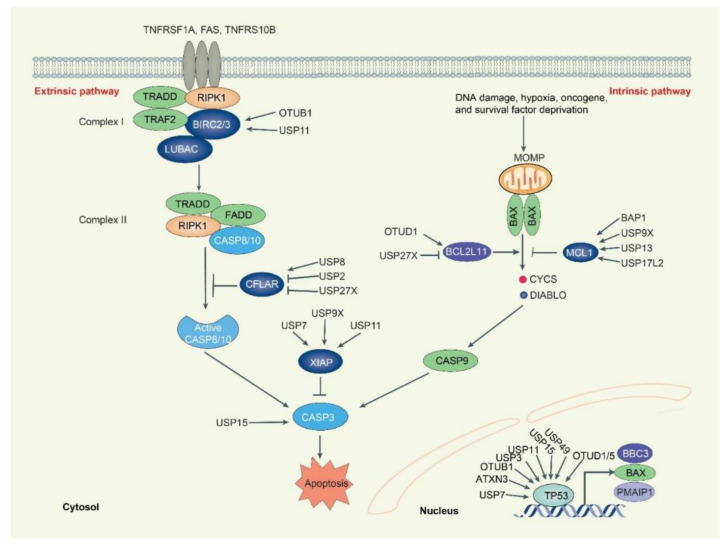
Figure 2.
Overview of DUBs-mediated regulation of apoptosis. Activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway forms complex 1 (TRADD-TRAF2-RIPK1-BIRC2/3 complex). BIRC2/3 regulates RIPK1 and its autoubiquitination, whereas USP11 and OTUB1 deubiquitinate and stabilize BIRC2/3. Active RIPK1, TRADD, FADD and CASP8/10 form complex II to trigger the CASP8/10-CASP3 cascade of the apoptotic process. The CASP8/10 inhibitor CFLAR is rapidly renewed and deubiquitinated by DUB USP8. USP2 and USP27X reduce CFLAR expression by deubiquitinating their E3 ligases TRIM28 and ITCH. The intrinsic apoptotic pathway is controlled at the level of the BCL2 family. The pro-apoptotic protein BCL2L11 and the anti-apoptotic protein MCL1 proteins are tightly controlled by DUBs. While OTUD1 stabilizes BCL2L11, USP27x promotes the binding of BCL2L11 to E3 ligases to facilitate its degradation. Three DUBs (USP9X, USP13, and USP17L2) deubiquitinate MCL1, while BAP1 promotes MCL1 transcription through H2A deubiquitinate. The extrinsic/intrinsic apoptotic signal is incorporated into CASP3, which is deubiquitinated by USP15. The TP53 protein is responsible for the expression of BBR3, BAX, and PMAIP1, which cause apoptosis. The expression of TP53 is controlled by as many as nine DUBs, including USP3/7/11/15/22/49, OTUB1, OTUD1/5, and ATXN3.