Abstract
In an end-stage midgut neuroendocrine tumor patient with carcinoid heart disease, right ventricular dysfunction, mildly reduced renal function, and refractory to 6 cycles of 177Lu-HA-DOTATATE therapy, planar, and 22 hours SPECT/CT images were acquired after injection of 224 MBq of 203Pb-VMT-α-NET to assess the feasibility of performing 212Pb-VMT-α-NET therapy. A comparison of the 1.5 and 22 hours SPECT/CT images with 68Ga-HA-DOTATATE PET/CT showed high uptake of 203Pb-VMT-α-NET in liver metastases matching with the results of the PET/CT investigation.
Key Words: 203Pb, 212Pb, VMT-α-NET, Tyr3-octreotide, SPECT/CT
FIGURE 1.
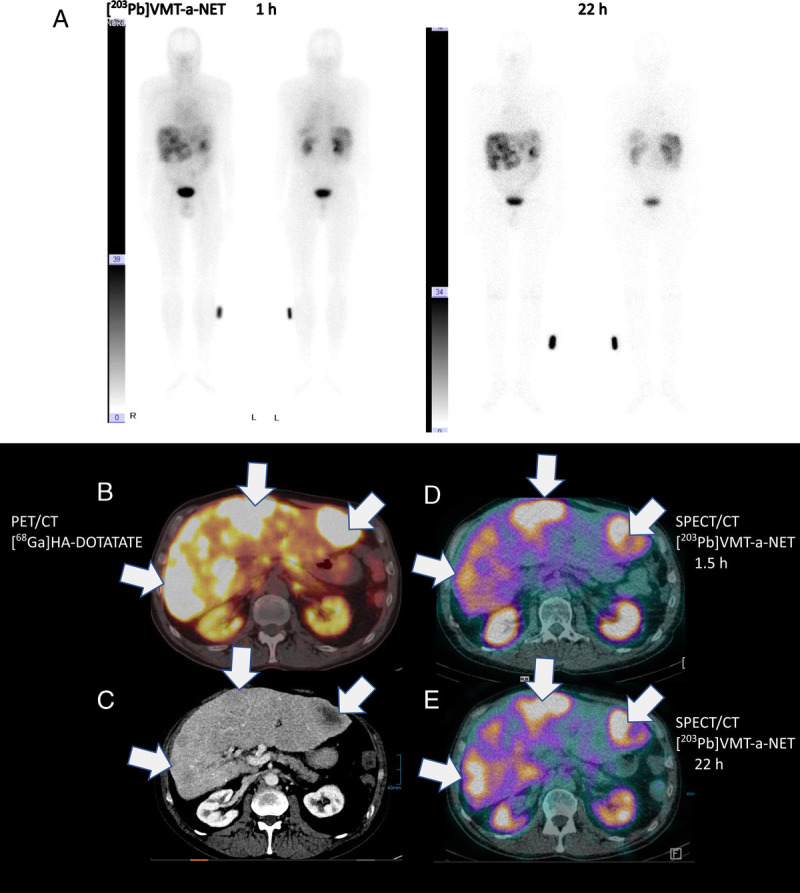
Tyr3-octreotide (TOC) variant VMT-α-NET is a novel and ideal ligand for 203Pb/212Pb that shows lower renal excretion, higher neuroendocrine tumor uptake, and high chelation properties for retention of daughter α-particle emitting radionuclide 212Bi. In an end-stage midgut neuroendocrine tumor patient with carcinoid heart disease, right ventricular dysfunction, mildly reduced renal function, and refractory to 6 cycles of 177Lu-HA-DOTATATE therapy, planar, and 22 hours 203Pb-VMT-α-NET SPECT/CT (low dose) images were acquired after injection of 224 MBq of 203Pb-VMT-α-NET to assess the feasibility of performing 212Pb-VMT-α-NET therapy. The patient tolerated the injection without any significant alteration in the vital parameters. There was rapid renal clearance of the tracer within the first hour itself as was evident from tracer excretion in the urinary bladder and in the renal pelvicalyceal system. Because of known right ventricular dysfunction, there was evidence of blood pool activity in the heart, which however decreased significantly after 21 hours. A comparison of the 1.5 and 22 hours SPECT/CT images with 68Ga-HA-DOTATATE PET/CT images (contrast-enhanced diagnostic CT) showed high uptake of 203Pb-VMT-α-NET in liver metastases matching with the results of the PET/CT. A, Anterior and posterior planar images acquired at 1 and 22 hours. B, Fused 68Ga-HA-DOTATATE PET/CT transverse slice. C, Transverse contrast-enhanced CT image. D and E, SPECT/CT (low-dose) fused transverse slice. Arrows are showing the liver metastases.1–8
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest and sources of funding: The author M.K.S. is inventor of the peptide VMT-α-NET and CSO (Chief Science Officer) of Viewpoint Molecular Targeting, Inc. There is no conflict of interest with respect to the other authors. The radiopharmaceutical 203Pb-VMT-α-NET was manufactured under cGMP conditions and applied in accordance with the German National Law (§13 [2b] AMG).
Contributor Information
Hendrik Herrmann, Email: hendrik.herrmann@uniklinik-ulm.de.
Michael K. Schultz, Email: Michael-schultz@uiowa.edu.
Christoph Solbach, Email: christoph.solbach@uniklinik-ulm.de.
Thomas Ettrich, Email: thomas.ettrich@uniklinik-ulm.de.
Vikas Prasad, Email: drvikaspd@me.com.
REFERENCES
- 1.Li M Zhang X Quinn TP, et al. Automated cassette-based production of high specific activity [203/212Pb]peptide-based theranostic radiopharmaceuticals for image-guided radionuclide therapy for cancer. Appl Radiat Isot. 2017;127:52–60. Erratum in: Appl Radiat Isot. 2020;156:108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li M Sagastume EA Lee D, et al. 203/212Pb theranostic radiopharmaceuticals for image-guided radionuclide therapy for cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2020;27:7003–7031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zaid NRR Kletting P Beer AJ, et al. Mathematical modeling of in vivo alpha particle generators and chelator stability. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2021. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2020.4112. Epub ahead of print. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zaid NRR Kletting P Winter G, et al. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for in vivo alpha particle generators targeting neuroendocrine tumors in mice. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li M Liu D Lee D, et al. Targeted alpha-particle radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors induces cooperative inhibition on tumor growth of malignant melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13:3676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dos Santos JC Schäfer M Bauder-Wüst U, et al. Development and dosimetry of 203Pb/212Pb-labelled PSMA ligands: bringing “the lead” into PSMA-targeted alpha therapy? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:1081–1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schottelius M Šimeček J Hoffmann F, et al. Twins in spirit—episode I: comparative preclinical evaluation of [(68)Ga]DOTATATE and [(68)Ga]HA-DOTATATE. EJNMMI Res. 2015;5:22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schottelius M Wester HJ Reubi JC, et al. Improvement of pharmacokinetics of radioiodinated Tyr(3)-octreotide by conjugation with carbohydrates. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13:1021–1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


