Abstract
Background
The permeability of plasma membrane aquaporins (PIPs) to small solutes other than water greatly diversifies their potential functions in plant development and metabolic processes. One such process is stress signalling in which hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) plays a major role. Based on transport assays carried out in yeast, there are differences in the degree to which PIPs of Arabidopsis thaliana, are permeable to H2O2 and thus they may differentially facilitate transmembrane diffusion. Here, we test whether specific PIPs aid in the transmembrane diffusion of H2O2 to such an extent that knocking-out PIPs affects plant phenotype. We examined changes in growth and morphology, including biomass accumulation, root system architecture and relative water content, as well as gas exchange, across two H2O2 treatments in knockout mutants of A. thaliana.
Results
We could infer that PIP-type aquaporins are permeable to H2O2 in planta and that this permeability is physiologically relevant in a plant’s response to oxidative stress. In particular, the lack of functional PIP2;3 confers resistance to exogenously applied H2O2 indicating that it facilitates H2O2 entry into root cells. Additionally, PIP1;1 and PIP2;6 were found to facilitate H2O2 diffusion, while PIP2;2 is required for proper root growth under controlled conditions.
Main findings
We conclude that PIPs are physiologically relevant conduits for H2O2 diffusion in the A. thaliana roots and participate in the regulation of stress responses.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12870-022-03962-6.
Keywords: Aquaporin, PIP, Hydrogen peroxide, Root length, Arabidopsis thaliana, Oxidative stress
Background
In addition to facilitating water movement across membranes, plasma membrane intrinsic proteins (PIPs) are permeable to other small molecules, including hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) [1–3]. This potentially endows them with a role in stress responses and signalling through the plant. This is because H2O2 mediates a variety of metabolic processes, such as apoptosis and pathogen defence when produced in response to a stressor or stimulus [4–7]. To initiate stress responses, H2O2 must diffuse across cellular membranes. It is electrochemically very similar to the water molecule [8] and thus likely to use the same diffusion pathways. Previous studies have indeed demonstrated that PIPs of Arabidopsis thaliana are permeable to H2O2 when expressed in yeast cells (Table 1) [1–3, 7, 9]. In fact, to date, aquaporins are the only known H2O2 transporters across phospholipid membranes [10].
Table 1.
Plasma membrane aquaporins examined in this study and their H2O2 permeability in yeast. The effect of exogenous H2O2 application to the roots on the gene expression of the individual PIPs was reported by Hooijmaijers et al. [1] for a concentration of 1 mM in a hydroponic solution. 1 Dynowski et al. (2008) [2], 2 Hooijmaijers et al. (2012) [1], 3 Wang et al. (2020) [11], 4 Groszmann et al. (2021) [3]
| Aquaporin | H2O2 permeability | Effect of exogenous H2O2 |
|---|---|---|
| AtPIP1;1 | None1,2,3/High4 | No effect |
| AtPIP1;2 | None2,3/High4 | No effect |
| AtPIP1;3 | None2,3/High4 | No effect |
| AtPIP2;2 | High2/Medium3,4 | Downregulated in roots |
| AtPIP2;3 | Low2/Medium3,4 | Downregulated in roots |
| AtPIP2;4 | High1,2,3/Medium4 | Downregulated in roots |
| AtPIP2;5 | High2/Medium3,4 | Downregulated in roots |
| AtPIP2;6 | Low2,4/Medium3 | No effect |
Aquaporins are channel proteins with six membrane-spanning units connected by three loops (A, C and E) on the apoplastic side and two loops (B and D) on the cytoplasmic side. Loops B and E contain a highly conserved asparagine-proline-alanine (NPA) sequence and fold back into the membrane where the two NPA sequences align to form a narrow passage at the centre of the channel [12]. A second narrow pore constriction is found towards the apoplastic side of the channel consisting of four amino acid residues of which arginine is highly conserved and often accompanied by the aromatic phenylalanine. This restriction is therefore also referred to as the ar/R selectivity filter and is essential for regulating aquaporin permeability to slightly larger neutral molecules such as urea and glycerol, as well as for the exclusion of protons from the pore [13]. The ar/R selectivity filter, however, does not appear to determine the water or H2O2 permeability of aquaporins as the residues making up this constriction are identical and yet their permeability to, H2O and H2O2, varies [1, 14, 15]. Furthermore, mutagenesis studies on the ar/R selectivity filter have failed to find evidence for variation in water or H2O2 permeability and altering the pore diameter at this location appears not to affect water permeability [13]. This leaves the pore constriction at the NPA sequence as the main candidate for determination of aquaporin water permeability. This sequence is also itself highly conserved among all plant PIPs and cannot alone account for differences in PIP water or H2O2 permeability. Nevertheless, these differences may at least in part be explained by subtle structural effects on the NPA motif [13], which could be brought about during tetramer formation [15–17]. Despite these long-standing unexplained results, there has to date only been one study of H2O2-permability of PIPs in planta, which found that AtPIP1;4 conducts this molecule, despite the fact that it appeared to be H2O2-impermeable when expressed in yeast [7].
Plant aquaporins are regulated by various mechanisms that may not be present in yeast or are unable to target plant isoforms [18–20]. Thus, a survey of all PIPs in the fully functional plant environment is required to evaluate the capacity of these aquaporins to facilitate transmembrane H2O2 diffusion. In this study, we examined various PIP knockout mutants of A. thaliana to verify whether their previously determined permeability to H2O2 has a physiologically relevant role in plant development and water relations.
In addition to permeating certain aquaporins, H2O2 has also been shown to inhibit water transport through aquaporins when used as a non-specific aquaporin inhibitor in plants due to its low toxicity compared to other inhibitors [21, 22]. However, application of H2O2 to the root system has also been found to regulate the gene expression of some PIP2 isoforms [1]. Application of exogenous H2O2 leads to a reduction in root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr) [23–25], which cannot be attributed to its direct effect on aquaporin activity, transcript levels or membrane trafficking, not to mention the regulation of aquaporin activity through phosphorylation or protein internalisation [24, 25]. Our goal was to use a top-down approach to shed light on the effect of exogenous H2O2 application to the roots on plant development by characterising whole-plant responses to this treatment.
Based on recent studies on the permeability of all 13 AtPIP isoforms to H2O2 in yeast (Table 1) [3], and the fact that a reduction in Lpr in response to exogenous H2O2 application has been corroborated in multiple studies [23, 24, 26, 27], we expected PIPs to be active in a plant’s response to oxidative stress in A. thaliana roots. We, therefore, hypothesized that the growth of knockout mutants lacking PIPs would be less affected by the exogenous H2O2 treatments than that of the wild type plants due to the reduced H2O2 influx from the apoplast. We also expected that mutant plants lacking PIP1s or PIP2s would respond differently to the H2O2 treatments due to their divergent H2O2 permeabilities (Table 1, [3]). To test this hypothesis, we exposed plant roots to two treatments of contrasting H2O2 concentrations and examined the effects of these treatments on plant growth and root system architecture. All PIPs investigated in this study and their previously determined H2O2 permeabilities are summarised in Table 1.
