Abstract
Background
Obesity reportedly increases the risk for developing multiple sclerosis (MS), but little is known about its association with disability accumulation.
Methods
This nationwide longitudinal cohort study included 1066 individuals with newly diagnosed MS from the German National MS cohort. Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) scores, relapse rates, MRI findings and choice of immunotherapy were compared at baseline and at years 2, 4 and 6 between obese (body mass index, BMI ≥30 kg/m2) and non-obese (BMI <30 kg/m2) patients and correlated with individual BMI values.
Results
Presence of obesity at disease onset was associated with higher disability at baseline and at 2, 4 and 6 years of follow-up (p<0.001). Median time to reach EDSS 3 was 0.99 years for patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 and 1.46 years for non-obese patients. Risk to reach EDSS 3 over 6 years was significantly increased in patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 compared with patients with BMI <30 kg/m2 after adjustment for sex, age, smoking (HR 1.87; 95% CI 1.3 to 2.6; log-rank test p<0.001) and independent of disease-modifying therapies. Obesity was not significantly associated with higher relapse rates, increased number of contrast-enhancing MRI lesions or higher MRI T2 lesion burden over 6 years of follow-up.
Conclusions
Obesity in newly diagnosed patients with MS is associated with higher disease severity and poorer outcome. Obesity management could improve clinical outcome of MS.
Keywords: multiple sclerosis, immunology
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
A high body mass index during childhood and adolescence increases the risk to develop multiple sclerosis (MS).
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
Presence of obesity at onset of MS is associated with higher disability scores and faster disability accumulation over an observation period of up to 6 years.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
A healthy weight may potentially improve outcomes for people with MS.
Introduction
Obesity and obesity-related diseases are serious and costly public health problems and increased in prevalence worldwide over the past few decades. In multiple sclerosis (MS), a high body mass index (BMI) during childhood and adolescence reportedly increases the risk for disease development.1–8 Whether obesity is associated with higher MS disease activity and severity after disease onset is incompletely understood. Therefore, we evaluated whether BMI, obesity and obesity-related comorbidities are related to disease severity and progression in a nationwide cohort of 1066 people with newly diagnosed MS.
Methods
Patients and data source
The German National MS (NationMS) cohort is a multicentre prospective longitudinal observational study comprising (1) detailed assessment of patients with first diagnosis of MS or clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) according to the 2005 McDonald criteria and (2) assessment every 2 years with a standardised protocol across 22 centres in Germany. All centres belong to the German Competence Network Multiple Sclerosis. Only patients fulfilling 2017 McDonald criteria at baseline or follow-up were included (n=1066). Demographical and clinical characteristics are provided in table 1.
Table 1.
Demographical and clinical characteristics of patients at baseline
| Clinical values | All patients (n=1066) | BMI ≥30 (n=159) | BMI <30 (n=907) | P value | |
| BMI, median (IQR), kg/m² | 24.17 (21.55–27.46) | 33.62 (31.56–36.81) | 23.39 (21.22–25.83) | ||
| sNfL, median (IQR), pg/mL | 11.49 (7.5–21) | 8.84 (6.49–18.87) | 11.87 (7.75–21.09) | 0.029* | |
| Age, median (IQR), years | 31 (26–40) | 33 (28–41) | 31 (25–41) | 0.012* | |
| EDSS, median (IQR) | 1.5 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 1.5 (1–2) | 0.001* | |
| No (%) | |||||
| Sex | Male | 315 (29.5) | 42 (26.4) | 273 (30.1) | 0.348† |
| Female | 751 (70.5) | 117 (73.6) | 634 (69.9) | ||
| OCB | Negative | 44 (4.2) | 7 (4.4) | 37 (4.1) | 0.856† |
| Positive | 542 (50.8) | 92 (57.9) | 450 (49.6) | ||
