Abstract
Background
An unprecedented global monkeypox outbreak started in May, 2022. No data are yet available about the dynamics of the immune response against monkeypox virus. The aim of this study was to describe kinetics of T-cell response, inflammatory profile, and pox-specific T-cell induction in patients with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox.
Methods
17 patients with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox admitted at the Lazzaro Spallanzani National Institute for Infectious Diseases (Rome, Italy), from May 19, to July 7, 2022, were tested for differentiation and activation profile of CD4 and CD8 T (expression of CD38, PD-1, and CD57 assessed by flow cytometry), frequency of pox-specific T cells (by standard interferon-γ ELISpot), and release of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in plasma (by ELISA). All patients were tested 10–12 days after symptoms onset. In a subgroup of nine patients with a laboratory-confirmed monkeypox, the kinetics of the immune response were analysed longitudinally according to timing from symptoms onset and compared with ten healthy donors (ie, health-care workers recruited from the same institution).
Findings
Among the 17 patients, ten were HIV negative and seven HIV positive, all with good viro-immunological status. On days 0–3 from symptom onset, patients with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox were characterised by a statistically significant reduction in CD4+ T cells (p=0·0011) and a concurrent increase of CD8+ T cells (p=0·0057) compared with healthy donors. A lower proportion of naive (CD45RA+CD27+) CD4+ T cells was observed in six (67%) of nine patients and a concomitant higher proportion of effector memory (CD45RA-CD27-) CD4+ T cells in all patients; this skewed immune profile tended to normalise over time. A similar differentiated profile was also observed in CD8+ T cells with a consistent expansion of terminally differentiated CD8+ T cells. Patients with monkeypox had a higher proportion of CD4+CD38+ and CD38+CD8+ T-cells than healthy donors, which normalised after 12–20 days from symptom onset. The expression of PD-1 and CD57 on CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells showed kinetics similar to that observed for CD38. Furthermore, the inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF) were higher in patients with monkeypox than in healthy donors and, although they decreased over time, they remained elevated after recovery. Almost all patients (15 [94%] of 16) developed a pox-specific Th1 response. No differences in immune cells profile were observed between patients with and without HIV, whereas paucysimptomatic patients (without systemic symptoms, with less than five skin lesions, and no other mucosal localisation of monkeypox) showed a less perturbed immune profile early after symptom onset.
Interpretation
Our data showed the immunological signature of monkeypox virus infection, characterised by an early expansion of activated effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that persisted over time. Almost all patients, even regardless of HIV infection, developed a poxvirus-specific Th1 cell response. These results might have implications on the expected immunogenicity of monkeypox vaccination, suggesting that it might not be necessary to vaccinate people who have already been infected.
Funding
Italian Ministry of Health.
Translation
For the Italian translation of the abstract see Supplementary Materials section.
Introduction
Since May, 2022, more than 60 000 human cases of monkeypox have been reported in non-endemic countries.1 The clinical picture of the current outbreak is quite different from the previously described human monkeypox virus infections in west and central Africa because of the asynchronous evolution of lesions, and the more prevalent genital and perianal localisation.2, 3 The unprecedented outbreak of monkeypox virus induced the scientific community to discuss vaccination strategies for populations at high risk,4 considering that 92–98% of people involved in the current outbreak were men who have sex with men.3, 5 Although the smallpox vaccination has been estimated to be 85% cross-protective against monkeypox virus,6 the ability of the background immunity to be protective against monkeypox virus infection is still debated and, if any, it is restricted to people older than 40 years of age. Therefore, the absence of protective immunity in young people might contribute to the monkeypox virus circulation among humans.
Research in context.
Evidence before this study
Since May, 2022, an unprecedented spread of monkeypox in humans has been reported in non-endemic countries. The dynamics of the immune response against monkeypox virus are currently under investigation and very few data are available about the kinetics of immune cellular response. We searched PubMed, medRxiv, bioRxiv, Research Square, and WHO with the terms ‘‘Monkeypox’’ or “Orthopox virus” and “immune response” or “cellular immunity” or “inflammatory profile” or “poxvirus specific T cell” for articles published in English before Aug 22, 2022.
Although data on the immune response to monkeypox virus in humans are limited, experiments in animal models suggest that all immune players contribute to viral clearance, with CD8 T cells playing the main part. In humans, the few described cases of convalescent subjects developed orthopoxvirus-specific IgM, IgG, T cell, and B cell responses, as well as cases of asymptomatic contacts. Several points are under investigation and the current monkeypox epidemic can give a unique possibility to address some of them: the strength of the immune response in human monkeypox infection and its association with the clinical course of the disease and with its severity; the relationship between previous smallpox vaccination and the type of clinical presentation; the presence of asymptomatic infections that can have a deep impact on public health control measures; and the impact of immunodeficiency (eg, HIV) on the clinical presentation and on the ability to mount an effective and long-lasting antiviral immune response or to boost a previous vaccination-induced immunity. To date, no evidence is available on the dynamics of the immune response against monkeypox virus in humans in the current epidemic, which is characterised by a clinical picture that differs from previously described cases (fewer number of skin lesions and their asynchronous evolution, and higher proportion of mucosal tissue involvement) and is mostly spread in young men who have sex with men.
Added value of this study
In the context of the emergence of a new infection, our study attempts to shed light on the kinetics of the T-cell response, in particular on the differentiation and activation profile, the inflammatory cytokine production, and the induction of poxvirus-specific T-cells that develops during monkeypox virus infection.
Our data implement current knowledge on the inflammatory and adaptive immune response to monkeypox virus and their dynamic over time. By describing a rapid and potent T-cell response even in people with HIV, this study proposes this response as the immunological counterpart of a positive clinical prognosis, which has already been observed in other clinical series. The analysis on the short-term specific T-cell response to stimulation with MVA peptide also fits in the context of the known findings on vaccination of the high-risk target population, setting the stage for models of long-term immune protection.
Implications of all the available evidence
Further larger studies on the kinetic and durability of immune response to monkeypox infection and vaccination are important to better define surrogate of protection to manage the new current global outbreak. The extension of these data over time and the characterisation of the long-term cellular response will be important in creating the prerequisites for vaccine schedules for patients previously infected with monkeypox.
Experiments in animal models suggested that all the immune players contribute to viral clearance, with CD8+ T cells playing the main role.7 Few old data are available on the immune response to monkeypox virus in humans.8 All 92 convalescent cases, regardless of vaccination status, were positive for orthopoxvirus-specific IgM, IgG, T-cell, and B-cell responses. Despite the small number of cases, the generation of orthopoxvirus-specific immune response was reported in some contacts who did not develop monkeypox infection. Smallpox vaccination did not provide complete protection against monkeypox virus, but a weak association (although not significant) between a pre-existing vaccine-induced immunity and a milder disease has been suggested.8 Finally, cytokine profiling suggested an overproduction of some cytokines in patients with severe disease,9 linking the clinical severity with an unbalanced immune response. No data are available about the dynamics of the immune response against monkeypox virus in humans in the current outbreak. One multicountry series of patients with monkeypox infection reported that 218 (41%) of 528 cases occurred in people living with HIV,3 and the impact of HIV-related chronic dysregulation over immune response to monkeypox virus was not known. The aim of this study was to describe the kinetics of T-cell response (differentiation and activation profile), the inflammatory profile, and the pox-specific T-cell induction in human cases of monkeypox virus infection.
