Abstract
Additive manufacturing (AM), which is also known as three-dimensional (3D) printing, uses computer-aided design to build objects layer by layer. Here, we focus on the recent progress in the development of techniques for 3D printing of glass, an important optoelectronic material, including fused deposition modeling, selective laser sintering/melting, stereolithography (SLA) and direct ink writing. We compare these 3D printing methods and analyze their benefits and problems for the manufacturing of functional glass objects. In addition, we discuss the technological principles of 3D glass printing and applications of 3D printed glass objects. This review is finalized by a summary of the current achievements and perspectives for the future development of the 3D glass printing technique.
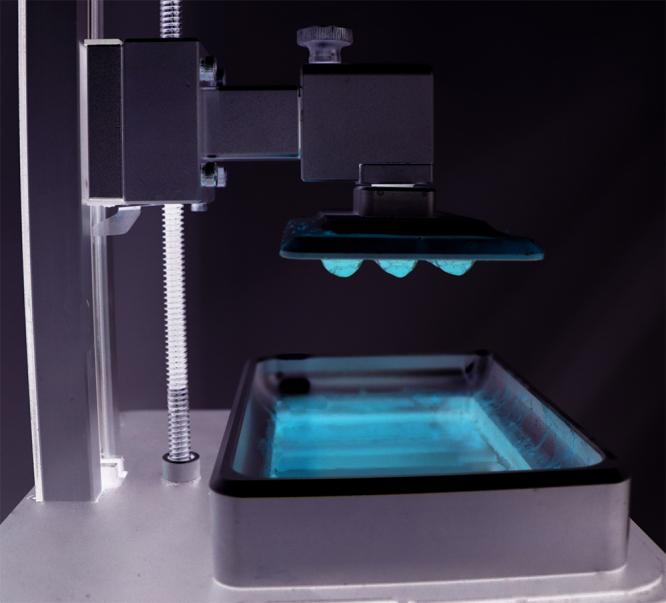
Keywords: three-dimensional (3D) printing, glass, fused deposition modeling (FDM), selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM), stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), direct ink write (DIW), optical devices, microfluidic
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFB1107200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51772270), the Open Project Program of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (No. 2018-WNLOKF005), and State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Footnotes
Dao Zhang received his bachelor’s degree from Jinan University, China. He is now a master student at Zhejiang University, China. His main research areas include 3D printing glass, high-power LED lighting and their applications. E-mail: 21860125@zju.edu.cn
Xiaofeng Liu received his Ph.D. degree from Shanghai Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, in 2010. He worked as a post-doc at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Japan) during 2010–2011, at Max Planck Institute for Colloids and Interfaces (Germany) during 2011–2013. He is now a professor in College of Optical Science and Engineering at Zhejiang University, China. His research interests cover non-linear optics, ultrafast laser, 2D material, and their applications. E-mail: xfliu@zju.edu.cn
Jianrong Qiu is a professor in College of Optical Science and Engineering at Zhejiang University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree from Okayama University (Japan) in 1992. He specializes in lasermatter interaction and optical materials. Prof. Qiu is the Chair Professor of Cheung Kong Scholars Program, fellow of the Optical Society of America (OSA), the American Ceramic Society (ACS), the International Glass Commission, and the Chinese Ceramics Society. He is also the vice Chairman of Photoelectronic Glasses Branch, Associate Editor (or International Advisory Board Member) of the Asian J Ceram Soc, Int J Appl Glass Sci, and J Non-Cryst Solids. E-mail: qjr@zju.edu.cn
References
- 1.Wong K V, Hernandez A. A review of additive manufacturing. ISRN Mechanical Engineering. 2012;2012:1–10. doi: 10.5402/2012/208760. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jariwala S H, Lewis G S, Bushman Z J, Adair J H, Donahue H J. 3D printing of personalized artificial bone scaffolds. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing. 2015;2(2):56–64. doi: 10.1089/3dp.2015.0001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bikas H, Stavropoulos P, Chryssolouris G. Additive manufacturing methods and modelling approaches: a critical review. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2015;83(1–4):389–405. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Balling P, Schou J. Femtosecond-laser ablation dynamics of dielectrics: basics and applications for thin films. Reports on Progress in Physics. 2013;76(3):036502. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/76/3/036502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chia H N, Wu B M. Recent advances in 3D printing of biomaterials. Journal of Biological Engineering. 2015;9(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13036-015-0001-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berman B. 3-D printing: the new industrial revolution. Business Horizons. 2012;55(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/j.bushor.2011.11.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bose S, Vahabzadeh S, Bandyopadhyay A. Bone tissue engineering using 3D printing. Materials Today. 2013;16(12):496–504. