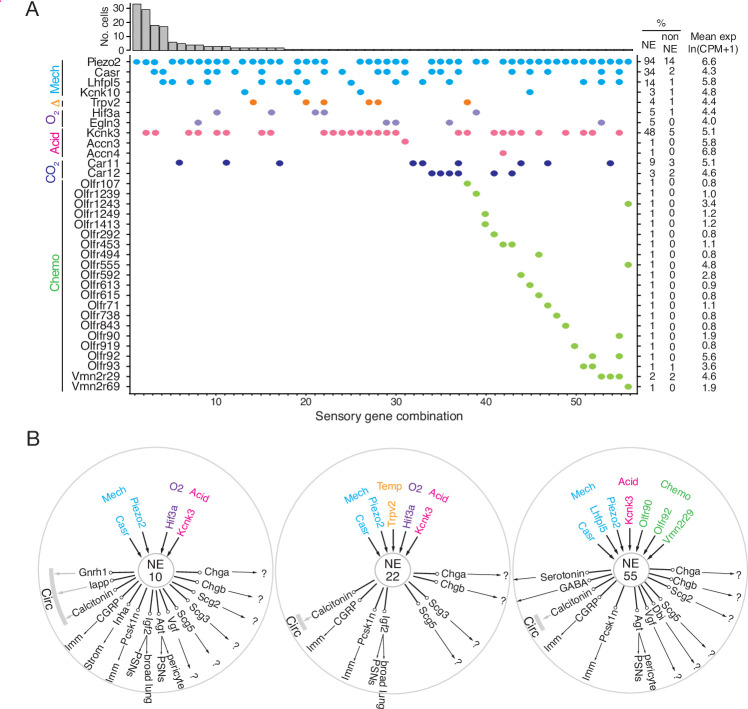
Figure 5. Patterns of sensory gene expression in individual PNECs.
(A) Patterns of expression from scRNA-seq profiles of sensory genes (colored dots, expressed genes) in individual PNECs (n=176). Histogram shows number of PNECs observed with the pattern of sensory gene expression below it. Values at right are percent of PNECs (NE) and other (non-NE) profiled cells that express the gene and the mean expression level for expressing PNECs. Sensory genes are grouped by modality: mechanosensing (Mech); thermosensing (Δ); oxygen sensing (O2); acid-sensing (Acid); CO2-sensing, carbonic anhydrases (CO2), chemosensing (Chemo). Note the 56 different combinations of expressed sensory genes, with most PNECs predicted to be multimodal because they express more than one class of sensor. (B) Schematics of sensor and signal genes expressed by three individual PNECs. Number in center indicates sensory gene combination in panel A. Genes above number are expressed sensory genes, and genes below number are expressed signal genes with arrows indicating lung targets (cells that express receptor) or signals without identified lung targets that may enter circulation (circ) to target other organs.?, signals without known receptors. Imm, multiple immune populations; PSN, pulmonary sensory neurons.