Methods
Study population
17 participants with a laboratory-confirmed monkeypox virus positivity admitted at the Lazzaro Spallanzani National Institute for Infectious Diseases (INMI; Rome, Italy), from May 19, to July 7, 2022, were prospectively enrolled in this study. All patients were tested 10–12 days after symptoms onset. In a subset of these patients (n=9), samples were obtained over time allowing the analyses of the kinetic of the immune response. Specifically, samples were divided into four groups based on the timing from the symptoms onset: T0–T3, T4–T7, T8–T11, T12–T20 days, and compared with ten healthy donors. Healthy donors were health-care workers from the same hospital matched by age. The study was approved by the ethical committee of the Lazzaro Spallanzani Institute, as part of biological studies on emerging infections (approval number 14/2015). All participants provided their written informed consent. Epidemiological, demographic, clinical, and laboratory data of patients, as well as therapy prescribed, were collected. Single reported cases were previously described from clinical and virological profiles,2, 10, 11 whereas several cases were included in a large international clinical series;3 here, we describe data on the T-cell immune response of these participants.
Procedures
To evaluate the impact of monkeypox infection, differentiation and activation of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were analysed by flow cytometry in nine patients (only those with available samples), using a dried reagent tube (DuraClone IM T cell subsets tube, Beckman Coulter, Hialeah, FL, USA). A DuraClone tube contains the following antibodies: CD45RA-FITC, CCR7-PE, CD28-ECD, PD1-PC5.5, CD27-PC7, CD4-APC, CD8-A700, CD3-APCA750, CD57-Pacific Blue, and CD45-Krome Orange. Briefly, 100 μL of fresh whole blood was added to the DuraClone tube and incubated for 15 min, at room temperature. After incubation, 2 mL of VersaLyse Lysing Solution (Beckman Coulter) was added and incubated for 15 min. Finally, the tubes were washed with 3 mL 1x PBS, fixed with 1x paraformaldehyde, and then the samples acquired by CytoFLEX LX (Beckman Coulter).
In a group of five patients and four healthy donors whose peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBCs) were still available, a wide flow cytometry analyses was performed using using a dried reagent tube (DuraClone IM T cell subsets tube) and several drop-in monoclonal antibodies. ViaKrome 808 dye (Beckman Coulter, Hialeah, FL, USA) was used as viability marker. PBMCs were stained at 37°C for 20 min with anti-chemokine monoclonal antibodies (CXCR3-BV785 [Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA]; CXCR5 BUV661 and CCR6 BUV496 [Beckton Dickinson, San José, CA, USA]) in staining buffer (Brilliant Stain buffer diluted 1:1 in PBS plus 2% FBS). Then samples were washed and stained with a monoclonal antibody mix containing CD69-BV650, CD95 BV605 (Biolegend, San Diego, CA, USA), CD137-BUV395 (Beckton Dickinson, San José, CA, USA) in staining buffer (Brilliant Stain buffer diluted 1:1 in PBS plus 2% FBS). Finally, PBMCs were washed and mixed in the DuraClone tube. PBMCs were incubated for 15 min, at room temperature. Finally, tubes were washed with 3 mL 1x PBS, fixed with 1x paraformaldehyde and then acquired by a six-laser CytoFLEX LX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter), as previously described.12
Flow cytometry standard files were uploaded in FlowJo (version 10.7.1) and checked to exclude aggregates, doublets, dead cells, and non-biological events. For each sample, we selected data from all living CD45+CD3+CD4+ and CD45+CD3+CD8+ cells and imported them in R (version 2.4.0) using the flowCore.13 The unsupervised analysis of cytometric data was performed using CATALYST (version 1. 14).14 All data obtained by flow cytometry were transformed in R using hyperbolic arcsine “arcsinh (x/cofactor)” applying manually defined cofactors (where x is the fluorescence measured intensity value and cofactor as defined by Melsen and collegues15). Clustering and dimensional reduction were performed respectively using FlowSOM and uniform manifold approximation and projection algorithms, as previously described.16 Clustering was performed using the following markers: CD45RA, CCR7, CD27, CD57, PD1, CCR6, CXCR3, CXCR5, and CD69. Dimensional reduction was performed using the following markers: CD45RA, CCR7, CD27, CD57, PD1, CCR6, CXCR3, CXCR5, CD69, CD95, and CD28.
The frequency of T-cells responding to peptides from modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) was assessed by standard interferon-γ ELISpot. The following peptides, obtained from JPT (Berlin, Germany), were used: MVA074R, a pool of 106 peptides derived from a peptide scan (15 mers with 11-amino acid [aa] overlap) through putative 49·8k protein (MVA 074R; Swiss Prot identification number: O57196) of vaccinia virus (VACV);17 MVA105L: a pool of 74 peptides derived from a peptide scan (15 mers with 11-aa overlap) through Cell surface-binding protein (MVA105L; Swiss-Prot identification number: O57211) of VACV-strain Ankara;18 and MVA121L: a pool of 220 peptides derived from a peptide scan (15 mers with 11-aa overlap) through Major core protein P4a (MVA 121L; Swiss-Prot identification number: O57223) of Vaccinia Virus.19
PBMCs were isolated by standard Histopaque (Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) gradient technique. Cryopreserved PBMC were thawed and rested overnight at 37°C in R10 medium (RPMI 1640 [Sigma Aldrich]) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated highly defined foetal bovine serum (FBS-HyClone; Sigma Aldrich), 2 mmol/L L-glutamine, 10 mmol/L HEPES buffer (N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N-2-ethane sulfonic acid, Sigma Aldrich), 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Gibco, Waltham, MA, USA). Rested PBMCs were plated at 3 × 105 cells per well in ELISpot plates (Human IFN-γ ELISpot plus kit; Mabtech, Nacka Strand, Sweden) and stimulated for 18–20 h with a pool of peptides spanning the 105-L, 074-L and 121-L of the MVA (JPT, Berlin, Germany) at 37°C (5% CO2). A T-cell mitogen (phytohemagglutinin) was used as a positive control. At the end of incubation, ELISpot assay was developed according to manufacturer's instructions. Spontaneous cytokine production (background) was assessed by incubating PBMC with DMSO, the peptides diluent (Sigma Aldrich). Results are expressed as spot forming cells (SFC) per 106 PBMCs in stimulating cultures after subtracting background. The evaluation of cytokine (interferon-γ, interleukin [IL]-2, and tumour necrosis factor [TNF]) produced after specific stimulation was performed by automated ELISA assay in supernatants of stimulated cultures. The detection limit of these assays was 0·17 pg/mL for interferon-γ, 0·54 pg/mL for IL-2, and 0·3 pg/mL for TNF.
