Abstract
The marine environment represents the largest ecosystem on the Earth’s surface. Marine-derived fungi are of remarkable importance as they are a promising pool of diverse classes of bioactive metabolites. Bergamotane sesquiterpenoids are an uncommon class of terpenoids. They possess diverse biological properties, such as plant growth regulation, phototoxic, antimicrobial, anti-HIV, cytotoxic, pancreatic lipase inhibition, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive traits. The current work compiles the reported bergamotane sesquiterpenoids from fungal sources in the period ranging from 1958 to June 2022. A total of 97 compounds from various fungal species were included. Among these metabolites, 38 compounds were derived from fungi isolated from different marine sources. Furthermore, the biological activities, structural characterization, and biosynthesis of the compounds are also discussed. The summary in this work provides a detailed overview of the reported knowledge of fungal bergamotane sesquiterpenoids. Moreover, this in-depth and complete review could provide new insights for developing and discovering new valuable pharmaceutical agents from these natural metabolites.
Keywords: bergamotanes, sesquiterpenoids, marine, fungi, biosynthesis, biological activities
1. Introduction
Nature has substantially participated in the discovery of drugs for human remedial treatments since the beginning of mankind [1]. The marine environment, with more than 70% of the surface of the Earth, represents the largest ecosystem and is characterized by quite variable physicochemical parameters (e.g., limited light access, low temperature, high pressure, and high salinity) [2]. Among the various marine microbes, fungi are a superabundant and ecologically substantial component of marine microbiota [3]. Fungi are one of nature’s treasures that inhabit various environments on the earth’s surface, including the marine environment [4,5,6,7]. They play a growing relevant role in drug development and biomedicine research, either directly as drugs or indirectly as lead structures for bio-inspired drug synthesis [8,9,10,11,12]. In the last decades, natural product chemists and pharmacologists have turned their research interests to marine-derived fungi, which are renowned as a vast unexploited reservoir of metabolic diverseness and found to have the capability to produce structurally unique bio-metabolites [6,7,12,13,14,15,16]. Furthermore, research on fungi-derived metabolites has tremendously increased because of the need for compounds with potential economical values and pharmaceutical applications. Sesquiterpenes belonging to various classes, including hirsutane, alliacane, tremulane, bergamotane, drimane, etc., are reported from fungi [17,18,19]. The biosynthesis of their C15 skeleton from FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate) was catalyzed by sesquiterpene synthases [19,20].
Among these metabolites, the bergamotane family represents an uncommon class of natural sesquiterpenes that includes bi-, tri-, or tetracyclic derivatives [19]. Bergamotane sesquiterpenoids having a bridged 6/4 bicyclic skeleton involved in an isopentyl unit are biosynthesized by fungi and plants [21,22]. Interestingly, polyoxygenated derivatives featuring a 6/4/5/5 tetracyclic framework represent a rare class of natural metabolites, and all polycyclic bergamotanes are mainly encountered in fungi [23,24,25,26]. Bergamotane sesquiterpenoids have been reported from various marine sources such as sponges, sea mud, deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposits, and sea sediments. These metabolites could gain the interest of chemists and biologists because of their unusual structural features and diversified activities, such as phytotoxicity, plant growth regulation, antimicrobial, anti-HIV, cytotoxic, pancreatic lipase inhibition, immunosuppressive, antidiabetic, and anti-inflammatory properties. It is noteworthy that no available work has addressed this class of sesquiterpenes in term of their sources, bioactivities, and biosynthesis. In the current work, the reported fungal bergamotane sesquiterpenoids ranging from 1958 to June 2022 have been listed. They have been classified according to their ring system, i.e., into bi-, tri-, or tetracyclic derivatives (Table 1). Additionally, their fungal sources, structural characterization, biosynthesis, and biological relevance have been provided. Moreover, some of their reported structural characteristics and methods of separation and characterization, as well as their structure–activity relation, are discussed.
Table 1.
Naturally occurring fungal bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (name, source, extract/fraction, molecular weights and formulae, and location).
| Compound Name | Fungal Source/Host | Extract/Fraction | Mol. Wt. | Mol. Formula | Location | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicyclic Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoids | ||||||
| α-trans Bergamotene (1) | Nectria sp. HLS206 (Nectriaceae)/Gelliodas carnosa (marine sponge Geodiidae) | EtOAc extract | 204 | C15H24 | China | [27] |
| β-trans Bergamotene (2) | Aspergillus fumigatus (Trichocomaceae)/Cultured | Acetone extract | 204 | C15H24 | Japan | [28] |
| β-trans-2β,5,15-Trihydroxybergamot-10-ene (3) | Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7 (Trichocomaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 254 | C15H26O3 | Intertidal zone sea mud, Yingkou, China | [29] |
| E-β-trans-5,8,11-Trihydroxybergamot-9-ene (4) | Aspergillus fumigatus YK-7 (Trichocomaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Intertidal zone sea mud, Yingkou, China | [29] |
| Massarinolin C (5) | Massarina tunicata (Lophiostomataceae)/Submerged twig | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | Lemonweir River in Adams County, Wisconsin, USA | [23] |
| Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | - | - | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] | |
| Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | - | - | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] | |
| Donacinoic acid B (6) | Montagnula donacina (Montagnulaceae)/Craterellus odoratus (fruiting bodies, Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | Southern part of the Gaoligong Mountains in Yunnan, China | [32] |
| Craterodoratin M (7) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin N (8) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 268 | C15H24O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin O (9) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin P (10) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin Q (11) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 308 | C17H24O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Necbergamotenoic acid A (12) | Nectria sp. HLS206 (Nectriaceae)/Gelliodas carnosa (marine sponge, Geodiidae) | EtOAc extract | 264 | C15H20O4 | China | [27] |
| Necbergamotenoic acid B (13) | Nectria sp. HLS206 (Nectriaceae)/Gelliodas carnosa (marine sponge, Geodiidae) | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | China | [27] |
| Sporulamide C (14) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 265 | C15H23NO3 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Sporulamide D (15) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 249 | C15H23NO2 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Xylariterpenoid A (16) | Xylariaceae fungus (No. 63-19-7-3)/Everniastrum cirrhatum (Fr.) Haleex Sipman (lichen, Parmeliaceae) | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Zixi Mountain, Yunnan, China | [33] |
| Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | - | - | Atlantic Ocean, China | [34] | |
| Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | - | - | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] | |
| Xylariterpenoid B (17) | Xylariaceae fungus (No. 63-19-7-3)/Everniastrum cirrhatum (Fr.) Haleex Sipman (lichen, Parmeliaceae) | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Zixi Mountain, Yunnan, China | [33] |
| Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | - | - | Atlantic Ocean, China | [34] | |
| Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | - | - | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] | |
| Eutypeterpene B (18) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 268 | C15H24O4 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| Eutypeterpene C (19) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| Eutypeterpene D (20) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| Eutypeterpene E (21) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| Eutypeterpene F (22) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| (10S)-Xylariterpenoid A (23) | Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Atlantic Ocean. China | [34] |
| (10R)-Xylariterpenoid B (24) | Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Atlantic Ocean. China | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid E (25) | Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | 208 | C12H16O3 | Atlantic Ocean. China | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid F (26) | Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | 270 | C15H26O4 | Atlantic Ocean. China | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid G (27) | Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421/Deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit | EtOAc extract | 270 | C15H26O4 | Atlantic Ocean. China | [34] |
| Eutypeterpene A (28) | Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (Diatrypaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 294 | C16H22O5 | South Atlantic Ocean, China | [35] |
| Craterodoratin A (29) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin C (30) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 268 | C15H24O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin D (31) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 268 | C15H24O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin E (32) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 284 | C15H24O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin F (33) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 284 | C15H24O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Dihydroprehelminthosporol (34) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 238 | C15H26O2 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36,37] |
| Helminthosporal acid (35) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36] |
| Helminthosporol (36) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 236 | C15H24O2 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36] |
| Helminthosporic acid (37) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 252 | C15H24O3 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36] |
| Tricyclic Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoids | ||||||
| Prehelminthosporol (38) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 236 | C15H24O2 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36,37] |
| Prehelminthosporolactone (39) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 234 | C15H22O2 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [37] |