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2013.11.017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gross B C, Erkal J L, Lockwood S Y, Chen C, Spence D M. Evaluation of 3D printing and its potential impact on biotechnology and the chemical sciences. Analytical Chemistry. 2014;86(7):3240–3253. doi: 10.1021/ac403397r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu N, Guo H, Fu L, Kaiser S, Schweizer H, Giessen H. Three-dimensional photonic metamaterials at optical frequencies. Nature Materials. 2008;7(1):31–37. doi: 10.1038/nmat2072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rengier F, Mehndiratta A, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Zechmann C M, Unterhinninghofen R, Kauczor H U, Giesel F L. 3D printing based on imaging data: review of medical applications. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery. 2010;5(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/s11548-010-0476-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wang X, Jiang M, Zhou Z, Gou J, Hui D. 3D printing of polymer matrix composites: a review and prospective. Composites, Part B, Engineering. 2017;110:442–458. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.11.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yap C Y, Chua C K, Dong Z L, Liu Z H, Zhang D Q, Loh L E, Sing S L. Review of selective laser melting: materials and applications. Applied Physics Reviews. 2015;2(4):041101. doi: 10.1063/1.4935926. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ikushima A J, Fujiwara T, Saito K. Silica glass: a material for photonics. Journal of Applied Physics. 2000;88(3):1201–1213. doi: 10.1063/1.373805. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Friend J, Tan H H, Spencer M J S, Morishita T, Bassett M R. Density functional theory calculations of phenol-modified monolayer silicon nanosheets; Melbourne: SPIE; 2013. p. 89230D. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Billiet T, Gevaert E, De Schryver T, Cornelissen M, Dubruel P. The 3D printing of gelatin methacrylamide cell-laden tissue-engineered constructs with high cell viability. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):49–62. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.09.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Elvira K S, Casadevall i Solvas X, Wootton R C, deMello A J. The past, present and potential for microfluidic reactor technology in chemical synthesis. Nature Chemistry. 2013;5(11):905–915. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kotz F, Plewa K, Bauer W, Schneider N, Keller N, Nargang T, Helmer D, Sachsenheimer K, Schäfer M, Worgull M, Greiner C, Richter C, Rapp B E. Liquid glass: a facile soft replication method for structuring glass. Advanced Materials. 2016;28(23):4646–4650. doi: 10.1002/adma.201506089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kotz F, Risch P, Arnold K, Sevim S, Puigmartí-Luis J, Quick A, Thiel M, Hrynevich A, Dalton P D, Helmer D, Rapp B E. Fabrication of arbitrary three-dimensional suspended hollow microstructures in transparent fused silica glass. Nature Communications. 2019;10(1):1439. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09497-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goh G D, Yap Y L, Tan H K J, Sing S L, Goh G L, Yeong W Y. Process-structure-properties in polymer additive manufacturing via material extrusion: a review. Critical Reviews in Solid State and Material Sciences. 2020;45(2):113–133. doi: 10.1080/10408436.2018.1549977. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huang J, Chen Q, Jiang H, Zou B, Li L, Liu J, Yu H. A survey of design methods for material extrusion polymer 3D printing. Virtual and Physical Prototyping. 2020;15(2):148–162. doi: 10.1080/17452759.2019.1708027. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kuznetsov V E, Solonin A N, Tavitov A G, Urzhumtsev O D, Vakulik A H. Increasing strength of FFF three-dimensional printed parts by influencing on temperature-related parameters of the process. Rapid Prototyping Journal. 2018;26:107–121. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-01-2019-0017. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ćwikła G, Grabowik C, Kalinowski K, Paprocka I, Ociepka P. The influence of printing parameters on selected mechanical properties of FDM/FFF 3D-printed parts. IOP Conference Series. Materials Science and Engineering. 2017;227:012033. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/227/1/012033. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wittbrodt B, Pearce J M. The effects of PLA color on material properties of 3-D printed components. Additive Manufacturing. 2015;8:110–116. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2015.09.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thirunahary S, Ketham M M R, Akhil H, Mavoori N K. A critical review on of 3D printing materials and details of materials used in FDM. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science, Engineering and Technology. 2017;3(2):353–361. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Polak R, Sedlacek F, Raz K. Determination of FDM printer settings with regard to geometrical accuracy. In: Proceedings of the 28th International DAAAM Symposium. 2017, 0561–0566