Results
Effects on biomass
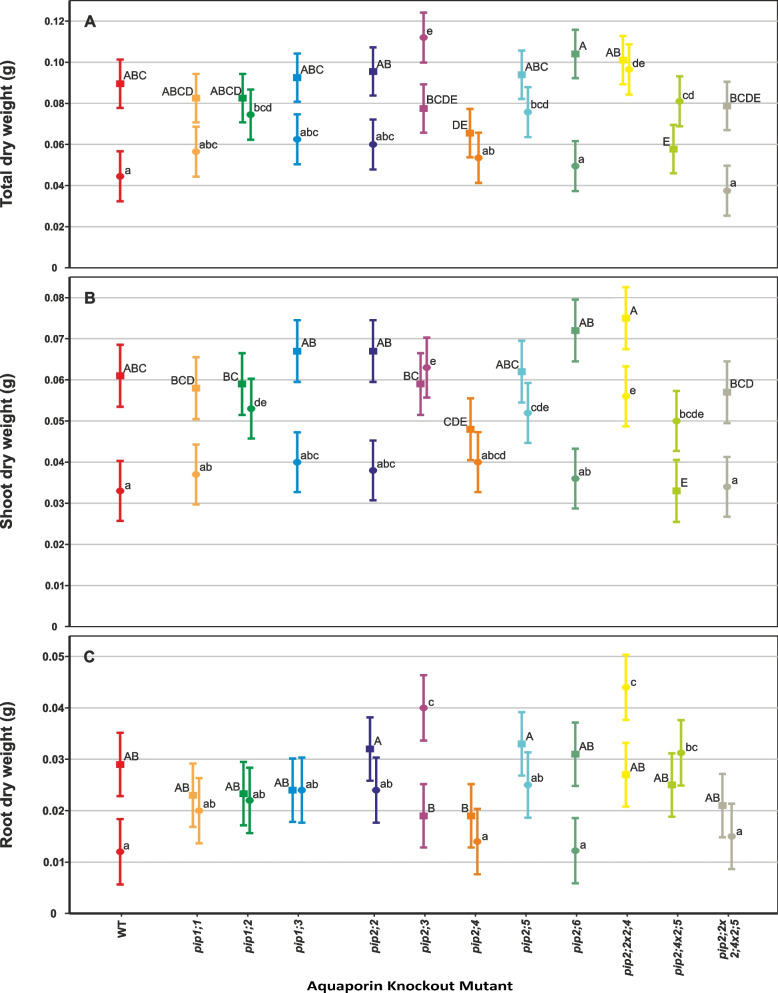
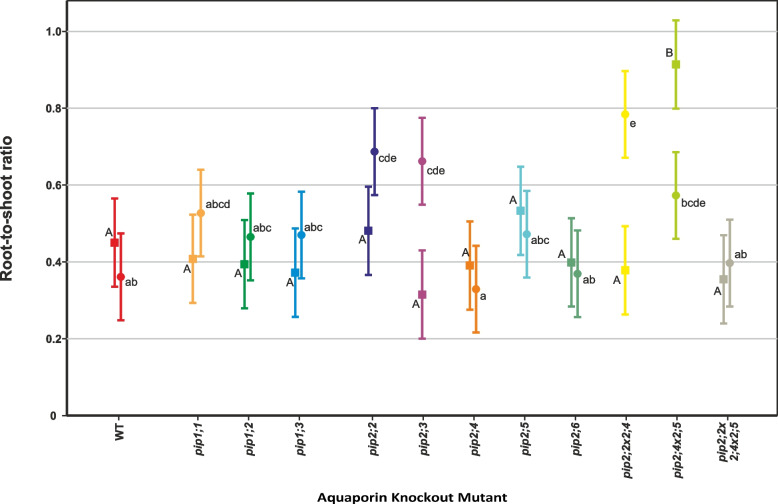
Under controlled conditions, total dry weight (DW) accumulation over the course of the experiment was uniform among most genotypes, but two mutant lines, pip2;4 and pip2;4 × 2;5, had statistically significantly lower DW compared to the wild type (WT) (p = 0.045 and 0.011 respectively, Fig. 1A, Table 2). In the case of pip2;4 × 2;5, this effect was due to a significantly lower shoot biomass (-46%, p < 0.001), which resulted in its root-shoot ratio being twice that of the WT (p < 0.001, Fig. 2, Table 2).
Fig. 1.
Biomass accumulation by PIP knockout-mutant plants over the course of the experiment. Means ± pooled SE, n = 8 – 10 plants. Square symbols denote control conditions and circles treatment with 1 mM H2O2. Different letters indicate significant differences between the lines under control (upper case) and H2O2 treatment (lower case) conditions. The relative increase/decrease in biomass due to the treatment is given for each plant line in Table 2. A Total dry mass. B Shoot dry mass. C Root dry mass
Table 2.
Summary of the H2O2 treatment effect on plant dry weights and root:shoot ratios. The treatment effects of each parameter are given for each plant line. The p-values are listed for mutants that significantly differed from the WT under the treatment
| Plant Line | Total Dry Weight | Shoot Dry Weight | Root Dry Weight | Root-Shoot Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | -50% | -46% | -59% | -20% |
| pip1;1 | -31% | -36% | -13% | + 29% |
| pip1;2 |
-10% p = 0.016 |
-10% p = 0.007 |
-4% | + 18% |
| pip1;3 | -32% | -40% | ± 0 | + 26% |
| pip2;2 | -38% | -43% | -25% |
+ 43% p = 0.005 |
| pip2;3 |
+ 44% p < 0.001 |
+ 7% p < 0.001 |
+ 111% p < 0.001 |
+ 110% p = 0.010 |
| pip2;4 | -18% | -17% | -26% | -16% |
| pip2;5 |
-19% p = 0.013 |
-16% p = 0.009 |
-24% p = 0.045 |
-11% |
| pip2;6 | -52% | -50% | -61% | -8% |
| pip2;2 × 2;4 |
-4% p < 0.001 |
-25% p = 0.001 |
+ 63% p < 0.001 |
+ 107% p < 0.001 |
| pip2;4 × 2;5 |
+ 40% p = 0.006 |
+ 52% p = 0.017 |
+ 24% p = 0.006 |
-37% |
| pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5 | -39% | -40% | -29% | + 12% |
Fig. 2.
Root-to-shoot ratio of individual plants at 31 days old. Means ± SE, n = 8 – 10 plants. Square symbols denote control conditions and circles treatment with 1 mM H2O2. Different letters indicate significant differences between the lines under control (upper case) and H2O2 treatment (lower case) conditions. The relative increase/decrease in the ratio due to the treatment is given for each plant line in Table 2
The 1 mM H2O2 treatment caused a 50% reduction of total DW accumulation (shoot + root) in the WT plants, but a much smaller reduction in most of the mutant lines, while pip2;3 and pip2;4 × 2;5 even increased their total DW accumulation due to the H2O2 treatment (Fig. 1A, Table 2). Thus, the following lines accumulated significantly more dry mass than the wild type under the H2O2 treatment: pip1;2 (+ 67%, p = 0.016), pip2;3 (+ 149%, p < 0.001), pip2;5 (+ 69%, p = 0.013), pip2;2 × 2;4 (+ 116%, p < 0.001) and pip2;4 × 2;5 (+ 80%, p = 0.006). This was largely due to shoot DW, which was also significantly greater compared to the wild type: pip1;2 (+ 61%, p = 0.007), pip2;3 (+ 91%, p < 0.001), pip2;5 (+ 58%, p = 0.009), pip2;2 × 2;4 (+ 70%, p = 0.001) and pip2;4 × 2;5 (+ 52%, p = 0.017) (Fig. 1B, Table 2). With the exception of pip1;2, the same set of plant lines also had a longer roots compared to the WT under the treatment, though the contribution of root DW to total DW was smaller: pip2;3 (+ 233%, p < 0.001), pip2;5 (+ 108%, p = 0.045), pip2;2 × 2;4 (+ 267%, p < 0.001) and pip2;4 × 2;5 (+ 158%, p = 0.006) (Fig. 1C). In line with the differential responses of the mutant plants to H2O2, the root-shoot ratios of the following mutants were significantly higher compared to the wild type in this treatment: pip2;2 (+ 90%, p = 0.005), pip2;3 (+ 83%, p = 0.010) and pip2;2 × 2;4 (+ 117%, p < 0.001).
