Abstract
Objective
Current evidence suggests a decrease in elective diagnostic imaging procedures during the COVID-19 pandemic with potentially severe long-term consequences. The aim of this study was to quantify recent trends in public interest and related online search behavior for a range of imaging modalities, and “nowcast” future scenarios with respect to imaging use.
Methods
We used Google Trends, a publicly available database to access search query data in systematic and quantitative fashion, to search for key terms related to clinical imaging. We queried the search volume for multiple imaging modalities, identified the most common terms, extracted data for the United States over the time range from August 1, 2016 to August 1, 2020. Results were given in relative terms, using the Google metric ‘search volume index’.
Results
We report a decrease in public interest across all imaging modalities since March 2020 with a subsequent slow increase starting in May 2020. Mean relative search volume (RSV) has changed by −19.4%, −38.3%, and −51.0% for the search terms “Computed tomography”, “Magnetic resonance imaging”, and “Mammography”, respectively, and comparing the two months prior to and following March 1, 2020. RSV has since steadily recuperated reaching all-year highs.
Conclusion
Decrease in public interest coupled with delays and deferrals of diagnostic imaging will likely result in a high demand for healthcare in the coming months. To respond to this challenge, measures such as risk-stratification algorithms must be developed to allocate resources and avoid the risk of overstraining the healthcare system.
Keywords: Google Trends, Infodemiology, Clinical imaging, Health promotion
1. Introduction
Imaging is in widespread clinical use for screening, diagnostic, staging, and therapeutic applications. COVID-19 has swiftly impacted clinical practice in unparalleled ways, leading to a decline of non-emergent medical care across medical specialties in order to preserve healthcare resources and prevent viral spread. Emerging evidence suggest a collateral damage of COVID-19 on other diseases due to a reduction in diagnostic and therapeutic availability.1 , 2 This initial suspicion, if true, may have devastating long-term consequences. It is thus with urgency to analyze patient awareness and behavior in seeking adequate and sufficient medical care.
Google Trends has previously been linked to nowcast patient behavior.3 , 4 The use of online health information sparked a new research discipline referred to as infodemiology.5 Here, we hypothesized a reduction in public interest in a range of imaging modalities.
2. Methods
Google Trends is a freely available tool enabling study of online search interest in keywords and topics over time.6 We sought to quantify public interest and related online search behavior across a range of imaging modalities since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, including computed tomography (CT), X-ray, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and mammography. We extracted data for the United States over the specified time range from August 1, 2016 to August 1, 2020. Results are reported in relative search volume (RSV) which ranges from 0 to 100, with the value ‘100’ reflecting the peak in search volume in a given time range and location. Details on the methodology have been published elsewhere.7 All searches were carried out on August 13, 2020.
3. Results
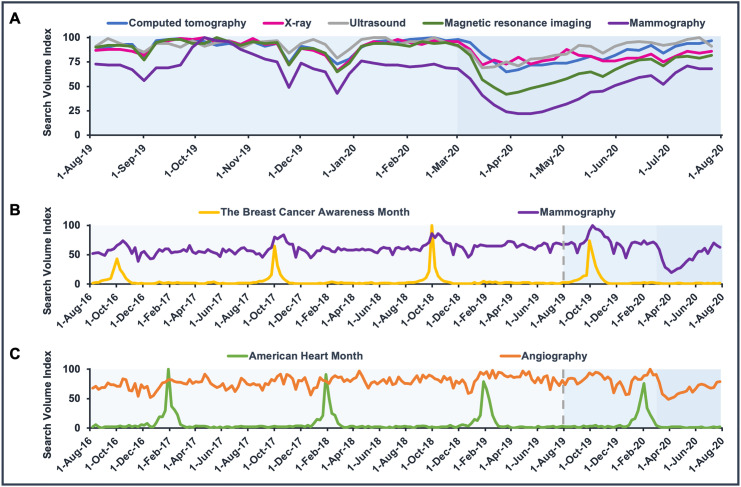
Across imaging modalities, relative search volume (RSV) declined steadily since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic (Fig. 1A). Comparing the mean search volume of the two months prior to and after March 1, 2020 RSV changes were −19.4%, −16.6%, −19.9%, −38.3%, and −51.0% for “Computed tomography”, “X-ray”, “Ultrasound”, “Magnetic resonance imaging”, and “Mammography”, respectively. In the same order of search terms, interest increased by 10.4%, 2.5%, 18.7%, 24.6%, and 53.9% in the following three months plateauing in July 2020. Search interest in other clinical imaging tools followed a similar trend (Supplemental Fig. 1). Stratifying “Computed tomography” by anatomic region, solely search interest for the term “Chest CT” has transiently increased during March 2020 – for other CT indications including CT head, CT abdomen, and CT angiography, search interest fell notably (Supplemental Fig. 2). To place recent trends in context of historical seasonality in images searches, we conducted analysis of long-term search volume data showing peaks in search interest during October for “The Breast Cancer Awareness Month” and “Mammography (Fig. 1B). Peaks were also noted for “American Heart Month” and Angiography” in February of each year (Fig. 1C), adding context to the above-mentioned changes during the COVID-19 era.
Fig. 1.
US interest in search terms related to a selection of common clinical imaging tools:
Google Trends RSV for the time periods (A) August 1, 2019 to August 1, 2020 presented as weekly data and (B & C) August 1, 2016 to August 1, 2020 presented as weekly data for common clinical imaging tools and other terms related to health awareness, namely “Computed tomography” (blue), “X-ray” (pink), “Ultrasound” (grey), “Magnetic resonance imaging” (dark green), “Mammography” (purple), “The Breast Cancer Awareness Month” (yellow), “American Heart Month” (green), and “Angiography” (orange). All depicted lines represent data from Google Trends. (Search query on: August 13, 2020).
