Abstract
Transglutaminase 2 (TG2) is an important cancer stem-like cell survival protein that is highly expressed in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma and drives an aggressive cancer phenotype. In the present study we show that TG2 knockdown or inactivation results in a reduction in mTOR level and activity in epidermal cancer stem-like cells which is associated with reduced spheroid formation, invasion and migration, and reduced cancer stem cell and EMT marker expression. Similar changes were observed in both cultured cells and tumors. mTOR knockdown or treatment with rapamycin phenocopies the reduction in spheroid formation, invasion and migration, and cancer stem cell and EMT marker expression. Moreover, mTOR appears to be a necessary mediator of TG2 action, as forced expression of constitutively active mTOR in TG2 knockdown cells partially restores the aggressive cancer phenotype and cancer stem cell and EMT marker expression. Tumor studies show that rapamycin reduces tumor growth and cancer stem cell marker expression and EMT. These studies suggest that TG2 stimulates mTOR activity to stimulate cancer cell stemness and EMT and drive aggressive tumor growth.
Keywords: Transglutaminase 2, mTOR, epidermal squamous cell carcinoma, cancer stem cells
Introduction
TG2 is a uniquely oncogenic member of the transglutaminase family that is a focus of intense study relating to its role as a cancer cell survival factor 1,2. TG2 displays transamidase and GTP binding activity, and recent studies show that GTP binding activity is required to maintain the cancer phenotype 1–4. TG2 level and signaling activity are markedly increased in tumors and tumor cell lines 5–9 where it suppresses expression of tumor suppressor genes, drives synthesis and deposition of fibronectin and collagen, stabilizes the extracellular matrix, and stimulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) 4,9,10. Recent studies indicate that TG2 is highly enriched in epidermal cancer stem-like cells (ECS cells) where it stimulates an aggressive cancer phenotype 2–4,11. It localizes in the extra- and intracellular environment where it regulates a host of pro-cancer plasma membrane receptors and intracellular signaling cascades 3,11–15.
mTORC1 and mTORC2 comprise two distinct functional complexes. mTORC1 (mTOR) is involved in driving survival of cancer cells 16. mTOR is activated in response to nutrient conditions favorable for cell growth and in response to signaling stimuli. Activation of mTOR marks cellular entry into a growth regime characterized by increased cell proliferation 16. mTOR activates protein synthesis by phosphorylating 4E-BP1 leading to release of eIF4E which then acts to enhance 5’ cap-dependent mRNA translation 17,18. mTOR also promotes the sterol regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP) transcription program by phosphorylating the SREBP inhibitor, lipin 1, which leads to SREBP-dependent lipid and cholesterol synthesis 16. These responses are tuned to provide the cell with energy and substrates required for rapid proliferation. In addition, to prevent breakdown of these newly synthesized products, mTOR inhibits autophagy activating kinase 1 (ULK1) and autophagy related protein 3 (ATG3) 19,20. Activation of mTOR is also associated with enhanced epithelial-mesenchymal transition 21.
In the present study we confirm that the TG2 ECS cell survival factor maintains mTOR signaling and that TG2 inactivation reduces cancer cell spheroid formation, invasion, migration, tumor formation and EMT. Inhibiting mTOR function replicates these responses and restoration of mTOR function partially reverses the reduction in cancer phenotype in TG2 knockdown cells. These findings suggest that a TG2/mTOR signaling pathway is required to maintain the cancer phenotype.
Materials and Methods
Antibodies and reagents
DMEM (11960–077), sodium pyruvate (11360–070), L-Glutamine (25030–164) and 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (25200–056) were purchased from Gibco (Grand Island, NY). DMEM/F12 (1:1) medium (DMT-10–090-CV) was purchased from Mediatech INC (Manassa, VA). B27 serum-free supplement (17504–044) was purchased from Invitrogen (Frederick, MD). TG2 (MAB3839) and β-Actin (A5441) antibodies, DAPI (D9542), bovine serum albumin (B4287), epidermal growth factor (EGF) (E4269), insulin (19278), and Heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Cell lysis buffer (9803), rapamycin (9904) and mTOR (2972S), mTOR-P (5536S) and E-Cadherin (3195S) antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA). Sox2 (ab15830–100), CD44v6 (ab78960), Slug (ab27568) and Twist (ab49254) antibodies were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, MA). Fibronectin antibody (610077), Matrigel (354234) and BD BioCoat Millicell inserts (d = 1 cm, 8 mM pore size, #353097) were purchased from BD Bioscience (Frankin Lakes, NJ). Peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (NXA931) and peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (NA934V) antibodies were purchased from GE Healthcare (Laurel, MD). Human mTOR-siRNA (SMARTpool, M-003008–03-0005) was obtained from Dharmacon (Lafayyette, CO). Control-siRNA (sc-37007) and human TG2-siRNA (sc-37514) were purchased from Santa Cruz (Dallas, TX). The TG2 inhibitor NC9 was provided by Dr. Jeffrey Keilor 11,22. Captisol (S4592) were purchased from SelleckChem (Houston, TX). pcDNA3.1 control vector (V79020) and pcDNA3-FLAG-mTOR(S2215Y) (69013) plasmid were purchased from Addgene (Watertown, MA). The mTOR(S2215Y) plasmid encodes a constitutively active form of mTOR 23. Two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for binary comparison between control and experimental groups.
Immunoblot
Cells and tissues were prepared in Laemmli buffer (0.063 M Tris-HCI, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol, 5% SDS, 5% β-mercaptoethanol). Equivalent amounts of proteins were electrophoresed on 8% –12% denaturing polyacrylamide gels and then transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked in 5% non-fat milk for one hour and incubated in the primary antibodies diluted as 1:500 – 1:1000 overnight. The membranes were washed and incubated with secondary antibodies (1:5000) for 2 h before visualization using chemiluminescence detection.
Cell Culture
SCC-13 24 and HaCaT 25 cells were routinely maintained as monolayer cultures in growth medium consisting of DMEM, 4.5 mg/mL D-glucose, 2 μmol/l L-glutamine, 100 mmol/l sodium pyruvate, and 10% heat-inactivated FCS 26. Epidermal cancer stem-like cell enriched cultures (ECS cells) were used in all experiments 26,27. The ECS cells were derived by growth of cells as unattached spheroids in DMEM/F12 (1:1) medium containing 2% B27 serum-free supplement, 20 ng/ml EGF, 0.4% bovine serum albumin and 4 μg/ml insulin. The resulting spheroids were dissociated into single cells and used for proliferation, invasion, migration and tumor growth experiments. Spheroid enrichment increases the ECS cell population from 0.15% (monolayer cultures) to 15 – 20% of the total cell population. The enriched ECS cells were used in these experiments because the ECS cell population is more aggressive in proliferation, spheroid formation, invasion, migration and tumor formation 26.