H2O2 treatment had a large effect on the wild type with a 46% and 59% reduction in shoot and root DW accumulation, respectively (Table 2). Many of the mutant lines tested here responded differently. However, pip1;2, pip2;4 and pip2;5, remained fairly unresponsive to the treatment, while only the shoot DW of pip2;4 × 2;5 double mutant significantly increased but there was little change in its root DW. Furthermore, the single mutant pip2;3 displayed an increase of total DW in response to the H2O2 treatment, which was almost entirely due to greatly enhanced root DW, as is apparent in the two-fold increase of its root-shoot ratio. In fact, pip2;6 was the only mutant line to have displayed a similar response to the treatment as the wild type in terms of its direction as well as magnitude.
Rates of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance were uniform amongst all plant lines as well as between the control and H2O2 treatment, and thus there were no significant differences in rates of gas exchange between PIP knockout mutants. Values for the rates of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance are shown in Supplementary Table S1 of Additional file 2.
Effects on relative (RWC) and absolute (AWC) water content
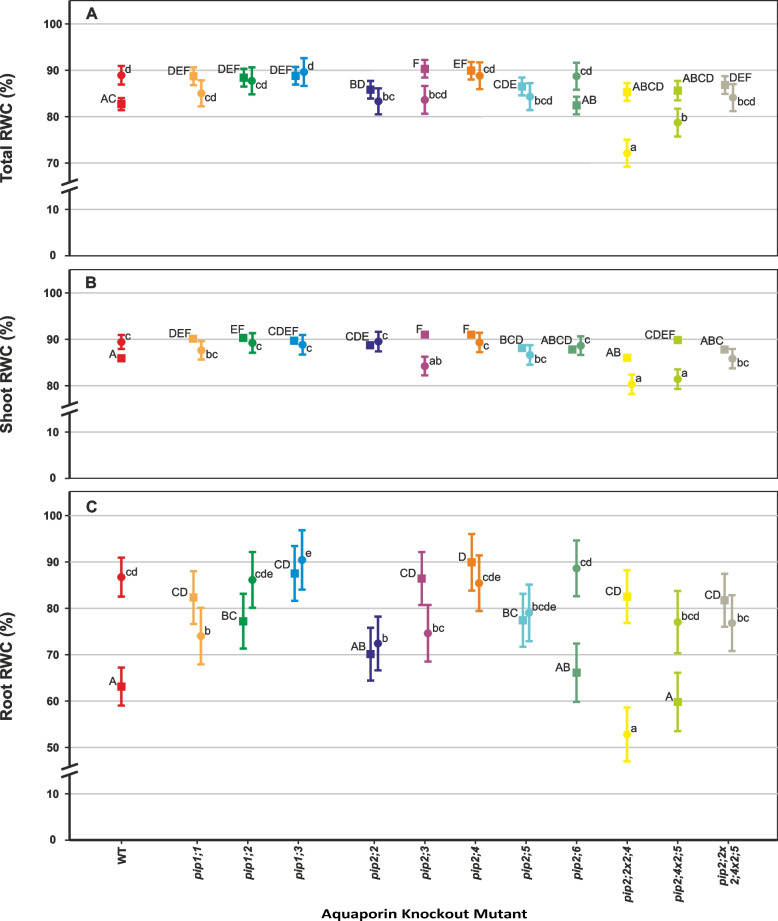
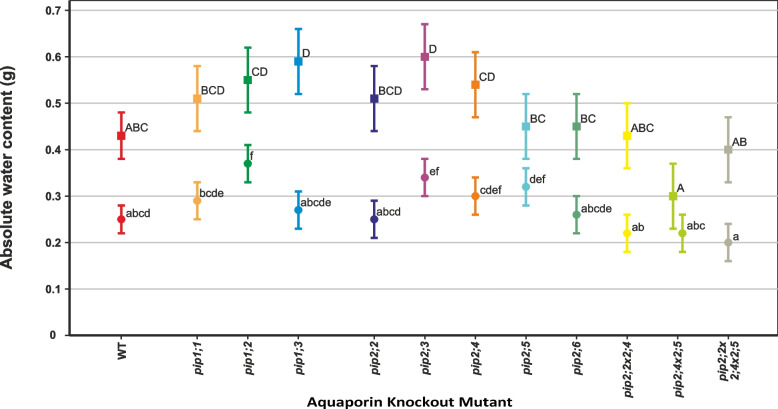
Under controlled conditions, the relative water content (RWC) of most mutants was significantly higher than the WT in both the roots and shoots (Fig. 3). The exceptions were pip2;6 that did not differ from the WT; pip2;2 × 2;4 and pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5 that only had significantly higher root RWC (p < 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively), but not shoot RWC. Also, pip2;2 and pip2;4 × 2;5, had increased shoot RWC but not root RWC compared to the WT (p = 0.012 and p < 0.001, respectively). Absolute water content (AWC) of the shoots was uniform among most genotypes, but significantly higher in pip1;3 and pip2;3 compared to the WT (p = 0.019 and 0.010 respectively, Fig. 4).
Fig. 3.
Relative water content (RWC) of individual plants at 31 days old. Means ± SE, n = 8 – 10 plants. Square symbols denote control conditions and circles treatment with 1 mM H2O2. Different letters indicate significant differences between the lines under control (upper case) and H2O2 treatment (lower case) conditions. The relative increase/decrease in RWC due to the treatment is given for each plant line in Table 3. A Whole-plant RWC. B Shoot RWC. C Root RWC
Fig. 4.
Absolute water content (AWC) of individual rosettes at 31 days old. Means ± SE, n = 8 – 10 plants. Square symbols denote control conditions and circles treatment with 1 mM H2O2. Different letters indicate significant differences between the lines under control (upper case) and H2O2 treatment (lower case) conditions. The relative decrease in AWC due to the treatment is given for each plant line in Table 3
Most of the plant’s water was present in the shoot, therefore the shoot RWC and RWC of the whole plant were very similar, and both changed little in response to the H2O2 treatment (Fig. 3A and B). However, there were large differences in root RWC between some mutants under control conditions as well as a large effect of the H2O2 treatment on root RWC in others (Fig. 3C; Table 3). Most notably, compared to the control treatment (0 mM H2O2), the root RWC was increased in pip2;6 and pip2;4 × 2;5 (+ 34% and + 29% respectively), whereas root RWC was reduced in pip2;2 × 2;4 by 36% in response to the H2O2 treatment (Fig. 3).
Table 3.
Summary of the H2O2 treatment effect on RWC and AWC. The percentage values indicate change in the measured parameters for plants of each line subjected to the 1 mM H2O2 treatment compared with untreated control. The p-values are listed for mutants that significantly differed from the WT under the treatment
| Plant Line | Total RWC | Shoot RWC | Root RWC | Shoot AWC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | + 7% | + 4% | + 37% | -42% |
| pip1;1 | -4% | -3% |
-10% p = 0.042 |
-43% |
| pip1;2 | -1% | -1% | + 12% |
-33% p = 0.003 |
| pip1;3 | + 1% | -1% | + 3% | -54% |
| pip2;2 |
-3% p = 0.050 |
+ 1% |
+ 3% p = 0.016 |
-51% |
| pip2;3 | -7% |
-7% p = 0.012 |
-14% |
-43% p = 0.026 |
| pip2;4 | -1% | -2% | -5% | -44% |
| pip2;5 | -3% | -2% | + 2% | -29% |
| pip2;6 | + 8% | + 1% | + 34% | -42% |
| pip2;2 × 2;4 |
-15% p < 0.001 |
-7% p < 0.001 |
-36% p < 0.001 |
-49% |
| pip2;4 × 2;5 |
-8% p < 0.001 |
-9% p < 0.001 |
+ 29% | -27% |
| pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5 | -3% | -2% | -6% | -50% |
The AWC of the shoot was reduced in all plant lines in response to the H2O2 treatment (Fig. 4; Table 3). Of these, pip1;2 experienced one of the smallest relative reductions and had significantly higher AWC than the WT under the H2O2 treatment (p = 0.003). pip2;3 had significantly higher AWC than the WT under both conditions (p = 0.010 under 0 mM H2O2 and p = 0.026 under 1 mM H2O2), despite an equivalent relative decrease in response to H2O2.
