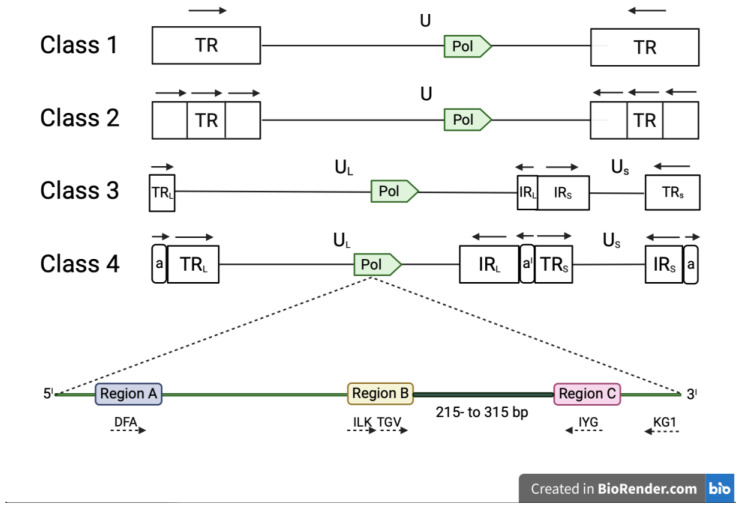
Figure 2.
Classes of viruses belonging to the family Hespesviridae based on the arrangement of repeated sequences in the genome. Human herpesvirus-6A and Human herpesvirus-6B (subfamily β-herpesvirinae) and Equine herpesvirus-2 (subfamily γ-herpesvirinae) genomes belong to class 1, while many members of the subfamily γ-herpesvirinae belong to class 2; members of the genus Varicellavirus (subfamily α-herpesvirinae) belong to class 3 genome, whereas Herpes simplex virus (subfamily α-herpesvirinae) and Cytomegalovirus (subfamily α-herpesvirinae) belong to class 4. The pol gene, which contains three conserved regions (A, B and C), is present in the architecture of all genome classes (illustrations not at scale). These regions encode highly conserved amino acid domains (DFA, ILK, TGV, IYG and KG1). PCR primers (dashed arrows) according to VanDevanter et al. are shown under the different class architectures. Primer’s directions are specified by dashed arrows. The product obtained by the Panherpes nested PCR is between region B and region C. The nomenclature used in all classes is U (unique), UL (unique long), US (unique short), TR (terminal repeat), TRL (terminal long repeat), IRL (internal long repeat), TRS (terminal short repeat), IRS (internal short repeat); TRL and TRS include a (terminal direct repeat) and IRL and IRS aI (internal inverse repeat). The orientations of repeated sequences are specified by block arrows.