Abstract
Aims
The aim of this study was to report the 30-day technical and clinical success with endovascular repair using the ultra-low-profile Ovation stent graft in patients judged to be outside the instructions for use (IFU) for conventional endografts, while amenable to treatment within the IFU for Ovation.
Methods and results
One hundred and twenty-two patients (78.65±7.67 years; 111 male) were enrolled. Patients were evaluated as being outside the IFU for standard endografts because of the absence of a suitable proximal aortic neck in 109 cases (89.3%), of inadequate access vessels in 13 (10.7%), or both in 111 (90.9%). Mean aneurysm (abdominal aortic aneurysm [AAA]) diameter was 52.96±10.1 mm; mean aortic neck length was 7.75±6.05 mm. Technical success (98.4%) was achieved in all but two patients due to a type Ia endoleak. At completion angiography, 15 (12.3%) patients presented a type II endoleak. All patients underwent 30-day follow-up. Primary clinical success at one month was 96.8%, assisted clinical success 98.4%. There were no type I endoleaks, while 12 (9.8%) type II endoleaks were still evident, in the absence of sac expansions. Two patients (1.6%) presented an asymptomatic limb occlusion.
Conclusions
Our experience suggests that, in a selected population of patients with challenging anatomy outside the IFU for conventional endografts, endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) using the Ovation stent graft can be performed safely with satisfactory immediate outcomes.
Introduction
Endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) has become the standard of care for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) in patients presenting with standard anatomies1,2. Nowadays, performing EVAR outside the devices’ specific instructions for use (IFU), particularly in the presence of a so-called “challenging neck”3, yields a not negligible rate of immediate complications and reinterventions4,5. Of note, any differences in outcome between patients presenting with or without a challenging anatomy were lost during follow-up6. Consequently, several different technical solutions, such as parallel grafts, fenestrated or branched devices, have been developed as an alternative to standard EVAR grafts in patients with a “challenging neck”. However, all those solutions present a relevant risk of reintervention due to branch-related complications7.
In recent years, a new sealing concept based on polymer has become available for the treatment of AAA, and two devices have become available, the Ovation™ stent graft8,9, and Nellix™10 (both from Endologix Inc., Irvine, CA, USA).
The Ovation endograft in particular represents a new technical step in EVAR8,9, separating fixation from sealing. It seems to increase the range of AAAs suitable for standard EVAR procedures, as reported in several, although limited, series11,12,13 (Supplementary Appendix 1).
To confirm the results in a larger, multicentre, and coordinated series, a new physician-initiated study has been designed – Expanding Indications for Treatment with Standard EVAR in Patients with Challenging Anatomies, a Multi-Centric Prospective Evaluation (EXTREME) – aiming to report technical and clinical success of EVAR using the Ovation platform in patients judged to be outside the IFU for conventional bifurcated endografts, while amenable to treatment inside the IFU for the Ovation stent graft. In the present paper, 30-day technical success and clinical success are reported14.
Methods and material
From March 2017 to March 2018 investigators enrolled all consecutive patients matching the inclusion criteria for the study. Clinical and anatomical data are collected in an anonymised prospectively compiled database including baseline, hospital discharge, 1-month, and 12-month evaluations.
The inclusion criterion for the study was AAA requiring elective treatment in patients judged to be outside of the IFU for commercially available bifurcated endografts, while inside the IFU for the Ovation.
According to the manufacturer’s IFU, anatomical requirements, evaluated on preoperative computed tomography angiography (CTA), were: proximal aortic landing zone presenting an inner wall diameter of no less than 16 mm and no greater than 30 mm at 13 mm below the inferior renal artery (IR), and an aortic angle of ≤60° if the proximal neck is ≥10 mm and ≤45° if the proximal neck is <10 mm; presence of an iliac landing zone at least 10 mm in length, and with an inner wall diameter of no less than 8 mm and no greater than 25 mm; iliac and femoral access compatible with vascular access techniques, devices, and accessories.
This study complied with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and, when requested, the data collection and acquisition were approved by the local ethics committee and respective institutional review boards of each site. Informed consent from the patients was obtained for the procedures but was not required for the study.
Endovascular procedures were performed by vascular surgeons in the operating theatre equipped with a portable fluoroscopy unit (Supplementary Appendix 2).