The amount of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF in plasma of patients was quantified using automated multiplex immunoassays on Ella (San José, CA, USA). The detection limit of these assays was 0·16 pg/mL for IL-1β, 0·28 pg/mL for IL-6, 0·19 pg/mL for IL-8, and 0·30 pg/mL for TNF.
Statistical analysis
The statistical methods for differential discovery analyses in high-dimensional cytometry data were based on a combination of high-resolution clustering and empirical Bayes moderated tests adapted from transcriptomics. Analysis of differential cell populations abundances was performed using generalized linear mixed model implemented within diffcyt package20 applying a false discovery rate cutoff of 0·05.
The correlation analysis between the concentrations of inflammatory cytokines was performed by use of Spearman test. The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare the frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells between healthy controls and patients with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox; and the frequency of differentiation and activation markers between patients infected with monkeypox with or without HIV. Finally, the longitudinal analysis of T differentiation subsets between T0–3 and T12–20 in patients with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox was performed with the Wilcoxon test. Data representation was done with GraphPad Prism (version 8).
Role of the funding source
The funder of the study had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Results
The 17 participants with laboratory-confirmed monkeypox were men who had sex with men with a median age of 39·5 years (IQR 33·5–45·25). Seven (41%) were HIV-positive, all on antiretroviral therapy with undetectable HIV-RNA, and a CD4+ T-cell count greater than 350 cells/μl. Among the ten participants who were HIV negative, seven were on pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP). 14 (82%) reported sexual intercourse as a possible transmission route. Only one patient received smallpox vaccination during childhood. Systemic symptoms (eg. fever, headache, and fatigue) occurred in 14 (82%) participants. Patients who presented without systemic symptoms, with less than five skin lesions, and no other particular localisation of disease were considered paucisymptomatic. Five patients were treated with an antiviral drug (tecovirimat or cidofovir). Clinical recovery was considered at the time of the fall of all the scabs. Median time to recovery was 15 days (IQR 13–21). The demographical and clinical characteristics of the enrolled patients are summarised in the table .
Table.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with monkeypox virus infection (n=17)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 39 | 38 | 32 | 28 | 30 | 31 | 46 | 43 | 38 | 40 | 46 | 42 | 33 | 35 | 46 | 42 | 47 | |
| Sex | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | |
| Men who have sex with men | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| HIV status | Pos | Pos | Neg | Neg | Pos | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | Neg | Pos | Pos | Neg | Neg | Pos | Neg | Pos | |
| CD4 count in the past 3 months* (cells/μl) | 884 | 413 | NA | NA | 686 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 787 | 792 | NA | NA | 1622 | NA | 828 | |
| CD4/CD8 ratio | NA | 2·13 | NA | NA | 1·9 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1·2 | 1·0 | NA | NA | 0·8 | NA | NA | |
| Last viral load (copies per mL) | ND | ND | ·· | ·· | ND | ·· | ·· | ·· | ·· | ·· | ND | ND | ·· | ·· | ND | ·· | ND | |
| Receipt of antiretroviral therapies | TC plus DTG | TAF plus FTC plus BIC | ·· | ·· | TC plus DTG | ·· | ·· | ·· | ·· | ·· | TAF plus FTC plus BIC | TC plus DTG | ·· | ·· | TAF plus FTC plus BIC | ·· | TC plus DTG | |
| Receipt of pre-exposure prophylaxis | No | No | Yes | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Total lymphocytes count, cells/μl | NA | 890 | 1630 | 2140 | NA | 2960 | 3440 | 4660 | NA | NA | 1870 | 3200 | 2880 | 2880 | 4280 | NA | NA | |
| Transmission route | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | Household | Household | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | SCC | Not known | |
| Systemic symptoms | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Number of lesions | >20 | 11–20 | >20 | <5 | <5 | >20 | 11–20 | >20 | 5–10 | <5 | <5 | 11–20 | 11–20 | <5 | <5 | 5–10 | 5–10 | |
| Lesions in face or body skin | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Lesions on palms or soles | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | |
| Genital lesions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | |
| Anal lesions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Nasal or oral lesions | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| PCR positive | ||||||||||||||||||
| Skin lesions | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Throat swab | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | |
| Monkeypox treatment | No | No | No | Cidofovir | No | No | No | No | No | No | no | No | Tecovirimat | Tecovirimat | Tecovirimat | No | Tecovirimat | |
| Smallpox vaccination history | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
BIC=bictegravir. DTG=dolutegravir. FTC=emtricitabine. NA=not available. ND=not detected. Neg=negative. Pos=positive. SCC=sexual close contact. TAF=tenofovir. TC=lamivudine.
Most recent CD4 count in the 3 months before monkeypox diagnosis.
The healthy donors were ten health-care workers: six men and four women with a median age of 39 years (IQR 35·5–40). Healthy controls were tested negative for HIV, hepatitis C virus, hepatitis B Virus, and were unvaccinated for smallpox. None were taking PrEP.
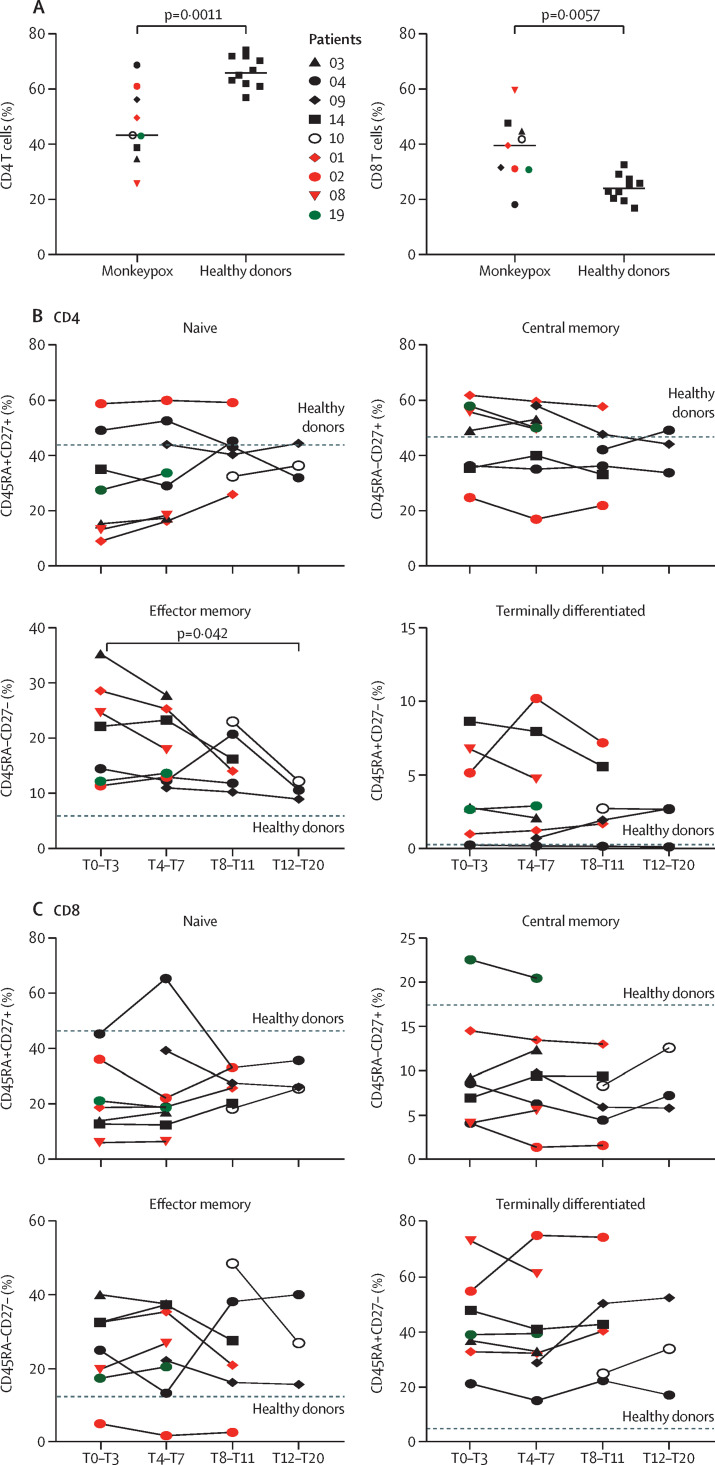
Early after infection (day T0–T3), a significant lower frequency of CD4+ T-cells and a concurrent higher percentage of CD8+ T cells was measured in patients with confirmed monkeypox virus than in healthy donors (figure 1A ). Moreover, six (67%) of nine monkeypox cases had a lower frequency of naive (ie, CD45RA+CD27+) CD4+ T cells than healthy donors; an increase of effector memory (CD45RA–CD27–) CD4+ T cells was observed in all patients (figure 1B). A similar differentiated profile was also observed in CD8+ T cells, with a reduction of naive and an increase of terminally differentiated CD8+ T cells in all patients (figure 1C). This T-cell profile, skewed toward a terminal differentiation, normalised over after 12–20 days of synptoms onset, and the frequency of CD4+ effector memory T cells in patients with monkeypox reached a similar proportion measured in healthy donors after this timeperiod.
