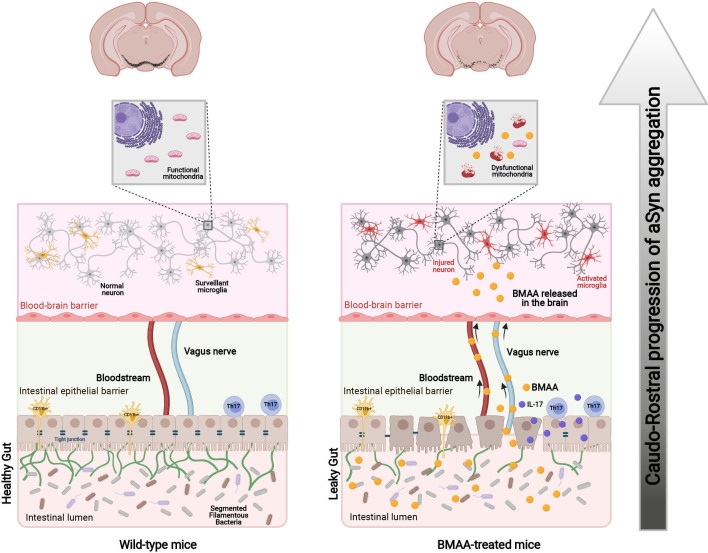
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of ‘Gut-first’ PD. Environmental microbial toxins lead to the erosion of segmented filamentous bacteria (SFB, green) in the ileum, which potentiates a Th17 proinflammatory response and the loss of intestinal barrier integrity. These events in the gut allow the progression of the disease into the brain either through the blood or the vagus nerve. Microbial toxins target mesencephalic mitochondria and activate neuronal innate immunity followed by aSyn expression, microglial activation and ultimately PD. aSyn, alpha-synuclein; BMAA, β-N-methylamino-L-alanine; IL, interleukin; PD, Parkinson’s disease; Th17, T helper 17. (This image was created at BioRender.com).