Albeit local anaesthesia was generally preferred for frail patients15, the centres involved were left free to choose between general and local anaesthesia.
All patients were monitored postoperatively with clinical evaluation and duplex ultrasound examination before discharge and at one month. CTA was performed per protocol in all enrolled patients one month after the index EVAR procedure.
In all cases, the landing distance, defined as the distance between the lowest renal artery ostium and the endograft proximal markers, was noted. Complications that occurred during and after the EVAR procedure were classified as per the reporting standards for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair16.
Clinical endpoints were freedom from AAA-related mortality, procedure-related serious and non-serious adverse events, AAA enlargement (≥5 mm), and AAA rupture. Technical endpoints were procedural success (complete delivery and deployment of one aortic body and two iliac limbs), access-related vascular complications, freedom from type I and III endoleaks, freedom from graft migration (≥5 mm), conversion to open repair, and all AAA-related secondary interventions.
Clinical success is defined as successful deployment of the endovascular device at the intended location without death as a result of aneurysm-related treatment, type I or III endoleak, graft infection or thrombosis, aneurysm expansion (diameter >5 mm, or volume >5%), aneurysm rupture, or conversion to open repair.
An AAA-related adverse event is defined as a composite of the following: direct (type I or III) or undetermined type endoleaks, aneurysm sac growth, migration, device integrity failure, AAA-related death, late post-implantation AAA rupture or any AAA-related secondary intervention.
Secondary interventions are considered if performed to resolve or prevent a possible complication. These include endovascular procedures (proximal cuff and stent implant, coil or glue embolisation, distal extension implant, catheter-based thrombolysis, iliac angioplasty) as well as surgical procedures (balloon thrombectomy, femoro-femoral crossover, conversion to open repair, open or laparoscopic ligation of collaterals).
To avoid any potential interpretation bias, preoperative, and postoperative CTA data were collected and sent for blind reading by a centralised core laboratory (Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, “Sapienza” University of Rome) using dedicated software with multiplanar and volume reconstructions (OsiriX MD; Pixmeo SARL, Bernex, Switzerland) on a Mac OS computer (Apple Inc., Cupertino, CA, USA)17. AAA diameter, infrarenal diameter, IR+13 diameter, aortic neck length and shape, aortic neck thrombosis and calcification, α and β angles, aortic bifurcation diameter, area, thrombosis, and calcification were noted and evaluated as potentially influencing the outcome. Iliac artery anatomical features are common iliac artery (CIA) and external iliac artery (EIA) diameters, iliac access thrombosis/calcification, and iliac tortuosity ratio (ITR)18. For both the aortic neck and the iliac access vessels, calcification and thrombosis were considered as “severe”, and potentially influencing results, when accounting for >50% of circumferential involvement in an axial projection.
All CTAs were independently evaluated by two vascular surgeons (P. Sirignano, S. Cuozzo). Disagreements were discussed and resolved by consensus.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Continuous data are reported as mean, median, standard deviation and range, for continuous variables. Frequency and percentages are reported for categorical variables.
Results
One hundred and thirty-four patients were screened; 122 (mean age, 78.65±7.67 years; 111 male) were treated with EVAR using the Ovation stent graft system at 16 European vascular centres from a total of 527 EVAR procedures performed (median 32.9 patients/year per centre) during the entire study period. Demographic data and risk factors for all enrolled patients are described in Supplementary Table 1. Patients who were screened but not enrolled were treated by different surgical or endovascular (chimney EVAR, or fenestrated endograft) procedures.
Detailed anatomical features of all patients enrolled in the present series are reported in Table 1 and Supplementary Appendix 3.
Table 1. Preoperative anatomical features of abdominal aortic aneurysms treated in the present series.