Figure 1.
Kinetic of the differentiation profile of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during monkeypox virus infection
(A) Comparison of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell frequency between patients with monkeypox (n=9) and healthy donors (n=10); statistical analysis was performed by Mann-Whitney test. (B, C) Analysis of naive (CD45RA+CD27+), central memory (CD45RA–CD27+), effector memory (CD45RA–CD27–), and terminally differentiated (CD45RA+CD27–) CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was performed by flow cytometry. The dashed line identified the median proportion of cells of healthy donors sampled at a single timepoint (n=10). Green dots identify paucisymptomatic patients; the red dots identify HIV-positive patients. Statistical analysis was done with Wilcoxon test. The number next to the dots represent the participant identification number as shown in the table.
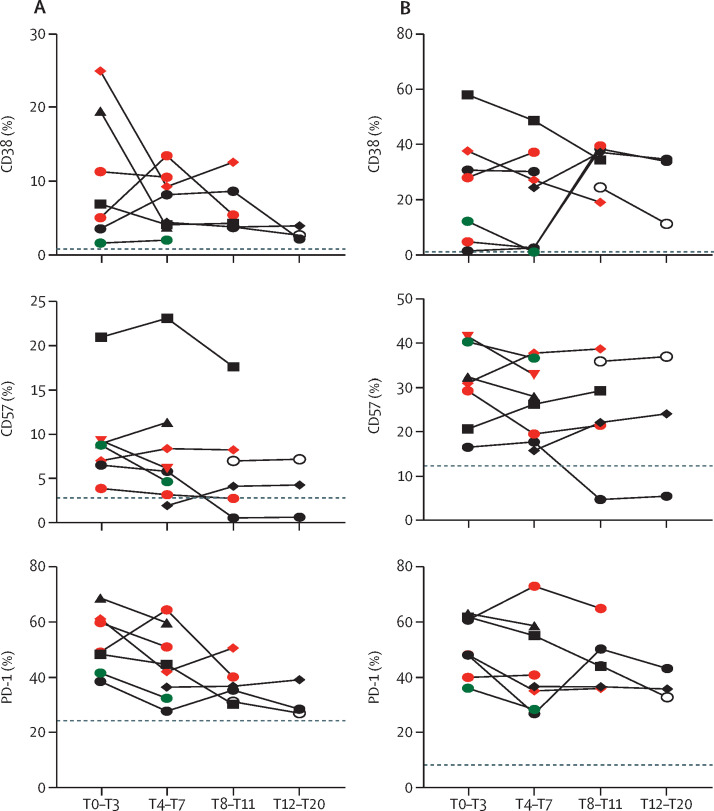
To evaluate the activation profile of T cells, we analysed the expression of CD38, PD-1, and CD57 markers on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (figure 2A–B ). Early after infection, a significant higher frequency of CD4+CD38+ (p=0·0061) and CD8+CD38+ T-cells (p=0·0024) has been observed in the large majority of patients (eight [89%] of nine) with monkeypox respect to healthy donors, reaching the highest values in patients showing an expansion of effector cells. The analysis of the T-cells kinetics showed a decrease over time, which tended to normalise 12–20 days from symptoms onset. Accordingly, a similar kinetic was observed also for the expression of PD-1 and CD57 cells (figure 2A–B). Effector cells expanded in some patients with monkeypox, including the most activated cells respect to naive compartments (figure 2C). No differences in immune-cell profile were observed between HIV-positive and HIV-negative patients infected with monkeypox virus. Paucisymptomatic patients showed a less altered immune profile. Early after symptoms onset the inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF) were higher in patients with monkeypox than in healthy donors and, although the cytokine concentrations decreased over time, they remained elevated after recovery (appendix 2 p 2). Moreover, the concentration of inflammatory cytokines correlated positively with each other (interferon-γ vs IL-2: Spearman test r=0·78, p=0·0044; interferon-γ vs TNF: Spearman test r=0·67, p=0·0021).
Figure 2.
Kinetic profile of the activation or senescence profile of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during monkeypox virus infection
Expression of activation or senescence markers on CD4+ (A) and CD8+ T cells (B; CD38, PD-1, CD57) was performed by flow cytometry in patients with monkeypox. The dashed line identified the median frequency of CD38, PD-1, and CD57 in healthy controls (n=10). Green dots identify paucisymptomatic patients, whereas the red dots identify patients with HIV.
