Abstract
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) are major foodborne pathogens that cause human diseases ranging from diarrhea to life-threatening complications including hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Virulence of STEC strains and their ability to cause severe diseases are associated with the activity of prophage-encoded Shiga toxins (Stxs). The first objective of this work was to isolate and characterize the Stx2d phage from STEC O80:H2 and to study the transfer of this phage in non-STEC strains. The second objective was to assess the survival of Galleria mellonella larvae inoculated with these transduced strains. Firstly, one bacteriophage isolated from a STEC O80:H2 strain was used to infect six non-STEC strains, resulting in the conversion of three strains. Then, stability assays were performed, showing that this phage was stable in the new STEC strains after three successive subculturing steps, as confirmed by a combination of short and long read genome sequencing approaches. This phage, vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d, is resistant to moderate temperature and pH. It belongs to a currently unclassified genus and family within the Caudoviricetes class, shares 98% identity with Stx2_112808 phage and encodes several proteins involved in the lysogenic cycle. The yecE gene was identified at the insertion site. Finally, G. mellonella experiments showed that the transduced strains caused significantly higher mortality rates than the corresponding non-STEC strains. In conclusion, this study showed that stx2d gene from O80:H2 E. coli can be transferred to non-STEC strains and contributes to their virulence.
Subject terms: Bacteriophages, Bacterial pathogenesis
Introduction
Shiga toxin (Stx)-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) are notorious foodborne pathogens that cause several human diseases, such as diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)1. Shiga toxin (Stx), encoded by Stx-converting bacteriophages (Stx phages), is one of the primary virulence factors of STEC strains and can exhibit cytotoxicity to various target cells2,3. Stx toxins belong to two families (Stx1 and Stx2). Each of these types are further divided into subtypes, three for Stx1 (Stx1a, Stx1c and Stx1d) and at least seven for Stx2 (Stx2a, Stx2b, Stx2c, Stx2d, Stx2e, Stx2f and Stx2g)4, although new Stx2 subtypes are regularly described, including Stx2h to m5. The stx1 and stx2 genes which encode these toxins are contained within temperate bacteriophage genomes of the former Podoviridae, Myoviridae or Siphoviridae families3, integrated as prophages within the bacterial chromosome. The Stx phages ability to excise themselves and infect other hosts, e.g. in the gastrointestinal tract, makes them important drivers of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) of stx genes among E. coli serotypes and other Enterobacteriaceae. This ability to quickly gain, lose or exchange genes through Stx phages impacts the pathogenicity profile and evolution of STEC strains. Integrated stx genes either remain silent within the lysogens6 or are expressed at low levels following infection with a Stx-converting phage.
STEC can be exposed to various stresses, including heat, mitomycin C, and UV, leading to a bacterial S.O.S response. This response is characterized by the excision of the prophage DNA from the host chromosome and the initiation of the lytic cycle7. This results in host cell lysis and the release of phage particles that can transduce the stx genes to other bacteria8–10.
Nine Stx phage insertion sites have been described to date, including wrbA, which encodes for a tryptophan repressor-binding protein11, yehV encoding a transcriptional regulator12 and yecE, whose function is unknown13.
Evidence suggests that STEC O157:H7 is responsible for numerous outbreaks and has evolved from an EPEC O55:H7 strain by acquisition of Stx2c phage followed by multiple introductions of Stx2a and Stx1a phages14. Other studies have shown that the enteroaggregative STEC strain (EAEC) O104:H4, responsible for the German epidemic in 2011, was driven by the Stx phage transfer from a STEC strain15. Stx phage transfers have also been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo for specific classic serotypes, such as O26:H11, after extraction of the phage from the donor bacterium9,16. Over the last 10 years, a novel serotype of STEC, O80:H2, has emerged as a cause of STEC-HUS17. This serotype has been isolated from patients with STEC-HUS presenting multi-organ failure, and extensive thrombotic microangiopathy18. STEC O80:H2 has been described as a hybrid pathotype that combines the diarrhoeagenic E. coli virulence factors (VFs) Stx, Eae (intimin) and EhxA (enterohaemolysin), with extra-intestinal VFs19.
Initially described in France20, serotype O80:H2 emerged in the 2010s to become one of the three leading serotypes involved in HUS cases21. Moreover, this serogroup has also been isolated from cattle in Spain22, humans and cattle in Belgium23–25, human in Switzerland26 and the Netherlands18. It now represents the third most frequent serotype isolated from HUS cases in Europe, responsible for 9% of European HUS in 201927.
It has been hypothesized that EPEC O80 is the ancestor of STEC O8028. According to this hypothesis, the acquisition of stx2 by EPEC O80 gave rise to globally distributed toxigenic STEC O80. Historically, epidemiological studies have focused on stx2-harboring strains because they are typically associated with more severe clinical outcomes29,30.
A recent study highlighted the circulation of EPEC strains of the same serotype in diarrheic calves25. Genomic analysis showed that the bovine O80:H2 EPEC are closely associated to human O80:H2 STEC but contain neither the stx genes nor the Stx phages. It is therefore possible that the bovine EPEC strains were AE-STEC that lost the Stx phage or represent precursors of AE-STEC which have acquired the Stx phage.
The objective of this work was to isolate and characterize the Stx2d phage from STEC O80:H2, to study the STX phage transfer in non-STEC strains and to assess the virulence of the newly converted strains in vivo in a Galleria mellonella larvae model.