| Total patients 122 | |
| AAA max diameter, mean±SD (range) | 52.96±10.1 mm (33-102) |
| IR diameter, mean±SD (range) | 21.96±3.46 mm (15.9-32) |
| IR+13 diameter, mean±SD (range) | 24.24±3.31 mm (18-30) |
| IR+16 diameter, mean±SD (range) | 24.67±4.72 mm (17-33) |
| Aortic neck length, mean±SD (range) | 7.75±6.05 mm (1-29.5) |
| Aortic neck length <5 mm (n; %) | 35; 28.7 |
| Aortic neck length 5-10 mm (n; %) | 51; 41.8 |
| Aortic neck length >10 mm (n; %) | 36; 29.5 |
| Cylindrical aortic neck shape (n; %) | 41; 33.60 |
| Aortic neck thrombosis/calcification (n; %) | 73; 59.83 |
| α angle, mean±SD (range) | 17.73±11.58° (2-63) |
| β angle, mean±SD (range) | 21.39±18.99° (2-60) |
| Aortic bifurcation diameter, mean±SD (range) | 24.14±8.62 mm (8.1-57.6) |
| Aortic bifurcation area, mean±SD (range) | 5.69±4.54 mm2 (1.1-25.3) |
| Aortic bifurcation area thrombosis/calcification (n; %) | 64; 52.45 |
| Right CIA diameter, mean±SD (range) | 14.23±9.77 mm (6-90) |
| Right CIA diameter >20 mm (n; %) | 9; 7.37 |
| Right CIA diameter 10-20 mm (n; %) | 90; 73.77 |
| Right CIA diameter <10 mm (n; %) | 23; 18.85 |
| Left CIA diameter, mean±SD (range) | 13.61±8.73 mm (4-77) |
| Left CIA diameter >20 mm (n; %) | 20; 16.39 |
| Left CIA diameter 10-20 mm (n; %) | 86; 70.49 |
| Left CIA diameter <10 mm (n; %) | 29; 23.77 |
| Right EIA diameter, mean±SD (range) | 7.6±2.07 mm (4.1-7.7) |
| Right EIA diameter <10 mm (n; %) | 106; 86.88 |
| Right EIA diameter <7 mm (n; %) | 32; 26.22 |
| Left EIA diameter, mean±SD (range) | 7.33±1.59 mm (2-11.1) |
| Left EIA diameter <10 mm (n; %) | 114; 93.44 |
| Left EIA diameter <7 mm (n; %) | 42; 34.42 |
| Iliac access thrombosis/calcification (n; %) | 52; 42.66 |
| Right iliac access ITR, mean±SD (range) | 0.76±0.09 (0.5-0.96) |
| Left iliac access ITR, mean±SD (range) | 0.8±0.1 (0.5-0.98) |
| AAA: abdominal aortic aneurysm; CIA: common iliac artery; EIA: external iliac artery; IR: infrarenal; ITR: iliac tortuosity ratio | |
All procedures in this series were performed by highly skilled vascular surgeons with an experience of at least 30 Ovation stent-graft implantations. Percutaneous access was used in 101 (82.8%) patients, and local anaesthesia in 109 (89.3%). Mean endograft oversizing was 19.59±5.68% (range 8.6-36%). Mean operative time was 64±26 minutes and contrast amount 76±18 ml. No patient required postoperative intensive care unit stay; mean postoperative length of stay was 2.27±1.43 days (range 1-10).
Technical success was achieved in all but two patients (1.6%) due to a type Ia endoleak, and in one case (0.8%) a partial polymer leak was noted during ring inflation without evidence of endoleak. At completion angiography, 15 (12.3%) patients presented a type II endoleak. The patient with a polymer leak suffered a lumbar skin necrosis treated by vacuum-assisted therapy with complete healing at the one-month follow-up visit.
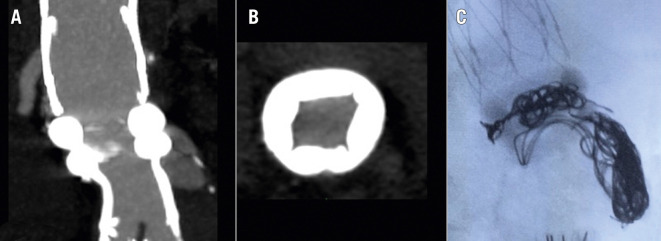
Regarding the two reported type Ia endoleaks, one case was secondary to infolding of the first ring (Figure 1A, Figure 1B) as a result of an excessive oversizing of the endograft (>30%), while in the other case the endoleak was due to an intraprocedural error, i.e., the endograft was released below the preoperatively evaluated sealing zone (at IR+18, instead of IR+13). Both type Ia endoleaks were successfully treated by endovascular coil embolisation during the same hospitalisation (Figure 1C) with complete aneurysm exclusion and absence of further complications.
Figure 1.