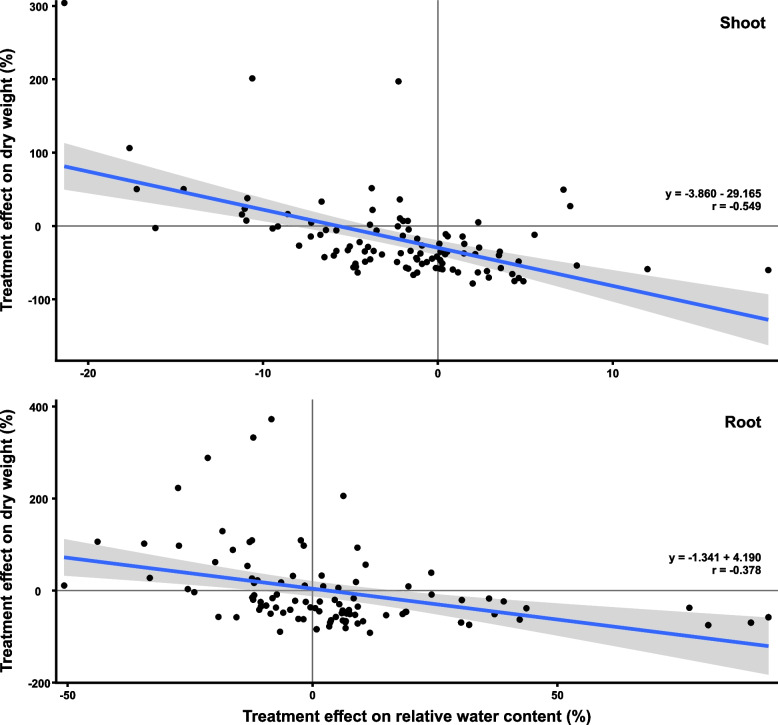
Since we noticed that the change in RWC caused by H2O2 was in the opposite direction compared to the change in dry weight we tested this relationship (Fig. 5). There was indeed a statistically significant (p < 0.001) negative correlation between the H2O2 treatment effect on dry weight and on RWC (-0.378 in roots and -0.549 in shoots) across all genotypes.
Fig. 5.
Relationship between the treatment effect on dry mass and RWC. The shaded area indicates the 95% confidence interval. The correlation was statistically significant for both, shoots and roots (p < 0.001)
Effects on root system architecture
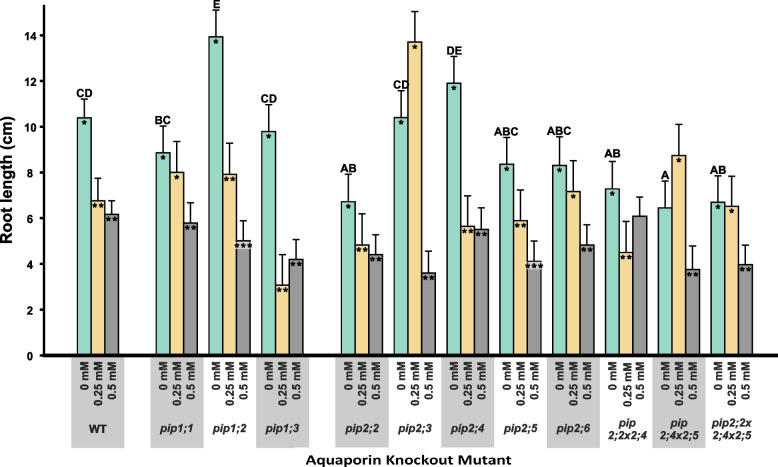
When grown on MS medium without added H2O2, only the pip1;2 mutant had significantly greater root length compared to the WT (+ 34%, p = 0.003), while pip2;2 (-35%, p = 0.003), pip2;2 × 2;4 (-30%, p = 0.011), pip2;4 × 2;5 (-38%, p = 0.001) and pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5 (-36%, p = 0.002) significantly shorter roots (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
Total root length for all plant lines under three H2O2 concentrations. Given are means with SE for n = 9 – 18. Letters indicate statistically significant differences between the plant lines under control conditions. For reasons of clarity, letters indicating significant differences for the H2O2 treatments have been omitted from the graph but can be found in Supplementary Table S2 of Additional file 2. Asterisks indicate statistically significant effects of the treatment on a plant line. Different numbers of asterisks indicate a significant effect by the treatment, while columns with no asterisk do not differ from either of the treatments
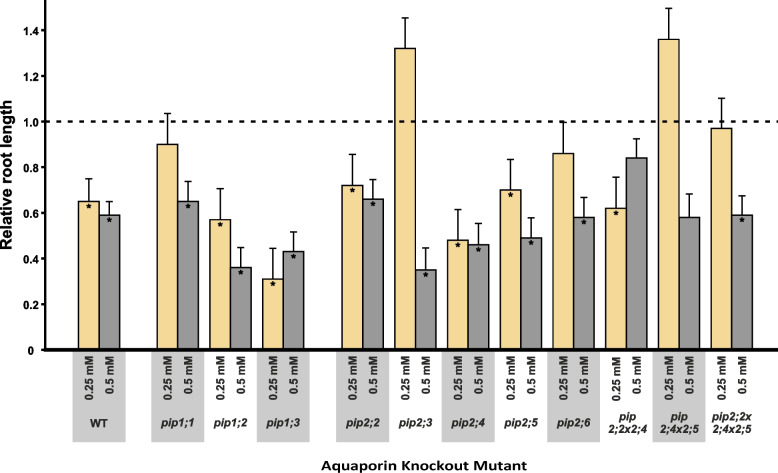
Almost all the plant lines responded to the H2O2 treatment with a reduction in root length as shown in Fig. 6, albeit the length and number of lateral roots were affected less by the treatments than total root length (Figure S1 in Additional file 1 and Table S2 in Additional file 2). The WT responded strongly to the H2O2 treatments displaying a significant reduction in root length by about 40% (p < 0.001 at both H2O2 concentrations, Fig. 6), as did most knockout mutants. However, pip1;1, pip2;5 as well as pip2;6, were less responsive to H2O2, with no significant effect at 0.25 mM H2O2. The pip2;2 × 2;4 double-mutant remained unaffected even at 0.5 mM H2O2 (Fig. 7). The increase in root length in the two mutants, pip2;3 and pip2;4 × 2;5, in response to 0.25 mM H2O2 was not statistically significant.
Fig. 7.
