、Ceratopteris richardii), gymnosperms (Thuja plicata), monocotyledon(Oryza sativa Japonica、Acorus americanus、Oryza sativa Indica、Sorghum bicolor、Zea mays), and dicotyledon(Arabidopsis thaliana、Beta vulgaris、Corchorus capsularis) obtained after the screening, were used for sequence alignment and protein phylogenetic tree construction in MEGA X software. Selected the maximum likelihood method, set bootstrap to 1000, and applied the best fit model JTT + G. The evolutionary tree was beautified using Itol (https://itol.embl.de/) [39]. MEGA X and DNASP v6 software for Ka and Ks analysis [40]. Information on conserved domains of BSK members in various species was obtained from the NCBI database.
Gene structure and protein structure analysis
Gene structure analysis of the OsBSK family was performed using TBtools. The motif of the OsBSK family protein was analyzed by MEME (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme), and the protein secondary structure was predicted by prabi (https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html) [41], and the protein tertiary structure was predicted by SwissModel (http://swissmodel.expasy.org/) [42]. In addition, the promoter sequence 2000 bp upstream of the gene translation initiation site was extracted and submitted to Plant CARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) [43] for cis-element analysis and used TBtools to make a statistical map of the number of cis-elements.
Protein interaction prediction
The protein sequences of OsBSK family members were used to predict the protein interaction relationship through the string (https://cn.string-db.org/) database [44]. The expression data and heatmap of genes with predicted protein interactions under different hormone treatments were from the RiceXPro (https://ricexpro.dna.affrc.go.jp/) database [45]. NetPhos-3.1(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetPhos-3.1) was used to analyze the phosphorylation sites of the OsBSK proteins [46].
Analysis of tissue expression profiling throughout the growth period
The expression data of the tested genes at different developmental stages were obtained from the GEO database (GSE7951) on the NCBI website [47, 48], and expression profiles were analyzed by TBtools software.
Expression profile construction
Total RNA was extracted using the TRIZOL reagent (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Then, the cDNA was synthesized through Fermentas (# 1622) reverse transcription kit for reverse transcription. The primer sequences of BSK genes and internal reference gene actin are shown in Table 3, which were synthesized by Sanbo Yuanzhi Company. Each gene was amplified three times, and the gene expression was calculated using the 2-∆∆CT method [49]. Excel was used for data processing, GraphPad was used for histogram analysis, and SPSS 25.0 was used for significant difference analysis.
Table 3.
qRT-PCR specific primers
| Gene Name | Forward Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| OsBSK1–1 | ACAACCACAACACCCTCTATCC | CCTCATCTGCTGAGTCCATTCC |
| OsBSK1–2 | AGCACAGTGTGTGTATCCCG | AGCTGTGATGCCTCGTTCAA |
| OsBSK2 | TGCCAACTATTCTTTCTCCCCT | TGCACTTGCTGAGTCCATTCT |
| OsBSK3 | GCCATGCCCTTGACCTGATT | ATCGCACTAGTTCTGTCCCTTC |
| OsBSK4 | TGGTGTTGATGGACTCTTGCTT | AGAGCAGACACCACCGATTT |
| OsBSK5 | AGATTGGAGAAGGTGGGTTTGG | ACCTCTTGTTCGAACTGTGATT |
| OsActin | CATGCTATCCCTCGTCTCGACCT | GCACTTCATGATGGAGTTGTAT |
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Ze-Jian Guo, Prof. Peng Youliang, and Prof. Sun Wenxian from the School of Plant Protection of China Agricultural University for supplying the test pathogens.
Abbreviations
- BR
Brassinosteroid
- BSK
BR-signalling kinases
- Os
Oryza sativa Japonica
Authors’ contributions
SZ, XWH, and CJZ conceived and designed the study; SZ and XWH executed the experiments; JJD, MXD, JQS, and SYX made important contributions to data analysis; SZ, XWH, and CJZ analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31101429), Youth Innovative Talent Project of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University (CXRC2016-02).
Availability of data and materials
All gene accession numbers referred to herein are provided in the corresponding tables in the text and can be obtained in the Rice Genome Database (http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/index.htm). The expression data of protein interaction genes are obtained from the RiceXPro database (https://ricexpro.dna.affrc.go.jp/). The tissue expression data of OsBSKs are from the GEO database (GSE7951).
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Experimental research on plants, including the collection of plant material, comply with relevant institutional, national, and international guidelines and legislation. All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Shuo Zhang and Xuwei Hu contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Shuo Zhang, Email: zhangz2020z@163.com.
Xuewei Hu, Email: huxueweihxw@163.com.
Jiejing Dong, Email: 13614598061@163.com.
Mengxiang Du, Email: dum4213585@163.com.
Juqi Song, Email: s13054207002@163.com.
