In the mitigation of ischaemic heart disease as the world’s greatest contributor to mortality, coronary vasomotor disorders (CVaD) remain frequently overlooked in their diagnosis and management. CVaD, consisting of vasospastic angina (VSA) and microvascular angina (MVA) as endotypes, are commonly found in 7-50% of patients with ischaemia with non-obstructive coronary arteries (INOCA), with a three-year major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE; death or myocardial infarction [MI]) rate of ~5-37%. The European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI) consensus document helped raise awareness of INOCA among clinicians and patients worldwide1. However, despite highlighting the critical role of coronary functional testing (CFT) in routine clinical practice, its application is still far from optimised. In this issue, Feenstra et al conducted a comprehensive review of various CFT diagnostic protocols for CVaD2.
Discrepancies in coronary vasomotor function testing protocols
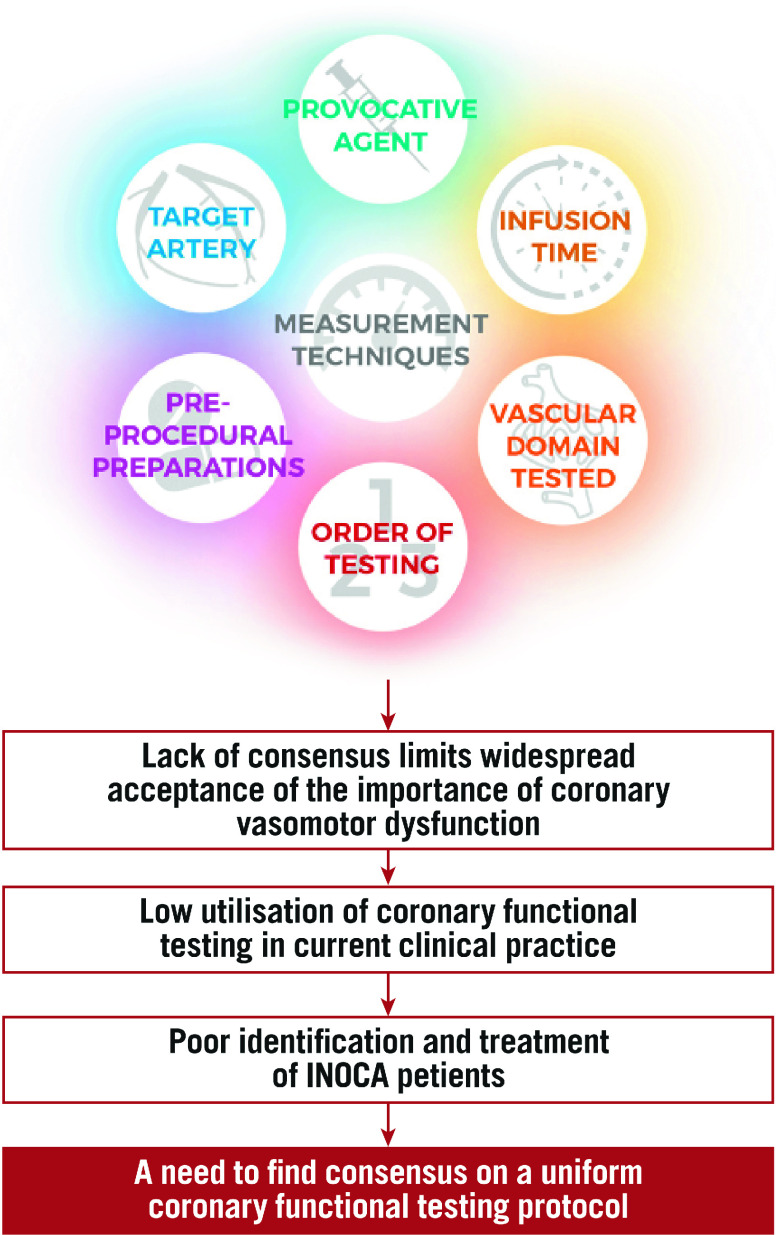
Feenstra et al noted significant variations in study protocols, including the aspect of vascular domains tested, the method of testing, and the techniques utilised to measure coronary function to determine the presence of CVaD (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Current challenges in coronary functional testing to diagnose coronary vasomotor disorders.
Firstly, the vascular domain being assessed may be differentiated into the epicardial vessels (>500 μm in diameter) and the microvasculature (<500 μm) which includes pre-arterioles, arterioles, capillaries, and venules. The authors emphasise the importance of distinguishing these domains, as diagnostic and treatment modalities require different approaches. Indeed, the Coronary Vasomotor Disorders International Study (COVADIS) group define VSA as angina precipitated by spasms of the epicardial domain, whereas MVA is defined as that caused by dysfunction in the microcirculation.