| Victoxinine (40) | Helminthosporium victoriae (Totiviridae) | Diethyl ether extract | 263 | C17H29NO | USA | [36,38,39] |
| Helminthosporium sativum (Totiviridae) | Diethyl ether fraction/CHCl3 extract | - | - | Canada | [40] | |
| Victoxinine-α-glycerophosphate (41) | H. sativum (Totiviridae) | n-BuOH extract | 417 | C20H36NO6P | USA | [41] |
| Craterodoratin S (42) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 277 | C17H27NO2 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Isosativenediol (43) | Bipolaris sp. No. 36/Johnson grass leaf | EtOAc extract | 236 | C15H24O2 | Wake County, North Carolina, USA | [36] |
| Pinthunamide (44) | Ampulliferina sp. No. 27 (Ampullicephala)/Pinus thunbergii (dead tree, Pinaceae) | Acetone extract | 277 | C15H19NO4 | Japan | [42] |
|
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
Acetone extract | - | - | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [43] | |
| Brasilamide A (45) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
Acetone extract | 293 | C15H19NO5 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [43,44] |
| Brasilamide B (46) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
Acetone extract | 265 | C15H23NO3 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [43] |
| Brasilamide C (47) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
Acetone extract | 279 | C15H21NO4 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [43,44] |
| Brasilamide D (48) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
Acetone extract | 321 | C17H23NO5 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [43] |
| Brasilamide K (49) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
EtOAc extract | 279 | C15H21NO4 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [44] |
| Brasilamide L (50) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
EtOAc extract | 265 | C15H23NO3 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [44] |
| Brasilamide M (51) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
EtOAc extract | 293 | C15H19NO5 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China, | [44] |
| Brasilamide N (52) |
Paraconiothyrium brasiliense Verkley (M3–3341) (Leptosphaeriaceae)/ Acer truncatum Bunge (branches, Sapindaceae) |
EtOAc extract | 279 | C15H21NO4 | Dongling Mountain, Beijing, China | [44] |
| Craterodoratin I (53) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 250 | C15H22O3 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin J (54) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 282 | C15H22O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin K (55) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 282 | C15H22O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin L (56) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 278 | C15H18O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Sporulosoic acid A (57) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 282 | C15H22O5 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Sporulosoic acid B (58) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 280 | C15H20O5 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Sporulamide A (59) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 265 | C15H23NO3 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Sporulamide B (60) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 249 | C15H23NO2 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Massarinolin B (61) | Massarina tunicata (Lophiostomataceae)/Submerged twig | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | Lemonweir River in Adams County, Wisconsin, USA | [23] |
| Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | - | - | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] | |
| Massarinolin B methyl ester (62) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 280 | C16H24O4 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Craterodoratin R (63) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 282 | C15H22O5 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin G (64) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 278 | C16H22O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Craterodoratin H (65) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 278 | C16H22O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
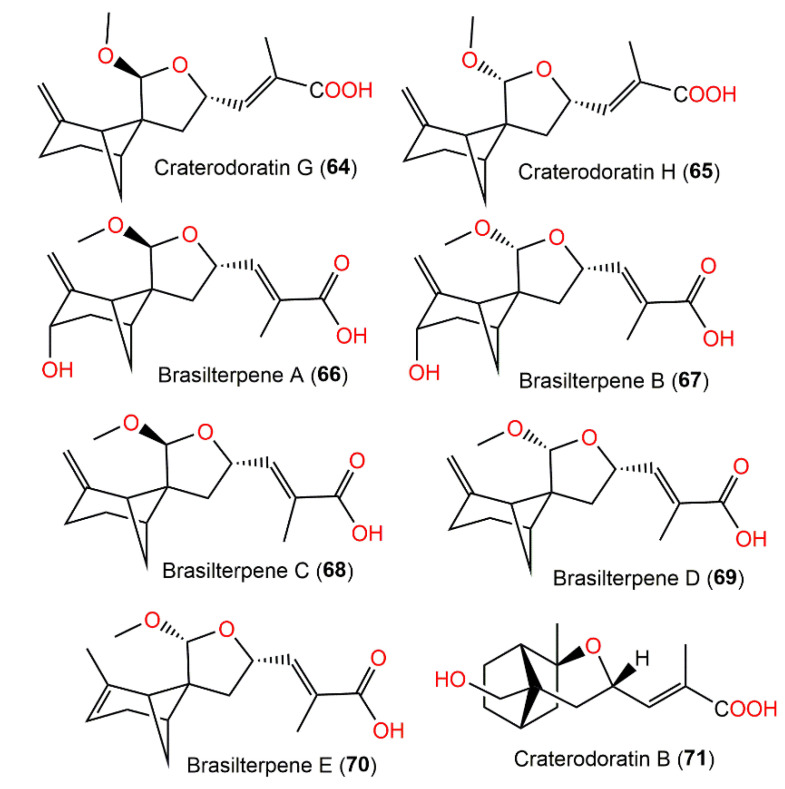
| Brasilterpene A (66) | Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 294 | C16H22O5 | Indian Ocean, China | [45] |
| Brasilterpene B (67) | Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 294 | C16H22O5 | Indian Ocean, China | [45] |
| Brasilterpene C (68) | Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 278 | C16H22O4 | Indian Ocean, China | [45] |
| Brasilterpene D (69) | Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 278 | C16H22O4 | Indian Ocean, China | [45] |
| Brasilterpene E (70) | Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Deep-sea sediment | EtOAc extract | 278 | C16H22O4 | Indian Ocean, China | [45] |
| Craterodoratin B (71) | Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 266 | C15H22O4 | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] |
| Tetracyclic Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoids | ||||||
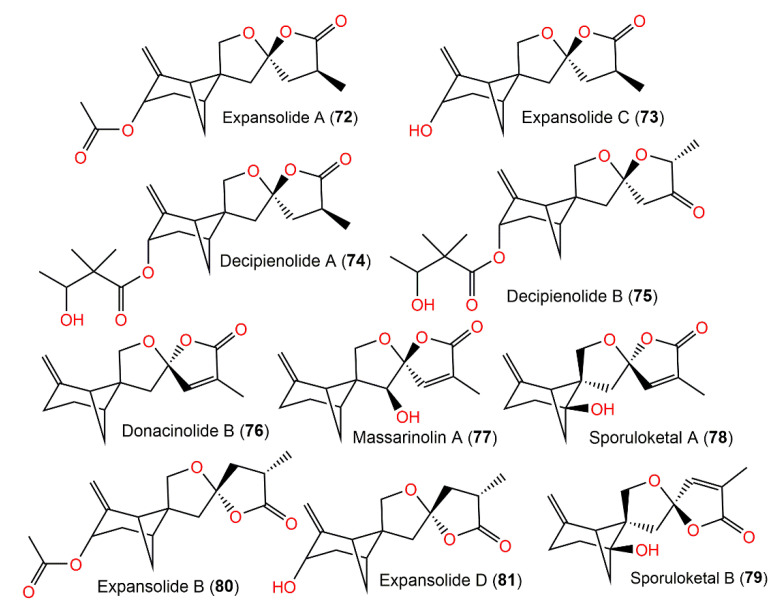
| Expansolide A (72) | Penicillium expansum (Trichocomaceae)/Fruit | EtOAc extract | 306 | C17H22O5 | France | [25] |
| Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius (Trichocomaceae)/Leaf litter | EtOAc extract | - | - | Waipoua Forest, New Zealand | [26] | |
| Expansolide C (73) | Penicillium expansum ACCC37275/Agricultural Culture | Acetone extract | 264 | C15H20O4 | China | [46] |
| Decipienolide A (74) | Podospora decipiens Niessl (JS 270) (Podosporaceae)/Sheep dung | EtOAc extract | 378 | C21H30O6 | South Australia | [24] |
| Decipienolide B (75) | Podospora decipiens Niessl (JS 270) (Podosporaceae)/Sheep dung | EtOAc extract | 378 | C21H30O6 | South Australia | [24] |
| Donacinolide B (76) | Montagnula donacina (Montagnulaceae)/Craterellus odoratus (fruiting bodies, Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 246 | C15H18O3 | Southern part of the Gaoligong Mountains in Yunnan, China | [32] |
| Massarinolin A (77) | Massarina tunicata (Lophiostomataceae)/Submerged twig | EtOAc extract | 262 | C15H18O4 | LemonweirRiver in Adams County, Wisconsin, USA | [23] |
| Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | - | - | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] | |
| Sporuloketal A (78) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 262 | C15H18O4 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Sporuloketal B (79) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 Verkley (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 262 | C15H18O4 | Intertidal zone of Bohai Bay river in Liaoning, China | [31] |
| Expansolide B (80) | Penicillium expansum (Trichocomaceae) | EtOAc extract | 306 | C17H22O5 | France | [25] |
| Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius (Trichocomaceae)/Leaf litter | EtOAc extract | - | - | Waipoua Forest, New Zealand | [26] | |
| Expansolide D (81) | Penicillium expansum ACCC37275, (Trichocomaceae)/Agricultural Culture | Acetone extract | 264 | C15H20O4 | China | [46] |
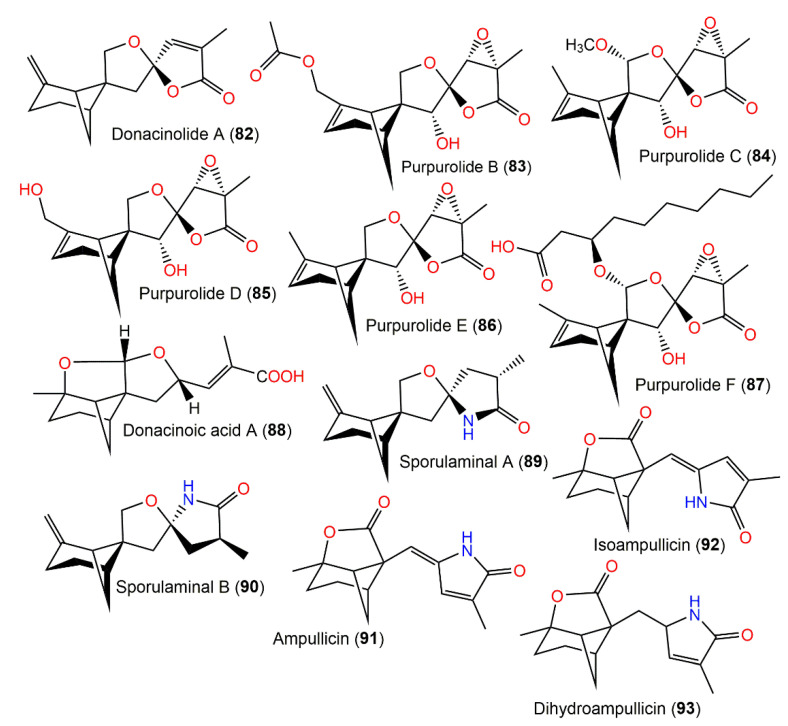
| Donacinolide A (82) | Montagnula donacina (Montagnulaceae)/Craterellus odoratus (fruiting bodies, Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 246 | C15H18O3 | Southern part of the Gaoligong Mountains in Yunnan, China | [32] |
| Purpurolide B (83) | Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 (Trichocomaceae)/Edgeworthia Chrysantha (leaves, Thymelaeaceae) | EtOAc extract | 336 | C17H20O7 | Hangzhou Bay, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | [47] |
| Purpurolide C (84) | Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 (Trichocomaceae)/Edgeworthia Chrysantha (leaves, Thymelaeaceae) | EtOAc extract | 308 | C16H20O6 | Hangzhou Bay, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | [47] |
| Purpurolide D (85) | Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 (Trichocomaceae)/Edgeworthia Chrysantha (leaves, Thymelaeaceae) | EtOAc extract | 294 | C15H18O6 | Hangzhou Bay, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | [48] |
| Purpurolide E (86) | Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 (Trichocomaceae)/Edgeworthia Chrysantha (leaves, Thymelaeaceae) | EtOAc extract | 278 | C15H18O5 | Hangzhou Bay, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | [48] |
| Purpurolide F (87) | Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 (Trichocomaceae)/Edgeworthia Chrysantha (leaves, Thymelaeaceae) | EtOAc extract | 464 | C25H36O8 | Hangzhou Bay, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China | [48] |
| Donacinoic acid A (88) | Montagnula donacina (Montagnulaceae)/Craterellus odoratus (fruiting bodies, Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | 264 | C15H20O4 | Southern part of the Gaoligong Mountains in Yunnan, China | [32] |
| Craterellus odoratus (Cantharellaceae) | EtOAc extract | - | - | Southern part of the GaoligongMountains, Yunnan, China | [30] | |
| Sporulaminal A (89) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 247 | C15H21NO2 | Intertidal zone of Bohai river in Liaonign, China | [49] |
| Sporulaminal B (90) | Paraconiothyrium sporulosum YK-03 (Leptosphaeriaceae)/Sea mud | EtOAc extract | 247 | C15H21NO2 | Intertidal zone of Bohai river in Liaonign, China | [49] |
| Ampullicin (91) | Ampulliferina-like sp. No. 27 (Ampullicephala)/Pinus thunbergii (dead tree, Pinaceae) | Acetone extract | 259 | C15H17NO3 | Japan | [50,51] |
| Isoampullicin (92) | Ampulliferina-like sp. No. 27 (Ampullicephala)/Pinus thunbergii (dead tree, Pinaceae) | Acetone extract | 259 | C15H17NO3 | Japan | [50] |
| Dihydroampullicin (93) | Ampulliferina-like sp. No. 27 (Ampullicephala)/Pinus thunbergii (dead tree, Pinaceae) | Acetone extract | 261 | C15H19NO3 | Japan | [51] |
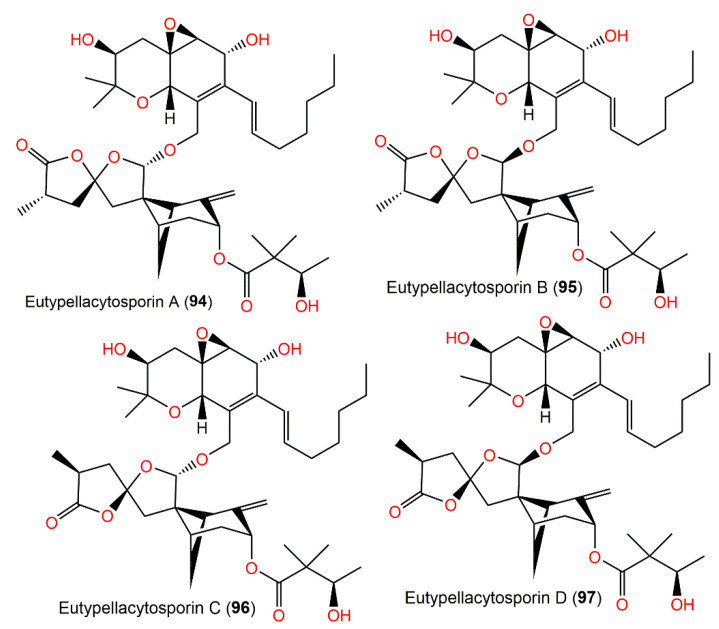
| Eutypellacytosporin A (94) | Eutypella sp. D-1 (Diatrypaceae)/Soil sample | CH2Cl2 fraction of EtOAc extract | 714 | C40H58O11 | London Island of Kongsfjorden of the Ny-Ålesund District, Arctic, Norway | [52] |
| Eutypellacytosporin B (95) | Eutypella sp. D-1 (Diatrypaceae)/Soil sample | CH2Cl2 fraction of EtOAc extract | 714 | C40H58O11 | London Island of Kongsfjorden of the Ny-Ålesund District, Arctic, Norway | [52] |
| Eutypellacytosporin C (96) | Eutypella sp. D-1 (Diatrypaceae)/Soil sample | CH2Cl2 fraction of EtOAc extract | 714 | C40H58O11 | London Island of Kongsfjorden of the Ny-Ålesund District, Arctic, Norway | [52] |
| Eutypellacytosporin D (97) | Eutypella sp. D-1 (Diatrypaceae)/Soil sample | CH2Cl2 fraction of EtOAc extract | 714 | C40H58O11 | London Island of Kongsfjorden of the Ny-Ålesund District, Arctic, Norway | [52] |
Surveying their bioactivities may open a new research area for the synthesis of new agents from these metabolites by synthetic and medicinal chemists. The literature search for the reported data was performed using diverse databases and publishers, including Web of Science, Google Scholar, PubMed, Scopus, SciFinder, Wiley, SpringerLink, and ACS Publications, using specific keywords (bergamotane, marine, fungi, biosynthesis, and biological activities).