| Unknown | 480 (45) | 60 (37.7) | 420 (53.7) | ||
| T2 lesions | 1–8 | 355 (33.3) | 50 (31.4) | 305 (33.6) | 0.628† |
| >8 | 697 (65.4) | 106 (66.7) | 591 (65.2) | ||
| Unknown | 14 (1.3) | 3 (1.9) | 11 (1.2) | ||
| GD enhancement | No | 593 (55.6) | 87 (54.7) | 506 (55.8) | 0.795† |
| Yes | 426 (40) | 65 (40.9) | 361 (39.7) | ||
| Unknown | 47 (4.4) | 7 (4.4) | 40 (4.5) | ||
| Receiving DMT | No | 755 (70.8) | 111 (69.8) | 644 (71.1) | 0.909† |
| Yes | 287 (26.9) | 43 (27) | 244 (26.9) | ||
| Unknown | 24 (2.3) | 5 (3.2) | 19 (2.1) | ||
| Relapse before BL | 0 | 3 (0.3) | 1 (0.6) | 2 (0.2) | 0.46† |
| 1 | 621 (58.3) | 94 (59.1) | 527 (58.1) | ||
| 2 | 382 (35.8) | 52 (32.7) | 330 (36.4) | ||
| >2 | 60 (5.7) | 12 (7.6) | 48 (5.2) | ||
| Smoking at BL | No | 712 (66.8) | 99 (62.3) | 613 (67.5) | 0.128† |
| Yes | 337 (31.6) | 59 (37.1) | 278 (30.7) | ||
| Unknown | 17 (1.6) | 1 (0.6) | 16 (1.8) | ||
*Mann-Whitney U tests to investigate group differences for metric variables.
† χ2 tests to investigate group differences for categorical variables.
BL, baseline; BMI, body mass index; CIS, clinically isolated syndrome; DMT, Disease-modifying therapy; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale; GD, Gadolinium; OCB, oligoclonal bands; RRMS, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; sNfL, serum neurofilament light chain.
Demographical and clinical parameters of patients with complete 6-year follow-up data (n=511) did not differ significantly from demographical and clinical parameters obtained in all patients recruited at baseline (n=1066). BMI was calculated as weight divided by height squared (kg/m²). Information on relapse rates, disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) and comorbidities was acquired by the treating physician using a standardised questionnaire. Conventional MRIs were acquired at different 3T scanners with a 32-channel receive-only head coil, according to a standardised imaging protocol in all centres.9
Statistical analyses
Demographical and medical data obtained from the nationwide database are presented as mean (SD) or median (IQR, 75–25th percentile) values for continuous variables and numbers (percentages) for categorical variables. The variables were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests for continuous variables or χ2 tests for categorical variables. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient was used to describe the relationship between the groups. The primary outcome was Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). Cox proportional hazard models and quantile regression model were used to assess risk by obesity with adjustment for confounding variables. The proportional hazard assumption was verified by plotting the estimated log-cumulative hazard function against the log-transformed survival times. Variables were defined by time to event and censored at date of last contact. Differences were considered significant at two-sided p ≤ 0.05. No adjustment for multiple comparisons was applied. We used SPSS (IBM SPSS Statistics V.27) to perform the statistical analyses. Data were analysed from September 2021 to March 2022.
Results
Baseline characteristics of the 1066 participants (315 male (29.5%); mean (SD) age 33.31 (9.62) years) can be found in table 1. At disease onset, 159 patients (14.9%) had a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 and obesity-related comorbidities (type 2 diabetes, arterial hypertension) were documented in 68 patients (6.4%). Patients recruited at baseline had follow-up visits at year 2 (871, 81.7%), at year 4 (656, 61.5%) and at year 6 (511, 47.9%). Follow-up data at year 6 were available from 430 (47.4%) of non-obese patients and from 81 (50.9%) of obese patients. Differences in recruiting obese versus non-obese patients at baseline versus year 6 were not statistically significant (χ2-test, p=0.41). Information on smoking at baseline was available in 1049/1066 (94.4%) patients. Although the prevalence of smoking was higher in obese (37.1%) compared with non-obese (30.7%) patients, differences were not statistically significant (χ2 test, p=0.13).