For siRNA or plasmid electroporation, 1 million cells were electroporated with 3 μg target siRNA or plasmid by using 100 μl of VPD-1002 nucleofection reagent (Walkersville, MD). In some experiments, a second electroporation was performed at 48 h after the initial electroporation. Mycoplasma tests were performed at regular intervals to assure an absence of contamination.
Spheroid formation, invasion, and migration assay
These assays are outlined as in our previous studies 26,28. For spheroid formation assay, cells were seeded as 4,000 cells/well into 6 well Ultra-Low attachment plates and growth was monitored from 0 – 3 days and spheroid number and/or diameter was measured using image J. For invasion assay, BD BioCoat Millicell inserts were pre-coated with 250 μg/ml Matrigel and 20,000 cells, suspended in medium containing 1% serum were seeded into the BD BioCoat Millicell insert upper chamber. The lower chamber contained medium supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum. The cells were allowed to migrate for 0 – 20 h and the membranes were fixed and stained with DAPI to detect nuclei for cell counting. For migration assay, a 10 μl pipette tip was used to create uniform wounds on a confluent cell monolayer and wound closure was monitored from 0 – 24 h.
Tumor xenograft assay
Single cell suspensions of SCC-13 ECS cells were resuspended in PBS containing 30% Matrigel and 0.1 million cells were subcutaneously injected into each front flank of eight -week-old female NSG (NOD/SCID/IL2Rg−/−) mice and tumor growth was monitored from 0 – 4 wks. Five mice were used per treatment group. The mice were treated with 1 mg/kg rapamycin (dissolved in 20% Captisol) or 20 mg/kg NC9, delivered by IP injection, three times per week. Tumor size was calculated as volume = 4/3π × (diameter/2)3. At the end of the experiment, the tumors were photographed, and the tumor tissue was collected for immunohistochemistry and immunoblot.
Results
ECS cell enriched cultures, derived by culturing monolayer cells as unattached spheroids in stem cell selection medium 26, were used in all experiments. This enriches the ECS cell population from 0.15% (monolayer cultures) to 15 – 20% of the total cell population. Enriched ECS cells are used because they are more aggressive in proliferation, spheroid formation, invasion, migration and tumor formation 26. We first confirmed that TG2 knockdown or treatment with TG2 specific inhibitor suppresses the cancer phenotype. TG2 knockdown (Fig. 1A) reduces SCC-13 cell spheroid formation (Fig. 1B) and invasion (Fig. 1C) and reduced spheroid formation and invasion are also observed following treatment with NC9, a TG2-specific inhibitor (Fig. 1D/E) 22,29. We also tested the impact of these treatments in HaCaT cells where spheroid formation and invasion (Fig. 1G) are reduced following TG2 knockdown (Fig. 1F) or treatment with NC9 (Fig. 1H). An important finding is that mTOR/mTOR-P levels are reduced following TG2 knockdown and NC9 treatment (Fig. 1I) and this is associated with reduced EMT as evidenced by reduced expression of Twist, Slug and fibronectin, and increased expression of E-cadherin (Fig. 1I). In addition, expression of the TG2, CD44v6 and Sox2 stem cell markers are reduced (Fig. 1I). Similar changes were observed in both SCC-13 and HaCaT cells. Note that in few the reduction in level of some markers is modest (e.g., Sox2 and fibronectin reduction in TG2-siRNA treated SCC13 spheroids). We next determined if these changes in expression are observed in TG2 inhibitor treated tumors. Fig. 1J shows that NC9 treatment markedly reduces tumor formation and that is associated with reduced mTOR-P, fibronectin, Twist, Slug, CD44v6, and Sox2, and increased E-cadherin.
Fig. 1. TG2 enhances mTOR signaling to drive tumor formation.
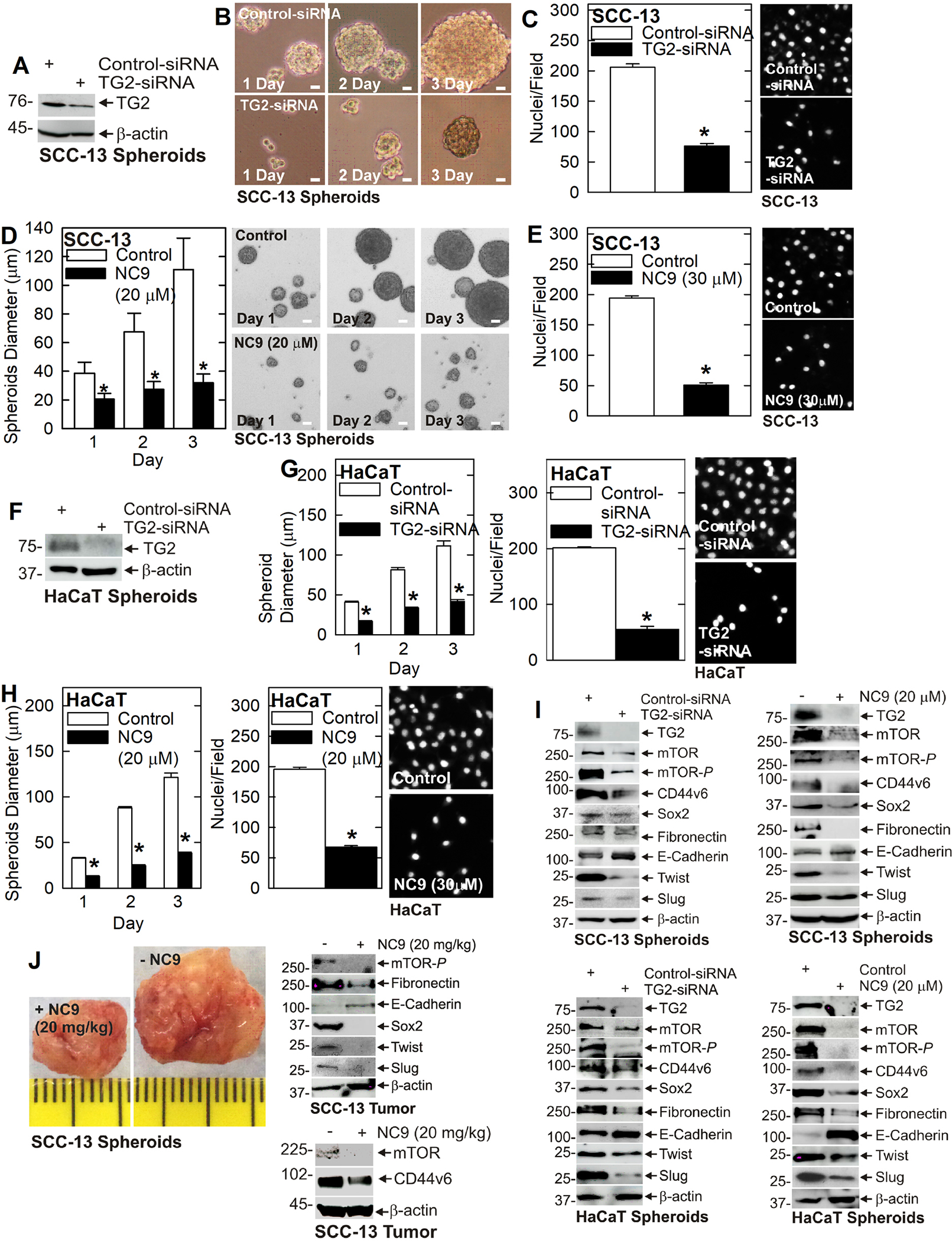
A/B/C TG2 knockdown reduces SCC-13 cell spheroid formation and invasion. Invasion was monitored by measuring cell migration through Matrigel as detected by DAPI staining of nuclei. D/E Treatment with TG2 inhibitor (NC9) reduces SCC-13 cell spheroid formation and invasion. F/G TG2 knockdown attenuates HaCaT cell spheroid formation and invasion. H NC9 treatment reduces HaCaT cell spheroid formation and invasion. I TG2 knockdown or NC9 treatment reduces SCC-13 and HaCaT EMT and reduces cancer stem cell marker expression. J Treatment of NSG mice with TG2 inhibitor (NC9) reduces SCC-13 derived ECS cell tumor growth and this is associated with reduced EMT and reduces cancer stem marker levels. Each experiment is repeated three times. A single asterisk indicates a significant reduction, n = 3, p = 0.001.