Results
Isolation, host range analysis of Stx2d phages and horizontal transfer of stx2d gene from O80:H2 E. coli to non-pathogenic E. coli
Three temperate phages were induced and isolated from three bovine O80:H2 STEC strains by UV radiation. Lytic plaque formation was analyzed to assess the ability of Stx2d phages to infect a range of host strains (Table 1). The host range analysis showed that the three Stx2d phages isolated from O80:H2 donor strains EH3155, EH3160 and EH3320 produced plaque lysis on strains K12-MG1655, K12-DH5α, O80:H26 and O80:H2.
Table 1.
Escherichia coli strains used in this study.
| Bacterial strains | stx gene | Serotype | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donor strains | |||
| EH3155 | stx2d | O80:H2 | 23 |
| EH3160 | stx2d | O80:H2 | |
| EH3320 | stx2d | O80:H2 | |
| Host (recipient) strains | |||
| K12-MG1655 | – | – | Laboratory strain |
| K12-DH5α | – | – | Laboratory strain |
| ATCC700973 | – | O18:K1 | ATCC |
| ATCC25922 | – | – | ATCC |
| O80:H2 | – | O80:H2 | Laboratory strain |
| O80:H26 | – | O80:H26 | 25 |
The three phages were used to transduce these four positively lysed strains. Three transduced strains (K12-MG1655, K12-DH5a, O80:H26) were confirmed by PCR targeting the stx2d gene. A stability study indicated that the phage isolated from the strain EH3320 was stable in the new STEC strains after three successive subculturing steps unlike the two others (EH3155 and EH3160). This phage was therefore selected for further analysis.
Genome-based characterization of vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d confirms this phage as a temperate lambda-like virus
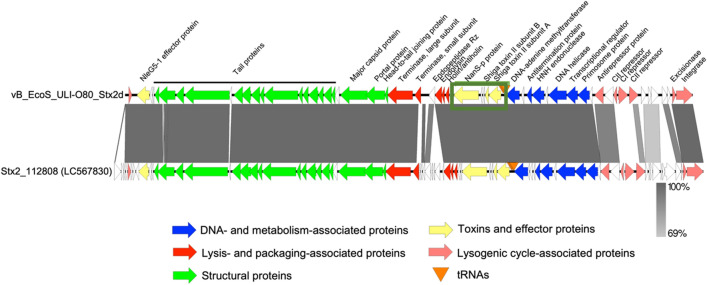
This Stx2d phage was analysed by whole genome sequencing, revealing a dsDNA genome of 40,147 bp (Fig. 1). The phage was named according to the standardized phage nomenclature vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d, belongs to the Caudoviricetes class and a yet unclassified family and genus (Supplementary Fig. 1). The closest similar virus is phage Stx2_112808 (LC567830.1, 88% query coverage, 98.03% sequence identity) and vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d shares > 95% identity with seven other phages according to BLASTn analysis. Homology detection by BLASTp and structure prediction by HHpred analysis31 revealed that the two phages encode several lysogeny associated proteins including an integrase (Int), excisionase (Xis) and different repressors like CI, CII and the antirepressor Cro involved in maintaining the lysogenic cycle. Comparison of phage genomes are shown in Fig. 1. The “stx region”, defined as the phage’s genome region encompassed by the genes Q and S and containing the Stx-coding genes was localized. Noteworthy, the presence of nanS-p gene exclusively in the “stx region” of the phage identified (Fig. 1). Sequencing was submitted to NCBI GenBank under accession number ON416862.
Figure 1.
Comparative genomics of phage vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d and Stx2_112808. Each arrow represents a coding sequence. In red, genes coding packaging and lysis-associated proteins are displayed; in green, structural proteins; in blue, DNA and metabolism-associated proteins; in pink, lysogenic-associated proteins. The stx region is highlighted in a box with toxins and effectors proteins like the two Shiga toxin II subunit A and B and the the nanS-p gene represented in yellow.
Bacteriophage characterization
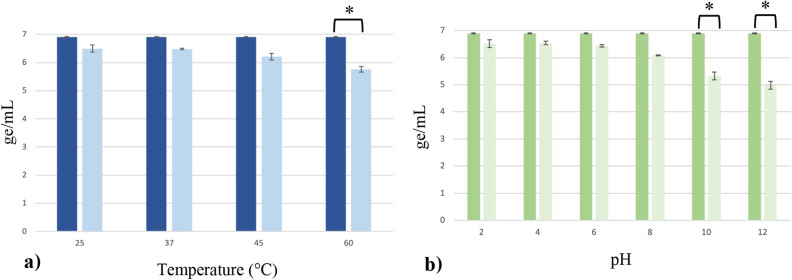
The phage vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d isolated from the EH3320 strain was first characterized for its pH and temperature stability. This one remained stable (< 1 ge/mL) at temperatures of 25 °C, 37 °C and 45 °C. At 60 °C, the phage showed a 1 ge/mL reduction (Fig. 2a). Concerning the pH stability, the phage remained stable between pH 2 and pH 8 and began to decrease with 1 ge/mL at pH 10 and 2 ge/mL at pH 12 (Fig. 2b). This phage thus presented resistance to moderate temperature (45 °C) and a broad pH spectrum (2–8).
Figure 2.
(a) Temperature (b) pH stability results of phage vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d after 1 h. The means of three experiments (± σ) are represented and the concentrations measured before testing are represented by the dark bars. p value (*) ≤ 0.05. ge genomic copies.
The vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d morphology was also characterized by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). This phage presented an icosahedral symmetric non-enveloped head, with a diameter of approximately 60 nm, and a non-contractile and flexible tail of approximately 245 nm in length corresponding to a siphovirus morphology (Fig. 3).
Figure 3.