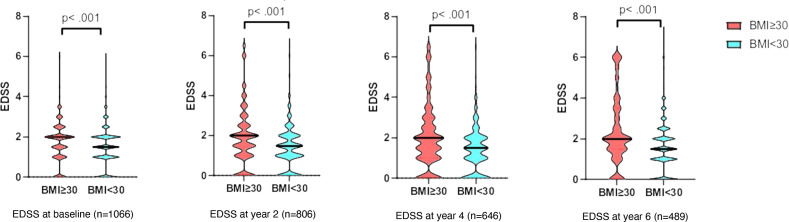
Obesity as defined by BMI ≥30 kg/m2 at disease onset was associated with higher EDSS at baseline and at 2, 4 and 6 years of follow-up (p<0.001 for each time point investigated; figure 1). The median EDSS was 0.38 (baseline), 0.36 (at year 2), 0.39 (at year 4), 0.42 (at year 6) points higher in the obese cohort after adjusting for sex and age, and 0.35 (baseline), 0.34 (at year 2), 0.43 (at year 4), 0.46 (at year 6) points higher in the obese cohort after additional adjustment for sex, age and smoking.
Figure 1.
Clinical disability as assessed by EDSS in MS patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 compared with <30 kg/m2 at disease onset. EDSS at baseline was significantly higher in the cohort (median (IQR): 2 (1–2) (vs 1.5 (1–2) =0.118; p<0.001), determined by Mann-Whitney U test) EDSS after 2 years deteriorated and showed a stronger correlation and at year 2 (r=0.13; p<0.001) year 4 (r=0.155; p<0.001), year 6 (r=0.186; p<0.001). BMI, body mass index; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale.
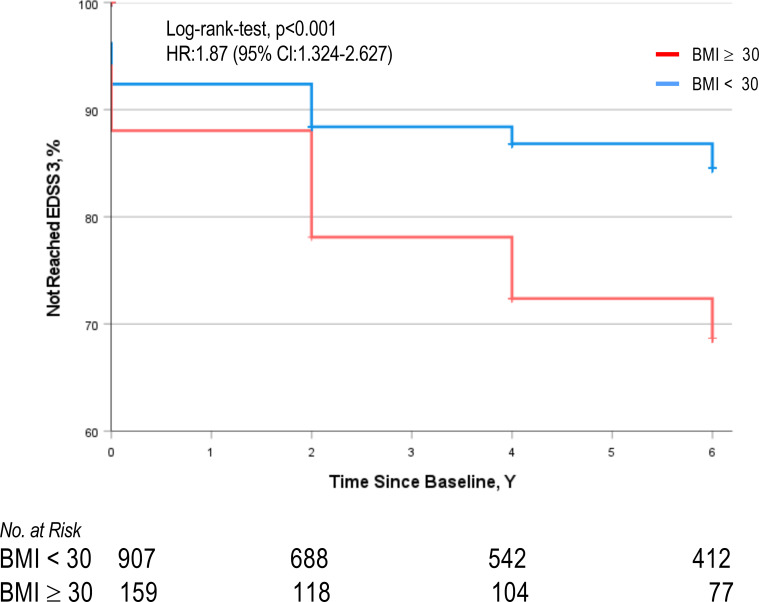
Median time to reach EDSS 3 was 0.99 years (95% CI 0.74 to 1.24) for patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 and 1.46 years (95% CI 0.95 to 1.97) for non-obese patients (HR 1.47; 95% CI 0.341 to 0.668; log-rank test p<0.001). Risk to reach EDSS 3 over 6 years was significantly increased in patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 compared with patients with BMI <30 (35 % vs 14%; HR 2.1; 95% CI 1.5 to 2.94; p<0.001). Obesity at baseline remained to be associated with an increased risk to reach an EDSS of 3 after 6 years after adjustment for sex and age (HR 1.92; CI 1.4 to 2.7; log-rank test p<0.001) and following additional adjustment for sex, age and smoking (HR 1.87; 95% CI 1.3 to 2.6; log-rank test p<0.001; figure 2).
Figure 2.
Comparison of the cumulative hazard of reaching EDSS of 3 in obese versus non-obese patients with MS. HR=1.87 (95% CI 1.324 to 2.627, p<0.001), adjusted for sex, age and smoking. BMI, body mass index; EDSS, Expanded Disability Status Scale; MS, multiple sclerosis.