Secondly, how CFT is done also varies between protocols in terms of the agent used, injection time, dose, artery being catheterised, order of testing, and techniques for measurement. Acetylcholine (ACh) is the most commonly used pharmacological agent among the reviewed protocols for vasoconstriction assessment and for testing endothelial-dependent vasodilation when injected in low doses. The use of ACh is preferred over its substitute, ergonovine, as the latter is more likely to cause extended vasospasm. ACh protocols range from 20-second injections of incremental ACh doses up to 200 μg to trigger spasms, to suggesting 3-minute infusions of up to 44 μg of ACh—the latter mostly focusing on endothelial-dependent changes. Some protocols combine both by giving slow, low-dose infusions followed by rapid, high-dose boluses of ACh to gain insight into both endothelial-dependent changes and vasospasticity. The matter of dose is especially important as it will affect sensitivity and specificity—essentially a balancing act to find the right dose to best identify dysfunction without compromising on false positives.
A majority of protocols measure the entire left circulation by injecting the agent into the left main stem while some prefer to inject specifically into the left anterior descending artery to avoid spasm affecting a large area of the heart. In an effort to avoid complications affecting the atrioventricular node, most protocols also avoid testing the right coronary artery unless indicated. Although most protocols agree that vasoactive medications should be stopped before CFT, the range may vary from 24-72 hours prior to testing. Despite discrepancies in testing methods, the six protocols reviewed still agree upon a common diagnostic criteria for types of CVaD. For positive findings of epicardial vasoconstriction with ACh, all protocols follow the COVADIS definitions involving appearance of chest pain, ischaemic electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, and >90% constriction of vessels on angiography.
But why is there reluctance in vasomotor testing?
The use of ACh for the diagnosis of VSA and MVA is recommended by the 2019 European Society of Cardiology Chronic Coronary Syndromes (ESC CCS) clinical practice guidelines3, based on its demonstrated safety and efficacy4. There might be reluctance to use CFT due to fear of complications or lack of experience. However, previous studies have suggested that severe side effects such as an abrupt coronary flow obstruction, which can result in cardiac arrhythmias including ventricular fibrillation, occur in the same order of magnitude as described for diagnostic cardiac catheterisation. The most often reported side effect is ACh-induced bradycardia, occurring in 3.2% of cases. This is always transient, providing reassurance to clinicians in the use of ACh. Figure 2 summarises a stepwise algorithm for CFT that may be adopted in the cardiac catheterisation laboratory for the diagnosis of CVaD5. Informed consent should be obtained for unlicensed, parenteral use of ACh and it should only be administered by experienced interventional cardiologists.
Figure 2. Proposed algorithm for CFT to diagnose coronary vasomotor disorder.
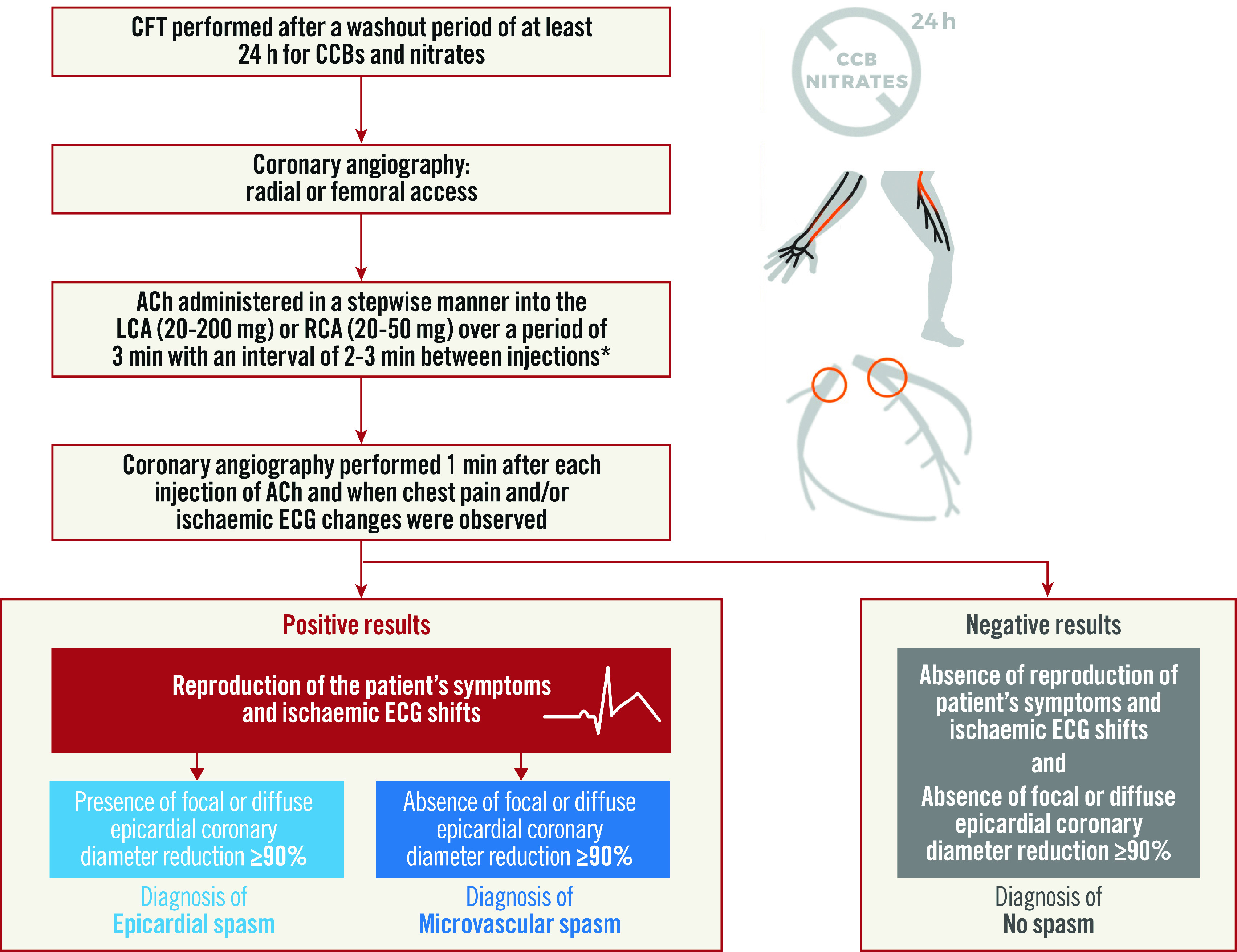