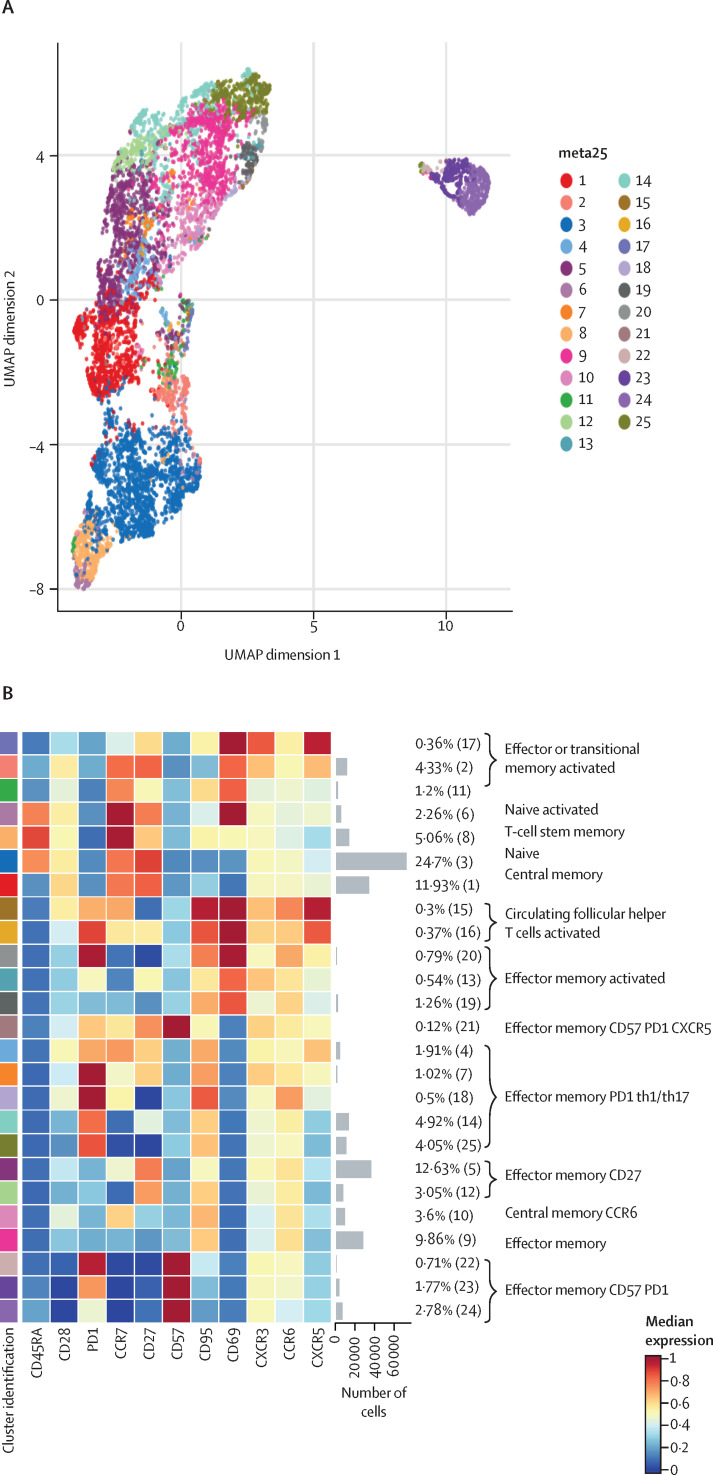
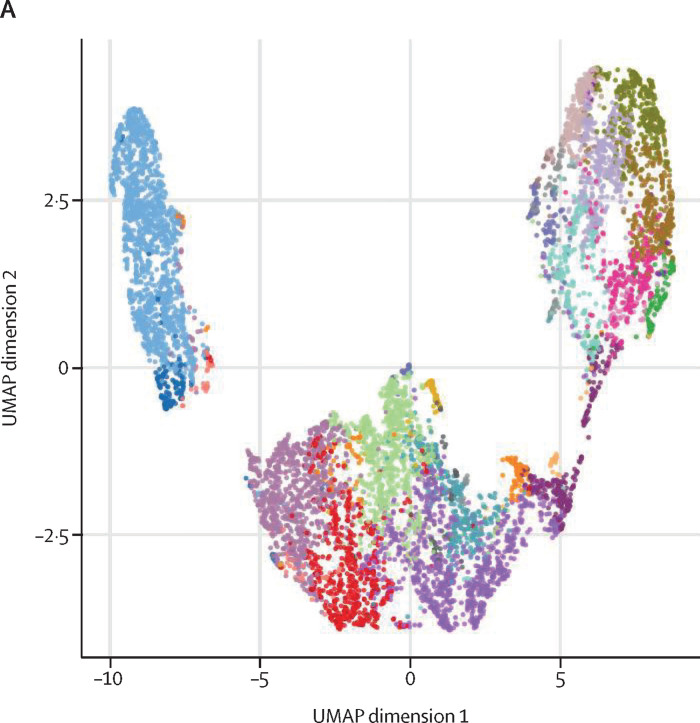
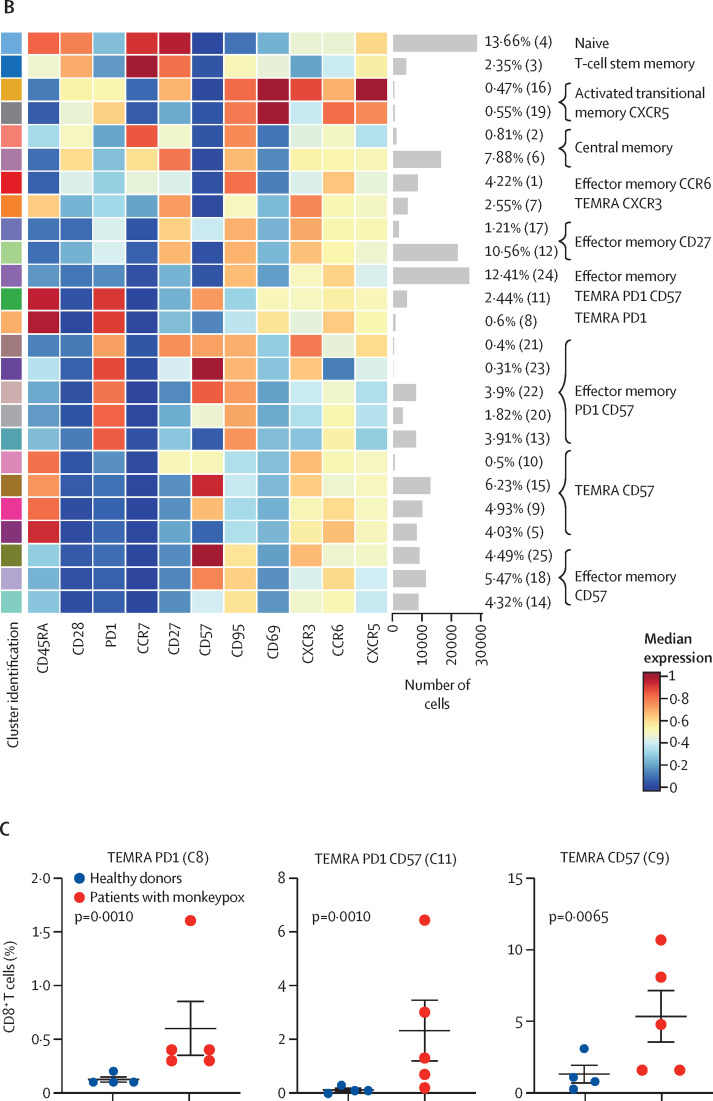
To characterise the landscape of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells during monkeypox virus infection in the post-acute phase (ie, 8–10 days from symptom onset), a subgroup of four healthy donors and five patients with monkeypox was analysed by unsupervised cluster analysis. 25 metaclusters represented the different subpopulations within CD4+ T cells. The main populations have been identified according to the expression of CD4RA, CCR7, CD27, CD28, CD95, CXCR3, CCR6, CXCR5, and CD69 (figure 3A–B ). We were able to identify naive T cells, T cells stem memory, central memory, central memory expressing CCR6, circulating follicular helper T cells expressing CD69, and different subsets of effector memory, some of which expressing senescent marker (CD57) and activation marker (PD1). A population of transitional memory and effector memory expressing CD69, CXCR3, and CCR6 have been found. These populations are activated and likely skewed toward Th1/Th17 profile and the percentage of these clusters (C17, C2, C13) was higher in patients with monkeypox than in healthy donors (figure 3C). Similar frequency of all other clusters (all identified CD4 clusters except C17, C2, and C13) have been reported (appendix 2 pp 3–6). Regarding CD8+ T cells, besides the presence of naive T-cells, T cells stem memory, and effector memory, the most abundant population was that representing terminally differentiated effector memory T cells re-expressing CD45RA (EMRA; figure 4A–B ). Patients with monkeypox had higher percentages of EMRA expressing PD1 (C8), CD57 (C9), or both (C11) than healthy donors (figure 4C). Similar percentages of all other clusters (all identified CD8 clusters except C8, C9, and C11) were found between patients with monkeypox and healthy donors (appendix 2 pp 7–9).