Type Ia endoleaks following EVAR procedure. A) Multiplanar reconstruction of the postoperative CTA showing a type Ia endoleak. B) Axial postoperative CTA image showing infolding of the proximal sealing ring due to excessive oversizing. C) Intraoperative lateral image with coils placed between the two rings, exactly where the infolding was responsible for the leakage.
All enrolled patients underwent a scheduled 30-day follow-up visit and CTA. Primary clinical success at one month was 96.8% (defined as the absence of aneurysm-related death, type I or III endoleak, graft infection or thrombosis, aneurysm expansion >5 mm, aneurysm rupture, or conversion to open repair). Assisted clinical success at one month was 98.4% (Table 2). Mean landing distance at postoperative CTA was 0.92±0.18 mm (range 0-5 mm).
Table 2. Primary and assisted clinical success at 1 month in the present series.
| Total patients 122 | |
| Primary clinical success (n; %) | 118; 96.8% |
| Aneurysm-related death | 0 |
| Type I or III endoleak* | 2; 1.6% |
| Aneurysm expansion* | 0 |
| Graft infection | 0 |
| Graft thrombosis* | 2; 1.6% |
| Conversion to open repair | 0 |
| Assisted primary clinical success (n; %) | 120; 98.4% |
| Aneurysm-related death | 0 |
| Type I or III endoleak* | 0 |
| Aneurysm expansion* | 0 |
| Graft infection | 0 |
| Graft thrombosis* | 2**; 1.6% |
| Conversion to open repair | 0 |
| * assessed by CT and/or ultrasound follow-up. ** asymptomatic iliac limb occlusion, medically managed. | |
There were no type I or III endoleaks, although 12 (9.8%) type II endoleaks were still evident, in the absence of sac expansions. Two patients (1.6%) presented an asymptomatic iliac limb occlusion, medically managed. No further complications, reinterventions or deaths were recorded at that time.
Discussion
Anatomic constraints represent the main exclusion criteria for EVAR in a real-world setting. However, with increasing operator experience, a tendency to push limits has become apparent and there are now data to indicate that EVAR may be safe even if the AAA configuration does not entirely fall within the pre-specified requirements of each endograft. Several reports suggesting a similar technical and clinical success rate between patients treated within or outside the endograft’s IFU have been published3,6,19,20. On the other hand, other authors have reported significantly inferior outcomes among patients treated outside the IFU. Sac enlargement and type Ia endoleak rates were both significantly related to adherence to device guidelines21,22,23,24. Indeed, patients with hostile anatomy were found to present a fourfold increased risk of developing type I endoleak and a ninefold increased risk of aneurysm-related mortality25.
Historically, irrespective of the type of endograft, EVAR eligibility has been considered for aortic neck length >15 mm, angulation <60° and diameter 18-30 mm, and a distal landing zone <20 mm in diameter with an access vessel diameter >7 mm. During the evolution from the first to the fourth generation of endografts, significant refinements have been introduced in order to accommodate a broader range of anatomies, for example a neck length of 10 mm, a juxtarenal angulation up to 90°, and adaptability to navigate vessels as narrow as 4.7 mm. Considering these parameters, suitability for EVAR has reportedly been extremely low26. A meta-analysis published by Ulug et al in 2017 evaluated the morphological eligibility for EVAR in 1,507 men and 400 women. The overall pooled proportion of eligible women was 34%, which was lower than that in men, estimated at 54%27. Sweet et al, examining >1,000 patients using the traditional criteria to define suitable anatomy, reported low rates of both men (32%) and women (12%) meeting all neck criteria and having adequate iliac lumen diameters28.
As mentioned above, the Ovation stent graft presents a unique design and concept, uncoupling the sealing and fixation modes of the device, and a very low profile29. Those differences increased eligibility rates remarkably compared with other commercially available endografts, as demonstrated by Kontopodis et al. In their retrospective analysis of 158 consecutive AAA patients treated with EVAR or open surgical repair, eligibility rates were significantly higher for the Ovation (72%) compared to the other endografts13. A high rate of eligibility was confirmed by data presented in our series: only 12 out of 134 patients evaluated were judged not to fit the Ovation IFU and were treated with different surgical or endovascular procedures. In the 122 treated patients, technical success was achieved in all but two patients. Assisted clinical success at one month was 98.4% in patients who were judged to be outside the IFU for standard endografts because of the absence of a suitable proximal aortic neck (89.3%), inadequate access vessels (10.7%), or both (90.9%). Our results in such a highly selected anatomically challenging population were consistent with those reported in a pivotal study30, confirming the initial hypothesis of the study. In the present series, two patients presented a type Ia endoleak (1.6%), both consequent to preprocedural or intraprocedural mistakes, while no type Ia endoleak but four undefined endoleaks (2.48%) were reported by Mehta et al in the pivotal study. The rates of iliac occlusion were similar (1.6% in the present study and 0.6% in the pivotal study). Notably, type II endoleak incidence was slightly lower in our series, i.e., 9.8% vs 25.46%30.