Shangyuan Xu, Email: xuxu825320272@163.com.
Changjiang Zhao, Email: zhaocj15@byau.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Grove MD, Spencer GF, Rohwedder WK, Mandava N, Worley JF, Warthen JD Jr, et al. Brassinolide, a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen. Nature. 1979. 10.1038/281216a0.
- 2.Rao X, Dixon RA. Brassinosteroid mediated cell wall remodeling in grasses under abiotic stress. Front Plant Sci. 2017. 10.3389/fpls.2017.00806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Sharma P, Kumar A, Bhardwaj R. Plant steroidal hormone epibrassinolide regulate-heavy metal stress tolerance in Oryza sativa L. by modulating antioxidant defense expression. Environ Exp Bot. 2016. 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2015.08.005.
- 4.Nawaz F, Naeem M, Zulfiqar B, Akram A, Ashraf MY, Raheel M, et al. Understanding brassinosteroid-regulated mechanisms to improve stress tolerance in plants: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2017. 10.1007/s11356-017-9163-6. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Caesar K, Elgass K, Chen Z, Huppenberger P, Witthöft J, Schleifenbaum F, et al. A fast brassinolide-regulated response pathway in the plasma membrane of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2011. 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04510.x. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Ye K, Li H, Ding Y, Shi Y, Song C, Gong Z, et al. BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE2 negatively regulates the stability of transcription factor ICE1 in response to cold stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2019. 10.1105/tpc.19.00058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Sun Y, Fan XY, Cao DM, Tang W, He K, Zhu JY, et al. Integration of brassinosteroid signal transduction with the transcription network for plant growth regulation in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell. 2010. 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.10.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Ross JJ, Reid JB. Evolution of growth-promoting plant hormones. Funct Plant Biol. 2010. 10.1071/FP10063.
- 9.Vriet C, Lemmens K, Vandepoele K, Reuzeau C, Russinova E. Evolutionary trails of plant steroid genes. Trends Plant Sci. 2015. 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Kim TW, Guan S, Burlingame AL, Wang ZY. The CDG1 kinase mediates brassinosteroid signal transduction from BRI1 receptor kinase to BSU1 phosphatase and GSK3-like kinase BIN2. Mol Cell. 2011. 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.05.037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Tang W, Kim TW, Oses-Prieto JA, Sun Y, Deng Z, Zhu S, et al. BSKs mediate signal transduction from the receptor kinase BRI1 in Arabidopsis. Science. 2008. 10.1126/science.1156973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 12.Shiu SH, Karlowski WM, Pan R, Tzeng YH, Mayer KFX, Li WH. Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell. 2004. 10.1105/tpc.020834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Sreeramulu S, Mostizky Y, Sunitha S, Shani E, Nahum H, Salomon D, et al. BSKs are partially redundant positive regulators of brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013. 10.1111/tpj.12175. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Jia Z, Giehl RFH, Meyer RC, Altmann T, van Wirén N. Natural variation of BSK3 tunes brassinosteroid signaling to regulate root foraging under low nitrogen. Nat Commun. 2019. 10.1038/s41467-019-10331-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Ren H, Willige BC, Jaillais Y, Geng S, Park MY, Gray WM, et al. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE 3, a plasma membrane-associated scaffold protein involved in early brassinosteroid signaling. PLoS Genet. 2019. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Shi H, Shen Q, Qi Y, Yan H, Nie H, Chen Y, et al. BR-SIGNALING KINASE1 physically associates with FLAGELLIN SENSING2 and regulates plant innate immunity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2013. 10.1105/tpc.112.107904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Majhi BB, Sobol G, Gachie S, Sreeramulu S, Sessa G. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALLING KINASES 7 and 8 associate with the FLS2 immune receptor and are required for flg22-induced PTI responses. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. 10.1111/mpp.13062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Majhi BB, Sessa G. Overexpression of BSK5 in Arabidopsis thaliana provides enhanced disease resistance. Plant Signal Behav. 2019. 10.1080/15592324.2019.1637665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Majhi BB, Sreeramulu S, Sessa G. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE5 associates with immune receptors and is required for immune responses. Plant Physiol. 2019. 10.1104/pp.18.01492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Wang J, Shi H, Zhou L, Peng C, Liu D, Zhou X, et al. OsBSK1-2, an orthologous of AtBSK1, is involved in rice immunity. Front Plant Sci. 2017. 10.3389/fpls.2017.00908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Zhang B, Wang X, Zhao Z, Wang R, Huang X, Zhu Y, et al. OsBRI1 activates BR signaling by preventing binding between the TPR and kinase domains of OsBSK3 via phosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 2016. 10.1104/pp.15.01668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Yuan H, Xu Z, Chen W, Deng C, Liu Y, Yuan M, et al. OsBSK2, a putative brassinosteroid-signaling kinase, positively controls grain size in rice. J Exp Bot. 2022. 10.1093/jxb/erac222. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 23.Anwar A, Liu Y, Dong R, Bai L, Yu X, Li Y. The physiological and molecular mechanism of brassinosteroid in response to stress: a review. Biol Res. 2018. 