Abstract
As an outstanding two-dimensional material, black phosphorene, has attracted significant attention in the biomedicine field due to its large surface area, strong optical absorption, distinct bioactivity, excellent biocompatibility, and high biodegradability. In this review, the preparation and properties of black phosphorene are summarized first. Thereafter, black phosphorene-based multifunctional platforms employed for the diagnosis and treatment of diseases, including cancer, bone injuries, brain diseases, progressive oxidative diseases, and kidney injury, are reviewed in detail. This review provides a better understanding of the exciting properties of black phosphorene, such as its high drug-loading efficiency, photothermal conversion capability, high 1O2 generation efficiency, and high electrical conductivity, as well as how these properties can be exploited in biomedicine. Finally, the research perspectives of black phosphorene are discussed.
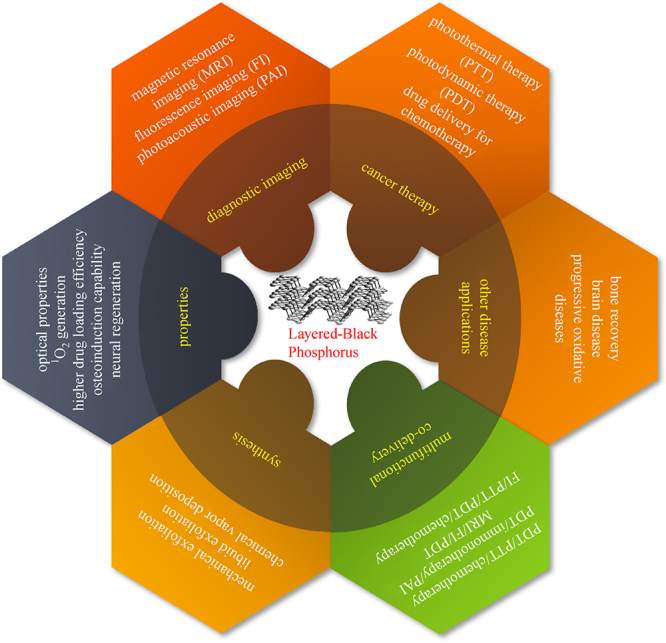
Keywords: black phosphorus (BP), delivery nanoplatform, bioimaging, cancer therapy, bone regeneration
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant Nos. 81930048, 81627805, and 81671726), Guangdong Science and Technology Commission (Nos. 2019BT02X105, 2019A1515011374), Hong Kong Research Grant Council (Nos. 25204416, R5029-19), Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission (Nos. ITS/022/18, GHP/043/19SZ, GHP/044/19GD), Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (No. JCYJ20170818104421564), Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars (No. 2020B1515020027), and Guangzhou Science and Technology Bureau (No. 202002020070).
Footnotes
Xiazi Huang received her bachelor’s degree in Pharmacy from Sun Yat-Sen University, China, in 2015 and M.Sc. degree in Biomedical Engineering from Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China, in 2016. After that, she joined a biophotonics laboratory at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China, as a research assistant. She is currently a Ph.D. student at Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China. Her research focuses on the design of nanoparticles for enhanced imaging diagnosis and cancer treatment.
Yingying ZHOU is a Ph.D. student at Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China. She received her bachelor’s degree from Sun Yat-Sen University, China. Her research focuses on photoacoustic microscopy and its applications.
Chi Man Woo received her M.Sc. degree in Biomedical Engineering from Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China, in 2019 and B.Eng. degree in Medical Engineering from The University of Hong Kong, China, in 2017. She is currently a research assistant in a biophotonics laboratory at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China. Her research focuses on biomedical imaging and optical wavefront shaping for deep-tissue focusing.
Yue Pan received his B.Sc. degree in 2003, followed by a M.Sc. degree from University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), China, in 2006. He obtained his Ph.D. degree in 2012 from Brandeis University, USA, under the supervision of Prof. Bing Xu. Before starting his independent research at Soochow University, China, in 2013, he was a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard Medical School, USA. He is now a full professor at Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, China. He has published 32 papers as the corresponding author and 7 as the first author in several journals, including Chemical Society Reviews, Journal of the American Chemical Society, Nano Energy, and Biosensors and Bioelectronics. His research focuses on the biomedical applications of functionalized nanomaterials, which have been widely reported and cited by Nature Materials, Nature Reviews Chemistry, Nature Protocols, Nature Biomedical Engineering, etc. His research has also been highlighted by “Chemistry World” of the Royal Society of Chemistry, “Advanced Science News”, and “Chemistry Views” by Wiley and ranked by “Faculty of 1000” among the top 2% of published articles in biology and medicine. He was honored as one of the “Top 1% Most Cited Chinese Researchers” by the Royal Society of Chemistry and Distinguished Young Scholars by Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation.