*some centres administer over 20 seconds. CCB: calcium channel blocker; CFT: coronary functional testing; ECG: electrocardiogram; LCA: left coronary atery; RCA: right coronary artery
Conclusion
Despite being safe, CFT remains far from being optimally applied in clinical settings, which leads to the underdiagnosis and undermanagement of patients with INOCA. Whilst further research is awaited, a coronary vasomotor disorder diagnostic algorithm, based on available studies, can be implemented in cardiac catheterisation laboratories. As long as INOCA remains overlooked, our relentless fight in mitigating cardiovascular disease will stagnate due to the morbidity and mortality arising from this hidden disease.
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Contributor Information
Vijay Kunadian, Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom; Cardiothoracic Centre, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom.
Daniell Edward Raharjo, Translational and Clinical Research Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom; Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia.
References
- Kunadian V, Chieffo A, Camici PG, Berry C, Escaned J, Maas AHEM, Prescott E, Karam N, Appelman Y, Fraccaro C, Buchanan GL, Manzo-Silberman S, Al-Lamee R, Regar E, Lansky A, Abbott JD, Badimon L, Duncker DJ, Mehran R, Capodanno D, Baumbach A. An EAPCI Expert Consensus Document on Ischaemia with Non-Obstructive Coronary Arteries in Collaboration with European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Coronary Pathophysiology & Microcirculation Endorsed by Coronary Vasomotor Disorders International Study Group. EuroIntervention. 2021;16:1049–69. doi: 10.4244/EIJY20M07_01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra R, Seitz A, Boerhout C, Bukkems L, Stegehuis V, Teeuwisse P, de Winter, Sechtem U, Piek JJ, van de, Ong P, Beijk M. Principles and pitfalls in coronary vasomotor function testing. EuroIntervention. 2022;17:1271–80. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-21-00402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuuti J, Wijns W, Saraste A, Capodanno D, Barbato E, Funck-Brentano C, Prescott E, Storey RF, Deaton C, Cuisset T, Agewall S, Dickstein K, Edvardsen T, Escaned J, Gersh BJ, Svitil P, Gilard M, Hasdai D, Hatala R, Mahfoud F, Masip J, Muneretto C, Valgimigli M, Achenbach S, Bax JJ ESC Scientific Document Group. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:407–77. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei J, Mehta PK, Johnson BD, Samuels B, Kar S, Anderson RD, Azarbal B, Petersen J, Sharaf B, Handberg E, Shufelt C, Kothawade K, Sopko G, Lerman A, Shaw L, Kelsey SF, Pepine CJ, Merz CN. Safety of coronary reactivity testing in women with no obstructive coronary artery disease: results from the NHLBI-sponsored WISE (Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation) study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5:646–53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2012.01.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montone RA, Niccoli G, Fracassi F, Russo M, Gurgoglione F, Camma G, Lanza GA, Crea F. Patients with acute myocardial infarction and non-obstructive coronary arteries: safety and prognostic relevance of invasive coronary provocative tests. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:91–8. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]