2. Structural Assignment and Stereochemistry Determination
A total of 97 metabolites have been separated from various fungal source extracts using different chromatographic techniques and characterized by NMR, MS, and IR spectral analyses as well as chemical derivatization. The relative configuration of these metabolites was established using NOESY or ROESY spectral analyses. Various studies reported the assigning of their absolute stereochemistry using total synthesis [53,54], Mosher’s method [26], X-ray diffraction, chemical conversion [34,43,55], and ECD analyses [31]. The reported metabolites have been categorized into bi-, tri-, and tetracyclic derivatives.
3. Biological Activities of Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoids
Various reported studies revealed the assessment of bergamotane sesquiterpenoids for diverse bioactivities, including plant growth regulation, phototoxic, antimicrobial, anti-HIV, cytotoxic, pancreatic lipase inhibition, antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, and immunosuppressive, which were summarized in this work (Table 2). Additionally, the reported structure–activity relation was included.
Table 2.
Biological activities of fungal naturally occurring in bergamotane sesquiterpenoids.
| Compound Name | Biological Activity | Assay, Organism, or Cell Line | Biological Results | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | Positive Control | ||||
| E-β-trans-5,8,11-trihydroxybergamot-9-ene (4) | Cytotoxicity | MTT/U937 | 84.9 (IC50) | Doxorubicin 0.021 µM (IC50) | [29] |
| Craterodoratin M (7) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 15.43 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin N (8) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 13.26 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin O (9) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 17.12 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin Q (11) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/Concanavalin A | 31.50 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.04 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Xylariterpenoid A (16) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 17.5 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Xylariterpenoid B (17) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 21.0 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Eutypeterpene B (18) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 13.4 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Eutypeterpene C (19) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 16.8 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Eutypeterpene D (20) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 21.4 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Eutypeterpene E (21) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 18.7 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Eutypeterpene F (22) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 24.3 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| (10S)-Xylariterpenoid A (23) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 86.0 μM (IC50) | Aminoguanidine 23.0 μM (IC50) | [34] |
| (10R)-Xylariterpenoid B (24) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 230.0 μM (IC50) | Aminoguanidine 23.0 μM (IC50) | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid E (25) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 120.0 μM (IC50) | Aminoguanidine 23.0 μM (IC50) | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid F (26) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 85.0 μM (IC50) | Aminoguanidine 23.0 μM (IC50) | [34] |
| Xylariterpenoid G (27) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 85.0 μM (IC50) | Aminoguanidine 23.0 μM (IC50) | [34] |
| Eutypeterpene A (28) | Anti-inflammatory | Spectrophotometrically/LPS | 21.0 μM (IC50) | Quercetin 17.0 μM (IC50) NG-monomethyl-L-arginine 9.7 μM (IC50) |
[35] |
| Craterodoratin C (30) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 12.62 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin S (42) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 22.68 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin J (54) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 19.40 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Craterodoratin L (56) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 13.71 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Massarinolin B (61) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/Concanavalin A | 0.98 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.04 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Brasilterpene A (66) | Hypoglycemic | Spectrophotometrically/Diabetic zebrafish model | 449.3 pmol/larva (IC50) | Rosiglitazone 395.6 pmol/larva (IC50) | [45] |
| Brasilterpene C (68) | Hypoglycemic | Spectrophotometrically/Diabetic zebrafish model | 420.4 pmol/larva (IC50) | Rosiglitazone 395.6 pmol/larva (IC50) | [45] |
| Expansolide C (73) | α-Glucosidase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/α-glucosidase enzyme | 0.50 mM (IC50) | Acarbose 1.90 mM (IC50) | [46] |
| Expansolide D (81) | α-Glucosidase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/α-glucosidase enzyme | 0.50 mM (IC50) | acarbose 1.90 mM (IC50) | [46] |
| Purpurolide B (83) | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/pancreatic lipase enzyme | 5.45 μM (IC50) | Kaempferol 1.50 μM (IC50) | [47] |
| Purpurolide C (84) | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/pancreatic lipase enzyme | 6.63 μM (IC50) | Kaempferol 1.50 μM (IC50) | [47] |
| Purpurolide D (85) | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/pancreatic lipase enzyme | 1.22 μM (IC50) | Kaempferol 1.50 μM (IC50) | [48] |
| Purpurolide E (86) | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/pancreatic lipase enzyme | 6.50 μM (IC50) | Kaempferol 1.50 μM (IC50) | [48] |
| Purpurolide F (87) | Pancreatic lipase inhibition | Spectrophotometrically/pancreatic lipase enzyme | 7.88 μM (IC50) | Kaempferol 1.50 μM (IC50) | [48] |
| Donacinoic acid A (88) | Immunosuppressive | BALB/c mice T and B lymphocyte/LPS | 13.23 μM (IC50) | Cyclosporin A 0.47 μM (IC50) | [30] |
| Eutypellacytosporin A (94) | Cytotoxicity | CCK-8/DU145 | 17.1 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.9 μM (IC50) | [52] |
| CCK-8/SW1990 | 7.3 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 1.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/Huh7 | 8.4 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/PANC-1 | 9.7 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 4.5 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| Eutypellacytosporin B (95) | Cytotoxicity | CCK-8/DU145 | 11.0 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.9 μM (IC50) | [52] |
| CCK-8/SW1990 | 4.9 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 1.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/Huh7 | 4.9 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/PANC-1 | 7.9 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 4.5 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| Eutypellacytosporin C (96) | Cytotoxicity | CCK-8/DU145 | 13.5 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.9 μM (IC50) | [52] |
| CCK-8/SW1990 | 9.6 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 1.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/Huh7 | 11.2 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/PANC-1 | 10.2 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 4.5 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| Eutypellacytosporin D (97) | Cytotoxicity | CCK-8/DU145 | 13.4 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.9 μM (IC50) | [52] |
| CCK-8/SW1990 | 8.2 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 1.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/Huh7 | 9.6 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 2.2 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
| CCK-8/PANC-1 | 7.5 μM (IC50) | Cisplatin 4.5 μM (IC50) | [52] | ||
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
NO (nitric oxide) is a substantial pro-inflammatory mediator, and its excessive production is accompanied with various inflammatory illnesses; therefore, it possesses a remarkable role for regulating immune responses and inflammation [56]. NO production inhibitors may represent the potential capacity for treating various inflammatory disorders. Thus, further research for fungal metabolites must be conducted to discover novel anti-inflammation agents.
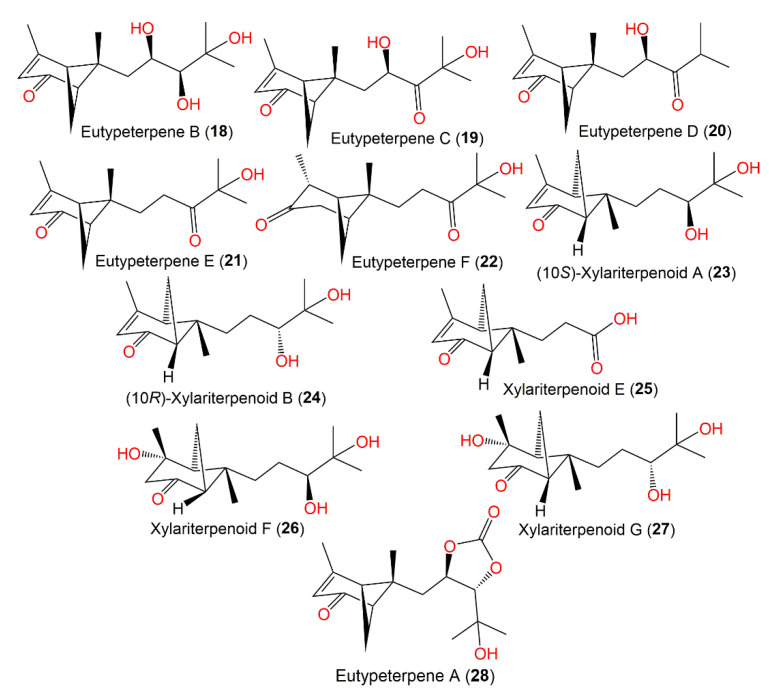
The epigenetic chemical manipulation of Eutypella sp. derived from deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide deposit by co-treatment with SBHA (histonedeacetylase inhibitor, suberohydroxamic acid) and 5-Aza (DNA methyltransferase inhibitor, 5-azacytidine) was shown to activate a biosynthetic sesquiterpene-linked gene cluster [35]. From elicitor-treated cultures EtOAc extract, eutypeterpenes A–F (18–22 and 28) along with xylariterpenoids A (16) and B (17) were purified using SiO2/RP-18/HPLC that were identified by spectral analyses, as well as by using chemical conversion, X-ray diffraction, ECD, and calculated NMR for configuration assignments.
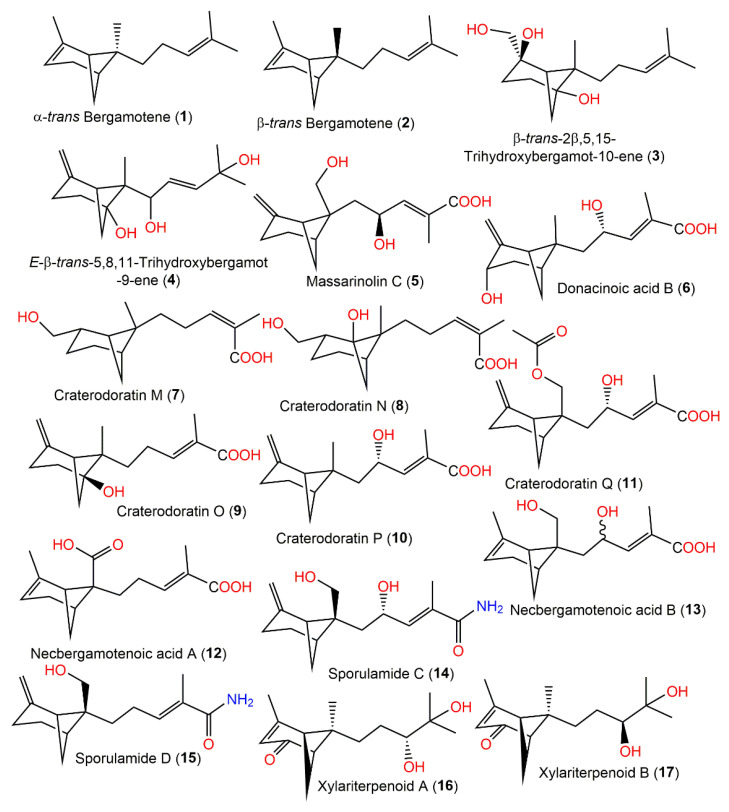
Eutypeterpene A (28) is the first bergamotene sesquiterpene incorporating a dioxolanone moiety. These metabolites were assessed for their NO production inhibitory capacity induced by LPS-(lipopolysaccharide) in RAW 264.7 macrophages [35]. The results indicated thatcompound 18 and 19 (IC50 13.4 and 16.8 μM, respectively) displayed more effectiveness than quercetin (IC50 of 17.0 μM), whereas other metabolites had noticeable potentials (IC50 values ranged from 18.7 to 24.3 μM) with weak cytotoxic capacities (IC50 > 100 μM). A structure–activity study revealed that the analog with a triol unit (18) at the side chain was more effective than compound 16, 17, and 19 with a diol unit, which were more potent than compound 20, 21, and 28 with one hydroxy group. Furthermore, the α,β-unsaturated ketone unit (as in compound 21 and 22) and the OH-linked carbon configuration also affected the activities (16 versus 17) [35] (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Structures of bicyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (1–17).