Relative root length of PIP knockout mutants under control and H2O2 treatments. Root length under control conditions has been set to 100% (indicated by the dashed line). Absolute values for root length can be found in Fig. 6 and Supplementary Table S2 in Additional file 2. Asterisks inside the columns indicate statistically significant treatment effects. Given are means ± SE for n = 9 – 18 plants
Effects on gene expression
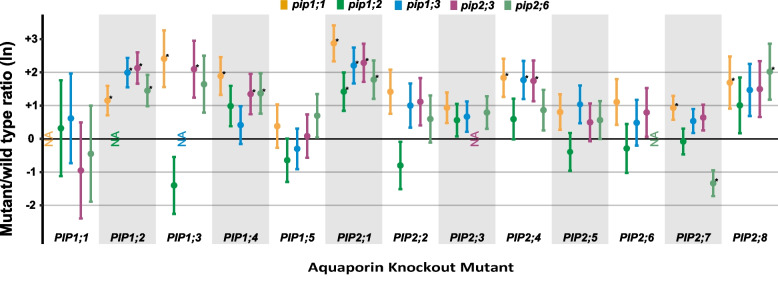
Knocking out individual PIPs resulted in an overall upregulation of other PIPs under standard growing conditions (Fig. 8), which is in line with results previously reported on PIP gene expression in pip2;2, pip2;4, pip2;5, pip2;2 × 2;4, pip2;4 × 2;5 and pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5 [28]. This upregulation was most apparent in plant lines lacking aquaporins belonging to the PIP1 subgroup. For example, PIP1;2 (p = 0.023), PIP1;3 (p = 0.018), PIP1;4 (p = 0.005), PIP2;1 (p < 0.001), PIP2;4 (p = 0.006), PIP2;7 (p = 0.021) as well as PIP2;8 (p = 0.049) were all significantly upregulated in the pip1;1 mutant. In pip1;3, PIP1;2 (p < 0.001), PIP2;1 (p = 0.001) and PIP2;4 (p = 0.008) were significantly upregulated. Amongst the PIP2 subgroup, knocking out PIP2;3 had the highest impact on the expression of other PIP genes; causing the significant upregulation of PIP1;2 (p < 0.001), PIP1;3 (p = 0.034), PIP1;4 (p = 0.043), PIP2;1 (p = 0.001) as well as PIP2;4 (p = 0.013). In the pip2;6 mutant, we found a significant upregulation of PIP1;2 (p = 0.010), PIP1;4 (p = 0.041), PIP2;1 (p = 0.008) and PIP2;8 (p = 0.030) as well as a downregulation PIP2;7 (p = 0.004).
Fig. 8.
PIP gene expression in the mutant lines. Ratios (ln) of AtPIP expression levels for pip1;1, pip1;2, pip1;3, pip2;3 and pip2;6 knockout mutants. Values are means ± SE for n = 4 biological replicates. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences compared to the WT
Discussion
Efficient root water uptake and transport are vital for a plant’s survival and growth. A major factor limiting plant water transport is root hydraulic conductivity (Lpr), which is highly responsive to the expression and activity of PIPs [29–33]. Lpr as well as PIP expression and activity have been reported to be reduced by H2O2 treatments in various plant species [1, 24, 27, 34]. This is consistent with the reduced root and shoot biomass accumulation, as well as decreased root length, that we found here and was reported by Claeys et al., 2014 [35] in WT A. thaliana plants subject to H2O2 treatment. Reduced productivity was not accompanied by a change in the rates of gas exchange due to the H2O2 treatment (Supplementary Table S1 in Additional file 2). We found stomatal conductance to be unresponsive to oxidative stress applied to the roots, which is in agreement with previous observations [26]. This suggests that in our hydroponic set-up Lpr may not constitute a limiting factor, because water is abundantly available [36] or alternately it may imply that the expression of PIP genes in leaves remains unaffected by H2O2 application to the roots as reported previously [1]. Thus, the reduced biomass of WT plants is most likely due to impairment of cell expansion by H2O2 [10]. Reduced cell expansion would also impact leaf area, which we estimated using absolute water content (AWC) as a proxy [37]; allowing us to verify that the H2O2 treatment reduced shoot growth (Fig. 4).
AWC was significantly increased in pip1;3 and pip2;3 under controlled conditions (Fig. 4), wherein both these knockout mutants showed increased expression of PIP1;2, PIP2;1 and PIP2;4 (Fig. 8); genes which have all been implicated in plant water transport [28, 38–41]. Thus, the increased AWC of these two knock-out mutants may be due to compensatory upregulation of other aquaporins [28]. Nevertheless, the increased shoot growth of pip2;3 compared to the WT was maintained when grown with H2O2 (Fig. 4), indicating a certain tolerance of the applied treatment. Furthermore, the H2O2 treatment only had a modest effect on the root growth of pip2;3 (Figs. 7), which points to a role of PIP2;3 in facilitating H2O2 diffusion. Rosette growth is very sensitive to a large range of stress intensities, including mild stress not producing a visible phenotype [35], and thus the fact that AWC of pip2;3 differed from the WT in the control as well as H2O2 treatment could indicate an intrinsically higher tolerance of these plants to oxidative stress. However, our current knowledge of the roles of PIP2;3 does not allow for the clear separation of its contributions to cell expansion and growth as opposed to stress signalling. This is an aspect of aquaporin function that will need to be addressed in future studies.
At low concentrations (i.e., 0.01 mM for A. thaliana and ≤ 0.5 mM for Phaseolus vulgaris), H2O2 can have a minor stimulatory effect on root growth [24, 27, 42]. This may imply that the absence of a specific H2O2-permeable PIP in planta could impede entry of H2O2, limiting its intracellular concentration, and resulting in either a diminished stress response or even a stimulatory effect on growth [24, 27]. This was the case for pip2;3 and pip2;4 × 2;5 in terms of their increased root length at 0.25 mM H2O2 (Fig. 7). The differential results we obtained at different H2O2 concentrations suggest that there is a threshold concentration at which H2O2 switches from constituting a potentially stimulatory signal to a stressor [24, 27], and that this threshold changes according to the specific PIPs expressed in the roots. Both pip2;3 and pip2;4 × 2;5 had higher root, as well as shoot, biomass at 1 mM H2O2 (Fig. 1). We, therefore, argue that the lack of functional PIP2;3 and, both, PIP2;4 and PIP2;5 reduces plasma membrane permeability to H2O2, allowing only a non-inhibitory amount of H2O2 to enter root cells at the concentrations used in our treatments. However, confirmation of this hypothesis will require the direct measurement of intracellular levels of H2O2 concentrations.
A plant’s response under stress conditions is not only determined by the stress itself, but also that plant’s tolerance of the stress [35, 42]. The lack of PIPs permeable to H2O2 should enhance stress tolerance and, thus, knockout mutants would be expected to display a less pronounced response to H2O2 compared to the WT. At 0.25 mM H2O2, root length was unresponsive to H2O2 in pip1;1, pip2;6 and pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5, whereas similarly to the WT, pip2;2 × 2;4 responded by decreasing root growth but was far less responsive at 0.5 mM H2O2 (Fig. 7). We see this as further evidence that reduced PIP expression lowers the plasma membrane’s permeability to H2O2 in the roots and raises plants’ resistance to, or perception of, oxidative stress. It furthermore points to non-redundant roles of aquaporins in facilitating H2O2 diffusion and in stress signalling.
The accumulation of DW was reduced by the H2O2 treatment in most plant lines [10, 35], but interestingly, this treatment effect was accompanied by an increase in RWC (Fig. 3). In the roots, one possible explanation for this correlation would be that root volume remained constant despite the reduction in DW caused by the treatment. We found the H2O2 treatment to cause a significant reduction in root length in all plant lines (Fig. 7).