Liming Nie earned his Ph.D. degree in Optics from South China Normal University, China. He received his postdoctoral training under Dr. Lihong V. Wang at Washington University in St. Louis, USA, from 2010 to 2012. Thereafter, he worked on molecular imaging as a research associate at National Institute of Health, USA. In 2014, he joined Xiamen University, China, as a faculty member and was promoted to full professor in 2018. His laboratory is transitioning to the Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, China. He edited and co-authored two textbooks on molecular imaging. His laboratory focuses on optical molecular imaging technology advancement and applications, mainly on photoacoustic microscopy, functional photoacoustic tomography, and other imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography. He has published over 70 peer-reviewed articles in several journals, including Nature Communications, Angewandte Chemie International Edition, European Radiology, and The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, and has delivered more than 30 plenary speeches or invited talks in international conferences. His work has been cited by Nature Method, Neuron, PNAS, etc. His Google Scholar H-index and citations have reached 34 and 4300, respectively. He has received numerous research funding awards from the National Natural Science Foundation of China as well as the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. He received the ACS Young Scientist Award and the first-place award of Huaxia Medical Technology.
Puxiang Lai received his bachelor’s degree from Tsinghua University, China, in 2002, M.Sc. degree from Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, in 2005, and Ph.D. degree from Boston University, USA, in 2011. After that, he joined Dr. Lihong V. Wang’s laboratory at Washington University in St. Louis, USA, as a Postdoctoral Research Associate. In September 2015, he joined Department of Biomedical Engineering at Hong Kong Polytechnic University, China, as a tenure-track assistant professor.
Dr. Lai’s research focuses on the synergy of light and sound as well as their applications in biomedicine, such as wavefront shaping, photoacoustic imaging, acousto-optic imaging, and computational optical imaging. His research has fueled more than 50 publications in top journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, and Advanced Sciences. Since 2015, his research has been continuously supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), Hong Kong Research Grant Council (RGC), Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission (ITC), Department of Science and Technology of Guangdong Province, and Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission (STIC), with an allocated budget of more than 19 million Hong Kong dollars.
Dr. Lai was awarded the 2016–2017 Hong Kong RGC Early Career Award, 2018 Hong Kong Polytechnic University Faculty of Engineering Research Grant Achievement Award, 2019 PolyU K.C. Wong Belt and Road Visiting Fellowship Award, and 2020 Hong Kong Polytechnic University Faculty of Engineering Faculty Research Award. In recognition of his contribution to the field, currently, Puxiang serves as an Associate Editor of Journal of Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art (VCIBA); a Guest Editor of Journal of Innovative Optics in Health and Science (JIOHS); a Committee Member of the Biomedical Optics Panel in the Chinese Society of Biomedical Engineering; and a Member of the Medical Instrument Judging Panel in the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission.
Equal contribution
References
- 1.Shi Y, Liang X, Yuan B, Chen V, Li H, Hui F, Yu Z, Yuan F, Pop E, Wong H S P, Lanza M. Electronic synapses made of layered two-dimensional materials. Nature Electronics. 2018;1(8):458–465. doi: 10.1038/s41928-018-0118-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Koppens F H, Mueller T, Avouris P, Ferrari A C, Vitiello M S, Polini M. Photodetectors based on graphene, other two-dimensional materials and hybrid systems. Nature Nanotechnology. 2014;9(10):780–793. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kang K, Lee K H, Han Y, Gao H, Xie S, Muller D A, Park J. Layer-by-layer assembly of two-dimensional materials into wafer-scale heterostructures. Nature. 2017;550(7675):229–233. doi: 10.1038/nature23905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Deng D, Novoselov K S, Fu Q, Zheng N, Tian Z, Bao X. Catalysis with two-dimensional materials and their heterostructures. Nature Nanotechnology. 2016;11(3):218–230. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jin L, Zhou J, Lai P. Tunable absorption characteristics in multilayered structures with graphene for biosensing. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences. 2020;13(04):2050017. doi: 10.1142/S1793545820500170. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang Y, Tang T T, Girit C, Hao Z, Martin M C, Zettl A, Crommie M F, Shen Y R, Wang F. Direct observation of a widely tunable bandgap in bilayer graphene. Nature. 2009;459(7248):820–823. doi: 10.1038/nature08105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Radovic L R, Bockrath B. On the chemical nature of graphene edges: origin of stability and potential for magnetism in carbon materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2005;127(16):5917–5927. doi: 10.1021/ja050124h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tassin P, Koschny T, Soukoulis C M. Graphene for terahertz applications. Science. 2013;341(6146):620–621. doi: 10.1126/science.1242253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yang K, Feng L, Liu Z. Stimuli responsive drug delivery systems based on nano-graphene for cancer therapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2016;105(PtB):228–241. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vogt P, De Padova P, Quaresima C, Avila J, Frantzeskakis E, Asensio M C, Resta A, Ealet B, Le Lay G. Silicene: compelling experimental evidence for graphenelike two-dimensional silicon. Physical Review Letters. 2012;108(15):155501. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.155501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Seyler K L, Rivera P, Yu H, Wilson N P, Ray E L, Mandrus D G, Yan J, Yao W, Xu X. Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers. Nature. 2019;567(7746):66–70. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0957-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Radisavljevic B, Radenovic A, Brivio J, Giacometti V, Kis A. Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nature Nanotechnology. 2011;6(3):147–150. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Coleman J N, Lotya M, O’Neill A, Bergin S D, King P J, Khan U, Young K, Gaucher A, De S, Smith R J, Shvets I V, Arora S K, Stanton G, Kim H Y, Lee K, Kim G T, Duesberg G S, Hallam T, Boland J J, Wang J J, Donegan J F, Grunlan J C, Moriarty G, Shmeliov A, Nicholls R J, Perkins J M, Grieveson E M, Theuwissen K, McComb D W, Nellist P D, Nicolosi V. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science. 2011;331(6017):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.1194975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ge X, Xia Z, Guo S. Recent advances on black phosphorus for biomedicine and biosensing. Advanced Functional Materials. 2019;29(29):1900318. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201900318. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.An D, Fu J, Xie Z, Xing C, Zhang B, Wang B, Qiu M. Progress in the therapeutic applications of polymer-decorated black phosphorus and black phosphorus analog nanomaterials in biomedicine. Journal of Materials Chemistry. B, Materials for Biology and Medicine. 2020;8(32):7076–7120. doi: 10.1039/D0TB00824A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Qiu M, Ren W X, Jeong T, Won M, Park G Y, Sang D K, Liu L P, Zhang H, Kim J S. Omnipotent phosphorene: a next-generation, two-dimensional nanoplatform for multidisciplinary biomedical applications. Chemical Society Reviews. 2018;47(15):5588–5601. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00342D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.You H, Jia Y, Wu Z, Wang F, Huang H, Wang Y. Room-temperature pyro-catalytic hydrogen generation of 2D few-layer black phosphorene under cold-hot alternation. Nature Communications. 2018;9(1):2889. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05343-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lei W, Liu G, Zhang J, Liu M. Black phosphorus nanostructures: recent advances in hybridization, doping and functionalization. Chemical Society Reviews. 2017;46(12):3492–3509. doi: 10.1039/C7CS00021A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Castellanos-Gomez A, Vicarelli L, Prada E, Island J O, Narasimha-Acharya K L, Blanter S I, Groenendijk D J, Buscema M, Steele G A, Alvarez J V, Zandbergen H W, Palacios J J, van der Zant H S J. Isolation and characterization of few-layer black phosphorus. 2D Materials. 2014;1(2):025001. doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/1/2/025001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Xiong S, Chen X, Liu Y, Fan T, Wang Q, Zhang H, Chen T. Black phosphorus as a versatile nanoplatform: from unique properties to biomedical applications. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences. 2020;13(5):2030008. doi: 10.1142/S1793545820300086. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Abellán G, Lloret V, Mundloch U, Marcia M, Neiss C, Görling A, Varela M, Hauke F, Hirsch A. Noncovalent functionalization of black phosphorus. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 2016;55(47):14557–14562. doi: 10.1002/anie.201604784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bolognesi M, Moschetto S, Trapani M, Prescimone F, Ferroni C, Manca G, Ienco A, Borsacchi S, Caporali M, Muccini M, Peruzzini M, Serrano-Ruiz M, Calucci L, Castriciano M A, Toffanin S. Noncovalent functionalization of 2D black phosphorus with fluorescent boronic derivatives of pyrene for probing and modulating the interaction with molecular oxygen. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2019;11(25):22637–22647. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b04344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Feng Q, Liu H, Zhu M, Shang J, Liu D, Cui X, Shen D, Kou L, Mao D, Zheng J, Li C, Zhang J, Xu H, Zhao J. Electrostatic functionalization and passivation of water-exfoliated few-layer black phosphorus by poly dimethyldiallyl ammonium chloride and its ultrafast laser application. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2018;10(11):9679–9687. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b00556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhang L, Gao L F, Li L, Hu C X, Yang Q Q, Zhu Z Y, Peng R, Wang Q, Peng Y, Jin J, Zhang H L. Negatively charged 2D black phosphorus for highly efficient covalent functionalization. Materials Chemistry Frontiers. 2018;2(9):1700–1706. doi: 10.1039/C8QM00237A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Meng Z, Stolz R M, Mendecki L, Mirica K A. Electrically-transduced chemical sensors based on two-dimensional nanomaterials. Chemical Reviews. 2019;119(1):478–598. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jiang X, Jin H, Sun Y, Sun Z, Gui R. Assembly of black phosphorus quantum dots-doped MOF and silver nanoclusters as a versatile enzyme-catalyzed biosensor for solution, flexible substrate and latent fingerprint visual detection of baicalin. Biosensors & Bioelectronics. 2020;152:112012. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Irshad R, Tahir K, Li B, Sher Z, Ali J, Nazir S. A revival of 2D materials, phosphorene: its application as sensors. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 2018;64:6460–6469. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2018.03.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xu Z, Hu L, Yuan J, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Jin Z, Long F, Long Y, Liang H, Ruan S, Zeng Y J. A fluorescence probe for metal ions based on black phosphorus quantum dots. Advanced Materials Interfaces. 2020;7(7):1902075. doi: 10.1002/admi.201902075. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sun Y, Jin H, Jiang X, Gui R. Black phosphorus nanosheets adhering to thionine-doped 2D MOF as a smart aptasensor enabling accurate capture and ratiometric electrochemical detection of target microRNA. Sensors and Actuators. B, Chemical. 2020;309:127777. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.127777. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sun Z, Zhao Y, Li Z, Cui H, Zhou Y, Li W, Tao W, Zhang H, Wang H, Chu P K, Yu X F. TiL4-coordinated black phosphorus quantum dots as an efficient contrast agent for in vivo photoacoustic imaging of cancer. Small. 2017;13(11):1602896. doi: 10.1002/smll.201602896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sun C, Wen L, Zeng J, Wang Y, Sun Q, Deng L, Zhao C, Li Z. One-pot solventless preparation of PEGylated black phosphorus nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Biomaterials. 2016;91:81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tao W, Zhu X, Yu X, Zeng X, Xiao Q, Zhang X, Ji X, Wang X, Shi J, Zhang H, Mei L. Black phosphorus nanosheets as a robust delivery platform for cancer theranostics. Advanced Materials. 2017;29(1):1603276. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang H, Yang X, Shao W, Chen S, Xie J, Zhang X, Wang J, Xie Y. Ultrathin black phosphorus nanosheets for efficient singlet oxygen generation. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2015;137(35):11376–11382. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b06025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Qian X, Gu Z, Chen Y. Two-dimensional black phosphorus nanosheets for theranostic nanomedicine. Materials Horizons. 2017;4(5):800–816. doi: 10.1039/C7MH00305F. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Choi J R, Yong K W, Choi J Y, Nilghaz A, Lin Y, Xu J, Lu X. Black phosphorus and its biomedical applications. Theranostics. 2018;8(4):1005–1026. doi: 10.7150/thno.22573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Childers D L, Corman J, Edwards M, Elser J J. Sustainability challenges of phosphorus and food: solutions from closing the human phosphorus cycle. Bioscience. 2011;61(2):117–124. doi: 10.1525/bio.2011.61.2.6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Qiu M, Singh A, Wang D, Qu J, Swihart M, Zhang H, Prasad P N. Biocompatible and biodegradable inorganic nanostructures for nanomedicine: silicon and black phosphorus. Nano Today. 2019;25:135–155. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2019.02.012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang Z, Liu Z, Su C, Yang B, Fei X, Li Y, Hou Y, Zhao H, Guo Y, Zhuang Z, Zhong H, Guo Z. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanomaterials in biomedicine: theranostic applications. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2019;26(10):1788–1805. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170920152529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Anju S, Ashtami J, Mohanan P V. Black phosphorus, a prospective graphene substitute for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering C. 2019;97:978–993. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.12.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yu J, Wang Q, O’Hare D, Sun L. Preparation of two dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheets and their applications. Chemical Society Reviews. 2017;46(19):5950–5974. doi: 10.1039/C7CS00318H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.López-Cabrelles J, Mañas-Valero S, Vitórica-Yrezábal I J, Bereciartua P J, Rodríguez-Velamazán J A, Waerenborgh J C, Vieira B J C, Davidovikj D, Steeneken P G, van der Zant H S J, Mínguez Espallargas G, Coronado E. Isoreticular two-dimensional magnetic coordination polymers prepared through pre-synthetic ligand functionalization. Nature Chemistry. 2018;10(10):1001–1007. doi: 10.1038/s41557-018-0113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Han J H, Kwak M, Kim Y, Cheon J. Recent advances in the solution-based preparation of two-dimensional layered transition metal chalcogenide nanostructures. Chemical Reviews. 2018;118(13):6151–6188. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Eswaraiah V, Zeng Q, Long Y, Liu Z. Black phosphorus nanosheets: synthesis, characterization and applications. Small. 2016;12(26):3480–3502. doi: 10.1002/smll.201600032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bridgman P W. Two new modifications of phosphorus. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1914;36(7):1344–1363. doi: 10.1021/ja02184a002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Aldave S H, Yogeesh M N, Zhu W, Kim J, Sonde S S, Nayak A P, Akinwande D. Characterization and sonochemical synthesis of black phosphorus from red phosphorus. 2D Materials. 2016;3(1):014007. doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/3/1/014007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Endo S, Akahama Y, Terada S, Narita S. Growth of large single crystals of black phosphorus under high pressure. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. 1982;21(8):L482–L484. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.21.L482. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Krebs H, Weitz H, Worms K H. About the structure and properties of semimetals VIII. The catalytic representation of black phosphorus. Zeitschrift fur Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie. 1955;280(1–3):119–133. doi: 10.1002/zaac.19552800110. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Baba M, Izumida F, Takeda Y, Morita A. Preparation of black phosphorus single crystals by a completely closed bismuth-flux method and their crystal morphology. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics. 1989;28(6):1019–1022. doi: 10.1143/JJAP.28.1019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lange S, Schmidt P, Au Nilges T. 3SnP7@black phosphorus: an easy access to black phosphorus. Inorganic Chemistry. 2007;46(10):4028–4035. doi: 10.1021/ic062192q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Köpf M, Eckstein N, Pfister D, Grotz C, Krüger I, Greiwe M, Hansen T, Kohlmann H, Nilges T. Access and in situ growth of phosphorene-precursor black phosphorus. Journal of Crystal Growth. 2014;405:6–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2014.07.029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sun Q, Zhao X, Feng Y, Wu Y, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Wang X, Feng S, Liu X. Pressure quenching: a new route for the synthesis of black phosphorus. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers. 2018;5(3):669–674. doi: 10.1039/C7QI00775B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang D, Yi P, Wang L, Zhang L, Li H, Lu M, Xie X, Huang L, Huang W. Revisiting the growth of black phosphorus in Sn-I assisted reactions. Frontiers in Chemistry. 2019;7:21. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Novoselov K S, Jiang D, Schedin F, Booth T J, Khotkevich V V, Morozov S V, Geim A K. Two-dimensional atomic crystals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005;102(30):10451–10453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502848102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hultgren R, Gingrich N S, Warren B E. The atomic distribution in red and black phosphorus and the crystal structure of black phosphorus. Journal of Chemical Physics. 1935;3(6):351–355. doi: 10.1063/1.1749671. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Liu F, Wu W, Bai Y, Chae S H, Li Q, Wang J, Hone J, Zhu X Y. Disassembling 2D van der Waals crystals into macroscopic monolayers and reassembling into artificial lattices. Science. 2020;367(6480):903–906. doi: 10.1126/science.aba1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kou L, Chen C, Smith S C. Phosphorene: fabrication, properties, and applications. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters. 2015;6(14):2794–2805. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b01094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Huang Y, Sutter E, Shi N N, Zheng J, Yang T, Englund D, Gao H J, Sutter P. Reliable exfoliation of large-area high-quality flakes of graphene and other two-dimensional materials. ACS Nano. 2015;9(11):10612–10620. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b04258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Cai X, Luo Y, Liu B, Cheng H M. Preparation of 2D material dispersions and their applications. Chemical Society Reviews. 2018;47(16):6224–6266. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00254A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Guan L, Xing B, Niu X, Wang D, Yu Y, Zhang S, Yan X, Wang Y, Sha J. Metal-assisted exfoliation of few-layer black phosphorus with high yield. Chemical Communications (Cambridge) 2018;54(6):595–598. doi: 10.1039/C7CC08488A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lu W, Nan H, Hong J, Chen Y, Zhu C, Liang Z, Ma X, Ni Z, Jin C, Zhang Z. Plasma-assisted fabrication of monolayer phosphorene and its Raman characterization. Nano Research. 2014;7(6):853–859. doi: 10.1007/s12274-014-0446-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pei J, Gai X, Yang J, Wang X, Yu Z, Choi D Y, Luther-Davies B, Lu Y. Producing air-stable monolayers of phosphorene and their defect engineering. Nature Communications. 2016;7(1):10450. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hanlon D, Backes C, Doherty E, Cucinotta C S, Berner N C, Boland C, Lee K, Harvey A, Lynch P, Gholamvand Z, Zhang S, Wang K, Moynihan G, Pokle A, Ramasse Q M, McEvoy N, Blau W J, Wang J, Abellan G, Hauke F, Hirsch A, Sanvito S, O’Regan D D, Duesberg G S, Nicolosi V, Coleman J N. Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nature Communications. 2015;6(1):8563. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kang J, Wells S A, Wood J D, Lee J H, Liu X, Ryder C R, Zhu J, Guest J R, Husko C A, Hersam M C. Stable aqueous dispersions of optically and electronically active phosphorene. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2016;113(42):11688–11693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602215113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Brent J R, Savjani N, Lewis E A, Haigh S J, Lewis D J, O’Brien P. Production of few-layer phosphorene by liquid exfoliation of black phosphorus. Chemical Communications (Cambridge) 2014;50(87):13338–13341. doi: 10.1039/C4CC05752J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Lin S, Chui Y, Li Y, Lau S P. Liquid-phase exfoliation of black phosphorus and its applications. FlatChem. 2017;2:15–37. doi: 10.1016/j.flatc.2017.03.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yasaei P, Kumar B, Foroozan T, Wang C, Asadi M, Tuschel D, Indacochea J E, Klie R F, Salehi-Khojin A. High-quality black phosphorus atomic layers by liquid-phase exfoliation. Advanced Materials. 2015;27(11):1887–1892. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Woomer A H, Farnsworth T W, Hu J, Wells R A, Donley C L, Warren S C. Phosphorene: synthesis, scale-up, and quantitative optical spectroscopy. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):8869–8884. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Chu P. Plasma-surface modification of biomaterials. Materials Science and Engineering R Reports. 