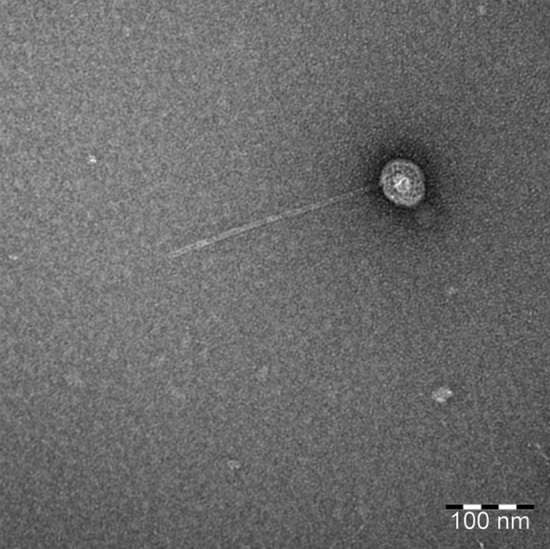
Negative staining transmission electron microscopic image of the phage vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d.
Insertion sites of the phage vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d
Bacterial genomic analysis were performed in order to highlight the presence and the type of insertion sites. The identified insertion site of vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d into the chromosome of the three transduced strains was the same as within the donor strains: the yecE gene (Fig. 4).
Figure 4.
Insertion site yecE of the three transduced strains. tRNA synthetase: Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase, YecD: isochorismatase-family protein, YecN: Inner membrane protein YecN, ComA: Carboxy-S-adenosyl-l-methionine synthase, ComB: tRNA ho5U(34) carboxymethyltransferase, Tor-Z: Trimethylamine-N-oxide reductase.
Assessing the in vivo virulence properties of the prophage in the Galleria mellonella larvae model
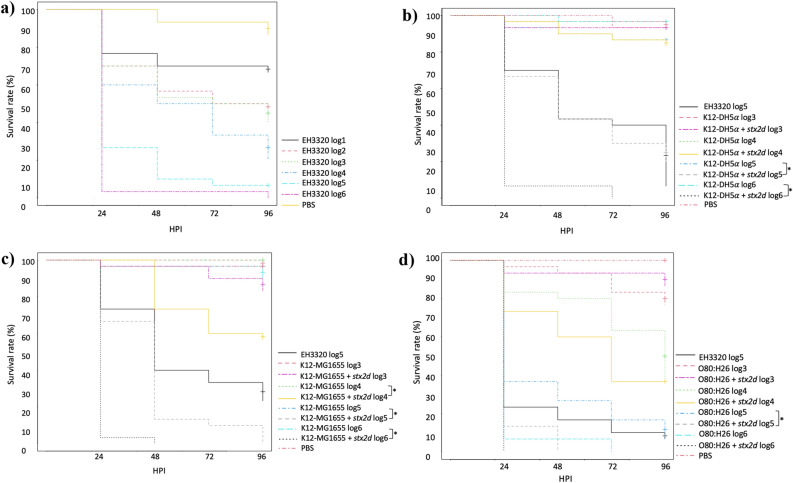
To assess the virulence of the stx2d gene, G. mellonella larvae were inoculated with transduced and host bacterial strains. The optimal inoculation dose for the strain EH3320 causing a lethality between 90 and 100% after 4 days was 105 CFU/10 µL. The larvae survival rates were lower in the infected groups compared to the PBS control group [0–60% vs. 90% of survival at 96 h post infection (HPI)] (Fig. 5a). The non-converted strain K12-DH5α showed a larvae mortality < 10% for all concentrations, whereas converted K12-DH5α strain showed a larvae mortality of 60–70% in 105 CFU/10 µL after 4 days and of 90% at 106 CFU/10 µL after 1 day (Fig. 5b). For the non-converted K12-MG1655 strain, the larvae mortality was also below 10% for all concentrations, whereas the converted strain showed a larvae mortality rate of 90–100% after 4 days at 105 CFU/10 µL and of 90–100% after 1 day at 106 CFU/10 µL (Fig. 5c). Converted O80:H26 strain showed larvae mortality of 100% after 2 days (Fig. 5d).
Figure 5.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves of the experiments with G. mellonella larvae inoculated with (a) EH3320 at different concentrations (b) K12-DH5α with or without vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d (c) K12-MG1655 with or without vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d (d) O80:H26 with or without vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d. Each group contained 30 larvae separated in three groups of 10 larvae. HPI hours post inoculation. *p < 0.05.
Discussion
Lysogenic phage conversion constitutes an efficient mechanism for rapid dissemination of phage-encoded virulence genes32. While in vitro phage-mediated transmission of the stx2 gene between different laboratory bacterial strains and E. coli O157:H7 has already been described33, studies providing information on transduction in the O80:H26 strain and the identification of the insertion sites of this stx2d gene were lacking. The choice to limit this study to the phage encoding Stx2d was due to the observation that this toxin type is associated with the most severe forms of the infections in humans34.
After being challenged with Stx2d phage stock solutions, the K12-MG1655, K12-DHα5, O80:H2 and O80:H26 E. coli strains produced lysis areas, but the O18-K1 and ATCC 25922 E. coli strains failed to produce any visible lysis. Many factors may contribute to the inability of this phage to infect these bacterial strains, including the lack of the correct receptor for the Stx2d phages or the presence of glucose moieties instead of galactose residues in the terminal position of cell wall lipopolysaccharides35. Systems such as Crispr-Cas936 or BREX could also inhibit the phage infection37.