Regarding the two reported limb occlusions, core lab analysis was unable to identify a possible cause: limbs were implanted in relatively straight anatomies, in the absence of severe stenosis. Speculatively, both patients presented a chronic peripheral arterial disease that could have favoured the occlusions.
Moreover, the polymer-filled sealing rings (an exclusive characteristic of the Ovation stent graft) conform to patients’ proximal aortic neck anatomy, creating an uninterrupted concentric seal reminiscent of an O-ring or the gasket-like seals that have long been considered the standard in other sealing applications. Providing a simple, precise and reliable seal in a variety of applications and functions by introducing a calculated mechanical stress between the O-ring and the surface, the ring is in contact with a solution to prevent fluid or air from passing between two surfaces. Being cast in situ to form a custom-modelled O-ring seal at the margin of the AAA, the polymer guarantees high seal conformability on irregular surfaces, such as in the presence of calcium and thrombus28. This feature played a crucial role in treating AAA patients presenting an extremely short or even absent proximal aortic neck.
A previously published paper demonstrated that the filled polymer does not apply chronic outward force on the aorta, which is likely with other endografts that employ oversized, self-expanding stents to achieve sealing in the proximal aortic neck31, while the use of self-expanding stent grafts has been clearly related to neck progression because those grafts continue to expand until the nominal diameter is reached32, unless tissue resistance limits expansion33.
It is well known that when aortic neck dilation occurs it affects EVAR procedural outcomes in the midterm and long term34. Conversely, Ovation stent graft implantation has not been associated with this phenomenon and should be considered protective in midterm and long-term follow-up, as reported by de Donato et al31. This finding needs to be confirmed in our series of very selected, extremely challenging patients once 12-month CTA becomes available.
Limitations
The present study has several limitations. Firstly, it is a non-randomised study with a relatively small number of enrolled subjects. Furthermore, the procedures included in this cohort were performed by operators in an advanced phase of their learning curve, which could partially explain the small number of reinterventions in such a complex cohort of patients.
Despite the early results presented in this study demonstrating the safety and technical efficacy of the Ovation endografts implanted in patients not amenable to be treated with other standard devices within the IFU, we should admit that it is well known that the great majority of adverse events after EVAR occur in the midterm and long-term follow-up35. With the aim of confirming our initial findings, follow-up data collection and analysis are still ongoing.
Conclusions
Preliminary available data from this real-world multicentric study seem to confirm the hypothesis that AAA repair by EVAR with Ovation stent-graft implantation can be performed safely, even in extremely complex anatomies evaluated as being unfit for conventional stent grafts. Preliminary one-month data are promising, showing only a 1.6% rate of high flow proximal endoleak requiring endovascular reintervention and a very high assisted clinical success rate at one month. However, a longer follow-up is needed to confirm these initial findings.
Impact on daily practice
The present paper concerns a multicentre prospective non-randomised study. Our key finding was that endovascular treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms in 122 patients judged to be outside of the instructions for use (IFU) for conventional endografts, and amenable to treatment within the IFU for the Ovation stent graft resulted in 96.8% primary clinical success, and 98.4% assisted clinical success at one month. Data suggest that AAA repair by EVAR with Ovation stent-graft implantation can be performed safely even in extremely complex anatomies evaluated unfit for conventional stent grafts.