A role for mTOR signaling
A key finding from these studies is the reduction in mTOR signaling. The fact that mTOR and mTOR-P are reduced in TG2 deficient cells and tumors suggests that mTOR may mediate TG2 maintenance of the cancer phenotype. To test this, we treated SCC-13 cells with Control- and mTOR-siRNA and monitored the effects on the cancer endpoints. Treatment with mTOR-siRNA resulted in a marked reduction in mTOR and mTOR-P in SCC-13 cells (Fig. 2A) and this is associated with a reduction in spheroid formation (Fig. 2B), invasion (Fig. 2C) and migration (Fig. 2D). Examination of biochemical changes shows a marked reduction in mTOR/mTOR-P, reduced levels of the CD44v6 and Sox2 stem cell markers, reduced EMT marker (fibronectin, Twist and Slug) expression and increased E-cadherin (Fig. 2E). Treatment with rapamycin, the mTOR inhibitor, also reduced cancer cell spheroid formation (Fig. 2F), invasion (Fig. 2G) and migration (Fig. 2H). Biochemical analysis revealed a marked reduction in mTOR-P, decreased CD44v6, Sox2, Twist and Slug, and increased E-cadherin (Fig. 2I). To confirm this in a second cell line, we treated HaCaT cells with mTOR-siRNA which resulted in reduced levels of mTOR-P, CD44v6, Sox2, Slug, and Twist, and increased E-cadherin (Fig. 3A). These changes are associated with reduced spheroid formation (Fig. 3B), invasion (Fig. 3C) and migration (Fig. 3D). In addition, rapamycin suppressed mTOR signaling and EMT marker expression (Fig. 3E) leading to a reduction in HaCaT cell spheroid formation (Fig. 3F), invasion (Fig. 3G) and migration (Fig. 3H).
Fig. 2. mTOR maintains the SCC-13 cell aggressive cancer phenotype.
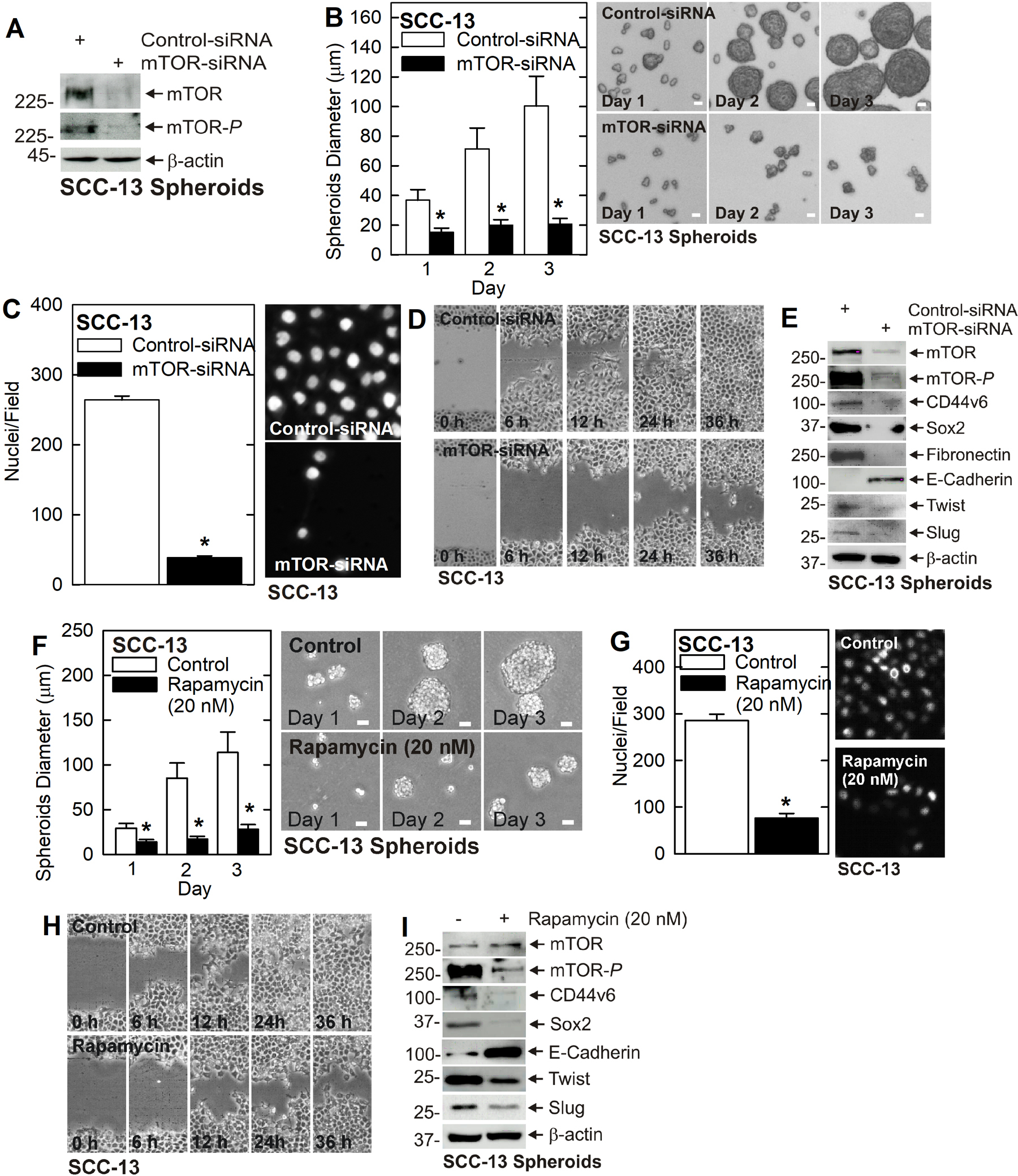
A/B/C/D mTOR knockdown reduces cancer cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration. E mTOR knockdown decreases EMT and cell stem cell marker expression. F/G/H Rapamycin treatment reduces spheroid formation, invasion and migration. I Rapamycin treatment suppresses EMT and reduces stem cell marker expression. A single asterisk indicates a significantly decrease, n = 3, p = 0.0005.