Figure 3.
Deep immune profiling of CD4+ T cells
(A) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot shows the 2D spatial distribution of CD4+ T cells from healthy donors (n=4) and patients with monkeypox (n=5) embedded with FlowSOM clusters. The colour of each cluster corresponds to the colour of the heatmap in figure 3B. (B) Heatmap of the median marker intensities of the lineage markers across the 25 cell populations obtained with FlowSOM algorithm. The colours of the cluster identification column correspond to the colours used to label the UMAP plot clusters. The colour in the heatmap is referred to the median of the arcsinh marker expression (0 to 1 scale) calculated over cells from all the samples. Light grey bar along the rows (clusters) and values in brackets indicate the relative sizes of clusters. Each column identifies the expression of a single marker. (C) Relative cell proportion of different clusters between healthy donors (n=4), and Monkeypox patients (n=5). The central bar represents the mean (SD). CD=cluster differentiation. CXCR=chemokine receptors.
Figure 4.
Deep immune profiling of CD8+ T cells
(A) Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection (UMAP) plot shows the 2D spatial distribution of CD8+ T cells from healthy donors (n=4) and patients with monkeypox (n=5) embedded with FlowSOM clusters. The colour of each cluster corresponds to the colour of the heatmap in figure 4B. (B) Heatmap of the median marker intensities of the lineage markers across the 25 cell populations obtained with FlowSOM algorithm. The colours of cluster identification column correspond to the colours used to label the UMAP plot clusters. The colour in the heatmap is referred to the median of the arcsinh marker expression (0 to 1 scale) calculated over cells from all the samples. Light grey bar along the rows (clusters) and values in brackets indicate the relative sizes of clusters. (C) Relative cell proportion of different clusters between healthy donors (n=4), and Monkeypox patients (n=5). The central bar represents the mean (SD). CD=cluster differentiation. CXCR=chemokine receptors. TEMRA=T effector memory re-expressing CD45RA.
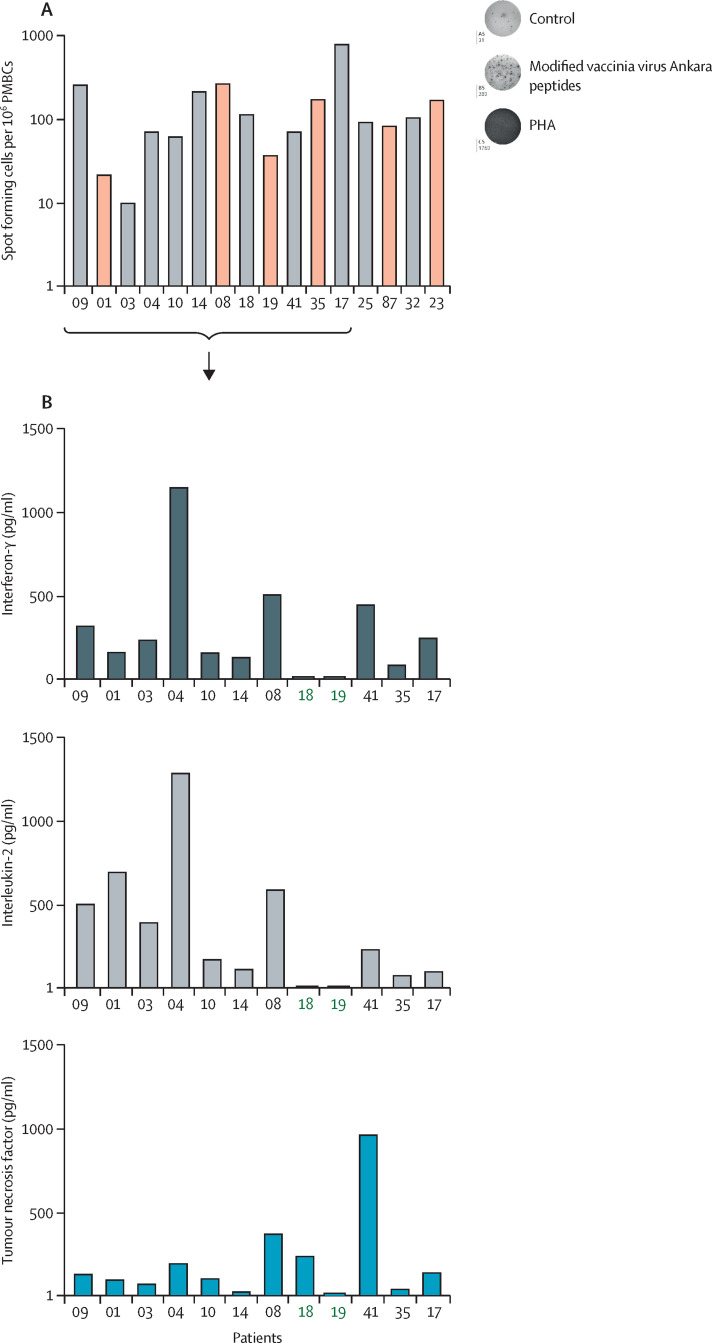
The analysis of the monkeypox-specific T-cell response showed that monkeypox virus infection was able to induce poxvirus-specific T cells in all patients but one (figure 5A ).
Figure 5.
Poxvirus-specific T-cell response
(A) Poxvirus-specific T-cell analysis in patients with monkeypox 8–10 days after symptoms onset (n=16). (B) Th1 cytokine profile in selected patients with monkeypox (n=12). Green numbers identify paucisymptomatic patients. PMBC=peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PHA=phytohaemagglutinin.