The stability of transduced stx genes based on the ability of the lysogenized strains to retain the acquired genes up to three subculturing steps in LB broth was determined. The phage Stx2d from the EH3320 strain was stably maintained in all lysogenized hosts as confirmed by PCR. Conversely, the Stx2d phages originating from EH3155 and EH3160 E. coli strains were less stable and appeared to be carried transiently in subcultured cells consistent with what was already described by Tozzoli et al.38.
Several non-O157 AE-STEC serogroups are important causes of human disease, one of the most common being O80:H2, for which hypotheses of stx genes transduction were already discussed in the literature39,40. This study demonstrates that stx2d-harboring phages from AE-STEC O80:H2 can transduce EPEC O80:H26 and to non-pathogenic strains, and convert them to stable lysogens unlike the O80:H2 strain. Even if this variant of O80:H2 strain is phylogenetically related to the donor strains23, it is possible that strain O80:H2 could contain active defense systems like nucleic acid restriction, abortive infection or even chemical defense41. Conversely, O80 STEC can lose stx genes at appreciable frequencies, thereby reverting to being EPEC as showed in this study. STEC O80 and EPEC O80 represent a dynamic system in which bidirectional conversion yields different pathotypes. Stx-encoding bacteriophages are the major elements facilitating this conversion. The ability of STEC O80 strains to cause HUS indicates that such organisms are more virulent than EPEC strains lacking the stx gene.
If this is true, a change in the pathotype of the infecting E. coli O80 strain during an infection by the lost or acquisition of an Stx-encoding bacteriophage might have clinical implications. For instance, using the paradigm that Stx causes HUS, the loss of a stx gene during early infection, before Stx production, might prevent the development of HUS for the patient.
Genome analysis revealed that the phage belongs to a currently unclassified genus and family within the Caudoviricetes class. It shares 98% identity with Stx2_112808 phage (isolated from an E. coli O145:H28 strain isolated in Japan and represent 20.3% of HUS cases in Argentina42) and > 95% identity with seven other phages (Supplementary Fig. 1). Homology detection and structure prediction showed that the phage encodes different lysogenic cycle-associated proteins like an integrase, an excisionase, the different repressors CI, CII and the antirepressor Cro. The integrase gene plays an important role in the lysogenic cycle of temperate phages43. It is an enzyme associated with phage genome insertion within the bacterial chromosomes at certain attachment sites (attP and attB) by a site-specific recombination process44. Shiga toxin containing prophages can convert the host strain since they integrate their genome using specific gene insertion sites. In these three transduced strains, the encoded gene present was the unknown function yecE, which is consistent with results from Nyambe et al.45,46. A previous study indicated that the genetic diversity of the integrase-encoding genes among various Stx prophages is related to the different insertion sites of these prophages within the bacterial chromosome47. While multiple integration sites for Stx phage and formation of double lysogens occurs often48, it was not the case in this study. The excisionase controls integrase-mediated DNA rearrangements. It is strongly associated with the Stx prophage regulation induction process, triggering a lytic cycle of Stx prophages to lyse bacterial host and release Stx-converting phages in the environment3,33. The different repressors enable the entry of the phage into the lysogenic cycle. The nanS-p gene present in the Stx region is the phage homologue of the bacterial gene nanS, which encodes an esterase involved in the metabolization of sialic acids produced by submaxillary glands of bovines and present in great quantities in their gastrointestinal tract49.
In vivo experiments with G. mellonella larvae showed decreased survival rates in larvae treated with the transduced E. coli strains. Indeed, only a few hours after bacterial inoculation, some larvae already showed visible signs of infection (decreased activity, melanization). The bacterial dose used (106 CFU/larvae) resulted in a very high mortality within 24 HPI in the infected group. In vivo experiments support the in vitro results with the fact that the phage Stx2 harboring stx2 genes bring at least a part of the virulence. The difference is less obvious between the two O80 E. coli strains because the EPEC O80:H26 E. coli strain already possess virulence factors like intimine (eae), enterohemolysin (hly) and genes present on the pS88 plasmid (iron, iss, iha).
In conclusion, the vB_EcoS_ULI-O80_Stx2d phage is stable and can resist to moderate pH and temperature conditions, which may be interesting for its survival in various environments. Our data demonstrate that UV radiation cause induction of lambdoid prophages carrying stx genes which can convert non-pathogenic E. coli into STECs. This result is in line with the hypothesis that EPEC O80:H2 can become AE-STEC by acquisition of the stx phage presented in a recent study23.
These findings provide insights into the role of Stx-converting phage in the bacterial pathogenicity evolution through lysogenization in STEC strains. The consequences of this HGT over extended periods of time (frequency of gene acquisition upon transduction, gene stability) may result in a great clinical concern. Moreover, this study showed that newly converted strains are significantly more virulent than the non-converted ones suggesting the important role of the Stx2d phage in the pathogenicity.
Further studies are needed to analyze the Stx production of newly converted STEC and to attempt the transduction between different serotypes strains. Comparison of the genome structure and morphology of all Stx2d phages and stx2d genes would allow a better understanding of their epidemiology in the different STEC serotypes. Additional studies are needed to confirm the predicted protein functions of the Stx-convertig phages and the coevolution of Stx-converting phages with their STEC hosts.
Materials and methods
Bacterial strains
The three stx2d positive EH3155 (SAMN14087149), EH3160 (SAMN14087151) and EH3320 (SAMN14087146) strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. These three strains are phylogenetically very close based on previous work23 and also produce the AE lesion. They were provided by ARSIA (Regional Association for Animal Health and Identification) and were used as the donor strains for the phage transduction experiments. Recipient strains for lysogenization experiments were selected based on their avirulent background (E. coli K12-MG1655, E. coli K12-DH5α, E. coli ATCC O18-K1 and E. coli ATCC 25922) and their seropathotype (EPEC E. coli O80:H26 and EPEC E. coli O80:H2).