Appendix. Study collaborators
Federico Accrocca, MD; Department of Vascular Surgery, “Sant’Eugenio” Hospital, Rome, Italy. Stefano Bartoli, MD; Department of Vascular Surgery, “Sant’Eugenio” Hospital, Rome, Italy. Javier Martinez Gamez, MD; Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Hospital Universitario Virgen de la Victoria de Málaga, Malaga, Spain. Arnaldo Ippoliti, MD; Vascular Surgery Unit, Department of Biomedicine and Prevention, University of “Tor Vergata”, Rome, Italy. Gaetano La Barbera, MD; Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Ospedale Civico, Palermo, Italy. Massimo Lenti, MD; Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, University Hospital of Perugia, Perugia, Italy. Rafael Gomez Medialdea, MD; ClÃnica Vascular Francisco, Jaen, Spain. Claudio Novali, MD; Vascular Surgery Unit, Santa Croce and Carle Hospital, Cuneo, Italy. Manuel Rodriguez Pinero, MD; Angiology and Vascular Surgery, Hospital Universitario Puerta del Mar, Cádiz, Spain. Giovanni Pratesi, MD; Vascular Surgery Unit, Department of Biomedicine and Prevention, University of “Tor Vergata”, Rome, Italy. Carlo Rivellini, MD; Vascular Surgery Unit, Santa Croce and Carle Hospital, Cuneo, Italy. Andrea Siani, MD; Department of Vascular Surgery, “Sant’Eugenio” Hospital, Rome, Italy. Roberto Silingardi, MD; Department of Vascular Surgery, Ospedale Civile S. Agostino-Estense, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Modena, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, Modena, Italy. Francesco Spinelli, MD; Division of Vascular Surgery, Campus Bio-Medico University, Rome, Italy. Maurizio Taurino, MD; Department of Vascular Surgery, Sant’Andrea Hospital, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Supplementary data
Ovation stent graft characteristics.
Description of ovation stent graft.
Anatomical characteristics of patients included in present analysis.
Patient demographics, characteristics, and risk factors in the present series.
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest statement
The authors/study collaborators have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Abbreviations
- AAA
abdominal aortic aneurysm
- CIA
common iliac artery
- CTA
computed tomography angiography
- EIA
external iliac artery
- EVAR
endovascular aneurysm repair
- IFU
instructions for use
- IR
inferior renal artery
- ITR
iliac tortuosity ratio
Contributor Information
Pasqualino Sirignano, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery “Paride Stefanini”, Policlinico Umberto I of Rome, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Wassim Mansour, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery “Paride Stefanini”, Policlinico Umberto I of Rome, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Laura Capoccia, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery “Paride Stefanini”, Policlinico Umberto I of Rome, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Simone Cuozzo, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery “Paride Stefanini”, Policlinico Umberto I of Rome, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
Stefano Camparini, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Thoraco-Vascular Surgery, Azienda Ospedaliera Brotzu, Cagliari, Italy.
Gianmarco de Donato, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Medicine, Surgery, and Neuroscience, University of Siena, Siena, Italy.
Nicola Mangialardi, Department of Vascular Surgery, “San Camillo Forlanini” Hospital, Rome, Italy.
Sonia Ronchey, Department of Vascular Surgery, “San Filippo Neri” Hospital, Rome, Italy.
Francesco Talarico, Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Ospedale Civico, Palermo, Italy.
Carlo Setacci, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Medicine, Surgery, and Neuroscience, University of Siena, Siena, Italy.
Francesco Speziale, Vascular and Endovascular Surgery Unit, Department of Surgery “Paride Stefanini”, Policlinico Umberto I of Rome, “Sapienza” University of Rome, Rome, Italy.