Regarding the Th1 cytokine profile (IFN- γ, IL-2, and TNF), although a wide variability in the immunological response was observed, all responders were able to produce the three cytokines. Patients with a paucisymptomatic infection showed a very low concentration of cytokines (figure 5B).
Discussion
In this study, we described the engagement of T-cell response in patients infected with monkeypox virus during the 2022 outbreak. To date, scarce information is available about the in-vivo kinetics of T-cell responses in monkeypox virus infection. It was previously observed that T-cells expressing a Vγ9Vd2 T-cell receptor underwent in-vivo long expansion after monkeypox virus challenge in macaque model,21 but consistent data on the kinetics of T cells in human monkeypox virus infection are still lacking. In men aged between 28 and 40 years, mostly not previously receiving vaccinia virus vaccination, we found, very early after symptoms onset, a marked reduction of naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, with a rapid expansion of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells expressing an effector memory phenotype, suggestive of a highly engaged immune system. Confirming this suggestion, both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells showed a strong immune activation, with an increased expression of CD38, PD-1, and CD57 markers, and this activation profile was associated with the differentiation in effector cells.
This immune perturbation and activation profile decreased with recovery and clinical evolution. Moreover, in most patients, specific T cells produced several Th1 inflammatory cytokines, already early after clinical onset, and pro-inflammatory cytokines production persisted until, and even after, clinical recovery. Interestingly, our paucisymptomatic patients monkeypox showed less differentiated and activated T cells, suggesting a possible link with the clinical severity and immune activation and T-cell differentiation.
Previously reported data suggested that several viral proteins of orthopoxvirus modulate the host immune response, affecting cytokines such as IL-1, TNF, and type I interferons. Genetic differences in these immune-modulating viral genes (eg, BR-203, BR-209, and COP-C3L) might contribute to virulence diversity between monkeypox clade I and clade II (central Africa and west Africa, respectively), through a different modulation of the innate immunity.22 In our patients, although with a high variability, we showed an early inflammatory response, suggestive of an effective innate immunity. We therefore speculate that the magnitude and the effectiveness of innate and adaptive immune response could protect from the onset of the severe clinical picture observed in our cases.
Importantly, this rapid and potent T-cell engagement was observed regardless of the presence of the immune dysregulation due to HIV infection. People living with HIV in the present work, all with well controlled viraemia and high CD4+ T-cell recovery, did not display a specific immune signature due to monkeypox virus infection. In a large series of clinical cases of monkeypox in the current outbreak,3 the clinical presentation and severity of monkeypox did not significantly differ among people with or without HIV infection. Interestingly, in almost all HIV-infected people plasma viraemia was well controlled, with a median CD4+ T-cell count largely higher than 500 cells/mm3. Our data showed a prompt and powerful T-cell response also in patients with monkeypox infected by HIV, and they might represent the immunological counterpart for the positive clinical prognosis. The effect of advanced HIV disease, as well as of poor CD4+ recovery after prolonged viral suppression, on the immune response and the clinical outcome might be a very interesting issue to be addressed.
To characterise the specific T-cell response against poxvirus, we measured IFN-γ T-cell production by ELISpot assay after stimulation with MVA peptides. Our results indicate that monkeypox virus infection was able to induce a potent antigen-specific T-cell response in nearly all patients, already 10–12 days away from symptoms onset, and this response did not seem to be affected by clinical severity or presence of HIV infection. During natural monkeypox virus infection, it has been previously demonstrated the occurrence of immune evasion mechanisms able to block T-cell recognition process that can reduce the strength of the immune response.23 Nevertheless, patients who recover from monkeypox virus infection were able to mount antiviral T-cell responses similar or stronger than that elicited by vaccinia virus infection probably through alternative antigen presentation, cross-priming mechanisms, or both. Moreover, immunological studies on survivors of monkeypox virus infection after the 2003 outbreak in the USA showed that they had strong cell mediated responses up to at least one year after infection, suggesting a prolonged persistence of memory CD4+ T cells after natural infection.24 Comparable results were also obtained after smallpox vaccination, providing a long-lasting CD4+ T-cell help that might be crucial for long-lived B-cell memory.25 Even if we could not confirm this long-time immune protective pattern, our result on short-term specific T-cell response to MVA peptide stimulation might be considered relevant in the light of monkeypox vaccination of high-risk target population.
This hypothesis is in agreement with the observation that patients with a history of chickenpox, another poxvirus, have a recognisable T-cell response measured by cytokine-producing and polyfunctional CD4+ T cells.26 Unlike chickenpox, which confers permanent immunity, the duration of natural immunity conferred by monkeypox virus infection is currently unknown. Long-term results on the characteristics and durability of the immune response to monkeypox virus, both humoral and T cell-mediated, might be useful in defining the possible need for a vaccination strategy even in people with previous infection.
People living with HIV represent a consistent part of those infected by monkeypox virus and of those at risk of acquiring infection. HIV infection might play a part on the function or senescence of the B and T immune compartments and contribute to a reduced level or persistence of protective response to natural infection, as reported for other viral diseases.27 An important concern has been raised about a possible poor functional response to MVA vaccination in people living with HIV,28 according to previously reported data on vaccines for other viruses, such as influenza,29 hepatitis B,30 or even SARS-CoV-2.31, 32 Our observation that people living with HIV had a poxvirus-specific T-cell response after natural monkeypox virus infection might suggest a comparable response of people living with HIV also to MVA vaccine, avoiding a differentiated vaccination schedule for this target population.
Our analysis has some limitations. First, we lack data on humoral response analysis, and used only three poxvirus proteins as antigens for T cells. Second, this is an observational study, conducted in a single centre, hence we do not have a randomised selection of patients. Finally, the study has a limited number of patients, and the proportion of cells within each cluster could change if additional patients with monkeypox are included. Thus, some aspects should be considered exploratory and hypothesis generating, although our data are consistent over different assays.
In conclusion, our data show the immunological signature of monkeypox virus infection, characterised by an early expansion of activated effector CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, persisting over time. Almost all participants, regardless of HIV infection, developed a strong poxvirus-specific Th1 cell response. These results might have implications on the expected immunogenicity of anti-monkeypox virus vaccination by MVA vaccine in high-risk population. The extent of the immune response to natural infection suggests that it might not be needed to administer a booster dose of vaccine in recently infected individuals, although data on prolonged immunity are needed to definitively support this hypothesis.
Data sharing
Immunological and patient data are available under restricted access for confidentiality reasons, because these patients might be identified by combinations of person-specific characteristics within the database; access can be obtained by specific request to the corresponding author. The raw data on demographics and clinical status of participants, are protected and not available due to data privacy laws.
For ELISpot assay instructions see https://www.mabtech.com/sites/default/files/datasheets/3420-4HPT-2.pdf
Declaration of interests
We declare no competing interests.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the nurse staff, laboratory technicians, and all the patients. The members of the INMI Monkeypox Study Group are listed in the appendix 2 (p 10).
