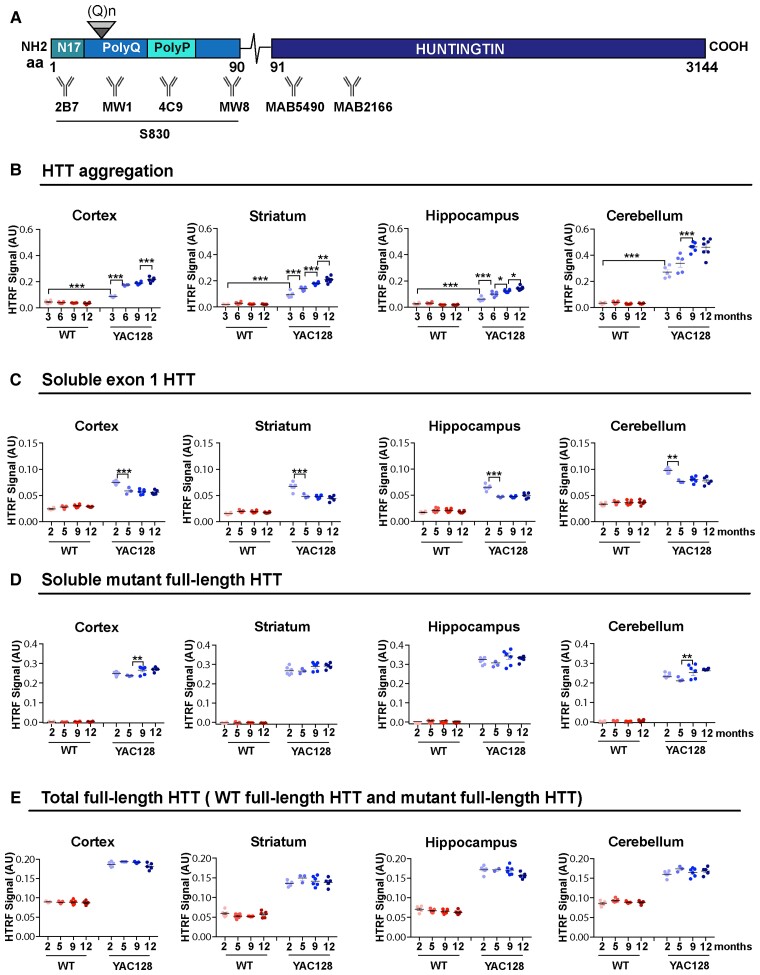
Figure 4.
HTRF assays detect greater levels of soluble exon 1 HTT and HTT aggregation in the cerebellum than in forebrain regions. (A) Schematic indicating the position of the HTT epitopes detected by the antibodies used in the HTRF assays (Supplementary Table 3). S830 is a polyclonal sheep antibody that was raised against exon 1 HTT with 53Q. (B) HTT aggregation, as detected by the 4C9-MW8 assay, increased from 3 to 12 months of age in all brain regions. (C) Exon 1 mutant HTT (2B7-MW8) levels decreased between 2 and 5 months of age in all brain regions and then remained relatively stable. (D) Full-length mutant HTT (MW1-MAB5490) remained relatively stable up to 12 months of age in all brain regions. (E) The levels of total full-length HTT (MAB5490-MAB2166) were higher in the YAC128 mice, which contain three copies of the huntingtin gene. Samples for any given HTT assay were run on the same plate, and therefore the levels between brain regions can be compared. n = 6. Statistical analysis was one- or two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc correction. Error bars = mean ± SEM *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. M = months; WT = wild-type; aa = amino acid.