Comparing the PIP knockout mutants to the WT under control conditions, we found some differences that are indicative of the, perhaps overlapping, but nevertheless non-redundant roles of plasma membrane aquaporins. For example, pip1;2 had significantly longer roots (Fig. 6), which supports previous results by Kaldenhoff et al. [30] who observed 5-times larger root systems (in terms of fresh weight) in PIP1;1/PIP1;2 antisense lines. Notably, in the present work, root dry mass was not altered in pip1;2, but instead root RWC was significantly higher than that of the WT (Figs. 1 and 3) and AWC was significantly increased under the H2O2 treatment (Fig. 4). Significantly decreased root length compared to the WT was recorded in pip2;2, pip2;2 × 2;4, pip2;4 × 2;5 and pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2,5 (Fig. 6); a set which includes all mutant lines lacking functional PIP2;2. PIP2;2 is abundantly expressed in roots [25, 29, 32, 33, 41] and has been found to contribute to lateral root emergence [40] as well as hydraulic conductivity in cortex cells [29]. It is thus not surprising, that the absence of functional PIP2;2 has a detrimental effect on root development and growth. Interestingly, despite its abundant expression in the plant, non-functional PIP2;2 does not cause the upregulation of other PIP genes [28, 29]. Increased root length and thus a larger surface area for water absorption could effectively compensate for diminished water uptake due to the lack of functional PIPs, supporting past reports that PIP-type aquaporins facilitate root water uptake [29–31, 33, 40], while at the same time providing an explanation for why greenhouse-grown PIP knockout mutants do not display visible phenotypes [28–30, 43].
We found that the RWC was higher in most of our mutant lines than in the WT under control conditions (Fig. 3). Though counterintuitive, as one might expect that a lower RWC in plants would be indicative of disrupted water uptake and translocation, our results could be explained by compensatory upregulation of other PIPs (Fig. 8, [28]). However, clear compensatory upregulation was not present in all knockout mutants (e.g., pip1;2, pip2;4, pip2;5, pip2;6) despite their significantly elevated RWC. Furthermore, changes in PIP expression in response to the lack of another isoform were only modest [28]. This suggests that the role of individual PIPs in regulating RWC may be relatively minor, but to establish this would require further research into its significance and specificity among plants.
Conclusion
Using knockout mutants lacking specific plasma membrane aquaporins, we were able to show that PIP1;1, PIP2;3 and PIP2;6 are permeable to H2O2 in planta and that transmembrane diffusion of H2O2 plays a physiologically relevant role in plant responses to oxidative stress. We found that PIP2;2 is involved in the regulation of root growth, specifically root length in A. thaliana. Since PIPs are physiologically relevant conduits for H2O2 diffusion into root cells, they are implicated in regulating the effects of H2O2 on plant growth. Further clarification of the roles of PIPs in H2O2 signalling and stress responses will require precise measurements of intracellular H2O2 concentrations as well as a better understanding of how PIP knockout mutations impact plant development.
Materials and methods
Plant material and hydrogen peroxide treatment
Seeds for the following single knock-out T-DNA mutants were obtained from the Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre (NASC – www.arabidopsis.org): PIP1;1 (N590778), PIP1;2 (N657533), PIP1;3 (N551107), PIP2;2 (N871747), PIP2;3 (N617876), PIP2;4 (N105980), PIP2;5 (N117303) and PIP2;6 (N573519). The correct T-DNA insertion of all plant lines was confirmed by PCR using the primers listed in Supplementary Table S3 of Additional file 2 and only plants homozygous for the knock-out mutation were used to produce a seeds stock. Double and triple mutants (pip2;2 × 2;4, pip2;4 × 2;5, pip2;2 × 2;4 × 2;5) were created by crossing and homozygosity confirmed by PCR [28].
Seeds were sown in horticultural soil and kept at 4 °C for four days before being transferred to a controlled-environment growth room with a photoperiod of 12 h, photosynthetically active radiation 350 µmol m−2 s−1 (Philips 86 W 96in T8 High Output Neutral White Fluorescent Tube, F96T8/TL835/HO/PLUS ALTO, USA), 23 °C/18 °C day/night temperatures and ≈30% daytime relative humidity. Three days after germination, seedlings were transplanted into 8 × 8 cm pots (one plant/pot) and grown for another 10 days before washing their roots and transferring to a hydroponic system in the same growth room. The hydroponic system consisted of 4 L-containers with aerated nutrient solution containing 1.25 mM KNO3, 1.5 mM Ca(NO3)2, 0.75 mM MgSO4, 0.5 mM KH2PO4, 50 mM H3BO3, 10 mM MnCl, 2 mM ZnSO4, 1.5 mM CuSO4, 75 µM (NH4)2MoO4, and 74 mM Fe-EDTA. The solution was renewed every three days.
To begin the treatment, H2O2 was applied to the nutrient solution to yield a final concentration of 1 mM H2O2. An exogenous concentration of 1 mM H2O2 has been reported to inhibit A. thaliana growth [35] and was thus chosen as the upper limit for all our experiments. It has to be noted that H2O2 is unstable and degrades, resulting in lower average concentrations over the course of the treatment [27]. Plants designated for biomass measurements (8–10 plants per line and treatment) were three weeks old at the beginning of the H2O2 treatment and were harvested nine days later. Gas exchange measurements required slightly larger plants (6 per line and treatment) and, therefore, these measurements were carried out with 31-day-old plants treated with 1 mM H2O2 for one and three days.
For root system analysis, the plants were grown on square petri dishes containing 0.7% agarose supplemented with full-strength Murashige and Skoog medium (MS) [44] and 1,5% sucrose. For the treatment, H2O2 was added into the agar medium to yield final concentrations of 0.25 mM and 0.5 mM. These concentrations were chosen based on a preliminary experiment (not included in the results presented here) during which we observed that at concentrations of 0.75 mM and above, root growth ceased entirely for all plant lines. Seeds of all plant lines were first germinated on agarose without H2O2 after stratification at 4 °C for 3 days. Three days after germination, 9 – 18 seedlings were transferred to H2O2-containing growth medium (treatment) or H2O2-free growth medium (control). The root system was scanned using a flat-bed scanner after 10 days of treatment and the images analysed with RootReader2D software [45] (http://www.plantmineralnutrition.net/software/rootreader2d/downloads/index.html).
Measurements of biomass and water content
Fresh weights, turgid weights, dry weights, and root:shoot (R:S) dry weight ratios were measured in plants growing in hydroponics and treated for 9 days with 1 mM H2O2. After drying the roots gently with paper towels, roots and shoots were weighed separately to obtain their respective fresh weights. Turgid weights were obtained after floating the shoots and roots on water overnight. They were then dried at 60 °C for two days and re-weighed to obtain their dry weights.
Relative water content was calculated separately for roots, shoots, and whole plants using the following formula:
where FW denotes fresh weight, DW dry weight and TW turgid weight.
Absolute water content (AWC) has been found to be linearly correlated with the leaf area under various treatments even when leaf morphology was altered [37] and was thus used as a proxy for leaf area in this study:
All numeric values for measurements of biomass and water content as well as statistically significant differences between mutant plants and treatments are shown in Supplementary Table S4 of Additional file 2.
Gene expression
Transcript abundance was measured by qRT-PCR for pip1;1, pip1;2, pip1;3, pip2;3 and pip2;6 grown under ideal conditions. The gene expression for the remaining plant lines used in this study has been reported earlier for the same growing conditions [28]. Twelve rosettes per genotype were harvested and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. For RNA extraction, three samples of the same genotype were combined and treated together, resulting in n = 4. RNA was extracted using the GeneJET Plant RNA Purification Mini Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions with the exception that the Plant RNA Lysis Solution was supplemented with β–mercaptoethanol instead of DTT. The quality and concentration of the extracted RNA was determined with an ND-1000 Spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher Scientific) and 1 µg of RNA was used for cDNA synthesis following DNase1 treatment. Maxima H Minus Reverse Transcriptase, oligo(dT) 19 and dNTP (ThermoFisher Scientific) were used in a 30 µl reaction volume for cDNA synthesis, which was then diluted to a final volume of 70 µl. 1 μl of cDNA was used for PCR in triplicate with 5 × HOT FIREPol EvaGreen qPCR Mix Plus (Solis BioDyne, Tartu, Estonia) using a CFX 384 Real-Time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). PIP-specific primers were taken from Alexandersson et al. 2010 [46]. Ct values were converted using the ΔΔCt-method using all three reference genes listed in Table S5 of Additional file 2 and ln-transformed for statistical analysis.