RSV = Relative search volume. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
4. Discussion
In line with a rapid decrease in the number of healthcare visits and elective procedures,8 we report a decrease in public interest in clinical imaging across all imaging modalities. The initial spike in search interest solely for “Chest CT” compared with other anatomic regions associated with computed tomography may be linked to its potential use in diagnosing and managing manifestations of COVID-19.[9], [10], [11] Here, we also showed that search interest in a broad range of imaging tools has largely recuperated suggesting that public interest and potential need for real-world clinical diagnostic procedures is rising.
Rosenkrantz and Prabhu have previously identified the sensitivity of search engine data for temporal and spatial variation.12 The Breast Cancer Awareness Month and the American Heart Month are success stories in fostering patient education and health behavior that can be measured in terms of online search interest. Conversely, the reduction in search interest we showed here point towards a decrease in health awareness for search terms not related to COVID-19. This may have potential long-term implications. First, non-emergent health conditions could go undiagnosed with reduced imaging. Second, once normal imaging schedules are resumed, longer waiting periods can be expected with potentially delayed diagnoses as a direct consequence. Both a delay or lack of diagnosis could bring about increased mortality rates in the coming years. This would be consistent with already emerging data, most recently in the reduction of US patients undergoing neuroimaging for stroke evaluation during the pandemic.2
These scenarios underscore the need to strategies to accommodate a potential spike in patients seeking imaging in the coming months. For some diseases this shift from a drastic reduction of in-hospital procedures to an increase in demand for healthcare has already partly been recognized, for instance in the care of patients needing breast cancer surgery.13 Data on changes in patient care during the pandemic are now starting to become available. However, our analysis has future implications as clear strategies for the most effective use of healthcare resources in coming months are not yet well developed.14
Our study has limitations. First, public interest as expressed in search engine volume is not meant to substitute for traditional clinical data and recorded procedure numbers. Second, the selection of imaging modalities in this analysis is by no means exhaustive and offers rather an overview of the most common diagnostic tools. Third, we cannot exclude that the chosen query terms may have been entered for other reasons (i.e. by scientists or healthcare professionals themselves). Linguistically, terms related to a specific subject may also change over time and are not free of geographic bias. Overall, however, we believe that our comprehensive approach has captured the most representable query terms for clinical imaging whilst conducting this study. Lastly, even though search volume data are valuable for studying the population at large, younger people are likely overrepresented due to more frequent internet use.
5. Conclusion
We report an unprecedented decline in search interest in clinical imaging during the unfolding of the COVID-19 pandemic with a subsequent recuperation of search interest until August 2020. A decrease in pursuit of imaging related information and likely a decrease in real-world clinical imaging may bring about collateral damage in the long run and must be addressed proactively. A recent strong increase in public interest may be the first indicator of a new medical urgency. Risk stratification algorithms for prioritizing use of imaging-based diagnostic tools may contribute to an effective care of patients whilst ensuring healthcare resources are less strained during the ongoing pandemic.
Declaration of competing interest
None of the authors report conflicts of interest related to this project.
Acknowledgments
None.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.11.037.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary material
References
- 1.Lange S.J., Ritchey M.D., Goodman A.B., et al. Potential indirect effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on use of emergency departments for acute life-threatening conditions - United States, January-May 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(25):795–800. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6925e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kansagra A.P., Goyal M.S., Hamilton S., Albers G.W. Collateral effect of Covid-19 on stroke evaluation in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(4):400–401. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2014816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang Y., Yakob L., Bonsall M.B., Hu W. Predicting seasonal influenza epidemics using cross-hemisphere influenza surveillance data and local internet query data. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):3262. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39871-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jacobsen G.D., Jacobsen K.H. Health awareness campaigns and diagnosis rates: evidence from National Breast Cancer Awareness Month. J Health Econ. 2011;30(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jhealeco.2010.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eysenbach G. Infodemiology and infoveillance: framework for an emerging set of public health informatics methods to analyze search, communication and publication behavior on the internet. J Med Internet Res. 2009;11(1):e11. doi: 10.2196/jmir.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nuti S.V., Wayda B., Ranasinghe I., et al. The use of google trends in health care research: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109583. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mavragani A., Ochoa G. Google Trends in Infodemiology and Infoveillance: methodology framework. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2019;5(2):e13439. doi: 10.2196/13439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Diaz A., Sarac B.A., Schoenbrunner A.R., Janis J.E., Pawlik T.M. Elective surgery in the time of COVID-19. Am J Surg. 2020;219(6):900–902. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kim H., Hong H., Yoon S.H. Diagnostic performance of CT and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for coronavirus disease 2019: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 2020:201343. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020201343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fields B.K.K., Demirjian N.L., Gholamrezanezhad A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) diagnostic technologies: a country-based retrospective analysis of screening and containment procedures during the first wave of the pandemic. Clin Imaging. 2020;67:219–225. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.08.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Demirjian N.L., Fields B.K.K., Gholamrezanezhad A. Role of chest CT in resource-driven healthcare systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(3):W36. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rosenkrantz A.B., Prabhu V. Public interest in imaging-based Cancer screening examinations in the United States: analysis using a web-based search tool. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016;206(1):113–118. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.14840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Smith B.L., Nguyen A., Korotkin J.E., et al. A system for risk stratification and prioritization of breast cancer surgeries delayed by the COVID-19 pandemic: preparing for re-entry. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020;183(3):515–524. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05792-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Azam S.A., Myers L., Fields B.K.K., et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: review of guidelines for resuming non-urgent imaging and procedures in radiology during phase II. Clin Imaging. 2020;67:30–36. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2020.05.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material