Subgroup analysis on patients with complete 6-year follow-up data (n=511) confirmed that risk to reach EDSS 3 over 6 years was significantly increased in patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 compared with patients with BMI<30 (37 % vs 17.7%; HR 2.26; 95% CI 1.5 to 3.5; log-rank test p<0.001). Obesity at baseline remained to be associated with an increased risk to reach an EDSS of 3 after 6 years after adjustment for sex and age (HR 2.05; 95% CI 1.34 to 3.14; log-rank test p<0.001), and after additional adjustment for sex, age and smoking (HR 2.13; 95% CI 1.39 to 3.27; p<0.001).
Notably, only presence of obesity (BMI ≥30 kg/m2 vs BMI <30 kg/m2) but not overweight (BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2 vs BMI <25 kg/m2) at disease onset was significantly associated with higher disability at baseline and at 2, 4 and 6 years of follow-up and with an increased risk to develop an EDSS of 3 after 6 years. Obesity at disease onset was not significantly associated with a higher annual relapse rate, increased number of contrast-enhancing MRI lesions or higher MRI T2 lesion burden over 6 years of follow-up (data not shown).
Obesity-associated comorbidities (type 2 diabetes, arterial hypertension) at MS onset were enriched in patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 (19 %) as compared with patients with BMI<30 (4 %) (p<0.001). Higher age at MS onset was associated with increased prevalence of these comorbidities (mean (SD) age 38.7 (9.16) vs 32.9 (9.54), p<0.001). Comorbidities were not significantly associated with higher risk to reach EDSS 3 within 6 years of follow-up, higher annual relapse rate, increased number of contrast-enhancing MRI lesions or higher MRI T2-hyperintense lesions burden at baseline and follow-up. Obesity at baseline remained to be associated with an increased risk to reach an EDSS of 3 after 6 years after adjustment for sex, age, smoking and comorbidities (HR 1.84; 95% CI 1.29 to 2.61; log-rank test p<0.001).
The proportion of obese patients receiving high-potency therapies (natalizumab, ocrelizumab, rituximab, cladribine and fingolimod) at years 2, 4 and 6 of follow-up was not significantly different from the proportion of non-obese patients under these treatments. Obesity at baseline remained statistically associated with higher EDSS at year 2, 4 and 6 and increased disability accumulation to EDSS of 3 after 6 years after adjustment for sex, age, smoking and for receiving or not receiving DMT at baseline (HR 1.89; 95% CI 1.35 to 2.65; p<0.001). Furthermore, obesity at baseline remained statistically associated with increased disability accumulation to EDSS of 3 during follow-up even after adjustment for receiving either platform treatment (interferon beta-1b, interferon beta-1a, glatiramer acetate, teriflunomide, azathioprine (n=684; HR 1.9; 95% CI 1.4 to 2.7; p<0.001), high-potency therapies as defined above (n=175; HR 1.86; 95% CI 1.32 to 2.6; p<0.001) and for not receiving MS-modifying therapies during the follow-up (n=276; HR 1.86; 95% CI 1.3 to 2.6; p<0.001).
Discussion
In this nationwide study using a large real-world representative German cohort of newly diagnosed patients with relapse-onset MS, we demonstrate that presence of obesity at disease onset is associated with higher accumulation of disability over an observation period of up to 6 years.