Fig. 3. mTOR maintains the HaCaT cell cancer phenotype.
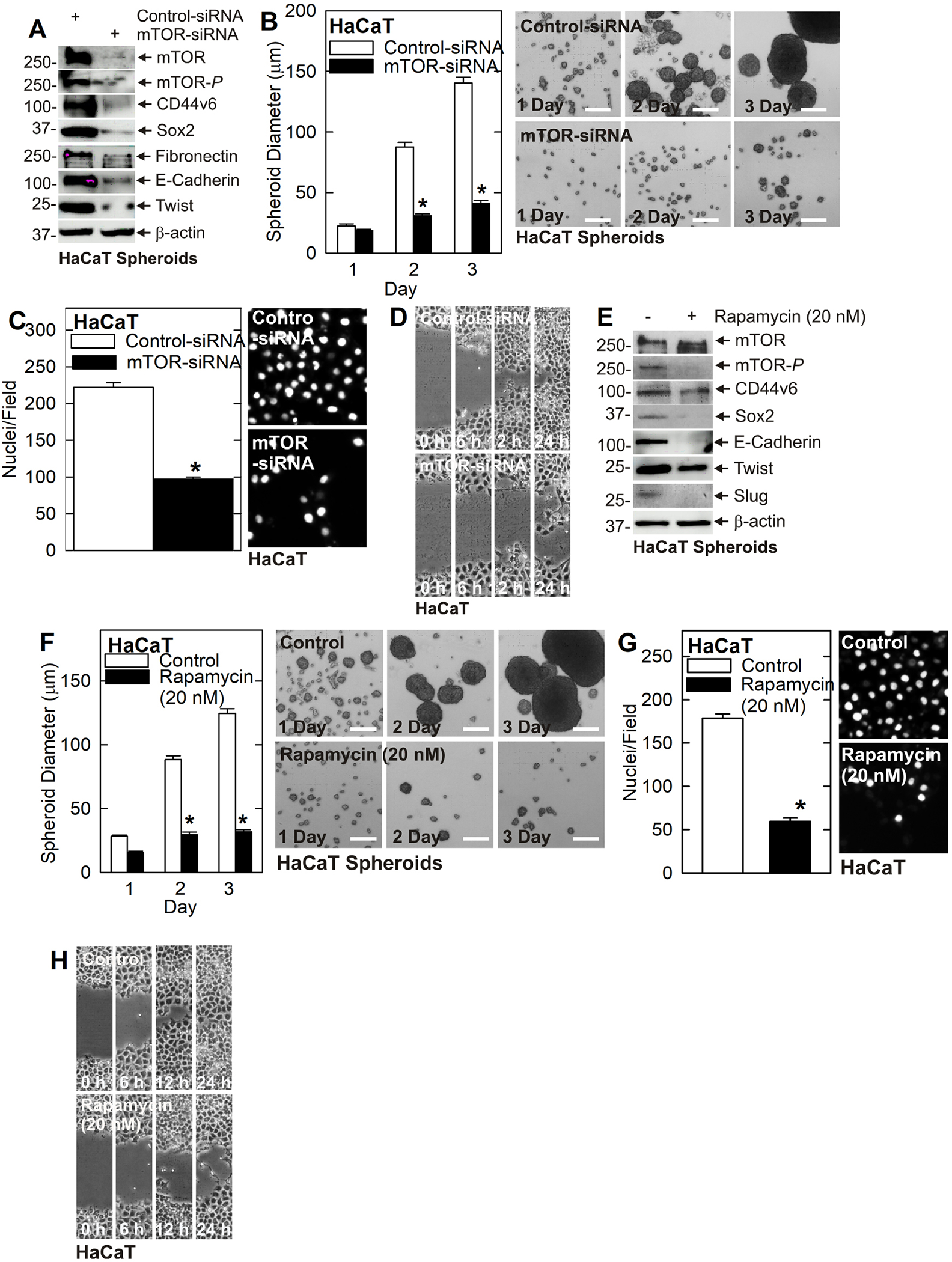
A mTOR knockdown reduces HaCaT cell EMT and reduces cancer stem cell marker expression. B/C/D mTOR knockdown reduces HaCaT cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration. E Rapamycin treatment decreases stem cell markers CD44v6 and Sox2, and several EMT markers in HaCaT cells. F/G/H Rapamycin reduces HaCaT cell spheroid formation, invasion, and migration. The asterisks indicate a significant reduction (n = 3, p = 0.001).
Constitutively active mTOR expression restores the cancer phenotype
We next wanted to determine if mTOR is a required and essential mediator of TG2 action. We therefore measured the impact of restoring mTOR expression in TG2 knockdown cells to determine if this would partially or completely restore the aggressive cancer phenotype. In Fig. 4A we expressed the constitutively active mTOR mutant, mTOR(S2215Y), in SCC-13 cells. This resulted in a substantial increase in mTOR activity (mTOR-P). Interestingly, total mTOR levels are decreased in mTOR(S2215Y) expressing cells, perhaps as a compensatory response to the mTOR hyperactivation. Consistent with previous data, CD44v6, Sox2, Twist and Slug levels are reduced following TG2 knockdown. Importantly, the reduction in expression of the Sox2 stem cell marker and slug EMT marker in TG2 knockdown cells is partially reversed by expression of mTOR(S2215Y) (Fig. 4A). This restoration of mTOR activity is reflected in the biological responses in that TG2 knockdown reduces spheroid formation (Fig 4B), invasion (Fig. 4C) and migration (Fig. 4D) and these reductions are partially reversed by mTOR(S2215Y) expression. TG2 knockdown and mTOR(S2215Y) expression produce similar biochemical (Fig. 4E) and biological changes (Fig. 4F/G/H) in HaCaT cells.