- 26.Sood A K, Ohdar R K, Mahapatra S S. Parametric appraisal of mechanical property of fused deposition modelling processed parts. Materials & Design. 2010;31(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.06.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Popescu D, Zapciu A, Amza C, Baciu F, Marinescu R. FDM process parameters influence over the mechanical properties of polymer specimens: a review. Polymer Testing. 2018;69:157–166. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.05.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Choi Y H, Kim C M, Jeong H S, Youn J H. Influence of bed temperature on heat shrinkage shape error in FDM additive manufacturing of the ABS-engineering plastic. World Journal of Engineering and Technology. 2016;4(3):186–192. doi: 10.4236/wjet.2016.43D022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Soares J B, Finamor J, Silva F P, Roldo L, Cândido L H. Analysis of the influence of polylactic acid (PLA) colour on FDM 3D printing temperature and part finishing. Rapid Prototyping Journal. 2018;24(8):1305–1316. doi: 10.1108/RPJ-09-2017-0177. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Klein J, Stern M, Franchin G, Kayser M, Inamura C, Dave S, Weaver J, Houk P, Colombo P, Yang M, Oxman N. Additive manufacturing of optically transparent glass. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing. 2015;2(3):92–105. doi: 10.1089/3dp.2015.0021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Baudet E, Ledemi Y, Larochelle P, Morency S, Messaddeq Y. 3D-printing of arsenic sulfide chalcogenide glasses. Optical Materials Express. 2019;9(5):2307. doi: 10.1364/OME.9.002307. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Engineering Niomta. Progress has been made in research on 3D printing technology and equipment for glass at Ningbo Institute of Materials Technique and Engineering. 2015 (in Chinese)
- 33.Garg A, Bhattacharya A, Batish A. On surface finish and dimensional accuracy of FDM parts after cold vapor treatment. Materials and Manufacturing Processes. 2016;31(4):522–529. doi: 10.1080/10426914.2015.1070425. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li G. Effect of FDM rapid prototyping process parameter on step effect. Mechanical Engineering & Automation. 2017;12(6):131–135. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ceretti E, Ginestra P, Neto P I, Fiorentino A, Da Silva J V L. Multi-layered scaffolds production via fused deposition modeling (FDM) using an open source 3D printer: process parameters optimization for dimensional accuracy and design reproducibility. Procedia CIRP. 2017;65:13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2017.04.042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kiendl J, Gao C. Controlling toughness and strength of FDM 3D-printed PLA components through the raster layup. Composites Part B, Engineering. 2020;180:107562. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107562. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mohan N, Senthil P, Vinodh S, Jayanth N. A review on composite materials and process parameters optimisation for the fused deposition modelling process. Virtual and Physical Prototyping. 2017;12(1):47–59. doi: 10.1080/17452759.2016.1274490. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hambali R H, Cheong K M, Azizan N. Analysis of the influence of chemical treatment to the strength and surface roughness of FDM. IOP Conference Series. Materials Science and Engineering. 2017;210:012063. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/210/1/012063. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hong H, Seo Y B, Kim D Y, Lee J S, Lee Y L, Lee H, Ajiteru O, Sultan M T, Lee O J, Kin S H, Park C H. Digital light processing 3D printed silk fibroin hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2018;232:119679. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kim S H, Yeon Y K, Lee J M, Chao J R, Lee Y J, Seo Y B, Sultan M T, Lee O J, Lee J S, Yoon S I, Hong I S, Khang G, Lee S J, Yoo J J, Park C H. Precisely printable and biocompatible silk fibroin bioink for digital light processing 3D printing. Nature Communications. 2018;9(1):1620. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03759-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Manapat J Z, Mangadlao J D, Tiu B D, Tritchler G C, Advincula R C. High-strength stereolithographic 3D printed nanocomposites: graphene oxide metastability. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2017;9(11):10085–10093. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b16174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kotz F, Arnold K, Bauer W, Schild D, Keller N, Sachsenheimer K, Nargang T M, Richter C, Helmer D, Rapp B E. Three-dimensional printing of transparent fused silica glass. Nature. 2017;544(7650):337–339. doi: 10.1038/nature22061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu C, Qian B, Ni R, Liu X, Qiu J. 3D printing of multicolor luminescent glass. RSC Advances. 2018;8(55):31564–31567. doi: 10.1039/C8RA06706F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sadeqi A, Rezaei Nejad H, Owyeung R E, Sonkusale S. Three dimensional printing of metamaterial embedded geometrical optics (MEGO) Microsystems & Nanoengineering. 2019;5(1):16. doi: 10.1038/s41378-019-0053-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Waheed S, Cabot J M, Macdonald N P, Lewis T, Guijt R M, Paull B, Breadmore M C. 3D printed microfluidic devices: enablers and barriers. Lab on a Chip. 2016;16(11):1993–2013. doi: 10.1039/C6LC00284F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Strano G, Hao L, Everson R M, Evans K E. A new approach to the design and optimisation of support structures in additive manufacturing. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2012;66(9–12):1247–1254. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yu E A, Yeom J, Tutum C C, Vouga E, Miikkulainen R. Evolutionary decomposition for 3D printing; Berlin: ACM Publication; 2017. pp. 1272–1279. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Liu C, Qian B, Liu X, Tong L, Qiu J. Additive manufacturing of silica glass using laser stereolithography with a top-down approach and fast debinding. RSC Advances. 2018;8(29):16344–16348. doi: 10.1039/C8RA02428F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wu D, Zhao Z, Zhang Q, Qi H J, Fang D. Mechanics of shape distortion of DLP 3D printed structures during UV post-curing. Soft Matter. 2019;15(30):6151–6159. doi: 10.1039/C9SM00725C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Komissarenko D A, Sokolov P S, Evstigneeva A D, Shmeleva I A, Dosovitsky A E. Rheological and curing behavior of acrylate-based suspensions for the DLP 3D printing of complex zirconia parts. Materials (Basel) 2018;11(12):2350. doi: 10.3390/ma11122350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Moore D G, Barbera L, Masania K, Studart A R. Three-dimensional printing of multicomponent glasses using phase-separating resins. Nature Materials. 2020;19(2):212–217. doi: 10.1038/s41563-019-0525-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cooperstein I, Shukrun E, Press O, Kamyshny A, Magdassi S. Additive manufacturing of transparent silica glass from solutions. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2018;10(22):18879–18885. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b03766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Voet V S D, Strating T, Schnelting G H M, Dijkstra P, Tietema M, Xu J, Woortman A J J, Loos K, Jager J, Folkersma R. Biobased acrylate photocurable resin formulation for stereolithography 3D printing. ACS Omega. 2018;3(2):1403–1408. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bertrand P, Bayle F, Combe C, Goeuriot P, Smurov I. Ceramic components manufacturing by selective laser sintering. Applied Surface Science. 2007;254(4):989–992. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.08.085. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rao H, Giet S, Yang K, Wu X, Davies C H J. The influence of processing parameters on aluminium alloy A357 manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Materials & Design. 2016;109:334–346. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rao J H, Zhang Y, Fang X, Chen Y, Wu X, Davies C H J. The origins for tensile properties of selective laser melted aluminium alloy A357. Additive Manufacturing. 