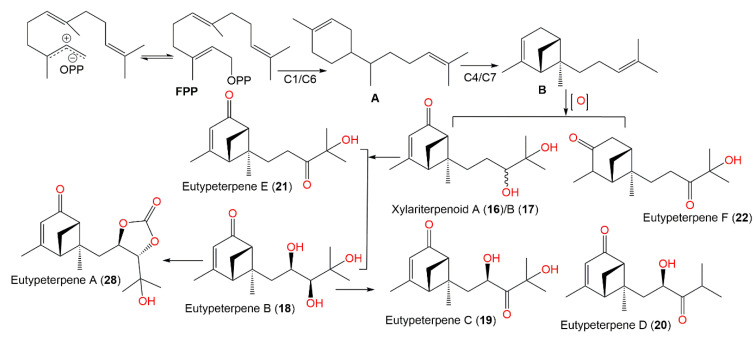
Biogenetically, compounds 18–22 are derived from FPP that performs a 1,6-cyclization to produce bisabolane (A). The 4,7-cyclization of A generates bergamotane (B), which further generates 18–22 via diverse oxidation and reduction processes. Additionally, compound 28 is formed from 18 by carbonate incorporation [35] (Scheme 1).
Scheme 1.
Biosynthetic pathway of eutypeterpenes A–F (compounds 18–22 and 28) [35].
The deep-sea-isolated Graphostroma sp. MCCC3A00421 associated with the Atlantic Ocean hydrothermal sulfide deposits biosynthesized new bergamotane sesquiterpenoids: (10S)-xylariterpenoid A (23), (10R)-xylariterpenoid B (24), xylariterpenoid E (25), xylariterpenoid F (26), and xylariterpenoid G (27), which were purified using SiO2/OSD/Sephadex LH-20/RP-18 CC and preparative TLC. They were characterized by extensive spectral data, and their absolute configuration was established by ECD, Cu-Ka-single-crystal X-ray diffraction, and modified Mosher’s method analyses. Compound 25 is trinor-bergamotane. Compounds 23, 26, and 27 revealed moderate inhibition potentials (IC50s of 86, 85, and 85 μM, respectively) of NO production in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages compared with aminoguanidine (IC50 of 23 μM). It was noted that bergamotane moiety’s 10S configuration obviously boosted the activity as in compound 23 (10S, IC50 of 85 μM) versus compound 24 (10R, of IC50 230 μM) (Figure 2) [34].
Figure 2.
Structures of bicyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (compounds 18–28).
3.2. Phytotoxic Activity
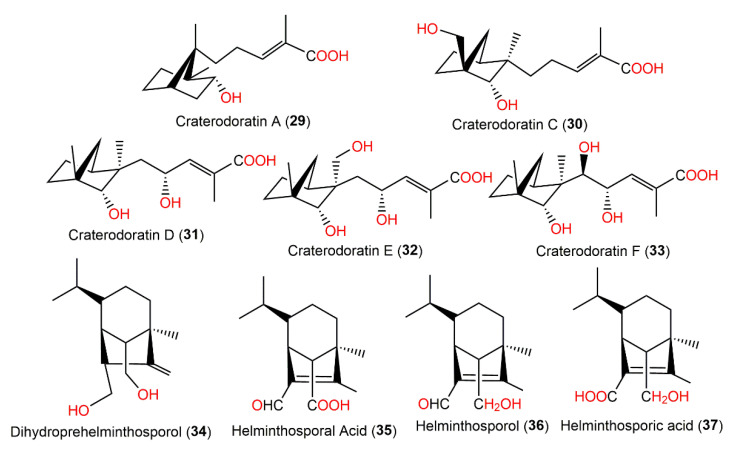
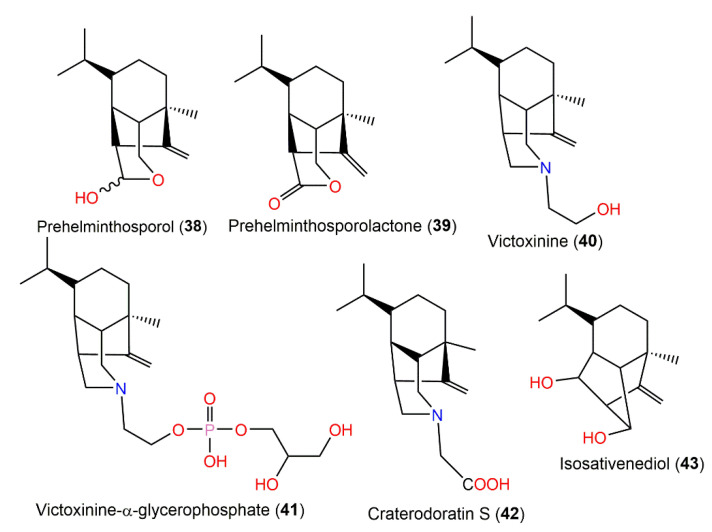
Prehelminthosporol (38) and dihydroprehelminthosporol (34) along with compounds 35–37, 39, 40, and 43 were separated by SiO2, flash CC, and preparative TLC from the EtOAc extract of the Bipolaris species, which is a Sorghum halepnse (Johnson grass) pathogen (Figure 3). These metabolites were assessed for their phytotoxic potential towards Sorghum bicolor (Sorghum) and Sorghum balepense (Johnson grass) in leaf spot assays [36,37]. Compounds 34, 38, and 39 produced similar lesions to those caused by the fungus in the field. The lesions appeared as a reddish-brown area (0.3–0.5 cm diameter) surrounded by a black circle with an outer chlorotic zone. Compounds 34 and 38 (concentration of 25 μg/5 μL) had comparable toxic effectiveness, while compound 38 maintained its effect at a lower concentration of 2.5 μg/5 μL; meanwhile, the other compounds were non-toxic [36,37]. Victoxinine was also toxic to cereals in the order of oats > rye and barley > wheat > sorghum in a root inhibition assay [37]. The phytotoxic influence of compounds 34 and 38–40 versus sorghum, corn, bent-grass, sickle-pod, and morning glory was also assessed in leaf spot assays. Moreover, victoxinine caused a water-soaked translucent appearance with defined irregular necrotic edges. It is worth mentioning that 3-deoxyanthocyanidins are sorghum stress response metabolites (phytoalexins), which were accountable for the red wound response. Compounds 34, 38, and 39 were elicitors of a very strong reddening compared with the wounding-produced reddening, but compound 40 did not elicit a sorghum phytoalexin response. In bent grass and corn, compounds 34 and 38–40 produced a light-brown area limited by a chlorotic region, whereas in sickle pod and morning glory, they showed necrotic lesions that extended at high concentrations beyond the under-drop area. It is noteworthy that compound 38 was the most toxic compound versus all tested plants except for the morning glory [37].
Figure 3.
Structures of the bicyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (compounds 29–37).
Helminthosporium victoriae, the causative agent of oats Victoria blight disease yielded phytotoxins, victoxinine (40) and victoxinine α-glycerophosphate (41), which were separated from its diethyl ether extract using Sephadex LH-20 and SiO2 CC and detected on the TLC plate by giving a blue color with 5% vanillin:H2SO4 [41] (Figure 4). The existence of α-glycerophosphate moiety was established by coupling between the phosphorous and carbon. Compound 40 completely prohibited the root growth of toxin-susceptible and toxin-resistant oats (concentration of 2.5 × 10−4 M); it was ≈ 7500 times more toxic for susceptible plants on a weight basis, while its toxicity for resistant plants was nearly similar, suggesting a role of the victoxinine moiety on the toxicity [38,39,41]. On the other side, compound 41 (concentration of 100 µg/mL) demonstrated little or no growth inhibition effectiveness on either susceptible or resistant oats [41].
Figure 4.
Structures of tricyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (compounds 38–43).
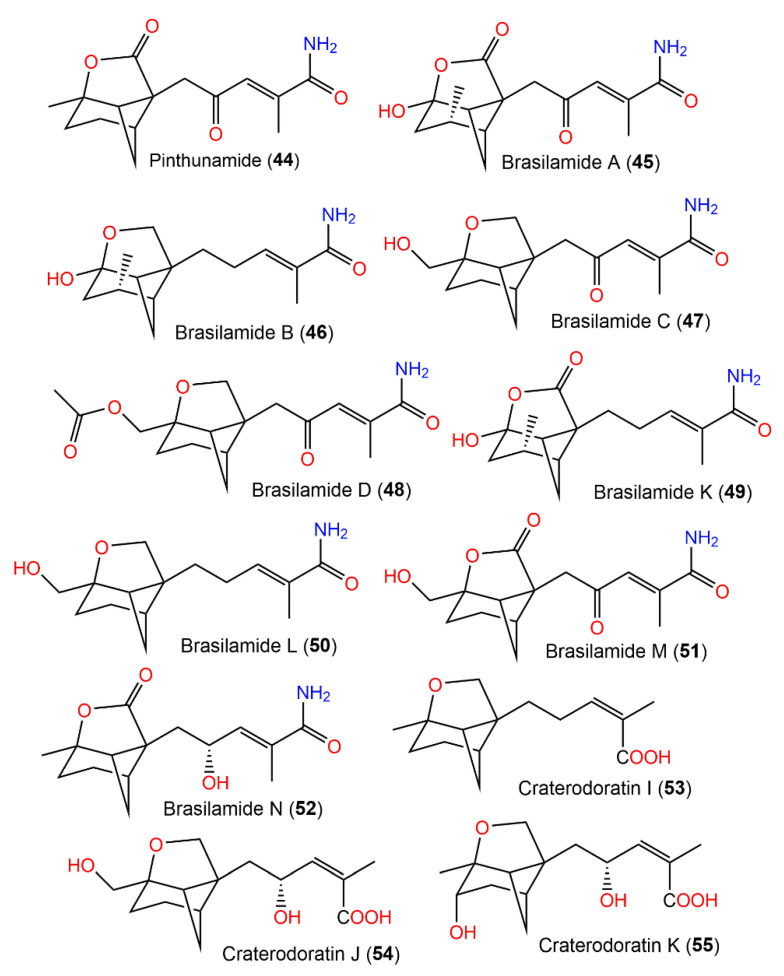
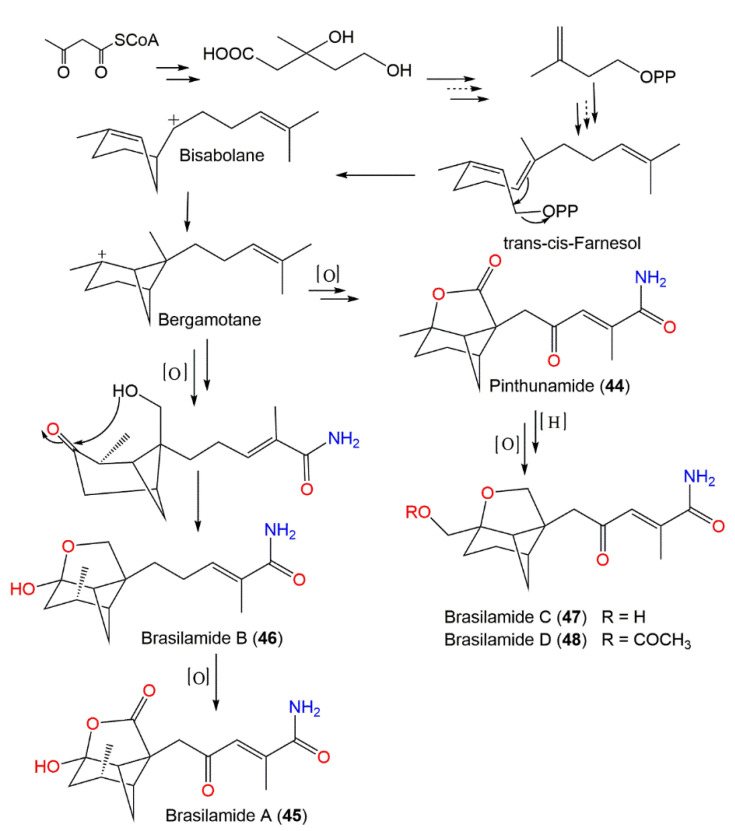
3.3. Anti-HIV Activity
From Paraconiothyrium brasiliense, new tricyclic sesquiterpenoids, brasilamides A–D (45–48) and the formerly reported pinthunamide (44), were separated from the culture’s EtOAc extract utilizing SiO2/Sephadex LH-20 CC and HPLC. Their structures were established using NMR and X-ray analyses (Figure 5). Compounds 45 and 46 are rare metabolites having a 4-oxatricyclo[3.3.1.02,7]nonane moiety with a tetrahydro-2H-pyrone or a tetrahydro-2H-pyran linked with bicyclo[3.1.1]heptane ring at C-5 and C-2, whereas compounds 47 and 48 are analogs of 44, possessing an unprecedented 9-oxatricyclo[4.3.0.04,7]-nonane core.