Large cohort studies consistently reported that obesity during childhood and adolescence increases the future risk of MS by ORs of 1.5–2.5, independent of other environmental and lifestyle factors.1–8 Only a few studies with partly conflicting results investigated whether obesity at MS onset is associated with disease severity and disability accumulation.10 11 Among 464 participants in the Betaferon/Betaseron in Newly Emerging Multiple Sclerosis for Initial Treatment trial, the presence of obesity increased the risk for conversion to MS defined by the 2001 McDonald criteria, while no associations were observed between obesity and conversion to clinically definite MS, EDSS progression or MRI outcomes.12 A longitudinal cohort study in the USA recruiting 469 patients with CIS and MS at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) reported that higher BMI at baseline was associated with grey matter decline and reduced brain parenchymal volumes.13 Higher BMI was associated with statistically significant, although not clearly clinically meaningful, increases in EDSS (per BMI 5 kg/m2, the EDSS score was 0.13 points higher, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.22, p=0.004).13 Limitations of previous studies include sample size and potential inclusion of CIS patients without confirmed conversion to MS. Furthermore, clinically relevant effects on disability were probably underestimated since EDSS usually shows little change over short observation periods. Here, we capitalised on a 6-year national cohort study of 1066 patients at baseline, all of them fulfilling the 2017 McDonald criteria at baseline or follow-up.
Despite earlier accumulation of clinical disability, annualised relapse rates and MRI parameters for disease activity were not significantly increased in obese patients with MS. These findings are supported by results obtained in the UCSF study mentioned above,13 which did not detect any association of obesity with MRI activity as defined as development of new T2 lesions despite brain and grey matter volume decline. In line with the aforementioned study reporting that higher BMI was associated with greater subsequent disability,13 our finding that obesity but not overweight in MS patients is associated with a poorer outcome suggests a threshold effect of body mass on disability accumulation in MS. Midlife overweight and obesity are risk factors for future loss of grey matter volume and development of dementia, an association thought to be driven by impaired insulin signalling, mitochondrial dysfunction, excess of reactive oxygen species, dyslipidaemia and low-grade, obesity-induced chronic inflammation.14 15 Such mechanisms are also thought to contribute to MS progression but are not necessarily depicted by T2-weighted imaging, number of contrast-enhancing lesions or clinical relapses.
Our study has limitations. First, BMI was assessed at baseline only which precludes evaluation of within-person change in BMI as a predictor of interest. Second, documentation of obesity-associated comorbidities was limited to type 2 diabetes and hypertension, and the number of patients diagnosed with these conditions was small. The analyses related to comorbidities would, therefore, benefit from confirmation in larger cohorts. Furthermore, our analysis focused on patients with relapse-onset MS. Whether obesity specifically increases the risk for accumulating disability in progressive MS has not been addressed so far and remains to be clarified.
Obesity is a modifiable risk factor. In line with the aforementioned studies indicating an association of obesity with grey matter decline, obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery are reported to build up grey and white matter volume as they regain healthy weight.16 17 These data suggest that dedicated management of obesity should be explored for its potential merit in improving long-term clinical outcomes of patients diagnosed with MS.
Acknowledgments
The authors and representatives of the KKNMS express their deep gratitude to all contributors of the study, especially the study nurses, for their motivated collaboration and recruitment efforts, all the patients and relatives for their participation and support, and the data monitoring and administrative personnel of the study.
Footnotes
Contributors: Conception and design of the study: IL, ME and JDL. Data acquisition, analysis and interpretation: all authors. Statistical analysis: IL and ME. Drafting of the manuscript: IL, ME, SB, FZ, HW and JDL. Revising the manuscript: all authors.
Funding: The German NationMS cohort and KKNMS were supported by grants from the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) Grant nos. 01GI0914, 01GI1601I (Bochum); 01GI0916, 01GI1601G (Lübeck); and 01GI1601B (Marburg). The authors acknowledge support by the German Research Foundation (Collaborative Research Centre SFB-TRR128 ‘Initiating/Effector versus Regulatory Mechanisms in Multiple Sclerosis-Progress towards Tackling the Disease’).