2017;17:113–122. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2017.08.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yadroitsev I, Bertrand P, Smurov I. Parametric analysis of the selective laser melting process. Applied Surface Science. 2007;253(19):8064–8069. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2007.02.088. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ahmed N. Direct metal fabrication in rapid prototyping: a review. Journal of Manufacturing Processes. 2019;42:167–191. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.05.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Klocke F, McClung A, Ader C. Direct laser sintering of borosilicate glass; Austi: The University of Texas; 2004. pp. 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Rahmani R, Rosenberg M, Ivask A, Kollo L. Comparison of mechanical and antibacterial properties of TiO2/Ag ceramics and Ti6Al4V-TiO2/Ag composite materials using combined SLM-SPS techniques. Metals. 2019;9(8):874. doi: 10.3390/met9080874. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tey C F, Tan X, Sing S L, Yeong W Y. Additive manufacturing of multiple materials by selective laser melting: Ti-alloy to stainless steel via a Cu-alloy interlayer. Additive Manufacturing. 2020;31:100970. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2019.100970. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kuo C N, Chua C K, Peng P C, Chen Y W, Sing S L, Huang S, Su Y L. Microstructure evolution and mechanical property response via 3D printing parameter development of Al-Sc alloy. Virtual and Physical Prototyping. 2020;15(1):120–129. doi: 10.1080/17452759.2019.1698967. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Luo J, Edward H P, Kinzel C. Additive manufacturing of glass. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering. 2014;136(6):061024. doi: 10.1115/1.4028531. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Luo J, Gilbert L J, Bristow D A, Landers R G, Goldstein J T, Urbas A M, Kinzel E C. Additive manufacturing of glass for optical applications; California: SPIE; 2016. p. 97380Y. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Luo J, Luke J G, Qu C, Robert G L, Douglas A B, Edward C K. Additive manufacturing of optically transparent soda-lime glass using a filament-fed process. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering. 2017;139(6):061006. doi: 10.1115/1.4035182. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ko S H, Pan H, Grigoropoulos C P, Luscombe C K, Fréchet J M J, Poulikakos D. All-inkjet-printed flexible electronics fabrication on a polymer substrate by low-temperature high-resolution selective laser sintering of metal nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2007;18(34):345202. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/18/34/345202. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Park B K, Kim D, Jeong S, Moon J, Kim J S. Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Films. 2007;515(19):7706–7711. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2006.11.142. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Nguyen D T, Meyers C, Yee T D, Dudukovic N A, Destino J F, Zhu C, Duoss E B, Baumann T F, Suratwala T, Smay J E, Dylla-Spears R. 3D-printed transparent glass. Advanced Materials. 2017;29(26):1701181. doi: 10.1002/adma.201701181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Destino J F, Dudukovic N A, Johnson M A, Nguyen D T, Yee T D, Egan G C, Sawvel A M, Steele W A, Baumann T F, Duoss E B, Suratwala T, Dylla-Spears R. 3D printed optical quality silica and silica-titania glasses from sol-gel feedstocks. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2018;3(6):1700323. doi: 10.1002/admt.201700323. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Dudukovic N A, Wong L L, Nguyen D T, Destino J F, Yee T D, Ryerson F J, Suratwala T, Duoss E B, Dylla-Spears R. Predicting nanoparticle suspension viscoelasticity for multimaterial 3D printing of silica-titania glass. ACS Applied Nano Materials. 2018;1(8):4038–4044. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.8b00821. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sasan K, Lange A, Yee T D, Dudukovic N, Nguyen D T, Johnson M A, Herrera O D, Yoo J H, Sawvel A M, Ellis M E, Mah C M, Ryerson R, Wong L L, Suratwala T, Destino J F, Dylla-Spears R. Additive manufacturing of optical quality germania-silica glasses. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2020;12(5):6736–6741. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b21136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Li V C, Dunn C K, Zhang Z, Deng Y, Qi H J. Direct ink write (DIW) 3D printed cellulose nanocrystal aerogel structures. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):8018. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07771-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Yuk H, Zhao X. A new 3D printing strategy by harnessing deformation, instability, and fracture of viscoelastic inks. Advanced Materials. 2018;30(6):1704028. doi: 10.1002/adma.201704028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lowell D, George D, Lutkenhaus J, Tian C, Adewole M, Philipose U, Zhang H, Lin Y. Flexible holographic fabrication of 3D photonic crystal templates with polarization control through a 3D printed reflective optical element. Micromachines. 2016;7(7):128. doi: 10.3390/mi7070128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Jonušauskas L, Juodkazis S, Malinauskas M. Optical 3D printing: bridging the gaps in the mesoscale. Journal of Optics. 2018;20(5):053001. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/aab3fe. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kotz F, Schneider N, Striegel A, Wolfschläger A, Keller N, Worgull M, Bauer W, Schild D, Milich M, Greiner C, Helmer D, Rapp B E. Glassomer-processing fused silica glass like a polymer. Advanced Materials. 2018;30(22):1707100. doi: 10.1002/adma.201707100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Thiele S, Arzenbacher K, Gissibl T, Giessen H, Herkommer A M. 3D-printed eagle eye: compound microlens system for foveated imaging. Science Advances. 2017;3(2):e1602655. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1602655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Cook K, Canning J, Leon-Saval S, Reid Z, Hossain M A, Comatti J E, Luo Y, Peng G D. Air-structured optical fiber drawn from a 3D-printed preform. Optics Letters. 2015;40(17):3966–3969. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.003966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Gissibl T, Thiele S, Herkommer A, Giessen H. Two-photon direct laser writing of ultracompact multi-lens objectives. Nature Photonics. 2016;10(8):554–560. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.121. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bhattacharjee N, Urrios A, Kang S, Folch A. The upcoming 3D-printing revolution in microfluidics. Lab on a Chip. 2016;16(10):1720–1742. doi: 10.1039/C6LC00163G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Weisgrab G, Ovsianikov A, Costa P F. Functional 3D printing for microfluidic chips. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2019;4(10):1900275. doi: 10.1002/admt.201900275. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.He Y, Wu Y, Fu J, Gao Q, Qiu J. Developments of 3D printing microfluidics and applications in chemistry and biology: a review. Electroanalysis. 2016;28(8):1658–1678. doi: 10.1002/elan.201600043. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lee J M, Zhang M, Yeong W Y. Characterization and evaluation of 3D printed microfluidic chip for cell processing. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. 2016;20(1):5. doi: 10.1007/s10404-015-1688-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Yazdi A, Popma A, Wong W, Nguyen T, Pan Y, Xu J. 3D printing: an emerging tool for novel microfluidics and lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. 2016;20(3):50. doi: 10.1007/s10404-016-1715-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Hinton T J, Hudson A, Pusch K, Lee A, Feinberg A W. 3D printing PDMS elastomer in a hydrophilic support bath via freeform reversible embedding. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering. 2016;2(10):1781–1786. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Trantidou T, Elani Y, Parsons E, Ces O. Hydrophilic surface modification of PDMS for droplet microfluidics using a simple, quick, and robust method via PVA deposition. Microsystems & Nanoengineering. 2017;3(1):16091. doi: 10.1038/micronano.2016.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lin Z J, Xu J, Song Y P, Li X L, Wang P, Chu W, Wang Z H, Cheng Y. Freeform microfluidic networks encapsulated in laser-printed 3D macroscale glass objects. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2020;5(2):1900989. doi: 10.1002/admt.201900989. [DOI] [Google Scholar]


