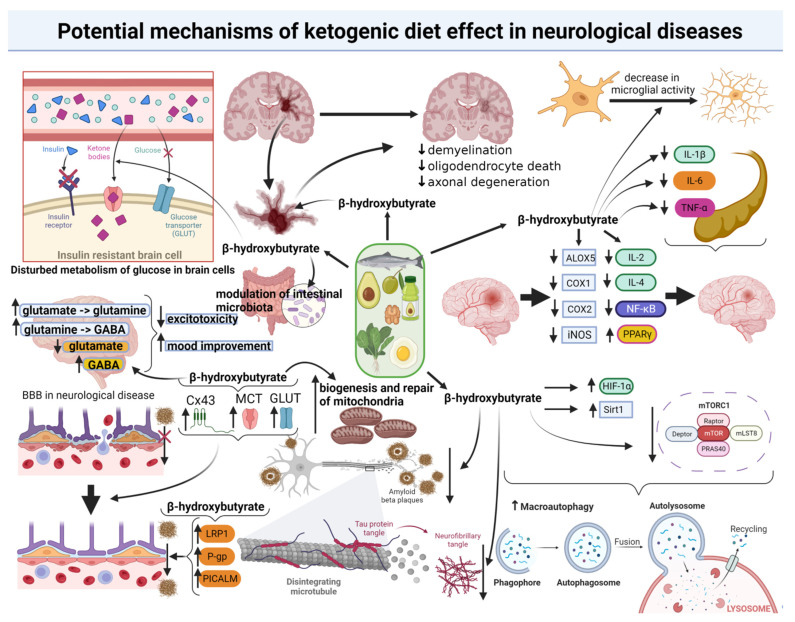
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms of the ketogenic diet effect in neurological diseases. GABA: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid; BBB: blood–brain barrier; Cx43: connexin-43; MCT: monocarboxylate transporters; GLUT: glucose transporters; LRP1: LDL receptor-related protein 1; P-gp: glycoprotein P; PICALM: phosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein; IL-1β: interleukin-1β; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; ALOX5: arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase gene; COX1: cyclooxygenase 1; COX2: cyclooxygenase 2; iNOS: inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-2: interleukin-2; IL-4: interleukin 4; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PPARγ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; HIF-1α: hypoxia-induced factor 1α; Sirt1: sirtuin 1; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; mLST8: mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8; PRAS40: proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin. The above figure was created with BioRender.com, accessed on 23 November 2022. Agreement number: TF24OJVLEL.