Competing interests: SB has received honoraria from Biogen Idec, Bristol Meyer Squibbs, Merck Serono, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Roche and Teva. His research is funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and Hertie Foundation. FL has served on the advisory board of Roche and received travel funding from Teva. AS has received speaker honoraria and/or travel compensation for activities with Bristol Myers Squibb, CSL Behring, Novartis and Roche, and research support by the Swiss MS Society and Baasch Medicus Foundation, not related to this manuscript. LK has received compensation for serving on Scientific Advisory Boards for Alexion, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genzyme, Horizon, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novartis and Roche. She has received speaker honoraria and travel support from Bayer, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genzyme, Grifols, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche, Santhera and Teva. She has received research support from the German Research Foundation, the IZKF Münster, IMF Münster, Biogen, Immunic AG, Novartis and Merck Serono. CK has received speaker fees, travel support and/or served on advisory boards by Biogen, Merck, Roche and Sanofi. BW has received grants from the German Ministry of Education and Research, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Dietmar Hopp Foundation and Klaus Tschira Foundation, grants and personal fees from Merck, and personal fees from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Teva; none related to this work. AB has received personal compensation from Merck Serono, Biogen, Novartis, Teva, Roche, Sanofi/Genzyme, Celgene/BMS and Janssen; he has received grants for congress travel and participation from Biogen, Teva, Novartis, Sanofi/Genzyme, Merck Serono and Celgene. None related to this report. HT has received consulting and/or speaker honoraria from Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Celgene, GSK, Jannssen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi Genzyme and Teva. SM has received honoraria for lecturing and travel expenses for attending meetings from Almirall, Amicus Therapeutics Germany, Bayer Health Care, Biogen, Celgene, Diamed, Genzyme, MedDay Pharmaceuticals, Merck Serono, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, ONO Pharma, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Chugai Pharma, QuintilesIMS and Teva. His research is funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Else Kröner Fresenius Foundation, German Academic Exchange Service, Hertie Foundation, Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Studies (IZKF) Muenster, German Foundation Neurology and by Almirall, Amicus Therapeutics Germany, Biogen, Diamed, Fresenius Medical Care, Genzyme, Merck Serono, Novartis, ONO Pharma, Roche and Teva. CT has received honoraria for consultation and expert testimony from Alexion Pharma Germany, Chugai Pharma Germany and Roche Pharma. None of this interfered with the current report. UKZ has received speaking fees, travel support and financial support for research activities from Alexion, Almirall, Bayer, Biogen, Bristol-Myers-Squibb, Janssen, Merck-Serono, Novartis, Octapharm, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme and Teva as well as EU, BMBF, BMWi. CH has received speaker honoraria from Merck and Roche. He has received grant support from Merck, Novartis and Roche. TK has received speaker honoraria and/or personal fees for advisory boards from Bayer Healthcare, Merck, Novartis Pharma, Sanofi-Aventis/Genzyme, Roche Pharma, Alexion and Biogen as well as grant support from Novartis and Chugai Pharma in the past. None of this interfered with the current report. RG has received speaker and board honoraria from Baxter, Bayer Schering, Biogen Idec, Bristol Meyer Squibb, CSL Behring, Eisai, Genzyme, Janssen, Merck Serono, Novartis, Stendhal, Talecris and Teva. His department has received grant support from Bayer Schering, BiogenIdec, Genzyme, Merck Serono, Novartis and Teva. All of RG’s declarations are unrelated to the content of this manuscript. BH has served on scientific advisory boards for Novartis; he has served as DMSC member for AllergyCare, Polpharma, Sandoz and TG therapeutics; he or his institution has received speaker honoraria from Desitin; his institution has received research grants from Regeneron for multiple sclerosis research. He holds part of two patents: one for the detection of antibodies against KIR4.1 in a subpopulation of patients with multiple sclerosis and one for genetic determinants of neutralising antibodies to interferon. FZ has recently received research grants and/or consultation funds from Biogen, Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), Bristol-Meyers-Squibb, Celgene, German Research Foundation (DFG), Janssen, Max-Planck-Society (MPG), Merck Serono, Novartis, Progressive MS Alliance (PMSA), Roche, Sanofi Genzyme and Sandoz. HW has received honoraria for acting as a member of Scientific Advisory Boards for Janssen, Merck and Novartis as well as speaker honoraria and travel support from Alexion, Amicus Therapeuticus, Biogen, Biologix, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cognomed, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Gemeinnützige Hertie-Stiftung, Medison, Merck, Novartis, Roche Pharma AG, Genzyme, Teva and WebMD Global. HW is acting as a paid consultant for Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Idorsia, Immunic, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, the Swiss Multiple Sclerosis Society and UCB. His research is funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG), Deutsche Myasthenie Gesellschaft e.V., Alexion, Amicus Therapeutics, Argenx, Biogen, CSL Behring, F. Hoffmann - La Roche, Genzyme, Merck KgaA, Novartis Pharma, Roche Pharma and UCB Biopharma. JDL has received speaker fees, research support, travel support, and/or served on advisory boards by Abbvie, Alexion, Argenx, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi and Takeda. JDL has received speaker fees, research support, travel support, and/or served on advisory boards by Abbvie, Alexion, Argenx, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi and Takeda.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data availability statement
Data are available on reasonable request.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
This study involves human participants and was approved by Ruhr-University Bochum, Registration no. 3714-10. Participants gave informed consent to participate in the study before taking part.
