Original citation: JCI Insight. 2021;6(4):e140180. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.140180
Citation for this corrigendum: JCI Insight. 2022;7(23):e167011. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.167011
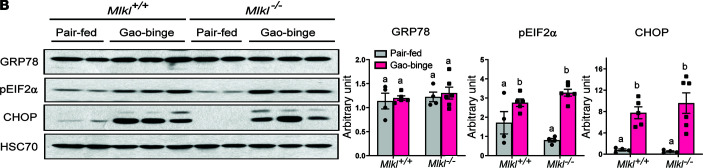
Following the publication of this article, the authors became aware of similarities between the CYP2E1 blot in Figure 4A and the pEIF2A blot in Figure 4B. After reviewing the original data, the authors determined that the pEIF2A blot in Figure 4B was incorrect and that this error was caused by misidentification of pEIF2A after reprobing of the CYP2E1 membrane for pEIF2A, CHOP, and GRP78. The authors have provided a correct version of Figure 4B with data obtained from a repeated experiment. This correct version appears below.
Figure 4B.
The authors regret the error.
Version 1. 12/08/2022
Electronic publication
Footnotes
See the related article at Differential role of MLKL in alcohol-associated and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice and human.