Figure 5.
Structures of tricyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (44–55).
The differences of the above-mentioned compounds from 44 were the existence of a tetrahydrofuran moiety connected to the bicycle[3.1.1]heptane unit instead of γ-lactone ring, as well as different C-10 substituents. Compounds 45–48 demonstrated inhibitory effectiveness (EC50s of 108.8, 57.4, and 48.3 µM, respectively) versus HIV-1 replication in C8166 cells compared with indinavir sulfate (EC50 of 8.2 nM) [43]. Biogenetically, they were derived from the mevalonate/trans-cis-farnesol/bisabolene/bergamotane pathway (Scheme 2).
Scheme 2.
Biosynthetic pathways of brasilamides A–D (45–48) [43].
3.4. Immunosuppressive Activity
Immunosuppressants are drugs that prohibit body immunity and are principally utilized in organ transplantation to overcome rejection and in auto-immune illnesses [57]. Currently, many immunosuppressive agents act by prohibiting T-cell proliferation; however, there is no new, safe, and efficient immune-suppressive agent that prohibits B-cell proliferation [58].
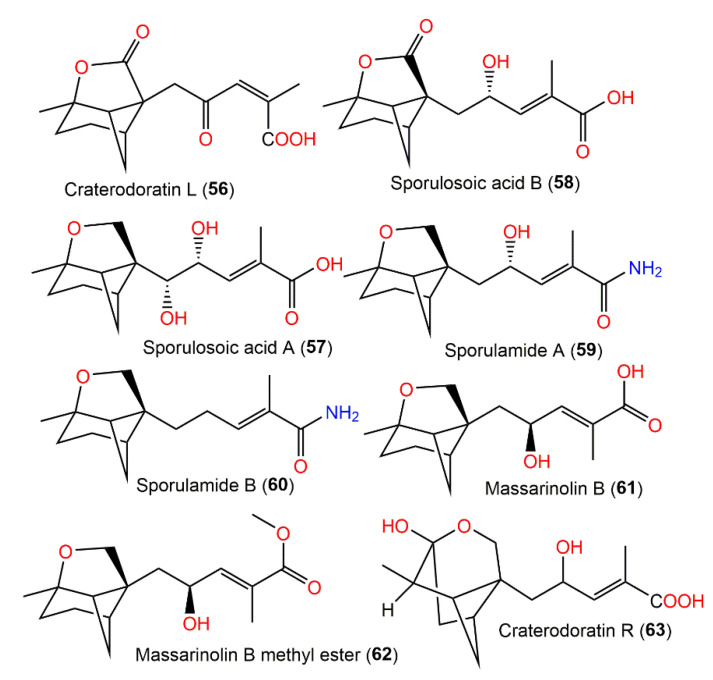
Dai et al. separated eighteen bergamotane sesquiterpenoids from the EtOAc extract of Craterellus ordoratus: craterodoratins A–R (7–11, 29–33, 53, 55, 56, 63–65, and 71) and a new victoxinine derivative, craterodoratin S (42), along with the previously isolated 5, 61, 77, and 88 by SiO2/RP-18/Sephadex LH-20/preparative HPLC (Figure 6) [30].
Figure 6.
Structures of tricyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (56–63).
Their structures with absolute configurations were established by spectral, X-ray diffraction, and ECD analyses and NMR calculations. Compounds 29 and 71 possess a rare skeleton, where the C-14methyl in 71 showed a further 1,2-migration. On the other hand, compounds 7–11, 53, 55, 56, and 63–65 belong to β-pinene derivatives that produced 30–33 through an alkyl migration (Figure 7). Compounds 7–10, 30, 42, 55, 61, and 88 demonstrated potent inhibitory potential versus LPS-caused B lymphocyte cell proliferation (IC50s ranged from 0.67 to 22.68 μM) in BALB/c mice compared with cyclosporin A (IC50 of 0.47 μM), where compound 61 (IC50 0.67 μM) had the most potent effectiveness. Moreover, compounds 11 and 61 possessed inhibition (IC50s of 31.50 and 0.98 μM, respectively) on T lymphocyte cells proliferation induced by ConA (concanavalin A) compared with cyclosporin A (IC50 0.04 μM). Structurally, it was noted that the α,β-unsaturated-carboxylic acid unit could be the key functional group for the immunosuppressive potential of these metabolites. Furthermore, compounds 61 and 7–10 with a β-pinene main core had a wider range of bioactivities [30].
Figure 7.
Structures of tricyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (64–71).
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity
From Podospora decipiens, two new tetracyclic sesquiterpenoids, decipienolides A (74) and B (75), were separated from the EtOAc extract by SiO2 CC and HPLC analyses. They were obtained as a mixture of inseparable epimers, having a 3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylbutyric acid sidechain as elucidated by an NMR analysis (Figure 8). The 74/75 mixture had an antibacterial influence versus B. subtilis (inhibition zone diameter of 9–10 mm, concentration of 200 µg/disk). Neither of them demonstrated capacity versus Ascobolus furfuraceus NRRL6460, Sordaria fimicola NRRL6459, and C. albicans ATCC90029 [24]. Donacinolides A (82) and B (76) (concentration of 50 μg/mL) revealed weak inhibition versus Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica (inhibition rates of 24.3, 23.9, and 26.2%) in the microdilution assay [32]. Furthermore, there were no observed antibacterial activity for purpurolides B (83) and C (84) (concentration of 50 μM) versus E. coli ATCC25922, M. smegmatis mc2155 ATCC70084, S. aureus ATCC25923, and S. epidermidis ATCC12228 [47].
Figure 8.
Structures of tetracyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (72–79).
3.6. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition
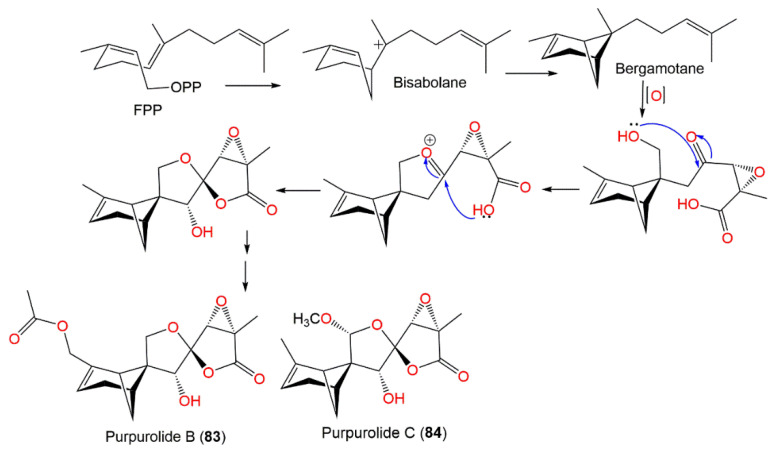
Purpurolides B (83) and C (84) are new 6/4/5/5-tetracyclic sesquiterpenoids that were separated from Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 cultures by SiO2/RP-18/preparative HPLC analysis. The structures and configurations of compounds 83 and 84 were established using spectral and X-ray analyses as well as ECD and GIAO NMR data calculations (Figure 9).
Figure 9.
Structures of tetracyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (80–93).
Compounds 83 and 84 demonstrated potent pancreatic lipase inhibition (IC50s of 5.45 and 6.63 μM, respectively), compared with kaempferol (IC50 of 1.50 μM) [47]. These compounds were possibly biosynthesized via numerous the cyclization and enzyme-catalyzed oxidation of FPP (farnesyl pyrophosphate), leading to four- and six-membered rings and the formation of two five-membered heterocyclic rings (Scheme 3) [47].
Scheme 3.
Biosynthetic pathway of purpurolides B and C (83 and 84) [47].
Xia et al. separated from Penicillium purpurogenum IMM003 purpurolides D–F (85–87), which are new polyoxygenated 6/4/5/5-tetracyclic bergamotanes, using SiO2/Sephadex-LH-20/RP-18 CC and preparative HPLC processing [48]. Their elucidation was accomplished using spectral 13C NMR calculations coupled with DP4+ probability and ECD analyses. Compound 87 had potent pancreatic lipase inhibition potential (IC50 of 1.22 μM) compared with kaempferol (IC50 of 1.50 μM) and orlistat (IC50 of 0.75 μM), whereas compounds 85 and 86 (IC50s of 6.50 and 7.88 μM, respectively) were five or six-fold less powerful than 87, revealing that the C-14 hydroxylated decanoic acid moiety increased the potency [48]. Therefore, polyoxygenated bergamotanes could be viable candidates as pancreatic lipase inhibitors for further clinical development [48].
3.7. Antidiabetic Activity
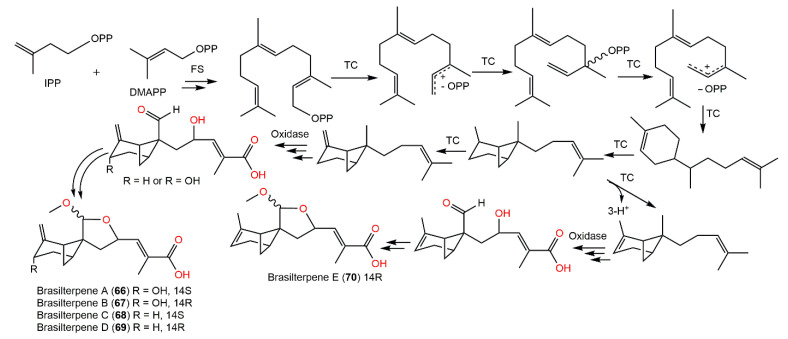
From the deep sea-derived Paraconiothyrium brasiliense HDN15-135 EtOAc extract, new bergamotane sesquiterpenoids, brasilterpenes A-E (66–70), featuring an uncommon 6/4/5-tricyclic ring system, were separated by SiO2/RP-18/Sephadex LH-20/HPLC and assigned by diverse NMR analyses and X-ray diffraction, ECD, and DFT-NMR (density functional theory calculations of nuclear magnetic resonance) data [45]. Their hypoglycemic potential was estimated utilizing β-cell-ablated zebrafish larvae. Compounds 66 and 68 (concentration of 10 μM) remarkably lessened the glucose level down to 449.3 and 420.4 pmol/larva respectively, compared with the β-cell-ablated group (Teton+) (glucose level of 502.8 pmol/larva) and rosiglitazone (glucose level 395.6 pmol/larva) with no toxic influence on zebrafish larvae up to 200 μM. It was found that compounds 66 and 68 notably minimized free blood glucose in vivo in hyperglycemic zebrafish by suppressing gluconeogenesis and improving insulin sensitivity, which revealed that compound 68 had promising antidiabetic potential [45]. The structure–activity study revealed that the activity may be linked to the C-14 S-configuration of compounds 66 and 68, which represent the main structural difference from 67 and 69. The existence of C-3-OH may weaken the influence in 68 versus 66; however, the △2 endocyclic double bond may enhance the potential in 70 versus 69 [45]. Therefore, compound 68 may provide a scaffold for hypoglycemic drug development. Compounds 66–70 are also biosynthesized by the FPP pathway (Scheme 4). The cyclization of FPP via NPP (nerolidyl diphosphate) followed by a bisabol intermediate yields the bergamotane skeleton. These compounds are created by further oxidation, 9-OH-nucleophilic attack, and methylation processes. Because of the nucleophilic attack direction flexibility during the furan ring formation, compounds 66–69 appeared as C14-epimers in pairs [45] (Scheme 4).