2002;36(5–6):143–206. doi: 10.1016/S0927-796X(02)00004-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu R, Wang Y, Liu D, Zou Y, Wang S. Water-plasma-enabled exfoliation of ultrathin layered double hydroxide nanosheets with multivacancies for water oxidation. Advanced Materials. 2017;29(30):1701546. doi: 10.1002/adma.201701546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lee H, Bratescu M A, Ueno T, Saito N. Solution plasma exfoliation of graphene flakes from graphite electrodes. RSC Advances. 2014;4(93):51758–51765. doi: 10.1039/C4RA03253E. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Elumalai S, Su C Y, Yoshimura M. Scalable one-pot synthesis of nitrogen and boron co-doped few layered graphene by submerged liquid plasma exfoliation. Frontiers in Materials. 2019;6:216. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2019.00216. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Huang H, Gao M, Kang Y, Li J, Wang J, Wu L, Chu P K, Huang Y, Ibarra M R, Yu X F. Rapid and scalable production of high-quality phosphorene by plasma-liquid technology. Chemical Communications (Cambridge) 2020;56(2):221–224. doi: 10.1039/C9CC07640A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hernandez Y, Nicolosi V, Lotya M, Blighe F M, Sun Z, De S, McGovern I T, Holland B, Byrne M, Gun’Ko Y K, Boland J J, Niraj P, Duesberg G, Krishnamurthy S, Goodhue R, Hutchison J, Scardaci V, Ferrari A C, Coleman J N. High-yield production of graphene by liquid-phase exfoliation of graphite. Nature Nanotechnology. 2008;3(9):563–568. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Li X, Cai W, An J, Kim S, Nah J, Yang D, Piner R, Velamakanni A, Jung I, Tutuc E, Banerjee S K, Colombo L, Ruoff R S. Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science. 2009;324(5932):1312–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.1171245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kim K S, Zhao Y, Jang H, Lee S Y, Kim J M, Kim K S, Ahn J H, Kim P, Choi J Y, Hong B H. Large-scale pattern growth of graphene films for stretchable transparent electrodes. Nature. 2009;457(7230):706–710. doi: 10.1038/nature07719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Li X, Deng B, Wang X, Chen S, Vaisman M, Karato S, Pan G, Lee L M, Cha J, Wang H, Xia F. Synthesis of thin-film black phosphorus on a flexible substrate. 2D Materials. 2015;2(3):031002. doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/2/3/031002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Smith J B, Hagaman D, Ji H F. Growth of 2D black phosphorus film from chemical vapor deposition. Nanotechnology. 2016;27(21):215602. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/21/215602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Li C, Wu Y, Deng B, Xie Y, Guo Q, Yuan S, Chen X, Bhuiyan M, Wu Z, Watanabe K, Taniguchi T, Wang H, Cha J J, Snure M, Fei Y, Xia F. Synthesis of crystalline black phosphorus thin film on sapphire. Advanced Materials. 2018;30(6):1703748. doi: 10.1002/adma.201703748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Deng L, Xu Y, Sun C, Yun B, Sun Q, Zhao C, Li Z. Functionalization of small black phosphorus nanoparticles for targeted imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Science Bulletin. 2018;63(14):917–924. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Xu Y, Ren F, Liu H, Zhang H, Han Y, Liu Z, Wang W, Sun Q, Zhao C, Li Z. Cholesterol-modified black phosphorus nanospheres for the first NIR-II fluorescence bioimaging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2019;11(24):21399–21407. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b05825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Guo T, Lin Y, Jin G, Weng R, Song J, Liu X, Huang G, Hou L, Yang H. Manganese-phenolic network-coated black phosphorus nanosheets for theranostics combining magnetic resonance/photoacoustic dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. Chemical Communications (Cambridge) 2019;55(6):850–853. doi: 10.1039/C8CC08833K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Zhang Q, Wang W, Zhang M, Wu F, Zheng T, Sheng B, Liu Y, Shen J, Zhou N, Sun Y. A theranostic nanocomposite with integrated black phosphorus nanosheet, Fe3O4@MnO2-doped upconversion nanoparticles and chlorin for simultaneous multimodal imaging, highly efficient photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020;391:123525. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123525. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhao Y, Tong L, Li Z, Yang N, Fu H, Wu L, Cui H, Zhou W, Wang J, Wang H, Chu P K, Yu X F. Stable and multifunctional dyemodified black phosphorus nanosheets for near-infrared imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Chemistry of Materials. 2017;29(17):7131–7139. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b01106. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Geng B, Shen W, Li P, Fang F, Qin H, Li X K, Pan D, Shen L. Carbon dot-passivated black phosphorus nanosheet hybrids for synergistic cancer therapy in the NIR-II window. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2019;11(48):44949–44960. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b15569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Huang W Q, Wang F, Nie X, Zhang Z, Chen G, Xia L, Wang L H, Ding S G, Hao Z Y, Zhang W J, Hong C Y, You Y Z. Stable black phosphorus nanosheets exhibiting high tumor-accumulating and mitochondria-targeting for efficient photothermal therapy via double functionalization. ACS Applied Bio Materials. 2020;3(2):1176–1186. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b01052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Chen B Q, Kankala R K, Zhang Y, Xiang S T, Tang H X, Wang Q, Yang D Y, Wang S B, Zhang Y S, Liu G, Chen A Z. Gambogic acid augments black phosphorus quantum dots (BPQDs)-based synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy through downregulating heat shock protein expression. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2020;390:124312. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124312. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Guo T, Wu Y, Lin Y, Xu X, Lian H, Huang G, Liu J Z, Wu X, Yang H H. Black phosphorus quantum dots with renal clearance property for efficient photodynamic therapy. Small. 2018;14(4):1702815. doi: 10.1002/smll.201702815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Liu J, Du P, Mao H, Zhang L, Ju H, Lei J. Dual-triggered oxygen self-supply black phosphorus nanosystem for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;172:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.04.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chen W, Ouyang J, Liu H, Chen M, Zeng K, Sheng J, Liu Z, Han Y, Wang L, Li J, Deng L, Liu Y N, Guo S. Black phosphorus nanosheet-based drug delivery system for synergistic photodynamic/photothermal/chemotherapy of cancer. Advanced Materials. 2017;29(5):1603864. doi: 10.1002/adma.201603864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Qiu M, Wang D, Liang W, Liu L, Zhang Y, Chen X, Sang D K, Xing C, Li Z, Dong B, Xing F, Fan D, Bao S, Zhang H, Cao Y. Novel concept of the smart NIR-light-controlled drug release of black phosphorus nanostructure for cancer therapy. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2018;115(3):501–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714421115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Gao N, Nie J, Wang H, Xing C, Mei L, Xiong W, Zeng X, Peng Z. A versatile platform based on black phosphorus nanosheets with enhanced stability for cancer synergistic therapy. Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology. 2018;14(11):1883–1897. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2018.2632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Zeng X, Luo M, Liu G, Wang X, Tao W, Lin Y, Ji X, Nie L, Mei L. Polydopamine-modified black phosphorous nanocapsule with enhanced stability and photothermal performance for tumor multimodal treatments. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2018;5(10):1800510. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Chen L, Qian M, Jiang H, Zhou Y, Du Y, Yang Y, Huo T, Huang R, Wang Y. Multifunctional mesoporous black phosphorus-based nanosheet for enhanced tumor-targeted combined therapy with biodegradation-mediated metastasis inhibition. Biomaterials. 2020;236:119770. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Hai L, Zhang A, Wu X, Cheng H, He D, Wang T, He X, Wang K. Liposome-stabilized black phosphorus for photothermal drug delivery and oxygen self-enriched photodynamic therapy. ACS Applied Nano Materials. 2020;3(1):563–575. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b02119. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Li Z, Hu Y, Fu Q, Liu Y, Wang J, Song J, Yang H. NIR/ROS-responsive black phosphorus QD vesicles as immunoadjuvant carrier for specific cancer photodynamic immunotherapy. Advanced Functional Materials. 2020;30(3):1905758. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201905758. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Liu J, Du P, Liu T, Córdova Wong B J, Wang W, Ju H, Lei J. A black phosphorus/manganese dioxide nanoplatform: oxygen self-supply monitoring, photodynamic therapy enhancement and feedback. Biomaterials. 2019;192:179–188. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Wang Z, Zhao J, Tang W, Hu L, Chen X, Su Y, Zou C, Wang J, Lu W W, Zhen W, Zhang R, Yang D, Peng S. Multifunctional nanoengineered hydrogels consisting of black phosphorus nanosheets upregulate bone formation. Small. 2019;15(41):1901560. doi: 10.1002/smll.201901560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Pan W, Dai C, Li Y, Yin Y, Gong L, Machuki J O, Yang Y, Qiu S, Guo K, Gao F. PRP-chitosan thermoresponsive hydrogel combined with black phosphorus nanosheets as injectable biomaterial for biotherapy and phototherapy treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Biomaterials. 2020;239:119851. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Xu C, Xu Y, Yang M, Chang Y, Nie A, Liu Z, Wang J, Luo Z. Black-phosphorus-incorporated hydrogel as a conductive and biodegradable platform for enhancement of the neural differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Advanced Functional Materials. 2020;30(39):2000177. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000177. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Chen W, Ouyang J, Yi X, Xu Y, Niu C, Zhang W, Wang L, Sheng J, Deng L, Liu Y N, Guo S. Black phosphorus nanosheets as a neuroprotective nanomedicine for neurodegenerative disorder therapy. Advanced Materials. 2018;30(3):1703458. doi: 10.1002/adma.201703458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yang J, Liu W, Sun Y, Dong X. LVFFARK-PEG-stabilized black phosphorus nanosheets potently inhibit amyloid-β fibrillogenesis. Langmuir. 2020;36(7):1804–1812. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b03612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Hou J, Wang H, Ge Z, Zuo T, Chen Q, Liu X, Mou S, Fan C, Xie Y, Wang L. Treating acute kidney injury with antioxidative black phosphorus nanosheets. Nano Letters. 2020;20(2):1447–1454. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b05218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Huang X, Shang W, Deng H, Zhou Y, Cao F, Fang C, Lai P, Tian J. Clothing spiny nanoprobes against the mononuclear phagocyte system clearance in vivo: photoacoustic diagnosis and photothermal treatment of early stage liver cancer with erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged gold nanostars. Applied Materials Today. 2020;18:100484. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2019.100484. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lai P, Wang L, Tay J W, Wang L V. Photoacoustically guided wavefront shaping for enhanced optical focusing in scattering media. Nature Photonics. 2015;9(2):126–132. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhou Y, Cao F, Li H, Huang X, Wei D, Wang L, Lai P. Photoacoustic imaging of microenvironmental changes in facial cupping therapy. Biomedical Optics Express. 2020;11(5):2394–2401. doi: 10.1364/BOE.387985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Shao J, Xie H, Huang H, Li Z, Sun Z, Xu Y, Xiao Q, Yu X F, Zhao Y, Zhang H, Wang H, Chu P K. Biodegradable black phosphorus-based nanospheres for in vivo photothermal cancer therapy. Nature Communications. 2016;7(1):12967. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Kenry Y, Duan Y, Liu B. Recent advances of optical imaging in the second near-infrared window. Advanced Materials. 2018;30(47):1802394. doi: 10.1002/adma.201802394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Gu C, Zheng C, Liu B, Feng T, Ma J, Sun H. Synthesis of a dithieno[3,2-b:2′,3′-d]silole-based conjugated polymer and characterization of its short wave near-infrared fluorescence properties. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences. 2020;13(5):2041002. doi: 10.1142/S1793545820410023. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Idris N M, Gnanasammandhan M K, Zhang J, Ho P C, Mahendran R, Zhang Y. In vivo photodynamic therapy using upconversion nanoparticles as remote-controlled nanotransducers. Nature Medicine. 2012;18(10):1580–1585. doi: 10.1038/nm.2933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Hemmer E, Benayas A, Légaré F, Vetrone F. Exploiting the biological windows: current perspectives on fluorescent bioprobes emitting above 1000 nm. Nanoscale Horizons. 2016;1(3):168–184. doi: 10.1039/C5NH00073D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Liu Y, Liu H, Yan H, Liu Y, Zhang J, Shan W, Lai P, Li H, Ren L, Li Z, Nie L. Aggregation-induced absorption enhancement for deep near-infrared II photoacoustic imaging of brain gliomas in vivo. Advanced Science (Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany) 2019;6(8):1801615. doi: 10.1002/advs.201801615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Brown S B, Brown E A, Walker I. The present and future role of photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment. The Lancet. Oncology. 2004;5(8):497–508. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(04)01529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Castano A P, Mroz P, Hamblin M R. Photodynamic therapy and anti-tumour immunity. Nature Reviews. Cancer. 2006;6(7):535–545. doi: 10.1038/nrc1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Fu J, An D, Song Y, Wang C, Qiu M, Zhang H. Janus nanoparticles for cellular delivery chemotherapy: recent advances and challenges. Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 2020;422:213467. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213467. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Devlin E J, Denson L A, Whitford H S. Cancer treatment side effects: a meta-analysis of the relationship between response expectancies and experience. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2017;54(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2017.03.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Rothenberg M, Ling V. Multidrug resistance: molecular biology and clinical relevance. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1989;81(12):907–910. doi: 10.1093/jnci/81.12.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Guo R, Peng H, Tian Y, Shen S, Yang W. Mitochondria-targeting magnetic composite nanoparticles for enhanced phototherapy of cancer. Small. 2016;12(33):4541–4552. doi: 10.1002/smll.201601094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Huang K, Wu J, Gu Z. Black phosphorus hydrogel scaffolds enhance bone regeneration via a sustained supply of calcium-free phosphorus. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2019;11(3):2908–2916. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b21179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Wang Y, Hu X, Zhang L, Zhu C, Wang J, Li Y, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhang Y, Yuan Q. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition-guided biomineralization. Nature Communications. 2019;10(1):2829. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10761-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Raucci M G, Fasolino I, Caporali M, Serrano-Ruiz M, Soriente A, Peruzzini M, Ambrosio L. Exfoliated black phosphorus promotes in vitro bone regeneration and suppresses osteosarcoma progression through cancer-related inflammation inhibition. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 2019;11(9):9333–9342. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b21592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lee Y B, Song S J, Shin Y C, Jung Y J, Kim B, Kang M S, Kwon I K, Hyon S H, Lee H U, Jung S H, Lim D, Han D W. Ternary nanofiber matrices composed of PCL/black phosphorus/collagen to enhance osteodifferentiation. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry. 2019;80:802–810. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2019.06.055. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Qian Y, Yuan W E, Cheng Y, Yang Y, Qu X, Fan C. Concentrically integrative bioassembly of a three-dimensional black phosphorus nanoscaffold for restoring neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and immune homeostasis. Nano Letters. 2019;19(12):8990–9001. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Querfurth H W, LaFerla F M. Alzheimer’s disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;362(4):329–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0909142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