Fig. 4. Evidence that mTOR is a key downstream mediator of TG2 activity.
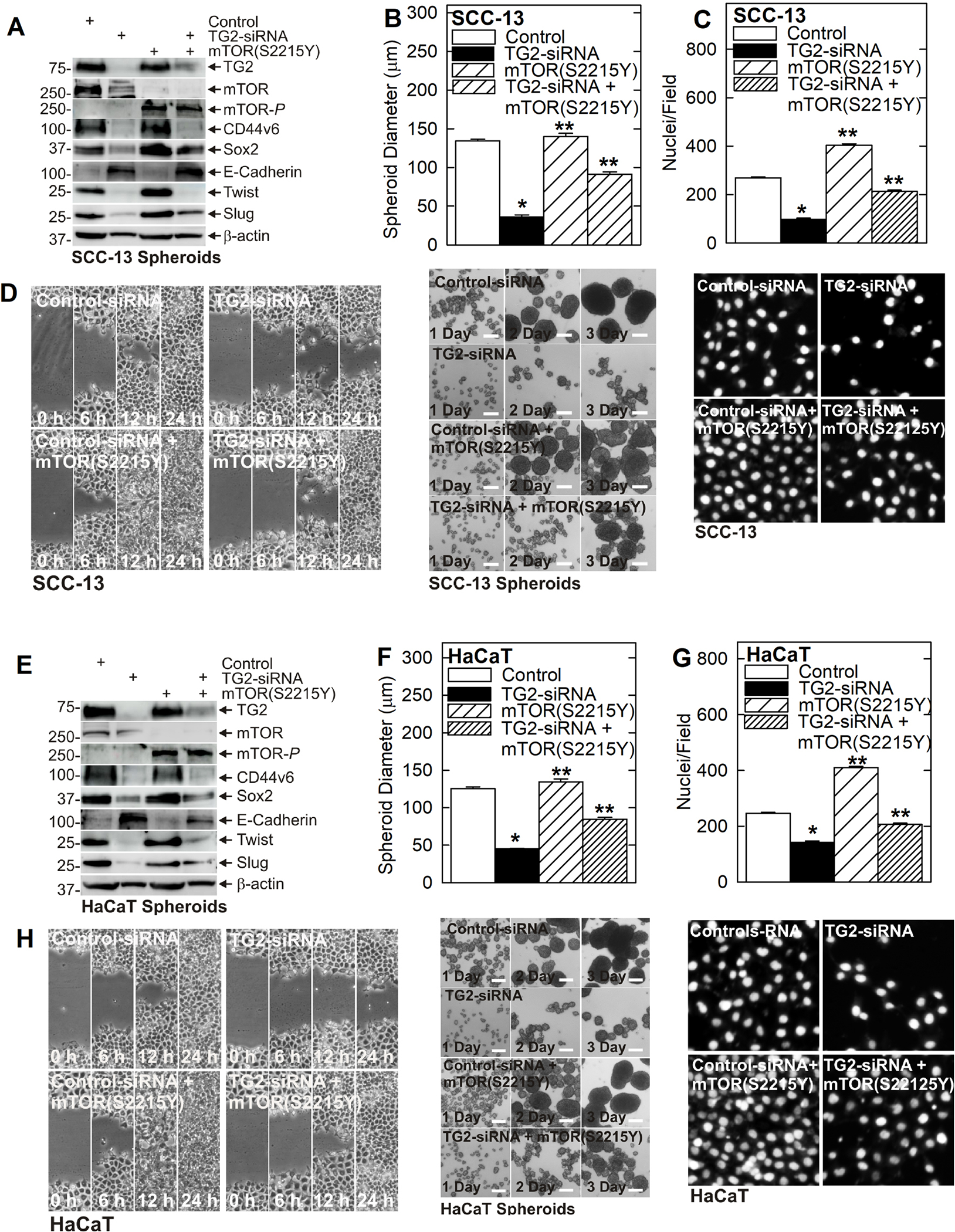
Cells were electroporated with control- or TG2-siRNA followed by transfection with empty vector or plasmid encoding constitutively active mTOR, mTOR(S2215Y). A Treatment with TG2-siRNA reduces SCC-13 cell cancer stem cell marker (CD44v6, Sox2) expression, and suppresses EMT (decreased Twist and Slug and increased E-cadherin), and these changes are reversed by expression of mTOR(S2215Y). B/C/D TG2-siRNA reduces SCC-13 derived ECS cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration and these changes are reversed by mTOR(S2215Y) expression. E TG2-siRNA treatment reduces HaCaT derived ECS cell stem cell marker (CD44v6, Sox2) expression, and suppresses EMT (decreased Twist and Slug and increased E-cadherin), and these changes are reversed by mTOR(S2215Y). F/G/H TG2-siRNA reduces HaCaT derived ECS cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration and these changes are reversed by mTOR(S2215Y) expression. The single asterisk indicates significantly decrease and double asterisks indicate a significant increase (n = 4, p = 0.005).
Impact of mTOR on tumor formation
The findings in Fig. 1J show that TG2 inhibitor treatment reduces mTOR activity and Sox2, CD44v6, Twist, and Slug levels while increasing E-cadherin level, and this is associated with reduced tumor formation. This suggests TG2 may stimulate mTOR activity to maintain tumor growth. This hypothesis predicts that inhibition of mTOR should produce similar changes in tumor growth. We therefore monitored the impact of rapamycin treatment on tumor formation. Rapamycin produced an extremely strong 65-fold reduction in tumor growth (Fig. 5A) and this is associated with reduce mTOR activity, reduced levels of TG2, CD44v6, Sox2, fibronectin, Twist and Slug, and increased E-cadherin expression (Fig. 5B). One exception is the minimal change in CD44v6 level in the second tumor set.
Fig. 5. Rapamycin inhibition of mTORC1 reduces tumor growth.