References
- 1. Munger KL, Chitnis T, Ascherio A. Body size and risk of MS in two cohorts of US women. Neurology 2009;73:1543–50. 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181c0d6e0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Chitnis T, Graves J, Weinstock-Guttman B, et al. Distinct effects of obesity and puberty on risk and age at onset of pediatric MS. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2016;3:897–907. 10.1002/acn3.365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Cortese M, Riise T, Bjørnevik K, et al. Body size and physical exercise, and the risk of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 2018;24:270–8. 10.1177/1352458517699289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Munger KL, Bentzen J, Laursen B, et al. Childhood body mass index and multiple sclerosis risk: a long-term cohort study. Mult Scler 2013;19:1323–9. 10.1177/1352458513483889 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Hedström AK, Lima Bomfim I, Barcellos L, et al. Interaction between adolescent obesity and HLA risk genes in the etiology of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2014;82:865–72. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Gianfrancesco MA, Stridh P, Rhead B, et al. Evidence for a causal relationship between low vitamin D, high BMI, and pediatric-onset MS. Neurology 2017;88:1623–9. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Huppke B, Ellenberger D, Hummel H, et al. Association of obesity with multiple sclerosis risk and response to first-line disease modifying drugs in children. JAMA Neurol 2019;76:1157–65. 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.1997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Høglund RAA, Meyer HE, Stigum H, et al. Association of body mass index in adolescence and young adulthood and long-term risk of multiple sclerosis: a population-based study. Neurology 2021;97:e2253–61. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012957 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Fleischer V, Ciolac D, Gonzalez-Escamilla G, et al. Subcortical volumes as early predictors of fatigue in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2022;91:192–202. 10.1002/ana.26290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kvistad SS, Myhr K-M, Holmøy T, et al. Body mass index influence interferon-beta treatment response in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2015;288:92–7. 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.09.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Tettey P, Simpson S, Taylor B, et al. An adverse lipid profile and increased levels of adiposity significantly predict clinical course after a first demyelinating event. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2017;88:395–401. 10.1136/jnnp-2016-315037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Manuel Escobar J, Cortese M, Edan G, et al. Body mass index as a predictor of MS activity and progression among participants in benefit. Mult Scler 2022;28:1277–85. 10.1177/13524585211061861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Mowry EM, Azevedo CJ, McCulloch CE, et al. Body mass index, but not vitamin D status, is associated with brain volume change in MS. Neurology 2018;91:e2256–64. 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006644 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Xu WL, Atti AR, Gatz M, et al. Midlife overweight and obesity increase late-life dementia risk: a population-based twin study. Neurology 2011;76:1568–74. 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182190d09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Bobb JF, Schwartz BS, Davatzikos C, et al. Cross-Sectional and longitudinal association of body mass index and brain volume. Hum Brain Mapp 2014;35:75–88. 10.1002/hbm.22159 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Tuulari JJ, Karlsson HK, Antikainen O, et al. Bariatric surgery induces white and grey matter density recovery in the morbidly obese: a voxel-based morphometric study. Hum Brain Mapp 2016;37:3745–56. 10.1002/hbm.23272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Michaud A, Dadar M, Pelletier M, et al. Neuroanatomical changes in white and grey matter after sleeve gastrectomy. Neuroimage 2020;213:116696. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on reasonable request.