Scheme 4.
Biosynthetic pathway of brasilterpenes A-E (66–70) [45]. IPP: isopentenyl diphosphate; FS: farnesyl synthase; NPP: nerolidyl diphosphate; TC: terpenyl cyclase; DMAPP: dimethylallyl diphosphate; FPP: farnesyl diphosphate.
Ying et al. isolated two new derivatives, expansolides C (73) and D (81), in addition to 72 and 80 from the plant pathogen Penicillium expansum ACCC37275 [46]. In an α-glucosidase inhibition assay; the 73/81 epimeric mixture (ratio 2:1) possessed a more powerful effectiveness (IC50 of 0.50 mM) compared with acarbose (IC50 1.90 mM), while the 72/80 epimeric mixture possessed no apparent potential. It was assumed that the acetyl group in compounds 72 and 80 impeded their binding with the α-glucosidase, resulting in loss of activity [46].
3.8. Plant Growth Regulation
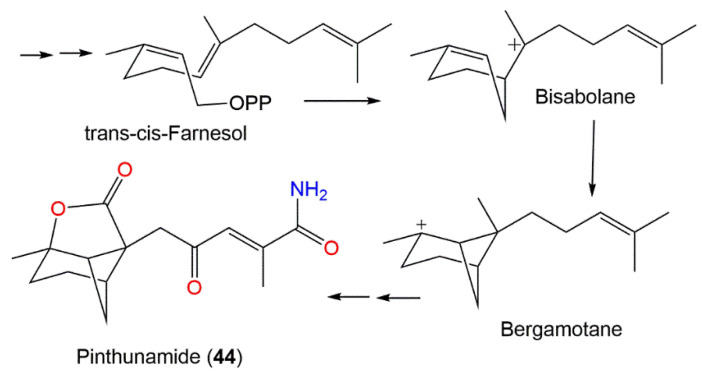
Kimura et al. purified the tricyclic amide sesquiterpenoid pinthunamide (44) from the acetone extract of Ampulliferina sp. at pH 2.0 utilizing SiO2 and sephadex LH20 CC processing as well as crystallization from EtOAc extract, which gave positive NH2OH-HCI-FeCl3 and KMnO4 reactions [42]. The compound was assigned by X-ray diffraction and NMR methods. Its plant growth regulation effectiveness was evaluated using a lettuce seedling assay, where it (dose 300 mg/L) produced a 150% root growth acceleration over the control seedlings (100%) while scarcely influencing the hypocotyl elongation at the tested concentrations [42]. Its structure combined a unique configuration of six-, five-, and four-membered rings that was proposed to be biosynthesized via the mevalonate/trans-cis-farnesol/bisabolene/bergamotane pathway (Scheme 5) [42].
Scheme 5.
Biosynthesis pathway of pinthunamide (44) [42].
Furthermore, in 1990, Kimura et al. purified another two new plant growth regulators, ampullicin (91) and isoampullicin (92) from Ampulliferina sp. No. 27 associated with Pinus thunbergii dead tree by SiO2 CC utilizing benzene:acetone as an eluent [50] (Figure 10). They were stereoisomers that had γ-lactam rings. Additionally, they (doses of 300 and 30 mg/L) were shown to promote lettuce seedling root growth by 200% over the control lettuce seedlings (100%) [50]. In 1993, the same group separated a minor metabolite, dihydroampullicin (93), characterized by the absence of the C8-C9 double bond. The compound promoted a 160% growth rate in lettuce seedling roots (dose of 300 mg/L) compared with the control; however, it had no influence on the hypocotyl growth, indicating that the C8-C9-double bond (C8-C9) was substantial in lettuce seedlings` root growth [51]. Bermejo et al. reported the synthesis of (+)−91 and 92 from (R)-(-)-carvone with a 4.5% overall yield using a stereo-selective 18-step sequence application [59]. The EtOAc extract of Aspergillus fumigatus Fresenius separated from leaf litter yielded expansolides A (72) and B (80). They had 2S/4S/6S/7R/9R/11S and 2S/4R/6S/7R/9R/11S, respectively, based on modified Mosher’s method. The compounds noticeably prohibited etiolated wheat coleoptiles growth by 100% and 59% at 10−3 M and 10−4 M solution compared with LOGRAN (commercial herbicide) (%inhibition of 80 and 42%) at the same concentrations [26].
Figure 10.
Structures of tetracyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids (94–97).
3.9. Cytotoxic Activity
Compounds 3 and 4, which were new β-bergamotane sesquiterpenoids, were separated by SiO2/RP-18/HPLC from the marine-associated Aspergillus fumigatus-YK-7 EtOAc extract. Their antiproliferative effects on the U937 and PC-3 cell lines were measured in vitro in an MTT assay. Compound 4 revealed a weak growth inhibition capacity (IC50 of 84.9 µM) versus the U937 cell line, while 3 had no activity (IC50 > 100 µM) compared with doxorubicin hydrochloride (IC50 of 0.021 µM). On the other sides, both had no effect versus PC-3 cells [29]. Wu et al. reported the separation of two new derivatives, xylariterpenoids A and B (16 and 17), from the EtOAc extract of Xylariaceae fungus by Sephadex LH-20/ODS CC and reversed-phase HPLC processing [33]. Their structures and stereo-configuration were proved utilizing NMR and CD methods. They are C-10 epimers having 2S/6S/7S/10R and 2S/6S/7S/10S configurations, respectively. Unfortunately, they (IC50 > 40 μM) exhibited no cytotoxic potential versus HL-60, MCF-7, SMMC-7721, A-549, and SW480 in an MTT assay [33].
From Paraconiothynium brasiliense Verkley, new bergamotane sesquiterpenoids brasilamides K-N (49–52), featuring 4-oxatricyclo-(3.3.1.02,7)-nonane (as in 49) and 9-oxatricyclo-(4.3.0.04,7)-nonane (as in 50–52) skeletons in addition to the formerly reported brasilamides A and C (45 and 46), were purified from the fungus scale-up fermentation cultures using SiO2/Sephadex LH-20/HPLC processing. They were elucidated via NMR analyses and compound 52’s configuration was assured using modified Mosher’s method. Compound 49 is a 45-hydrogenated analog that has a tetrahydro-2H-pyrone unit linked at C-2 and C-5 to the bicyclo(3.1.1)heptane framework, forming a 4-oxatricyclo-(3.3.1.0 2,7)-nonane skeleton, whereas compounds 50–52 displayed unusual 9-oxatricyclo-(4.3.0.0 4,7)-nonane skeletons. Compounds 50 and 51 are hydrogenated and oxygenated derivatives of 46, respectively, while 52 differed from 46 by having a C-8-carbonyl, C-1-methyl, and C-12 hydroxyl group instead of methylene, oxy-methylene, and ketone carbonyl, respectively. These metabolites (concentration of 50 µM) possessed no potential versus A549, A375, MCF-7, CNE1-LMP1, EC109, MGC, PANC-1, and Hep3B-2 in the MTS assay [44].
Montagnula donacina (edible mushroom) biosynthesized rare tetracyclic bergamotane sesquiterpenoids, donacinolides A (82) and B (76) and donacinoic acids A (88) and B (6), which were separated using SiO2 CC/Sephadex LH-20 CC/HPLC processing and were characterized using spectroscopic data, X-ray diffraction analysis, and computational methods. Compounds 76 and 82 are C9 epimers with a spiroketal moiety having 1S/5S/6S/9R and 1S/5S/6S/9S configurations, respectively, whereas 88 and 6 exhibited α,β-unsaturated carboxylic acid moiety and had 1R/2R/5S/6S/9S/14S and 1R/3S/5R/6R/9S configurations, respectively. These metabolites lacked a marked cytotoxic potential (IC50 > 40 μM) versus HL-60, SW480, A549, SMMC-7721, and MCF-7 [32].
In addition, purpurolides B (83) and C (84) had no cytotoxicity versus M14, HCT-116, U87, A2780, BGC-823, Bel-7402, and A549 [47], whereas compounds 85–87 (concentration of 50 μM) were inactive versus HCT-116, BGC-823, and Bel-7402 cell lines [48].
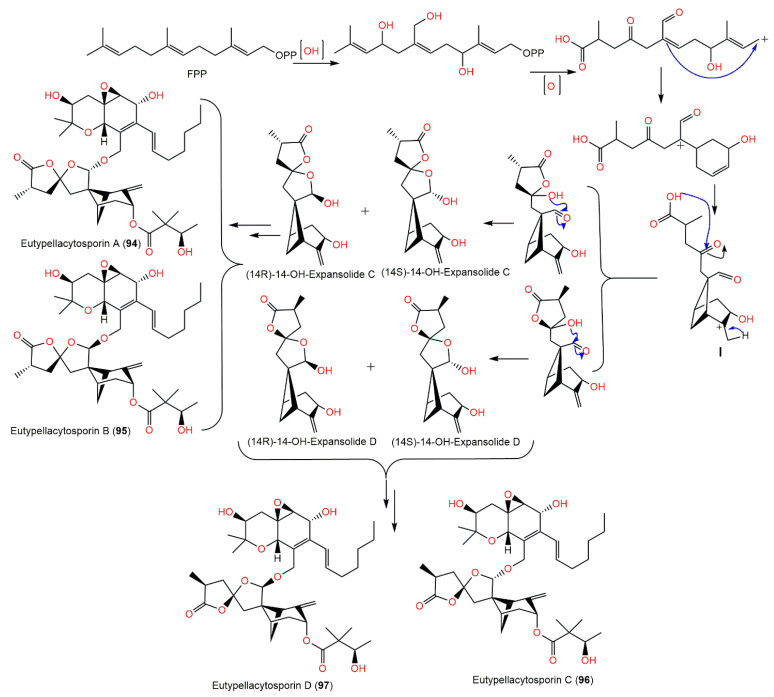
The chemical investigation of Arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1′s EtOAc extract yielded new derivatives, eutypellacytosporins A–D (94–97), which were established by spectroscopic analysis and modified Mosher’s method. Structurally, these metabolites are related to decipienolides and cytosporins. They exhibited (IC50s ranging from 4.9 to 17.1 μM) weak-to-moderate cytotoxic influence versus DU145, SW1990, Huh7, and PANC-1 in the CCK-8 assay, whereas Huh7 and SW1990 cell lines had more sensitivity to 94–97 (IC50s ranging from 4.9 to 8.4 μM). On the other hand, compounds 95 and 97 possessed noticeable potential versus PANC-1 (IC50s of 7.9 and 7.5 μM, respectively) compared with cisplatin (IC50 4.5 μM). The results revealed that the decipienolide moiety was substantial for activity; however, the C-33 configuration did not affect the activity [52]. It was proposed that compounds 94–97 are created from gentisaldehyde precursor with subsequent isoprenyl unit addition, double bond epoxidation, keto group hydrogenation, and an aliphatic chain addition (Scheme 6). The other precursor, the 14-OH of decipienolide A 74 or B 75, is produced from hydroxylation, allylic oxidation, and cyclization of farnesyl diphosphate to give I with a bicycle[3.1.1]heptane. Additionally, (14S)-14-OH-expansolide C, (14R)-14-OH-expansolide C, (14S)-14-OH-expansolide D, and (14R)-14-OH-expansolide D are formed via two steps of reface- and si-face attacks of the OH groups on the ketone and aldehyde groups, respectively. After these steps, compounds 94–97 were produced from the two groups of 14-OH-expansolides C and D through condensation reactions with (S)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethylbutanoic acid and cytosporin D, respectively [52].