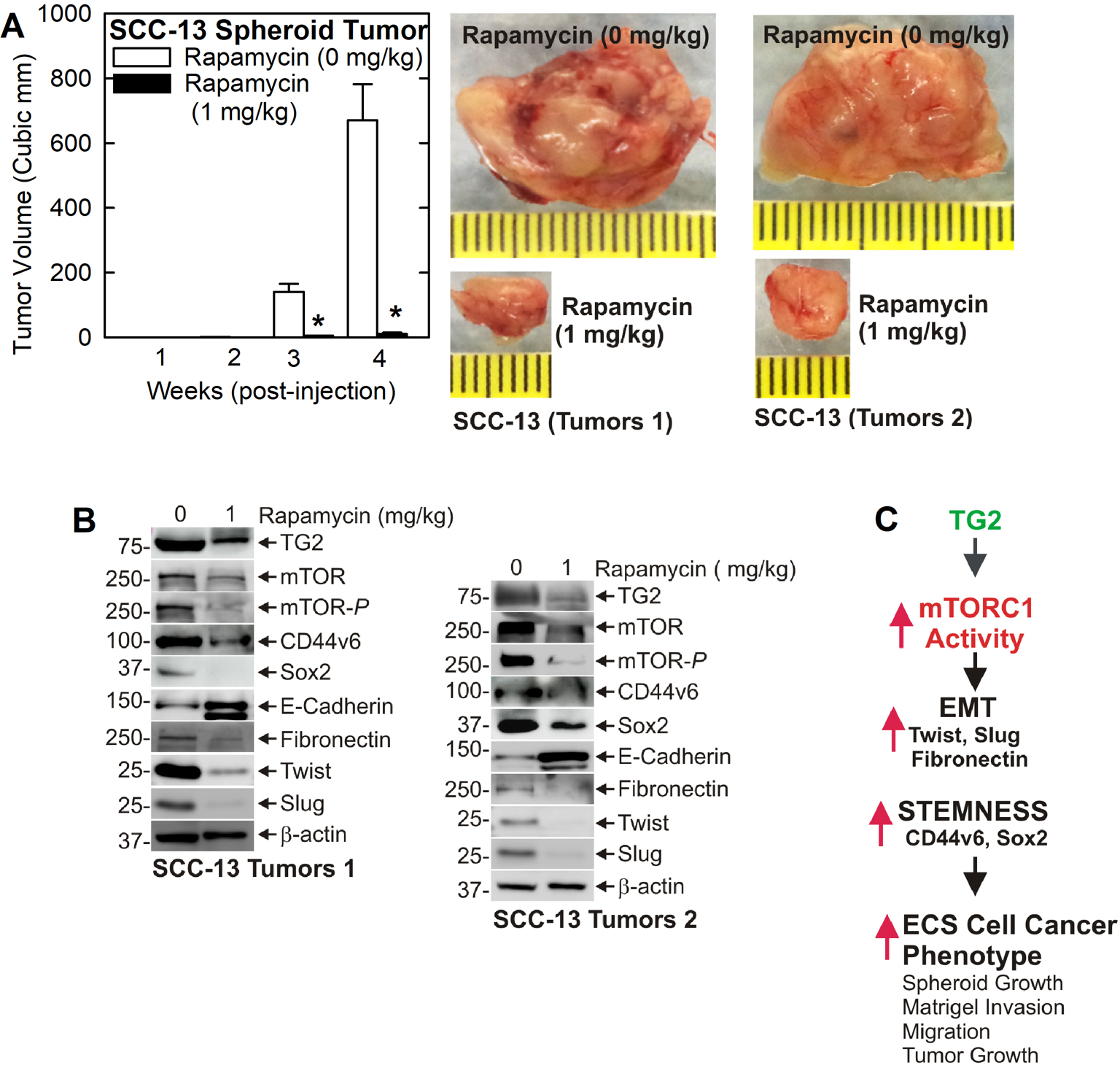
SCC-13 spheroid-derived ECS cells were injected into each front flank of NSG mice (5 mice/treatment group) and tumor size was measured weekly. Mice were treated with 0 or 1 mg/kg rapamycin delivered by IP injection three times per week, and the tumors were collected at the end of week four. A Rapamycin produces a dramatic reduction in tumor size. The values are mean + SEM, n = 3 experiments, p = 0.0001. B Rapamycin treatment reduces EMT and cancer stem cell marker (Sox2 and CD44v6) expression in tumors. C Signaling scheme: TG2 stimulates mTORC1 activity to induce EMT and stimulates stemness, and this is associated with a more aggressive cancer phenotype and enhanced tumor growth. This pathway can be inhibited by interfering with TG2 or mTOR function.
Discussion
TG2 regulation of ECS cell function
ECS cell enriched cultures, derived by culturing monolayer cells as unattached spheroids in stem cell selection medium 26, were used in all experiments. ECS cells were used because they are more aggressive in proliferation, spheroid formation, invasion, migration and tumor formation as compared to non-enriched monolayer cell cultures 26. For example, ECS cell tumors grow to be four times larger than tumors derived from non-stem cancer cells 26. Moreover, TG2 levels are highly enriched in these cells 4.
TG2 stimulates mTOR signaling to maintain the cancer phenotype
TG2 is a multifunctional cancer cell survival protein that activates a range of signaling cascades 2,9. In epidermal squamous cell carcinoma, TG2 maintains VEGF 12, α6/β4-integrin 3,11, NRP1 13, YAP1/TAZ 11 and GIPC1/SYX/RhoA/p38 13. However, the role of TG2 in maintaining cancer cell and cancer stem cell survival is far from completely understood. Our present studies confirm that TG2 knockdown or treatment with TG2 specific inhibitor reduces ECS cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration. A surprising finding is that this is associated with reduced mTOR level and activity. These findings suggest that mTOR is a key downstream mediator of TG2 action. To test this, we treated ECS cells with mTOR-siRNA, or rapamycin, an inhibitor that selectively inhibits mTORC1 30. We show that loss of mTOR activity reduces ECS cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration, indicating that interfering with mTOR function mimics responses observed in response to loss of TG2.
TG2 stimulation of mTOR enhances EMT and maintains cancer stem cell marker expression
TG2 knockdown or TG2 specific inhibitor treatment reduces expression of EMT control factors including Twist and Slug and this is associated with reduced fibronectin and increased E-cadherin levels. This is consistent with a previous report showing that TG2 controls EMT in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma and that inhibition of TG2 reduces EMT 4. Moreover, TG2 loss is also associated with reduced levels of cancer stem cell markers including CD44v6 and Sox2. A very interesting finding is that mTOR knockdown or treatment with rapamycin also reduces Twist, Slug and fibronectin and increases E-cadherin, consistent with a role for mTOR in regulating EMT. Moreover, CD44v6 and Sox2 are also reduced in these cells. Thus, these findings show that mTOR regulation of EMT and stem cell marker levels mimics that observed for TG2, suggesting that mTOR is a downstream mediator of TG2 action.