Contributors
CAgr, AC, and AA conceptualised and designed the study. CAgr, AC, AA, and VM wrote the manuscript and referred to appropriate literature. GG, RC, SG, DLT, SN, and SDB performed all the assays. CAgr, CAgu, and VM were responsible for data curation; CAgr and AC accessed and verify all the data. CP, AM, FC, GM, RG, LG, LS, AD, and GM revised the manuscript content, and edited the manuscript. CF, FM, EN, EG, and FV supervised the study and contributed to data interpretation. All authors had access to the data, agreed with and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
References
- 1.Centers for Disease Control. 2022 monkeypox outbreak global map. Sept 20, 2022 (accessed Sept 21, 2022).
- 2.Antinori A, Mazzotta C, Vita S, et al. Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of four cases of monkeypox support transmission through sexual contact, Italy, May 2022. Euro Surveill. 2022;27 doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.22.2200421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thornhill JP, Barkati S, Walmsley S, et al. Monkeypox virus infection in humans across 16 countries-April–June 2022. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:679–691. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2207323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Petersen E, Zumla A, Hui DS, et al. Vaccination for monkeypox prevention in persons with high-risk sexual behaviours to control on-going outbreak of monkeypox virus clade 3. Int J Infect Dis. 2022;122:569–571. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.06.047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tarín-Vicente EJ, Alemany A, Agud-Dios M, et al. Clinical presentation and virological assessment of confirmed human monkeypox virus cases in Spain: a prospective observational cohort study. Lancet. 2022;400:661–669. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01436-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rimoin AW, Mulembakani PM, Johnston SC, et al. Major increase in human monkeypox incidence 30 years after smallpox vaccination campaigns cease in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:16262–16267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005769107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Panchanathan V, Chaudhri G, Karupiah G. Correlates of protective immunity in poxvirus infection: where does antibody stand? Immunol Cell Biol. 2008;86:80–86. doi: 10.1038/sj.icb.7100118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Karem KL, Reynolds M, Hughes C, et al. Monkeypox-induced immunity and failure of childhood smallpox vaccination to provide complete protection. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007;14:1318–1327. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00148-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Johnston SC, Johnson JC, Stonier SW, et al. Cytokine modulation correlates with severity of monkeypox disease in humans. J Clin Virol. 2015;63:42–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mazzotta V, Mondi A, Carletti F, et al. Ocular involvement in monkeypox: description of an unusual presentation during the current outbreak. J Infect. 2022 doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.08.011. published online Aug 18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lapa D, Carletti F, Mazzotta V, et al. Monkeypox virus isolation from a semen sample collected in the early phase of infection in a patient with prolonged seminal viral shedding. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22:1267–1269. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00513-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cossarizza A, Chang HD, Radbruch A, et al. Guidelines for the use of flow cytometry and cell sorting in immunological studies (third edition) Eur J Immunol. 2021;51:2708–3145. doi: 10.1002/eji.202170126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hahne F, LeMeur N, Brinkman RR, et al. flowCore: a Bioconductor package for high throughput flow cytometry. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:106. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nowicka M, Krieg C, Crowell HL, et al. CyTOF workflow: differential discovery in high-throughput high-dimensional cytometry datasets. F1000Res. 2017;6:748. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.11622.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Melsen JE, van Ostaijen-Ten Dam MM, Lankester AC, Schilham MW, van den Akker EB. A comprehensive workflow for applying single-cell clustering and pseudotime analysis to flow cytometry data. J Immunol. 2020;205:864–871. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Biasi S, Tartaro DL, Gibellini L, et al. Endogenous control of inflammation characterizes pregnant women with asymptomatic or paucisymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Commun. 2021;12 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24940-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schoch CL, Ciufo S, Domrachev M, Hotton CL, Kannan S, Khovanskaya R. NCBI taxonomy: a comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database (Oxford) 2020;2020 doi: 10.1093/database/baaa062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Antoine G, Scheiflinger F, Dorner F, Falkner FG. The complete genomic sequence of the modified vaccinia Ankara strain: comparison with other orthopoxviruses. Virology. 1998;244:365–396. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Goebel SJ, Jognson GP, Perkus ME, Davis SW, Winslow JP, Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990;179:247–266. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. 517–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weber LM, Nowicka M, Soneson C. diffcyt: differential discovery in high-dimensional cytometry via high-resolution clustering. Commun Biol. 2019;2:183. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0415-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shao L, Huang D, Wei H, et al. Expansion, reexpansion, and recall-like expansion of Vgamma2Vdelta2 T cells in smallpox vaccination and monkeypox virus infection. J Virol. 2009;83:11959–11965. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00689-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Weaver JR, Isaacs SN. Monkeypox virus and insights into its immunomodulatory proteins. Immunol Rev. 2008;225:96–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00691.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hammarlund E, Dasgupta A, Pinilla C, Norori P, Früh K, Slifka MK. Monkeypox virus evades antiviral CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses by suppressing cognate T cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:14567–14572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800589105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sivapalasingam S, Kennedy JS, Borkowsky W, et al. Immunological memory after exposure to variola virus, monkeypox virus, and vaccinia virus. J Infect Dis. 2007;195:1151–1159. doi: 10.1086/512161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Amara RR, Nigam P, Sharma S, Liu J, Bostik V. Long-lived poxvirus immunity, robust CD4 help, and better persistence of CD4 than CD8 T cells. J Virol. 2004;78:3811–3816. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.8.3811-3816.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kang CK, Chang E, Jung J, et al. Different levels of humoral and cellular immunity to varicella-zoster virus in seropositive healthcare workers. J Infect Public Health. 2022;15:734–738. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2022.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Spinelli MA, Lynch KL, Yun C. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence, and IgG concentration and pseudovirus neutralising antibody titres after infection, compared by HIV status: a matched case-control observational study. Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e334–e341. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00072-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.British HIV Association BHIVA rapid guidance on monkeypox virus. Aug 17, 2022. https://www.bhiva.org/BHIVA-rapid-guidance-on-monkeypox-virus
- 29.Tebas P, Frank I, Lewis M, et al. Poor immunogenicity of the H1N1 2009 vaccine in well controlled HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 2010;24:2187–2192. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833c6d5c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Collier AC, Corey L, Murphy VL, Handsfield HH. Antibody to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and suboptimal response to hepatitis B vaccination. Ann Intern Med. 1988;109:101–115. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Antinori A, Cicalini S, Meschi S, et al. Humoral and cellular immune response elicited by mRNA vaccination against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in people living with human immunodeficiency virus receiving antiretroviral therapy based on current CD4 T-lymphocyte count. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:e552–e563. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Vergori A, Cozzi Lepri A, Cicalini S, et al. Immunogenicity to COVID-19 mRNA vaccine third dose in people living with HIV. Nat Commun. 2022;13 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32263-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Immunological and patient data are available under restricted access for confidentiality reasons, because these patients might be identified by combinations of person-specific characteristics within the database; access can be obtained by specific request to the corresponding author. The raw data on demographics and clinical status of participants, are protected and not available due to data privacy laws.
For ELISpot assay instructions see https://www.mabtech.com/sites/default/files/datasheets/3420-4HPT-2.pdf