Scheme 6.
Biosynthetic pathway of eutypellacytosporins A–D (94–97) [52].
4. Conclusions
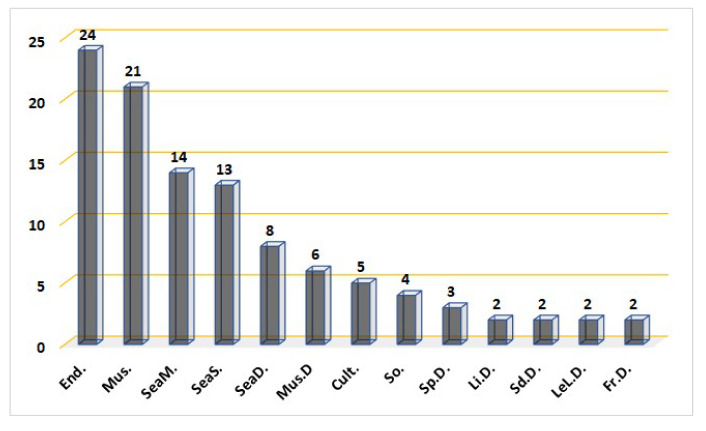
Fungal metabolites are an unparalleled pool for pharmaceutical lead discovery. Sesquiterpenoids involving the bergamotane skeleton have been separated from various sources, including fungi. In the current work, 97 bergamotane sesquiterpenoids were reported from various fungal species derived from different sources, including endophytic (24 compounds), mushroom (21 compounds), sea mud (14 compounds), sea sediment (13 compounds), deep-sea deposit (8 compounds), and sponges (3 compounds) (Figure 11).
Figure 11.
Number of bergamotane sesquiterpenoids reported from fungi derived from various sources. End.: endophytic; Mus.: mushroom; SeaM.: sea mud-derived; SeaS.: sea sediment-derived; SeaD.: sea deposit-derived; Mus.D: mushroom-derived; Cult.: cultured; So.: soil-derived; Sp.D.: sponge-derived; Li.D.: lichen-derived; Sd.D.: sheep dung-derived; LeL.D.: leaf litter-derived; Fr.D.: fruit-derived.
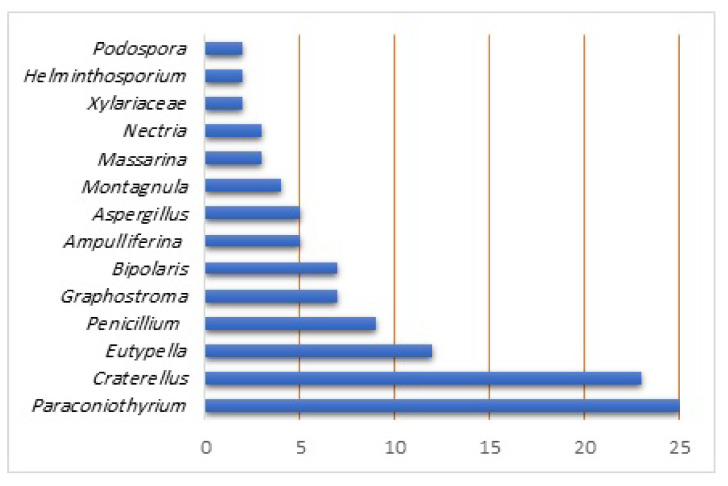
The majority of compounds have been reported from Paraconiothyrium (25 compounds), Craterellus (23 compounds), and Eutypella (12 compounds) species (Figure 12). Interestingly, many of these metabolites normally occurred as inseparable mixtures. These metabolites were assessed for diverse bio-activities. It is obvious that cytotoxic evaluation accounts for the largest proportion of biological assessments, where they had weak or no effectiveness on the tested cell lines. On the other hand, there are limited reports on their phytotoxic, plant growth regulation, antimicrobial, anti-HIV, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, pancreatic lipase inhibition, immunosuppressive, and antidiabetic activities. Therefore, this suggested more potential for trying other types of pharmacological effectiveness. Victoxinine (40) and prehelminthosporolactone (39) displayed potential phytotoxic capacities; therefore, they could be utilized as bioherbicides or as lead metabolites for synthesizing more efficacious phytotoxic compounds against various weeds. Pinthunamide (44), ampullicin (91), isoampullicin (92), and dihydroampullicin (93) were found to selectively promote the root growth. However, the phytotoxic and plant growth promotion potential should be transferred from laboratory experiments into field settings for assessing the environmental influences on these activities. Purpurolide F (87) had potent pancreatic lipase inhibition potential that could be a viable candidate as a pancreatic lipase inhibitor for further clinical development. Massarinolin B (61) had prominent immunosuppressive potential, suggesting further in vivo and mechanistic investigations for the development of this metabolite as an immunosuppressant. In silico studies for the reported metabolites that have not been tested or have had no noticeable effectiveness in the estimated activities could be a possible area of future research. Moreover, synthesis and structural modifications of these metabolites may produce more potential and useful tags of these metabolites through click chemistry, which is a new approach for synthesizing drug-like molecules that can boost the drug discovery process.
Figure 12.
Bergamotane sesquiterpenoids from various fungal species.
Biogenetically, these metabolites are generated from acyclic farnesyl-diphosphate, which undertakes various condensation and rearrangement reactions. This work could be a beneficial reference for researchers studying this class of fungal metabolites. Several strategies, including co-culture, molecular and epigenetic manipulations, OSMAC (one strain many compounds), heterologous gene expression, and inter-species cross-talk approaches could be successively employed to access undescribed natural metabolites from silent biosynthetic pathways. It was found that the selective epigenetic target manipulation utilizing small molecule inhibitors toward DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase activities resulted in the enhancement of biosynthetic pathway expression for new secondary metabolite production. Highlighting the biosynthesis of these metabolites in this review could draw the attention of molecular biologists and genetics-interested researchers for isolating genes accountable for the biosynthesis of these interesting metabolites; this could allow for the discovery of the detailed mechanisms of their formation by various enzymes, which could allow for the preparation these metabolites and their analogs by engineering their biosynthetic pathways.
Acknowledgments
This research work was funded by Institutional Fund Projects under grant no. (IFPDP-254-22). Therefore, the authors gratefully acknowledge technical and financial support from Ministry of Education and Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University (KAU), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Abbreviations
| 5-Aza | 5-azacytidine |
| A2780 | Human ovarian cancer cell line |
| 4-MUO | 4-methylumbelliferyl oleate |
| A549 | Lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line |
| Bel-7402 | Human hepatoma cell line |
| BGC-823 | Human stomach cancer cell line |
| BuOH | n-Butanol |
| C8166 | Human T-cell leukaemia |
| CC | Column chromatography |
| CC50 | The 50% cytotoxic concentration |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| CHCl3 | Chloroform |
| CH2Cl2 | Dichloromethane |
| CNE1-LMP1 | Stable oncoprotein LMP1 integrated nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line |
| DU145 | Human prostate carcinoma cell line |
| EC109 | Human esophageal cancer cell line |
| ED50 | Half-maximal effective concentration |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid |
| Hep3B-2 | Human hepatoma carcinoma cell line |
| HCT-116 | Human colon cancer cell line |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| Huh7 | Human hepatoma adenocarcinoma cell line |
| IR | Infrared |
| HL-60 | Human myeloid leukemia cell line |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| M14 | Human melanoma cell line |
| MCF-7 | Human breast cancer cell line |
| MGC | Human gastric cancer cell line |
| MTS | (3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazoliuminner salt) |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| RP-18 | Reversed phase-18 |
| SBHA | Histonedeacetylase inhibitor, suberohydroxamic acid |
| SiO2 | Silica gel |
| SMMC-7721 | Hepatocellular carcinoma cell line |
| SW480 | Colon cancer cell line |
| SW1990 | Human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line |
| PANC-1 | Human pancreatic carcinoma cell line |
| PC-3 | Human prostate cancer cell line |
| TLC | Thin-layer chromatography |
| U937 | Human leukemic monocyte lymphoma cell line |
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.R.M.I. and G.A.M.; resources, M.T.K., K.A.M. and A.M.O.; discussion of the contents, A.M.O., G.A.M. and S.R.M.I.; writing—original draft, M.T.K., K.A.M., A.M.O., G.A.M. and S.R.M.I.; writing—review and editing, G.A.M. and S.R.M.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research work was funded by Institutional Fund Projects under grant no. (IFPDP-254-22). Therefore, the authors gratefully acknowledge technical and financial support from Ministry of Education and Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR), King Abdulaziz University (KAU), Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Shen B. A New Golden Age of Natural Products Drug Discovery. Cell. 2015;163:1297–1300. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Krabberød A.K., Deutschmann I.M., Bjorbækmo M.F., Balagué V., Giner C.R., Ferrera I., Garcés E., Massana R., Gasol J.M., Logares R. Long-Term Patterns of an Interconnected Core Marine Microbiota. Environ. Microbiome. 2022;17:1–24. doi: 10.1186/s40793-022-00417-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Imhoff J.F. Natural Products from Marine fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource. Mar. Drugs. 2016;14:19. doi: 10.3390/md14010019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Alves A., Sousa E., Kijjoa A., Pinto M. Marine-Derived Compounds with Potential use as Cosmeceuticals and Nutricosmetics. Molecules. 2020;25:2536. doi: 10.3390/molecules25112536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ibrahim S.R., Fadil S.A., Fadil H.A., Hareeri R.H., Alolayan S.O., Abdallah H.M., Mohamed G.A. Dactylospongia Elegans—A Promising Drug Source: Metabolites, Bioactivities, Biosynthesis, Synthesis, and Structural-Activity Relationship. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:221. doi: 10.3390/md20040221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ibrahim S.R., Fadil S.A., Fadil H.A., Hareeri R.H., Abdallah H.M., Mohamed G.A. Genus Smenospongia: Untapped Treasure of Biometabolites—Biosynthesis, Synthesis, and Bioactivities. Molecules. 2022;27:5969. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mohamed G.A., Ibrahim S.R. Untapped Potential of Marine-Associated Cladosporium Species: An Overview on Secondary Metabolites, Biotechnological Relevance, and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs. 2021;19:645. doi: 10.3390/md19110645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ibrahim S.R.M., Mohamed G.A., Al Haidari R.A., El-Kholy A.A., Zayed M.F., Khayat M.T. Biologically Active Fungal Depsidones: Chemistry, Biosynthesis, Structural Characterization, and Bioactivities. Fitoterapia. 2018;129:317–365. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2018.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Omar A.M., Mohamed G.A., Ibrahim S.R.M. Chaetomugilins and Chaetoviridins-Promising Natural Metabolites: Structures, Separation, Characterization, Biosynthesis, Bioactivities, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics. J. Fungi. 2022;8:127. doi: 10.3390/jof8020127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ibrahim S.R.M., Sirwi A., Eid B.G., Mohamed S.G.A., Mohamed G.A. Fungal Depsides-Naturally Inspiring Molecules: Biosynthesis, Structural Characterization, and Biological Activities. Metabolites. 2021;11:683. doi: 10.3390/metabo11100683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ibrahim S.R.M., Fadil S.A., Fadil H.A., Eshmawi B.A., Mohamed S.G.A., Mohamed G.A. Fungal Naphthalenones; Promising Metabolites for Drug Discovery: Structures, Biosynthesis, Sources, and Pharmacological Potential. Toxins. 2022;14:154. doi: 10.3390/toxins14020154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ameen F., AlNadhari S., Al-Homaidan A.A. Marine Microorganisms as an Untapped Source of Bioactive Compounds. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021;28:224–231. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.09.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hasan S., Ansari M.I., Ahmad A., Mishra M. Major Bioactive Metabolites from Marine Fungi: A Review. Bioinformation. 2015;11:176. doi: 10.6026/97320630011176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wibowo J.T., Ahmadi P., Rahmawati S.I., Bayu A., Putra M.Y., Kijjoa A. Marine-Derived Indole Alkaloids and their Biological and Pharmacological Activities. Mar. Drugs. 2021;20:3. doi: 10.3390/md20010003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Giddings L., Newman D.J. Extremophilic Fungi from Marine Environments: Underexplored Sources of Antitumor, Anti-Infective and Other Biologically Active Agents. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:62. doi: 10.3390/md20010062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hafez Ghoran S., Taktaz F., Ayatollahi S.A., Kijjoa A. Anthraquinones and their Analogues from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:474. doi: 10.3390/md20080474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kramer R., Abraham W. Volatile Sesquiterpenes from Fungi: What are they Good for? Phytochem. Rev. 2012;11:15–37. doi: 10.1007/s11101-011-9216-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gui P., Fan J., Zhu T., Fu P., Hong K., Zhu W. Sesquiterpenoids from the Mangrove-Derived Aspergillus Ustus 094102. Mar. Drugs. 