To directly determine if mTOR loss is required for the reduction in cancer phenotype following TG2 knockdown or inhibition, we transfected plasmid encoding constitutively active mTORC1 into TG2 knockdown cells and assessed if this mutant, mTOR(S2215Y), could restore the cancer phenotype. These experiments show that the presence of mTOR(S2215Y) in TG2 knockdown cells partially restores mTOR-P, Twist and Slug expression and partially reduces E-cadherin levels. These biochemical changes are associated with a partially restoration of cancer cell spheroid formation, invasion and migration. Similar results were observed in both SCC-13 and HaCaT cells. These findings provide strong and direct evidence suggesting that TG2 activates mTOR activity to drive an aggressive cancer phenotype in ECS cells derived from SCC-13 and HaCaT cells.
Rapamycin impact on tumor growth and EMT/stem cell marker expression
As noted in Fig. 1J, NC9 inhibition of TG2 reduces tumor growth and this is associated with reduced EMT and cancer stem cell marker expression. To monitor the impact of inhibiting mTOR on these endpoints, we treated tumor bearing mice with rapamycin. We observed a marked reduction in tumor formation which was associated with a reduction in EMT (reduced Twist, Slug and fibronectin and increased E-cadherin) and a reduction in CD44v6 and Sox2 levels. Thus, TG2 and mTOR inhibitor treatment suppress tumor formation and this is associated with reduced EMT and cancer stemness.
TG2/mTOR signaling and EMT in squamous cell carcinoma
Previous studies show that TG2 enhances EMT in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma 4 a finding that is consistent with studies in other cancer types 31–35. Moreover, TG2 has been shown to regulate mTOR via a mechanism that involved TG2 interaction with Src and PI3K to enhance 3T3 cell survival 36. Previous studies also show that TGF-β stimulates TG2 expression to enhance EMT and stemness in ovarian cancer 37, TGF-β increases TG2 in human subconjunctival fibroblasts and in lung cancer 38,39 and TG2 can modulate TGF-β activation 40. Previous studies also show that mTOR signaling is involved in induction of EMT 21. Moreover, mTOR resistant breast cancer display increased expression of TG2 41. Based on these findings, future studies should consider a possible role for TGF-β and Src/PI3K in integrating the cooperative actions of TG2 and mTOR. Our present study suggests that TG2 activates mTOR to stimulate EMT, stem cell marker expression and the cancer phenotype in epidermal squamous cell carcinoma (Fig. 5C). Additional studies will be necessary to provide details regarding the mechanism whereby TG2 activates mTORC1.
Translational importance of TG2 and TG2 inhibitors
TG2 is highly enriched in cancer stem cells in many cancer models 1,2,42 where it regulates a host of critical pro-cancer signaling cascades. In epidermal squamous cell carcinoma, these cascades include VEGF 12, α6/β4-integrin 3,11, NRP1 13, YAP1/TAZ 11 and GIPC1/SYX/RhoA/p38 13. Other studies show that TG2 maintains inflammation and NFκB signaling in breast cancer and other cancer types 9,43 and can confer drug resistance 44. It also induces PD-L1 expression in breast cancer to attenuate response to immunotherapy 45.
Given the importance of TG2 in maintaining the cancer phenotype in a wide range of cancer types 14, there has been an effort to design TG2 inhibitors 46–50. Keillor and colleagues designed a versatile inhibitor called NC9 22. Cell-based studies show that NC9, and related inhibitors, covalently bind at the transamidase catalytic site of TG2 29,51. This interaction also produces a shift in the 3D structure of the protein that inhibits the ability of TG2 to bind GTP 29,51. This is important, since TG2 binding of GTP is required for TG2 pro-cancer activity 4,52. In addition, sulforaphane, a promising cancer prevention and treatment agent derived from cruciferous vegetables, covalently binds to TG2 to inhibit TG2 transamidase and GTP binding activities to reduce its ability to drive the cancer phenotype 53. These findings suggest that TG2 is an important anti-cancer target and the treatment with TG2 specific inhibitors alone and in combination with agents that suppress related intracellular signaling pathways, or chemotherapeutic agents, may be useful treatment strategies. Relevant to the present manuscript, TG2 inhibitor treatment coupled with mTOR inhibitor may be a useful strategy for treating epidermal squamous cell carcinoma.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institutes Grants (R01 CA211909) to Richard L. Eckert and utilized the facilities of the Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center (P30 CA134274) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Abbreviations:
- EMT
epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- TG2
transglutaminase 2
- mTOR
mammalian target of rapamycin
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data Sharing
The authors elect to not share data.
References
- 1.Eckert RL. Transglutaminase 2 takes center stage as a cancer cell survival factor and therapy target. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58(6):837–853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Eckert RL, Fisher ML, Grun D, Adhikary G, Xu W, Kerr C. Transglutaminase is a tumor cell and cancer stem cell survival factor. Mol Carcinog. 2015;54(10):947–958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fisher ML, Keillor JW, Xu W, Eckert RL, Kerr C. Transglutaminase is required for epidermal squamous cell carcinoma stem cell survival. Mol Cancer Res. 2015;13:1083–1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fisher ML, Adhikary G, Xu W, Kerr C, Keillor JW, Eckert RL. Type II transglutaminase stimulates epidermal cancer stem cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 2015;6(24):20525–20539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Verma A, Wang H, Manavathi B, et al. Increased expression of tissue transglutaminase in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its implications in drug resistance and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10525–10533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yuan L, Behdad A, Siegel M, Khosla C, Higashikubo R, Rich KM. Tissue transgluaminase 2 expression in meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2008;90(2):125–132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Satpathy M, Cao L, Pincheira R, et al. Enhanced peritoneal ovarian tumor dissemination by tissue transglutaminase. Cancer Res. 2007;67(15):7194–7202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Park KS, Kim HK, Lee JH, et al. Transglutaminase 2 as a cisplatin resistance marker in non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010;136(4):493–502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mehta K, Kumar A, Kim HI. Transglutaminase 2: a multi-tasking protein in the complex circuitry of inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80(12):1921–1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Verma A, Mehta K. Tissue transglutaminase-mediated chemoresistance in cancer cells. Drug Resist Updat. 2007;10(4–5):144–151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fisher ML, Kerr C, Adhikary G, et al. Transglutaminase interaction with α6/β4-integrin to stimulates YAP1-dependent ΔNp63α stabilization and leads to enhanced cancer stem cell survival and tumor formation. Cancer Res. 2016;76:7265–7276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Research Misconduct Found]