References
- Carpenter JP, Baum RA, Barker CF, Golden MA, Mitchell ME, Velazquez OC, Fairman RM. Impact of exclusion criteria on patient selection for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2001;34:1050–4. doi: 10.1067/mva.2001.120037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi ET, Wyble CW, Rubin BG, Sanchez LA, Thompson RW, Flye MW, Sicard GA. Evolution of vascular fellowship training in the new era of endovascular techniques. J Vasc Surg. 2001;33:S106–10. doi: 10.1067/mva.2001.111675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setacci F, Sirignano P, de Donato G, Chisci E, Iacoponi F, Galzerano G, Palasciano G, Cappelli A, Setacci C. AAA with a challenging neck: early outcomes using the Endurant stent-graft system. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012;44:274–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2012.04.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moise MA, Woo EY, Velazquez OC, Fairman RM, Golden MA, Mitchell ME, Carpenter JP. Barriers to endovascular aortic aneurysm repair: past experience and implications for future device development. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2006;40:197–203. doi: 10.1177/153857440604000304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira-Pinto J, Oliveira N, Bastos-Gonçalves F, Hoeks S, VAN Rijn MJ, Ten Raa S, Mansilha A, Verhagen HJ. Long-term results of outside “instructions for use” EVAR. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2017;58:252–60. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.16.09830-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speziale F, Sirignano P, Setacci F, Menna D, Capoccia L, Mansour W, Galzerano G, Setacci C. Immediate and two-year outcomes after EVAR in “on-label” and “off-label” neck anatomies using different commercially available devices. Analysis of the experience of two Italian vascular centers. Ann Vasc Surg. 2014;28:1892–900. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.06.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastracci TM, Greenberg RK, Eagleton MJ, Hernandez AV. Durability of branches in branched and fenestrated endografts. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57:926–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.09.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulakakis KG, Dalainas I, Kakisis J, Giannakopoulos TG, Liapis CD. Current knowledge on EVAR with the ultra-low profile Ovation Abdominal Stent-graft System. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2012;53:427–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgakarakos E, Ioannou CV, Georgiadis GS, Storck M, Trellopoulos G, Koutsias S, Lazarides MK. The Ovation abdominal stent graft for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms: current evidence and future perspectives. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13:253–62. doi: 10.1586/17434440.2016.1147949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossetti B, Martinelli O, Ferri M, Silingardi R, Verzini F IRENE Group Investigators. Preliminary results of endovascular aneurysm sealing from the multicenter Italian Research on Nellix Endoprosthesis (IRENE) study. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:1397–403. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.09.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Donato G, Setacci F, Bresadola L, Castelli P, Chiesa R, Mangialardi N, Nano G, Setacci C TriVascular Ovation Italian Study (TOIS) Collaborators. Midterm Results of Proximal Aneurysm Sealing With the Ovation Stent-Graft According to On- vs Off-Label Use. J Endovasc Ther. 2017;24:191–7. doi: 10.1177/1526602816685581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirignano P, Capoccia L, Menna D, Mansour W, Speziale F. Pushing forward the limits of EVAR: new therapeutic solutions for extremely challenging AAAs using the Ovation Stent Graft. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2016;57:839–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontopodis N, Papadopoulos G, Galanakis N, Tsetis D, Ioannou CV. Improvement of patient eligibility with the use of new generation endografts for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms. A comparison study among currently used endografts and literature review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2017;14:245–50. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2017.1281738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirignano P, Mansour W, Capoccia L, Speziale F. Rationale for a new registry on EVAR: The EXTREME study. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 2017;21:7–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.07.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setacci C, Sirignano A, Ricci G, Spagnolo AG, Pugliese F, Speziale F. A new ethical and medico-legal issue: vascular surgery and the postoperative cognitive dysfunction. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2015;56:607–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaikof EL, Blankensteijn JD, Harris PL, White GH, Zarins CK, Bernhard VM, Matsumura JS, May J, Veith FJ, Fillinger MF, Rutherford RB, Kent KC Ad Hoc Committee for Standardized Reporting Practices in Vascular Surgery of The Society for Vascular Surgery/American Association for Vascular Surgery. Reporting standards for endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2002;35:1048–160. doi: 10.1067/mva.2002.123763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setacci F, Sirignano P, Cappelli A, Setacci C. The wonders of a newly available post-analysis CT software in the hands of vascular surgeons. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2012;43:404–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2011.11.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirignano P, Speziale F, Capoccia L, Menna D, Mansour W, Montelione N, Setacci F, Galzerano G, Setacci C. Iliac and femoro-popliteal arteries morphological CTA features as determinants of outcome after standard EVAR procedures. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2019;60:375–81. doi: 10.23736/S0021-9509.16.09509-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J, Tucker LY, Goodney P, Candell L, Hua H, Okuhn S, Hill B, Chang RW. Adherence to endovascular aortic aneurysm repair device instructions for use guidelines has no impact on outcomes. J Vasc Surg. 2015;61:1151–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.12.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckerman WE, Tadros RO, Faries PL, Torres M, Wengerter SP, Vouyouka AG, Lookstein RA, Marin ML. No major difference in outcomes for endovascular aneurysm repair stent grafts placed outside of instructions for use. J Vasc Surg. 2016;64:63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T, Tanaka S, Okadome J, Kyuragi R, Fukunaga R, Kawakubo E, Itoh H, Okazaki J, Shirabe K, Fukuda A, Maehara Y. Midterm outcomes of endovascular repair for abdominal aortic aneurysms with the on-label use compared with the off-label use of an endoprosthesis. Surg Today. 2015;45:880–5. doi: 10.1007/s00595-014-0978-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanzer A, Greenberg RK, Hevelone N, Robinson WP, Eslami MH, Goldberg RJ, Messina L. Predictors of abdominal aortic aneurysm sac enlargement after endovascular repair. Circulation. 2011;123:2848–55. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.014902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai M, Sato M, Sato H, Sakaguchi H, Tanaka F, Ikoma A, Sanda H, Nakata K, Minamiguchi H, Kawai N, Sonomura T, Nishimura Y, Okamura Y. Midterm results of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: comparison of instruction-for-use (IFU) cases and non-IFU cases. Jpn J Radiol. 2013;31:585–92. doi: 10.1007/s11604-013-0223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aburahma AF, Campbell JE, Mousa AY, Hass SM, Stone PA, Jain A, Nanjundappa A, Dean LS, Keiffer T, Habib J. Clinical outcomes for hostile versus favorable aortic neck anatomy in endovascular aortic aneurysm repair using modular devices. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou GA, Georgiadis GS, Antoniou SA, Kuhan G, Murray D. A meta-analysis of outcomes of endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in patients with hostile and friendly neck anatomy. J Vasc Surg. 2013;57:527–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.09.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkouri S, Martelli E, Gloviczki P, McKusick MA, Panneton JM, Andrews JC, Noel AA, Bower TC, Sullivan TM, Rowland C, Hoskin TL, Cherry KJ. Most patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm are not suitable for endovascular repair using currently approved bifurcated stent-grafts. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004;38:401–12. doi: 10.1177/153857440403800502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulug P, Sweeting MJ, von Allmen RS, Thompson SG, Powell JT SWAN collaborators. Morphological suitability for endovascular repair, non-intervention rates, and operative mortality in women and men assessed for intact abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: systematic reviews with meta-analysis. Lancet. 2017;389:2482–91. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30639-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet MP, Fillinger MF, Morrison TM, Abel D. The influence of gender and aortic aneurysm size on eligibility for endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54:931–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.02.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Donato G, Setacci F, Sirignano P, Galzerano G, Borrelli MP, di Marzo L, Setacci C. Ultralow profile Ovation device: is it the definitive solution for EVAR? J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 2014;55:33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta M, Valdés FE, Nolte T, Mishkel GJ, Jordan WD, Gray B, Eskandari MK, Botti C A Pivotal Clinical Study to Evaluate the Safety and Effectiveness of the Ovation Abdominal Stent Graft System Investigators. One-year outcomes from an international study of the Ovation Abdominal Stent Graft System for endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2014;59:65–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.06.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Donato G, Setacci F, Bresadola L, Castelli P, Chiesa R, Mangialardi N, Nano G, Setacci C TriVascular Ovation Italian Study. Aortic neck evolution after endovascular repair with TriVascular Ovation stent graft. J Vasc Surg. 2016;63:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.07.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan TS, Chuter TA, Reilly LM, Rapp JH, Hiramoto JS. Long-term follow-up of neck expansion after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. 2010;52:303–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.03.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May J, White GH, Ly CN, Jones MA, Harris JP. Endoluminal repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm prevents enlargement of the proximal neck: a 9-year life-table and 5-year longitudinal study. J Vasc Surg. 2003;37:86–90. doi: 10.1067/mva.2003.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillavou ED, Muluk S, Makaroun MS. Is neck dilatation after endovascular aneurysm repair graft dependent? Results of 4 US Phase II trials. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2005;39:47–54. doi: 10.1177/153857440503900105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederle FA, Kyriakides TC, Stroupe KT, Freischlag JA, Padberg FT Jr, Matsumura JS, Huo Z, Johnson GR OVER Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study Group. Open versus Endovascular Repair of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126–35. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1715955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Ovation stent graft characteristics.
Description of ovation stent graft.
Anatomical characteristics of patients included in present analysis.
Patient demographics, characteristics, and risk factors in the present series.