2022;20:408. doi: 10.3390/md20070408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dai Q., Zhang F., Feng T. Sesquiterpenoids Specially Produced by Fungi: Structures, Biological Activities, Chemical and Biosynthesis (2015–2020) J. Fungi. 2021;7:1026. doi: 10.3390/jof7121026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Minami A., Ozaki T., Liu C., Oikawa H. Cyclopentane-Forming Di/Sesterterpene Synthases: Widely Distributed Enzymes in Bacteria, Fungi, and Plants. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018;35:1330–1346. doi: 10.1039/C8NP00026C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fraga B.M. Natural Sesquiterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013;30:1226–1264. doi: 10.1039/c3np70047j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cane D.E. Enzymic Formation of Sesquiterpenes. Chem. Rev. 1990;90:1089–1103. doi: 10.1021/cr00105a002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Oh H., Gloer J.B., Shearer C.A. Massarinolins A−C: New Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids from the Aquatic Fungus Massarina Tunicata. J. Nat. Prod. 1999;62:497–501. doi: 10.1021/np980447+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Che Y., Gloer J.B., Koster B., Malloch D. Decipinin A and Decipienolides A and B: New Bioactive Metabolites from the Coprophilous Fungus Podospora Decipiens. J. Nat. Prod. 2002;65:916–919. doi: 10.1021/np010575p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Massias M., Rebuffat S., Molho L., Chiaroni A., Riche C., Bodo B. Expansolides A and B: Tetracyclic Sesquiterpene Lactones from Penicillium Expansum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990;112:8112–8115. doi: 10.1021/ja00178a039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Macías F.A., Varela R.M., Simonet A.M., Cutler H.G., Cutler S.J., Hill R.A. Absolute Configuration of Bioactive Expansolides A and B from Aspergillus Fumigatus Fresenius. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003;44:941–943. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(02)02778-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wen Y., Chen T., Jiang L., Li L., Guo M., Peng Y., Chen J., Pei F., Yang J., Wang R. Unusual (2R, 6R)-Bicyclo [3.1. 1] Heptane Ring Construction in Fungal A-Trans-Bergamotene Biosynthesis. Iscience. 2022;25:104030. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nozoe S., Kobayashi H., Morisaki N. Isolation of Beta Trans Bergamotene from Aspergillus Fumigatus, a Fumagillin Producing Fungi. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976;50:4625–4626. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)93948-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang Y., Li D., Li Z., Sun Y., Hua H., Liu T., Bai J. Terpenoids from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Fumigatus YK-7. Molecules. 2016;21:31. doi: 10.3390/molecules21010031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dai Q., Zhang F., Li Z., He J., Feng T. Immunosuppressive Sesquiterpenoids from the Edible Mushroom Craterellus Odoratus. J. Fungi. 2021;7:1052. doi: 10.3390/jof7121052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pei Y., Zhang L., Wu X., Wu H., Wang H., Wang Y., Chen G. Polyhydroxylated Bergamotane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from Cultures of Paraconiothyrium Sporulosum YK-03 and their Absolute Configurations. Phytochemistry. 2022;194:113000. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.113000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhao Z., Zhao K., Chen H., Bai X., Zhang L., Liu J. Terpenoids from the Mushroom-Associated Fungus Montagnula Donacina. Phytochemistry. 2018;147:21–29. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wu Z., Wu Y., Chen G., Hu D., Li X., Sun X., Guo L., Li Y., Yao X., Gao H. Xylariterpenoids A–D, Four New Sesquiterpenoids from the Xylariaceae Fungus. RSC Adv. 2014;4:54144–54148. doi: 10.1039/C4RA10365C. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Niu S., Xie C., Zhong T., Xu W., Luo Z., Shao Z., Yang X. Sesquiterpenes from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Graphostroma Sp. MCCC 3A00421. Tetrahedron. 2017;73:7267–7273. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2017.11.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Niu S., Liu D., Shao Z., Liu J., Fan A., Lin W. Chemical Epigenetic Manipulation Triggers the Production of Sesquiterpenes from the Deep-Sea Derived Eutypella Fungus. Phytochemistry. 2021;192:112978. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2021.112978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pena-Rodriguez L.M., Armingeon N.A., Chilton W.S. Toxins from Weed Pathogens, I. Phytotoxins from a Bipolaris Pathogen of Johnson Grass. J. Nat. Prod. 1988;51:821–828. doi: 10.1021/np50059a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pena-Rodriguez L.M., Chilton W.S. Victoxinine and Prehelminthosporolactone, Two Minor Phytotoxic Metabolites Produced by Bipolaris Sp., a Pathogen of Johnson Grass. J. Nat. Prod. 1989;52:899–901. doi: 10.1021/np50064a046. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pringle R.B., Braun A.C. Constitution of the Toxin of Helminthosporium Victoriae. Nature. 1958;181:1205–1206. doi: 10.1038/1811205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dorn F., Arigoni D. Structure of Victoxinine. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1972;24:1342–1343. doi: 10.1039/c39720001342. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pringle R. Comparative Biochemistry of the Phytopathogenic Fungus Helminthosporium. XVI. the Production of Victoxinine by H. Sativum and H. Victoriae. Can. J. Biochem. 1976;54:783–787. doi: 10.1139/o76-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kono Y., Takeuchi S., Daly J.M. Isolation and Structure of a New Victoxinine Derivative Produced by Helminthosporium Victoriae. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1983;47:2701–2702. doi: 10.1271/bbb1961.47.2701. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kimura Y., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T., Sugawara F., Parkanyi L., Clardy J. Pinthunamide, a New Tricyclic Sesquiterpene Amide Produced by a Fungus, Ampullifernia Sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989;30:1267–1270. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)72732-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu L., Gao H., Chen X., Cai X., Yang L., Guo L., Yao X., Che Y. Brasilamides A–D: Sesquiterpenoids from the Plant Endophytic Fungus Paraconiothyrium Brasiliense. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010:3302–3306. doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201000284. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Guo Z., Ren F., Che Y., Liu G., Liu L. New Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoids from the Plant Endophytic Fungus Paraconiothyrium Brasiliense. Molecules. 2015;20:14611–14620. doi: 10.3390/molecules200814611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Wang W., Shi Y., Liu Y., Zhang Y., Wu J., Zhang G., Che Q., Zhu T., Li M., Li D. Brasilterpenes A-E, Bergamotane Sesquiterpenoid Derivatives with Hypoglycemic Activity from the Deep Sea-Derived Fungus Paraconiothyrium Brasiliense HDN15-135. Mar Drugs. 2022;20:514. doi: 10.3390/md20050338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Ying Y., Fang C., Yao F., Yu Y., Shen Y., Hou Z., Wang Z., Zhang W., Shan W., Zhan Z. Bergamotane Sesquiterpenes with Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitory Activity from the Plant Pathogenic Fungus Penicillium Expansum. Chem. Biodivers. 2017;14:e1600184. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201600184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang Y., Xia G., Wang L., Ge G., Zhang H., Zhang J., Wu Y., Lin S. Purpurolide A, 5/5/5 Spirocyclic Sesquiterpene Lactone in Nature from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium Purpurogenum. Org. Lett. 2018;20:7341–7344. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xia G., Wang L., Zhang J., Wu Y., Ge G., Wang Y., Lin P., Lin S. Three New Polyoxygenated Bergamotanes from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium Purpurogenum IMM 003 and their Inhibitory Activity Against Pancreatic Lipase. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020;18:75–80. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang L., Feng B., Chen G., Li S., Sun Y., Wu H., Bai J., Hua H., Wang H., Pei Y. Sporulaminals A and B: A Pair of Unusual Epimeric Spiroaminal Derivatives from a Marine-Derived Fungus Paraconiothyrium Sporulosum YK-03. RSC Adv. 2016;6:42361–42366. doi: 10.1039/C6RA01401A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kimura Y., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T., Matsumoto T., Matsuda Y., Tsuneda A. Ampullicin and Isoampullicin, New Metabolites from an Ampulliferina-Like Fungus Sp. no. 27. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990;54:813–814. doi: 10.1080/00021369.1990.10869993. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kimura Y., Matsumoto T., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T., Matsuda Y. Dihydroampullicin, a New Plant Growth Regulators Produced by the Ampulliferina-Like Fungus Sp. no. 27. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1993;57:687–688. doi: 10.1271/bbb.57.687. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang Y., Yu H., Xu W., Hu B., Guild A., Zhang J., Lu X., Liu X., Jiao B. Eutypellacytosporins A–D, Meroterpenoids from the Arctic Fungus Eutypella Sp. D-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2019;82:3089–3095. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bermejo F.A., Mateos A.F., Escribano A.M., Lago R.M., Burón L.M., López M.R., González R.R. Ti (III)-Promoted Cyclizations. Application to the Synthesis of (E)-Endo-Bergamoten-12-Oic Acids. Moth Oviposition Stimulants Isolated from Lycopersicon Hirsutum. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:8933–8942. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2006.07.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.López M.R., Bermejo F.A. Total Synthesis of ( )-Massarinolin B and ( )-4-Epi-Massarinolin B, Fungal Metabolites from Massarina Tunicata. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:8095–8102. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2006.06.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhao J., Feng J., Tan Z., Liu J., Zhang M., Chen R., Xie K., Chen D., Li Y., Chen X. Bistachybotrysins A-C, Three Phenylspirodrimane Dimers with Cytotoxicity from Stachybotrys Chartarum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018;28:355–359. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.12.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zamora R., Vodovotz Y., Billiar T.R. Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase and Inflammatory Diseases. Mol. Med. 2000;6:347–373. doi: 10.1007/BF03401781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Kovarik J.M., Burtin P. Immunosuppressants in Advanced Clinical Development for Organ Transplantation and Selected Autoimmune Diseases. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs. 2003;8:47–62. doi: 10.1517/14728214.8.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Klinker M.W., Lundy S.K. Multiple Mechanisms of Immune Suppression by B Lymphocytes. Mol. Med. 2012;18:123–137. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bermejo F.A., Rico-Ferreira R., Bamidele-Sanni S., García-Granda S. Total Synthesis of (+)-Ampullicin and (+)-Isoampullicin: Two Fungal Metabolites with Growth Regulatory Activity Isolated from Ampulliferina Sp. 27. J. Org. Chem. 2001;66:8. doi: 10.1021/jo010527+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.