Strains were routinely grown overnight in Lysogeny Broth (LB) broth at 37 °C with shaking at 150 rpm or on LB agar plates. Prior to infection experiments, the absence and the presence of stx2d was verified by colony PCR in the host and donor strains, respectively.
Induction of Stx2d phages
Escherichia coli EH3155, EH3160 and EH3320 (harboring Stx2d encoding prophage) were grown from frozen cryogenic vial stocks, streaked on LB agar plates, grown from single colonies overnight at 37 °C in LB broth and then 1:100 was inoculated into fresh LB medium. The inoculum was incubated at 37 °C, 250 rpm to an OD600nm of 0.6. For UV induction, 10 mL of the three STEC strains cultures were placed in a petri dish with open lid and exposed for 1 min to UV radiation (0.5 kJ/m2). Following UV radiation, cultures were maintained for 6 h at 37 °C with gentle shaking. Then, the cultures were centrifuged (10 min at 10,000×g) and the supernatants were filtered through a sterile 0.22 μm filter (VWR international) to completely remove bacteria33. The three phages were stored at 4 °C.
Host range and infectivity of Stx2d phages
A total of 200 μL aliquots of the exponential phase (OD600 ≅ 0.3) cultures of each host strain were mixed with 100 μL of phage, incubated at 37 °C for 20 min and 2 mL molten soft LB agar was added and poured onto LB Lennox agar plates, then allowed to solidify at room temperature (RT). Plates were incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. If clear lysis zones were observed, results were considered as positive for each Stx2d-phage stock solution.
Horizontal transfer of stx2d gene from O80:H2 E. coli to non-pathogenic E. coli
Escherichia coli strains presenting a clear lysis were grown at 37 °C in 3 mL of LB broth to the early exponential phase, from which 100 µL aliquots were mixed with 3 mL of LB broth tubes containing 100 µL of 1 M CaCl2 and 500 µL of each phage stock and incubated overnight at 37 °C without shaking. Infected cells were recovered by centrifugation at 6.000×g (20 min, 4 °C) and cell pellets were washed three times with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) to remove non-specifically bound phage particles50. The washed pellets were then suspended in 1 mL of LB broth, spread onto STEC agar plates and incubated overnight at 37 °C. A colony from each plate was randomly selected and subcultured three times on STEC agar to identify stable lysogenic bacteria. After DNA extraction, a stx2d specific PCR51 was performed to confirm whether the converted cells acquired the gene. Stock cultures were prepared of each strain by centrifugation (8000×g, 10 min). The pellets were suspended in 1 mL of LB broth and 0.5 mL was transferred to 2 mL beads-containing cryogenic vials and stored at − 80 °C for further use.
pH and temperature stabilities
To investigate the phage stability at high temperature, 1 mL of 108 PFU/mL of filtrate phage solution was added to a 1.5 mL microtube and incubated at 4 different temperatures (25 °C, 37 °C, 45 °C and 60 °C) for 1 h using a heat block. For pH stability, 100 µL of the phage solution (108 PFU/mL) was mixed with 900 µL PBS adjusted to pH 2–4–6–8–10 and 12 with HCl and NaOH and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. For all conditions, DNA was extracted with the DNA blood and tissue kit (Qiagen) and a qPCR was realized to compare the genomic copy numbers of each sample52. After the investigation of the normality of each distribution (corresponding to the concentration data of the phage and for both incubation condition), (by a histogram, a quantile–quantile plot (QQ-plot), a boxplot, and a Shapiro–Wilk test) a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (with multiple comparisons) was used to assess if the concentration obtained after 1 h incubation was significantly different from the original. All statistical analyses were performed using R (p value ≤ 0.05)53.
STX phage quantification
A quantitative PCR was performed using a customized stx2d sequence as a standard curve: -TCAGGCAGATACAGAGAGAATTTCGTCAGGCACTGTCTGAAACTGCTCCTGTGTATACGTGACGCCGG- (Eurogentec).
The qPCR assays were carried out in a 25 µL volume containing 1 × GoTaq® Master Mix 2.0 (Promega), primers and probe (final concentration 300 nM of each primer and 100 nM probe; Eurogentec) (Table 2) and 5 µL template DNA. qPCR was performed with the following amplification program: initial activation of the enzyme at 95 °C for 5 min followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, then 1 min annealing and elongation at 60 °C and cooling at 40 °C for 30 s54.
Table 2.
Primers and probes for qPCR quantification of stx2d55.
| Gene | Primer or probe | Sequence (5′–3′) | Position (5′–3′) | Accession number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stx2 | stx2-F | TCA GGC AIA TAC AGA GAG AAT TTC G | 578–602 | AY443044 |
| stx2-Ra | CCG GIG TCA TCG TAT ACA CAG | 646–626 | AY443044 | |
| stx2-PΦ | CAC TGT CTG AAA CTG CT | 608–624 | AY443044 |
Ф Probe tagged with minor groove-binding non-fluorescent quencher (MGBNFQ) and 6-carboxyfluorescin (FAM) fluorescent label (Eurogentec).
