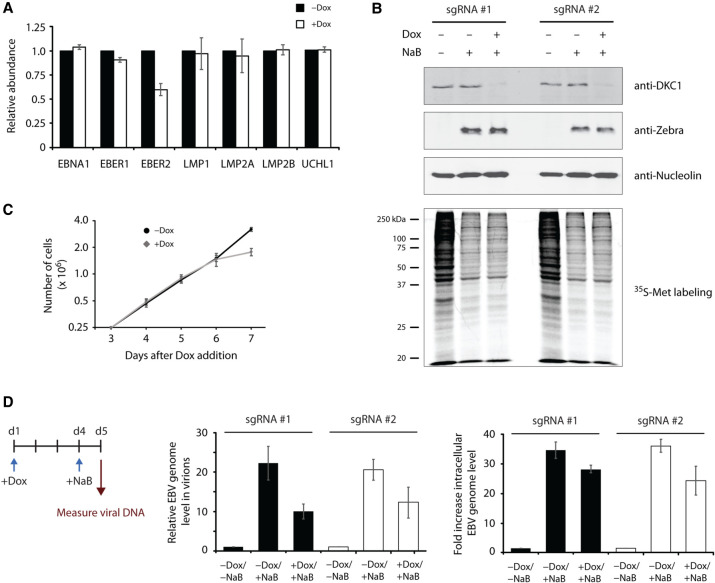
FIGURE 6.
Pseudouridylation of EBER2 is essential for efficient lytic replication of the EBV genome. (A) Pseudouridylation of EBER2 is not required for the regulation of EBV latent membrane protein (LMP) genes LMP1, LMP2A, and LMP2B. EBV latent genes were examined by qRT-PCR following DKC1 knockdown. Except for EBER2, none of the other latent genes tested here was affected. The mRNA level of UCHL1, a cellular EBER2-regulated gene, was also not affected. RNA levels were normalized to GAPDH mRNA abundance and are the average of three independent experiments; error bars represent standard deviation. (B) Two Tet-inducible DKC1-knockdown cell lines were established with the EBV-positive replication-competent cell line HH514-16. DKC1 depletion after 5 d of Dox-addition and induction of EBV lytic replication using sodium butyrate (NaB) was verified. Western blot analysis was performed for DKC1 to monitor knockdown as well as for Zebra to confirm robust induction of the lytic cycle by NaB. Anti-Nucleolin antibody served as a loading control. After Dox-addition, cells were also treated with a brief pulse of 35S-methionine to detect nascent protein production. No apparent difference was observed in control and DKC1-knockdown cells. (C) A representative growth curve for the inducible HH514-16 knockdown cell line is shown. A proliferation defect was observed only after 6 d of Dox-addition to the culture medium. Values are the mean of three measurements; error bars indicate standard deviation. (D) Viral lytic replication is decreased upon DKC1 knockdown. Left panel shows experimental outline. (Middle panel) Viral genome abundance in virions harvested from the culture supernatant was determined after DKC1 depletion (+Dox) and induction of lytic replication (+NaB). The EBV genome level was normalized to a spike-in control to account for sample loss during viral genome isolation. (Right panel) Measurement of intracellular EBV genome abundance normalized to the GAPDH locus. Results are the mean of three independent experiments; error bars represent standard deviation.