Figure 6. DH1017 clone interacts with envelope dimer.
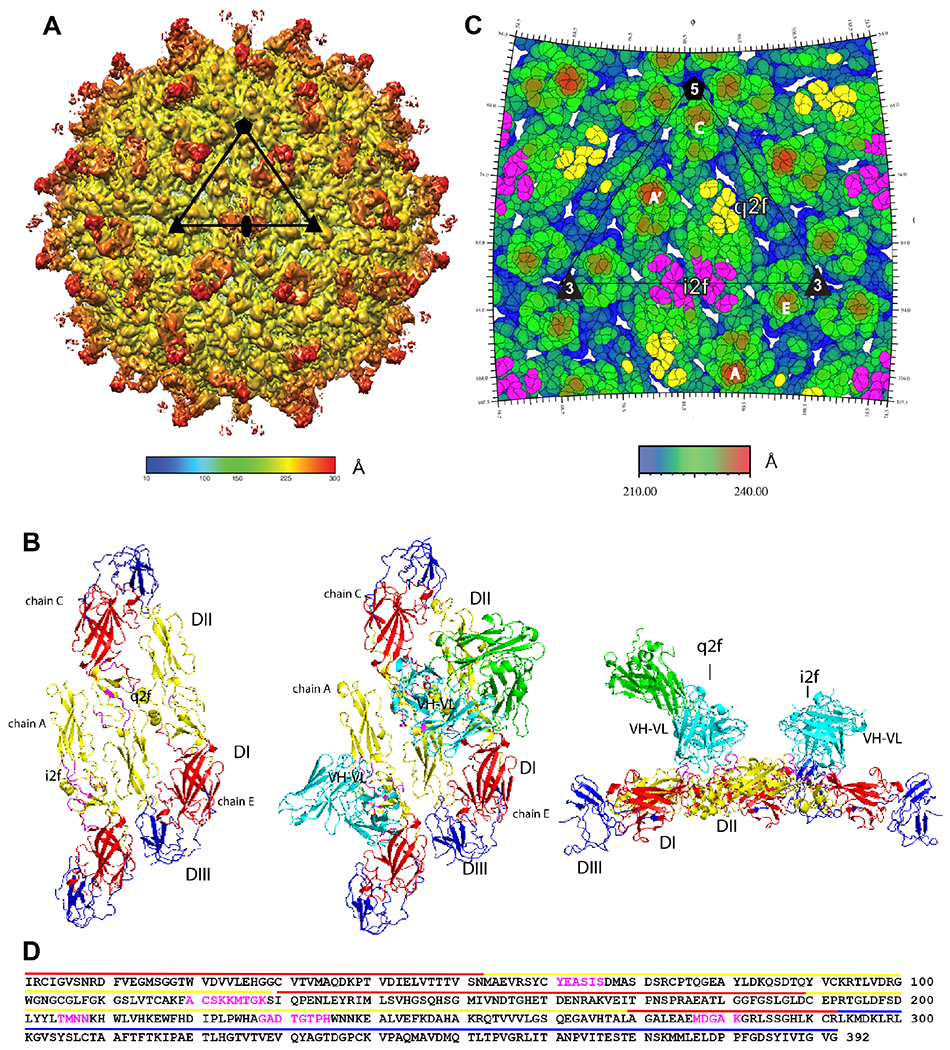
A. Surface-shaded view of the Zika virion bound with the DH1017 Fab. Shading represents the distance to the virion center (scale bar in Å). Black triangle: asymmetric unit; pentagon: five-fold axis; triangle: three-fold axis; oval: two-fold axis. B. Surface representation of the ZIKV E ectodomain asymmetric unit (PDB 6CO8) shown in top view unbound (left), bound with the DH1017.Fab variable (cyan) and constant (green) domains (middle), and in bound side view (right). E ectodomain DI: red, DII: yellow, and DIII: blue. DH1017.Fab footprint residues: magenta. C. Radially colored roadmap (scale bar in Å). The icosahedral and quasi two-fold axes are labelled i2f and q2f, respectively. The monomer chains of two E dimers are labeled A’ and A at the i2f, and C and E at the q2f. Residues on the surface of the virus within 6 Å of the variable domain structure fit to the density map are colored yellow on chain C at the q2f axis and magenta on chain A’ and A at the i2f axis. D. Fab DH1017 epitope shown on the primary sequence of E ectodomain. Epitope residues: magenta. Domains DI, DII, and DIII: red, yellow and blue lines, respectively. See also Figures S4, S5, S6 and Table S3.