Whole genome sequencing and genomic analysis
The phage genomic DNA was isolated using a phenol–chloroform extraction55. Sequencing was performed on an Illumina (San Diego, CA, USA) MiniSeq machine using the Nextera Flex DNA library kit (Illumina). After assembly of the raw sequencing data using Unicycler56, the most related phages were identified with BLASTn57 and Viptree v3.058. VIRIDIC59 was used for taxonomic classification. Annotation was performed with RASTtk60 on the PATRIC server61 followed by a manual curation using BLASTp and HHPred62 and visualization with Easyfig63. The data were submitted to NCBI GenBank under accession number ON416862. For the bacterial samples, total genomic DNA were extracted with the DNA blood and tissue kit (Qiagen). The DNA was subsequently prepared for Illumina sequencing similarly to the phage DNA and sequenced. In parallel, the DNA were also prepared for long read sequencing using the Rapid barcoding kit (Oxford Nanopore Technology, Oxford, UK) and sequenced on a MinION R9.4.1 flowcell (Oxford Nanopore Technology), with Guppy(v3.1.5) as basecaller64. The genomes were also constructed using Unicycler. The assemblies were visually inspected using Bandage65. A quality control with Quast66 revealed an N50 of 5,264,684 bp (13 contigs), 3,013,105 bp (43 contigs) and 3,012,995 bp (55 contigs) for K12-MG1655, K12-DH5α and O80:H26, respectively.
Transmission electron microscopy
Escherichia coli EH3320 was grown overnight at 37 °C in LB broth. The culture was subsequently diluted 50× in 50 mL of LB broth. Phage induction was carried out by adding mitomycin C (concentration of 1.0 μg/mL) to the culture bottles at OD600 ≅ 0.2, which were further incubated until an OD decrease. The culture was centrifuged at 10,000×g for 10 min at 4 °C. The phage was negatively stained and analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) by the Electron Microscopy unit (ULB, CMMI, Gosselies, Belgium). The grids were stained with 4% uranyl acetate. The sample was placed on the grid using the grid-on-drop method. Observations were made on a Tecnai10 TEM (FEI-TechnoFisher) and images were captured with a Veleta CCD cam.
In vivo assay: Galleria mellonella larvae model
A preliminary experiment aimed to determine the optimal inoculation dose was realized. Six groups of 10 G. mellonella larvae (Animal Confort, Loncin, Belgium) were inoculated using an automatic injector (Cole Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA) with 10 µL of EH3320 at six different concentrations, ranging from 10 to 106 CFU/10 µL. Each larva was inoculated in the last left proleg with a BD Plastipak™ 1 mL sterile syringe (Becton–Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) and a sterile 30-gauge needle (Terumo corporation, Tokyo, Japan). The optimal inoculation dose was expected to cause a lethality of 90–100% after 4 days.
The principal experiments were carried out in technical triplicate to compare the survival of G. mellonella larvae with the non-STEC strains converted or not with the Stx2d phage. For each experiment (three transduced strains), 270 larvae were divided into nine groups (Table 3). Each larvae was inoculated as previously described. The larvae were incubated at 37 °C and mortality was evaluated every 24 h. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were generated to assess the survival of the different groups using R-commander (Rcmdr v2.6-0). Logrank tests were performed to highlight any significant difference in survival rates between the groups (p < 0.05). Back-titration of bacteria was realized to verify the inoculated doses.
Table 3.
Summary table of the G. mellonella larvae groups inoculated in triplicate for the main experiments (survival and titration).
| Groups | Experiments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (CFU/10 µL) | 2 (CFU/10 µL) | 3 (CFU/10 µL) | |
| 1 | PBS | PBS | PBS |
| 2 | K12-DH5α (103) | K12-MG1655 (103) | O80:H26 (103) |
| 3 | K12-DH5α (104) | K12-MG1655 (104) | O80:H26 (104) |
| 4 | K12-DH5α (105) | K12-MG1655 (105) | O80:H26 (105) |
| 5 | K12-DH5α (106) | K12-MG1655 (106) | O80:H26 (106) |
| 6 | K12-DH5α + stx2d (103) | K12-MG1655 + stx2d (103) | O80:H26 + stx2d (103) |
| 7 | K12-DH5α + stx2d (104) | K12-MG1655 + stx2d (104) | O80:H26 + stx2d (104) |
| 8 | K12-DH5α + stx2d (105) | K12-MG1655 + stx2d (105) | O80:H26 + stx2d (105) |
| 9 | K12-DH5α + stx2d (106) | K12-MG1655 + stx2d (106) | O80:H26 + stx2d (106) |
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
The authors thank David Perez-Morga (CMMI, ULB) for the collaboration for the transmission electron microscopy. The CMMI is supported by the European Regional Development Fund and the Walloon Region. The authors also thank Dr Marc Saulmont from ARSIA for providing O80:H2 E. coli strains. The university of Liège provided financial support (‘Fonds Spéciaux de la Recherche Project HYBRID_COLI_O80’).
Author contributions
J.M. and D.T. conceived the project, A.H. and J.D. conducted the experiments, J.W. and A.H. performed the genomics analysis. A.H. and D.T. wrote the paper, R.L. and all other authors reviewed and edited the paper. M.V. produced the transmission electron microscopy image, F.L. performed the statistical analyzes, C.A. gave help and information during some experiments.
Data availability
The data were submitted to NCBI GenBank under accession number ON416862.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-022-26198-8.