10.1186/s40659-018-0195-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Takahashi A, Casais C, Ichimura K, Shirasu K. HSP90 interacts with RAR1 and SGT1 and is essential for RPS2-mediated disease resistance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2003. 10.1073/pnas.2033934100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Blatch GL, Lässle M. The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays. 1999; https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199911)21:11<932::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-N [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Yuan H, Xu Z, Chen W, Deng C, Liu Y, Yuan M, et al. OsBSK2, a putative brassinosteroid-signalling kinase, positively controls grain size in rice. J Exp Bot. 2022. 10.1093/jxb/erac222. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Yin W, Li L, Yu Z, Zhang F, Liu D, Wu H, et al. The divergence of brassinosteroid sensitivity between rice subspecies involves natural variation conferring altered internal auto-binding of OsBSK2. J Integr Plant Biol. 2022. 10.1111/jipb.13322. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Li ZY, Xu ZS, He GY, Yang GX, Chen M, Li LC, et al. A mutation in Arabidopsis BSK5 encoding a brassinosteroid-signaling kinase protein affects responses to salinity and abscisic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.08.118. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 29.Liu L, Sun Y, Di P, Cui Y, Meng Q, Wu X, et al. Overexpression of a Zea mays Brassinosteroid-signaling kinase gene ZmBSK1 confers salt stress tolerance in maize. Front Plant Sci. 2022. 10.3389/fpls.2022.894710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Liu L, Xiang Y, Yan J, Di P, Li J, Sun X, et al. BRASSINOSTEROID-SIGNALING KINASE 1 phosphorylating CALCIUM/CALMODULIN- DEPENDENT PROTEIN KINASE functions in drought tolerance in maize. New Phytol. 2021. 10.1111/nph.17403. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 31.Neu A, Eilbert E, Asseck LY, Slane D, Henschen A, Wang K, et al. Constitutive signaling activity of a receptor-associated protein links fertilization with embryonic patterning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2019. 10.1073/pnas.1815866116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Wang K, Chen H, Ortega-Perez M, Miao Y, Ma Y, Henschen A, et al. Independent parental contributions initiate zygote polarization in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Biol. 2021. 10.1016/j.cub.2021.08.033. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Li Z, Shen J, Liang J. Genome-wide identification, expression profile, and alternative splicing analysis of the Brassinosteroid-signaling kinase (BSK) family genes in Arabidopsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. 10.3390/ijms20051138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Yoshida S, Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA. Laboratory manual for physiological studies of rice. 3. Philippines: Int. Rice Res. Inst; 1976. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P. SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. 10.1093/nar/gkaa937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 36.Mistry J, Chuguransky S, Williams L, Qureshi M, Salazar GA, Sonnhammer ELL, et al. Pfam: the protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. 10.1093/nar/gkaa913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, et al. TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant. 2020. 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 38.Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, et al. Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. 10.1093/nar/gkr944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. 10.1093/nar/gkab301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 40.Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, et al. DnaSP v6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. 10.1093/molbev/msx248. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Geourjon C, Deléage G. SOPMA: significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Bioinformatics. 1995. 10.1093/bioinformatics/11.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, et al. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. 10.1093/nar/gky427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 43.Lescot M, Déhais P, Thijs G, Marchal K, Moreau Y, de Peer YV, et al. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. 10.1093/nar/30.1.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M, Wyder S, Simonovic M, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. 10.1093/nar/gkw937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Sato Y, Takehisa H, Kamatsuki K, Minami H, Namiki N, Ikawa H, et al. RiceXPro version 3.0: expanding the informatics resource for rice transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. 10.1093/nar/gks1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Blom N, Gammeltoft S, Brunak S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J Mol Biol. 1999. 10.1006/jmbi.1999.3310. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Li M, Xu W, Yang W, Kong Z, Xue Y. Genome-wide gene expression profiling reveals conserved and novel molecular functions of the stigma in rice. Plant Physiol. 2007. 10.1104/pp.107.101600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 48.Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, et al. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. 10.1093/nar/gks1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001. 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All gene accession numbers referred to herein are provided in the corresponding tables in the text and can be obtained in the Rice Genome Database (http://www.ricedata.cn/gene/index.htm). The expression data of protein interaction genes are obtained from the RiceXPro database (https://ricexpro.dna.affrc.go.jp/). The tissue expression data of OsBSKs are from the GEO database (GSE7951).