Gas exchange measurements
Leaf-level gas exchange was measured for one leaf per plant using the portable photosynthesis system LI6400XT infra-red gas analyser (IGRA) equipped with a fluorescence chamber (LI-COR Biosciences, Nebraska, USA). The leaf area covering the chamber window was calculated as described in Israel et al. [28]. Measurements were carried out one and three days after the application of the H2O2 treatment, when plants were 32 and 34 days old respectively. On each measurement day, a total of six replicate plants were measured for every plant line and treatment. The following settings were used during all measurements: flow 300 µmol s−1, Tblock 25 °C, PAR 1500 µmol m−2 s−1 (10% blue), leaf fan fast, CO2R 400 µmol mol−1.
Data analysis
ANOVAs were conducted in R (package Deducer) using a linear model with plant genotype and the measured variable as the factors to compare the means of all measured variables for the mutant lines to the WT. The number of replicates was n = 4 for gene expression analysis, n = 6 for gas exchange measurements, n = 9 – 18 for root system architecture and n = 8 – 10 for biomass and water content measurements.
The correlation between the treatment effect on dry mass and RWC was carried out in R using two-sided Pearson’s correlation with 95% confidence interval. The number of replicates included in the correlation was n = 97 for roots and n = 101 for shoots.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Supplementary Figure S1. Root system architecture. Given are means with SE for n = 9 - 18. Letters indicate statistically significant differences betwween the plant lines under control conditions. For reasons of clarity, letters indicating significant differences for the H2O2 treatments have been omitted from the graph but can be found in Supplementary Table S2. Asterisk indicate statiscally significant effects of the treatment on a plant line. Different numbers of asterisks indicate a significant effect by the treatment, while columns with no asterisk do not differ from either of the treatments. A) Total root length (taller and light columns) and primary root length (shorter and darker columns) with SE for all lines and treatments. Total as well as primary root length were measured as the growth after the onset of the treatment. B) Length of secondary roots (taller and lighter columns) and tertiary roots (shorter and darker columns) SE for all lines and treatments. C) Number of secondary roots (taller and lighter columns) tertiary roots (shorter and darker columns) for all lines and treatments with SE.
Additional file 2: Table S1. Gas exchange, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. TableS2. Root system architecture, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. Table S3. Primers used to genotype the stock lines obtained from NASC. Table S4. Biomass and water content, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. Table S5. Primers for PIP and reference genes used in the qRT-PCR.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mikael Brosché for providing the double and triple mutants.
Abbreviations
- ar/R
Aromatic/arginine
- AWC
Absolute water content
- DW
Dry weight
- FW
Fresh weight
- Lpr
Root hydraulic conductivity
- PAR
Photosynthetically active radiation
- PIP
Plasma membrane intrinsic protein
- qRT-PCR
Quantitative real-time PCR
- RWC
Relative water content
- WT
Wild type
Author’s contributions
DI, TMR and JJZ conceived the study; DI, JJZ and SHL designed and performed all experiments; DI analysed the data; DI, TMR, SHL, and JZZ interpreted the results DI wrote the first draft of the paper, which was revised by TMR and JZZ. All authors have read and approved the manuscript for publication. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
DI was supported by the Finnish Cultural Foundation Grant 00180402 and 00160334, and by the University of Helsinki YEB Doctoral School, Thesis Completion Grant. TMR was funded by the Academy of Finland decision #324555. The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests. JZ is a member of the BMC Plant Biology editorial board.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Thomas Matthew Robson and Janusz Jerzy Zwiazek are senior author contribution.
Contributor Information
David Israel, Email: david.israel@helsinki.fi.
Seong Hee Lee, Email: seongl@ualberta.ca.
Thomas Matthew Robson, Email: matthew.robson@helsinki.fi.
Janusz Jerzy Zwiazek, Email: jzwiazek@ualberta.ca.
References
- 1.Hooijmaijers C, Rhee JY, Kwak KJ, Chung GC, Horie T, Katsuhara M, et al. Hydrogen peroxide permeability of plasma membrane aquaporins of Arabidopsis thaliana. J Plant Res. 2012;125(1):147–153. doi: 10.1007/s10265-011-0413-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dynowski M, Schaaf G, Loque D, Moran O, Ludewig U. Plant plasma membrane water channels conduct the signalling molecule H2O2. Biochem J. 2008;414(1):53–61. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Groszmann M, De Rosa A, Chen W, Qiu J, McGaughey SA, Byrt CS, et al. Permeability profiling of all 13 Arabidopsis PIP aquaporins using a high throughput yeast approach. BioRXiv. 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Kaurilind E, Xu E, Brosche M. A genetic framework for H2O2 induced cell death in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:837. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1964-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Peleg-Grossman S, Volpin H, Levine A. Root hair curling and Rhizobium infection in Medicago truncatula are mediated by phosphatidylinositide-regulated endocytosis and reactive oxygen species. J Exp Bot. 2007;58(7):1637–1649. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erm013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yao Y, Liu X, Li Z, Ma X, Rennenberg H, Wang X, et al. Drought-induced H2O2 accumulation in subsidiary cells is involved in regulatory signaling of stomatal closure in maize leaves. Planta. 2013;238(1):217–227. doi: 10.1007/s00425-013-1886-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tian S, Wang X, Li P, Wang H, Ji H, Xie J, et al. Plant Aquaporin AtPIP1;4 Links Apoplastic H2O2 Induction to Disease Immunity Pathways. Plant Physiol. 2016;171(3):1635–1650. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bienert GP, Chaumont F. Aquaporin-facilitated transmembrane diffusion of hydrogen peroxide. Bba-Gen Subjects. 2014;1840(5):1596–1604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bienert GP, Moller AL, Kristiansen KA, Schulz A, Moller IM, Schjoerring JK, et al. Specific aquaporins facilitate the diffusion of hydrogen peroxide across membranes. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(2):1183–1192. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603761200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Smirnoff N, Arnaud D. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism and functions in plants. New Phytol. 2019;221(3):1197–1214. doi: 10.1111/nph.15488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang H, Schoebel S, Schmitz F, Dong H, Hedfalk K. Characterization of aquaporin-driven hydrogen peroxide transport. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020;1862(2):183065. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.183065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tornroth-Horsefield S, Hedfalk K, Fischer G, Lindkvist-Petersson K, Neutze R. Structural insights into eukaryotic aquaporin regulation. Febs Lett. 2010;584(12):2580–2588. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kitchen P, Salman MM, Pickel SU, Jennings J, Tornroth-Horsefield S, Conner MT, et al. Water channel pore size determines exclusion properties but not solute selectivity. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):20369. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56814-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wallace IS, Roberts DM. Homology modeling of representative subfamilies of Arabidopsis major intrinsic proteins. Classification based on the aromatic/arginine selectivity filter. Plant Physiol. 2004;135(2):1059–68. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.033415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berny MC, Gilis D, Rooman M, Chaumont F. Single mutations in the transmembrane domains of maize plasma membrane aquaporins affect the activity of monomers within a heterotetramer. Mol Plant. 2016;9(7):986–1003. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2016.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zelazny E, Borst JW, Muylaert M, Batoko H, Hemminga MA, Chaumont F. FRET imaging in living maize cells reveals that plasma membrane aquaporins interact to regulate their subcellular localization. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(30):12359–12364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701180104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Otto B, Uehlein N, Sdorra S, Fischer M, Ayaz M, Belastegui-Macadam X, et al. Aquaporin tetramer composition modifies the function of tobacco aquaporins. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(41):31253–31260. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Maurel C. Plant aquaporins: novel functions and regulation properties. Febs Lett. 2007;581(12):2227–2236. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Santoni V, Verdoucq L, Sommerer N, Vinh J, Pflieger D, Maurel C. Methylation of aquaporins in plant plasma membrane. Biochem J. 2006;400(1):189–197. doi: 10.1042/BJ20060569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Johansson I, Karlsson M, Shukla VK, Chrispeels MJ, Larsson C, Kjellbom P. Water transport activity of the plasma membrane aquaporin PM28A is regulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell. 1998;10(3):451–459. doi: 10.1105/tpc.10.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gambetta GA, Fei J, Rost TL, Knipfer T, Matthews MA, Shackel KA, et al. Water uptake along the length of grapevine fine roots: developmental anatomy, tissue-specific aquaporin expression, and pathways of water transport. Plant Physiol. 2013;163(3):1254–1265. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.221283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kim YX, Steudle E. Gating of aquaporins by light and reactive oxygen species in leaf parenchyma cells of the midrib of Zea mays. J Exp Bot. 2009;60(2):547–556. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee SH, Singh AP, Chung GC. Rapid accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in cucumber roots due to exposure to low temperature appears to mediate decreases in water transport. J Exp Bot. 2004;55(403):1733–1741. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erh189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Boursiac Y, Boudet J, Postaire O, Luu DT, Tournaire-Roux C, Maurel C. Stimulus-induced downregulation of root water transport involves reactive oxygen species-activated cell signalling and plasma membrane intrinsic protein internalization. Plant J. 2008;56(2):207–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Prak S, Hem S, Boudet J, Viennois G, Sommerer N, Rossignol M, et al. Multiple phosphorylations in the C-terminal tail of plant plasma membrane aquaporins: role in subcellular trafficking of AtPIP2;1 in response to salt stress. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008;7(6):1019–1030. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M700566-MCP200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ehlert C, Maurel C, Tardieu F, Simonneau T. Aquaporin-mediated reduction in maize root hydraulic conductivity impacts cell turgor and leaf elongation even without changing transpiration. Plant Physiol. 2009;150(2):1093–1104. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.131458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Benabdellah K, Ruiz-Lozano JM, Aroca R. Hydrogen peroxide effects on root hydraulic properties and plasma membrane aquaporin regulation in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Mol Biol. 2009;70(6):647–661. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Israel D, Khan S, Warren CR, Zwiazek JJ, Robson TM. The contribution of PIP2-type aquaporins to photosynthetic response to increased vapour pressure deficit. J Exp Bot. 2021;72(13):5066–5078. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Javot H, Lauvergeat V, Santoni V, Martin-Laurent F, Guclu J, Vinh J, et al. Role of a single aquaporin isoform in root water uptake. Plant Cell. 2003;15(2):509–522. doi: 10.1105/tpc.008888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kaldenhoff R, Grote K, Zhu JJ, Zimmermann U. Significance of plasmalemma aquaporins for water-transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998;14(1):121–128. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1998.00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lopez F, Bousser A, Sissoeff I, Gaspar M, Lachaise B, Hoarau J, et al. Diurnal regulation of water transport and aquaporin gene expression in maize roots: contribution of PIP2 proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003;44(12):1384–1395. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcg168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Boursiac Y, Chen S, Luu DT, Sorieul M, van den Dries N, Maurel C. Early effects of salinity on water transport in Arabidopsis roots. molecular and cellular features of aquaporin expression. Plant Physiol. 2005;139(2):790–805. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.065029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Takase T, Ishikawa H, Murakami H, Kikuchi J, Sato-Nara K, Suzuki H. The circadian clock modulates water dynamics and aquaporin expression in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011;52(2):373–383. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcq198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wudick MM, Li X, Valentini V, Geldner N, Chory J, Lin J, et al. Subcellular redistribution of root aquaporins induced by hydrogen peroxide. Mol Plant. 2015;8(7):1103–1114. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2015.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Claeys H, Van Landeghem S, Dubois M, Maleux K, Inze D. What is stress? dose-response effects in commonly used in vitro stress assays. Plant Physiol. 2014;165(2):519–527. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.234641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zimmermann HM, Steudle E. Apoplastic transport across young maize roots: effect of the exodermis. Planta. 1998;206:7–19. doi: 10.1007/s004250050368. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hughes AP, Cockshull KE, Heath OVS. Leaf area and absolute leaf water content. Ann Bot. 1970;34:259–265. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a084366. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Li L, Wang H, Gago J, Cui H, Qian Z, Kodama N, et al. Harpin Hpa1 Interacts with Aquaporin PIP1;4 to Promote the Substrate Transport and Photosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:17207. doi: 10.1038/srep17207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Postaire O, Tournaire-Roux C, Grondin A, Boursiac Y, Morillon R, Schaffner AR, et al. A PIP1 aquaporin contributes to hydrostatic pressure-induced water transport in both the root and rosette of arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2010;152(3):1418–1430. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.145326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Peret B, Li G, Zhao J, Band LR, Voss U, Postaire O, et al. Auxin regulates aquaporin function to facilitate lateral root emergence. Nat Cell Biol. 2012;14(10):991–998. doi: 10.1038/ncb2573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Da Ines O, Graf W, Franck KI, Albert A, Winkler JB, Scherb H, et al. Kinetic analyses of plant water relocation using deuterium as tracer - reduced water flux of Arabidopsis pip2 aquaporin knockout mutants. Plant Biol. 2010;12:129–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aroca R, Amodeo G, Fernandez-Illescas S, Herman EM, Chaumont F, Chrispeels MJ. The role of aquaporins and membrane damage in chilling and hydrogen peroxide induced changes in the hydraulic conductance of maize roots. Plant Physiol. 2005;137(1):341–353. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.051045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kromdijk J, Glowacka K, Long SP. Photosynthetic efficiency and mesophyll conductance are unaffected in Arabidopsis thaliana aquaporin knock-out lines. J Exp Bot. 2020;71(1):318–329. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Murashige T, Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plantarum. 1962;15(3):473–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Clark RT, Famoso AN, Zhao K, Shaff JE, Craft EJ, Bustamante CD, et al. High-throughput two-dimensional root system phenotyping platform facilitates genetic analysis of root growth and development. Plant Cell Environ. 2013;36(2):454–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Alexandersson E, Danielson JA, Rade J, Moparthi VK, Fontes M, Kjellbom P, et al. Transcriptional regulation of aquaporins in accessions of Arabidopsis in response to drought stress. Plant J. 2010;61(4):650–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.04087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Supplementary Figure S1. Root system architecture. Given are means with SE for n = 9 - 18. Letters indicate statistically significant differences betwween the plant lines under control conditions. For reasons of clarity, letters indicating significant differences for the H2O2 treatments have been omitted from the graph but can be found in Supplementary Table S2. Asterisk indicate statiscally significant effects of the treatment on a plant line. Different numbers of asterisks indicate a significant effect by the treatment, while columns with no asterisk do not differ from either of the treatments. A) Total root length (taller and light columns) and primary root length (shorter and darker columns) with SE for all lines and treatments. Total as well as primary root length were measured as the growth after the onset of the treatment. B) Length of secondary roots (taller and lighter columns) and tertiary roots (shorter and darker columns) SE for all lines and treatments. C) Number of secondary roots (taller and lighter columns) tertiary roots (shorter and darker columns) for all lines and treatments with SE.
Additional file 2: Table S1. Gas exchange, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. TableS2. Root system architecture, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. Table S3. Primers used to genotype the stock lines obtained from NASC. Table S4. Biomass and water content, means with SE, in bold significant differences compared to WT. Table S5. Primers for PIP and reference genes used in the qRT-PCR.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.