References
- 1.Mcallister LJ, et al. Genomic comparison of two O111:H− enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli isolates from a historic hemolytic-uremic syndrome outbreak in Australia. Infect. Immun. 2016;84(3):775–781. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01229-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bloch S, et al. UV-sensitivity of Shiga toxin-converting bacteriophage birions Φ 24B, 933W, P22, P27 and P32. Toxins. 2015;7(9):3727–3739. doi: 10.3390/toxins7093727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Smith DL, et al. Comparative genomics of Shiga toxin encoding bacteriophages. BMC Genom. 2012;13:311. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Scheutz F, et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012;50(9):2951–2963. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00860-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bai X, Scheutz F, Dahlgren HM, Hedenström I, Jernberg C. Characterization of clinical Escherichia coli strains producing a novel Shiga toxin 2 subtype in Sweden and Denmark. Microorganisms. 2021;17(9):2374. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Paul JH, Weinbauer M. Detection of lysogeny in marine environments. Man. Aquat. Viral Ecol. 2010;4:30–33. doi: 10.4319/mave.2010.978-0-9845591-0-7.30. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Imamovic L, Muniesa M. Characterizing RecA-independent induction of Shiga toxin2-encoding phages by EDTA treatment. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:2. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Allison HE, et al. Immunity profiles of wild-type and recombinant Shiga-like toxin-encoding bacteriophages and characterization of novel double lysogens. Infect. Immun. 2003;71(6):3409–3418. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Toth I, et al. Transduction of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with a derivative of a Shiga toxin 2-encoding bacteriophage in a porcine ligated ileal loop system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003;69(12):7242–7247. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.12.7242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fang Y, Mercer RG, Mcmullen LM, Gänzle MG. Induction of Shiga toxin-encoding prophage by abiotic environmental stress in food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017;83(19):1–13. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01378-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Plunkett G, III, Rose DJ, Durfee TJ, Blattner FR. Sequence of Shiga toxin 2 phage 933W from Escherichia coli O157:H7: Shiga toxin as a phage late-gene product. J. Bacteriol. 1999;181:1767–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.6.1767-1778.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Creuzburg K, et al. The Shiga toxin 1-converting bacteriophage BP-4795 encodes an NleA-like type III effector protein. J. Bacteriol. 2005;187:8494–8498. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.24.8494-8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De Greve H, Qizhi C, Deboeck F, Hernalsteens JP. The Shiga-toxin VT2-encoding bacteriophage phi297 integrates at a distinct position in the Escherichia coli genome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2002;1579:196–202. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4781(02)00539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wick LM, Weihong Q, Lacher DW, Whittam TS. Evolution of genomic content in the stepwise emergence of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J. Bacteriol. 2005;187(5):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.5.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brzuszkiewicz E, et al. Genome sequence analyses of two isolates from the recent Escherichia coli outbreak in Germany reveal the emergence of a new pathotype: Entero-aggregative-haemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EAHEC) Arch. Microbiol. 2011;193(12):883–891. doi: 10.1007/s00203-011-0725-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bielaszewska M, et al. Shiga toxin gene loss and transfer in vitro and in vivo during enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O26 infection in humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73(10):3144–3150. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02937-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Soysal N, et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hybrid pathotype O80:H2 as a new therapeutic challenge. Emerg. Infec. Dis. 2016;22(9):1604–1612. doi: 10.3201/eid2209.160304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wijnsma KL, et al. Unusual severe case of hemolytic uremic syndrome due to Shiga toxin 2d-producing E. coli O80:H2. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017;32(7):1263–1268. doi: 10.1007/s00467-017-3642-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Cointe A, et al. Emerging multidrug-resistant hybrid pathotype Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli O80 and related strains of clonal complex 165. Eur. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018;24(12):2262–2269. doi: 10.3201/eid2412.180272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mariani-Kurkdjian P, et al. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome with bacteremia caused by a new hybrid Escherichia coli pathotype. New Microbes New Infect. 2014;2(4):127–131. doi: 10.1002/nmi2.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bruyand M, et al. Paediatric haemolytic uraemic syndrome related to Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, an overview of 10 years of surveillance in France, 2007 to 2016. Eurosurveillance. 2019;24:8. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.8.1800068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Blanco M, et al. Serotypes, virulence genes, and intimin types of Shiga toxin (verotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from cattle in Spain and identification of a new intimin variant gene (eae-ξ) J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004;42(2):645–651. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.2.645-651.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Habets A, et al. Genetic characterization of Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from diarrhoeic and septicaemic calves and relatedness to human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;42(2):645–651. doi: 10.1111/jam.14759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.De Rauw K, et al. Characteristics of Shiga toxin producing and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of the emerging serotype O80:H2 isolated from humans and diarrhoeic calves in Belgium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019;25:23–26. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thiry D, et al. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 in young calves with diarrhea. Belgium. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017;23(12):2093–2095. doi: 10.3201/eid2312.170450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nüesch-Inderbinen M, et al. Serotypes and virulence profiles of Shigatoxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated during 2017 from human infections in Switzerland. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018;308(7):933–939. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.European Food Safety Authority. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control The European Union one health 2019 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2021;19:2. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Donnenberg MS, Whittam TS. Pathogenesis and evolution of virulence in enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Investig. 2001;107(5):539–548. doi: 10.1172/JCI12404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kawano K, Okada M, Haga T, Maeda K, Goto Y. Relationship between pathogenicity for humans and Stx genotype in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serotype O157. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008;27(3):227–232. doi: 10.1007/s10096-007-0420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Orth D, et al. The Shiga toxin genotype rather than the amount of Shiga toxin or the cytotoxicity of Shiga toxin in vitro correlates with the appearance of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007;59(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zimmermann L, et al. A completely reimplemented MPI bioinformatics toolkit with a new HHpred server at its core. J. Mol. Biol. 2018;430(15):2237–2243. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Feiner R, et al. A new perspective on lysogeny: Prophages as active regulatory switches of bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015;13(10):641–650. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yue WF, Du M, Zhu MJ. High temperature in combination with UV irradiation enhances horizontal transfer of Stx2 gene from E. coli O157:H7 to non-pathogenic E. coli. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:2. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Krüger A, Lucchesi PMA. Shiga toxins and Stx phages: Highly diverse entities. Microbiology. 2015;161(3):1–12. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rakhuba DV, Kolomiets EI, Dey ES, Novik GI. Bacteriophage receptors, mechanisms of phage adsorption and penetration into host cell. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2010;59(3):145–155. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2010-023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Asmamaw M, Zawdie B. Mechanism and applications of CRISPR/Cas-9-mediated genome editing. Biologics. 2021;21(15):353–361. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S326422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Goldfarb T, et al. BREX is a novel phage resistance system widespread in microbioal genomes. Embo J. 2015;34:169–183. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tozzoli R. Shiga toxin-converting phages and the emergence of new pathogenic Escherichia coli: A world in motion. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014;4:80. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cointe A, et al. Emergence of new ST301 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli clones harboring extra-intestinal virulence traits in Europe. Toxins. 2021;13:10. doi: 10.3390/toxins13100686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rodwell EV, Vishram B, Smith R, Browning L, Smith-Palmer A, Allison L, Holmes A, Godbole G, McCarthy N, Dallman TJ, Jenkins C. Epidemiology and genomic analysis of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli clonal complex 165 in the UK. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021;70:001471. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Egido JE, Costa AR, Aparicio-Maldonado C, Haas P-J, Brouns SJJ. Mechanisms and clinical importance of bacteriophage resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022 doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuab048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Carbonari CC, Miliwebsky ES, Zolezzi G, Deza NL, Fittipaldi N, Manfredi E, Baschkier A, D'Astek BA, Melano RG, Schesi C, Rivas M, Chinen I. The importance of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O145:NM[H28]/H28 infections in Argentina, 1998–2020. Microorganisms. 2022;7:10. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10030582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Balding C, Bromley SA, Pickup RW, Saunders JR. Diversity of phage integrases in Enterobacteriaceae: Development of markers for environmental analysis of temperate phages. Environ. Microbiol. 2005;7:1558–1567. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Colavecchio A, et al. Prophage integrase typing is a useful indicator of genomic diversity in Salmonella enterica. Front. Microbiol. 2017;8:1283. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nyambe S, Burgess C, Whyte P, Bolton D. An investigation of vtx2 bacteriophage transduction to different Escherichia coli patho-groups in food matrices and nutrient broth. Food. Microbiol. 2017;68:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Reckentenwald J, Schmidt H. The nucleotide sequence of Shiga toxin (Stx) 2e-encoding phage φP27 is not related to other Stx phage genomes, but the modular genetic structure is conserved. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2002;70(4):1896–1908. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.1896-1908.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Serra-Moreno R, Jofre J, Munesia M. Insertion site occupancy by Stx2 bacteriophages depends on the locus availability of the host strain chromosome. J. Bact. 2007;189(18):6645–6654. doi: 10.1128/JB.00466-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fogg PCM, Gossage SM, Smith DL, Saunders JR, McCarthy AJ, Allison HE. Identification of multiple integration sites for Stx-phage Phi24B in the Escherichia coli genome, description of a novel integrase and evidence for a functional anti-repressor. Microbiology. 2007;153:4098–4110. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/011205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Saile N, et al. Growth advantage of Escherichia coli O104:H4 strains on 5-N-acetyl-9-O-acetyl neuraminic acid as a carbon source is dependent on heterogeneous phage-Borne nanS-p esterases. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018;308(4):459–468. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2018.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Khalil RKS, Skinner C, Patfield S, He X. Phage-mediated Shiga toxin (Stx) horizontal gene transfer and expression in non-Shiga toxigenic Enterobacter and Escherichia coli strains. Pathog. Dis. 2016;74:5. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Iguchi A, et al. Escherichia coli O-genotyping PCR: A comprehensive and practical platform for molecular O serogrouping. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003;53:2427–2432. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00321-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Park D-S, Park J-H. Characteristics of bacteriophage isolates and expression of Shiga-toxin genes transferred to non Shiga toxin-producing E. coli by transduction. J. Microbiol. Technol. 2021;31(5):1–7. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2102.02040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/fr/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing.
- 54.Verstraete K, et al. A qPCR assay to detect and quantify Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) in cattle and on farms: A potential predictive tool for STEC culture-positive farms. Toxins. 2014;6(4):1201–1221. doi: 10.3390/toxins6041201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Eskenazi A, et al. Combination of pre-adapted bacteriophage therapy and antibiotics for treatment of fracture-related infection due to pandrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 2022;13:302. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27656-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. BioRxiv. 2016 doi: 10.1101/096412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Altschul S. Basic local alignment search tool (BLAST) J. Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1990.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nishimura Y, et al. ViPTree: The viral proteomic tree server. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(15):2379–2380. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Moraru C, Varsani A, Kropinski AM. VIRIDIC-A novel tool to calculate the intergenomic similarities of prokaryote-infecting viruses. Viruses. 2020;12(11):1268. doi: 10.3390/v12111268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Brettin T, et al. RASTtk: A modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:8365. doi: 10.1038/srep08365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wattam AR, et al. Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource center. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2017;45(D1):D535–D542. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Söding J, Biegert A, Lupas AN. The HHpred interactive server for protein homology detection and structure prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:244–248. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sullivan MJ, Petty NK, Beatson SA. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics. 2011;27(7):1009–1010. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wick RR, Judd LM, Holt KE. Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2019;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1727-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wick RR, Schultz MB, Zobel J, Holt KE. Bandage: Interactive visualization of de novo genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(20):3350–3352. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 2013;15(29):1072–1075. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data were submitted to NCBI GenBank under accession number ON416862.