- 12.Grun D, Adhikary G, Eckert RL. VEGF-A acts via neuropilin-1 to enhance epidermal cancer stem cell survival and formation of aggressive and highly vascularized tumors. Oncogene. 2016;35:4379–4387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Grun D, Adhikary G, Eckert RL. NRP-1 interacts with GIPC1 and SYX to activate p38 MAPK signaling and cancer stem cell survival. Mol Carcinog. 2019;58(4):488–499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Eckert RL, Kaartinen MT, Nurminskaya M, et al. Transglutaminase regulation of cell function. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(2):383–417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kuo TF, Tatsukawa H, Kojima S. New insights into the functions and localization of nuclear transglutaminase 2. FEBS J. 2011;278(24):4756–4767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu GY, Sabatini DM. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(4):183–203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gingras AC, Gygi SP, Raught B, et al. Regulation of 4E-BP1 phosphorylation: a novel two-step mechanism. Genes Dev. 1999;13(11):1422–1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hara K, Yonezawa K, Kozlowski MT, et al. Regulation of eIF-4E BP1 phosphorylation by mTOR. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(42):26457–26463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B, Guan KL. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(2):132–141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ganley IG, Lam du H, Wang J, Ding X, Chen S, Jiang X. ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(18):12297–12305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Karimi RM, Soltani A, Soleimani A, Rezaie KK, Afshari AR, Soukhtanloo M. Role of AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Biochimie. 2019;165:229–234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Keillor JW, Chica RA, Chabot N, et al. The bioorganic chemistry of transglutaminase - from mechanism to inhibition and engineering. Can J Chem. 2008;86:271–276. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Grabiner BC, Nardi V, Birsoy K, et al. A diverse array of cancer-associated MTOR mutations are hyperactivating and can predict rapamycin sensitivity. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(5):554–563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rheinwald JG, Beckett MA. Tumorigenic keratinocyte lines requiring anchorage and fibroblast support cultures from human squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981;41(5):1657–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988;106(3):761–771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Adhikary G, Grun D, Kerr C, et al. Identification of a population of epidermal squamous cell carcinoma cells with enhanced potential for tumor formation. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen X, Adhikary G, Shrestha S, et al. Transglutaminase 2 Maintains Hepatocyte Growth Factor Signaling to Enhance the Cancer Cell Phenotype. Mol Cancer Res. 2021;19(12):2026–2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fisher ML, Ciavattone N, Grun D, Adhikary G, Eckert RL. Sulforaphane reduces YAP/Np63alpha signaling to reduce cancer stem cell survival and tumor formation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(43):73407–73418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kerr C, Szmacinski H, Fisher ML, et al. Transamidase site-targeted agents alter the conformation of the transglutaminase cancer stem cell survival protein to reduce TG2 binding activity and cancer stem cell survival. Oncogene. 2017;36:2981–2990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Research Misconduct Found]
- 30.Huang J, Manning BD. A complex interplay between Akt, TSC2 and the two mTOR complexes. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37(Pt 1):217–222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kumar A, Xu J, Sung B, et al. Evidence that GTP-binding domain but not catalytic domain of transglutaminase 2 is essential for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2012;14(1):R4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kumar A, Xu J, Brady S, et al. Tissue transglutaminase promotes drug resistance and invasion by inducing mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ayinde O, Wang Z, Griffin M. Tissue transglutaminase induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition and the acquisition of stem cell like characteristics in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):20025–20041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kang S, Oh SC, Min BW, Lee DH. Transglutaminase 2 Regulates Self-renewal and Stem Cell Marker of Human Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Anticancer Res. 2018;38(2):787–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Karicheva O, Rodriguez-Vargas JM, Wadier N, et al. PARP3 controls TGFbeta and ROS driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness by stimulating a TG2-Snail-E-cadherin axis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(39):64109–64123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Boroughs LK, Antonyak MA, Cerione RA. A novel mechanism by which tissue transglutaminase activates signaling events that promote cell survival. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(14):10115–10125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cao L, Shao M, Schilder J, Guise T, Mohammad KS, Matei D. Tissue transglutaminase links TGF-beta, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and a stem cell phenotype in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31(20):2521–2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jung SA, Lee HK, Yoon JS, et al. Upregulation of TGF-beta-induced tissue transglutaminase expression by PI3K-Akt pathway activation in human subconjunctival fibroblasts. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48(5):1952–1958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Park MK, You HJ, Lee HJ, et al. Transglutaminase-2 induces N-cadherin expression in TGF-beta1-induced epithelial mesenchymal transition via c-Jun-N-terminal kinase activation by protein phosphatase 2A down-regulation. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(7):1692–1705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang L, Haylor JL, Fisher M, et al. Do changes in transglutaminase activity alter latent transforming growth factor beta activation in experimental diabetic nephropathy? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(12):3897–3910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cao J, Huang W. Compensatory Increase of Transglutaminase 2 Is Responsible for Resistance to mTOR Inhibitor Treatment. PLoS One. 2016;11(2):e0149388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Adhikary G, Grun D, Alexander HR, et al. Transglutaminase is a mesothelioma cancer stem cell survival protein that is required for tumor formation. Oncotarget. 2018; In press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Pietsch M, Wodtke R, Pietzsch J, Loser R. Tissue transglutaminase: an emerging target for therapy and imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013;23(24):6528–6543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Budillon A, Carbone C, Di GE. Tissue transglutaminase: a new target to reverse cancer drug resistance. Amino Acids. 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Choi J, Lee HJ, Yoon S, et al. Blockade of CCL2 expression overcomes intrinsic PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-resistance in transglutaminase 2-induced PD-L1 positive triple negative breast cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2020;10(9):2878–2894. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kim N, Kang JH, Lee WK, et al. Allosteric inhibition site of transglutaminase 2 is unveiled in the N terminus. Amino Acids. 2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ku BM, Kim SJ, Kim N, et al. Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor abrogates renal cell carcinoma in xenograft models. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140(5):757–767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Z, Griffin M. The role of TG2 in regulating S100A4-mediated mammary tumour cell migration. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yuan L, Siegel M, Choi K, et al. Transglutaminase 2 inhibitor, KCC009, disrupts fibronectin assembly in the extracellular matrix and sensitizes orthotopic glioblastomas to chemotherapy. Oncogene. 2007;26(18):2563–2573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Song M, Hwang H, Im CY, Kim SY. Recent Progress in the Development of Transglutaminase 2 (TGase2) Inhibitors. J Med Chem. 2017;60(2):554–567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Caron NS, Munsie LN, Keillor JW, Truant R. Using FLIM-FRET to measure conformational changes of transglutaminase type 2 in live cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kumar S, Mehta K. Tissue Transglutaminase Constitutively Activates HIF-1alpha Promoter and Nuclear Factor-kappaB via a Non-Canonical Pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Rorke EA, Adhikary G, Szmacinski H, et al. Sulforaphane covalently interacts with the transglutaminase 2 cancer maintenance protein to alter its structure and suppress its activity. Mol Carcinog. 2022;61(1):19–32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The authors elect to not share data.


